Square Tiling Honeycomb on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In the

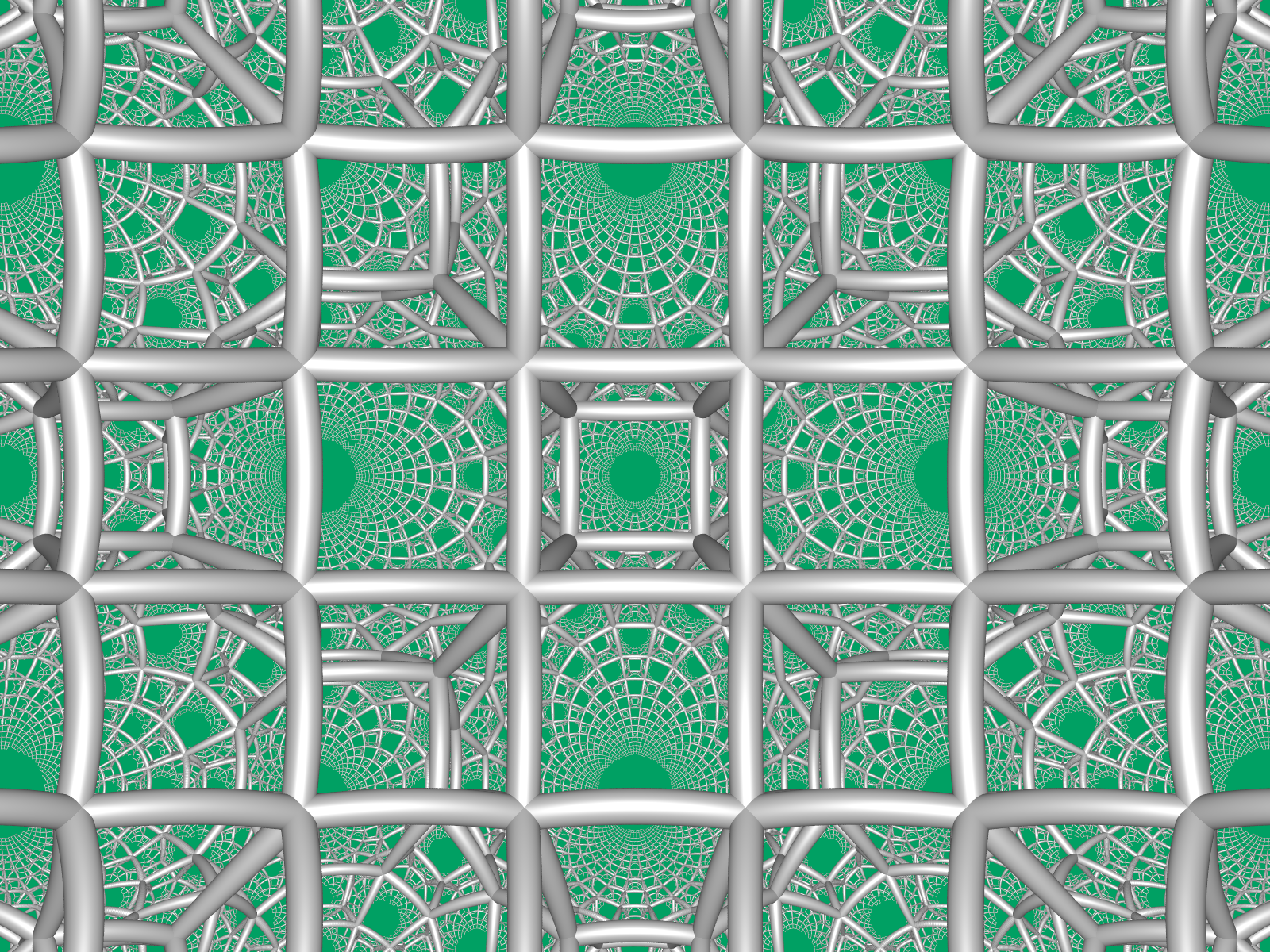 It is similar to the 2D hyperbolic uniform
It is similar to the 2D hyperbolic uniform 







Regular Honeycombs in Hyperbolic Space
Table III * Jeffrey R. Weeks ''The Shape of Space, 2nd edition'' {{ISBN, 0-8247-0709-5 (Chapter 16-17: Geometries on Three-manifolds I,II) * Norman Johnson ''Uniform Polytopes'', Manuscript ** N.W. Johnson: ''The Theory of Uniform Polytopes and Honeycombs'', Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Toronto, 1966 ** N.W. Johnson: ''Geometries and Transformations'', (2018) Chapter 13: Hyperbolic Coxeter groups ** Norman W. Johnson and Asia Ivic Weis
Quadratic Integers and Coxeter Groups
geometry
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is c ...
