Square (astrological Aspect) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
''Conjunctions of Jupiter and Saturn''
, Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society of Canada, Vol. 94, p.174 Greater importance is attributed to the beginning of a new cycle, which may occur after all four Trigons have been visited, which occurs in ~900 years. Typically, medieval astrologers used 960 years as the length of the full cycle, because, in some cases, it took 240 years to pass from one trigon to the next. If a cycle is defined by when the Conjunctions return to the same
Astrodienst
Typically, with a Square, Trine or Sextile, the outer or
 A
A
Regular star polygon 12-5.svg,
Regular star polygon 7-2.svg,
 An Octile or ''Semisquare'' is an angle of 45┬░, which is of the 360┬░
An Octile or ''Semisquare'' is an angle of 45┬░, which is of the 360┬░
Regular star polygon 8-3.svg,
Regular star polygon 9-2.svg,
 A Decile is an angle of 36┬░, which is of the 360┬░
A Decile is an angle of 36┬░, which is of the 360┬░  3 A Tridecile is an angle of 108┬░, which is of the 360┬░ ecliptic.
3 A Tridecile is an angle of 108┬░, which is of the 360┬░ ecliptic.
Regular star polygon 10-3.svg,
Regular star polygon 11-2.svg,
Regular star polygon 16-3.svg,
''The Classical Origin & Traditional Use of Aspects''
Deborah Houlding
Online Ephemeris from Khaldea.com
Ćö600BC to 2400ADŌĆöCalculated for
''Harmonices mundi''
("The Harmony of the Worlds") in fulltext facsimile;
astrology
Astrology is a range of Divination, divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that propose that information about human affairs and terrestrial events may be discerned by studying the apparent positions ...
, an aspect is an angle
In Euclidean geometry, an angle can refer to a number of concepts relating to the intersection of two straight Line (geometry), lines at a Point (geometry), point. Formally, an angle is a figure lying in a Euclidean plane, plane formed by two R ...
that planets
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is generally required to be in orbit around a star, stellar remnant, or brown dwarf, and is not one itself. The Solar System has eight planets by the most restrictive definition of the te ...
make to each other in the horoscope
A horoscope (or other commonly used names for the horoscope in English include natal chart, astrological chart, astro-chart, celestial map, sky-map, star-chart, cosmogram, vitasphere, radical chart, radix, chart wheel or simply chart) is an ast ...
; as well as to the Ascendant
The ascendant (Asc, Asc or As) or rising sign is the astrological sign on the eastern horizon when the person was born. It signifies a person's physical appearance, and awakening consciousness.
Because the ascendant is specific to a particula ...
, Midheaven
Most horoscopic traditions of astrology systems divide the horoscope into a number (usually twelve) of houses whose positions depend on time and location rather than on date. The houses of the horoscope represent different fields of experience ...
, Descendant, Lower Midheaven, and other points of astrological interest. As viewed from Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
, aspects are measured by the angular distance
Angular distance or angular separation is the measure of the angle between the orientation (geometry), orientation of two straight lines, ray (geometry), rays, or vector (geometry), vectors in three-dimensional space, or the central angle subtende ...
in degrees and minutes of ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of Earth's orbit, Earth around the Sun. It was a central concept in a number of ancient sciences, providing the framework for key measurements in astronomy, astrology and calendar-making.
Fr ...
longitude between two points. According to astrological tradition, they indicate the timing of transitions and developmental changes in the lives of people and affairs relative to the Earth.
For example, if an astrologer
Astrology is a range of Divination, divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that propose that information about human affairs and terrestrial events may be discerned by studying the apparent positions ...
creates a Horoscope
A horoscope (or other commonly used names for the horoscope in English include natal chart, astrological chart, astro-chart, celestial map, sky-map, star-chart, cosmogram, vitasphere, radical chart, radix, chart wheel or simply chart) is an ast ...
that shows the apparent positions of the celestial bodies at the time of a person's birth (Natal Chart
A horoscope (or other commonly used names for the horoscope in English include natal chart, astrological chart, astro-chart, celestial map, sky-map, star-chart, cosmogram, vitasphere, radical chart, radix, chart wheel or simply chart) is an ast ...
), and the angular distance between Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmosph ...
and Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is often called Earth's "twin" or "sister" planet for having almost the same size and mass, and the closest orbit to Earth's. While both are rocky planets, Venus has an atmosphere much thicker ...
is 92┬░ ecliptic longitude, the chart is said to have the aspect "Venus Square
In geometry, a square is a regular polygon, regular quadrilateral. It has four straight sides of equal length and four equal angles. Squares are special cases of rectangles, which have four equal angles, and of rhombuses, which have four equal si ...
Mars" with an orb of 2┬░ (i.e., it is 2┬░ away from being an exact Square; a Square being a 90┬░ aspect). The more exact an aspect, the stronger or more dominant it is said to be in shaping character or manifesting change.
With Natal charts, other signs may take precedence over a Sun sign. For example, an Aries may have several other planets in Cancer or Pisces. Therefore, the two latter signs may be more influential.
History and approach
In medieval astrology, certain aspects andplanet
A planet is a large, Hydrostatic equilibrium, rounded Astronomical object, astronomical body that is generally required to be in orbit around a star, stellar remnant, or brown dwarf, and is not one itself. The Solar System has eight planets b ...
s were considered to be either favorable (benefic
Benefic may refer to:
* Benefic planet
Babylonian astrology was the first known organized system of astrology, arising in the second millennium BC.
In Babylon as well as in Assyria as a direct offshoot of Babylonian culture, astrology takes its ...
) or unfavorable ( malefic). Modern usage places less emphasis on these fatalistic distinctions. The more modern approach to astrological aspects is exemplified by research on astrological harmonics. In 1619, Johannes Kepler
Johannes Kepler (27 December 1571 ŌĆō 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, Natural philosophy, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best know ...
advocates this in his book ''Harmonice Mundi
''Harmonice Mundi'' (Latin: ''The Harmony of the World'', 1619) is a book by Johannes Kepler. In the work, written entirely in Latin, Kepler discusses harmony and congruence in geometrical forms and physical phenomena. The final section of t ...
''. Thereafter, John Addey was a major proponent. However, even in modern times, aspects are considered to be either easy (60┬░ ''Sextile
Sextile may refer to
* Sextile (astrological aspect), an astrological aspect
** its corresponding Unicode character , a horizontally-aligned six-pointed asterisk
* Sextile (band), an American post-punk band
{{Disambiguation ...
'' or
120┬░ '' Trine'') or hard (90┬░ ''Square
In geometry, a square is a regular polygon, regular quadrilateral. It has four straight sides of equal length and four equal angles. Squares are special cases of rectangles, which have four equal angles, and of rhombuses, which have four equal si ...
'' or 180┬░ ''Opposition
Opposition may refer to:
Arts and media
* ''Opposition'' (Altars EP), 2011 EP by Christian metalcore band Altars
* The Opposition (band), a London post-punk band
* ''The Opposition with Jordan Klepper'', a late-night television series on Comedy ...
''). Depending on the involved planets, a '' Conjunction'' (0┬░, which is a discounting orb) may be in either category.
Easy aspects may be positive, because they enhance opportunity for talent to grow.
Hard aspects may be negative, because they enhance a challenge where an adjustment must be made to reach balance. Typically, manifestation may occur with a Conjunction, Square or Opposition.
Planets may be considered. Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmosph ...
and Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. It is a gaseous cyan-coloured ice giant. Most of the planet is made of water, ammonia, and methane in a Supercritical fluid, supercritical phase of matter, which astronomy calls "ice" or Volatile ( ...
tend to ignite while Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant, with an average radius of about 9 times that of Earth. It has an eighth the average density of Earth, but is over 95 tim ...
and Neptune
Neptune is the eighth and farthest known planet from the Sun. It is the List of Solar System objects by size, fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 t ...
inhibit. Whether a planet is direct
Direct may refer to:
Mathematics
* Directed set, in order theory
* Direct limit of (pre), sheaves
* Direct sum of modules, a construction in abstract algebra which combines several vector spaces
Computing
* Direct access (disambiguation), ...
or retrograde
Retrograde may refer to:
Film and television
* Retrograde (2004 film), ''Retrograde'' (2004 film), a film by Christopher Kulikowski
* Retrograde (2022 American film), ''Retrograde'' (2022 American film), a documentary film by Matthew Heineman
* ...
is of great significance. An eclipse
An eclipse is an astronomical event which occurs when an astronomical object or spacecraft is temporarily obscured, by passing into the shadow of another body or by having another body pass between it and the viewer. This alignment of three ...
of the Sun or Moon is even more significant. The South Node
A lunar node is either of the two orbital nodes of the Moon; that is, the two points at which the orbit of the Moon intersects the ecliptic. The ''ascending'' (or ''north'') node is where the Moon moves into the northern ecliptic hemisphere, wh ...
of the Moon denotes innate wisdom from past experience while the North Node
A lunar node is either of the two orbital nodes of the Moon; that is, the two points at which the orbit of the Moon intersects the ecliptic. The ''ascending'' (or ''north'') node is where the Moon moves into the northern ecliptic hemisphere, wh ...
denotes karma and evolution.
Astrological Signs may be considered. For example, the fire signs of Aries
Aries may refer to:
*Aries (astrology), an astrological sign
*Aries (constellation), a constellation in the zodiac
Arts, entertainment and media
* ''Aries'' (album), by Luis Miguel, 1993
* ''Aries'' (EP), by Alice Chater, 2020
* "Aries" (song), ...
, Leo
Leo is the Latin word for lion. It most often refers to:
* Leo (constellation), a constellation of stars in the night sky
* Leo (astrology), an astrological sign of the zodiac
* Leo (given name), a given name in several languages, usually mas ...
and Sagittarius
Sagittarius ( ) may refer to:
*Sagittarius (constellation)
*Sagittarius (astrology), a sign of the Zodiac
* Sagittarius of Gap, a 6th century bishop
*Sagittarius A*, the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way galaxy
Ships
*'' S ...
are more compatible with the air signs of Gemini
Gemini most often refers to:
* Gemini (constellation), one of the constellations of the zodiac
* Gemini (astrology), an astrological sign
Gemini may also refer to:
Science and technology Space
* Gemini in Chinese astronomy, the Gemini constellat ...
, Libra
Libra generally refers to:
* Libra (constellation), a constellation
* Libra (astrology), an astrological sign based on the star constellation
Libra may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Libra'' (novel), a 1988 novel by Don DeLillo
Musi ...
and Aquarius. The Earth signs of Taurus
Taurus is Latin for 'bull' and may refer to:
* Taurus (astrology), the astrological sign
** Vß╣øß╣Żabha, in vedic astrology
* Taurus (constellation), one of the constellations of the zodiac
* Taurus (mythology), one of two Greek mythological ch ...
, Virgo
Virgo may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Virgo (film), a 1970 Egyptian film
* Virgo (character), several Marvel Comics characters
* Virgo Asmita, a character in the manga ''Saint Seiya: The Lost Canvas''
* ''Virgo'' (album), by Virgo Four, ...
and Capricorn are more compatible with the water signs of Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
, Scorpio and Pisces
Pisces may refer to:
*Pisces (astrology), an astrological sign
Astronomy
*Pisces (constellation), a constellation
** Pisces Overdensity, an overdensity of stars in the Milky Way's halo that is situated in the Pisces constellation
** Pisces II, a ...
. The mutable signs of Gemini, Virgo, Sagittarius and Pisces may be flexible. The cardinal signs of Aries, Cancer, Libra and Capricorn may change their mind. The fixed signs of Taurus, Leo, Scorpio and Aquarius may be difficult.
Astrological Houses
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air condi ...
may be considered.
Ptolemaic Aspects
Since they were defined and used byPtolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; ŌĆō 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzant ...
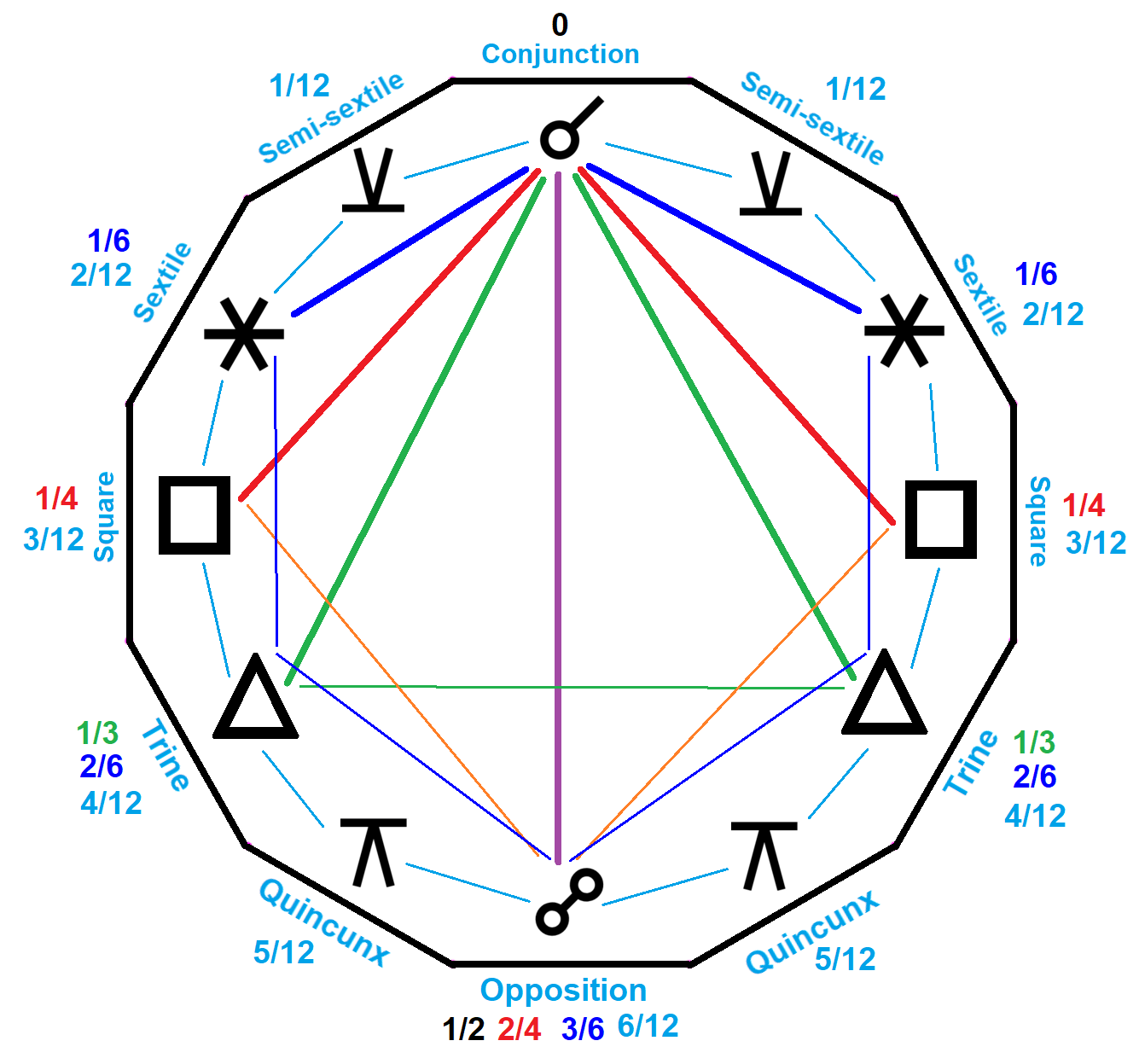
in the 1st Century AD, the traditional major aspects are sometimes called Ptolemaic Aspects. These aspects are the Conjunction (0┬░), Sextile (60┬░), Square (90┬░), Trine (120┬░), and Opposition (180┬░). Major aspects are those that are divisible by 10 and evenly divided in relation to 360┬░ (with the exception of the Semisextile and the Novile).
When calculating or using aspects, it is important to note that different astrologers and separate astrological systems/traditions utilize differing orbs, which is the degree of separation between exactitude. Orbs may also be subject to variation, depending on the need for detail and personal preferences. Although, when compared to other aspects, almost all astrologers use a larger orb for a Conjunction.
Kepler's Aspects
Collective astrological data along withJohannes Kepler
Johannes Kepler (27 December 1571 ŌĆō 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, Natural philosophy, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best know ...
described 13 aspects in his book ''Harmonice Mundi
''Harmonice Mundi'' (Latin: ''The Harmony of the World'', 1619) is a book by Johannes Kepler. In the work, written entirely in Latin, Kepler discusses harmony and congruence in geometrical forms and physical phenomena. The final section of t ...
''. Astrological data grouped together in five degrees of influentially picked from symbol ratios encountered in geometry and music: 0/2, 1/2, 1/5, 2/6, 1/3, 1/12 along with 1/5, 2/5, 15/5, 10, 10/3, 8, and 8/3. The general names for whole divisors are (Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
) ''n''-ile for whole fractions 1/''n'', and ''m''-''n''-ile for fraction ''m''/''n''. A Semi-''n''-tile is a ''2n''-tile, 1/(2''n''), and Sesqui-n-tile is a Tri-2''n''-tile, 3/(2''n'').
All aspects can be seen as small whole number harmonic
In physics, acoustics, and telecommunications, a harmonic is a sinusoidal wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the ''fundamental frequency'' of a periodic signal. The fundamental frequency is also called the ''1st har ...
s, (1/''n'' of 360┬░). Multiples of ''m''/''n'' create new aspects where there are no common factors between ''n'' and ''m'', gcd(n,m)=1.
Major aspects

Conjunction
A Conjunction (abbreviated as "Con") is an angle of approximately (~) 0ŌĆōŌüĀ10┬░. Typically, an orb of ~10┬░ is considered to be a Conjunction. If neither theSun
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light a ...
or Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar ...
are involved, some astrologers consider a maximum orb of 8┬░.
Conjunctions are a major aspect in a horoscope chart. They are said to be the most powerful aspects, because they mutually intensify the effects of the involved planets.
Depending on the involved planets, a Conjunction may be beneficial or detrimental. Highly favourable Conjunctions may involve the Sun, Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is often called Earth's "twin" or "sister" planet for having almost the same size and mass, and the closest orbit to Earth's. While both are rocky planets, Venus has an atmosphere much thicker ...
, and/or Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a Jupiter mass, mass more than 2.5 times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined a ...
as well as any of the three possible combinations. Highly ''un''favourable Conjunctions may involve the Moon, Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmosph ...
, and/or Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant, with an average radius of about 9 times that of Earth. It has an eighth the average density of Earth, but is over 95 tim ...
as well as any of the three possible combinations.
Exceptionally, on November 9ŌĆō10 of 1970, the Sun
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light a ...
, Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is often called Earth's "twin" or "sister" planet for having almost the same size and mass, and the closest orbit to Earth's. While both are rocky planets, Venus has an atmosphere much thicker ...
, and Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a Jupiter mass, mass more than 2.5 times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined a ...
were in a three-way beneficial Conjunction. In that same year, on March 10, the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar ...
, Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmosph ...
, and Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant, with an average radius of about 9 times that of Earth. It has an eighth the average density of Earth, but is over 95 tim ...
were in 3-way detrimental Conjunction.
If either of two planets involved in a Conjunction is also under tension from one or more hard aspects with one or more other planets, then the added presence of a Conjunction will further intensify the tension of that hard aspect.
If a planet is in ''very'' close Conjunction to the Sun (within 17 minutes of arc or only about 0.28┬░), the Conjunction is of great strength. The planet is said to be ''Cazimi'', which is an ancient astrological term meaning "in the heart" (of the Sun). For example, "Venus ''Cazimi''" means Venus is in Conjunction with the Sun with an orb of less than ~ŌüĀ0.28┬░.
If a planet is moderately close to the Sun, the specific orb limit may depend on the particular planet. It is said to be ''Combust''.
ŌüĀ
Every month of the year, during the New Moon
In astronomy, the new moon is the first lunar phase, when the Moon and Sun have the same ecliptic longitude. At this phase, the lunar disk is not visible to the naked eye, except when it is silhouetted against the Sun during a solar eclipse. ...
, the Sun and Moon experience a Conjunction.
Great Conjunctions
In the past, Great Conjunctions between the two slowest classical planets,Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a Jupiter mass, mass more than 2.5 times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined a ...
and Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant, with an average radius of about 9 times that of Earth. It has an eighth the average density of Earth, but is over 95 tim ...
, have attracted considerable attention as celestial omens. This interest can be traced back to Arabic translations found in Europe; most notably Albumasar
Abu MaŌĆśshar al-Balkhi, Latinized as Albumasar (also ''Albusar'', ''Albuxar'', ''Albumazar''; full name ''Ab┼½ Ma╩┐shar Ja╩┐far ibn MußĖźammad ibn ╩┐Umar al-Balkh─½'' ;
, AH 171ŌĆō272), was an early Persian Muslim astrologer, thought to be ...
's book on Conjunctions. During the late Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
and the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
, these omens were a topic broached by most astronomers. This included scholastic thinkers, such as Roger Bacon
Roger Bacon (; or ', also '' Rogerus''; ), also known by the Scholastic accolades, scholastic accolade ''Doctor Mirabilis'', was a medieval English polymath, philosopher, scientist, theologian and Franciscans, Franciscan friar who placed co ...
and Pierre D'Ailly
Pierre d'Ailly (; ; 13519 August 1420) was a French theologian, astrologer and cardinal of the Roman Catholic Church.
Academic career
D'Ailly was born in Compi├©gne in 1350 or 1351 of a prosperous bourgeois family. He studied in Paris at the Co ...
. Omens are also mentioned in popular literary writings by authors, such as Dante
Dante Alighieri (; most likely baptized Durante di Alighiero degli Alighieri; ŌĆō September 14, 1321), widely known mononymously as Dante, was an Italian Italian poetry, poet, writer, and philosopher. His ''Divine Comedy'', originally called ...
Woody K., ''Dante and the Doctrine of the Great Conjunctions'', Dante Studies, with the Annual Report of the Dante Society, No. 95 (1977), pp. 119ŌĆō134 and Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 23 April 1564 ŌĆō 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's natio ...
.Aston M., ''The Fiery Trigon Conjunction: An Elizabethan Astrological Prediction'', Isis, Vol. 61, No. 2 (Summer, 1970), pp. 158ŌĆō187 This interest continued up to the times of Tycho Brahe
Tycho Brahe ( ; ; born Tyge Ottesen Brahe, ; 14 December 154624 October 1601), generally called Tycho for short, was a Danish astronomer of the Renaissance, known for his comprehensive and unprecedentedly accurate astronomical observations. He ...
and Kepler
Johannes Kepler (27 December 1571 ŌĆō 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best known for his laws of p ...
.
Every 20 years, successive Great Conjunctions move retrograde ~120┬░. Sequential Conjunctions appear as triangular patterns. They repeat after every third Conjunction; they return after some 60 years to the vicinity of the first. These returns are observed to be shifted by ~8┬░ relative to the fixed stars; no more than four of them occur in the same zodiac sign. Typically, Conjunctions occur in one of the following '' Triplicities'' or ''Trigons'' of Zodiac
The zodiac is a belt-shaped region of the sky that extends approximately 8┬░ north and south celestial latitude of the ecliptic ŌĆō the apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere over the course of the year. Within this zodiac ...
signs:
After about 220 years the pattern shifts to the next Trigon; in ~900 years, the pattern returns to the first Trigon.If and designate the periods of Jupiter and Saturn then the return takes which comes to 883.15 years, but to be a whole number of Conjunction intervals it must be sometimes 913 years and sometimes 854. See Etz.
To each triangular pattern, astrologers have ascribed one from a series of four elements
The classical elements typically refer to earth, water, air, fire, and (later) aether which were proposed to explain the nature and complexity of all matter in terms of simpler substances. Ancient cultures in Greece, Angola, Tibet, India, a ...
. Particular importance has been accorded to the occurrence of a Great Conjunction in a new Trigon, which is bound to happen after ~240 years at most.Etz D., (2000)''Conjunctions of Jupiter and Saturn''
, Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society of Canada, Vol. 94, p.174 Greater importance is attributed to the beginning of a new cycle, which may occur after all four Trigons have been visited, which occurs in ~900 years. Typically, medieval astrologers used 960 years as the length of the full cycle, because, in some cases, it took 240 years to pass from one trigon to the next. If a cycle is defined by when the Conjunctions return to the same
right ascension
Right ascension (abbreviated RA; symbol ) is the angular distance of a particular point measured eastward along the celestial equator from the Sun at the equinox (celestial coordinates), March equinox to the (hour circle of the) point in questio ...
rather than to the same constellation, the cycle is only ~800 years, because of axial precession
In astronomy, axial precession is a gravity-induced, slow, and continuous change in the orientation of an astronomical body's rotational axis. In the absence of precession, the astronomical body's orbit would show axial parallelism. In parti ...
. Use of the Alphonsine tables apparently led to the use of precessing signs; Kepler
Johannes Kepler (27 December 1571 ŌĆō 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best known for his laws of p ...
gave a value of 794 years, which created 40 Conjunctions.
Up to the end of the 16th century, despite the inaccuracies and some disagreement about the beginning of the cycle, the belief in the significance of such events generated a steady stream of publications. In 1583, the last Great Conjunction occurred in the watery trigon. It was widely supposed to herald apocalyptic changes. In 1586, a Papal Bull
A papal bull is a type of public decree, letters patent, or charter issued by the pope of the Catholic Church. It is named after the leaden Seal (emblem), seal (''bulla (seal), bulla'') traditionally appended to authenticate it.
History
Papal ...
was issued against divinations. By 1603, public interest rapidly died, because nothing really significant had happened with the advent of a new Trigon.
Opposition
An Opposition (abbreviated as "Opp") is an angle of 180┬░, which is of the 360┬░ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of Earth's orbit, Earth around the Sun. It was a central concept in a number of ancient sciences, providing the framework for key measurements in astronomy, astrology and calendar-making.
Fr ...
. Depending on the involved planets, an orb of 5-10┬░ is allowed.
An Opposition is said by Ibn Ezra to be the most powerful aspect. An opposition is fundamentally relational but not unifying or blending like a conjunction. Some astrologers say the energies in opposition are prone to exaggeration, because it has a dichotomous quality and issues arising from it are often tense.
All important axes in astrology are essentially Oppositions. Therefore, at its most basic level, an Opposition may often signify a relationship that can be oppositional or complementary.
Sextile
A SextileŌÜ╣(U+26B9
U, or u, is the twenty-first letter and the fifth vowel letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet and the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''u'' (pronounced ), ...
)(abbreviated as "SXt or Sex") is an angle of 60┬░, which is of the 360┬░ ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of Earth's orbit, Earth around the Sun. It was a central concept in a number of ancient sciences, providing the framework for key measurements in astronomy, astrology and calendar-making.
Fr ...
or a trine (120┬░). Depending on the involved planets, an orb of 4-5┬░ is allowed. The symbol is the radii of a hexagon.
Traditionally, a Sextile is said to be similar in influence to a Trine, but less intense. It indicates compatibility and harmony, which eases communication between the two involved elements. It also provides opportunity. See information below on the Semisextile.
Square
A Square or ''Quartile'' (abbreviated as "SQr or Squ") is an angle of 90┬░, which is of the 360┬░ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of Earth's orbit, Earth around the Sun. It was a central concept in a number of ancient sciences, providing the framework for key measurements in astronomy, astrology and calendar-making.
Fr ...
or an opposition (180┬░). Depending on the involved planets, an orb of 5-10┬░ is allowed.Orbs used by Liz Greene
Liz Greene (born 4 September 1946) is an American-British astrologer and author. Her father was born in London, and her mother in the United States.
Career
Greene is one of the chief writers for astro.com, the website for her company Astrodiens ...
, seAstrodienst
Typically, with a Square, Trine or Sextile, the outer or
superior planet
In the Solar System, a planet is said to be inferior or interior with respect to another planet if its orbit lies inside the other planet's orbit around the Sun. In this situation, the latter planet is said to be superior to the former. In the refe ...
has an effect on the inner or inferior planet. A Square creates a strong and usable tension. It may integrate between two different areas of your life or it may offer a turning point where an important decision needs to be made that involves an opportunity at a cost. Typically, it involves Houses
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air condi ...
in different quadrants
Quadrant may refer to:
Companies
* Quadrant Cycle Company, 1899 manufacturers in Britain of the Quadrant motorcar
* Quadrant (motorcycles), one of the earliest British motorcycle manufacturers, established in Birmingham in 1901
* Quadrant Privat ...
.
Trine
A Trine (abbreviated as "Tri") is an angle of 120┬░, which is of the 360┬░ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of Earth's orbit, Earth around the Sun. It was a central concept in a number of ancient sciences, providing the framework for key measurements in astronomy, astrology and calendar-making.
Fr ...
. Depending on the involved planets, an orb of 5-10┬░ is allowed.
Traditionally, a Trine is extremely beneficial. It indicates harmony, ease and what is natural. A Trine may involve innate talent or ability. In transit
Transit may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film
* ''Transit'' (1980 film), a 1980 Israeli film
* ''Transit'' (1986 film), a Canadian short film
* ''Transit'' (2005 film), a film produced by MTV and Staying-Alive about four people in countrie ...
, an event may emerge from a current or past situation in a natural way.
Minor aspects
Semisextile
A Semisextile or ''Duodecile'' is an angle of 30┬░, which is of the 360┬░ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of Earth's orbit, Earth around the Sun. It was a central concept in a number of ancient sciences, providing the framework for key measurements in astronomy, astrology and calendar-making.
Fr ...
. An orb of ┬▒1.2┬░ is allowed. The symbol is a Sextile (60┬░), which is the top radii of a hexagon; the internal angles are 60┬░.
Of the minor aspects, it may be the most often used, because it can be easily seen. It indicates a mental interaction between planets; it is more sensually than externally experienced.
With a Semisextile, energy gradually builds and potentiates. Consider other planets, Signs and Houses
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air condi ...
. A major aspect transit may be involved. To gain its benefit, make an effort.
Quincunx
Quincunx
A quincunx ( ) is a geometry, geometric pattern consisting of five points arranged in a cross, with four of them forming a Square (geometry), square or rectangle and a fifth at its center. The same pattern has other names, including "in saltire" ...
or ''Quinduodecile'' or ''Inconjunct'' is an angle of 150┬░, which is of the 360┬░ ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of Earth's orbit, Earth around the Sun. It was a central concept in a number of ancient sciences, providing the framework for key measurements in astronomy, astrology and calendar-making.
Fr ...
. Depending on the involved planets, an orb of ┬▒3.5┬░ is allowed. The symbol is the bottom radii of a hexagon, which is a Sextile (60┬░) less than a semicircle; the internal angles are 60┬░.
An interpretation of a Quincunx may mostly rely on the involved planets, Signs and Houses
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air condi ...
. Different areas of your life, that are not usually in communication, may come together. Planets may be far apart in different house quadrants. With a shift in perspective, clarity may reveal what was not previously seen. If a third planet, in a major aspect, triangulates a Qunicunx, the effect may be very obvious.
For Quincunx, keywords are karmic, mystery, unpredictable, imbalance, surreal, resourceful, creative, and humor.
A Quincunx does not offer equal divisions of a circle. It represents the 150┬░ turn angle
In geometry, an angle of a polygon is formed by two adjacent sides. For a simple polygon (non-self-intersecting), regardless of whether it is convex or non-convex, this angle is called an internal angle (or interior angle) if a point withi ...
s of a dodecagram
In geometry, a dodecagram (╬│Žü╬▒╬╝╬╝╬«
Henry George Liddell, Robe ...
, .
Henry George Liddell, Robe ...
Dodecagram
In geometry, a dodecagram (╬│Žü╬▒╬╝╬╝╬«
Henry George Liddell, Robe ...
Henry George Liddell, Robe ...
Other minor aspects
Septile
A Septile is an angle of about 51.43┬░, which is of the 360┬░ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of Earth's orbit, Earth around the Sun. It was a central concept in a number of ancient sciences, providing the framework for key measurements in astronomy, astrology and calendar-making.
