Spearman on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A spear is a
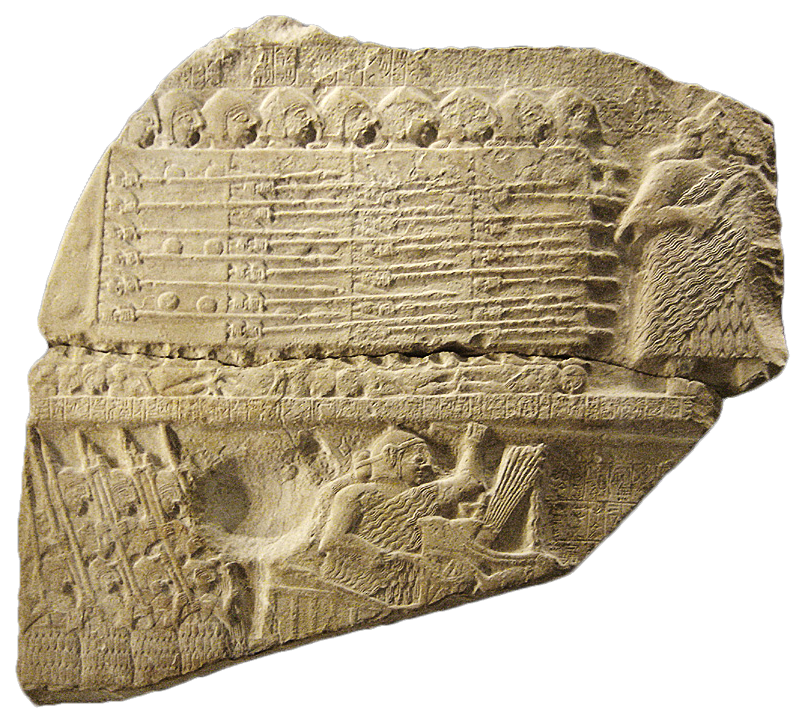

 The spear is the main weapon of the warriors of
The spear is the main weapon of the warriors of
 In the pre-Marian Roman armies, the first two lines of battle, the ''
In the pre-Marian Roman armies, the first two lines of battle, the ''
 The development of both the long, two-handed
The development of both the long, two-handed
polearm
A polearm or pole weapon is a close combat weapon in which the main fighting part of the weapon is fitted to the end of a long shaft, typically of wood, extending the user's effective range and striking power. Polearms are predominantly melee we ...
consisting of a shaft, usually of wood
Wood is a structural tissue/material found as xylem in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulosic fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin t ...
, with a pointed head. The head may be simply the sharpened end of the shaft itself, as is the case with fire hardened spears, or it may be made of a more durable material fastened to the shaft, such as bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
, flint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Historically, flint was widely used to make stone tools and start ...
, obsidian
Obsidian ( ) is a naturally occurring volcanic glass formed when lava extrusive rock, extruded from a volcano cools rapidly with minimal crystal growth. It is an igneous rock. Produced from felsic lava, obsidian is rich in the lighter element ...
, copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
, bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals (such as phosphorus) or metalloid ...
, iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
, or steel
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon that demonstrates improved mechanical properties compared to the pure form of iron. Due to steel's high Young's modulus, elastic modulus, Yield (engineering), yield strength, Fracture, fracture strength a ...
. The most common design for hunting and/or warfare, since modern times has incorporated a metal spearhead shaped like a triangle
A triangle is a polygon with three corners and three sides, one of the basic shapes in geometry. The corners, also called ''vertices'', are zero-dimensional points while the sides connecting them, also called ''edges'', are one-dimension ...
, diamond
Diamond is a Allotropes of carbon, solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Diamond is tasteless, odourless, strong, brittle solid, colourless in pure form, a poor conductor of e ...
, or leaf
A leaf (: leaves) is a principal appendage of the plant stem, stem of a vascular plant, usually borne laterally above ground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", while the leav ...
. The heads of fishing spears usually feature multiple sharp points
A point is a small dot or the sharp tip of something. Point or points may refer to:
Mathematics
* Point (geometry), an entity that has a location in space or on a plane, but has no extent; more generally, an element of some abstract topologica ...
, with or without barbs.
Spears can be divided into two broad categories: those designed for thrusting as a melee weapon (including weapons such as lances
The English term lance is derived, via Middle English ''wikt:launce#Noun 3, launce'' and Old French ''wikt:lance#Old French, lance'', from the Latin ''wikt:lancea#Noun, lancea'', a generic term meaning a spear or javelin employed by both infant ...
and pikes) and those designed for throwing as a ranged weapon (usually referred to as javelin
A javelin is a light spear designed primarily to be thrown, historically as a ranged weapon. Today, the javelin is predominantly used for sporting purposes such as the javelin throw. The javelin is nearly always thrown by hand, unlike the sling ...
s).
The spear has been used throughout human history as a weapon for hunting and/or fishing and for warfare. Along with the club
Club may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Club'' (magazine)
* Club, a ''Yie Ar Kung-Fu'' character
* Clubs (suit), a suit of playing cards
* Club music
* "Club", by Kelsea Ballerini from the album ''kelsea''
Brands and enterprises
* ...
, knife
A knife (: knives; from Old Norse 'knife, dirk') is a tool or weapon with a cutting edge or blade, usually attached to a handle or hilt. One of the earliest tools used by humanity, knives appeared at least Stone Age, 2.5 million years ago, as e ...
, and axe
An axe (; sometimes spelled ax in American English; American and British English spelling differences#Miscellaneous spelling differences, see spelling differences) is an implement that has been used for thousands of years to shape, split, a ...
, it is one of the earliest and most widespread tools ever developed by early humans. As a weapon, it may be wielded with either one or two hands. It was used in virtually every conflict up until the modern era
The modern era or the modern period is considered the current historical period of human history. It was originally applied to the history of Europe and Western history for events that came after the Middle Ages, often from around the year 1500 ...
, where even to this day, it lives on in the form of a bayonet
A bayonet (from Old French , now spelt ) is a -4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ... , now spelt ) is a knife, dagger">knife">-4; we might wonder whethe ...
fixed onto the muzzle of a long gun
A long gun is a category of firearms with long Gun barrel, barrels. In small arms, a ''long gun'' or longarm is generally designed to be held by both hands and braced against the shoulder, in contrast to a handgun, which can be fired being held w ...
.
Etymology
The word ''spear
A spear is a polearm consisting of a shaft, usually of wood, with a pointed head. The head may be simply the sharpened end of the shaft itself, as is the case with Fire hardening, fire hardened spears, or it may be made of a more durable materia ...
'' comes from the Old English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-S ...
'' spere'', from the Proto-Germanic ''speri'', from a Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. No direct record of Proto-Indo-European exists; its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-Euro ...
root ''*sper-'' "spear, pole".
Origins
Spear manufacture and use is not confined to humans. It is also practiced by thewestern chimpanzee
The western chimpanzee or West African chimpanzee (''Pan troglodytes verus'') is a Critically Endangered subspecies of the common chimpanzee. It inhabits western Africa, specifically Côte d'Ivoire, Guinea, Liberia, Mali, Senegal, Ghana, Guinea-B ...
. Chimpanzees near Kédougou
Kédougou ( Wolof: Keédugu) is a town in the Kédougou Region of south-eastern Senegal near the border with Mali and Guinea. It lies at an elevation of above sea level.
Founded by the Malinké people, Kédougou means the "Land of Man". The t ...
, Senegal have been observed to create spears by breaking straight limbs off trees, stripping them of their bark and side branches, and sharpening one end with their teeth. They then used the weapons to hunt galago
Galagos , also known as bush babies or ''nagapies'' (meaning "night monkeys" in Afrikaans), are small nocturnal primates native to continental, sub-Sahara Africa, and make up the family Galagidae (also sometimes called Galagonidae). They are ...
s sleeping in hollows.
Prehistory
TheClacton Spear
The Clacton Spear, or Clacton Spear Point, is the tip of a wooden spear discovered in Clacton-on-Sea in 1911. At approximately 400,000 years old, it is the oldest known worked wooden implement.Allington-Jones, L., (2015) ''Archaeological Journal ...
found in England and the Schöningen spears
The Schöningen spears are a set of ten Palaeolithic wooden weapons that were excavated between 1994 and 1999 from the 'Schöningen site, Spear Horizon' in the Open-pit mining, open-cast lignite mine in Schöningen, Helmstedt (district), Helmstedt ...
found in present-day Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
document that wooden spears have been used for hunting since at least 400,000 years ago. A 2012 study from the site of Kathu Pan in South Africa suggests that hominids, possibly ''Homo heidelbergensis
''Homo heidelbergensis'' is a species of archaic human from the Middle Pleistocene of Europe and Africa, as well as potentially Asia depending on the taxonomic convention used. The species-level classification of ''Homo'' during the Middle Pleis ...
'', may have developed the technology of hafted stone-tipped spears in Africa about 500,000 years ago. Wood does not preserve well, however, and Craig Stanford, a primatologist and professor of anthropology at the University of Southern California
The University of Southern California (USC, SC, or Southern Cal) is a Private university, private research university in Los Angeles, California, United States. Founded in 1880 by Robert M. Widney, it is the oldest private research university in ...
, has suggested that the discovery of spear use by chimpanzees means that early humans may have used wooden spears before this.
