Stator on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
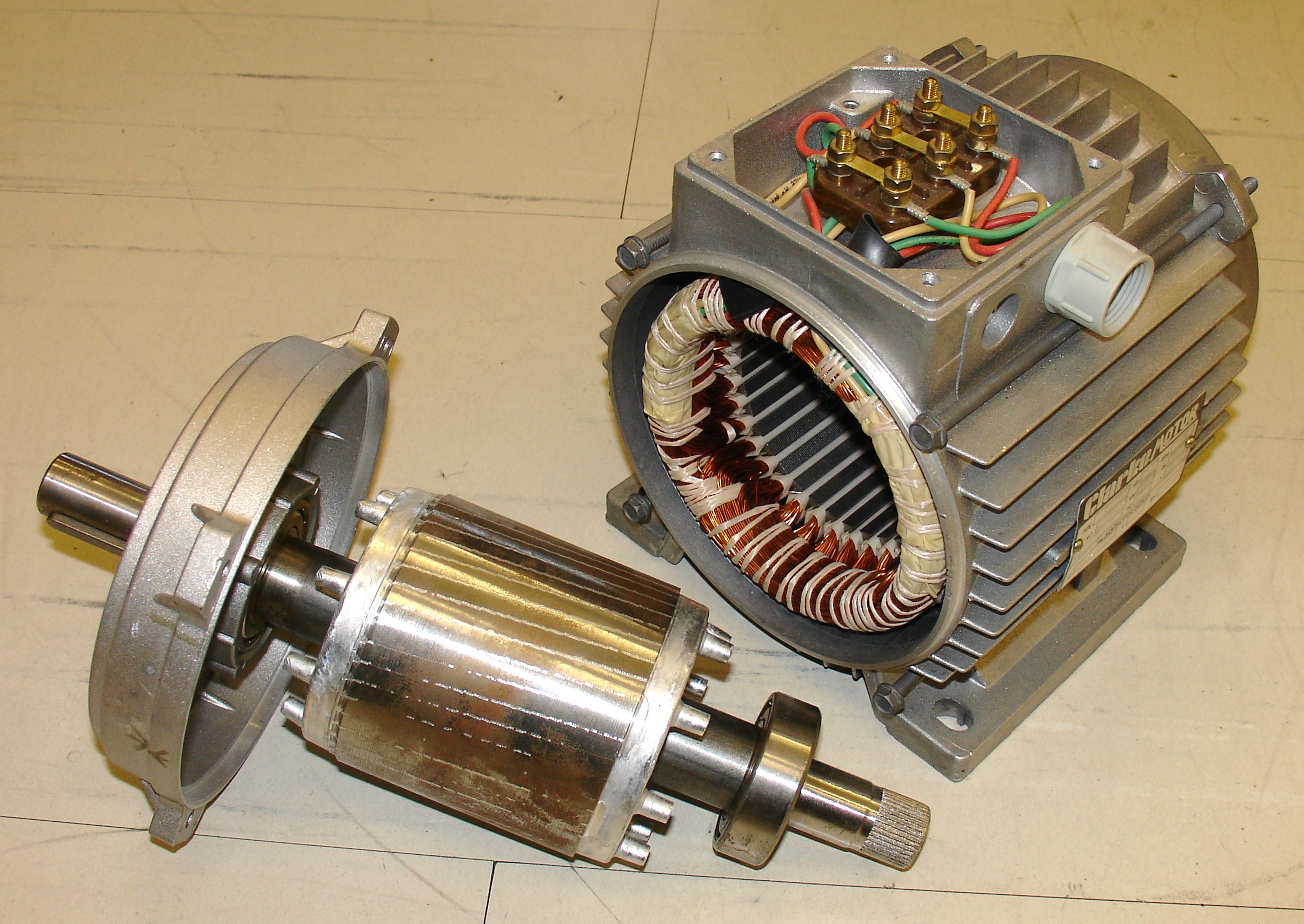 The stator is the stationary part of a rotary system, found in
The stator is the stationary part of a rotary system, found in
 The stator of these devices may be either a permanent
The stator of these devices may be either a permanent 
electric generator
In electricity generation, a generator, also called an ''electric generator'', ''electrical generator'', and ''electromagnetic generator'' is an electromechanical device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy for use in an externa ...
s, electric motor
An electric motor is a machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a electromagnetic coil, wire winding to gene ...
s, sirens, mud motors, or biological rotors (such as bacterial flagella
A flagellum (; : flagella) (Latin for 'whip' or 'scourge') is a hair-like appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, from fungal spores ( zoospores), and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many pr ...
or ATP synthase). Energy flows through a stator to or from the rotating component of the system, the rotor. In an electric motor, the stator provides a magnetic field
A magnetic field (sometimes called B-field) is a physical field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular ...
that drives the rotating armature; in a generator, the stator converts the rotating magnetic field to electric current
An electric current is a flow of charged particles, such as electrons or ions, moving through an electrical conductor or space. It is defined as the net rate of flow of electric charge through a surface. The moving particles are called charge c ...
