Staphylococcal Infection on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A staphylococcal infection or staph infection is an infection caused by members of the ''
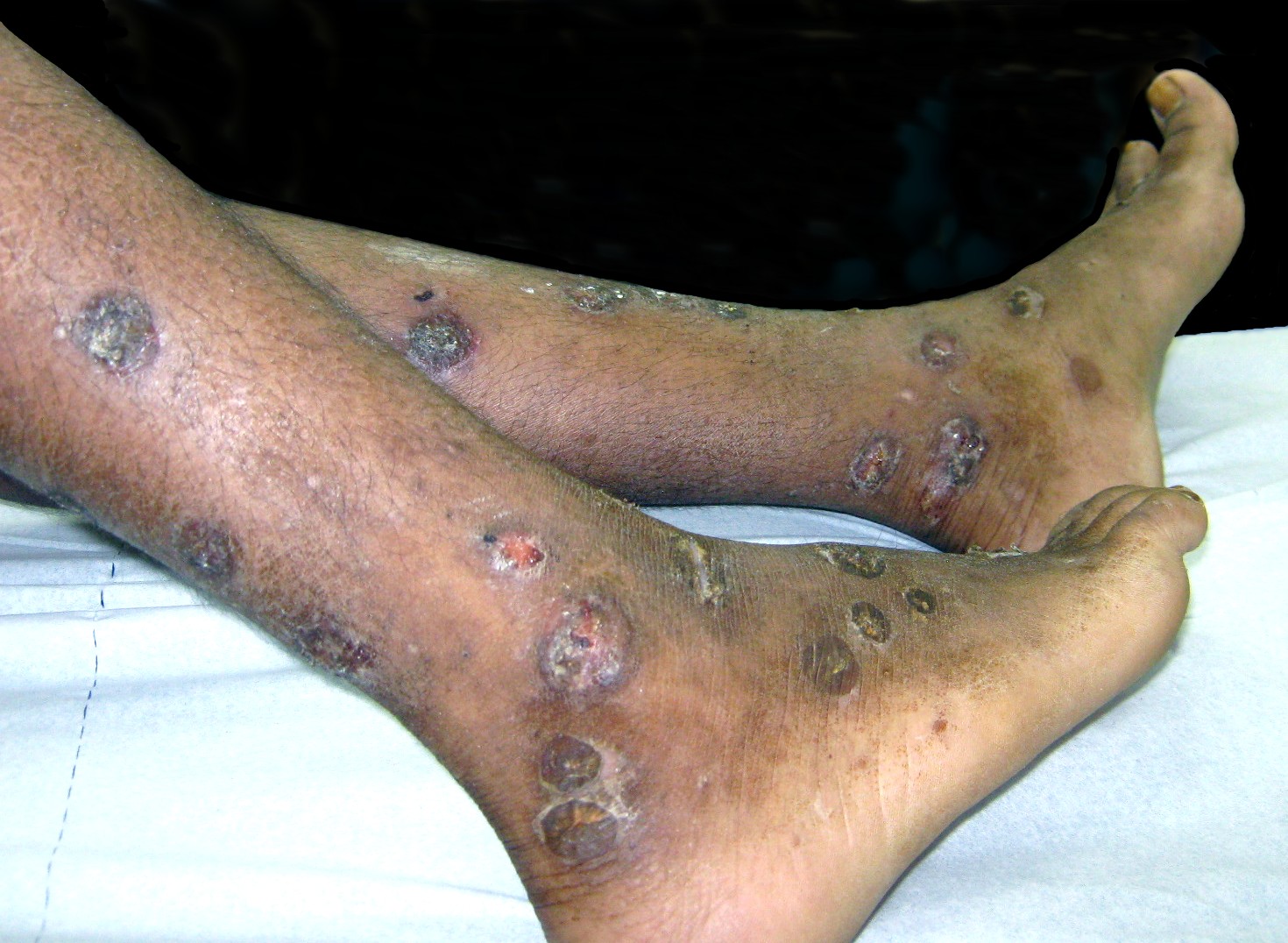
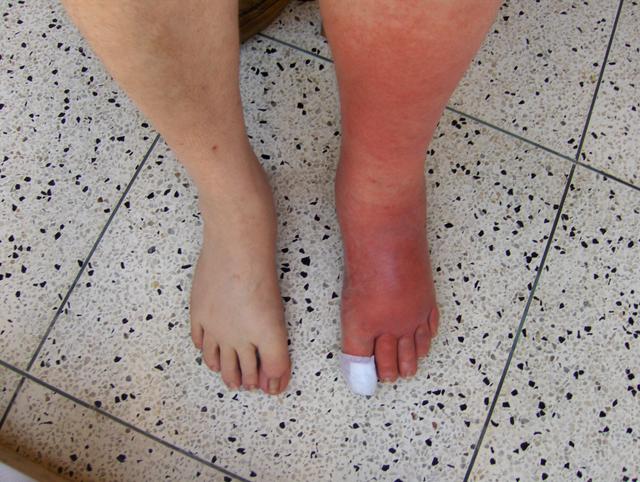 Staph infection is typically characterized by redness, pus, swelling, and tenderness in areas of the infection. But, each type of skin infection caused by staph bacteria is different.
A few common skin infections caused by staph bacteria are:
* Boils – Boils are the most common type of staph infection, they are pockets of white pus that start where a hair follicle or oil gland is. The boil is tender and red where the infection is located on the skin.
* Impetigo – Impetigo is most prominent among children, and is usually located around their mouth, nose, hands, and feet. It shows up like a rash of painful blisters, will eventually produce pus that is yellowish in color.
* Cellulitis – Cellulitis is also rash-like; the skin that is infected will be red, swollen, and usually warm to the touch. Cellulitis commonly infects the lower legs, but can also, less commonly, affect the face and arms.
* Staphylococcus scalded skin syndrome – Staphylococcus scalded skin syndrome is caused by toxins produced when a staph infection gets too severe. It is characterized by a fever, rash, and blisters.
* Methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA) – MRSA is one of the most common antibiotic-resistant strains of staph bacteria. It is more difficult to treat than other staph infections. MRSA causes rashes, boils, sores, and other abscesses.
Staph infection is typically characterized by redness, pus, swelling, and tenderness in areas of the infection. But, each type of skin infection caused by staph bacteria is different.
A few common skin infections caused by staph bacteria are:
* Boils – Boils are the most common type of staph infection, they are pockets of white pus that start where a hair follicle or oil gland is. The boil is tender and red where the infection is located on the skin.
* Impetigo – Impetigo is most prominent among children, and is usually located around their mouth, nose, hands, and feet. It shows up like a rash of painful blisters, will eventually produce pus that is yellowish in color.
* Cellulitis – Cellulitis is also rash-like; the skin that is infected will be red, swollen, and usually warm to the touch. Cellulitis commonly infects the lower legs, but can also, less commonly, affect the face and arms.
* Staphylococcus scalded skin syndrome – Staphylococcus scalded skin syndrome is caused by toxins produced when a staph infection gets too severe. It is characterized by a fever, rash, and blisters.
* Methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA) – MRSA is one of the most common antibiotic-resistant strains of staph bacteria. It is more difficult to treat than other staph infections. MRSA causes rashes, boils, sores, and other abscesses.
 In the microbiology lab, ''Staphylococcus'' is mainly suspected when seeing Gram-positive cocci in clusters.
In the microbiology lab, ''Staphylococcus'' is mainly suspected when seeing Gram-positive cocci in clusters.
Staphylococcus
''Staphylococcus'', from Ancient Greek σταφυλή (''staphulḗ''), meaning "bunch of grapes", and (''kókkos''), meaning "kernel" or " Kermes", is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillale ...
'' genus of bacteria.
These bacteria commonly inhabit the skin and nose where they are innocuous, but may enter the body through cuts or abrasions which may be nearly invisible. Once inside the body, the bacteria may spread to a number of body systems and organs, including the heart, where the toxins produced by the bacteria may cause cardiac arrest
Cardiac arrest (also known as sudden cardiac arrest CA is when the heart suddenly and unexpectedly stops beating. When the heart stops beating, blood cannot properly Circulatory system, circulate around the body and the blood flow to the ...
. Once the bacterium has been identified as the cause of the illness, treatment is often in the form of antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
and, where possible, drainage of the infected area. However, many strains of this bacterium have become antibiotic resistant
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR or AR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from antimicrobials, which are drugs used to treat infections. This resistance affects all classes of microbes, including bacteria (antibiotic resist ...
; for those with these kinds of infection, the body's own immune system
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to bacteria, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells, Parasitic worm, parasitic ...
is the only defense against the disease. If that system is weakened or compromised, the disease may progress rapidly. Anyone can contract staph, but pregnant women, children, and people with chronic diseases or who are immuno-deficient are often more susceptible to contracting an infection.
Types
Other infections include: * Closed-space infections of the fingertips, known asparonychia
Paronychia is an inflammation of the skin around the nail, often due to bacteria or fungi.
Its sudden (acute) occurrence is usually due to the bacterium ''Staphylococcus aureus''. Gradual (chronic) occurrences are typically caused by fungi ...
.
* Suspected involvement in atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis (AD), also known as atopic eczema, is a long-term type of inflammation of the skin. Atopic dermatitis is also often called simply eczema but the same term is also used to refer to dermatitis, the larger group of skin conditi ...
(eczema), including related clinical trials.
Coagulase-positive
The maincoagulase
Coagulase is a protein enzyme produced by several microorganisms that enables the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin. In the laboratory, it is used to distinguish between different types of ''Staphylococcus'' isolates. Importantly, '' S. aureus' ...
-positive staphylococcus is ''Staphylococcus aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often posi ...
'', although not all strains of ''Staphylococcus aureus'' are coagulase positive. These bacteria can survive on dry surfaces, increasing the chance of transmission. ''S. aureus'' is also implicated in toxic shock syndrome
Toxic shock syndrome (TSS) is a condition caused by Exotoxin, bacterial toxins. Symptoms may include fever, rash, skin peeling, and low blood pressure. There may also be symptoms related to the specific underlying infection such as mastitis, ...
; during the 1980s some tampon
A tampon is a menstrual product designed to absorb blood and vaginal secretions by insertion into the vagina during menstruation. Unlike a pad, it is placed internally, inside of the vaginal canal. Once inserted correctly, a tampon is held ...
s allowed the rapid growth of ''S. aureus'', which released toxins that were absorbed into the bloodstream. Any S. aureus infection can cause the staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome, a cutaneous reaction to exotoxin
An exotoxin is a toxin secreted by bacteria. An exotoxin can cause damage to the host by destroying cells or disrupting normal cellular metabolism. They are highly potent and can cause major damage to the host. Exotoxins may be secreted, or, sim ...
absorbed into the bloodstream. It can also cause a type of septicaemia
Sepsis is a potentially life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs.
This initial stage of sepsis is followed by suppression of the immune system. Common signs and s ...
called pyaemia. The infection can be life-threatening. Problematically, methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA) has become a major cause of hospital-acquired infections. MRSA has also been recognized with increasing frequency in community-acquired infections. The symptoms of a staphylococcal infection include a collection of pus, such as a boil or furuncle, or abscess. The area is typically tender or painful and may be reddened or swollen.
Coagulase-negative
* '' S. epidermidis'', acoagulase
Coagulase is a protein enzyme produced by several microorganisms that enables the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin. In the laboratory, it is used to distinguish between different types of ''Staphylococcus'' isolates. Importantly, '' S. aureus' ...
-negative staphylococcus species, is a commensal of the skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
, but can cause severe infections in immune-suppressed patients and those with central venous catheters
A central venous catheter (CVC), also known as a central line (c-line), central venous line, or central venous access catheter, is a catheter placed into a large vein. It is a form of venous access. Placement of larger catheters in more centr ...
.
* '' S. saprophyticus'', another coagulase
Coagulase is a protein enzyme produced by several microorganisms that enables the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin. In the laboratory, it is used to distinguish between different types of ''Staphylococcus'' isolates. Importantly, '' S. aureus' ...
-negative species that is part of the normal vaginal flora
Vaginal flora, vaginal microbiota or vaginal microbiome are the microorganisms that colonize the vagina. They were discovered by the German gynecologist Albert Döderlein in 1892 and are part of the overall human flora.
The amount and type of ba ...
, is predominantly implicated in uncomplicated lower genitourinary tract infections in young sexually active women.
* Other staphylococcal species have been implicated in human infections, notably '' S. lugdunensis'', '' S. schleiferi'', and '' S. caprae''.
Causes
Staph infections have a multitude of different causes, such as: * Open wounds – This is by far the biggest cause of staph infection. Any open wound, even ones as small as a paper cut, are vulnerable to being infected. Staph bacteria will enter the body through any open wound, so it is important to properly treat, disinfect, and bandage any wounds. * Contact with infected persons or surfaces – Staph infections are very contagious when in contact with a person that is already infected. A person with staph infection is contagious until the bacteria are completely out of their body, and any wounds from the infection are healed. It is common to see the spread of staph in contact sports; i.e. wrestling, through contact in locker rooms, or by sharing any equipment. * Weakened immune system – Anyone with a weakened immune system for any reason can be more easily affected by staph bacteria, because their bodies are unable to defend against infectious bacteria as well. * Unwashed linens – Staph bacteria are very resistant under harsh conditions, and they will cling to objects where they can create a niche. Unwashed bath towels, blanket, bed sheets, and clothes can create a great environment for these bacteria to grow. This is important to recognize, because every single day people use linens in their daily lives. * Infection after surgery – Hospitals are a very common place for staph bacteria to contaminate. This becomes problematic when people are in surgery, because in some cases staph can be introduced to a person's body when an incision is opened. * Invasive devices – Medical devices that have any connection to organs to the outside of the body are very problematic, because they allow an easy open pathway into the body. Examples of these devices are; catheters, dialysis tubing, feeding tubes, breathing tubes, etc.Signs and symptoms

Bacterial identification
 In the microbiology lab, ''Staphylococcus'' is mainly suspected when seeing Gram-positive cocci in clusters.
In the microbiology lab, ''Staphylococcus'' is mainly suspected when seeing Gram-positive cocci in clusters.
Treatment
Treatment for staph infection varies depending on the type and severity of infection. Common treatments are antibiotics, topical creams, and drainage/cleaning of infectious wounds.Etymology
The generic name Staphylococcus is derived from theGreek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
word "staphyle", meaning bunch of grapes
In viticulture, the grape cluster (also bunch of grapes) is a fertilized inflorescence of the grapevine, the primary part of this plant used for food (grape leaves are also used in some culinary traditions). The size of the grape bunch greatly va ...
, and "kokkos", meaning granule. The bacteria, when seen under a microscope, appear like a branch of grapes or nuts.
Epidemiology
Staphylococcus bacteria is one of the leading community-acquired bacteria. According to the CDC, after a push from hospitals to better prevent staph infections, the percentage of people affected has dropped dramatically. However, staph infections are still prominent and a cause for concern among healthcare professionals, especially new antibiotic-resistant strains. In the U.S., the incidence of staph infection is around 38.2 to 45.7 per 100,000 person-years, whereas otherFirst World
The concept of the First World was originally one of the " Three Worlds" formed by the global political landscape of the Cold War, as it grouped together those countries that were aligned with the Western Bloc of the United States. This groupin ...
countries have an average incidence rate of 10 to 30 per 100,000 person-years.
References
External links
{{Bacterial cutaneous infections Staphylococcaceae Bacterial toxins