|
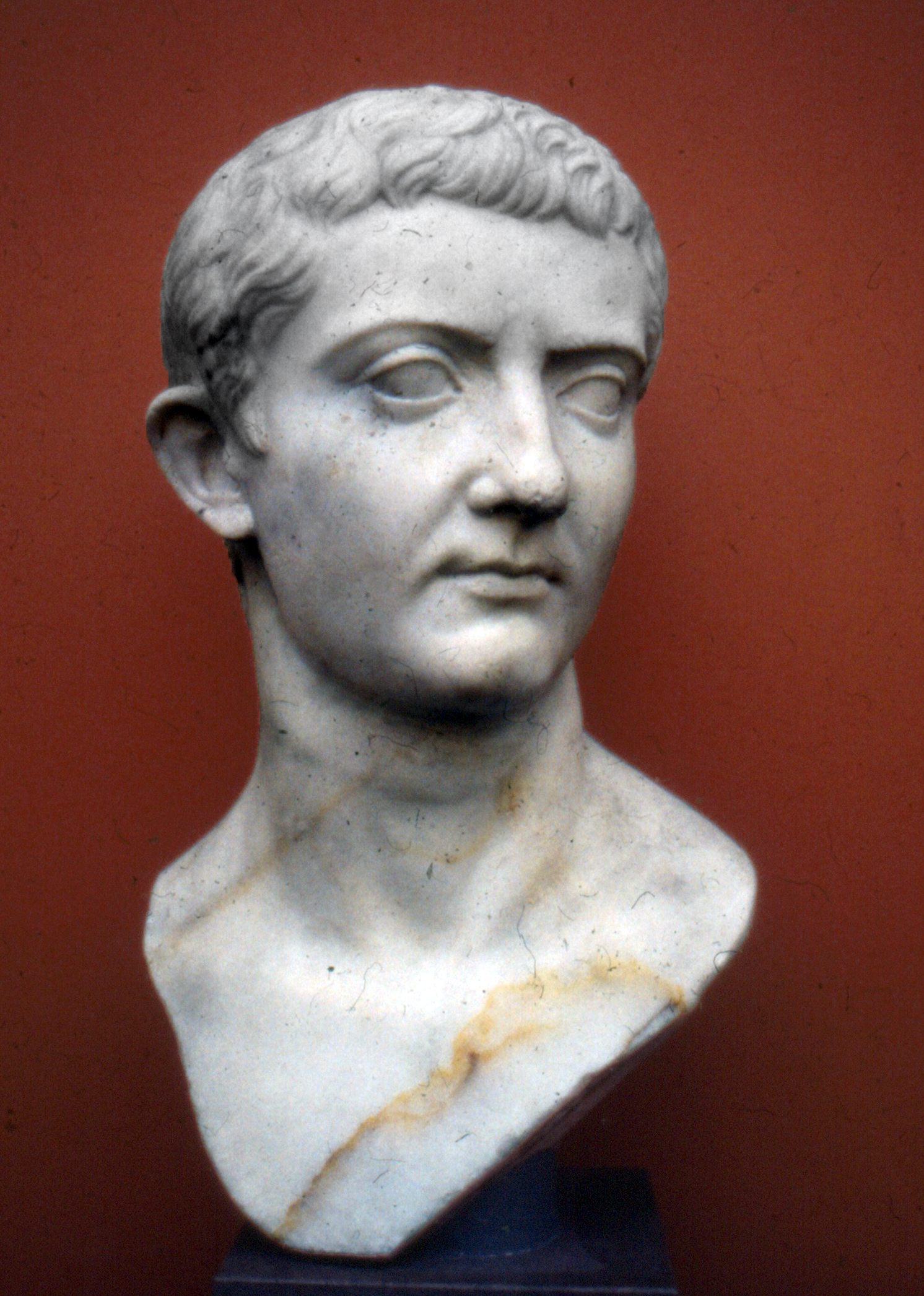
Sejanus
Lucius Aelius Sejanus ( – 18 October AD 31), commonly known as Sejanus (), was a Roman soldier and confidant of the Roman Emperor Tiberius. Of the Equites class by birth, Sejanus rose to power as prefect of the Praetorian Guard, the imperial bodyguard, of which he was commander from AD 14 until his execution for treason in AD 31. While the Praetorian Guard was formally established under Emperor Augustus, Sejanus introduced a number of reforms which saw the unit evolve beyond a mere bodyguard into a powerful and influential branch of the government involved in public security, civil administration and ultimately political intercession; these changes had a lasting impact on the course of the Principate. During the 20s, Sejanus gradually accumulated power by consolidating his influence over Tiberius and eliminating potential political opponents, including the emperor's son Drusus Julius Caesar. When Tiberius withdrew to Capri in AD 26, Sejanus was left in control of the admin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus ( ; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was Roman emperor from AD 14 until 37. He succeeded his stepfather Augustus, the first Roman emperor. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC to Roman politician Tiberius Claudius Nero (father of Tiberius Caesar), Tiberius Claudius Nero and his wife, Livia Drusilla. In 38 BC, Tiberius's mother divorced his father and married Augustus. Following the untimely deaths of Augustus's two grandsons and adopted heirs, Gaius Caesar, Gaius and Lucius Caesar, Tiberius was designated Augustus's successor. Prior to this, Tiberius had proved himself an able diplomat and one of the most successful Roman generals: his conquests of Pannonia, Dalmatia (Roman province), Dalmatia, Raetia, and (temporarily) parts of Germania laid the foundations for Roman Empire, the empire's northern frontier. Early in his career, Tiberius was happily married to Vipsania, daughter of Augustus's friend, distinguished general and intended heir, Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drusus Julius Caesar
Drusus Julius Caesar (7 October – 14 September AD 23), also called Drusus the Younger, was the son of Emperor Tiberius, and heir to the Roman Empire following the death of his adoptive brother Germanicus in AD 19. He was born at Rome to a prominent branch of the ''gens Claudia'', the son of Tiberius and his first wife, Vipsania Agrippina. His name at birth was Nero Claudius Drusus after his paternal uncle Nero Claudius Drusus (Drusus the Elder). In AD 4, he assumed the name ''Julius Caesar'' following his father's adoption into the Julia gens, Julii by Augustus, and became Drusus Julius Caesar. Drusus first entered politics with the office of quaestor in AD 10. His political career mirrored that of Germanicus, and he assumed all his offices at the same age as him. Following the model of Augustus, it was intended that the two would rule together. They were both popular, and many dedications have been found in their honor across Roman Italy. Cassius Dio calls him "Castor" in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucius Seius Strabo
