Suica Electronic Money Service Logo on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 is a prepaid rechargeable
is a prepaid rechargeable



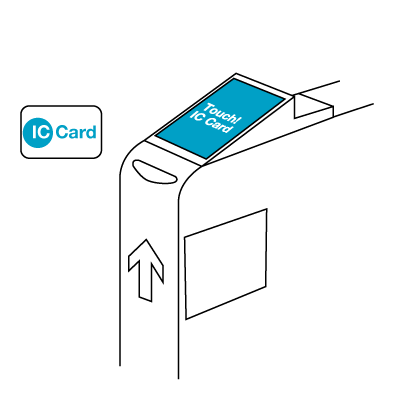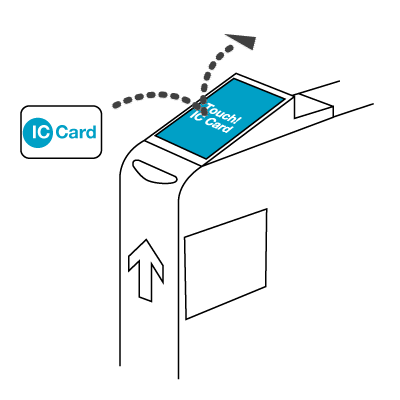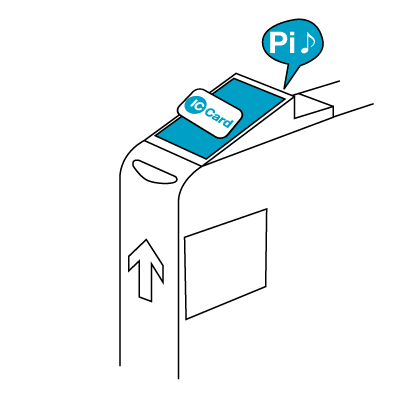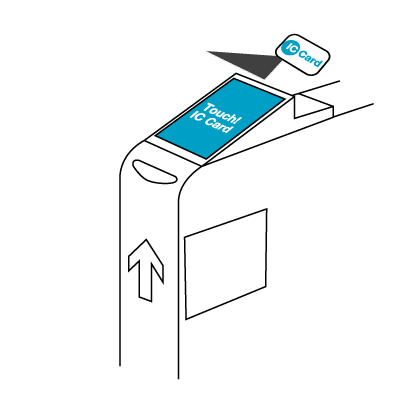
 Usage of the card involves scanning it at a card reader. The technology allows for the card to be read at a short distance from the reader, so contact is not required. This functionality is in contrast to the instructions which frequently inform the user to the card to the reader, a misnomer since it works with or without physical contact. In fact, it is possible to leave the card in most wallets and just pass the wallet over the reader as they enter the ticket gate.
Usage of the card involves scanning it at a card reader. The technology allows for the card to be read at a short distance from the reader, so contact is not required. This functionality is in contrast to the instructions which frequently inform the user to the card to the reader, a misnomer since it works with or without physical contact. In fact, it is possible to leave the card in most wallets and just pass the wallet over the reader as they enter the ticket gate.
 The balance on the card is displayed when the user enters the ticket gate this way. The minimum fare is needed on the card when entering the train system, which is not deducted at that time. The balance is also displayed whenever the card is inserted into ticket or fare adjustment machines. A travel record is stored on the card, and can be displayed or printed out at the same places where cards can be purchased and reloaded. On exit, the card is again scanned at a card reader. At this time the fare is deducted from the remaining balance from the card and the new balance is displayed.
The card can also be used to store a commuter pass. This is available for purchase from regular ticket machines and allows a Monthly, 3-monthly or Annual pass for travel between two JR stations to be stored on the card.
On some occasions, when traveling to a station where Suica is not supported, the card must be handed over to the staff at the exiting station, so that they can calculate the remaining fare and return a slip of paper which must be given to the staff at the next station where Suica is used. Since the system keeps track of when a card enters and leaves a station, if the records show that the card had entered a station but not left (due to the situation such as described above, or technical malfunctions), the station staff can reset the card.
