|
Triarii
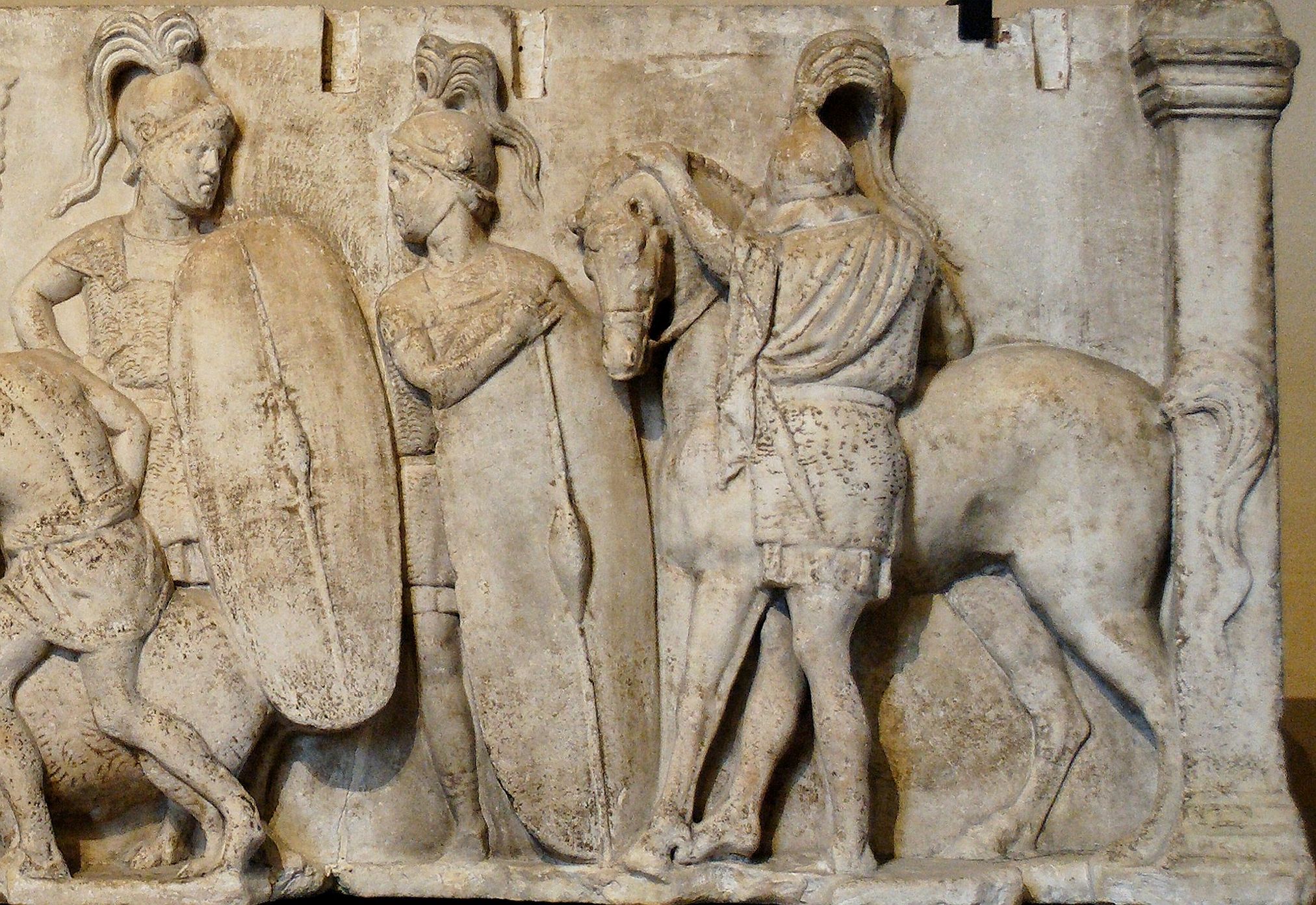
''Triarii'' (: ''triarius'') ("the third liners") were one of the elements of the early Roman military manipular legions of the early Roman Republic (509 BC – 107 BC). They were the oldest and among the wealthiest men in the army and could afford high quality equipment. They wore heavy metal armor and carried large shields, their usual position being the third battle line. They were equipped with spears and were considered to be elite soldiers among the legion. During the Camillan era, they fought in a shallow phalanx formation, supported by light troops. In most battles ''triarii'' were not used because the lighter troops usually defeated the enemy before the ''triarii'' were committed to the battle. They were meant to be used as a decisive force in the battle, thus prompting an old Roman saying: ''res ad triarios venit'', 'it comes down to the triarii', which meant carrying on to the bitter end. History and deployment According to author Pat Southern, ''triarii'' may ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural History Of The Roman Military
The structural history of the Roman military concerns the major transformations in the organization and constitution of ancient Rome's armed forces, "the most effective and long-lived military institution known to history."''Encyclopædia Britannica'', Eleventh Edition (1911), ''The Roman Army'' At the highest level of structure, the forces were split into the Roman army and the Roman navy, although these two branches were less distinct than in many modern national defense forces. Within the top levels of both army and navy, structural changes occurred as a result of both positive military reform and organic structural evolution. These changes can be divided into four distinct phases. ;Phase I: The army was derived from obligatory annual military service levied on the citizenry, as part of their duty to the state. During this period, the Roman army would wage seasonal campaigns against largely local adversaries. ;Phase II: As the extent of the territories falling under Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principes
''Principes'' (: ''princeps'') were Spear, spearmen, and later Swordsmanship, swordsmen, in the Roman army of the mid-Republic, armies of the early Roman Republic. They were men in the prime of their lives who were fairly wealthy, and could afford decent equipment. They were the heavy infantry, heavier infantry of the Roman legion, legion who carried large shields and wore good quality armor. Their usual position was the second battle line. They fought in a Roman infantry tactics#Layout of the triple line, quincunx formation, supported by light troops. They were eventually disbanded after the so-called "Marian reforms" of the late Roman Republic. History and deployment According to Pat Southern, ''principes'' appear to have been born from remnants of the old second class of the army under the Kings of Rome, Etruscan kings when it was reformed by Marcus Furius Camillus. The second class stood in some of the first few ranks of a very large Phalanx formation, phalanx and were equip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hastati
''Hastati'' (: ''hastatus'') were a class of infantry employed in the Structural history of the Roman military#Manipular legion (315 BC – 107 BC), armies of the early Roman Republic, who originally fought as spearmen and later as swordsmen. These soldiers were the staple unit after Rome threw off Etruscan civilization, Etruscan rule. They were originally some of the poorest men in the legion, and could afford only modest Roman military personal equipment, equipment—light chainmail and other miscellaneous equipment. The Senate supplied their soldiers with only a short stabbing sword, the gladius, and their distinctive squared shield, the Scutum (shield), scutum. The ''hastatus'' was typically equipped with these, and one or two soft iron tipped throwing spears called Pilum, pila. This doubled their effectiveness, not only as a strong leading edge to their Maniple (military unit), maniple, but also as a stand-alone missile troop. Later, the ''hastati'' contained the younger men ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maniple (military Unit)
