starvation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Starvation is a severe deficiency in caloric

 The following are some of the symptoms of starvation:
The following are some of the symptoms of starvation:
 Starvation occurs when the body expends more energy than it takes in for an extended period of time. This imbalance can arise from one or more medical conditions or circumstantial situations, which can include:
Medical reasons
*
Starvation occurs when the body expends more energy than it takes in for an extended period of time. This imbalance can arise from one or more medical conditions or circumstantial situations, which can include:
Medical reasons
*
 According to estimates by the
According to estimates by the
 A son and daughter of Agrippina were also executed by starvation for political reasons; Drusus Caesar, her second son, was put in prison in 33 AD, and starved to death by orders of Tiberius (he managed to stay alive for nine days by chewing the stuffing of his bed); Agrippina's youngest daughter, Julia Livilla, was exiled on an island in 41 by her uncle, Emperor
A son and daughter of Agrippina were also executed by starvation for political reasons; Drusus Caesar, her second son, was put in prison in 33 AD, and starved to death by orders of Tiberius (he managed to stay alive for nine days by chewing the stuffing of his bed); Agrippina's youngest daughter, Julia Livilla, was exiled on an island in 41 by her uncle, Emperor
U.N. Chief: Hunger Kills 17,000 Kids Daily
- by CNN * *
energy
Energy () is the physical quantity, quantitative physical property, property that is transferred to a physical body, body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of Work (thermodynamics), work and in the form of heat and l ...
intake, below the level needed to maintain an organism's life. It is the most extreme form of malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
. In humans, prolonged starvation can cause permanent organ damage and eventually, death
Death is the end of life; the irreversible cessation of all biological functions that sustain a living organism. Death eventually and inevitably occurs in all organisms. The remains of a former organism normally begin to decompose sh ...
. The term ''inanition'' refers to the symptoms and effects of starvation. Starvation by outside forces is a crime according to international criminal law and may also be used as a means of torture
Torture is the deliberate infliction of severe pain or suffering on a person for reasons including corporal punishment, punishment, forced confession, extracting a confession, interrogational torture, interrogation for information, or intimid ...
or execution
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty and formerly called judicial homicide, is the state-sanctioned killing of a person as punishment for actual or supposed misconduct. The sentence ordering that an offender be punished in ...
.
According to the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
(WHO), hunger
In politics, humanitarian aid, and the social sciences, hunger is defined as a condition in which a person does not have the physical or financial capability to eat sufficient food to meet basic nutritional needs for a sustained period. In t ...
is the single gravest threat to the world's public health. The WHO also states that malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
is by far the biggest contributor to child mortality
Child mortality is the death of children under the age of five. The child mortality rate (also under-five mortality rate) refers to the probability of dying between birth and exactly five years of age expressed per 1,000 live births.
It encompa ...
, present in half of all cases. Undernutrition is a contributory factor in the death of 3.1 million children under five every year. The results also demonstrates that as global hunger levels have stabilized, however, despite some progress in specific areas such as stunting and exclusive breastfeeding, an alarming number of people still face food insecurity and malnutrition. In fact, the world has been set back 15 years, with levels of undernourishment similar to those in 2008-2009, with between 713 and 757 million people undernourished in 2023, and over 152 million more than in 2019 when the mid-range was 733 million.
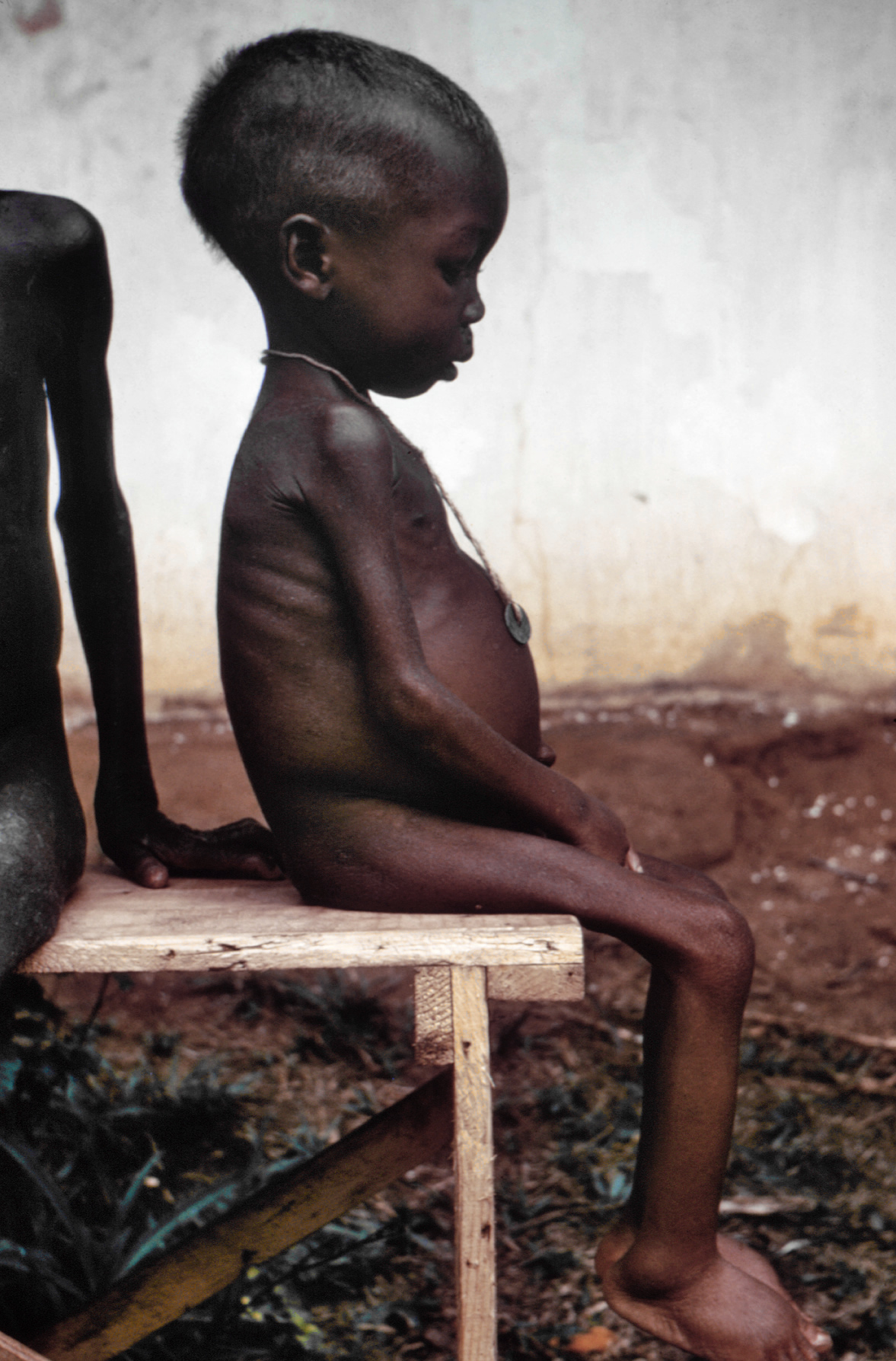
The bloated stomach represents a form of malnutrition called kwashiorkor. The exact pathogenesis of kwashiorkor is not clear, as initially it was thought to relate to diets high in carbohydrates (e.g. maize
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native American ...
) but low in protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
. While many patients have low albumin, this is thought to be a consequence of the condition. Possible causes such as aflatoxin poisoning, oxidative stress, immune dysregulation, and altered gut microbiota have been suggested. Treatment can help mitigate symptoms such as the pictured weight loss
Weight loss, in the context of medicine, health, or physical fitness, refers to a reduction of the total body mass, by a mean loss of fluid, body fat (adipose tissue), or lean mass (namely bone mineral deposits, muscle, tendon, and other conn ...
and muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contra ...
wasting, however prevention is of utmost importance.
Without any food, humans usually die in around 2 months. There was a case when someone survived over a year (382 days) under medical supervision. Lean people can usually survive with a loss of up to 18% of their body mass; obese people can tolerate more, possibly over 20%. Females may survive longer than males due to their higher body fat content at the same BMI.