of hyperbolic 3-space
In mathematics, hyperbolic space of dimension n is the unique simply connected, n-dimensional Riemannian manifold of constant sectional curvature equal to -1. It is homogeneous, and satisfies the stronger property of being a symmetric space. The ...
, the square tiling honeycomb is one of 11 paracompact regular honeycombs. It is called ''paracompact'' because it has infinite cells
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ...
, whose vertices exist on horospheres and converge to a single ideal point
In hyperbolic geometry, an ideal point, omega point or point at infinity is a well-defined point outside the hyperbolic plane or space.
Given a line ''l'' and a point ''P'' not on ''l'', right- and left- limiting parallels to ''l'' through ''P' ...
at infinity. Given by Schläfli symbol
In geometry, the Schläfli symbol is a notation of the form \ that defines regular polytopes and tessellations.
The Schläfli symbol is named after the 19th-century Swiss mathematician Ludwig Schläfli, who generalized Euclidean geometry to mor ...
, it has three square tiling
In geometry, the square tiling, square tessellation or square grid is a regular tiling of the Euclidean plane. It has Schläfli symbol of meaning it has 4 squares around every vertex.
Conway called it a quadrille.
The internal angle of th ...
s, , around each edge, and six square tilings around each vertex, in a cubic vertex figure
In geometry, a vertex figure, broadly speaking, is the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.
Definitions
Take some corner or vertex of a polyhedron. Mark a point somewhere along each connected edge. Draw lines ...
.Coxeter ''The Beauty of Geometry'', 1999, Chapter 10, Table III
Rectified order-4 square tiling
It is also seen as a rectified order-4 square tiling honeycomb, r:Symmetry
The square tiling honeycomb has three reflective symmetry constructions: as a regular honeycomb, a half symmetry construction ↔ , and lastly a construction with three types (colors) of checkered square tilings ↔ . It also contains an index 6 subgroup ,4,3*↔ 1,1,1 and a radial subgroup ,(4,3)*of index 48, with a right dihedral-angledoctahedral
In geometry, an octahedron (plural: octahedra, octahedrons) is a polyhedron with eight faces. The term is most commonly used to refer to the regular octahedron, a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at ea ...
fundamental domain
Given a topological space and a group acting on it, the images of a single point under the group action form an orbit of the action. A fundamental domain or fundamental region is a subset of the space which contains exactly one point from each o ...
, and four pairs of ultraparallel mirrors: .
This honeycomb contains that tile 2- hypercycle surfaces, which are similar to the paracompact order-3 apeirogonal tiling
In geometry, the order-3 apeirogonal tiling is a regular tiling of the hyperbolic plane. It is represented by the Schläfli symbol , having three regular apeirogons around each vertex. Each apeirogon is inscribed in a horocycle.
The order-2 a ...
:
: Related polytopes and honeycombs
The square tiling honeycomb is a regular hyperbolic honeycomb in 3-space. It is one of eleven regular paracompact honeycombs. There are fifteen uniform honeycombs in the ,4,3Coxeter group
In mathematics, a Coxeter group, named after H. S. M. Coxeter, is an abstract group that admits a formal description in terms of reflections (or kaleidoscopic mirrors). Indeed, the finite Coxeter groups are precisely the finite Euclidean ref ...
family, including this regular form, and its dual, the order-4 octahedral honeycomb, .
The square tiling honeycomb is part of the order-4 square tiling honeycomb family, as it can be seen as a rectified order-4 square tiling honeycomb.
It is related to the 24-cell
In geometry, the 24-cell is the convex regular 4-polytope (four-dimensional analogue of a Platonic solid) with Schläfli symbol . It is also called C24, or the icositetrachoron, octaplex (short for "octahedral complex"), icosatetrahedroid, oc ...
, , which also has a cubic vertex figure.
It is also part of a sequence of honeycombs with square tiling
In geometry, the square tiling, square tessellation or square grid is a regular tiling of the Euclidean plane. It has Schläfli symbol of meaning it has 4 squares around every vertex.
Conway called it a quadrille.
The internal angle of th ...
cells:
Rectified square tiling honeycomb
The rectified square tiling honeycomb, t1, hascube
In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. Viewed from a corner it is a hexagon and its net is usually depicted as a cross.
The cube is the on ...
and square tiling
In geometry, the square tiling, square tessellation or square grid is a regular tiling of the Euclidean plane. It has Schläfli symbol of meaning it has 4 squares around every vertex.
Conway called it a quadrille.
The internal angle of th ...
facets, with a triangular prism
In geometry, a triangular prism is a three-sided prism; it is a polyhedron made of a triangular base, a translated copy, and 3 faces joining corresponding sides. A right triangular prism has rectangular sides, otherwise it is ''oblique''. ...
vertex figure
In geometry, a vertex figure, broadly speaking, is the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.
Definitions
Take some corner or vertex of a polyhedron. Mark a point somewhere along each connected edge. Draw lines ...
.
 It is similar to the 2D hyperbolic uniform
It is similar to the 2D hyperbolic uniform triapeirogonal tiling
In geometry, the triapeirogonal tiling (or trigonal-horocyclic tiling) is a uniform tiling of the hyperbolic plane with a Schläfli symbol of r.
Uniform colorings
The half-symmetry form, , has two colors of triangles:
: Related polyhedra and t ...
, r, with triangle
A triangle is a polygon with three edges and three vertices. It is one of the basic shapes in geometry. A triangle with vertices ''A'', ''B'', and ''C'' is denoted \triangle ABC.
In Euclidean geometry, any three points, when non- colli ...
and apeirogon
In geometry, an apeirogon () or infinite polygon is a generalized polygon with a countably infinite number of sides. Apeirogons are the two-dimensional case of infinite polytopes.
In some literature, the term "apeirogon" may refer only to ...
al faces.
: 
Truncated square tiling honeycomb
The truncated square tiling honeycomb, t, hascube
In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. Viewed from a corner it is a hexagon and its net is usually depicted as a cross.
The cube is the on ...
and truncated square tiling
In geometry, the truncated square tiling is a semiregular tiling by regular polygons of the Euclidean plane with one square and two octagons on each vertex. This is the only edge-to-edge tiling by regular convex polygons which contains an octagon ...
facets, with a triangular pyramid vertex figure
In geometry, a vertex figure, broadly speaking, is the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.
Definitions
Take some corner or vertex of a polyhedron. Mark a point somewhere along each connected edge. Draw lines ...
. It is the same as the cantitruncated order-4 square tiling honeycomb, tr, .

Bitruncated square tiling honeycomb
The bitruncated square tiling honeycomb, 2t, hastruncated cube
In geometry, the truncated cube, or truncated hexahedron, is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 regular faces (6 octagonal and 8 triangular), 36 edges, and 24 vertices.
If the truncated cube has unit edge length, its dual triakis octahedron has edg ...
and truncated square tiling
In geometry, the truncated square tiling is a semiregular tiling by regular polygons of the Euclidean plane with one square and two octagons on each vertex. This is the only edge-to-edge tiling by regular convex polygons which contains an octagon ...
facets, with a digonal disphenoid
In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the ...
vertex figure
In geometry, a vertex figure, broadly speaking, is the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.
Definitions
Take some corner or vertex of a polyhedron. Mark a point somewhere along each connected edge. Draw lines ...
.

Cantellated square tiling honeycomb
The cantellated square tiling honeycomb, rr, hascuboctahedron
A cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with 8 triangular faces and 6 square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with 2 triangles and 2 squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such, it ...
, square tiling
In geometry, the square tiling, square tessellation or square grid is a regular tiling of the Euclidean plane. It has Schläfli symbol of meaning it has 4 squares around every vertex.
Conway called it a quadrille.
The internal angle of th ...
, and triangular prism
In geometry, a triangular prism is a three-sided prism; it is a polyhedron made of a triangular base, a translated copy, and 3 faces joining corresponding sides. A right triangular prism has rectangular sides, otherwise it is ''oblique''. ...
facets, with an isosceles triangular prism
In geometry, a triangular prism is a three-sided prism; it is a polyhedron made of a triangular base, a translated copy, and 3 faces joining corresponding sides. A right triangular prism has rectangular sides, otherwise it is ''oblique''. ...
vertex figure
In geometry, a vertex figure, broadly speaking, is the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.
Definitions
Take some corner or vertex of a polyhedron. Mark a point somewhere along each connected edge. Draw lines ...
.

Cantitruncated square tiling honeycomb
The cantitruncated square tiling honeycomb, tr, hastruncated cube
In geometry, the truncated cube, or truncated hexahedron, is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 regular faces (6 octagonal and 8 triangular), 36 edges, and 24 vertices.
If the truncated cube has unit edge length, its dual triakis octahedron has edg ...
, truncated square tiling
In geometry, the truncated square tiling is a semiregular tiling by regular polygons of the Euclidean plane with one square and two octagons on each vertex. This is the only edge-to-edge tiling by regular convex polygons which contains an octagon ...
, and triangular prism
In geometry, a triangular prism is a three-sided prism; it is a polyhedron made of a triangular base, a translated copy, and 3 faces joining corresponding sides. A right triangular prism has rectangular sides, otherwise it is ''oblique''. ...
facets, with an isosceles triangular pyramid vertex figure
In geometry, a vertex figure, broadly speaking, is the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.
Definitions
Take some corner or vertex of a polyhedron. Mark a point somewhere along each connected edge. Draw lines ...
.

Runcinated square tiling honeycomb
The runcinated square tiling honeycomb, t0,3, hasoctahedron
In geometry, an octahedron (plural: octahedra, octahedrons) is a polyhedron with eight faces. The term is most commonly used to refer to the regular octahedron, a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at e ...
, triangular prism
In geometry, a triangular prism is a three-sided prism; it is a polyhedron made of a triangular base, a translated copy, and 3 faces joining corresponding sides. A right triangular prism has rectangular sides, otherwise it is ''oblique''. ...
, cube
In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. Viewed from a corner it is a hexagon and its net is usually depicted as a cross.
The cube is the on ...
, and square tiling
In geometry, the square tiling, square tessellation or square grid is a regular tiling of the Euclidean plane. It has Schläfli symbol of meaning it has 4 squares around every vertex.
Conway called it a quadrille.
The internal angle of th ...
facets, with an irregular triangular antiprism
In geometry, an octahedron (plural: octahedra, octahedrons) is a polyhedron with eight faces. The term is most commonly used to refer to the regular octahedron, a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at ea ...
vertex figure
In geometry, a vertex figure, broadly speaking, is the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.
Definitions
Take some corner or vertex of a polyhedron. Mark a point somewhere along each connected edge. Draw lines ...
.

Runcitruncated square tiling honeycomb
The runcitruncated square tiling honeycomb, t0,1,3, hasrhombicuboctahedron
In geometry, the rhombicuboctahedron, or small rhombicuboctahedron, is a polyhedron with eight triangular, six square, and twelve rectangular faces. There are 24 identical vertices, with one triangle, one square, and two rectangles meeting at ...
, octagonal prism
In geometry, the octagonal prism is the sixth in an infinite set of prisms, formed by rectangular sides and two regular octagon caps.
If faces are all regular, it is a semiregular polyhedron.
Symmetry
Images
The octagonal prism can also ...
, triangular prism
In geometry, a triangular prism is a three-sided prism; it is a polyhedron made of a triangular base, a translated copy, and 3 faces joining corresponding sides. A right triangular prism has rectangular sides, otherwise it is ''oblique''. ...
and truncated square tiling
In geometry, the truncated square tiling is a semiregular tiling by regular polygons of the Euclidean plane with one square and two octagons on each vertex. This is the only edge-to-edge tiling by regular convex polygons which contains an octagon ...
facets, with an isosceles-trapezoidal pyramid
A pyramid (from el, πυραμίς ') is a structure whose outer surfaces are triangular and converge to a single step at the top, making the shape roughly a pyramid in the geometric sense. The base of a pyramid can be trilateral, quadrila ...
vertex figure
In geometry, a vertex figure, broadly speaking, is the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.
Definitions
Take some corner or vertex of a polyhedron. Mark a point somewhere along each connected edge. Draw lines ...
.

Runcicantellated square tiling honeycomb
The runcicantellated square tiling honeycomb is the same as the runcitruncated order-4 octahedral honeycomb.Omnitruncated square tiling honeycomb
The omnitruncated square tiling honeycomb, t0,1,2,3, hastruncated square tiling
In geometry, the truncated square tiling is a semiregular tiling by regular polygons of the Euclidean plane with one square and two octagons on each vertex. This is the only edge-to-edge tiling by regular convex polygons which contains an octagon ...