The balance on the card is displayed when the user enters the ticket gate this way. The minimum fare is needed on the card when entering the train system, which is not deducted at that time. The balance is also displayed whenever the card is inserted into ticket or fare adjustment machines. A travel record is stored on the card, and can be displayed or printed out at the same places where cards can be purchased and reloaded. On exit, the card is again scanned at a card reader. At this time the fare is deducted from the remaining balance from the card and the new balance is displayed.
The card can also be used to store a commuter pass. This is available for purchase from regular ticket machines and allows a Monthly, 3-monthly or Annual pass for travel between two JR stations to be stored on the card.
On some occasions, when traveling to a station where Suica is not supported, the card must be handed over to the staff at the exiting station, so that they can calculate the remaining fare and return a slip of paper which must be given to the staff at the next station where Suica is used. Since the system keeps track of when a card enters and leaves a station, if the records show that the card had entered a station but not left (due to the situation such as described above, or technical malfunctions), the station staff can reset the card.
 On 18 March 2007, the Tokyo-area private railways, bus companies, and subways implemented Pasmo, a
On 18 March 2007, the Tokyo-area private railways, bus companies, and subways implemented Pasmo, a
 Since January 2006, a version called was incorporated into
Since January 2006, a version called was incorporated into
JR-East: Mobile Suica
(In Japanese)
JR-East: Research and Development > R&D Story
{{Tokyo transit 2001 introductions 2001 establishments in Japan Japanese inventions Contactless smart cards Fare collection systems in Japan East Japan Railway Company
 is a prepaid rechargeable
is a prepaid rechargeable contactless smart card
A contactless smart card is a contactless credential whose dimensions are credit-card size. Its embedded integrated circuits can store (and sometimes process) data and communicate with a terminal via NFC. Commonplace uses include transit tickets ...
, electronic money
Digital currency (digital money, electronic money or electronic currency) is any currency, money, or money-like asset that is primarily managed, stored or exchanged on digital computer systems, especially over the internet. Types of digital cu ...
used as a fare card on train lines in Japan, launched on November 18, 2001. The card can be used interchangeably with JR West's ICOCA in the Kansai region and San'yō region in Okayama
is the capital city of Okayama Prefecture in the Chūgoku region of Japan. The city was founded on June 1, 1889. , the city has an estimated population of 720,841 and a population density of 910 persons per km2. The total area is .
The city is ...
, Hiroshima
is the capital of Hiroshima Prefecture in Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 1,199,391. The gross domestic product (GDP) in Greater Hiroshima, Hiroshima Urban Employment Area, was US$61.3 billion as of 2010. Kazumi Matsui h ...
, and Yamaguchi prefectures, and also with JR Central
is the main railway company operating in the Chūbu (Nagoya) region of central Japan. It is officially abbreviated in English as JR Central and in Japanese as JR Tōkai ( ja, JR東海, links=no). ''Tōkai'' is a reference to the geographical ...
's TOICA, JR Kyushu's SUGOCA
is a Japanese rechargeable contactless smart card ticketing system for public transport in Fukuoka Prefecture and environs. The Kyūshū Railway Company (JR Kyūshū) introduced the system on 1 March 2009. The name is an acronym of "Smart Urban ...
, Nishitetsu's Nimoca, and Fukuoka City Subway's Hayakaken area in Fukuoka City and its suburb areas. The card is also increasingly being accepted as a form of electronic money
Digital currency (digital money, electronic money or electronic currency) is any currency, money, or money-like asset that is primarily managed, stored or exchanged on digital computer systems, especially over the internet. Types of digital cu ...
for purchases at stores and kiosks, especially within train stations. As of 2018, JR East reports 69.4 million Suica UID's have been issued, usable at 476,300 point of sale locations, with 6.6 million daily transactions.
Since Suica is completely interchangeable with Pasmo (see ''Interoperation'' for the complete listing of companies and lines that accept Suica) in the greater Tokyo area, it is supported on virtually any train, tramway, and bus system (excluding various limited and shinkansen trains, as well as a few local buses as the system is still in the process of being extended to all routes).
Etymology
Suica stands for "Super Urban Intelligent CArd". In the logo, the "ic" is highlighted, standing for the initialism ofintegrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny ...
in "IC card", which in turn is common Japanese vernacular for smart card
A smart card, chip card, or integrated circuit card (ICC or IC card) is a physical electronic authentication device, used to control access to a resource. It is typically a plastic credit card-sized card with an embedded integrated circuit (IC) c ...
. An additional meaning comes from the ideophone "sui sui" which means "to move smoothly", intended to highlight the smooth simplicity of using the card compared with traditional train tickets. Since penguins can also swim smoothly through water, a penguin is used as a motif.
Uses
While Suica's primary usage is as a fare card for transportation services, it can also be used as electronic money for general purchases. With the exception of archaic models of the Suica, all Suica have the logo, which indicates that the card can be used as an electronic money in addition to train fare usage. Older cards without the logo can be replaced at no cost. As of 2004, JR East employees use the card as an employee ID card. Most vending machines, kiosks, and coin-operated lockers within JR stations can be paid with the card. In addition to payment, the card is also used as an electronic key to open the specific locker used. Outside of train stations, chain stores such as FamilyMart,7-Eleven
7-Eleven, Inc., stylized as 7-ELEVE, is a multinational chain of retail convenience stores, headquartered in Dallas, Texas. The chain was founded in 1927 as an ice house storefront in Dallas. It was named Tote'm Stores between 1928 and 1946. A ...
, Ministop, Yodobashi Camera
is a major Japanese retail chain specializing in electronics, PCs, cameras and photographic equipment.
Yodobashi Camera's sales rank fourth among consumer electronics mass retailers in Japan, after Yamada Denki, Bic Camera and the EDION Gro ...
and Bic Camera support transactions with Suica, however mostly restricted to the Kantō region
The is a geographical area of Honshu, the largest island of Japan. In a common definition, the region includes the Greater Tokyo Area and encompasses seven prefectures: Gunma, Tochigi, Ibaraki, Saitama, Tokyo, Chiba and Kanagawa. Slight ...
only. A few shops at Narita International Airport
Narita International Airport ( ja, 成田国際空港, Narita Kokusai Kūkō) , also known as Tokyo-Narita, formerly and originally known as , is one of two international airports serving the Greater Tokyo Area, the other one being Haneda Airport ...
, and taxis accept Suica. Stores that accept Suica are indicated by displaying either a Suica, Pasmo, Kitaca, Icoca, Toica, Sugoca, Nimoca, or Hayakaken logo. The card can also be used to make payments at supporting online shops, which requires the consumer to own a Sony FeliCa Reader hardware and a PC running the Windows operating system alongside the necessary drivers.
Functions and services


 Usage of the card involves scanning it at a card reader. The technology allows for the card to be read at a short distance from the reader, so contact is not required. This functionality is in contrast to the instructions which frequently inform the user to the card to the reader, a misnomer since it works with or without physical contact. In fact, it is possible to leave the card in most wallets and just pass the wallet over the reader as they enter the ticket gate.
Usage of the card involves scanning it at a card reader. The technology allows for the card to be read at a short distance from the reader, so contact is not required. This functionality is in contrast to the instructions which frequently inform the user to the card to the reader, a misnomer since it works with or without physical contact. In fact, it is possible to leave the card in most wallets and just pass the wallet over the reader as they enter the ticket gate.
 The balance on the card is displayed when the user enters the ticket gate this way. The minimum fare is needed on the card when entering the train system, which is not deducted at that time. The balance is also displayed whenever the card is inserted into ticket or fare adjustment machines. A travel record is stored on the card, and can be displayed or printed out at the same places where cards can be purchased and reloaded. On exit, the card is again scanned at a card reader. At this time the fare is deducted from the remaining balance from the card and the new balance is displayed.
The card can also be used to store a commuter pass. This is available for purchase from regular ticket machines and allows a Monthly, 3-monthly or Annual pass for travel between two JR stations to be stored on the card.
On some occasions, when traveling to a station where Suica is not supported, the card must be handed over to the staff at the exiting station, so that they can calculate the remaining fare and return a slip of paper which must be given to the staff at the next station where Suica is used. Since the system keeps track of when a card enters and leaves a station, if the records show that the card had entered a station but not left (due to the situation such as described above, or technical malfunctions), the station staff can reset the card.
The balance on the card is displayed when the user enters the ticket gate this way. The minimum fare is needed on the card when entering the train system, which is not deducted at that time. The balance is also displayed whenever the card is inserted into ticket or fare adjustment machines. A travel record is stored on the card, and can be displayed or printed out at the same places where cards can be purchased and reloaded. On exit, the card is again scanned at a card reader. At this time the fare is deducted from the remaining balance from the card and the new balance is displayed.
The card can also be used to store a commuter pass. This is available for purchase from regular ticket machines and allows a Monthly, 3-monthly or Annual pass for travel between two JR stations to be stored on the card.
On some occasions, when traveling to a station where Suica is not supported, the card must be handed over to the staff at the exiting station, so that they can calculate the remaining fare and return a slip of paper which must be given to the staff at the next station where Suica is used. Since the system keeps track of when a card enters and leaves a station, if the records show that the card had entered a station but not left (due to the situation such as described above, or technical malfunctions), the station staff can reset the card.
Points of purchase
These cards are available at card vending machines at the train stations that allows Suica. A new card costs 2,000 yen, which includes a 500 yen deposit that will be refunded if the card is returned. The remaining 1,500 yen is immediately available for train rides, and more money can be charged on to the card (in 500 yen, 1,000 yen, 2,000 yen, 3,000 yen, 4,000 yen, 5,000 yen, and 10,000 yen increments), up to a card maximum of 20,000 yen, at similar ticket vending machines or fare adjustment machines displaying the Suica logo inside each station.Types of cards
Suica are sold by JR East and two of its subsidiaries: *Suica, MySuica, Welcome Suica and View Suica cards are sold directly by JR East *Rinkai Suica cards are sold by Tokyo Waterfront Area Rapid Transit (Rinkai Line) *Monorail Suica cards are sold by Tokyo MonorailCredit card integrations
The View Suica cards pairs the prepaid Suica with a credit card. Various types exist, including at least one available through JR and View, and others such as the Bic Camera Suica. These function both as a prepaid Suica as well as a regular credit card, and provide an auto-charge feature to prevent exhausting the Suica balance unintentionally. The automatically recharged amount is added to the user's credit card bill. Thus, these cards have two balances: a prepaid Suica balance and a credit balance for which monthly bills are sent. Thus, store-related cards like the Bic Suica can include fully three separate functions: serving as a store point card, a general use Suica, and as a credit card. Any credit purchase (restricted, in the case of Bic, toJCB
JCB may refer to:
* JCB (company), a British manufacturer of heavy industrial and agricultural vehicles
* JCB Co., Ltd., originally Japan Credit Bureau, a credit card company based in Tokyo, Japan
* JCB Prize, a literary award sponsored by the c ...
) adds a small amount to the available points on the store point card. Yet another type of Suica offered by Japan Airlines that is called JALCARD Suica. In addition to having Suica and credit card functionalities, a JALCARD Suica can also function as an electronic boarding pass for a JAL-operated domestic flight in Japan at an airport that offers the JAL IC service.
MySuica
MySuica allows users to input personal information at the time the card is created. If the card is later lost or stolen, the user can obtain a new card with the previous balance.Welcome Suica
In August 2019, JR East unveiled Welcome Suica, a Suica variant designed for use by tourists to Japan. The card's design features white cherry blossoms on a red background. Welcome Suica is also reloadable, but unlike regular Suica cards, Welcome Suica does not require the user to make a deposit. However, Welcome Suica can only be used for 28 days from the date of purchase after which it stops working. It is also nonrefundable, regardless of the balance or user's activity. JR East request customers always carry with them a reference sheet, or receipt, to accompany the card.Card stacking
Ticket gates return an error when the scan encounters more than one compatible card. Although it is intended that each person have only one Suica, many people have more than one. Further, since the introduction of Pasmo in March 2007, more people have at least one of each. Consequently, JR has begun, and intensified since March, an awareness campaign to discourage commuters from storing multiple cards together. Incompatible cards, such asEdy
Edy, provided by Rakuten, Inc. in Japan is a prepaid rechargeable contactless smart card. While the name derives from euro, dollar, and yen, it works with yen only.
History
Edy was launched on January 18, 2001 by BitWallet, with fincanin ...
, seem to have an inconsistent effect on a machine's ability to read the card which may depend on the reading device. On the other hand, the Express-IC (EX-IC) card for Tokaido Shinkansen reservations is meant to be used in this manner (stacked on either a Suica or ICOCA to facilitate transfer between Shinkansen and regular lines).
Technology
The card incorporates a contactless Near Field Communication (NFC
NFC may refer to:
Psychology
* Need for cognition, in psychology
* Need for closure, social psychological term
Sports
* NFC Championship Game, the National Football Conference Championship Game
* NCAA Football Championship (Philippines)
* Nati ...
) technology developed by Sony, called FeliCa. The same technology is also deployed in the Edy
Edy, provided by Rakuten, Inc. in Japan is a prepaid rechargeable contactless smart card. While the name derives from euro, dollar, and yen, it works with yen only.
History
Edy was launched on January 18, 2001 by BitWallet, with fincanin ...
electronic cash cards used in Japan, the Octopus card in Hong Kong, and the EZ-Link Card in Singapore.
Interoperation
smart card
A smart card, chip card, or integrated circuit card (ICC or IC card) is a physical electronic authentication device, used to control access to a resource. It is typically a plastic credit card-sized card with an embedded integrated circuit (IC) c ...
solution to replace the existing Passnet magnetic card system. Through collaboration with JR East, passengers can use Suica wherever Pasmo cards are accepted to ride any railway or bus in the Tokyo metropolitan area. Monthly passes for JR East lines can only be on Suica, while monthly passes for Tokyo Metro can only be on Pasmo cards but otherwise, the cards are functionally identical for commuters.
This agreement has since been implemented with other systems across Japan. On 23 March 2013, a nationwide inter-operation among 10 transportation smart cards started. As of 2014 Suica has interoperability with ICOCA, Kitaca, PASMO, TOICA, manaca
Manaca, written in lower-case letters, is a rechargeable contactless smart card used in Nagoya, Japan and the surrounding area since February 11, 2011, when it replaced the Tranpass magnetic fare card system. As of March 23, 2013, it became ...
, PiTaPa, SUGOCA
is a Japanese rechargeable contactless smart card ticketing system for public transport in Fukuoka Prefecture and environs. The Kyūshū Railway Company (JR Kyūshū) introduced the system on 1 March 2009. The name is an acronym of "Smart Urban ...
, nimoca, hayakaken and several other local smart cards.
In 22 July 2014, Nintendo
is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational video game company headquartered in Kyoto, Japan. It develops video games and video game consoles.
Nintendo was founded in 1889 as by craftsman Fusajiro Yamauchi and originally produce ...
added support for Suica and Pasmo cards in the Nintendo eShop
The Nintendo eShop is a digital distribution service powered by the Nintendo Network for the Wii U and Nintendo 3DS, and by a dedicated online infrastructure for the Nintendo Switch. Launched in June 2011 on the Nintendo 3DS, the eShop was en ...
through the NFC
NFC may refer to:
Psychology
* Need for cognition, in psychology
* Need for closure, social psychological term
Sports
* NFC Championship Game, the National Football Conference Championship Game
* NCAA Football Championship (Philippines)
* Nati ...
function of the Wii U GamePad and the New Nintendo 3DS. The service was then discontinued on 18 January 2022.
Mobile devices
Mobile Suica
 Since January 2006, a version called was incorporated into
Since January 2006, a version called was incorporated into mobile FeliCa
FeliCa is a contactless RFID smart card system from Sony in Japan, primarily used in electronic money cards. The name stands for ''Felicity Card''. First utilized in the Octopus card system in Hong Kong, the technology is used in a variety of card ...
wallet phones by Japan's mobile operators. This system includes Java applications to manage the Suica function in the mobile phone, to recharge the Suica stored in the mobile phone, review the stored value and perform other functions via the mobile phone. An enhancement for 2007 allowed for Suica charges to be added directly to the phone bill, eliminating the requirement to constantly add to and monitor the remaining balance. On 23 May 2011, JR announced debut of Mobile Suica app for Android Smartphones supporting Osaifu-Keitai.
Mobile Suica is a service for Osaifu Keitai
, literally "Wallet Mobile", is the ''de facto'' standard mobile payment system in Japan. Osaifu-Keitai services include electronic money, identity card, loyalty card, fare collection of public transits (including railways, buses, and airplanes), ...
mobile phones, first launched on 28 January 2006 by NTT DoCoMo and au in Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
, and now also offered by SoftBank Mobile and Willcom.
Just like traditional Suica cards, which are prepaid rechargeable contactless smart cards mainly used to pay for fares on the JR East
The is a major passenger railway company in Japan and is the largest of the seven Japan Railways Group companies. The company name is officially abbreviated as JR-EAST or JR East in English, and as in Japanese. The company's headquarters are ...
railway network, Mobile Suica can also be charged when the remaining balance gets low. Other features supported by the mobile phone includes the ability to review past Suica transactions via the mobile's display. Suica uses Sony's FeliCa chip for its main functionalities. Mobile Suica interacts with the FeliCa chip using Java technology.
Since October 2006, it is possible to register for Mobile Suica using any major credit card, a Suica VIEW card is no longer required. A limited e-money
Digital currency (digital money, electronic money or electronic currency) is any currency, money, or money-like asset that is primarily managed, stored or exchanged on digital computer systems, especially over the internet. Types of digital cu ...
only application called "Easy Mobile Suica" (which does not require a credit card) was also launched in late October 2006.
Apple Pay
On September 7, 2016, Apple announced that Suica cards could be added to Apple Pay in the Wallet app and used in the same way as a physical card. This functionality was limited to devices purchased in Japan which included FeliCa support: iPhone 7 (model A1779 and A1785) andApple Watch Series 2
Apple Watch is a line of smartwatches produced by Apple Inc. It incorporates activity tracker, fitness tracking, Health (Apple), health-oriented capabilities, and wireless telecommunication, and integrates with iOS and other Apple products and s ...
.
With the release of the iPhone 8, iPhone X and the Apple Watch Series 3, and later, devices purchased anywhere in the world could be used with Apple Pay Suica.
iOS 13 introduced support for creating a virtual Suica card from the Wallet app.
iOS 15 introduced new Wallet app improvements and a dedicated category for adding Suica and other transit cards regardless of the device region setting.
Google Pay
On 24 May 2018, Google announced that Suica cards could be added toGoogle Pay Google Pay may refer to:
* Google Pay (mobile app), a mobile payments app introduced in 2020
* Google Pay (2018–2022), a digital wallet app introduced in 2018, now Google Wallet
* Google Pay (payment method), a digital payments service introduced ...
. This functionality is limited to Android devices that are purchased in Japan that support Osaifu-Keitai and have their Google Account's region set to Japan.
See also
*Mass transit system
Public transport (also known as public transportation, public transit, mass transit, or simply transit) is a system of transport for passengers by group travel systems available for use by the general public unlike private transport, typical ...
*Electronic money
Digital currency (digital money, electronic money or electronic currency) is any currency, money, or money-like asset that is primarily managed, stored or exchanged on digital computer systems, especially over the internet. Types of digital cu ...
* List of smart cards
References
External links
* * * http://www.sony.net/Products/felica/JR-East: Mobile Suica
(In Japanese)
JR-East: Research and Development > R&D Story
{{Tokyo transit 2001 introductions 2001 establishments in Japan Japanese inventions Contactless smart cards Fare collection systems in Japan East Japan Railway Company