Signs and symptoms

 The following are some of the symptoms of starvation:
The following are some of the symptoms of starvation:
Changes in behaviour or mental status
The beginning stages of starvation impact mental status and behaviours. These symptoms show up as irritable and/or unstable mood, fatigue, trouble concentrating, and preoccupation with food thoughts. People with those symptoms tend to be easily distracted and have no energy. Psychological effects are profound, including depression, anxiety, and a decrease in cognitive functions.Physical signs
As starvation progresses, the physical symptoms set in. The timing of these symptoms depends on age, size, and overall health. It usually takes days to weeks, and includes weakness, fast heart rate, shallow breaths that are slowed, thirst, and constipation. There may also be diarrhea in some cases. The eyes begin to sink in and glass over. The muscles begin to become smaller and muscle wasting sets in. Tiredness and dizziness also commonly occur, especially from any physical task. The skin is often overly pale. One prominent sign in children is a swollen belly. Skin loosens and turns pale in color, and there may be swelling of the feet and ankles.Weakened immune system
Symptoms of starvation may also appear as a weakened immune system, slow wound healing, and poor response to infection. Rashes may develop on the skin. The body directs any nutrients available to keeping organs functioning.Other symptoms
Other effects of starvation may include: *Anemia
Anemia (also spelt anaemia in British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen. This can be due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin availabl ...
* Gallstones
* Hypotension
Hypotension, also known as low blood pressure, is a cardiovascular condition characterized by abnormally reduced blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps out blood and is ...
* Stomach disease
* Cardiovascular
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart a ...
and respiratory diseases
* Irregular or absent menstrual periods in women
* Kidney disease
Kidney disease, or renal disease, technically referred to as nephropathy, is damage to or disease of a kidney. Nephritis is an Inflammation, inflammatory kidney disease and has several types according to the location of the inflammation. Infla ...
or failure
Failure is the social concept of not meeting a desirable or intended objective, and is usually viewed as the opposite of success. The criteria for failure depends on context, and may be relative to a particular observer or belief system. On ...
* Electrolyte imbalance
* Emaciation
* Oliguria
Stages of starvation
The symptoms of starvation show up in three stages. Phase one and two can show up in anyone that skips meals, diets, and goes through fasting. Phase three is more severe, can be fatal, and results from long-term starvation. Phase one: When meals are skipped, the body begins to maintain blood sugar levels by degrading glycogen in the liver and breaking down stored fat and protein. The liver can provide glucose for the first few hours. After that, the body begins to break down fat and protein. The body uses fatty acids as an energy source for muscles but lowers the amount of glucose sent to the brain. Another chemical that comes from fatty acids is glycerol. It can be used as glucose for energy but eventually runs out. Phase two: Phase two can last for weeks at a time. In this phase, the body mainly uses stored fat for energy. The breakdown occurs in the liver and turns fat into ketones. After fasting for one week, the brain will use these ketones and any available glucose. Using ketones lowers the need for glucose, and the body slows the breakdown of proteins. Phase three: By this point, the fat stores are gone, and the body begins to turn to stored protein for energy. This means it needs to break down muscle tissues full of protein; the muscles break down very quickly. Protein is essential for cells to work correctly, and when it runs out, the cells can no longer function. The cause of death due to starvation is usually an infection or the result of tissue breakdown. This is due to the body becoming unable to produce enough energy to fight off bacteria and viruses. The final stage of starvation includes signals like hair color loss, skin flaking, swelling in the extremities, and a bloated belly. Even though they may feel hunger, people in the final stage of starvation usually cannot eat enough food to recover without significant medical intervention.Causes
 Starvation occurs when the body expends more energy than it takes in for an extended period of time. This imbalance can arise from one or more medical conditions or circumstantial situations, which can include:
Medical reasons
*
Starvation occurs when the body expends more energy than it takes in for an extended period of time. This imbalance can arise from one or more medical conditions or circumstantial situations, which can include:
Medical reasons
*Anorexia nervosa
Anorexia nervosa (AN), often referred to simply as anorexia, is an eating disorder characterized by Calorie restriction, food restriction, body image disturbance, fear of gaining weight, and an overpowering desire to be thin.
Individuals wit ...
*Bulimia nervosa
Bulimia nervosa, also known simply as bulimia, is an eating disorder characterized by binge eating (eating large quantities of food in a short period of time, often feeling out of control) followed by compensatory behaviors, such as self-indu ...
* Eating disorder, not otherwise specified
* Esophageal achalasia
*Celiac disease
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine. Patients develop intolerance to gluten, which is present in foods such as wheat, rye, spel ...
*Coma
A coma is a deep state of prolonged unconsciousness in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to Nociception, respond normally to Pain, painful stimuli, light, or sound, lacks a normal Circadian rhythm, sleep-wake cycle and does not initiate ...
*Major depressive disorder
Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of pervasive depression (mood), low mood, low self-esteem, and anhedonia, loss of interest or pleasure in normally ...
*Diabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained hyperglycemia, high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or th ...
* Digestive disease
*Constant vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis, puking and throwing up) is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteritis, pre ...
Circumstantial causes
*Child
A child () is a human being between the stages of childbirth, birth and puberty, or between the Development of the human body, developmental period of infancy and puberty. The term may also refer to an unborn human being. In English-speaking ...
, elder, or dependent abuse
*Famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food caused by several possible factors, including, but not limited to war, natural disasters, crop failure, widespread poverty, an Financial crisis, economic catastrophe or government policies. This phenom ...
for any reason, such as political strife and war
* Hunger striking
*Excessive fasting
*Poverty
Poverty is a state or condition in which an individual lacks the financial resources and essentials for a basic standard of living. Poverty can have diverse Biophysical environmen ...
*Torture
Torture is the deliberate infliction of severe pain or suffering on a person for reasons including corporal punishment, punishment, forced confession, extracting a confession, interrogational torture, interrogation for information, or intimid ...
Biochemistry
With a typical high-carbohydrate diet, the human body relies on free blood glucose as its primary energy source. Glucose can be obtained directly from dietary sugars and by the breakdown of other carbohydrates. In the absence of dietary sugars and carbohydrates, glucose is obtained from the breakdown of stored glycogen. Glycogen is a readily-accessible storage form of glucose, stored in notable quantities in the liver and skeletal muscle. After the exhaustion of the glycogen reserve, and for the next two to three days, fatty acids become the principal metabolic fuel. At first, the brain continues to use glucose. If a non-brain tissue is using fatty acids as its metabolic fuel, the use of glucose in the same tissue is switched off. Thus, when fatty acids are being broken down for energy, all of the remaining glucose is made available for use by the brain. After two or three days of fasting, the liver begins to synthesize ketone bodies from precursors obtained from fatty acid breakdown. The brain uses these ketone bodies as fuel, thus cutting its requirement for glucose. After fasting for three days, the brain gets 30% of its energy from ketone bodies. After four days, this may increase to 70% or more. Thus, the production of ketone bodies cuts the brain's glucose requirement from 80 g per day to 30 g per day, about 35% of normal, with 65% derived from ketone bodies. But of the brain's remaining 30 g requirement, 20 g per day can be produced by the liver fromglycerol
Glycerol () is a simple triol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, sweet-tasting, viscous liquid. The glycerol backbone is found in lipids known as glycerides. It is also widely used as a sweetener in the food industry and as a humectant in pha ...
(itself a product of fat breakdown). This still leaves a deficit of about 10 g of glucose per day that must be supplied from another source; this other source will be the body's own proteins.
After exhaustion of fat stores, the cells in the body begin to break down protein. This releases alanine and lactate produced from pyruvate
Pyruvic acid (CH3COCOOH) is the simplest of the alpha-keto acids, with a carboxylic acid and a ketone functional group. Pyruvate, the conjugate base, CH3COCOO−, is an intermediate in several metabolic pathways throughout the cell.
Pyruvic ...
, which can be converted into glucose by the liver. Since much of human muscle mass is protein, this phenomenon is responsible for the wasting away of muscle mass seen in starvation. However, the body is able to choose which cells will break down protein and which will not. About 2–3 g of protein has to be broken down to synthesize 1 g of glucose; about 20–30 g of protein is broken down each day to make 10 g of glucose to keep the brain alive. However, this number may decrease the longer the fasting period is continued, in order to conserve protein.
Starvation ensues when the fat reserves are completely exhausted and protein is the only fuel source available to the body. Thus, after periods of starvation, the loss of body protein affects the function of important organs, and death results, even if there are still fat reserves left. In a leaner person, the fat reserves are depleted faster, and the protein, sooner, therefore death occurs sooner. Ultimately, the cause of death is in general cardiac arrhythmia
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. Essentially, this is anything but normal sinus rhythm. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beat ...
or cardiac arrest
Cardiac arrest (also known as sudden cardiac arrest CA is when the heart suddenly and unexpectedly stops beating. When the heart stops beating, blood cannot properly Circulatory system, circulate around the body and the blood flow to the ...
, brought on by tissue degradation and electrolyte
An electrolyte is a substance that conducts electricity through the movement of ions, but not through the movement of electrons. This includes most soluble Salt (chemistry), salts, acids, and Base (chemistry), bases, dissolved in a polar solven ...
imbalances. Conditions like metabolic acidosis may also kill starving people.
Prevention
Starvation can be caused by factors beyond the control of the individual. The Rome Declaration on World Food Security outlines several policies aimed at increasingfood security
Food security is the state of having reliable access to a sufficient quantity of affordable, healthy Human food, food. The availability of food for people of any class, gender, ethnicity, or religion is another element of food protection. Simila ...
and, consequently, preventing starvation. These include:
* Poverty reduction
*Prevention of wars
War is an armed conflict between the armed forces of State (polity), states, or between governmental forces and armed groups that are organized under a certain command structure and have the capacity to sustain military operations, or betwe ...
and political instability
* Food aid
* Agricultural sustainability
*Reduction of economic inequality
Supporting farmer
A farmer is a person engaged in agriculture, raising living organisms for food or raw materials. The term usually applies to people who do some combination of raising field crops, orchards, vineyards, poultry, or other livestock. A farmer ...
s in areas of food insecurity through such measures as free or subsidized fertilizers and seed
In botany, a seed is a plant structure containing an embryo and stored nutrients in a protective coat called a ''testa''. More generally, the term "seed" means anything that can be Sowing, sown, which may include seed and husk or tuber. Seeds ...
s increases food harvest and reduces food prices
Food prices refer to the average price level for food across countries, regions and on a global scale. Food prices affect producers and consumers of food. Price levels depend on the food production process, including food marketing and food di ...
.
Starvation is commonly used as a method of warfare, however, it has been outlawed and is now a crime. Notable incidents in history include the blockade of Germany and blockade of Biafra.
Treatment
Patients that suffer from starvation can be treated, but this must be done cautiously to avoid refeeding syndrome. Rest and warmth must be provided and maintained. Food can be given gradually in small quantities. The quantity of food can be increased over time. Proteins may be administered intravenously to raise the level of serum proteins. For worse situations, hospice care and opioid medications can be used.Organizations
Many organizations have been highly effective at reducing starvation in different regions. Aid agencies give direct assistance to individuals, while political organizations pressure political leaders to enact more macro-scale policies that will reduce famine and provide aid.Statistics
Food and Agriculture Organization
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; . (FAO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger and improve nutrition and food security. Its Latin motto, , translates ...
, between 720 and 811 million people were affected by hunger globally in 2020. This was a decrease from estimated 925 million in 2010 and roughly 1 billion in 2009. In 2007, 923 million people were reported as being undernourished, an increase of 80 million since 1990–92.
An estimated 820 million people did not have enough to eat in 2018, up from 811 million in the previous year, which is the third year of increase in a row.
As the definitions of starving and malnourished people are different, the number of starving people is different from that of malnourished. Generally, far fewer people are starving than are malnourished.
The proportion of malnourished and starving people in the world has been more or less continually decreasing for at least several centuries. This is due to an increasing supply of food and to overall gains in economic efficiency. In 40 years, the proportion of malnourished people in the developing world has been more than halved. The proportion of starving people has decreased even faster.
Capital punishment
Historically, starvation has been used as a death sentence. From the beginning of civilization to theMiddle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
, people were immured, and died for want of food.
In ancient Greco-Roman societies, starvation was sometimes used to dispose of guilty upper-class citizens, especially erring female members of patrician families. In the year 31, Livilla
Claudia Livia (Classical Latin: CLAVDIA•LIVIA; – AD 31) was the only daughter of Nero Claudius Drusus and Antonia Minor and sister to Roman Emperor Claudius and general Germanicus, and thus paternal aunt of emperor Caligula and mate ...
, the niece and daughter-in-law of Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus ( ; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was Roman emperor from AD 14 until 37. He succeeded his stepfather Augustus, the first Roman emperor. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC to Roman politician Tiberius Cl ...
, was discreetly starved to death by her mother for her adulterous relationship with Sejanus
Lucius Aelius Sejanus ( – 18 October AD 31), commonly known as Sejanus (), was a Roman soldier and confidant of the Roman Emperor Tiberius. Of the Equites class by birth, Sejanus rose to power as prefect of the Praetorian Guard, the imperia ...
and for her complicity in the murder of her own husband, Drusus the Younger.
Another daughter-in-law of Tiberius, named Agrippina the Elder
(Vipsania) Agrippina the Elder (also, in Latin, , "Germanicus's Agrippina"; – AD 33) was a prominent member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty. She was the daughter of Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa (a close supporter of the first Roman emperor, Aug ...
(a granddaughter of Augustus
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in A ...
and the mother of Caligula
Gaius Caesar Augustus Germanicus (31 August 12 – 24 January 41), also called Gaius and Caligula (), was Roman emperor from AD 37 until his assassination in 41. He was the son of the Roman general Germanicus and Augustus' granddaughter Ag ...
), also died of starvation, in 33 AD; however, it is unclear if her starvation was self-inflicted. A son and daughter of Agrippina were also executed by starvation for political reasons; Drusus Caesar, her second son, was put in prison in 33 AD, and starved to death by orders of Tiberius (he managed to stay alive for nine days by chewing the stuffing of his bed); Agrippina's youngest daughter, Julia Livilla, was exiled on an island in 41 by her uncle, Emperor
A son and daughter of Agrippina were also executed by starvation for political reasons; Drusus Caesar, her second son, was put in prison in 33 AD, and starved to death by orders of Tiberius (he managed to stay alive for nine days by chewing the stuffing of his bed); Agrippina's youngest daughter, Julia Livilla, was exiled on an island in 41 by her uncle, Emperor Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; ; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54), or Claudius, was a Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Nero Claudius Drusus, Drusus and Ant ...
, and her death by starvation was arranged by the empress Messalina.
It is also possible that Vestal Virgin
In ancient Rome, the Vestal Virgins or Vestals (, singular ) were priestesses of Vesta, virgin goddess of Rome's sacred hearth and its flame.
The Vestals were unlike any other public priesthood. They were chosen before puberty from several s ...
s were starved when found guilty of breaking their vows of celibacy
Celibacy (from Latin ''caelibatus'') is the state of voluntarily being unmarried, sexually abstinent, or both. It is often in association with the role of a religious official or devotee. In its narrow sense, the term ''celibacy'' is applied ...
.
Ugolino della Gherardesca, his sons, and other members of his family were immured in the Muda, a tower of Pisa
Pisa ( ; ) is a city and ''comune'' (municipality) in Tuscany, Central Italy, straddling the Arno just before it empties into the Ligurian Sea. It is the capital city of the Province of Pisa. Although Pisa is known worldwide for the Leaning Tow ...
, and starved to death in the thirteenth century. Dante
Dante Alighieri (; most likely baptized Durante di Alighiero degli Alighieri; – September 14, 1321), widely known mononymously as Dante, was an Italian Italian poetry, poet, writer, and philosopher. His ''Divine Comedy'', originally called ...
, his contemporary, wrote about Gherardesca in his masterpiece '' The Divine Comedy''.
In Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
in 1317, King Birger of Sweden imprisoned his two brothers for a coup they had staged several years earlier ( Nyköping Banquet). According to legend they died of starvation a few weeks later, since their brother had thrown the prison key in the castle moat.
In Cornwall in the UK in 1671, John Trehenban from St Columb Major was condemned to be starved to death in a cage at Castle An Dinas for the murder of two girls.
The Makah, a Native American tribe inhabiting the Pacific Northwest near the modern border of Canada and the United States, practiced death by starvation as a punishment for slaves.Donald, Leland (1997). Aboriginal Slavery on the Northwest Coast of North America, University of California Press, p. 23
See also
*2007–2008 world food price crisis
World food prices increased dramatically in 2007 and the first and second quarter of 2008, creating a International crisis, global crisis and causing political and economic instability and social unrest in both Poor countries, poor and develop ...
* Anorexia mirabilis
* Cachexia
Cachexia () is a syndrome that happens when people have certain illnesses, causing muscle loss that cannot be fully reversed with improved nutrition. It is most common in diseases like cancer, Heart failure, congestive heart failure, chronic o ...
* Global Hunger Index
* Starvation mode
* Famine scales
* Hunger strike
* List of famines
List
Table
See also
Main article lists
* Bengal famine (disambiguation), Bengal famine
* Droughts and famines in Russia and the Soviet Union
* Famine in India
* Famines in the Czech lands
* Famines in Ethiopia
* Great Bengal famine ...
* List of people who died of starvation
* Marasmus
* Protein poisoning
References
Further reading
U.N. Chief: Hunger Kills 17,000 Kids Daily
- by CNN * *
External links
* * {{Authority control Causes of death Effects of external causes Execution methods Famines Hunger Malnutrition Physical torture techniques Suicide by starvation and dehydration Weight loss