. In fluid powered devices, the stator guides the flow of fluid to or from the rotating part of the system.
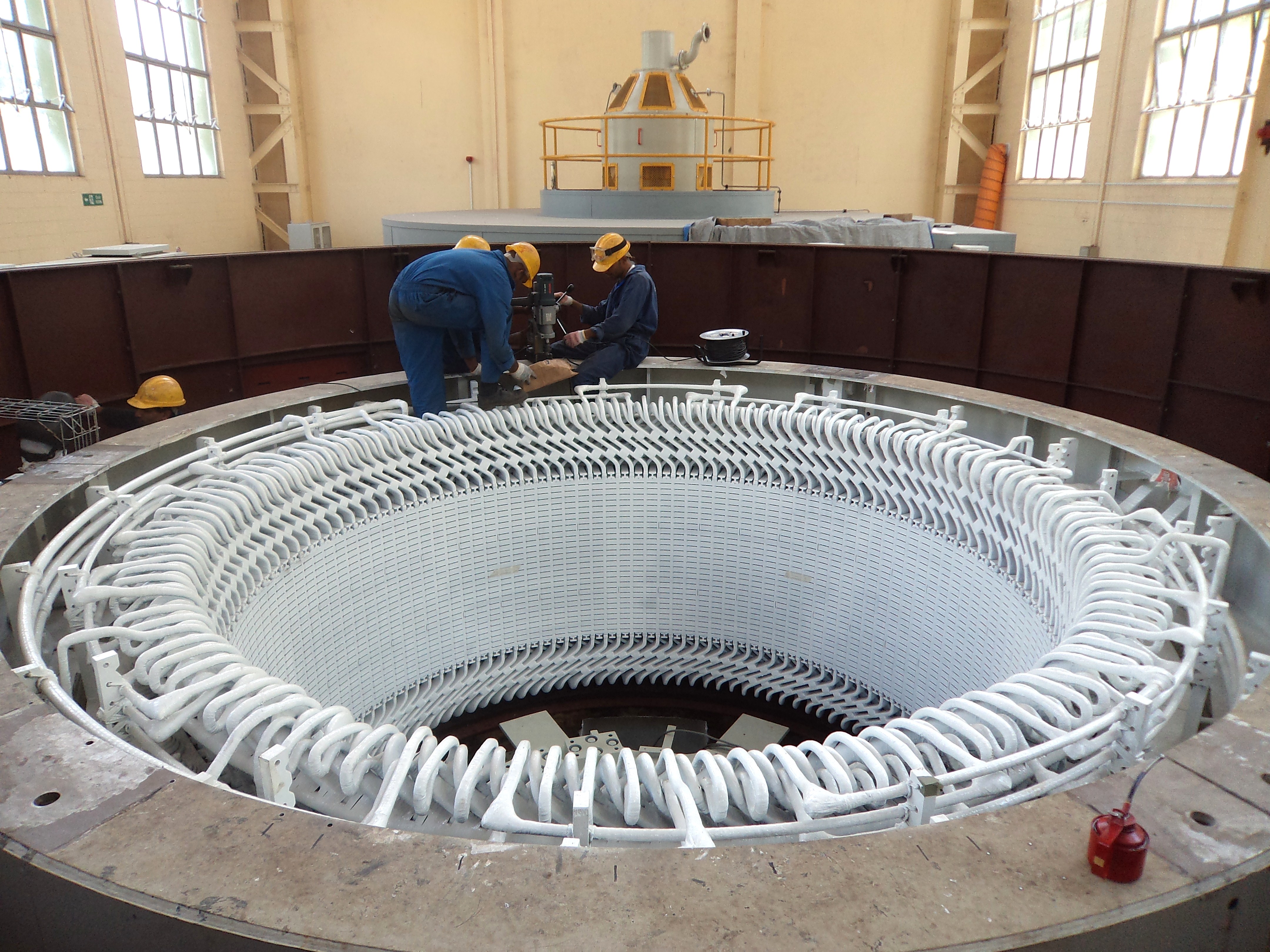
Design
Motor stators are made either from iron/steel or from aprinted circuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB), also called printed wiring board (PWB), is a Lamination, laminated sandwich structure of electrical conduction, conductive and Insulator (electricity), insulating layers, each with a pattern of traces, planes ...
(PCB). Originally applied to low-power applications, PCB stators can be lighter, smaller, and less noisy.
One design embeds thin copper traces in the PCB stator that serve as the windings. The traces are interleaved with epoxy-glass laminates, that insulate each coil from its neighbors. An air core replaces the traditional iron core, saving space and weight, and allowing a smaller air gap.
Hairpin windings may be used in the construction of electric motor stators. This technology, uses windings with wires that individually, may have larger cross sections than those used in conventional windings.
Motors
Depending on the configuration of a spinning electromotive device the stator may act as the ''field magnet'', interacting with the armature to create motion, or it may act as the ''armature'', receiving its influence from moving field coils on the rotor. The first DC generators (known asdynamo
"Dynamo Electric Machine" (end view, partly section, )
A dynamo is an electrical generator that creates direct current using a commutator. Dynamos employed electromagnets for self-starting by using residual magnetic field left in the iron cores ...
s) and DC motors put the field coils on the stator, and the power generation or motive reaction coils on the rotor. This is necessary because a continuously moving power switch known as the commutator
In mathematics, the commutator gives an indication of the extent to which a certain binary operation fails to be commutative. There are different definitions used in group theory and ring theory.
Group theory
The commutator of two elements, ...
is needed to keep the field correctly aligned across the spinning rotor. The commutator must become larger and more robust as the current increases.
magnet
A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, steel, nickel, ...
or an electromagnet
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. Electromagnets usually consist of wire (likely copper) wound into a electromagnetic coil, coil. A current through the wire creates a magnetic ...
.
An AC alternator
An alternator (or synchronous generator) is an electrical generator that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy in the form of alternating current. For reasons of cost and simplicity, most alternators use a rotating magnetic field wit ...
produces power across multiple high-current power generation coils connected in parallel, eliminating the commutator.

Fluid devices
In aturbine
A turbine ( or ) (from the Greek , ''tyrbē'', or Latin ''turbo'', meaning vortex) is a rotary mechanical device that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful work. The work produced can be used for generating electrical ...
, the stator element contains blades or ports used to redirect the flow of fluid. Such devices include the steam turbine
A steam turbine or steam turbine engine is a machine or heat engine that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam and uses it to do mechanical work utilising a rotating output shaft. Its modern manifestation was invented by Sir Charles Par ...
and the torque converter
A torque converter is a device, usually implemented as a type of fluid coupling, that transfers rotating power from a prime mover, like an internal combustion engine, to a rotating driven load. In a vehicle with an automatic transmission, the ...
. In a mechanical siren, the stator contains one or more rows of holes that admit air into the rotor; by controlling the flow of air through the holes, the sound of the siren can be altered. A stator can reduce the turbulence and rotational energy introduced by an axial turbine fan, creating a steady column of air with a lower Reynolds number
In fluid dynamics, the Reynolds number () is a dimensionless quantity that helps predict fluid flow patterns in different situations by measuring the ratio between Inertia, inertial and viscous forces. At low Reynolds numbers, flows tend to ...
.
Application
In electric vehicles (EV), the stator plays an important role in the motor, generating the torque and power needed for smooth and efficient operation. By working seamlessly with the rotor, the stator ensures high energy efficiency and reliability of electric vehicles, making it a crucial component in the transition to more environmentally friendly modes of transport. Stators are essential in industrial machines such as pumps, compressors, and conveyor systems. They ensure the smooth and efficient operation of these systems by converting electrical energy into precise mechanical movement necessary for performing heavy-duty tasks. In renewable energy systems, stators make a significant contribution to the operation of wind turbines and hydroelectric power plants. By converting the mechanical energy of wind or water into electricity, stators help produce clean and sustainable energy, aiding in reducing the world's dependency on fossil fuels. Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems use stators to power efficient motors that circulate air, regulate temperature, and humidity. Their performance directly impacts the energy efficiency and reliability of HVAC systems, ensuring comfort in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.References
External links
{{Authority control Electric motors Sirens