From circa 200,000 BC onwards, Middle Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic ( years ago) ( ), also called the Old Stone Age (), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone tools, and which represents almost the entire period of human prehist ...
humans began to make complex stone blades with flaked edges which were used as spear heads. These stone heads could be fixed to the spear shaft by gum or resin or by bindings made of animal sinew, leather strips or vegetable matter. During this period, a clear difference remained between spears designed to be thrown and those designed to be used in hand-to-hand combat. By the Magdalenian
Magdalenian cultures (also Madelenian; ) are later cultures of the Upper Paleolithic and Mesolithic in western Europe. They date from around 17,000 to 12,000 years before present. It is named after the type site of Abri de la Madeleine, a ro ...
period (c. 15,000–9500 BC), spear-throwers similar to the later atlatl
A spear-thrower, spear-throwing lever, or ''atlatl'' (pronounced or ; Classical Nahuatl, Nahuatl ''ahtlatl'' ) is a tool that uses leverage to achieve greater velocity in Dart (missile), dart or javelin-throwing, and includes a Plain bearing, b ...
were in use.
Military

Europe
Classical antiquity
=Ancient Greeks
= The spear is the main weapon of the warriors of
The spear is the main weapon of the warriors of Homer
Homer (; , ; possibly born ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Despite doubts about his autho ...
's ''Iliad
The ''Iliad'' (; , ; ) is one of two major Ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the ''Odyssey'', the poem is divided into 24 books and ...
''. The use of both a single thrusting spear and two throwing spears are mentioned. It has been suggested that two styles of combat are being described; an early style, with thrusting spears, dating to the Mycenaean period in which the Iliad is set, and, anachronistically, a later style, with throwing spears, from Homer's own Archaic period.
In the 7th century BC, the Greeks evolved a new close-order infantry formation, the phalanx
The phalanx (: phalanxes or phalanges) was a rectangular mass military formation, usually composed entirely of heavy infantry armed with spears, pikes, sarissas, or similar polearms tightly packed together. The term is particularly used t ...
. The key to this formation was the hoplite
Hoplites ( ) ( ) were citizen-soldiers of Ancient Greek city-states who were primarily armed with spears and shields. Hoplite soldiers used the phalanx formation to be effective in war with fewer soldiers. The formation discouraged the sold ...
, who was equipped with a large, circular, bronze-faced shield (aspis
An ''aspis'' (; : aspides, ) or ''porpax'' shield was the heavy wooden shield used by the infantry in various periods of ancient Greece.
Construction
An ''aspis'' was deeply dished and made primarily of wood. Some had a thin sheet of bronze ...
) and a spear with an iron head and bronze butt-spike ( doru). The hoplite phalanx dominated warfare among the Greek City States from the 7th into the 4th century BC.
The 4th century saw major changes. One was the greater use of peltast
A ''peltast'' (, ) was a type of light infantry originating in Thracians, Thrace and Paeonia (kingdom), Paeonia and named after the kind of shield he carried.
s, light infantry armed with spear and javelins. The other was the development of the sarissa
The sarissa or sarisa was a long spear or pike about in length. It was introduced by Philip II of Macedon and was used in his Macedonian phalanxes as a replacement for the earlier dory, which was considerably shorter. These longer spears imp ...
, a two-handed pike in length, by the Macedon
Macedonia ( ; , ), also called Macedon ( ), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, which later became the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by the royal ...
ians under Phillip of Macedon
Philip II of Macedon (; 382 BC – October 336 BC) was the king (''basileus'') of the ancient kingdom of Macedonia from 359 BC until his death in 336 BC. He was a member of the Argead dynasty, founders of the ancient kingdom, and the fath ...
and Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
. The pike phalanx, supported by peltasts and cavalry, became the dominant mode of warfare among the Greeks from the late 4th century onward until Greek military systems were supplanted by the Roman legions.
=Ancient Romans
= In the pre-Marian Roman armies, the first two lines of battle, the ''
In the pre-Marian Roman armies, the first two lines of battle, the ''hastati
''Hastati'' (: ''hastatus'') were a class of infantry employed in the Structural history of the Roman military#Manipular legion (315 BC – 107 BC), armies of the early Roman Republic, who originally fought as spearmen and later as swordsmen. Th ...
'' and ''principes
''Principes'' (: ''princeps'') were Spear, spearmen, and later Swordsmanship, swordsmen, in the Roman army of the mid-Republic, armies of the early Roman Republic. They were men in the prime of their lives who were fairly wealthy, and could affo ...
'', often fought with a sword called a ''gladius
''Gladius'' () is a Latin word properly referring to the type of sword that was used by Ancient Rome, ancient Roman foot soldiers starting from the 3rd century BC and until the 3rd century AD. Linguistically, within Latin, the word also came t ...
'' and ''pila
Pila may refer to:
Architecture
* Pila (architecture), a type of veranda in Sri Lankan farm houses
Places
*Pila, Buenos Aires, a town in Buenos Aires Province, Argentina
*Pila Partido, a country subdivision in Buenos Aires Province, Argentina
*P ...
'', heavy javelins that were specifically designed to be thrown at an enemy to pierce and foul a target's shield. Originally the ''principes
''Principes'' (: ''princeps'') were Spear, spearmen, and later Swordsmanship, swordsmen, in the Roman army of the mid-Republic, armies of the early Roman Republic. They were men in the prime of their lives who were fairly wealthy, and could affo ...
'' were armed with a short spear called a '' hasta'', but these gradually fell out of use, eventually being replaced by the gladius. The third line, the ''triarii
''Triarii'' (: ''triarius'') ("the third liners") were one of the elements of the early Roman military manipular legions of the early Roman Republic (509 BC – 107 BC). They were the oldest and among the wealthiest men in the army and could a ...
'', continued to use the ''hasta''.
From the late 2nd century BC, all legionaries
The ancient Rome, Roman legionary (in Latin ''legionarius''; : ''legionarii'') was a citizen soldier of the Roman army. These soldiers would conquer and defend the territories of ancient Rome during the Crisis of the Roman Republic, Republic and ...
were equipped with the ''pilum''. The ''pilum'' continued to be the standard legionary spear until the end of the 2nd century AD. ''Auxilia
The (; ) were introduced as non-citizen troops attached to the citizen Roman legion, legions by Augustus after his reorganisation of the Imperial Roman army from 27 BC. By the 2nd century, the contained the same number of infantry as the ...
'', however, were equipped with a simple hasta and, perhaps, javelins or darts. During the 3rd century AD, although the ''pilum'' continued to be used, legionaries usually were equipped with other forms of throwing and thrusting spear, similar to ''auxilia'' of the previous century. By the 4th century, the ''pilum'' had effectively disappeared from common use.
In the late period of the Roman Empire, the spear became more often used because of its anti-cavalry capacities as the barbarian invasions were often conducted by people with a developed culture of cavalry in warfare.
Medieval period
After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, the spear and shield continued to be used by nearly all Western European cultures. Since a medieval spear required only a small amount ofsteel
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon that demonstrates improved mechanical properties compared to the pure form of iron. Due to steel's high Young's modulus, elastic modulus, Yield (engineering), yield strength, Fracture, fracture strength a ...
along the sharpened edges (most of the spear-tip was wrought iron), it was an economical weapon. Quick to manufacture, and needing less smithing
A metalsmith or simply smith is a craftsperson fashioning useful items (for example, tools, kitchenware, tableware, jewelry, armor and weapons) out of various metals. Smithing is one of the oldest metalworking occupations. Shaping metal with a ...
skill than a sword, it remained the main weapon of the common soldier. The Vikings
Vikings were seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway, and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded, and settled throughout parts of Europe.Roesdahl, pp. 9� ...
, for instance, although often portrayed with an axe
An axe (; sometimes spelled ax in American English; American and British English spelling differences#Miscellaneous spelling differences, see spelling differences) is an implement that has been used for thousands of years to shape, split, a ...
, sword
A sword is an edged and bladed weapons, edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter ...
, or lance
The English term lance is derived, via Middle English '' launce'' and Old French '' lance'', from the Latin '' lancea'', a generic term meaning a wikt:lancea#Noun">lancea'', a generic term meaning a spear">wikt:lancea#Noun">lancea'', a generi ...
in hand, were armed mostly with spears, as were their Anglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons, in some contexts simply called Saxons or the English, were a Cultural identity, cultural group who spoke Old English and inhabited much of what is now England and south-eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. They traced t ...
, Irish, or continental contemporaries. Spears eventually evolved into lances; this is where the lance depiction comes from. With a good majority of Medieval weapons being spears they became integrated into many war tactics. Spears were very commonly used while providing a defensive block. When men on horses tried to get by these blocks, they would often be killed by the spears that could poke through the shield walls. Spears became more common than swords and axes because of how cheap, long, and fast spears were made.
=Infantry
= Broadly speaking, spears were either designed to be used in melee, or to be thrown. Within this simple classification, there was a remarkable range of types. For example, M. J. Swanton identified thirty different spearhead categories and sub-categories in early Saxon England. Most medieval spearheads were generally leaf-shaped. Notable types of early medieval spears include the ''angon
The ''angon'' (Medieval Greek , Old High German ''ango'', Old English ''anga'' "hook, point, spike") is a type of javelin that was used during the Early Middle Ages by the Anglo-Saxons, Franks, Goths, and other Germanic peoples. It was similar ...
'', a throwing spear with a long head similar to the Roman ''pilum
The ''pilum'' (; : ''pila'') was a javelin commonly used by the Roman army in ancient times. It was generally about long overall, consisting of an iron shank about in diameter and long with a pyramidal head, attached to a wooden shaft by eith ...
'', used by the Franks and Anglo-Saxons, and the winged (or lugged) spear, which had two prominent wings at the base of the spearhead, either to prevent the spear penetrating too far into an enemy or to aid in spear fencing. Originally a Frankish weapon, the winged spear also was popular with the Vikings. It would become the ancestor of later medieval polearms, such as the partisan
Partisan(s) or The Partisan(s) may refer to:
Military
* Partisan (military), paramilitary forces engaged behind the front line
** Francs-tireurs et partisans, communist-led French anti-fascist resistance against Nazi Germany during WWII
** Ital ...
and spetum
A spetum is a polearm that was used in Europe during the 13th century. Other names include chauve souris, corseca, corsèsque, korseke, runka, and rawcon. It consists of a pole, some long, on which is mounted a spear head with two projections ...