Lucius Seius Strabo (46 BCafter 16 AD) was a prefect of the Roman imperial bodyguard, known as the Praetorian Guard, during the rule of the emperors Augustus and Tiberius. The length of Strabo's tenure as Praetorian prefect is unknown, but he held the position together with various colleagues until 15, after which he was appointed to the governorship of Egypt. With this career Strabo distinguished himself by attaining the two highest offices open to men of the equestrian class in the Roman Empire. His son was Lucius Aelius Sejanus, who succeeded his father as Praetorian prefect in 15, and gained great influence under Emperor Tiberius before dramatically falling from power in 31. Family Lucius Seius Strabo was born around 46 BC in Volsinii, Etruria, to the family of Marcus Seius Strabo and Terentia.Adams, 75 Although the Seii were Romans of the equestrian class, Strabo's father maintained relations with senatorial families through his marriage with Terentia. Her brother was A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praetorian Guard
The Praetorian Guard (Latin language, Latin: ''cohortes praetoriae'') was the imperial guard of the Imperial Roman army that served various roles for the Roman emperor including being a bodyguard unit, counterintelligence, crowd control and gathering military intelligence. During the Roman Republic, the Praetorian Guards were escorts for high-ranking political officials (Roman Senate, senators and procurator (ancient Rome), procurators) and were bodyguards for the senior officers of the Roman legions. In 27 BC, after Rome's transition from republic to empire, the first emperor of Rome, Augustus, designated the Praetorians as his personal security escort. For three centuries, the guards of the Roman emperor were also known for their palace intrigues, by whose influence upon imperial politics the Praetorians could overthrow an emperor and then proclaim his successor as the new ''Caesar (title), caesar'' of Rome. In AD 312, Constantine the Great disbanded the and destroyed their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seia Gens
The gens Seia was a minor plebeian family of equestrian rank at ancient Rome. Members of this gens are first mentioned in the time of Cicero, and a few of them held various magistracies under the late Republic and into imperial times. Origin The nomen ''Seius'' is derived from the name of Seia, the goddess of sowing. Chase classifies it among those gentilicia that either originated at Rome, or cannot be shown to have come from anywhere else. Praenomina The main praenomina of the Seii were '' Lucius'' and '' Marcus'', two of the most common names throughout Roman history. Other common names were occasionally used, including '' Gnaeus'', '' Publius'', and '' Quintus''. Members * Marcus Seius L. f., a friend of Cicero, who despite having been heavily fined early in his career, spent lavishly as curule aedile. He was the accuser of Marcus Saufeius, whom Cicero defended on the charge that he had participated in the murder of Publius Clodius Pulcher. * Quintus Seius Postumus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucius Seius Tubero