, truncated cuboctahedron
In geometry, the truncated cuboctahedron is an Archimedean solid, named by Kepler as a truncation of a cuboctahedron. It has 12 square faces, 8 regular hexagonal faces, 6 regular octagonal faces, 48 vertices, and 72 edges. Since each of its fa ...
, hexagonal prism
In geometry, the hexagonal prism is a prism with hexagonal base. Prisms are polyhedrons; this polyhedron has 8 faces, 18 edges, and 12 vertices..
Since it has 8 faces, it is an octahedron. However, the term ''octahedron'' is primarily used t ...
, and octagonal prism
In geometry, the octagonal prism is the sixth in an infinite set of prisms, formed by rectangular sides and two regular octagon caps.
If faces are all regular, it is a semiregular polyhedron.
Symmetry
Images
The octagonal prism can also ...
facets, with an irregular tetrahedron
In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the ...
vertex figure
In geometry, a vertex figure, broadly speaking, is the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.
Definitions
Take some corner or vertex of a polyhedron. Mark a point somewhere along each connected edge. Draw lines ...
.

Omnisnub square tiling honeycomb
The alternated omnitruncated square tiling honeycomb (or omnisnub square tiling honeycomb), h(t0,1,2,3), has snub square tiling, snub cube,triangular antiprism
In geometry, an octahedron (plural: octahedra, octahedrons) is a polyhedron with eight faces. The term is most commonly used to refer to the regular octahedron, a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at ea ...
, square antiprism
In geometry, the square antiprism is the second in an infinite family of antiprisms formed by an even-numbered sequence of triangle sides closed by two polygon caps. It is also known as an ''anticube''.
If all its faces are regular, it is a se ...
, and tetrahedron
In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the ...
cells, with an irregular tetrahedron
In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the ...
vertex figure
In geometry, a vertex figure, broadly speaking, is the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.
Definitions
Take some corner or vertex of a polyhedron. Mark a point somewhere along each connected edge. Draw lines ...
.
Alternated square tiling honeycomb
The alternated square tiling honeycomb, h, is a quasiregular paracompact uniform honeycomb in hyperbolic 3-space. It hascube
In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. Viewed from a corner it is a hexagon and its net is usually depicted as a cross.
The cube is the on ...
and square tiling
In geometry, the square tiling, square tessellation or square grid is a regular tiling of the Euclidean plane. It has Schläfli symbol of meaning it has 4 squares around every vertex.
Conway called it a quadrille.
The internal angle of th ...
facets in a cuboctahedron
A cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with 8 triangular faces and 6 square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with 2 triangles and 2 squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such, it ...
vertex figure.
Cantic square tiling honeycomb
The cantic square tiling honeycomb, h2, is a paracompact uniform honeycomb in hyperbolic 3-space. It hastruncated square tiling
In geometry, the truncated square tiling is a semiregular tiling by regular polygons of the Euclidean plane with one square and two octagons on each vertex. This is the only edge-to-edge tiling by regular convex polygons which contains an octagon ...
, truncated cube
In geometry, the truncated cube, or truncated hexahedron, is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 regular faces (6 octagonal and 8 triangular), 36 edges, and 24 vertices.
If the truncated cube has unit edge length, its dual triakis octahedron has edg ...
, and cuboctahedron
A cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with 8 triangular faces and 6 square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with 2 triangles and 2 squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such, it ...
facets, with a rectangular
In Euclidean plane geometry, a rectangle is a quadrilateral with four right angles. It can also be defined as: an equiangular quadrilateral, since equiangular means that all of its angles are equal (360°/4 = 90°); or a parallelogram containin ...
pyramid
A pyramid (from el, πυραμίς ') is a structure whose outer surfaces are triangular and converge to a single step at the top, making the shape roughly a pyramid in the geometric sense. The base of a pyramid can be trilateral, quadrila ...
vertex figure
In geometry, a vertex figure, broadly speaking, is the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.
Definitions
Take some corner or vertex of a polyhedron. Mark a point somewhere along each connected edge. Draw lines ...
.
Runcic square tiling honeycomb
The runcic square tiling honeycomb, h3, is a paracompact uniform honeycomb in hyperbolic 3-space. It hassquare tiling
In geometry, the square tiling, square tessellation or square grid is a regular tiling of the Euclidean plane. It has Schläfli symbol of meaning it has 4 squares around every vertex.
Conway called it a quadrille.
The internal angle of th ...
, rhombicuboctahedron
In geometry, the rhombicuboctahedron, or small rhombicuboctahedron, is a polyhedron with eight triangular, six square, and twelve rectangular faces. There are 24 identical vertices, with one triangle, one square, and two rectangles meeting at ...
, and octahedron
In geometry, an octahedron (plural: octahedra, octahedrons) is a polyhedron with eight faces. The term is most commonly used to refer to the regular octahedron, a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at e ...
facets in a square
In Euclidean geometry, a square is a regular quadrilateral, which means that it has four equal sides and four equal angles (90-degree angles, π/2 radian angles, or right angles). It can also be defined as a rectangle with two equal-length a ...
frustum
In geometry, a (from the Latin for "morsel"; plural: ''frusta'' or ''frustums'') is the portion of a solid (normally a pyramid or a cone) that lies between two parallel planes cutting this solid. In the case of a pyramid, the base faces are ...
vertex figure.
Runcicantic square tiling honeycomb
The runcicantic square tiling honeycomb, h2,3, ↔ , is a paracompact uniform honeycomb in hyperbolic 3-space. It hastruncated square tiling
In geometry, the truncated square tiling is a semiregular tiling by regular polygons of the Euclidean plane with one square and two octagons on each vertex. This is the only edge-to-edge tiling by regular convex polygons which contains an octagon ...
, truncated cuboctahedron
In geometry, the truncated cuboctahedron is an Archimedean solid, named by Kepler as a truncation of a cuboctahedron. It has 12 square faces, 8 regular hexagonal faces, 6 regular octagonal faces, 48 vertices, and 72 edges. Since each of its fa ...
, and truncated octahedron
In geometry, the truncated octahedron is the Archimedean solid that arises from a regular octahedron by removing six pyramids, one at each of the octahedron's vertices. The truncated octahedron has 14 faces (8 regular hexagons and 6 squares), 36 ...
facets in a mirrored sphenoid vertex figure
In geometry, a vertex figure, broadly speaking, is the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.
Definitions
Take some corner or vertex of a polyhedron. Mark a point somewhere along each connected edge. Draw lines ...
.
Alternated rectified square tiling honeycomb
The alternated rectified square tiling honeycomb is a paracompact uniform honeycomb in hyperbolic 3-space.See also
*Convex uniform honeycombs in hyperbolic space
In hyperbolic geometry, a uniform honeycomb in hyperbolic space is a uniform tessellation of uniform polyhedral cells. In 3-dimensional hyperbolic space there are nine Coxeter group families of compact convex uniform honeycombs, generated as ...
* Regular tessellations of hyperbolic 3-space
* Paracompact uniform honeycombs
References
*Coxeter
Harold Scott MacDonald "Donald" Coxeter, (9 February 1907 – 31 March 2003) was a British and later also Canadian geometer. He is regarded as one of the greatest geometers of the 20th century.
Biography
Coxeter was born in Kensington to ...
, '' Regular Polytopes'', 3rd. ed., Dover Publications, 1973. . (Tables I and II: Regular polytopes and honeycombs, pp. 294–296)
* ''The Beauty of Geometry: Twelve Essays'' (1999), Dover Publications, , (Chapter 10Regular Honeycombs in Hyperbolic Space
Table III * Jeffrey R. Weeks ''The Shape of Space, 2nd edition'' {{ISBN, 0-8247-0709-5 (Chapter 16-17: Geometries on Three-manifolds I,II) * Norman Johnson ''Uniform Polytopes'', Manuscript ** N.W. Johnson: ''The Theory of Uniform Polytopes and Honeycombs'', Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Toronto, 1966 ** N.W. Johnson: ''Geometries and Transformations'', (2018) Chapter 13: Hyperbolic Coxeter groups ** Norman W. Johnson and Asia Ivic Weis
Quadratic Integers and Coxeter Groups
PDF
Portable Document Format (PDF), standardized as ISO 32000, is a file format developed by Adobe in 1992 to present documents, including text formatting and images, in a manner independent of application software, hardware, and operating systems. ...
Can. J. Math. Vol. 51 (6), 1999 pp. 1307–1336
Honeycombs (geometry)
Square tilings