.
The thrusting spear also has the advantage of reach, being considerably longer than other weapon types. Exact spear lengths are hard to deduce as few spear shafts survive archaeologically, but would seem to have been the average length. Some nations were noted for their long spears, including the Scots and the Flemish. Spears usually were used in tightly ordered formations, such as the shield wall
A shield wall ( or in Old English, in Old Norse) is a military formation that was common in ancient and medieval warfare. There were many slight variations of this formation,
but the common factor was soldiers standing shoulder to shoulder ...
or the schiltron
A schiltron (also spelled sheltron, sceld-trome, schiltrom, or shiltron) is a compact body of troops forming a battle array, shield wall or phalanx. The term is most often associated with Scottish pike formations during the Wars of Scottish In ...
. To resist cavalry, spear shafts could be planted against the ground. William Wallace drew up his schiltrons in a circle at the Battle of Falkirk
The Battle of Falkirk (; ), on 22 July 1298, was one of the major battles in the First War of Scottish Independence. Led by Edward I of England, King Edward I of England, the English army defeated the Scottish people, Scots, led by William Wal ...
in 1298 to deter charging cavalry; this was a widespread tactic sometimes known as the "crown" formation. Thomas Randolph, 1st Earl of Moray
Thomas Randolph, Earl of Moray (c. 1285 20 July 1332) was a soldier and diplomat in the Wars of Scottish Independence, who later served as regent of Scotland. He was a nephew of Robert the Bruce, who created him as the first earl of M ...
used a circular schiltron on the first day of the Battle of Bannockburn
The Battle of Bannockburn ( or ) was fought on 23–24 June 1314, between the army of Robert the Bruce, King of Scots, and the army of King Edward II of England, during the First War of Scottish Independence. It was a decisive victory for Ro ...
. However, the rectangular schiltron was much more common and was used by King Robert the Bruce
Robert I (11 July 1274 – 7 June 1329), popularly known as Robert the Bruce (), was King of Scots from 1306 until his death in 1329. Robert led Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland during the First War of Scottish Independence against Kingdom of Eng ...
on the second day of the Battle of Bannockburn and in the Battle of Old Byland
The Battle of Old Byland (also known as the Battle of Byland Abbey, the Battle of Byland Moor and the Battle of Scotch Corner) was a significant encounter between Scots and English troops in Yorkshire in October 1322, forming part of the War ...
when he defeated English armies.
Throwing spears became rarer as the Middle Ages drew on, but survived in the hands of specialists such as the Catalan Almogavars
Almogavars (; ; ; ; originally ) is the name of a class of light infantry soldier originated in the Crown of Aragon used in the later phases of the Reconquista, during the 13th and 14th centuries.
Almogavars were lightly clad, quick-moving fr ...
. They were commonly used in Ireland until the end of the 16th century.
Spears began to lose fashion among the infantry during the 14th century, being replaced by polearm
A polearm or pole weapon is a close combat weapon in which the main fighting part of the weapon is fitted to the end of a long shaft, typically of wood, extending the user's effective range and striking power. Polearms are predominantly melee we ...
s that combined the thrusting properties of the spear with the cutting properties of the axe, such as the halberd
A halberd (also called halbard, halbert or Swiss voulge), is a two-handed polearm that was in prominent use from the 13th to 16th centuries. The halberd consists of an axe blade topped with a spike mounted on a long shaft. It may have a hook or ...
. Where spears were retained they grew in length, eventually evolving into pike
Pike, Pikes or The Pike may refer to:
Fish
* Blue pike or blue walleye, an extinct color morph of the yellow walleye ''Sander vitreus''
* Ctenoluciidae, the "pike characins", some species of which are commonly known as pikes
* ''Esox'', genus of ...
s, which would be a dominant infantry weapon in the 16th and 17th centuries.
=Cavalry
= Cavalry spears were originally the same as infantry spears and were often used with two hands or held with one hand overhead. In the 12th century, after the adoption ofstirrup
A stirrup is a light frame or ring that holds the foot of a rider, attached to the saddle by a strap, often called a ''stirrup leather''. Stirrups are usually paired and are used to aid in mounting and as a support while using a riding animal ...
s and a high-cantled saddle, the spear became a decidedly more powerful weapon. A mounted knight would secure the lance
The English term lance is derived, via Middle English '' launce'' and Old French '' lance'', from the Latin '' lancea'', a generic term meaning a wikt:lancea#Noun">lancea'', a generic term meaning a spear">wikt:lancea#Noun">lancea'', a generi ...
by holding it with one hand and tucking it under the armpit (the ''couched lance'' technique) In combination with a lance rest
A lance rest ( French: ''arrêt de cuirasse'' or ''arrêt'') is a metal flange or hook that is typically attached to the right side of a breastplate, just under the armpit. The lance rest appeared in the late 14th century, remaining in use until ...
, this allowed all the momentum of the horse and knight to be focused on the weapon's tip, whilst still retaining accuracy and control. This use of the spear spurred the development of the lance
The English term lance is derived, via Middle English '' launce'' and Old French '' lance'', from the Latin '' lancea'', a generic term meaning a wikt:lancea#Noun">lancea'', a generic term meaning a spear">wikt:lancea#Noun">lancea'', a generi ...
as a distinct weapon that was perfected in the medieval sport of jousting
Jousting is a medieval and renaissance martial game or hastilude between two combatants either on horse or on foot. The joust became an iconic characteristic of the knight in Romantic medievalism.
The term is derived from Old French , ultim ...
.
In the 14th century, tactical developments meant that knights and men-at-arms often fought on foot. This led to the practice of shortening the lance to about to make it more manageable. As dismounting became commonplace, specialist polearms such as the pollaxe were adopted by knights and this practice ceased.
Introduction of gunpowder
 The development of both the long, two-handed
The development of both the long, two-handed pike
Pike, Pikes or The Pike may refer to:
Fish
* Blue pike or blue walleye, an extinct color morph of the yellow walleye ''Sander vitreus''
* Ctenoluciidae, the "pike characins", some species of which are commonly known as pikes
* ''Esox'', genus of ...
and gunpowder
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, charcoal (which is mostly carbon), and potassium nitrate, potassium ni ...
firearms in Renaissance Europe saw an ever-increasing focus on integrated infantry tactics. Those infantry not armed with these weapons carried variations on the polearm, including the halberd
A halberd (also called halbard, halbert or Swiss voulge), is a two-handed polearm that was in prominent use from the 13th to 16th centuries. The halberd consists of an axe blade topped with a spike mounted on a long shaft. It may have a hook or ...
and the bill
Bill(s) may refer to:
Common meanings
* Banknote, paper cash (especially in the United States)
* Bill (law), a proposed law put before a legislature
* Invoice, commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer
* Bill, a bird or animal's beak
Pl ...
. At the start of the Renaissance, cavalry remained predominantly lance-armed; gendarmes
A gendarmerie () is a paramilitary or military force with law enforcement duties among the civilian population. The term ''gendarme'' () is derived from the medieval French expression ', which translates to "men-at-arms" (). In France and som ...
with the heavy knightly lance and lighter cavalry with a variety of lighter lances. By the 1540s, however, pistol-armed cavalry called reiter
''Reiter'' or ''Schwarze Reiter'' ("black riders", anglicized ''swart reiters'') were a type of cavalry in 16th to 17th century Central Europe including Holy Roman Empire, Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Tsardom of Russia, and others.
Cont ...
s were beginning to make their mark. Cavalry armed with pistols and other lighter firearms, along with a sword, had virtually replaced lance armed cavalry in Western Europe by the beginning of the 17th century.
Ultimately, the spear proper was rendered obsolete on the battlefield. Its last flowering was the half-pike or spontoon
A spontoon, sometimes known by the variant spelling espontoon or as a half-pike, is a type of European polearm that came into being alongside the pike. The spontoon was in common use from the mid-17th century to the early 19th century, but it wa ...
, a shortened version of the pike carried by officers of various ranks. While originally a weapon, this came to be seen more as a badge of office, or ''leading staff'' by which troops were directed. The half-pike, sometimes known as a boarding pike, was also used as a weapon on board ships until the late 19th century.
Middle East
Modern era
Muslim warriors used a spear that was called an '' az-zaġāyah''.Berbers
Berbers, or the Berber peoples, also known as Amazigh or Imazighen, are a diverse grouping of distinct ethnic groups indigenous to North Africa who predate the arrival of Arab migrations to the Maghreb, Arabs in the Maghreb. Their main connec ...
pronounced it ''zaġāya'', but the English term, derived from the Old French
Old French (, , ; ) was the language spoken in most of the northern half of France approximately between the late 8th
 There are many words in Chinese that would be classified as a spear in English. The ''Mao'' is the predecessor of the '' Qiang''. The first bronze ''Mao'' appeared in the
There are many words in Chinese that would be classified as a spear in English. The ''Mao'' is the predecessor of the '' Qiang''. The first bronze ''Mao'' appeared in the  After the Tang dynasty, the popularity of the ''Mao'' declined and was replaced by the '' Qiang'' (枪). The Tang dynasty divided the ''Qiang'' in four categories: "一曰漆枪, 二曰木枪, 三曰白杆枪, 四曰扑头枪。” Roughly translated the four categories are: Qi (a kind of wood) Spears, Wooden Spears, Bai Gan (A kind of wood) Spears and Pu Tou Qiang. The Qiang that were produced in the Song and Ming dynasties consisted of four major parts: Spearhead, Shaft, End Spike and Tassel. The types of Qiang that exist are many. Among the types there are cavalry Qiang that were the length of one ''zhang'' (approximately ), Litte-Flower Spears (Xiao Hua Qiang 小花枪) that are the length of one person and their arm extended above his head, double hooked spears, single hooked spears, ringed spears and many more.
There is some confusion as to how to distinguish the ''Qiang'' from the ''Mao'', as they are obviously very similar. Some people say that a ''Mao'' is longer than a ''Qiang'', others say that the main difference is between the stiffness of the shaft, where the ''Qiang'' would be flexible and the ''Mao'' would be stiff. Scholars seem to lean toward the latter explanation more than the former. Because of the difference in the construction of the ''Mao'' and the ''Qiang'', the usage is also different, though there is no definitive answer as to what exactly the differences are between the ''Mao'' and the ''Qiang''.
After the Tang dynasty, the popularity of the ''Mao'' declined and was replaced by the '' Qiang'' (枪). The Tang dynasty divided the ''Qiang'' in four categories: "一曰漆枪, 二曰木枪, 三曰白杆枪, 四曰扑头枪。” Roughly translated the four categories are: Qi (a kind of wood) Spears, Wooden Spears, Bai Gan (A kind of wood) Spears and Pu Tou Qiang. The Qiang that were produced in the Song and Ming dynasties consisted of four major parts: Spearhead, Shaft, End Spike and Tassel. The types of Qiang that exist are many. Among the types there are cavalry Qiang that were the length of one ''zhang'' (approximately ), Litte-Flower Spears (Xiao Hua Qiang 小花枪) that are the length of one person and their arm extended above his head, double hooked spears, single hooked spears, ringed spears and many more.
There is some confusion as to how to distinguish the ''Qiang'' from the ''Mao'', as they are obviously very similar. Some people say that a ''Mao'' is longer than a ''Qiang'', others say that the main difference is between the stiffness of the shaft, where the ''Qiang'' would be flexible and the ''Mao'' would be stiff. Scholars seem to lean toward the latter explanation more than the former. Because of the difference in the construction of the ''Mao'' and the ''Qiang'', the usage is also different, though there is no definitive answer as to what exactly the differences are between the ''Mao'' and the ''Qiang''.
 The hoko spear was used in ancient Japan sometime between the
The hoko spear was used in ancient Japan sometime between the
 Filipino spears (sibat) were used as both a weapon and a tool throughout the Philippines. It is also called a ''bangkaw'' (after the Bankaw Revolt.), ''sumbling'' or ''palupad'' in the islands of Visayas and Mindanao. Sibat are typically made from rattan, either with a sharpened tip or a head made from metal. These heads may either be single-edged, double-edged or barbed. Styles vary according to function and origin. For example, a sibat designed for fishing may not be the same as those used for hunting.
The spear was used as the primary weapon in expeditions and battles against neighbouring island kingdoms and it became famous during the 1521 Battle of Mactan, where the chieftain Lapu Lapu of Cebu fought against Spanish forces led by Ferdinand Magellan who was subsequently killed.
Filipino spears (sibat) were used as both a weapon and a tool throughout the Philippines. It is also called a ''bangkaw'' (after the Bankaw Revolt.), ''sumbling'' or ''palupad'' in the islands of Visayas and Mindanao. Sibat are typically made from rattan, either with a sharpened tip or a head made from metal. These heads may either be single-edged, double-edged or barbed. Styles vary according to function and origin. For example, a sibat designed for fishing may not be the same as those used for hunting.
The spear was used as the primary weapon in expeditions and battles against neighbouring island kingdoms and it became famous during the 1521 Battle of Mactan, where the chieftain Lapu Lapu of Cebu fought against Spanish forces led by Ferdinand Magellan who was subsequently killed.
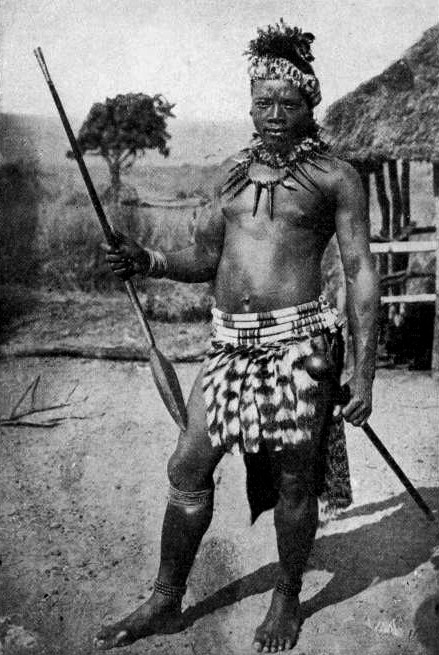 The various types of the assegai (a light spear or
The various types of the assegai (a light spear or
 One of the earliest forms of killing prey for humans, hunting game with a spear and spear fishing continues to this day as both a means of catching food and as a cultural activity. Some of the most common prey for early humans were megafauna such as mammoths which were hunted with various kinds of spear. One theory for the Quaternary extinction event#Hunting hypothesis, Quaternary extinction event was that most of these animals were hunted to extinction by humans with spears. Even after the invention of other hunting weapons such as the Bow and arrow, bow and Sling (weapon), sling, the spear continued to be used, either as a projectile weapon or used by hand, such as in bear hunting and boar hunting.
One of the earliest forms of killing prey for humans, hunting game with a spear and spear fishing continues to this day as both a means of catching food and as a cultural activity. Some of the most common prey for early humans were megafauna such as mammoths which were hunted with various kinds of spear. One theory for the Quaternary extinction event#Hunting hypothesis, Quaternary extinction event was that most of these animals were hunted to extinction by humans with spears. Even after the invention of other hunting weapons such as the Bow and arrow, bow and Sling (weapon), sling, the spear continued to be used, either as a projectile weapon or used by hand, such as in bear hunting and boar hunting.
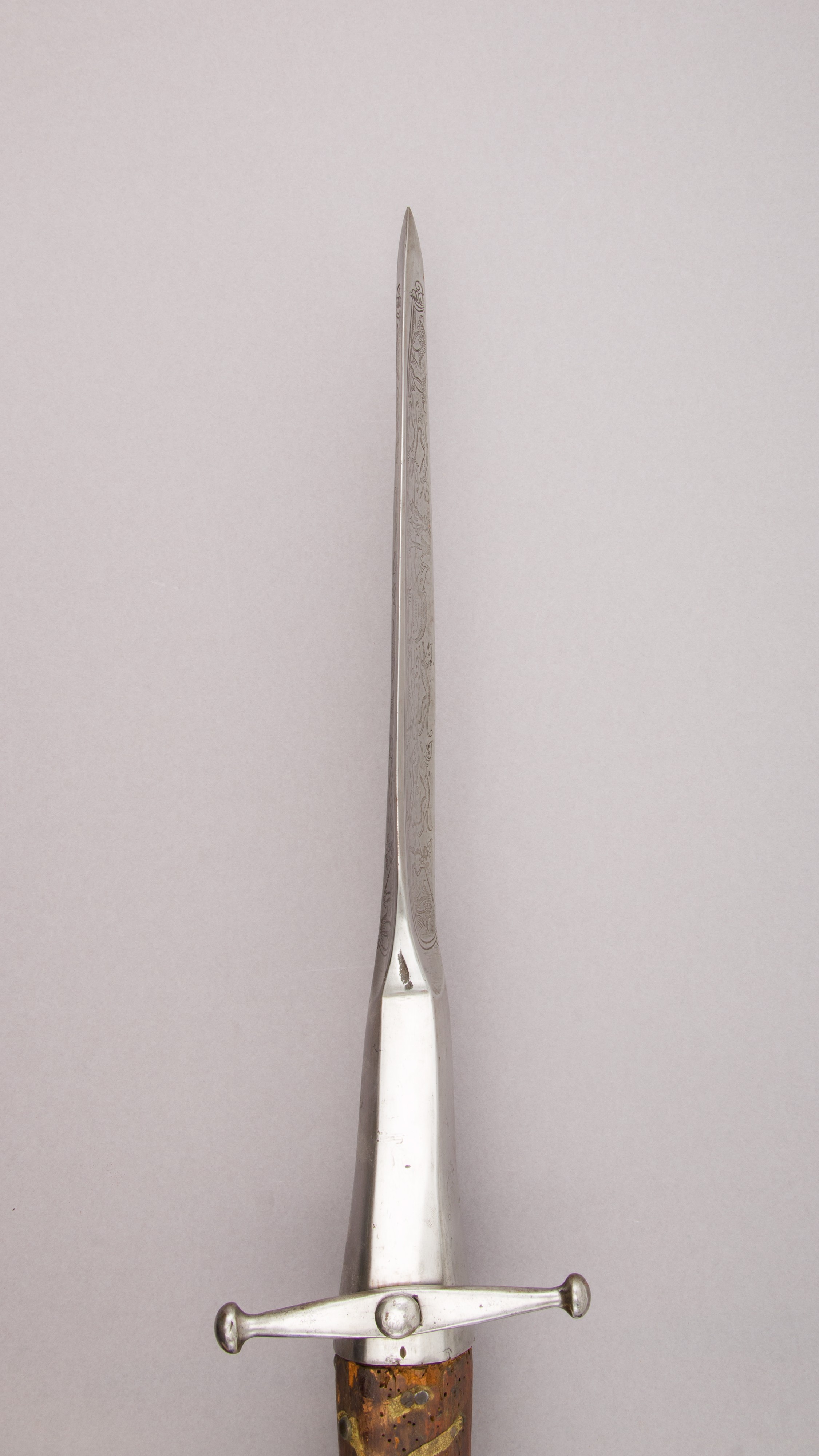 * Barred spears: A barred spear has a crossbar beneath the blade, to prevent too deep a penetration of the spear into an animal. The bar may be forged as part of the spearhead or may be more loosely tied by means of loops below the blade. Barred spears are known from the Bronze Age, but the first historical record of their use in Europe is found in the writings of Xenophon in the 5th century BC. Examples also are shown in Roman art. In the Middle Ages, a winged or lugged war-spear was developed (#Infantry, see above), but the later Middle Ages saw the development of specialised types, such as the boar-spear and the bear-spear. The boar-spear could be used both on foot or horseback.
* Javelin
* Harpoon
* Trident
* Barred spears: A barred spear has a crossbar beneath the blade, to prevent too deep a penetration of the spear into an animal. The bar may be forged as part of the spearhead or may be more loosely tied by means of loops below the blade. Barred spears are known from the Bronze Age, but the first historical record of their use in Europe is found in the writings of Xenophon in the 5th century BC. Examples also are shown in Roman art. In the Middle Ages, a winged or lugged war-spear was developed (#Infantry, see above), but the later Middle Ages saw the development of specialised types, such as the boar-spear and the bear-spear. The boar-spear could be used both on foot or horseback.
* Javelin
* Harpoon
* Trident
 Like many weapons, a spear may also be a symbol of power.
The Celts would symbolically destroy a dead warrior's spear either to prevent its use by another or as a sacrificial offering.
In classical Greek mythology Zeus' bolts of lightning may be interpreted as a symbolic spear. Some would carry that interpretation to the spear that frequently is associated with Athena, interpreting her spear as a symbolic connection to some of Zeus' power beyond the Aegis once he rose to replacing other deities in the Pantheon (gods), pantheon. Athena was depicted with a spear prior to that change in myths, however. Chiron's wedding-gift to Peleus when he married the nymph Thetis in classical Greek mythology, was an ashen spear as the nature of ashwood with its straight grain made it an ideal choice of wood for a spear.
The Romans and their early enemies would force prisoners to walk underneath a 'yoke of spears', which humiliated them. The yoke would consist of three spears, two upright with a third tied between them at a height which made the prisoners stoop. It has been suggested that the arrangement has a magic (paranormal), magical origin, a way to trap evil spirits.
In Norse mythology, the god Odin's spear (named Gungnir) was made by the sons of Ivaldi. It had the special property that it never missed its mark. During the War with the Vanir, Odin symbolically threw Gungnir into the Vanir host. This practice of symbolically casting a spear into the enemy ranks at the start of a fight was sometimes used in historic clashes, to seek Odin's support in the coming battle. In Richard Wagner, Wagner's opera ''Siegfried (opera), Siegfried'', the haft of Gungnir is said to be from the "World-Tree" Yggdrasil.
Other spears of religious significance are the Holy Lance and the Spear Luin, Lúin of Celtchar, believed by some to have vast mystical powers.
James Frazer, Sir James George Frazer in ''The Golden Bough'' noted the phallic nature of the spear and suggested that in the Arthurian legends the spear or lance functioned as a symbol of male fertility, paired with the Grail (as a symbol of female fertility).
Like many weapons, a spear may also be a symbol of power.
The Celts would symbolically destroy a dead warrior's spear either to prevent its use by another or as a sacrificial offering.
In classical Greek mythology Zeus' bolts of lightning may be interpreted as a symbolic spear. Some would carry that interpretation to the spear that frequently is associated with Athena, interpreting her spear as a symbolic connection to some of Zeus' power beyond the Aegis once he rose to replacing other deities in the Pantheon (gods), pantheon. Athena was depicted with a spear prior to that change in myths, however. Chiron's wedding-gift to Peleus when he married the nymph Thetis in classical Greek mythology, was an ashen spear as the nature of ashwood with its straight grain made it an ideal choice of wood for a spear.
The Romans and their early enemies would force prisoners to walk underneath a 'yoke of spears', which humiliated them. The yoke would consist of three spears, two upright with a third tied between them at a height which made the prisoners stoop. It has been suggested that the arrangement has a magic (paranormal), magical origin, a way to trap evil spirits.
In Norse mythology, the god Odin's spear (named Gungnir) was made by the sons of Ivaldi. It had the special property that it never missed its mark. During the War with the Vanir, Odin symbolically threw Gungnir into the Vanir host. This practice of symbolically casting a spear into the enemy ranks at the start of a fight was sometimes used in historic clashes, to seek Odin's support in the coming battle. In Richard Wagner, Wagner's opera ''Siegfried (opera), Siegfried'', the haft of Gungnir is said to be from the "World-Tree" Yggdrasil.
Other spears of religious significance are the Holy Lance and the Spear Luin, Lúin of Celtchar, believed by some to have vast mystical powers.
James Frazer, Sir James George Frazer in ''The Golden Bough'' noted the phallic nature of the spear and suggested that in the Arthurian legends the spear or lance functioned as a symbol of male fertility, paired with the Grail (as a symbol of female fertility).
 The Hindu god of war Kartikeya, Murugan is worshipped by
The Hindu god of war Kartikeya, Murugan is worshipped by
Berber
Berber or Berbers may refer to:
Ethnic group
* Berbers, an ethnic group native to Northern Africa
* Berber languages, a family of Afro-Asiatic languages
Places
* Berber, Sudan, a town on the Nile
People with the surname
* Ady Berber (1913–196 ...
, is "assegai". It is a polearm used for throwing or hurling, usually a light spear or javelin made of hard wood and pointed with a forged iron tip. The ''az-zaġāyah'' played an important role during the Early Muslim conquests, Islamic conquest as well as during later periods, well into the 20th century. A longer pole ''az-zaġāyah'' was being used as a hunting weapon from horseback. The ''az-zaġāyah'' was widely used. It existed in various forms in areas stretching from Southern Africa
Southern Africa is the southernmost region of Africa. No definition is agreed upon, but some groupings include the United Nations geoscheme for Africa, United Nations geoscheme, the intergovernmental Southern African Development Community, and ...
to the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
, although these places already had their own variants of the spear. This javelin was the weapon of choice during the ''Fulani jihad
The Jihad of Usman dan Fodio was a religio-military conflict in present-day Nigeria and Cameroon. The war began when Usman dan Fodio, a prominent Islamic scholar and teacher, was exiled from Gobir by King Yunfa, one of his former students.
Us ...
'' as well as during the Mahdist War
The Mahdist War (; 1881–1899) was fought between the Mahdist Sudanese, led by Muhammad Ahmad bin Abdullah, who had proclaimed himself the "Mahdi" of Islam (the "Guided One"), and the forces of the Khedivate of Egypt, initially, and later th ...
in Sudan. It is still being used by certain wandering Sufi ascetics ''( Derwishes)''.
Asia
China
In theChinese martial arts
Chinese martial arts, commonly referred to with umbrella terms Kung fu (term), kung fu (; ), kuoshu () or wushu (sport), wushu (), are Styles of Chinese martial arts, multiple fighting styles that have developed over the centuries in Greater Ch ...
, the Chinese
Chinese may refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people identified with China, through nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**Han Chinese, East Asian ethnic group native to China.
**'' Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic ...
spear ( Qiang 槍) is popularly known as the "king of weapons". The spear is listed in the group of the four major weapons (along with the gun
A gun is a device that Propulsion, propels a projectile using pressure or explosive force. The projectiles are typically solid, but can also be pressurized liquid (e.g. in water guns or water cannon, cannons), or gas (e.g. light-gas gun). So ...
( staff), dao
The Tao or Dao is the natural way of the universe, primarily as conceived in East Asian philosophy and religion. This seeing of life cannot be grasped as a concept. Rather, it is seen through actual living experience of one's everyday being. T ...
(a single-edged blade similar to a sabre
A sabre or saber ( ) is a type of backsword with a curved blade associated with the light cavalry of the Early Modern warfare, early modern and Napoleonic period, Napoleonic periods. Originally associated with Central European cavalry such a ...
), and the jian
The ''jian'' (Mandarin Chinese: , , English approximation: , Cantonese: ) is a double-edged straight sword used during the last 2,500 years in China. The first Chinese sources that mention the ''jian'' date to the 7th century BCE, during the S ...
(sword
A sword is an edged and bladed weapons, edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter ...
)).
Spears were used first as hunting weapons amongst the ancient Chinese. They became popular as infantry weapons during the Warring States
The Warring States period in Chinese history (221 BC) comprises the final two and a half centuries of the Zhou dynasty (256 BC), which were characterized by frequent warfare, bureaucratic and military reforms, and struggles for gre ...
and Qin era, when spearmen were used as especially highly disciplined soldiers in organized group attacks. When used in formation fighting, spearmen would line up their large rectangular or circular shields in a shieldwall manner. The Qin also employed long spears (more akin to a pike) in formations similar to Swiss pikemen in order to ward off cavalry. The Han Empire would use similar tactics as its Qin predecessors. Halberds, polearms, and dagger axes were also common weapons during this time.
Spears were also common weaponry for Warring States, Qin, and Han era cavalry units. During these eras, the spear would develop into a longer lance-like weapon used for cavalry charges.
Shang dynasty
The Shang dynasty (), also known as the Yin dynasty (), was a Chinese royal dynasty that ruled in the Yellow River valley during the second millennium BC, traditionally succeeding the Xia dynasty and followed by the Western Zhou d ...
. This weapon was less prominent on the battlefield than the ''ge'' (dagger-axe
The dagger-axe () is a type of polearm that was in use from the Longshan culture until the Han dynasty in China. It consists of a dagger-shaped blade, mounted by its tang to a perpendicular wooden shaft. The earliest dagger-axe blades were m ...
). In some archaeological examples two tiny holes or ears can be found in the blade of the spearhead near the socket, these holes were presumably used to attach tassels, much like modern day wushu
Wushu may refer to:
Martial arts
* Chinese martial arts, the various martial arts of China
* Wushu (sport)
Wushu () (), or kung fu, is a competitive Chinese martial art. It integrates concepts and forms from various traditional and modern ...
spears.
In the early Shang
The Shang dynasty (), also known as the Yin dynasty (), was a Chinese royal dynasty that ruled in the Yellow River valley during the second millennium BC, traditionally succeeding the Xia dynasty and followed by the Western Zhou dyn ...
, the ''Mao'' appeared to have a relatively short shaft as well as a relatively narrow shaft as opposed to ''Mao'' in the later Shang and Western Zhou
The Western Zhou ( zh, c=西周, p=Xīzhōu; 771 BC) was a period of Chinese history corresponding roughly to the first half of the Zhou dynasty. It began when King Wu of Zhou overthrew the Shang dynasty at the Battle of Muye and ended in 77 ...
period. Some ''Mao'' from this era are heavily decorated as is evidenced by a Warring States period
The Warring States period in history of China, Chinese history (221 BC) comprises the final two and a half centuries of the Zhou dynasty (256 BC), which were characterized by frequent warfare, bureaucratic and military reforms, and ...
''Mao'' from the Ba Shu area.
In the Han dynasty the ''Mao'' and the '' Ji'' (戟 ''Ji'' can be loosely defined as a halberd) rose to prominence in the military. Interesting to note is that the amount of iron Mao-heads found exceeds the number of bronze heads. By the end of the Han dynasty (Eastern Han
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC ...
) the process of replacement of the iron ''Mao'' had been completed and the bronze ''Mao'' had been rendered completely obsolete. After the Han dynasty toward the Sui and Tang dynasties the ''Mao'' used by cavalry were fitted with much longer shafts, as is mentioned above. During this era, the use of the ''Shuo'' (矟) was widespread among the footmen. The ''Shuo'' can be likened to a pike or simply a long spear.
 After the Tang dynasty, the popularity of the ''Mao'' declined and was replaced by the '' Qiang'' (枪). The Tang dynasty divided the ''Qiang'' in four categories: "一曰漆枪, 二曰木枪, 三曰白杆枪, 四曰扑头枪。” Roughly translated the four categories are: Qi (a kind of wood) Spears, Wooden Spears, Bai Gan (A kind of wood) Spears and Pu Tou Qiang. The Qiang that were produced in the Song and Ming dynasties consisted of four major parts: Spearhead, Shaft, End Spike and Tassel. The types of Qiang that exist are many. Among the types there are cavalry Qiang that were the length of one ''zhang'' (approximately ), Litte-Flower Spears (Xiao Hua Qiang 小花枪) that are the length of one person and their arm extended above his head, double hooked spears, single hooked spears, ringed spears and many more.
There is some confusion as to how to distinguish the ''Qiang'' from the ''Mao'', as they are obviously very similar. Some people say that a ''Mao'' is longer than a ''Qiang'', others say that the main difference is between the stiffness of the shaft, where the ''Qiang'' would be flexible and the ''Mao'' would be stiff. Scholars seem to lean toward the latter explanation more than the former. Because of the difference in the construction of the ''Mao'' and the ''Qiang'', the usage is also different, though there is no definitive answer as to what exactly the differences are between the ''Mao'' and the ''Qiang''.
After the Tang dynasty, the popularity of the ''Mao'' declined and was replaced by the '' Qiang'' (枪). The Tang dynasty divided the ''Qiang'' in four categories: "一曰漆枪, 二曰木枪, 三曰白杆枪, 四曰扑头枪。” Roughly translated the four categories are: Qi (a kind of wood) Spears, Wooden Spears, Bai Gan (A kind of wood) Spears and Pu Tou Qiang. The Qiang that were produced in the Song and Ming dynasties consisted of four major parts: Spearhead, Shaft, End Spike and Tassel. The types of Qiang that exist are many. Among the types there are cavalry Qiang that were the length of one ''zhang'' (approximately ), Litte-Flower Spears (Xiao Hua Qiang 小花枪) that are the length of one person and their arm extended above his head, double hooked spears, single hooked spears, ringed spears and many more.
There is some confusion as to how to distinguish the ''Qiang'' from the ''Mao'', as they are obviously very similar. Some people say that a ''Mao'' is longer than a ''Qiang'', others say that the main difference is between the stiffness of the shaft, where the ''Qiang'' would be flexible and the ''Mao'' would be stiff. Scholars seem to lean toward the latter explanation more than the former. Because of the difference in the construction of the ''Mao'' and the ''Qiang'', the usage is also different, though there is no definitive answer as to what exactly the differences are between the ''Mao'' and the ''Qiang''.
India
Spears are known as Bhala in Indian languages. Spears in theIndian society
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Associated with India
* of or related to India
** Indian people
** Indian diaspora
** Languages of India
** Indian English, a dialect of the English language
** Indian cuisine
Associated with indigenous peoples o ...
were used both in missile and non-missile form, both by cavalry and foot-soldiers. Mounted spear-fighting was practiced using with a , ball-tipped wooden lance called a ''bothati'', the end of which was covered in dye so that hits may be confirmed. Spears were constructed from a variety of materials such as the ''sang'' made completely of steel, and the ''ballam'' which had a bamboo shaft.
The Arab presence in Sindh and the Mameluks of Delhi introduced the Middle Eastern javelin into India.
The Rajput
Rājpūt (, from Sanskrit ''rājaputra'' meaning "son of a king"), also called Thākur (), is a large multi-component cluster of castes, kin bodies, and local groups, sharing social status and ideology of genealogical descent originating fro ...
s wielded a type of spear for infantrymen which had a club integrated into the spearhead, and a pointed butt end. Other spears had forked blades, several spear-points, and numerous other innovations. One particular spear unique to India was the ''vita'' or corded lance.
Used by the Maratha Army
The Maratha Army was the land-based armed forces of the Maratha Confederacy, which existed from the late 17th to the early 19th centuries in the Indian subcontinent.
17th century
Shivaji, The great the founder of Maratha Kingdom, raised a small ...
, it had a rope connecting the spear with the user's wrist, allowing the weapon to be thrown and pulled back. The ''Vel
Vel () is a divine spear associated with Murugan, the Tamil Hindu god of war.
Significance
According to Shaiva tradition, the goddess Parvati presented the Vel to her son Kartikeya(also known as Murugan), as an embodiment of her shakti, in ...
'' is a type of spear or lance, originated in Southern India
South India, also known as Southern India or Peninsular India, is the southern part of the Deccan Peninsula in India encompassing the states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Telangana as well as the union territories of ...
, primarily used by Tamils
The Tamils ( ), also known by their endonym Tamilar, are a Dravidian peoples, Dravidian ethnic group who natively speak the Tamil language and trace their ancestry mainly to the southern part of the Indian subcontinent. The Tamil language is o ...
.
Sikh Nihang
The Nihang (also spelt as Nihung lit. "Crocodiles") or Akali (lit. "Immortals"), also known as '' Dal Khalsa'', is an armed Sikh warrior order originating in the Indian subcontinent. Nihangs are believed to have originated either from Fateh Sin ...
s sometimes carry a spear even today. Spears were used in conflicts and training by armed paramilitary units such as the razakar
Razakar (رضا کار) is etymologically an Arabic word which literally means volunteer. The word is also common in Urdu language as a loanword. On the other hand, in Bangladesh, razakar is a pejorative word meaning a traitor or Judas.
In Paki ...
s of Nizam
Nizam of Hyderabad was the title of the ruler of Hyderabad State ( part of the Indian state of Telangana, and the Kalyana-Karnataka region of Karnataka). ''Nizam'' is a shortened form of (; ), and was the title bestowed upon Asaf Jah I ...
s of Hyderabad State
Hyderabad State () was a princely state in the Deccan region of south-central India with its capital at the city of Hyderabad. It is now divided into the present-day state of Telangana, the Kalyana-Karnataka region of Karnataka, and the ...
as late as the second half of the 20th century.
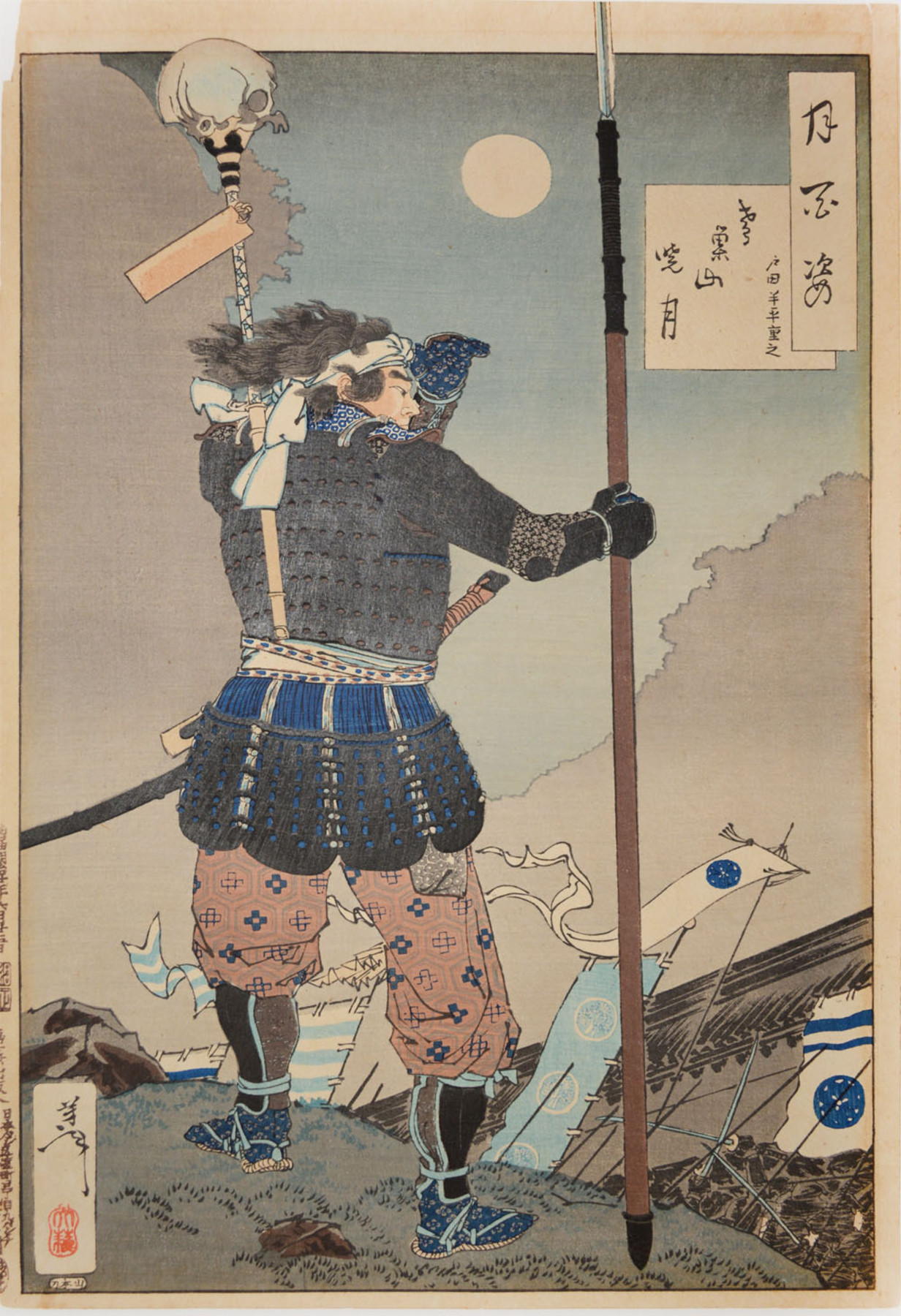
Japan
 The hoko spear was used in ancient Japan sometime between the
The hoko spear was used in ancient Japan sometime between the Yayoi period
The Yayoi period (弥生時代, ''Yayoi jidai'') (c. 300 BC – 300 AD) is one of the major historical periods of the Japanese archipelago. It is generally defined as the era between the beginning of food production in Japan and the emergence o ...
and the Heian period
The is the last division of classical Japanese history, running from 794 to 1185. It followed the Nara period, beginning when the 50th emperor, Emperor Kammu, moved the capital of Japan to Heian-kyō (modern Kyoto). means in Japanese. It is a ...
, but it became unpopular as early samurai
The samurai () were members of the warrior class in Japan. They were originally provincial warriors who came from wealthy landowning families who could afford to train their men to be mounted archers. In the 8th century AD, the imperial court d ...
often acted as Mounted archery, horseback archers. Medieval Japan employed spears again for infantrymen to use, but it was not until the 11th century in that samurai began to prefer spears over bows. Several polearms were used in the Japanese theatres; the naginata was a glaive-like weapon with a long, curved blade popularly among the samurai and the sōhei, Buddhist warrior-monks, often used against cavalry; the yari was a longer polearm, with a straight-bladed spearhead, which became the weapon of choice of both the samurai and the ashigaru (footmen) during the Sengoku Period, Warring States Era; the horseback samurai used shorter yari for his single-armed combat; on the other hand, ashigaru infantries used long yari (similar with European pike
Pike, Pikes or The Pike may refer to:
Fish
* Blue pike or blue walleye, an extinct color morph of the yellow walleye ''Sander vitreus''
* Ctenoluciidae, the "pike characins", some species of which are commonly known as pikes
* ''Esox'', genus of ...
) for their massed combat formation.
Philippines
 Filipino spears (sibat) were used as both a weapon and a tool throughout the Philippines. It is also called a ''bangkaw'' (after the Bankaw Revolt.), ''sumbling'' or ''palupad'' in the islands of Visayas and Mindanao. Sibat are typically made from rattan, either with a sharpened tip or a head made from metal. These heads may either be single-edged, double-edged or barbed. Styles vary according to function and origin. For example, a sibat designed for fishing may not be the same as those used for hunting.
The spear was used as the primary weapon in expeditions and battles against neighbouring island kingdoms and it became famous during the 1521 Battle of Mactan, where the chieftain Lapu Lapu of Cebu fought against Spanish forces led by Ferdinand Magellan who was subsequently killed.
Filipino spears (sibat) were used as both a weapon and a tool throughout the Philippines. It is also called a ''bangkaw'' (after the Bankaw Revolt.), ''sumbling'' or ''palupad'' in the islands of Visayas and Mindanao. Sibat are typically made from rattan, either with a sharpened tip or a head made from metal. These heads may either be single-edged, double-edged or barbed. Styles vary according to function and origin. For example, a sibat designed for fishing may not be the same as those used for hunting.
The spear was used as the primary weapon in expeditions and battles against neighbouring island kingdoms and it became famous during the 1521 Battle of Mactan, where the chieftain Lapu Lapu of Cebu fought against Spanish forces led by Ferdinand Magellan who was subsequently killed.
Africa
South Africa
 The various types of the assegai (a light spear or
The various types of the assegai (a light spear or javelin
A javelin is a light spear designed primarily to be thrown, historically as a ranged weapon. Today, the javelin is predominantly used for sporting purposes such as the javelin throw. The javelin is nearly always thrown by hand, unlike the sling ...
made of wood
Wood is a structural tissue/material found as xylem in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulosic fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin t ...
and pointed with iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
or fire-hardened tip) were used throughout Africa and it was the most common weapon used before the introduction of firearms. The Zulu people, Zulu, Xhosa people, Xhosa and other Nguni people, Nguni tribes of South Africa were renowned for their use of the assegai.
Shaka of the Zulu people, Zulu invented a shorter stabbing spear with a shaft and a larger, broader blade one foot (0.3m) long. This weapon is otherwise known as the ''iklwa'' or ''ixwa'', after the sound that was heard as it was withdrawn from the victim's wound. The traditional spear was not abandoned, but was used to range attack enemy formations before closing in for close quarters battle with the iklwa. This tactical combination originated during Shaka#Social and military revolution, Shaka's military reforms. This weapon was typically used with one hand while the off hand held a cowhide shield for protection.
Egypt
Similar to most armies of their period, Ancient Egypt, Ancient Egyptian forces were centered around the use of the spear. In battle, spearmen would be armed with abronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals (such as phosphorus) or metalloid ...
-tipped spear (dja) and shield (ikem), which were used in elaborate formations much like Greek and Roman forces. Before the Hyksos invasion into Egypt, wooden spears were used, which were prone to splinter, but the influx of a new population brought innovations around bronze technology. Unlike other cultures who wielded spears at this time, the Egyptians did not treat their Javelin, javelins (around 1 meter to 3.3 feet long) as disposable, using them both for thrusting and throwing.
The Americas
West Mexico and South America (Pre-Colombia)
As advanced metallurgy was largely unknown in Pre-Columbian era, pre-Columbian America outside of Metallurgy in pre-Columbian America, Western Mexico and South America, most weapons in Meso-America were made of wood orobsidian
Obsidian ( ) is a naturally occurring volcanic glass formed when lava extrusive rock, extruded from a volcano cools rapidly with minimal crystal growth. It is an igneous rock. Produced from felsic lava, obsidian is rich in the lighter element ...
. This did not mean that they were less lethal, as obsidian may be sharpened to become many times sharper than steel. Meso-American spears varied greatly in shape and size. While the Aztecs preferred the sword-like macuahuitl clubs for fighting, the advantage of a far-reaching thrusting weapon was recognised, and a large portion of the army would carry the tepoztopilli into battle. The tepoztopilli was a polearm, and to judge from depictions in various Aztec codices, it was roughly the height of a man, with a broad wooden head about twice the length of the users' palm or shorter, edged with razor-sharp obsidian blades which were deeply set in grooves carved into the head, and cemented in place with bitumen or plant resin as an adhesive. The tepoztopilli was able both to thrust and slash effectively.
Throwing spears also were used extensively in Meso-American warfare, usually with the help of an atlatl
A spear-thrower, spear-throwing lever, or ''atlatl'' (pronounced or ; Classical Nahuatl, Nahuatl ''ahtlatl'' ) is a tool that uses leverage to achieve greater velocity in Dart (missile), dart or javelin-throwing, and includes a Plain bearing, b ...
. Throwing spears were typically shorter and more stream-lined than the tepoztopilli, and some had obsidian edges for greater penetration.
Native Americans
Typically, most spears made by Native Americans were created from materials surrounding their communities. Usually, the shaft of the spear was made with a wooden stick while the head of the spear was fashioned from arrowheads, pieces of metal such as copper, or a bone that had been sharpened. Spears were a preferred weapon by many since it was inexpensive to create, could more easily be taught to others, and could be made quickly and in large quantities. Native Americans used the buffalo pound method to kill buffalo, which required a hunter to dress as a buffalo and lure one into a ravine where other hunters were hiding. Once the buffalo appeared, the other hunters would kill him with spears. A variation of this technique, called the buffalo jump, was when a runner would lead the animals towards a cliff. As the buffalo got close to the cliff, other members of the tribe would jump out from behind rocks or trees and scare the buffalo over the cliff. Other hunters would be waiting at the bottom of the cliff to spear the animal to death.Hunting
 One of the earliest forms of killing prey for humans, hunting game with a spear and spear fishing continues to this day as both a means of catching food and as a cultural activity. Some of the most common prey for early humans were megafauna such as mammoths which were hunted with various kinds of spear. One theory for the Quaternary extinction event#Hunting hypothesis, Quaternary extinction event was that most of these animals were hunted to extinction by humans with spears. Even after the invention of other hunting weapons such as the Bow and arrow, bow and Sling (weapon), sling, the spear continued to be used, either as a projectile weapon or used by hand, such as in bear hunting and boar hunting.
One of the earliest forms of killing prey for humans, hunting game with a spear and spear fishing continues to this day as both a means of catching food and as a cultural activity. Some of the most common prey for early humans were megafauna such as mammoths which were hunted with various kinds of spear. One theory for the Quaternary extinction event#Hunting hypothesis, Quaternary extinction event was that most of these animals were hunted to extinction by humans with spears. Even after the invention of other hunting weapons such as the Bow and arrow, bow and Sling (weapon), sling, the spear continued to be used, either as a projectile weapon or used by hand, such as in bear hunting and boar hunting.
Types
 * Barred spears: A barred spear has a crossbar beneath the blade, to prevent too deep a penetration of the spear into an animal. The bar may be forged as part of the spearhead or may be more loosely tied by means of loops below the blade. Barred spears are known from the Bronze Age, but the first historical record of their use in Europe is found in the writings of Xenophon in the 5th century BC. Examples also are shown in Roman art. In the Middle Ages, a winged or lugged war-spear was developed (#Infantry, see above), but the later Middle Ages saw the development of specialised types, such as the boar-spear and the bear-spear. The boar-spear could be used both on foot or horseback.
* Javelin
* Harpoon
* Trident
* Barred spears: A barred spear has a crossbar beneath the blade, to prevent too deep a penetration of the spear into an animal. The bar may be forged as part of the spearhead or may be more loosely tied by means of loops below the blade. Barred spears are known from the Bronze Age, but the first historical record of their use in Europe is found in the writings of Xenophon in the 5th century BC. Examples also are shown in Roman art. In the Middle Ages, a winged or lugged war-spear was developed (#Infantry, see above), but the later Middle Ages saw the development of specialised types, such as the boar-spear and the bear-spear. The boar-spear could be used both on foot or horseback.
* Javelin
* Harpoon
* Trident
Modern revival
Spear hunting fell out of favor in most of Europe in the 18th century, but continued in Germany, enjoying a revival in the 1930s. Spear hunting is still practiced in the United States. Animals taken are primarily wild boar and deer, although trophy animals as large as Cape Buffalo have been hunted with spears. Alligators are hunted in Florida with a type of harpoon. In underwater settings, the practice of sport fishing with Speargun, spearguns is also quite prominent. The invention of the speargun is attributed to either Alec Kramarenko in the mid-1930s or Georges Beuchat in 1947.Gymnastics
One of the gymnastic exercises performed by the ancient Greeks was the throwing of a spear, referred to as ἀκυντισμός.In myth and legend
Symbolism
 Like many weapons, a spear may also be a symbol of power.
The Celts would symbolically destroy a dead warrior's spear either to prevent its use by another or as a sacrificial offering.
In classical Greek mythology Zeus' bolts of lightning may be interpreted as a symbolic spear. Some would carry that interpretation to the spear that frequently is associated with Athena, interpreting her spear as a symbolic connection to some of Zeus' power beyond the Aegis once he rose to replacing other deities in the Pantheon (gods), pantheon. Athena was depicted with a spear prior to that change in myths, however. Chiron's wedding-gift to Peleus when he married the nymph Thetis in classical Greek mythology, was an ashen spear as the nature of ashwood with its straight grain made it an ideal choice of wood for a spear.
The Romans and their early enemies would force prisoners to walk underneath a 'yoke of spears', which humiliated them. The yoke would consist of three spears, two upright with a third tied between them at a height which made the prisoners stoop. It has been suggested that the arrangement has a magic (paranormal), magical origin, a way to trap evil spirits.
In Norse mythology, the god Odin's spear (named Gungnir) was made by the sons of Ivaldi. It had the special property that it never missed its mark. During the War with the Vanir, Odin symbolically threw Gungnir into the Vanir host. This practice of symbolically casting a spear into the enemy ranks at the start of a fight was sometimes used in historic clashes, to seek Odin's support in the coming battle. In Richard Wagner, Wagner's opera ''Siegfried (opera), Siegfried'', the haft of Gungnir is said to be from the "World-Tree" Yggdrasil.
Other spears of religious significance are the Holy Lance and the Spear Luin, Lúin of Celtchar, believed by some to have vast mystical powers.
James Frazer, Sir James George Frazer in ''The Golden Bough'' noted the phallic nature of the spear and suggested that in the Arthurian legends the spear or lance functioned as a symbol of male fertility, paired with the Grail (as a symbol of female fertility).
Like many weapons, a spear may also be a symbol of power.
The Celts would symbolically destroy a dead warrior's spear either to prevent its use by another or as a sacrificial offering.
In classical Greek mythology Zeus' bolts of lightning may be interpreted as a symbolic spear. Some would carry that interpretation to the spear that frequently is associated with Athena, interpreting her spear as a symbolic connection to some of Zeus' power beyond the Aegis once he rose to replacing other deities in the Pantheon (gods), pantheon. Athena was depicted with a spear prior to that change in myths, however. Chiron's wedding-gift to Peleus when he married the nymph Thetis in classical Greek mythology, was an ashen spear as the nature of ashwood with its straight grain made it an ideal choice of wood for a spear.
The Romans and their early enemies would force prisoners to walk underneath a 'yoke of spears', which humiliated them. The yoke would consist of three spears, two upright with a third tied between them at a height which made the prisoners stoop. It has been suggested that the arrangement has a magic (paranormal), magical origin, a way to trap evil spirits.
In Norse mythology, the god Odin's spear (named Gungnir) was made by the sons of Ivaldi. It had the special property that it never missed its mark. During the War with the Vanir, Odin symbolically threw Gungnir into the Vanir host. This practice of symbolically casting a spear into the enemy ranks at the start of a fight was sometimes used in historic clashes, to seek Odin's support in the coming battle. In Richard Wagner, Wagner's opera ''Siegfried (opera), Siegfried'', the haft of Gungnir is said to be from the "World-Tree" Yggdrasil.
Other spears of religious significance are the Holy Lance and the Spear Luin, Lúin of Celtchar, believed by some to have vast mystical powers.
James Frazer, Sir James George Frazer in ''The Golden Bough'' noted the phallic nature of the spear and suggested that in the Arthurian legends the spear or lance functioned as a symbol of male fertility, paired with the Grail (as a symbol of female fertility).
 The Hindu god of war Kartikeya, Murugan is worshipped by
The Hindu god of war Kartikeya, Murugan is worshipped by Tamils
The Tamils ( ), also known by their endonym Tamilar, are a Dravidian peoples, Dravidian ethnic group who natively speak the Tamil language and trace their ancestry mainly to the southern part of the Indian subcontinent. The Tamil language is o ...
in the form of the spear called ''Vel
Vel () is a divine spear associated with Murugan, the Tamil Hindu god of war.
Significance
According to Shaiva tradition, the goddess Parvati presented the Vel to her son Kartikeya(also known as Murugan), as an embodiment of her shakti, in ...
'', which is his primary weapon.
The term ''spear'' is also used (in a somewhat archaic manner) to describe the male line of a family, as opposed to the distaff or female line.
Legends
*Amenonuhoko, spear of Izanagi and Izanami, creator gods in Japanese mythology *Gáe Bulg, spear of Cúchulainn, hero in Irish mythology *Gáe Buide and Gáe Derg, spears of Diarmuid Ua Duibhne which could inflict wounds that none can recover from *Green Dragon Crescent Blade, a guan dao wielded by General Guan Yu in the ''Romance of the Three Kingdoms'' *Gungnir, spear of Odin, a god in Norse mythology *Holy Lance, said to be the spear that pierced the side of Jesus *Pelian Spear, a spear that only Achilles could wield, inherited from his father Peleus, made by Chiron from an ash tree on Mount Pelion. *Excalibur#Arthur's other weapons, Rhongomyniad referred to simply as Ron ("spear") in Geoffrey of Monmouth's ''History of Britain'', the spear of King Arthur.P. K. Ford, "On the Significance of some Arthurian Names in Welsh", in ''Bulletin of the Board of Celtic Studies'' 30 (1983), pp.268–273 at p.71; R. Bromwich and D. Simon Evans, ''Culhwch and Olwen. An Edition and Study of the Oldest Arthurian Tale'' (Cardiff: University of Wales Press, 1992), p.64 *Zhang Fei#In Romance of the Three Kingdoms, Serpent Spear wielded by General Zhang Fei in the ''Romance of the Three Kingdoms'' *Spear of Fuchai, the spear used by Goujian's arch-rival, King Fuchai of Wu, in China *Spear of Lugh, named after Lugh, a god in Irish mythology *Trident, a three-pronged fishing spear associated with a number of water deity, water deities, including the Etruscan Nethuns, Greek Poseidon, and Roman Neptune (mythology), Neptune. *Trishula, a three-pronged spear wielded by the Hindu deities Durga and Shiva *Vel
Vel () is a divine spear associated with Murugan, the Tamil Hindu god of war.
Significance
According to Shaiva tradition, the goddess Parvati presented the Vel to her son Kartikeya(also known as Murugan), as an embodiment of her shakti, in ...
, a flattened broad tipped spear used by the Hindu deity Murugan
See also
* List of types of spears * Viking Age arms and armour * ProjectileRelated weapons
* Arrow (weapon), Arrow * Assegai * Atlatl * Bill (weapon), Bill * Dart (missile), Dart * Glaive * Halberd * Javelin * Kontos (weapon), Kontos * Lance * Naginata * Pike (weapon), Pike * Pilum * Polearm * Spear thrower * Woomera (spear-thrower), Woomera * XystonNotes and references
{{Authority control Spears, * Polearms Projectiles