Lucius Seius Tubero was a Roman senator, who flourished under the reign of Tiberius. He was suffect consul for February through July of the year 18, succeeding the emperor Tiberius, and as the colleague first of Germanicus, then of Livineius Regulus. The family connections of Seius Tubero have posed a problem for students of ancient history. For example, he is the only consul of either the Roman Republic or Empire to use "Tubero" as a cognomen who was not of the ''gens'' Aelia. The consensus is that Tubero is one of the two brothers of Sejanus alluded to by Velleius Paterculus; however, theories defining this fraternal relationship have changed over the years. Bartolomeo Borghesi first proposed that Seius Tubero was the son of Lucius Seius Strabo. Then it was proposed that Seius Tubero was by birth the nephew of Strabo's wife, whom Strabo later adopted. The latest theory of his fraternal relationship to Sejanus, proposed by Ronald Syme, is that Seius Tubero was the son of h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junius Blaesus
Quintus Junius Blaesus (died AD 31) was a Roman politician who lived during the reigns of Augustus and Tiberius. He was the maternal uncle of Lucius Aelius Sejanus, the Praetorian Prefect of Emperor Tiberius. Career Almost nothing is known of the career of Quintus Junius Blaesus prior to AD 10, when he served as suffect consul with Servius Cornelius Lentulus Maluginensis. The exception is a lead ingot attesting he was proconsul of Sicily; the date of his office can be dated no closer than the long reign of Augustus. Blaesus subsequently appears as commander of the armies stationed in Pannonia when a mutiny broke out after the death of Augustus in the year 14. According to Tacitus, after military service in the Great Illyrian Revolt, soldiers were unhappy with their payment of swampy and mountainous Pannonian lands and demanded restitution. To ease tensions, Blaesus offered to commit suicide, but his request was ignored. According to the Roman historian Cassius Dio, the sold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aelia Gens
The gens Aelia, occasionally written Ailia, was a plebeian family in Rome, which flourished from the fifth century BC until at least the third century AD, a period of nearly eight hundred years. The archaic spelling ''Ailia'' is found on coins, but must not be confused with '' Allia'', which is a distinct gens. The first member of the family to obtain the consulship was Publius Aelius Paetus in 337 BC. Under the empire the Aelian name became still more celebrated. It was the name of the emperor Hadrian, and consequently of the Antonines, whom he adopted. A number of landmarks built by Hadrian also bear the name ''Aelius''. The '' Pons Aelius'' is a bridge in Rome, now known as the ''Ponte Sant'Angelo''. '' Pons Aelius'' also refers to a Roman settlement in Britannia Inferior, now the site of Newcastle upon Tyne, while '' Aelia Capitolina'' was a Roman colony built on the ruins of Jerusalem.'' Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology'', William Smith, Editor. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volsinii
Volsinii or Vulsinii (Etruscan language, Etruscan: Velzna or Velusna; Ancient Greek, Greek: Ouolsinioi, ; ), is the name of two ancient cities of Etruria, one situated on the shore of Lacus Volsiniensis (modern Lago di Bolsena), and the other on the Via Clodia, between Clusium (Chiusi) and Forum Cassii (Vetralla). The latter was Etruscan civilization, Etruscan and was destroyed by the Romans in 264 BC following an attempted revolt by its slaves, while the former was founded by the Romans using the remainder of the Etruscan population rescued from the razed city. Modern Bolsena, Italy, in the region of Lazio, descends from the Roman city. The location of the Etruscan city is debated. Umbrian Orvieto, about from Bolsena, is a strong candidate. Situation The Byzantine Empire, Byzantine historian Joannes Zonaras states that the Etruscan Volsinii (Velzna or Velusna) lay on a steep height;Zonaras, ''Annals'' (or ''Chronicle'' or ''Epitome'' - he does not state a name of his own) vii ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praetorian Prefect
The praetorian prefect (; ) was a high office in the Roman Empire. Originating as the commander of the Praetorian Guard, the office gradually acquired extensive legal and administrative functions, with its holders becoming the Emperor's chief aides. Under Constantine I, the office was much reduced in power and transformed into a purely civilian administrative post, while under his successors, territorially-defined praetorian prefectures emerged as the highest-level administrative division of the Empire. The prefects again functioned as the chief ministers of the state, with many laws addressed to them by name. In this role, praetorian prefects continued to be appointed by the Eastern Roman Empire (and the Ostrogothic Kingdom) until the reign of Heraclius in the 7th century AD, when wide-ranging reforms reduced their power and converted them to mere overseers of provincial administration. The last traces of the prefecture disappeared in the Byzantine Empire by the 840s. The term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Annals (Tacitus)/Book 4
The ''Annals'' () by Roman historian and senator Tacitus is a history of the Roman Empire from the reign of Tiberius to that of Nero, the years AD 14–68. The ''Annals'' are an important source for modern understanding of the history of the Roman Empire during the 1st century AD. Tacitus' final work, modern historians generally consider it his magnum opus which historian Ronald Mellor says represents the "pinnacle of Roman historical writing". Tacitus' ''Histories'' and ''Annals'' together amounted to 30 books, although some scholars disagree about which work to assign some books to, traditionally 14 are assigned to ''Histories'' and 16 to ''Annals''. Of the 30 books referred to by Jerome about half have survived. Modern scholars believe that as a Roman senator, Tacitus had access to '' Acta Senatus''—the Roman senate's records—which provided a solid basis for his work. Although Tacitus refers to part of his work as "my annals", the title of the work ''Annals'' used tod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sextus Aelius Catus
Sextius Aelius Catus was a Roman senator and consul ''ordinarius'' for 4 AD with Gaius Sentius Saturninus as his colleague. Catus was the father of Aelia Paetina, the second wife of the emperor Claudius from 28 AD to about 31 AD (when Aelia's adoptive brother Sejanus fell from power). His only known grandchild was Aelia and Claudius's daughter Claudia Antonia, born in 30. Catus was possibly descended from Sextus Aelius Q.f. Paetus Catus, consul of 198 BC and later a censor, or possibly from Quintus Aelius Tubero, consul in 11 BC. His daughter Aelia Paetina is said to belong to the Aelii Tuberones, implying a descent from the consul of 11 BC. Except for his consulship, the only position Catus is known to have held was governorship of Moesia. This is based on a mention by Strabo that Catus moved 50,000 Getae across the Danube and settled them in Moesia. When he held this appointment is uncertain: Ronald Syme speculates that he was either a praetor ''Praetor'' ( , ), also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |