Stobi on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Stobi or Stoboi (; ; ; ), was an ancient town of Paeonia, later conquered by
Stobi or Stoboi (; ; ; ), was an ancient town of Paeonia, later conquered by

 A well-preserved marble head of Augustus was unearthed at Stobi in April 2009.
A well-preserved marble head of Augustus was unearthed at Stobi in April 2009.
 The ethnonym ''Albanos'', likely a reference to
The ethnonym ''Albanos'', likely a reference to
 The Grand Palace near the eastern wall of the city was built during the Roman period and contains beautiful
The Grand Palace near the eastern wall of the city was built during the Roman period and contains beautiful
 The House of the Psalms, in front of the Central Basilica, has a central room with a mosaic floor, a room with colonnades, a big pool and columns in the western part of the yard.
Via Axia is one of the main streets in Stobi, oriented east-west. Only a small part of the street has been discovered.
The Main Town Public Fountain is located on a small square created by the streets Via Axia and Via Principalis Inferior.
The Magnae Thermae, or Big Bath, discovered in 1931, consisted of two rooms: one large room with a statue and a pool made of stone blocks. The reconstructed bath was in use until the late 6th century.
Via Principalis Inferior was a major street of the city running from the central basilica to the main town fountain, then to house of Partenius, the 'Palace of Theodosius' and the house of Psalms.
The House of Peristerius was a large living complex for several families and also had rooms for shops. The Peristerius family owned the rooms in the southern part of the complex. The central part of this complex is a yard under open sky, with fountains on the western side. In the eastern part is an excellent example of floor mosaics and in the middle there is a fountain made of marble. The complex and the mosaics date from the late 4th or the early 5th century. The Via Theodosia street is parallel to Via Axia and it is located between the house of Peristerius and the 'palace of Theodosius'.
The Palace of Theodosius was where the emperor Theodosius first stayed while in Stobi. The floor is covered with marble blocks and the peristyle with mosaics in the technique opus sectile. The other rooms are also decorated, dating from the 4th to the 5th century.
The House of Partenius is located near the southern part of the Palace of Theodosius, and is connected to it by a wall making it into an L-shaped building.
Valavica (''Domus Fullonica'') is a complex of connected shops and residences, built on older objects. The name describes only an earlier phase of the complex, as later in the 5th century there was also a workshop for painting and making carpets. The complex was in use from the 1st century to the 6th century.
The House of the Psalms, in front of the Central Basilica, has a central room with a mosaic floor, a room with colonnades, a big pool and columns in the western part of the yard.
Via Axia is one of the main streets in Stobi, oriented east-west. Only a small part of the street has been discovered.
The Main Town Public Fountain is located on a small square created by the streets Via Axia and Via Principalis Inferior.
The Magnae Thermae, or Big Bath, discovered in 1931, consisted of two rooms: one large room with a statue and a pool made of stone blocks. The reconstructed bath was in use until the late 6th century.
Via Principalis Inferior was a major street of the city running from the central basilica to the main town fountain, then to house of Partenius, the 'Palace of Theodosius' and the house of Psalms.
The House of Peristerius was a large living complex for several families and also had rooms for shops. The Peristerius family owned the rooms in the southern part of the complex. The central part of this complex is a yard under open sky, with fountains on the western side. In the eastern part is an excellent example of floor mosaics and in the middle there is a fountain made of marble. The complex and the mosaics date from the late 4th or the early 5th century. The Via Theodosia street is parallel to Via Axia and it is located between the house of Peristerius and the 'palace of Theodosius'.
The Palace of Theodosius was where the emperor Theodosius first stayed while in Stobi. The floor is covered with marble blocks and the peristyle with mosaics in the technique opus sectile. The other rooms are also decorated, dating from the 4th to the 5th century.
The House of Partenius is located near the southern part of the Palace of Theodosius, and is connected to it by a wall making it into an L-shaped building.
Valavica (''Domus Fullonica'') is a complex of connected shops and residences, built on older objects. The name describes only an earlier phase of the complex, as later in the 5th century there was also a workshop for painting and making carpets. The complex was in use from the 1st century to the 6th century.
 The Episcopal Basilica, dating from the 5th and 6th centuries, with a baptistery to the south. A peacock from the baptistery's mosaic floor is depicted on the reverse of the Macedonian 10 denars banknote, issued in 1996, and of the 10 denars coin, issued in 2008.
The Episcopal Basilica, dating from the 5th and 6th centuries, with a baptistery to the south. A peacock from the baptistery's mosaic floor is depicted on the reverse of the Macedonian 10 denars banknote, issued in 1996, and of the 10 denars coin, issued in 2008.National Bank of the Republic of North Macedonia
Macedonian currency
Coins in circulation
. – Retrieved 30 March 2009.
Official web page of the archaeological site and National Institution Stobi
* ttp://users.stlcc.edu/mfuller/macedonia/stobi.html St. Louis Community College Article and Photographs about Stobibr>Coins from Stobi
{{Ancient synagogues Populated places disestablished in the 6th century 1924 archaeological discoveries Geography of ancient Paeonia Archaeological sites in North Macedonia Former populated places in the Balkans Macedonia (Roman province) Gradsko Municipality North Macedonia in the Roman era Ancient synagogues
 Stobi or Stoboi (; ; ; ), was an ancient town of Paeonia, later conquered by
Stobi or Stoboi (; ; ; ), was an ancient town of Paeonia, later conquered by Macedon
Macedonia ( ; , ), also called Macedon ( ), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, which later became the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by the royal ...
, and finally turned into the capital of the Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
province of Macedonia Salutaris. It is located near Gradsko, North Macedonia
North Macedonia, officially the Republic of North Macedonia, is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe. It shares land borders with Greece to the south, Albania to the west, Bulgaria to the east, Kosovo to the northwest and Serbia to the n ...
, on the main road that leads from the Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
to the Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans and Anatolia, and covers an area of some . In the north, the Aegean is connected to the Marmara Sea, which in turn con ...
and is considered by many to be the most famous archaeological site in North Macedonia. Stobi was built where the Erigon
The Crna River (Macedonian language, Macedonian: Црна Река ;"Black River"), also known in English as Cherna (), is a river in North Macedonia. It is a right tributary of the Vardar River. It runs through much of the south and west of the c ...
(Crna River) joins the Axios
Axios commonly refers to:
* Axios (river), a river that runs through Greece and North Macedonia
* ''Axios'' (website), an American news and information website
Axios may also refer to:
Brands and enterprises
* Axios, a brand of suspension produ ...
(Vardar), making it strategically important as a center for both trade and warfare.
The pre-Roman period
Stobi developed from a Paeonian settlement established in the Archaic period. Located on the northern side of a terrace, the early town covered an area of about . Its proximity to the junction of the Erigón and Axiós Rivers as well as its position in the fertile central Vardar valley allowed it quickly to develop a flourishing economy and to establish trade. Nearby Mount Klepa was a lucrative source of marble. The initial Paeonian population was later supplemented by other immigrant groups. It is believed that in 217 BCE, Philip V annexed Paionia during his campaign against theDardani
The Dardani (; ; ) or Dardanians were a Paleo-Balkan languages, Paleo-Balkan people, who lived in a region that was named Kingdom of Dardania, Dardania after their settlement there. They were among the oldest Balkan peoples, and their society wa ...
who had entered Bylazora, the largest Paeonian town.

The Roman period
The city was first mentioned in writing by the historianLivy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding i ...
, in connection with a victory of Philip V of Macedon
Philip V (; 238–179 BC) was king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon from 221 to 179 BC. Philip's reign was principally marked by the Social War (220–217 BC), Social War in Greece (220-217 BC) ...
over the Dardani
The Dardani (; ; ) or Dardanians were a Paleo-Balkan languages, Paleo-Balkan people, who lived in a region that was named Kingdom of Dardania, Dardania after their settlement there. They were among the oldest Balkan peoples, and their society wa ...
in 197 BC. In 168 BC, the Romans defeated Perseus
In Greek mythology, Perseus (, ; Greek language, Greek: Περσεύς, Romanization of Greek, translit. Perseús) is the legendary founder of the Perseid dynasty. He was, alongside Cadmus and Bellerophon, the greatest Greek hero and slayer of ...
and Macedonia
Macedonia (, , , ), most commonly refers to:
* North Macedonia, a country in southeastern Europe, known until 2019 as the Republic of Macedonia
* Macedonia (ancient kingdom), a kingdom in Greek antiquity
* Macedonia (Greece), a former administr ...
was divided into four nominally independent republics. In 148 BC, the four areas of Macedonia were brought together in a unified Roman province. In the reign of Augustus
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in A ...
the city grew in size and population. The city grew further in 69 BC once it became a municipium
In ancient Rome, the Latin term (: ) referred to a town or city. Etymologically, the was a social contract among ('duty holders'), or citizens of the town. The duties () were a communal obligation assumed by the in exchange for the privileges ...
, at which time it began to produce coins printed with ''Municipium Stobensium''. The citizens of Stobi enjoyed Ius Italicum
''Ius Italicum'' or ''ius italicum'' (Latin, Italian or Italic law) was a law in the early Roman Empire that allowed the emperors to grant cities outside Italy the legal fiction that they were on Italian soil. This meant that the city would be go ...
and were citizens of Rome. Most belonged to the Roman tribes Aemila and Tromentina. During Roman times Stobi was the capital of the Roman province Macedonia Salutaris. Emperor Theodosius I
Theodosius I ( ; 11 January 347 – 17 January 395), also known as Theodosius the Great, was Roman emperor from 379 to 395. He won two civil wars and was instrumental in establishing the Nicene Creed as the orthodox doctrine for Nicene C ...
stayed in Stobi in 388. Late in the 5th century the city underwent a terrible turn of events. In 479, it was sacked by Theodoric
Theodoric is a Germanic given name. First attested as a Gothic name in the 5th century, it became widespread in the Germanic-speaking world, not least due to its most famous bearer, Theodoric the Great, king of the Ostrogoths.
Overview
The name w ...
, an Ostrogothic
The Ostrogoths () were a Roman-era Germanic peoples, Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Goths, Gothic kingdoms within the Western Roman Empire, drawing upon the large Gothic populatio ...
king. The citizens reconstructed the city, but in 518 it was struck by a powerful earthquake. Avaro-Slavic invasions in the 6th century destroyed the city's economy and infrastructure.
Etymology
The name ''Stobi'' is thought to have been aPaeonian
In antiquity, Paeonia or Paionia () was the land and kingdom of the Paeonians (or Paionians; ).
The exact original boundaries of Paeonia, like the early history of its inhabitants, are obscure, but it is known that it roughly corresponds to m ...
word meaning "post, pillar" and is akin to Old Prussian
Old Prussian is an extinct West Baltic language belonging to the Baltic branch of the Indo-European languages, which was once spoken by the Old Prussians, the Baltic peoples of the Prussian region. The language is called Old Prussian to av ...
''stabis'' "rock," Old Church Slavonic
Old Church Slavonic or Old Slavonic ( ) is the first Slavic languages, Slavic literary language and the oldest extant written Slavonic language attested in literary sources. It belongs to the South Slavic languages, South Slavic subgroup of the ...
''stoborъ'', ''stъlbъ'' "post, pillar," English ''staff'', Old English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-S ...
''stapol'' "post archaic Greek ''stobos'' "scolding, bad language''b''k ''stephein'' "to tie around, encircle," ''staphyle'' "grapevine, grape bunch," and Middle Irish
Middle Irish, also called Middle Gaelic (, , ), is the Goidelic language which was spoken in Ireland, most of Scotland and the Isle of Man from AD; it is therefore a contemporary of Late Old English and Early Middle English. The modern Goideli ...
