Spirit (rover) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Spirit'', also known as MER-A (Mars Exploration Rover – A) or MER-2, is a Mars robotic rover, active from 2004 to 2010. ''Spirit'' was operational on Mars for sols or 3.3 Martian years (
NASA. October 5, 2010. JPL continued to attempt to regain contact until May 24, 2011, when NASA announced that efforts to communicate with the unresponsive rover had ended, calling the mission complete. A formal farewell took place at NASA headquarters shortly thereafter.
 The scientific objectives of the Mars Exploration Rover mission were to:
*Search for and characterize a variety of rocks and soils that hold clues to past
The scientific objectives of the Mars Exploration Rover mission were to:
*Search for and characterize a variety of rocks and soils that hold clues to past
 ''Opportunity'' and ''Spirit'' rovers were part of the
''Opportunity'' and ''Spirit'' rovers were part of the
 The MER-A (''Spirit'') and MER-B (''Opportunity'') were launched on June 10, 2003 and July 7, 2003, respectively. Though both probes launched on
The MER-A (''Spirit'') and MER-B (''Opportunity'') were launched on June 10, 2003 and July 7, 2003, respectively. Though both probes launched on
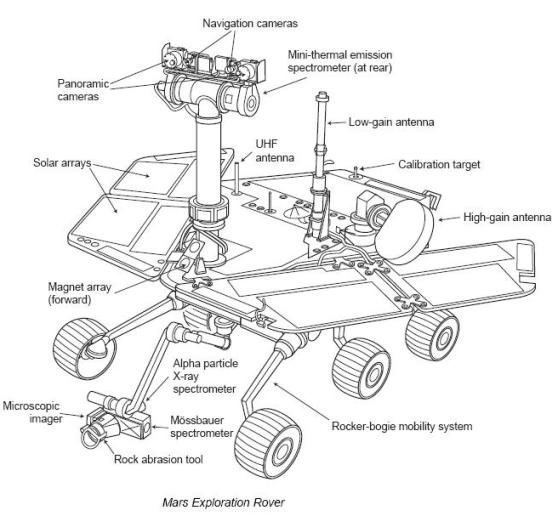
 ''Spirit'' (and its twin, '' Opportunity'') are six-wheeled,
''Spirit'' (and its twin, '' Opportunity'') are six-wheeled,
Pancam Projects: Spirit Night-time Imaging
Retrieved October 21, 2008 These observations included a " lunar" (or rather phobian)
JPL's Mars Exploration Rover Mission home page
(obsolete JPL Mars Exploration Rover home page)
Planetary Photojournal
NASA JPL's Planetary Photojournal for ''Spirit''
for MER News Briefings at JPL
* Wikisource:NASA MER press briefings
MER Analyst's Notebook
Interactive access to mission data and documentation
Status Page last updated May 2004
Cornell's rover site: Athena
last update 2006
(not working as of June 4, 2008) * ttp://www.google.com/mars/#lat=-14.569960&lon=175.469512&zoom=12&map=infrared&q=spacecraft Google map with ''Spirit'' landing site marked
''New Scientist'' on ''Spirit'' Dust Devils
, March 15, 2005
April 3, 2006
Unmanned Spaceflight.com discussion on ''Spirit''
as of 2008-06-04 last updated 2008-06-04
High-resolution video
by Seán Doran that zooms in on ''Spirit''s final location
Archive
of MER progress reports by A.J.S. Rayl at planetary.org {{DEFAULTSORT:Spirit Rover 2003 robots 2004 on Mars Aeolis quadrangle Derelict landers (spacecraft) * Mars robots Mars rovers Missions to Mars Robots of the United States Six-wheeled robots Soft landings on Mars Solar-powered robots Space probes launched in 2003 Spacecraft decommissioned in 2011 Spacecraft launched by Delta II rockets
days
A day is the time period of a full rotation of the Earth with respect to the Sun. On average, this is 24 hours (86,400 seconds). As a day passes at a given location it experiences morning, afternoon, evening, and night. This daily cyc ...
