Sphenoidal Sinuses on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The sphenoid sinus is a paired
 On average, a sphenoid sinus measures 2.2 cm vertical height, 2 cm in transverse breadth; and 2.2 cm antero-posterior depth.
Each spehoid sinus is in the
On average, a sphenoid sinus measures 2.2 cm vertical height, 2 cm in transverse breadth; and 2.2 cm antero-posterior depth.
Each spehoid sinus is in the
paranasal sinus
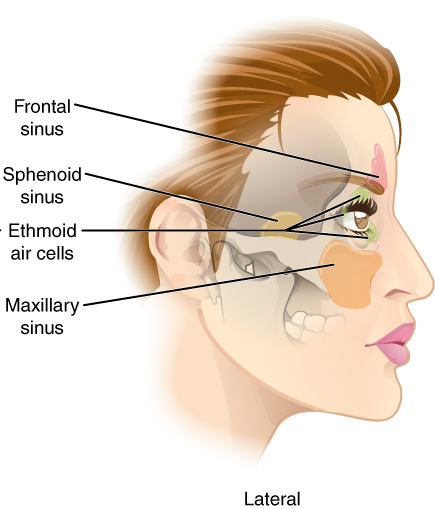
Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired skeletal pneumaticity, air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity. The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes; the frontal sinuses are above the eyes; the Ethmoid sinus, ethmoidal sinuses a ...
in the body
Body may refer to:
In science
* Physical body, an object in physics that represents a large amount, has mass or takes up space
* Body (biology), the physical material of an organism
* Body plan, the physical features shared by a group of anim ...
of the sphenoid bone
The sphenoid bone is an unpaired bone of the neurocranium. It is situated in the middle of the skull towards the front, in front of the basilar part of occipital bone, basilar part of the occipital bone. The sphenoid bone is one of the seven bon ...
. It is one pair of the four paired paranasal sinuses.Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, page 64 The two sphenoid sinuses are separated from each other by a septum. Each sphenoid sinus communicates with the nasal cavity
The nasal cavity is a large, air-filled space above and behind the nose in the middle of the face. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. The nas ...
via the opening of sphenoidal sinus. The two sphenoid sinuses vary in size and shape, and are usually asymmetrical.
Structure
 On average, a sphenoid sinus measures 2.2 cm vertical height, 2 cm in transverse breadth; and 2.2 cm antero-posterior depth.
Each spehoid sinus is in the
On average, a sphenoid sinus measures 2.2 cm vertical height, 2 cm in transverse breadth; and 2.2 cm antero-posterior depth.
Each spehoid sinus is in the body of sphenoid bone
The body of the sphenoid bone, more or less cubical in shape, is hollowed out in its interior to form two large cavities, the sphenoidal sinuses, which are separated from each other by a septum.
Superior surface
The superior surface of the body ...
, just under the sella turcica
The sella turcica (Latin for 'Turkish saddle') is a saddle-shaped depression in the body of the sphenoid bone of the human skull and of the skulls of other hominids including chimpanzees, gorillas and orangutans. It serves as a cephalometric la ...
. The sphenoid sinuses are separated from each other medially by the septum of sphenoidal sinuses, which is usually asymmetrical.
An opening of sphenoidal sinus forms a passage between each sphenoidal sinus and the nasal cavity. Posteriorly, an opening of sphenoidal sinus opens into the sphenoidal sinus by an aperture high on the anterior wall the sinus; anteriorly, an opening of sphenoidal sinus opens into the roof of the nasal cavity via an aperture on the posterior wall of the sphenoethmoidal recess
The sphenoethmoidal recess is a small triangular space superior to the superior nasal meatus of the nasal cavity into which the sphenoidal sinus opens. The sphenoethmoidal recess is situated supero posterior to the superior nasal concha
The supe ...
, just over the choana
The choanae (: choana), posterior nasal apertures or internal nostrils are two openings found at the back of the nasal passage between the nasal cavity and the pharynx, in humans and other mammals (as well as crocodilians and most skinks). They ...
.Human Anatomy, Jacob, Elsevier, 2008, page 211
Innervation
The mucous membrane receives sensory innervation from theposterior ethmoidal nerve
The posterior ethmoidal nerve is a nerve of the head. It is a branch of the nasociliary nerve (itself a branch of the Ophthalmic nerve, ophthalmic nerve (CN V1)). It provides sensory innervation to the sphenoid sinus and ethmoid sinus, and part o ...
(branch of the ophthalmic nerve (CN V1)) and from branches of the maxillary nerve (CN V2).
Postganglionic
In the autonomic nervous system, nerve fibers from the ganglion to the wikt:effector, effector organ are called postganglionic nerve fibers.
Neurotransmitters
The neurotransmitters of postganglionic fibers differ:
* In the parasympathetic div ...
parasympathetic
The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the sympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system.
The autonomic nervous system is responsible for regulat ...
fibers of the facial nerve
The facial nerve, also known as the seventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve VII, or simply CN VII, is a cranial nerve that emerges from the pons of the brainstem, controls the muscles of facial expression, and functions in the conveyance of ta ...
that synapse
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that allows a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or a target effector cell. Synapses can be classified as either chemical or electrical, depending o ...
d at the pterygopalatine ganglion
The pterygopalatine ganglion (aka Meckel's ganglion, nasal ganglion, or sphenopalatine ganglion) is a parasympathetic ganglion in the pterygopalatine fossa. It is one of four parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck, (the others being the s ...
control mucus
Mucus (, ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both Serous fluid, serous and muc ...
secretion
Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical mec ...
.
Anatomical relations
Nearby structures include theoptic canal
The ''optic foramen'' is the opening to the optic canal. The canal is located in the sphenoid bone; it is bounded medially by the body of the sphenoid and laterally by the lesser wing of the sphenoid.
The superior surface of the sphenoid bone is ...
, the optic nerve
In neuroanatomy, the optic nerve, also known as the second cranial nerve, cranial nerve II, or simply CN II, is a paired cranial nerve that transmits visual system, visual information from the retina to the brain. In humans, the optic nerve i ...
, the internal carotid artery
The internal carotid artery is an artery in the neck which supplies the anterior cerebral artery, anterior and middle cerebral artery, middle cerebral circulation.
In human anatomy, the internal and external carotid artery, external carotid ari ...
, the cavernous sinus
The cavernous sinus within the human head is one of the dural venous sinuses creating a cavity called the lateral sellar compartment bordered by the temporal bone of the skull and the sphenoid bone, lateral to the sella turcica.
Structure
The ...
, the trigeminal nerve
In neuroanatomy, the trigeminal nerve (literal translation, lit. ''triplet'' nerve), also known as the fifth cranial nerve, cranial nerve V, or simply CN V, is a cranial nerve responsible for Sense, sensation in the face and motor functions ...
, the pituitary gland
The pituitary gland or hypophysis is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, the pituitary gland is located at the base of the human brain, brain, protruding off the bottom of the hypothalamus. The pituitary gland and the hypothalamus contr ...
, and the anterior ethmoidal cells
The ethmoid sinuses or ethmoid air cells of the ethmoid bone are one of the four paired paranasal sinuses. Unlike the other three pairs of paranasal sinuses which consist of one or two large cavities, the ethmoidal sinuses entail a number of smal ...
. One study found that carotid canal
The carotid canal is a passage in the petrous part of the temporal bone of the skull through which the internal carotid artery and its internal carotid (nervous) plexus pass from the neck into (the middle cranial fossa of) the cranial cavity.
...
protrudation into the sphenoid sinus wall was present in 23.9–32.1% of males and 35.5–36.2% of females, dehiscence in carotid canal was detected more in females (34%) than in males (22%), optic canal
The ''optic foramen'' is the opening to the optic canal. The canal is located in the sphenoid bone; it is bounded medially by the body of the sphenoid and laterally by the lesser wing of the sphenoid.
The superior surface of the sphenoid bone is ...
protrudation was 33.3 and 30.5% in males and females, and optic canal dehiscence was detected in 11.3% of males and 9.9% of females.
Anatomical variation
The sphenoid sinuses vary in size and shape; because of the lateral displacement of the interveningseptum
In biology, a septum (Latin language, Latin for ''something that encloses''; septa) is a wall, dividing a Body cavity, cavity or structure into smaller ones. A cavity or structure divided in this way may be referred to as septate.
Examples
Hum ...
of sphenoid sinuses, the pair rarely is symmetrical.
When exceptionally large, the sphenoid sinuses may extend into the roots of the pterygoid processes
The pterygoid processes of the sphenoid (from Greek ''pteryx'', ''pterygos'', "wing"), one on either side, descend perpendicularly from the regions where the body and the greater wings of the sphenoid bone unite.
Each process consists of a me ...
or greater wings of sphenoid bone, and may invade the basilar part of the occipital bone
The occipital bone () is a neurocranium, cranial dermal bone and the main bone of the occiput (back and lower part of the skull). It is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself like a shallow dish. The occipital bone lies over the occipital lob ...
.
The septum of the sphenoidal sinuses may be partly or completely absent. Other septa also may be incomplete.
Development
The sphenoidal sinuses are minute at birth; their main development takes place after puberty.Clinical significance
The sphenoid sinuses cannot be palpated on physical examination. However, patients with isolated sphenoid sinusitis may complain ofoccipital
The occipital bone () is a cranial dermal bone and the main bone of the occiput (back and lower part of the skull). It is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself like a shallow dish. The occipital bone lies over the occipital lobes of the cere ...
or vertex headache, retro-orbital pain, otalgia
Ear pain, also known as earache or otalgia, is pain in the ear. Primary ear pain is pain that originates from the ear. Secondary ear pain is a type of referred pain, meaning that the source of the pain differs from the location where the pain is ...
, drowsiness, or meningitis
Meningitis is acute or chronic inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, collectively called the meninges. The most common symptoms are fever, intense headache, vomiting and neck stiffness and occasion ...
-like symptoms.
A potential complication of sphenoidal sinusitis
Sinusitis, also known as rhinosinusitis, is an inflammation of the mucous membranes that line the sinuses resulting in symptoms that may include production of thick nasal mucus, nasal congestion, facial congestion, facial pain, facial pressure ...
is cavernous sinus thrombosis
Cavernous sinus thrombosis (CST) is the formation of a blood clot within the cavernous sinus, a cavity at the base of the brain which drains deoxygenated blood from the brain back to the heart. This is a rare disorder and can be of two types–sept ...
.
If a fast-growing tumor erodes the floor of the sphenoidal sinus, the vidian nerve
The nerve of the pterygoid canal (Vidian nerve) is formed by the union of the (parasympathetic) greater petrosal nerve and (sympathetic) deep petrosal nerve within the cartilaginous substance filling the foramen lacerum. From the foramen lacerum ...
may be in danger. If the tumor spreads laterally, the cavernous sinus
The cavernous sinus within the human head is one of the dural venous sinuses creating a cavity called the lateral sellar compartment bordered by the temporal bone of the skull and the sphenoid bone, lateral to the sella turcica.
Structure
The ...
and all its constituent nerves may be in danger.
Sphenoidotomy, a form of endonasal surgery, may be done to enlarge the sphenoid sinus, usually in order to drain it.
The sphenoid sinus should be distinguished from an Onodi cell, an anatomic variant that is the rearmost ethmoidal air cell. Onodi cells typically extend back to lie superolateral to the sphenoid sinus and thus near the optic nerve
In neuroanatomy, the optic nerve, also known as the second cranial nerve, cranial nerve II, or simply CN II, is a paired cranial nerve that transmits visual system, visual information from the retina to the brain. In humans, the optic nerve i ...
and internal carotid artery
The internal carotid artery is an artery in the neck which supplies the anterior cerebral artery, anterior and middle cerebral artery, middle cerebral circulation.
In human anatomy, the internal and external carotid artery, external carotid ari ...
. Failure to recognize an Onodi cell on CT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
before surgery may put these structures at risk. One study found that an Onodi cell was present in 26.6% of males and 19.1% of females.
Transsphenoidal surgery
Because only thin shelves of bone separate the sphenoidal sinuses from the nasal cavities, below, and from thehypophyseal fossa
The sella turcica (Latin for 'Turkish saddle') is a saddle-shaped depression in the body of the sphenoid bone of the human skull and of the skulls of other hominids including chimpanzees, gorillas and orangutans. It serves as a cephalometric la ...
, above, the pituitary gland
The pituitary gland or hypophysis is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, the pituitary gland is located at the base of the human brain, brain, protruding off the bottom of the hypothalamus. The pituitary gland and the hypothalamus contr ...
can be reached surgically through the roof of the nasal cavities by passage through the anterioinferior aspect of the sphenoid bone and into the sinuses, followed by entry through the top of the sphenoid bone into the hypophyseal fossa.
References
External links
* * () {{Authority control Bones of the head and neck Rhinology Otorhinolaryngology Sinus surgery