Fr ...
. An orb of ┬▒1┬░ is allowed.
A Septile is a mystical aspect that indicates a hidden flow of energy between the involved planets. Often, it involves spiritual or energetic sensitivity as well as an inner awareness of a more subtle, hidden level of reality.
;Irreducible multiples:
: A Biseptile is an angle of 102.86┬░, which is of the 360┬░ ecliptic.
: A Triseptile is an angle of 154.29┬░, which is of the 360┬░ ecliptic.
Heptagram
A heptagram, septagram, septegram or septogram is a seven-point star polygon, star drawn with seven straight strokes.
The name ''heptagram'' combines a numeral prefix, ''hepta-'', with the Greek language, Greek suffix ''wikt:-gram, -gram ...
Regular star polygon 7-3.svg, Heptagram
A heptagram, septagram, septegram or septogram is a seven-point star polygon, star drawn with seven straight strokes.
The name ''heptagram'' combines a numeral prefix, ''hepta-'', with the Greek language, Greek suffix ''wikt:-gram, -gram ...
Octile
ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of Earth's orbit, Earth around the Sun. It was a central concept in a number of ancient sciences, providing the framework for key measurements in astronomy, astrology and calendar-making.
Fr ...
. An orb of ┬▒3┬░ is allowed. The symbol is drawn with a 60-90┬░ angle; the original angle is 90┬░, which is a Square.
An Octile is an important minor aspect. It indicates stimulating or challenging energy. It is similar to a Square, but doesn't last as long as it has a smaller orb.
;Irreducible Multiples:
A Sesquiquadrate or ''Trioctile'' is an angle of 135┬░, which is of the 360┬░ ecliptic. An orb of ┬▒1.5┬░ is allowed.
A Sesquiquadrate is a harmonic of a Semisquare, which involves challenge. It is not an exact division of the 360┬░ ecliptic. Therefore, when a Semisquare is present, it does not function as a standalone aspect, but as part of a series.
Octagram
In geometry, an octagram is an eight-angled star polygon.
The name ''octagram'' combine a Greek numeral prefix, ''wikt:octa-, octa-'', with the Greek language, Greek suffix ''wikt:-gram, -gram''. The ''-gram'' suffix derives from ╬│Žü╬▒╬╝╬╝╬« ...
Novile
A Novile is an angle of 40┬░, which is of the 360┬░ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of Earth's orbit, Earth around the Sun. It was a central concept in a number of ancient sciences, providing the framework for key measurements in astronomy, astrology and calendar-making.
Fr ...
. An orb of ┬▒1┬░ is allowed.
A Novile indicates an energy of perfection and/or idealization.
;Irreducible Multiples:
: A Binovile is an angle of 80┬░, which is of the 360┬░ ecliptic.
: A Quadnovile is an angle of 160┬░, which is of the 360┬░ ecliptic.
Enneagram
Enneagram may refer to:
* Enneagram (geometry), a nine-sided star polygon with various configurations
* Enneagram of Personality, a model of human personality illustrated by an enneagram figure
See also
* Enneagon
In geometry, a nonagon () or ...
Regular star polygon 9-4.svg, Enneagram
Enneagram may refer to:
* Enneagram (geometry), a nine-sided star polygon with various configurations
* Enneagram of Personality, a model of human personality illustrated by an enneagram figure
See also
* Enneagon
In geometry, a nonagon () or ...
Decile
ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of Earth's orbit, Earth around the Sun. It was a central concept in a number of ancient sciences, providing the framework for key measurements in astronomy, astrology and calendar-making.
Fr ...
.
;Irreducible Multiples:
: Decagram Decagram may refer to:
* 10 gram, or 0.01 kilogram, a unit of mass, in SI referred to as a ''dag''
* Decagram (geometry)
In geometry, a decagram is a 10-point star polygon. There is one regular decagram, containing the vertices of a regular dec ...
Undecile
An Undecile or ''Elftile'' is an angle of 32.73┬░, which is of the 360┬░ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of Earth's orbit, Earth around the Sun. It was a central concept in a number of ancient sciences, providing the framework for key measurements in astronomy, astrology and calendar-making.
Fr ...
. An orb of ┬▒1┬░ is allowed.
;Irreducible Multiples:
: A Biundecile is an angle of 65.45┬░, which is of the 360┬░ ecliptic.
: A Triundecile is an angle of 98.18┬░, which is of the 360┬░ ecliptic.
: A Quadundecile is an angle of 130.91┬░, which is of the 360┬░ ecliptic.
: A Quinundecile is an angle of 163.63┬░, which is of the 360┬░ ecliptic.
Hendecagram
In geometry, a hendecagram (also endecagram or endekagram) is a star polygon that has eleven Vertex (geometry), vertices.
The name ''hendecagram'' combines a Greek numeral prefix, ''wikt:hendeca-, hendeca-'', with the Greek language, Greek suffix ...
Regular star polygon 11-3.svg, Hendecagram
In geometry, a hendecagram (also endecagram or endekagram) is a star polygon that has eleven Vertex (geometry), vertices.
The name ''hendecagram'' combines a Greek numeral prefix, ''wikt:hendeca-, hendeca-'', with the Greek language, Greek suffix ...
Regular star polygon 11-4.svg, Hendecagram
In geometry, a hendecagram (also endecagram or endekagram) is a star polygon that has eleven Vertex (geometry), vertices.
The name ''hendecagram'' combines a Greek numeral prefix, ''wikt:hendeca-, hendeca-'', with the Greek language, Greek suffix ...
Regular star polygon 11-5.svg, Hendecagram
In geometry, a hendecagram (also endecagram or endekagram) is a star polygon that has eleven Vertex (geometry), vertices.
The name ''hendecagram'' combines a Greek numeral prefix, ''wikt:hendeca-, hendeca-'', with the Greek language, Greek suffix ...
Semioctile
A Semioctile or ''Sexdecile'' is an angle of 22.5┬░, which is of the 360┬░ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of Earth's orbit, Earth around the Sun. It was a central concept in a number of ancient sciences, providing the framework for key measurements in astronomy, astrology and calendar-making.
Fr ...
. An orb of ┬▒0.75┬░ is allowed.
A Semioctile is part of the square family. It is considered to be a version of the Semisquare, which triggers challenge. Its harmonic aspects are 45┬░, 67.5┬░, 90┬░, 112.5┬░, 135┬░, 157.5┬░ and 180┬░. It was discovered by Uranian astrologers.
;Irreducible Multiples:
: A Sesquioctile or ''Bisexdecile'' is an angle of 67.5┬░, which is of the 360┬░ ecliptic.
: A Quinsemioctile or ''Quinsexdecile'' is an angle of 112.5┬░, which is of the 360┬░ ecliptic.
: A Sepsemioctile or ''Sepsexdecile'' is an angle of 157.5┬░, which is of the 360┬░ ecliptic.
Hexadecagram
In mathematics, a hexadecagon (sometimes called a hexakaidecagon or 16-gon) is a sixteen-sided polygon.
Regular hexadecagon
A ''regular hexadecagon'' is a hexadecagon in which all angles are equal and all sides are congruent. Its Schl├żfli symbo ...
Regular star polygon 16-5.svg, Hexadecagram
In mathematics, a hexadecagon (sometimes called a hexakaidecagon or 16-gon) is a sixteen-sided polygon.
Regular hexadecagon
A ''regular hexadecagon'' is a hexadecagon in which all angles are equal and all sides are congruent. Its Schl├żfli symbo ...
Regular star polygon 16-7.svg, Hexadecagram
In mathematics, a hexadecagon (sometimes called a hexakaidecagon or 16-gon) is a sixteen-sided polygon.
Regular hexadecagon
A ''regular hexadecagon'' is a hexadecagon in which all angles are equal and all sides are congruent. Its Schl├żfli symbo ...
Declinations
The Parallel and Contraparallel or ''Antiparallel'' are two other aspects which refer to degrees ofdeclination
In astronomy, declination (abbreviated dec; symbol ''╬┤'') is one of the two angles that locate a point on the celestial sphere in the equatorial coordinate system, the other being hour angle. The declination angle is measured north (positive) or ...
above or below the Celestial Equator
The celestial equator is the great circle of the imaginary celestial sphere on the same plane as the equator of Earth. By extension, it is also a plane of reference in the equatorial coordinate system. Due to Earth's axial tilt, the celestial ...
. They are not widely used by astrologers.
Parallel and Contra Parallel
A The same declination of two planets. The declination is the vertical angle between a planet and the celestial equator, in a southern (S) or northern (N) direction. Planets in a parallel relationship are compared to a conjunction. A contra parallel or "split" parallel occurs when two planets have the same number of degrees of declination, but in opposite hemispheres. For example, the moon might be at 20 degrees north latitude, while Pluto appears at 20 degrees south latitude. Its meaning is similar to that of the opposition.See also
*Astrological symbols
Historically, astrological and astronomical symbols have overlapped. Frequently used symbols include signs of the zodiac and classical planets. These originate from medieval Byzantine codices. Their current form is a product of the European Re ...
* Conjunction
*Opposition
Opposition may refer to:
Arts and media
* ''Opposition'' (Altars EP), 2011 EP by Christian metalcore band Altars
* The Opposition (band), a London post-punk band
* ''The Opposition with Jordan Klepper'', a late-night television series on Comedy ...
*Cosmobiology
Historically, the term 'Kosmobiologie' was used by the Germans, German medical astrologer Friedrich Feerhow and Swiss statistician Karl Krafft in a more general sense "to designate that branch of astrology working on scientific foundations and key ...
*Hamburg School of Astrology
The German Hamburg School of Astrology (root school of the international Uranian Astrology offshoot) is a school of astrology based on the teachings of surveyor, astrologer and amateur astronomer Alfred Witte. It is characterized by use of astr ...
*Quadrature (astronomy)
In spherical astronomy, quadrature is the configuration of a celestial object in which its elongation is a right angle (90 degrees), i.e., the direction of the object as viewed from Earth is perpendicular to the position of the Sun relative to ...
References
External links
''The Classical Origin & Traditional Use of Aspects''
Deborah Houlding
Online Ephemeris from Khaldea.com
Ćö600BC to 2400ADŌĆöCalculated for
Midnight
Midnight is the transition time from one day to the next – the moment when the date changes, on the local official clock time for any particular jurisdiction. By clock time, midnight is the opposite of noon, differing from it by 12 hours.
...
GMT; also with an Aspectarian included for years 1900 to 2005
''Harmonices mundi''
("The Harmony of the Worlds") in fulltext facsimile;
Carnegie-Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) is a Private university, private research university in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States. The institution was established in 1900 by Andrew Carnegie as the Carnegie Technical Schools. In 1912, it became t ...
{{Authority control
Technical factors of Western astrology