''sab'' "shaft." Such a name suggests that it was the site of a large local cultic pillar, though there is no evidence of this.
History of excavation
The Museum of Belgrade was the first and only institution to investigate the city from 1924 to 1936. Yugoslavian archaeologists first discovered public and private buildings in the city and then the city's theater, built in the 3rd century, and religious artifacts from the central and western part of the city. Research into the city officially ended in 1940. DuringWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
late Hellenistic
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the R ...
graves were found in the Palace of Peristerius, many of which had been covered by buildings. In 1970, between the North and Central Basilica and in the western necropolis 55 graves were discovered. In 1955 in the southern part of the North Basilica 23 Slavic graves dating from the 9th to 12th centuries were discovered. Bronze statues from the archaic and classical periods as well as ceramic objects from the Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
era were discovered in the two parts of the civil basilica
In Ancient Roman architecture, a basilica (Greek Basiliké) was a large public building with multiple functions that was typically built alongside the town's forum. The basilica was in the Latin West equivalent to a stoa in the Greek Eas ...
. An older part of the second synagogue was discovered in the Central Basilica, as well as architectonic structures and 23 Slavic graves in the North Basilica. The most significant finds were uncovered between 1970 and 1980 by Yugoslav and American archaeologists. In this period more buildings were discovered and new expeditions in the western necropolis, the ''Casa Romana'' and in the aqueduct network of Stobi revealed more mosaics. From 1981 to 1988 the Episcopal Basilica was unearthed. These investigations confirmed predictions concerning the religion, culture and daily life of its population.
 A well-preserved marble head of Augustus was unearthed at Stobi in April 2009.
A well-preserved marble head of Augustus was unearthed at Stobi in April 2009.
 The ethnonym ''Albanos'', likely a reference to
The ethnonym ''Albanos'', likely a reference to Albanians
The Albanians are an ethnic group native to the Balkan Peninsula who share a common Albanian ancestry, Albanian culture, culture, Albanian history, history and Albanian language, language. They are the main ethnic group of Albania and Kosovo, ...
, was found on a funeral inscription from ancient Stobi in present-day North Macedonia
North Macedonia, officially the Republic of North Macedonia, is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe. It shares land borders with Greece to the south, Albania to the west, Bulgaria to the east, Kosovo to the northwest and Serbia to the n ...
, near Gradsko about 90 km to the southeast of Gorno Sonje. The inscription in ancient Greek reads "ΦΛ(ΑΒΙΩ) ΑΛΒΑΝΩ ΤΩ ΤΕΚΝΩ ΑΙΜΙΛΙΑΝΟΣ ΑΛΒΑΝΟ(Σ) ΜΝΗΜ(Η)Σ �ΑΡΗΝ ("In memory of Flavios Albanos, his son Aemilianos Albanos"). It dates to the 2nd/3rd century AD.
Religion in Stobi
 The Grand Palace near the eastern wall of the city was built during the Roman period and contains beautiful
The Grand Palace near the eastern wall of the city was built during the Roman period and contains beautiful fresco
Fresco ( or frescoes) is a technique of mural painting executed upon freshly laid ("wet") lime plaster. Water is used as the vehicle for the dry-powder pigment to merge with the plaster, and with the setting of the plaster, the painting become ...
es. The Temple of Nemesis
In ancient Greek religion and myth, Nemesis (; ) also called Rhamnousia (or Rhamnusia; ), was the goddess who personified retribution for the sin of hubris: arrogance before the gods.
Etymology
The name ''Nemesis'' is derived from the Greek ...
in the theater, and religious items related to Hygeia and Telesphorus, Artemis Locheia, Apollo Clarious, Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a Jupiter mass, mass more than 2.5 times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined a ...
, Dionysus
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, myth, Dionysus (; ) is the god of wine-making, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, festivity, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstasy, and theatre. He was also known as Bacchus ( or ; ...
and Hera
In ancient Greek religion, Hera (; ; in Ionic Greek, Ionic and Homeric Greek) is the goddess of marriage, women, and family, and the protector of women during childbirth. In Greek mythology, she is queen of the twelve Olympians and Mount Oly ...
were common during this time. In the early Christian period Stobi was an episcopal see by 325, when the bishop Budius took part in the First Council of Nicaea
The First Council of Nicaea ( ; ) was a council of Christian bishops convened in the Bithynian city of Nicaea (now İznik, Turkey) by the Roman Emperor Constantine I. The Council of Nicaea met from May until the end of July 325.
This ec ...
. Stobi is one of a small number of cities from the late antique
Late antiquity marks the period that comes after the end of classical antiquity and stretches into the onset of the Early Middle Ages. Late antiquity as a period was popularized by Peter Brown in 1971, and this periodization has since been wide ...
and early Christian period that kept a large number of mosaics. From the 4th to 5th century, several big churches were built and were known for their interior decoration of mosaics and frescoes. Decorative mosaics can also be found in private luxury buildings from late Antiquity, such as the Villas of Theodosius, Policharmosius and Peristerius. New archaeological research has shown that all Christian basilicas in the city discovered thus far were built over ancient buildings.
An ancient synagogue
A synagogue, also called a shul or a temple, is a place of worship for Jews and Samaritans. It is a place for prayer (the main sanctuary and sometimes smaller chapels) where Jews attend religious services or special ceremonies such as wed ...
dating from the 3rd or 4th century AD attests to a Jew
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, religion, and community are highly inte ...
ish presence in the city. By the close of the 4th century, this synagogue was demolished and replaced by a Christian basilica.
Historical sites in Stobi
The Northern Basilica has three main parts: anarthex
The narthex is an architectural element typical of Early Christian art and architecture, early Christian and Byzantine architecture, Byzantine basilicas and Church architecture, churches consisting of the entrance or Vestibule (architecture), ve ...
, an exonarthex separated by colonnades and an atrium constructed mostly of marble. In the northern part there is a baptistry
In Christian architecture the baptistery or baptistry (Old French ''baptisterie''; -4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ... ''baptisterie''; Latin ''baptist ...
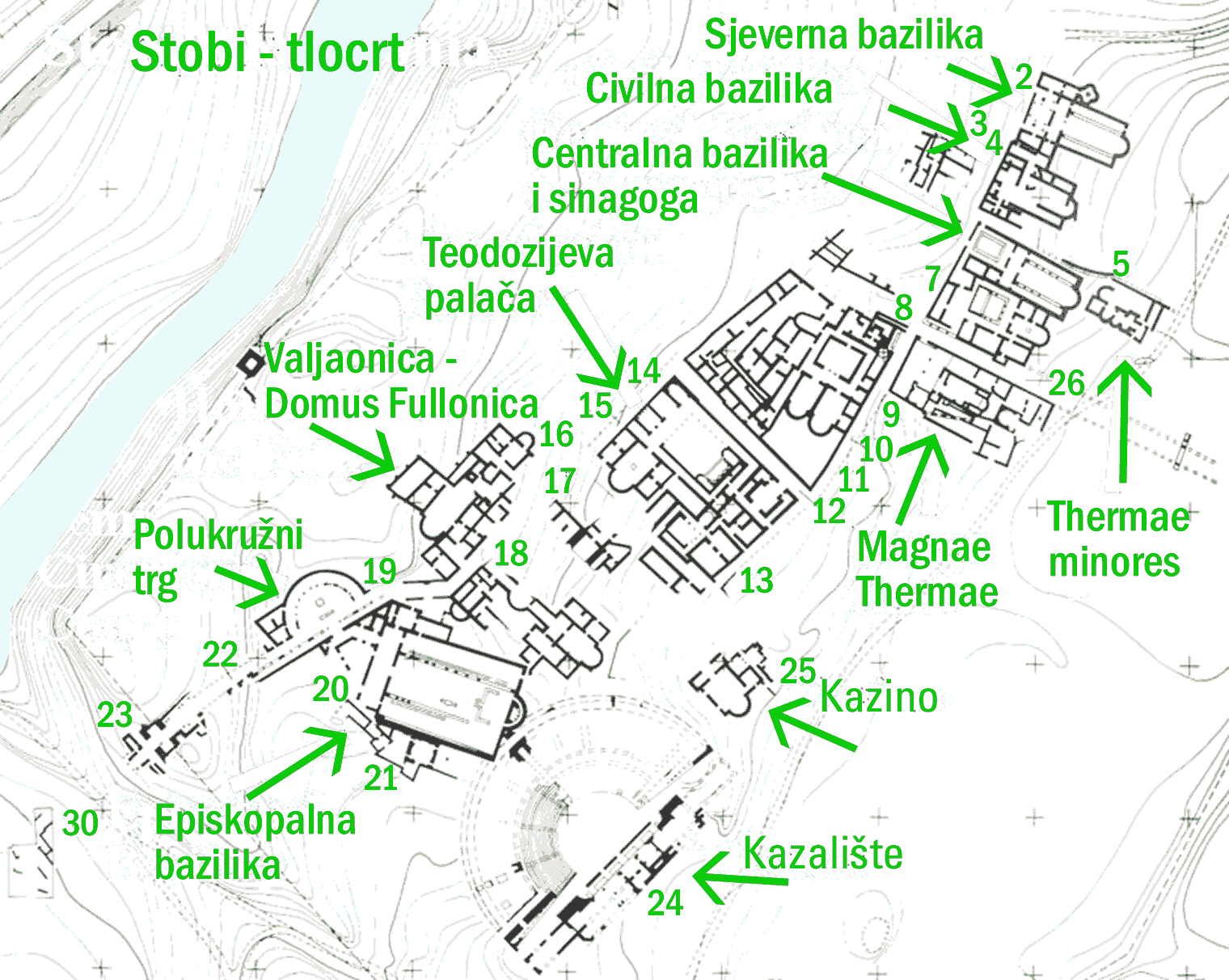
and in the southern part are Slavic graves. The church, which was built at the beginning of the 5th century, can be entered from the street Via Principalis Inferior. The Civil Basilica is south of the north basilica and was discovered in 1937. In 1956 archaeologists found that there were seven building phases. Between the North and Civil Basilicas are the ancient Thermae Minores, or "Little Baths" made of stone blocks.
The Central Basilica and synagogue can be entered from the Via Principalis street. The Central Basilica was built on a synagogue at the beginning of the 5th century and had two building phases. The floor of the synagogue was discovered under the level of the Central Basilica. Dating from the 4th century, it was built on an older synagogue from the 3rd century, created by the father of the Synagogue of Stobi, Tiberius Claudius Polycharmos. Inside were two vases dating from 121 to 125.
 The House of the Psalms, in front of the Central Basilica, has a central room with a mosaic floor, a room with colonnades, a big pool and columns in the western part of the yard.
Via Axia is one of the main streets in Stobi, oriented east-west. Only a small part of the street has been discovered.
The Main Town Public Fountain is located on a small square created by the streets Via Axia and Via Principalis Inferior.
The Magnae Thermae, or Big Bath, discovered in 1931, consisted of two rooms: one large room with a statue and a pool made of stone blocks. The reconstructed bath was in use until the late 6th century.
Via Principalis Inferior was a major street of the city running from the central basilica to the main town fountain, then to house of Partenius, the 'Palace of Theodosius' and the house of Psalms.
The House of Peristerius was a large living complex for several families and also had rooms for shops. The Peristerius family owned the rooms in the southern part of the complex. The central part of this complex is a yard under open sky, with fountains on the western side. In the eastern part is an excellent example of floor mosaics and in the middle there is a fountain made of marble. The complex and the mosaics date from the late 4th or the early 5th century. The Via Theodosia street is parallel to Via Axia and it is located between the house of Peristerius and the 'palace of Theodosius'.
The Palace of Theodosius was where the emperor Theodosius first stayed while in Stobi. The floor is covered with marble blocks and the peristyle with mosaics in the technique opus sectile. The other rooms are also decorated, dating from the 4th to the 5th century.
The House of Partenius is located near the southern part of the Palace of Theodosius, and is connected to it by a wall making it into an L-shaped building.
Valavica (''Domus Fullonica'') is a complex of connected shops and residences, built on older objects. The name describes only an earlier phase of the complex, as later in the 5th century there was also a workshop for painting and making carpets. The complex was in use from the 1st century to the 6th century.
The House of the Psalms, in front of the Central Basilica, has a central room with a mosaic floor, a room with colonnades, a big pool and columns in the western part of the yard.
Via Axia is one of the main streets in Stobi, oriented east-west. Only a small part of the street has been discovered.
The Main Town Public Fountain is located on a small square created by the streets Via Axia and Via Principalis Inferior.
The Magnae Thermae, or Big Bath, discovered in 1931, consisted of two rooms: one large room with a statue and a pool made of stone blocks. The reconstructed bath was in use until the late 6th century.
Via Principalis Inferior was a major street of the city running from the central basilica to the main town fountain, then to house of Partenius, the 'Palace of Theodosius' and the house of Psalms.
The House of Peristerius was a large living complex for several families and also had rooms for shops. The Peristerius family owned the rooms in the southern part of the complex. The central part of this complex is a yard under open sky, with fountains on the western side. In the eastern part is an excellent example of floor mosaics and in the middle there is a fountain made of marble. The complex and the mosaics date from the late 4th or the early 5th century. The Via Theodosia street is parallel to Via Axia and it is located between the house of Peristerius and the 'palace of Theodosius'.
The Palace of Theodosius was where the emperor Theodosius first stayed while in Stobi. The floor is covered with marble blocks and the peristyle with mosaics in the technique opus sectile. The other rooms are also decorated, dating from the 4th to the 5th century.
The House of Partenius is located near the southern part of the Palace of Theodosius, and is connected to it by a wall making it into an L-shaped building.
Valavica (''Domus Fullonica'') is a complex of connected shops and residences, built on older objects. The name describes only an earlier phase of the complex, as later in the 5th century there was also a workshop for painting and making carpets. The complex was in use from the 1st century to the 6th century.
 The Episcopal Basilica, dating from the 5th and 6th centuries, with a baptistery to the south. A peacock from the baptistery's mosaic floor is depicted on the reverse of the Macedonian 10 denars banknote, issued in 1996, and of the 10 denars coin, issued in 2008.
The Episcopal Basilica, dating from the 5th and 6th centuries, with a baptistery to the south. A peacock from the baptistery's mosaic floor is depicted on the reverse of the Macedonian 10 denars banknote, issued in 1996, and of the 10 denars coin, issued in 2008.Macedonian currency
Coins in circulation
. – Retrieved 30 March 2009.
See also
* Heraclea Lyncestis *Scupi
Scupi (; ) is an archaeological site located between Zajčev Rid (''Зајчев Рид'' 'Rabbit Hill') and the Vardar River, several kilometers from the center of modern Skopje in North Macedonia. A Roman military camp was founded here in the se ...
* Nikola Vulić
References
External links
Official web page of the archaeological site and National Institution Stobi
* ttp://users.stlcc.edu/mfuller/macedonia/stobi.html St. Louis Community College Article and Photographs about Stobibr>Coins from Stobi
{{Ancient synagogues Populated places disestablished in the 6th century 1924 archaeological discoveries Geography of ancient Paeonia Archaeological sites in North Macedonia Former populated places in the Balkans Macedonia (Roman province) Gradsko Municipality North Macedonia in the Roman era Ancient synagogues