; '). It was one of two rovers of NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
's Mars Exploration Rover
NASA's Mars Exploration Rover (MER) mission was a robotic space mission involving two Mars rovers, ''Spirit (rover), Spirit'' and ''Opportunity (rover), Opportunity'', exploring the planet Mars. It began in 2003 with the launch of the two rove ...
Mission managed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) is a Federally funded research and development centers, federally funded research and development center (FFRDC) in La Cañada Flintridge, California, Crescenta Valley, United States. Founded in 1936 by Cali ...
(JPL). Spirit landed successfully within the impact crater Gusev on Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmosph ...
at 04:35 Ground UTC
Spacecraft Event Time (SCET) is the spacecraft-local time for events that happen at the spacecraft. SCET is used for command programs that control the timing of spacecraft operations and to identify when specific events occur on the spacecraft rel ...
on January 4, 2004, three weeks before its twin, '' Opportunity'' (MER-B), which landed on the other side of the planet. Its name was chosen through a NASA-sponsored student essay competition. The rover got stuck in a "sand trap" in late 2009 at an angle that hampered recharging of its batteries; its last communication with Earth was on March 22, 2010.
The rover completed its planned 90- sol mission (slightly less than 92.5 Earth days). Aided by cleaning event
__NOTOC__
A cleaning event is a phenomenon whereby dust is removed from solar panels, in the context of exploration and science rovers on Mars, supposedly by the action of wind. The term is used on several NASA webpages; generally supposing th ...
s that resulted in more energy from its solar panels, ''Spirit'' went on to function effectively over twenty times longer than NASA planners expected. ''Spirit'' also logged of driving instead of the planned , allowing more extensive geological analysis of Martian rocks and planetary surface features. Initial scientific results from the first phase of the mission (the 90-sol prime mission) were published in a special issue of the journal ''Science''.
On May 1, 2009 (5 years, 3 months, 27 Earth days after landing; 21 times the planned mission duration), ''Spirit'' became stuck in soft sand. This was not the first of the mission's "embedding events" and for the following eight months NASA carefully analyzed the situation, running Earth-based theoretical and practical simulations, and finally programming the rover to make extrication
Vehicle extrication is the process of removing a patient from a vehicle which has been involved in a motor vehicle collision. Patients who have not already exited a crashed vehicle may be medically (cannot exit a vehicle due to their injuries) or ...
drives in an attempt to free itself. These efforts continued until January 26, 2010, when NASA officials announced that the rover was likely irrecoverably obstructed by its location in soft sand,
though it continued to perform scientific research from its current location.
The rover continued in a stationary science platform role until communication with ''Spirit'' stopped on March 22, 2010 (sol ).September 30 – October 5, 2010 Spirit Remains Silent at TroyNASA. October 5, 2010. JPL continued to attempt to regain contact until May 24, 2011, when NASA announced that efforts to communicate with the unresponsive rover had ended, calling the mission complete. A formal farewell took place at NASA headquarters shortly thereafter.
Objectives
 The scientific objectives of the Mars Exploration Rover mission were to:
*Search for and characterize a variety of rocks and soils that hold clues to past
The scientific objectives of the Mars Exploration Rover mission were to:
*Search for and characterize a variety of rocks and soils that hold clues to past water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...
activity. In particular, samples sought include those that have minerals deposited by water-related processes such as precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls from clouds due to gravitational pull. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, rain and snow mixed ("sleet" in Commonwe ...
, evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the Interface (chemistry), surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. A high concentration of the evaporating substance in the surrounding gas significantly slows down evapora ...
, sedimentary cementation, or hydrothermal activity.
*Determine the distribution and composition of minerals, rocks, and soils surrounding the landing sites.
*Determine what geologic processes have shaped the local terrain and influenced the chemistry. Such processes could include water or wind erosion, sedimentation, hydrothermal mechanisms, volcanism, and cratering.
*Perform calibration and validation of surface observations made by Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) instruments. This will help determine the accuracy and effectiveness of various instruments that survey Martian geology from orbit.
*Search for iron-containing minerals, and to identify and quantify relative amounts of specific mineral types that contain water or were formed in water, such as iron-bearing carbonates.
*Characterize the mineralogy
Mineralogy is a subject of geology specializing in the scientific study of the chemistry, crystal structure, and physical (including optical mineralogy, optical) properties of minerals and mineralized artifact (archaeology), artifacts. Specific s ...
and textures of rocks and soils to determine the processes that created them.
*Search for geological clues to the environmental conditions that existed when liquid water was present.
*Assess whether those environments were conducive to life.
Mission timeline
 ''Opportunity'' and ''Spirit'' rovers were part of the
''Opportunity'' and ''Spirit'' rovers were part of the Mars Exploration Rover
NASA's Mars Exploration Rover (MER) mission was a robotic space mission involving two Mars rovers, ''Spirit (rover), Spirit'' and ''Opportunity (rover), Opportunity'', exploring the planet Mars. It began in 2003 with the launch of the two rove ...
program in the long-term Mars Exploration Program
Mars Exploration Program (MEP) is a long-term effort Exploration of Mars, to explore the planet Mars, funded and led by NASA. Formed in 1993, MEP has made use of orbital spacecraft, lander (spacecraft), landers, and Mars rovers to explore the p ...
. The Mars Exploration Program's four principal goals were to determine if the potential for life exists on Mars (in particular, whether recoverable water may be found on Mars), to characterize the Mars climate and its geology, and then to prepare for a potential human mission to Mars. The Mars Exploration Rovers were to travel across the Martian surface and perform periodic geologic analyses to determine if water ever existed on Mars as well as the types of minerals available, as well as to corroborate data taken by the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). Both rovers were designed with an expected 90 sols (92 Earth days) lifetime, but each lasted much longer than expected. ''Spirit'' mission lasted 20 times longer than its expected lifetime, and its mission was declared ended on May 25, 2011, after it got stuck in soft sand and expended its power reserves trying to free itself. ''Opportunity'' lasted 55 times longer than its 90 sol planned lifetime, operating for days from landing to mission end. An archive of weekly updates on the rover's status can be found at the ''Opportunity'' Update Archive.
Launch and landing
 The MER-A (''Spirit'') and MER-B (''Opportunity'') were launched on June 10, 2003 and July 7, 2003, respectively. Though both probes launched on
The MER-A (''Spirit'') and MER-B (''Opportunity'') were launched on June 10, 2003 and July 7, 2003, respectively. Though both probes launched on Boeing
The Boeing Company, or simply Boeing (), is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and product support s ...
Delta II
Delta II was an expendable launch system, originally designed and built by McDonnell Douglas, and sometimes known as the Thorad Delta 1. Delta II was part of the Delta rocket family, derived directly from the Delta 3000, and entered service in ...
7925-9.5 rockets from Cape Canaveral Space Launch Complex 17 (CCAFS SLC-17), MER-B was on the heavy version of that launch vehicle, needing the extra energy for Trans-Mars injection. The launch vehicles were integrated onto pads right next to each other, with MER-A on CCAFS SLC-17A and MER-B on CCAFS SLC-17B. The dual pads allowed for working the 15- and 21-day planetary launch periods close together; the last possible launch day for MER-A was June 19, 2003 and the first day for MER-B was June 25, 2003. NASA's Launch Services Program managed the launch of both spacecraft.
''Spirit'' successfully landed on the surface of Mars on 04:35 Spacecraft Event Time (SCET) on January 4, 2004. This was the start of its 90-sol mission, but solar cell cleaning events would mean it was the start of a much longer mission, lasting until 2010. ''Spirit'' was targeted to a site that appears to have been affected by liquid water in the past, the crater Gusev, a possible former lake in a giant impact crater
An impact crater is a depression (geology), depression in the surface of a solid astronomical body formed by the hypervelocity impact event, impact of a smaller object. In contrast to volcanic craters, which result from explosion or internal c ...
about from the center of the target ellipse at . After the airbag-protected landing craft settled onto the surface, the rover rolled out to take panoramic images. These give scientists the information they need to select promising geological targets and drive to those locations to perform on-site scientific investigations. The MER team named the landing site "''Columbia'' Memorial Station," in honor of the seven astronauts
An astronaut (from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'star', and (), meaning 'sailor') is a person trained, equipped, and deployed by a List of human spaceflight programs, human spaceflight program to serve as a commander or crew member of a spa ...
killed in the Space Shuttle ''Columbia'' disaster.
On May 1, 2009 (sol ), the rover became stuck in soft sand, the machine resting upon a cache of iron(III) sulfate
Iron(III) sulfate or ferric sulfate (British English: sulphate instead of sulfate) is a family of inorganic compounds with the formula Fe2(SO4)3(H2O)n. A variety of hydrates are known, including the most commonly encountered form of "ferric sulf ...
( jarosite) hidden under a veneer of normal-looking soil. Iron sulfate has very little cohesion, making it difficult for the rover's wheels to gain traction.
On January 26, 2010 (sol ), after several months attempting to free the rover, NASA abandoned this attempt and instead changed the mission to use the mobile robot as a stationary research platform. Efforts were directed towards orienting it toward the Sun to recharge its batteries, to keep systems operational during the winter. On March 30, 2010, Spirit skipped a planned communication session and as anticipated from recent power-supply projections, had probably entered a low-power hibernation mode.
The last communication with the rover was March 22, 2010 (sol ) and there is a strong possibility the rover's batteries lost so much energy that the mission clock stopped. In previous winters the rover was able to park on a Sun-facing slope and keep its internal temperature above , but since the rover was stuck on flat ground it is estimated that its internal temperature dropped to . If ''Spirit'' had survived these conditions and there had been a cleaning event, there was a possibility that with the southern summer solstice in March 2011, solar energy would increase to a level that would wake up the rover. ''Spirit'' remains silent at its location, called "Troy," on the west side of Home Plate.
It is likely that ''Spirit'' experienced a low-power fault and had turned off all sub-systems, including communication, and gone into a deep sleep, trying to recharge its batteries. It is also possible that the rover had experienced a mission clock fault. If that had happened, the rover would have lost track of time and tried to remain asleep until enough sunlight struck the solar arrays to wake it. This state is called "Solar Groovy." If the rover woke up from a mission clock fault, it would only listen. Starting on July 26, 2010 (sol ), a new procedure to address the possible mission clock fault was implemented but was unsuccessful.
End of mission
JPL continued attempts to regain contact with ''Spirit'' until May 25, 2011, when NASA announced the end of contact efforts and the completion of the mission. According to NASA, the rover likely experienced excessively cold "internal temperatures" due to "inadequate energy to run its survival heaters" that, in turn, was a result of "a stressful Martian winter without much sunlight." Many critical components and connections would have been "susceptible to damage from the cold." Assets that had been needed to support ''Spirit'' were transitioned to support ''Spirit's'' then still-active twin, ''Opportunity''. The primary surface mission for ''Spirit'' was planned to last at least 90 sols. The mission received several extensions and lasted about 2,208 sols. On August 11, 2007, ''Spirit'' obtained the second longest operational duration on the surface of Mars for a lander or rover at 1282 Sols, one sol longer than the Viking 2 lander. Viking 2 was powered by a nuclear cell whereas ''Spirit'' is powered by solar arrays. Until ''Opportunity'' overtook it on May 19, 2010, the Mars probe with longest operational period was Viking 1 that lasted for 2245 Sols on the surface of Mars. On March 22, 2010, ''Spirit'' sent its last communication, thus falling just over a month short of surpassing Viking 1's operational record. An archive of weekly updates on the rover's status can be found at the ''Spirit'' Update Archive. ''Spirit's'' total odometry is .Design and construction

solar-powered
Solar power, also known as solar electricity, is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV) or indirectly using concentrated solar power. Solar panels use the photovoltaic effect to conve ...
robots standing high, wide and long and weighing . Six wheels on a rocker-bogie system enabled mobility over rough terrain. Each wheel had its own motor. The vehicle was steered at front and rear and was designed to operate safely at tilts of up to 30 degrees. The maximum speed was ; , although the average speed was about . Both ''Spirit'' and ''Opportunity'' have pieces of the fallen World Trade Center's metal on them that were "turned into shields to protect cables on the drilling mechanisms".
Solar arrays generated about 140 watts for up to fourteen hours per sol, while rechargeable lithium ion batteries stored energy for use at night. ''Spirit''s onboard computer uses a 20 MHz RAD6000 CPU with 128 MB of DRAM and 3 MB of EEPROM. The rover's operating temperature
An operating temperature is the allowable temperature range of the local ambient environment at which an electrical or mechanical device operates. The device will operate effectively within a specified temperature range which varies based on the de ...
ranges from and radioisotope heaters provide a base level of heating, assisted by electrical heaters when necessary.
Communications depended on an omnidirectional low-gain antenna communicating at a low data rate and a steerable high-gain antenna, both in direct contact with Earth. A low-gain antenna was also used to relay data to spacecraft orbiting Mars.
Science payload
The science instruments included: * Panoramic Camera (Pancam) – examined the texture, color, mineralogy, and structure of the local terrain. * Navigation Camera (Navcam) – monochrome with a higher field of view but lower resolution, for navigation and driving. * Miniature Thermal Emission Spectrometer (Mini-TES) – identified promising rocks and soils for closer examination, and determined the processes that formed them. * Hazcams, two B&W cameras with 120 degree field of view, that provided additional data about the rover's surroundings. The rover arm held the following instruments: * Mössbauer spectrometer (MB) MIMOS II – used for close-up investigations of the mineralogy of iron-bearing rocks and soils. *Alpha particle X-ray spectrometer
:''APXS is also an abbreviation for APache eXtenSion tool, an extension for Apache web servers.''
An alpha particle X-ray spectrometer (APXS) is a spectrometer that analyses the chemical element composition of a sample from scattered alpha parti ...
(APXS) – close-up analysis of the abundances of elements that make up rocks and soils.
* Magnets – for collecting magnetic dust particles.
* Microscopic Imager (MI) – obtained close-up, high-resolution images of rocks and soils.
* Rock Abrasion Tool
The Rock Abrasion Tool (RAT) is a grinding and brushing installation on NASA’s twin Mars Exploration Rovers, '' Spirit'' (MER-A) and '' Opportunity'' (MER-B), which landed on Mars in January 2004. It was designed, developed and continues to be o ...
(RAT) – exposed fresh material for examination by instruments on board.
''Spirit'' was 'driven' by several operators throughout its mission.
Power
The rover uses a combination of solar cells and a rechargeable chemical battery. This class of rover has two rechargeable lithium batteries, each composed of 8 cells with 8 amp-hour capacity. At the start of the mission the solar panels could provide up to around 900 watt-hours (Wh) per day to recharge the battery and power system in one Sol, but this could vary due to a variety of factors. In Eagle crater the cells were producing about 840 Wh per day, but by Sol 319 in December 2004, it had dropped to 730 Wh per day. Like Earth, Mars has seasonal variations that reduce sunlight during winter. However, since the Martian year is longer than that of the Earth, the seasons fully rotate roughly once every 2 Earth years. By 2016, MER-B had endured seven Martian winters, during which times power levels drop which can mean the rover avoids doing activities that use a lot of power. During its first winter power levels dropped to under 300 Wh per day for two months, but some later winters were not as bad. Another factor that can reduce received power is dust in the atmosphere, especially dust storms. Dust storms have occurred quite frequently when Mars is closest to the Sun. Global dust storms in 2007 reduced power levels for ''Opportunity'' and ''Spirit'' so much they could only run for a few minutes each day. Due to the 2018 dust storms on Mars, ''Opportunity'' entered hibernation mode on June 12, but it remained silent after the storm subsided in early October.Discoveries
The rocks on the plains of Gusev are a type ofbasalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial ...
. They contain the minerals olivine
The mineral olivine () is a magnesium iron Silicate minerals, silicate with the chemical formula . It is a type of Nesosilicates, nesosilicate or orthosilicate. The primary component of the Earth's upper mantle (Earth), upper mantle, it is a com ...
, pyroxene
The pyroxenes (commonly abbreviated Px) are a group of important rock-forming inosilicate minerals found in many igneous and metamorphic rocks. Pyroxenes have the general formula , where X represents ions of calcium (Ca), sodium (Na), iron ( ...
, plagioclase
Plagioclase ( ) is a series of Silicate minerals#Tectosilicates, tectosilicate (framework silicate) minerals within the feldspar group. Rather than referring to a particular mineral with a specific chemical composition, plagioclase is a continu ...
and magnetite. They look like volcanic basalt, as they are fine-grained with irregular holes (geologists would say they have vesicles and vugs).
Much of the soil on the plains came from the breakdown of the local rocks. Fairly high levels of nickel were found in some soils; probably from meteorites
A meteorite is a rock that originated in outer space and has fallen to the surface of a planet or moon. When the original object enters the atmosphere, various factors such as friction, pressure, and chemical interactions with the atmospheri ...
.
Analysis shows that the rocks have been slightly altered by tiny amounts of water. Outside coatings and cracks inside the rocks suggest water deposited minerals, maybe bromine
Bromine is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a similarly coloured vapour. Its properties are intermediate between th ...
compounds. All the rocks contain a fine coating of dust and one or more harder rinds of material. One type can be brushed off, while another needed to be ground off by the Rock Abrasion Tool
The Rock Abrasion Tool (RAT) is a grinding and brushing installation on NASA’s twin Mars Exploration Rovers, '' Spirit'' (MER-A) and '' Opportunity'' (MER-B), which landed on Mars in January 2004. It was designed, developed and continues to be o ...
(RAT).
The dust in Gusev Crater is the same as dust all around the planet. All the dust was found to be magnetic. Moreover, ''Spirit'' found the magnetism
Magnetism is the class of physical attributes that occur through a magnetic field, which allows objects to attract or repel each other. Because both electric currents and magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, ...
was caused by the mineral magnetite
Magnetite is a mineral and one of the main iron ores, with the chemical formula . It is one of the iron oxide, oxides of iron, and is ferrimagnetism, ferrimagnetic; it is attracted to a magnet and can be magnetization, magnetized to become a ...
, especially magnetite that contained the element titanium
Titanium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in ...
. One magnet was able to completely divert all dust, hence all Martian dust is thought to be magnetic. The spectra of the dust was similar to spectra of bright, low thermal inertia regions like Tharsis and Arabia that have been detected by orbiting satellites. A thin layer of dust, maybe less than one millimeter thick, covers all surfaces. Something in it contains a small amount of chemically bound water.Bell, J (ed.) The Martian Surface. 2008. Cambridge University Press.
Astronomy
''Spirit'' pointed its cameras towards the sky and observed atransit
Transit may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film
* ''Transit'' (1980 film), a 1980 Israeli film
* ''Transit'' (1986 film), a Canadian short film
* ''Transit'' (2005 film), a film produced by MTV and Staying-Alive about four people in countrie ...
of the Sun
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light a ...
by Mars' moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar ...
Deimos (see Transit of Deimos from Mars
Transit may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film
* ''Transit'' (1980 film), a 1980 Israeli film
* ''Transit'' (1986 film), a Canadian short film
* ''Transit'' (2005 film), a film produced by MTV and Staying-Alive about four people in countrie ...
). It also took the first photo of Earth from the surface of another planet in early March 2004.
In late 2005, ''Spirit'' took advantage of a favorable energy situation to make multiple nighttime observations of both of Mars' moons Phobos and Deimos.Jim Bell (Cornell University) et alPancam Projects: Spirit Night-time Imaging
Retrieved October 21, 2008 These observations included a " lunar" (or rather phobian)
eclipse
An eclipse is an astronomical event which occurs when an astronomical object or spacecraft is temporarily obscured, by passing into the shadow of another body or by having another body pass between it and the viewer. This alignment of three ...
as ''Spirit'' watched Phobos disappear into Mars' shadow. Some of ''Spirits star gazing was designed to look for a predicted meteor shower
A meteor shower is a celestial event in which a number of meteors are observed to radiate, or originate, from one point in the night sky. These meteors are caused by streams of cosmic debris called meteoroids entering Earth's atmosphere at ext ...
caused by Halley's Comet
Halley's Comet is the only known List of periodic comets, short-period comet that is consistently visible to the naked eye from Earth, appearing every 72–80 years, though with the majority of recorded apparitions (25 of 30) occurring after ...
, and although at least four imaged streaks were suspect meteors, they could not be unambiguously differentiated from those caused by cosmic rays.
A transit of Mercury from Mars took place on January 12, 2005, from about 14:45 UTC to 23:05 UTC. Theoretically, this could have been observed by both ''Spirit'' and '' Opportunity''; however, camera resolution did not permit seeing Mercury's 6.1" angular diameter. They were able to observe transits of Deimos across the Sun, but at 2' angular diameter, Deimos is about 20 times larger than Mercury's 6.1" angular diameter. Ephemeris data generated by JPL Horizons indicates that ''Opportunity'' would have been able to observe the transit from the start until local sunset at about 19:23 UTC Earth time, while ''Spirit'' would have been able to observe it from local sunrise at about 19:38 UTC until the end of the transit.
Equipment wear and failures
Both rovers passed their original mission time of 90 sols many times over. The extended time on the surface, and therefore additional stress on components, resulted in some issues developing. On March 13, 2006 (sol ), the right front wheel ceased working after having covered on Mars. Engineers began driving the rover backwards, dragging the dead wheel. Although this resulted in changes to driving techniques, the dragging effect became a useful tool, partially clearing away soil on the surface as the rover traveled, thus allowing areas to be imaged that would normally be inaccessible. However, in mid-December 2009, to the surprise of the engineers, the right front wheel showed slight movement in a wheel-test on sol 2113 and clearly rotated with normal resistance on three of four wheel-tests on sol 2117, but stalled on the fourth. On November 29, 2009 (sol ), the right rear wheel also stalled and remained inoperable for the remainder of the mission. Scientific instruments also experienced degradation as a result of exposure to the harsh Martian environment and use over a far longer period than had been anticipated by the mission planners. Over time, the diamond in the resin grinding surface of theRock Abrasion Tool
The Rock Abrasion Tool (RAT) is a grinding and brushing installation on NASA’s twin Mars Exploration Rovers, '' Spirit'' (MER-A) and '' Opportunity'' (MER-B), which landed on Mars in January 2004. It was designed, developed and continues to be o ...
wore down, after that the device could only be used to brush targets. All of the other science instruments and engineering cameras continued to function until contact was lost; however, towards the end of ''Spirits life, the MIMOS II Mössbauer spectrometer took much longer to produce results than it did earlier in the mission because of the decay of its cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. ...
-57 gamma ray source that has a half life of 271 days.
Legacy and honors
To commemorate ''Spirits great contribution to theexploration of Mars
The planet Mars has been explored remotely by spacecraft. Uncrewed spacecraft, Probes sent from Earth, beginning in the late 20th century, have yielded a large increase in knowledge about the Martian system, focused primarily on understanding G ...
, the asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet—an object larger than a meteoroid that is neither a planet nor an identified comet—that orbits within the Solar System#Inner Solar System, inner Solar System or is co-orbital with Jupiter (Trojan asteroids). As ...
37452 Spirit has been named after it. The name was proposed by Ingrid van Houten-Groeneveld
Ingrid van Houten-Groeneveld (; ; 21 October 1921 – 30 March 2015) was a Dutch astronomer.
Background
In a jointly credited trio with Tom Gehrels and her husband Cornelis Johannes van Houten, she was the discoverer of many thousands of as ...
who along with Cornelis Johannes van Houten
Cornelis Johannes "Kees" van Houten (18 February 1920 – 24 August 2002) was a Dutch people, Dutch astronomer.
Early life and education
Born in The Hague, he spent his entire career at Leiden University except for a brief period (1954–1956) as ...
and Tom Gehrels discovered the asteroid on September 24, 1960.
To honor the rover, the JPL team named an area near Endeavour Crater
Endeavour is an impact crater located in the Meridiani Planum extraterrestrial plain within the Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle (MC-19) region of the planet Mars. Endeavour is about in diameter. Using ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' data, phy ...
explored by the ''Opportunity'' rover, 'Spirit Point'.
The 2022 documentary film, '' Good Night Oppy'', about ''Opportunity'', ''Spirit'', and their long missions, was directed by Ryan White
Ryan Wayne White (December 6, 1971 – April 8, 1990) was an American teenager from Kokomo, Indiana, who became a national poster child for HIV/AIDS in the United States after his school barred him from attending classes following a diagn ...
, and included support from JPL and Industrial Light & Magic
Industrial Light & Magic (ILM) is an American Film, motion picture visual effects, computer animation and stereo conversion digital studio founded by George Lucas on May 26, 1975. It is a division of the film production company Lucasfilm, which Lu ...
.
Gallery
The rover could take pictures with its different cameras, but only the PanCam camera had the ability to photograph a scene with different color filters. The panorama views were usually built up from PanCam images. ''Spirit'' transferred 128,224 pictures in its lifetime.See also
References
External links
JPL, MSSS, and NASA links
JPL's Mars Exploration Rover Mission home page
(obsolete JPL Mars Exploration Rover home page)
Planetary Photojournal
NASA JPL's Planetary Photojournal for ''Spirit''
for MER News Briefings at JPL
* Wikisource:NASA MER press briefings
MER Analyst's Notebook
Interactive access to mission data and documentation
Other links
Status Page last updated May 2004
Cornell's rover site: Athena
last update 2006
(not working as of June 4, 2008) * ttp://www.google.com/mars/#lat=-14.569960&lon=175.469512&zoom=12&map=infrared&q=spacecraft Google map with ''Spirit'' landing site marked
''New Scientist'' on ''Spirit'' Dust Devils
, March 15, 2005
April 3, 2006
Unmanned Spaceflight.com discussion on ''Spirit''
as of 2008-06-04 last updated 2008-06-04
High-resolution video
by Seán Doran that zooms in on ''Spirit''s final location
Archive
of MER progress reports by A.J.S. Rayl at planetary.org {{DEFAULTSORT:Spirit Rover 2003 robots 2004 on Mars Aeolis quadrangle Derelict landers (spacecraft) * Mars robots Mars rovers Missions to Mars Robots of the United States Six-wheeled robots Soft landings on Mars Solar-powered robots Space probes launched in 2003 Spacecraft decommissioned in 2011 Spacecraft launched by Delta II rockets