Maniple (; ) was a tactical unit of the Roman Republican armies, adopted during the Samnite Wars (343–290 BC). It was also the name of the military insignia carried by such units. Maniple members, called ''commanipulares'' (: ''commanipularis'') were seen as each other's brothers-in-arms, but without the domestic closeness of the eight-man '' contubernium''. Cohorts replaced maniples as organisational units. History The manipular system was adopted around 315 BC, during the Second Samnite War. The rugged terrain of Samnium, where the war was fought, was not conducive to the phalanx formation which the Romans had inherited from the Etruscans and Ancient Greeks. The main battle troops of the Etruscans and Latins of this period comprised Greek-style hoplite phalanxes, inherited from the original Greek phalanx military unit. After suffering a series of defeats, culminating in the surrender of the entire army without resistance at Caudine Forks, the Romans abandoned the ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accensi
The term ''accensi'' (: ''accensus'') is applied to two different groups. Originally, the ''accensi'' were light infantry in the armies of the early Roman Republic. They were the poorest men in the legion, and could not afford much equipment. They did not wear armour or carry shields, and their usual position was part of the third battle line. They fought in a loose formation, supporting the heavier troops. They were eventually phased out by the time of Second Punic War. In the later Roman Republic the term was used for civil servants who assisted the elected magistrates, particularly in the courts, where they acted as ushers and clerks. Infantry History and deployment ''Accensi'' appear to have evolved from the old fifth class of the army under the Etruscan kings when it was reformed by Marcus Furius Camillus. The fifth class was made up of the poorest soldiers in the legion who were equipped with slings and perhaps a small shield. They acted as skirmishers, screening the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rorarii
''Rorarii'' were soldiers who formed the final lines, or else provided a reserve thereby, in the ancient pre- Marian Roman army. They may have been used with the ''triarii'' in battle near the final stages of fighting, since they are recorded as being located at the rear of the main battle formation. They may have been similar in role to the ''accensi'', acting as supernumeraries and filling the places of fallen soldiers as a battle or campaign wore on. Alternatively, they may have been skirmishers akin to ''velites'' as stated by Livy in Book VIII.8. Unfortunately, the evidence is so limited that it is difficult to understand what direct role the ''rorarii'' may have had, if any, in fighting. It seems most likely that they were not part of the line in the same way as ''triarii'', ''principes'' and ''hastati'' were. They may also have been the light equivalent of the ''triarii'', just like the ''accensi'' would have been the light equivalent of the ''principes'', both ''rorarii'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heavy Infantry
Heavy infantry consisted of heavily armed and armoured infantrymen who were trained to mount frontal assaults and/or anchor the defensive center of a battle line. This differentiated them from light infantry who were relatively mobile and lightly armoured skirmisher troops intended for screening, scouting, and other tactical roles unsuited to soldiers carrying heavier loads. Heavy infantry typically made use of dense battlefield formations, such as shield wall or phalanx, multiplying their effective weight of arms with force concentration. Heavy infantry were critical to many ancient armies, such as the Greek hoplites, Macedonian phalangites, and Roman legionaries. After the fall of Rome, heavy infantry declined in Europe but returned to dominance in the Late Middle Ages with Swiss pikemen and German Landsknechts. With the rise of firearms during early modern warfare, dense formations became increasingly hazardous, and heavy armours were either ineffective o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoplites
Hoplites ( ) ( ) were citizen-soldiers of Ancient Greek city-states who were primarily armed with spears and shields. Hoplite soldiers used the phalanx formation to be effective in war with fewer soldiers. The formation discouraged the soldiers from acting alone, for this would compromise the formation and minimize its strengths. The hoplites were primarily represented by free citizens – propertied farmers and artisans – who were able to afford a linen or bronze armour suit and weapons (estimated at a third to a half of its able-bodied adult male population). Some states maintained a small elite professional unit, known as the '' epilektoi'' or logades ('the chosen') because they were picked from the regular citizen infantry. These existed at times in Athens, Sparta, Argos, Thebes, and Syracuse, among other places. Hoplite soldiers made up the bulk of ancient Greek armies. In the 8th or 7th century BC, Greek armies adopted the phalanx formation. The formation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
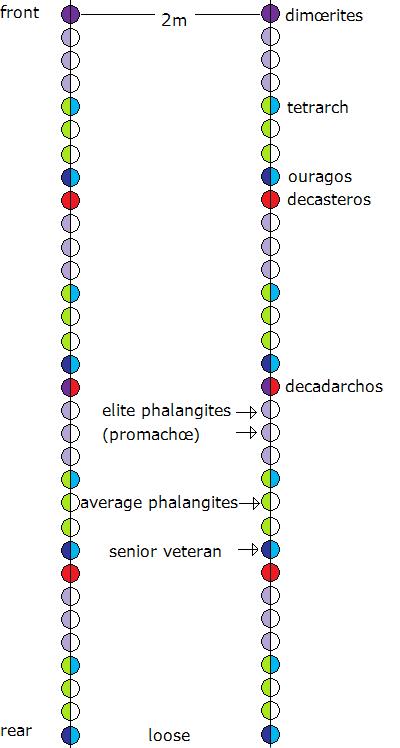
Phalanx Formation
The phalanx (: phalanxes or phalanges) was a rectangular mass military Tactical formation, formation, usually composed entirely of heavy infantry armed with spears, pike (weapon), pikes, sarissas, or similar polearms tightly packed together. The term is particularly used to describe the use of this formation in ancient Greek warfare, although the ancient Greek writers used it to also describe any massed infantry formation, regardless of its equipment. Arrian uses the term in his ''Array against the Alans'' when he refers to his legions. In Greek texts, the phalanx may be deployed for battle, on the march, or even camped, thus describing the mass of infantry or cavalry that would deploy in line during battle. They marched forward as one entity. The term itself, as used today, does not refer to a distinctive military unit or division (e.g., the Roman legion or the contemporary Western-type battalion), but to the type of formation of an army's troops. Therefore, this term does not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire following the War of Actium. During this period, Rome's control expanded from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean world. Roman society at the time was primarily a cultural mix of Latins (Italic tribe), Latin and Etruscan civilization, Etruscan societies, as well as of Sabine, Oscan, and Greek cultural elements, which is especially visible in the Ancient Roman religion and List of Roman deities, its pantheon. Its political organisation developed at around the same time as direct democracy in Ancient Greece, with collective and annual magistracies, overseen by Roman Senate, a senate. There were annual elections, but the republican system was an elective olig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spear
A spear is a polearm consisting of a shaft, usually of wood, with a pointed head. The head may be simply the sharpened end of the shaft itself, as is the case with Fire hardening, fire hardened spears, or it may be made of a more durable material fastened to the shaft, such as bone, flint, obsidian, copper, bronze, iron, or steel. The most common design for hunting and/or warfare, since modern times has incorporated a metal spearhead shaped like a triangle, lozenge (shape), diamond, or Glossary of leaf morphology, leaf. The heads of fishing spears usually feature multiple sharp Tine (structural), points, with or without barbs. Spears can be divided into two broad categories: those designed for thrusting as a melee weapon (including weapons such as lances and Pike (weapon), pikes) and those designed for throwing as a ranged weapon (usually referred to as javelins). The spear has been used throughout human history as a weapon for hunting and/or fishing and for warfare. Along with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phalanx
The phalanx (: phalanxes or phalanges) was a rectangular mass military formation, usually composed entirely of heavy infantry armed with spears, pikes, sarissas, or similar polearms tightly packed together. The term is particularly used to describe the use of this formation in ancient Greek warfare, although the ancient Greek writers used it to also describe any massed infantry formation, regardless of its equipment. Arrian uses the term in his ''Array against the Alans'' when he refers to his legions. In Greek texts, the phalanx may be deployed for battle, on the march, or even camped, thus describing the mass of infantry or cavalry that would deploy in line during battle. They marched forward as one entity. The term itself, as used today, does not refer to a distinctive military unit or division (e.g., the Roman legion or the contemporary Western-type battalion), but to the type of formation of an army's troops. Therefore, this term does not indicate a standard combat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |