Spanish Gothic Architecture on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Spanish Gothic architecture is the style of architecture prevalent in Spain in the Late Medieval period.
The
 *
*  spare grey walls
* central lantern
* altar placed at western entrance
* radiating chapels
* tympanum
* gargoyles
* ornate attributes such as elegant molding
spare grey walls
* central lantern
* altar placed at western entrance
* radiating chapels
* tympanum
* gargoyles
* ornate attributes such as elegant molding
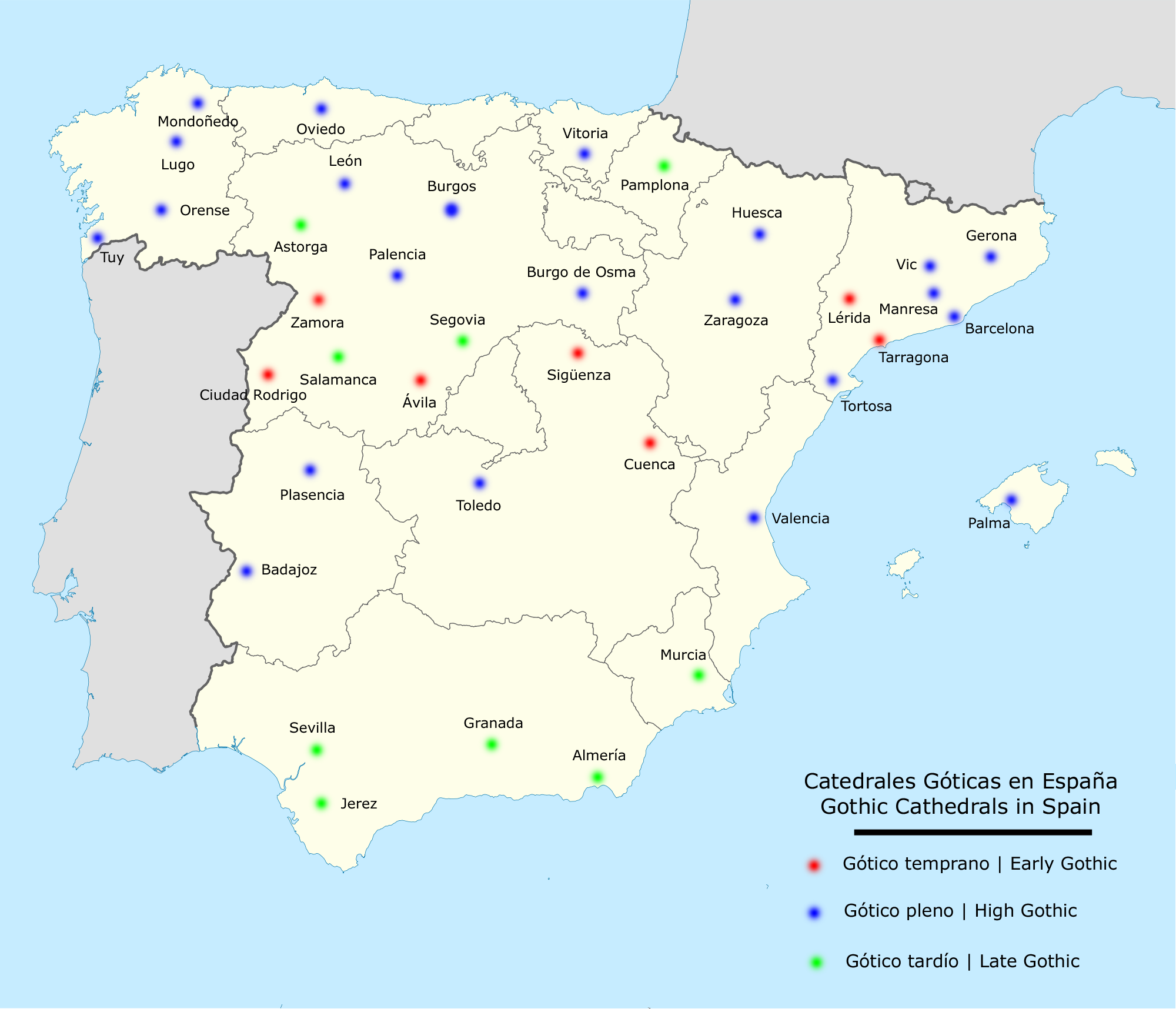 The designations of styles in Spanish Gothic architecture are as follows. Dates are approximate.
* Early Gothic (12th century)
* High Gothic (13th century)
*
The designations of styles in Spanish Gothic architecture are as follows. Dates are approximate.
* Early Gothic (12th century)
* High Gothic (13th century)
*
File:Cathedral of Avila, Gothic, 11th - 15th cents (21) (29304779331).jpg, Ávila Cathedral, Exterior
File:Cathedral of Avila, Gothic, 11th - 15th cents (8) (28761044424).jpg, Ávila Cathedral, Interior
File:Escaleras a la Catedral -- 2023 -- Burgos, Castilla y Le├│n, Espa├▒a.jpg, Burgos Cathedral
File:Toledo Cathedral (52142175573).jpg,
Gothic style
Gothic architecture is an architectural style that was prevalent in Europe from the late 12th to the 16th century, during the High and Late Middle Ages, surviving into the 17th and 18th centuries in some areas. It evolved from Romanesque ar ...
started in Spain as a result of Central European influence in the twelfth century when late Romanesque alternated with few expressions of pure Gothic architecture. The High Gothic arrives with all its strength via the pilgrimage route, the Way of St. James, in the thirteenth century. Some of the most pure Gothic cathedrals in Spain, closest related to the German and French Gothic, were built at this time.
In some cases the Gothic style was built and decorated with Mud├®jar elements by Mud├®jar
Mud├®jar were Muslims who remained in Iberia in the late medieval period following the Christian reconquest. It is also a term for Mud├®jar art, which was greatly influenced by Islamic art, but produced typically by Christian craftsmen for C ...
craftsmen and Christian craftsmen influenced by them, creating a highly distinctive Gothic style unique to Spain and Portugal. Some noteworthy postŌłÆthirteenth-century Gothic styles in Spain are the Levantine Gothic, characterized by its structural achievements and the unification of space, and the Isabelline Gothic
The Isabelline style, also called the Isabelline Gothic (), or Castilian late Gothic, was the dominant architectural style of the Crown of Castile during the reign of the Catholic Monarchs, Queen Isabella I of Castile and King Ferdinand II of A ...
, under the Catholic Monarchs
The Catholic Monarchs were Isabella I of Castile, Queen Isabella I of Crown of Castile, Castile () and Ferdinand II of Aragon, King Ferdinand II of Crown of Arag├│n, Aragon (), whose marriage and joint rule marked the ''de facto'' unification of ...
, that predicated a slow transition to Renaissance architecture
Renaissance architecture is the European architecture of the period between the early 15th and early 16th centuries in different regions, demonstrating a conscious revival and development of certain elements of Ancient Greece, ancient Greek and ...
. Gothic construction ended in Spain in the sixteenth century.
In 1172, French architect Giral Fruchel designed the first ever Gothic cathedral in Spain. Ávila Cathedral, a cathedral located in Central Spain, represents a blend of the Romanesque and Gothic styles. Alfonso VIII
Alfonso VIII (11 November 11555 October 1214), called the Noble (El Noble) or the one of Las Navas (el de las Navas), was King of Castile from 1158 to his death and King of Toledo. After having suffered a great defeat with his own army at Alarc ...
, former King of the Castile Kingdom, was inspired by the Basilica St. Denis in France and wanted Ávila's plan to incorporate double ambulatory and radiating chapels. A double ambulatory consists of an apse
In architecture, an apse (: apses; from Latin , 'arch, vault'; from Ancient Greek , , 'arch'; sometimes written apsis; : apsides) is a semicircular recess covered with a hemispherical Vault (architecture), vault or semi-dome, also known as an ' ...
that is surrounded by two walkways. Radiating chapels, are small, semicircular chapels
A chapel (from , a diminutive of ''cappa'', meaning "little cape") is a Christian place of prayer and worship that is usually relatively small. The term has several meanings. First, smaller spaces inside a church that have their own altar are o ...
that appear along the apse of a church. Alfonso's wish was granted, as Ávila Cathedral embodies these characteristics.
In 1227, Archbishop Rodrigo Jimenez de Rada initiated the rebuilding of the Toledo Cathedral
The Primatial Metropolitan Cathedral of Saint Mary of the Assumption (), is a Roman Catholic cathedral in Toledo, Spain. It is the seat of the Metropolitan Archdiocese of Toledo. Since 1088, it holds the honorific title of Primatial, granted by ...
in the Gothic style as well. Prior to this reconstruction, Toledo was under Muslim control and possessed Islamic architectural elements. Toledo's ground plan, for instance, resembled the ground plan of a mosque
A mosque ( ), also called a masjid ( ), is a place of worship for Muslims. The term usually refers to a covered building, but can be any place where Salah, Islamic prayers are performed; such as an outdoor courtyard.
Originally, mosques were si ...
. The fusion of Islamic and French Gothic influences gave rise to a distinctive and uniquely Spanish Gothic architectural style, and Toledo Cathedral was among the first to exhibit this. Other physical attributes that Toledo Cathedral possesses are great bronze doors that make up the central portal of the building, plain vaults, double staggered aisles, and elaborate stonemasonry with colored marbles. Toledo is a monumental Gothic cathedral and represents architectural experimentation, as this was built during the upsurge of Gothic architecture in Spain.
Similar to Toledo, Burgos Cathedral was constructed in the early thirteenth century, in 1221. Both Toledo and Burgos Cathedrals have been altered many times since their initial construction. However, Burgos Cathedral is still deemed a favorable example of High Gothic Spanish architectural style. This cathedral incorporates flying buttresses
The flying buttress (''arc-boutant'', arch buttress) is a specific form of buttress composed of a ramping arch that extends from the upper portion of a wall to a pier of great mass, to convey to the ground the lateral forces that push a wall out ...
, clerestory windows, pier arches, and a rose window
Rose window is often used as a generic term applied to a circular window, but is especially used for those found in Gothic cathedrals and churches. The windows are divided into segments by stone mullions and tracery. The term ''rose window'' wa ...
. In addition to this, the choir
A choir ( ), also known as a chorale or chorus (from Latin ''chorus'', meaning 'a dance in a circle') is a musical ensemble of singers. Choral music, in turn, is the music written specifically for such an ensemble to perform or in other words ...
in Burgos Cathedral is located in the center of the nave
The nave () is the central part of a church, stretching from the (normally western) main entrance or rear wall, to the transepts, or in a church without transepts, to the chancel. When a church contains side aisles, as in a basilica-type ...
. This was unique because most gothic cathedrals positioned the choir in between the nave and the altar
An altar is a table or platform for the presentation of religion, religious offerings, for sacrifices, or for other ritualistic purposes. Altars are found at shrines, temples, Church (building), churches, and other places of worship. They are use ...
. Burgos Cathedral also contains vaults that are slightly domical and diagonal ribs. These key attributes suggest that the architects of this structure were influenced by French Gothic architecture.
In the fourteenth century, Spain started to introduce ornate features in their Gothic structures. Catalonian architecture, architecture belonging to the Catalonian region in northeastern Spain, was seen as superior during this time due to their frequent use of design elements. The Chapel of Santa Ágata in the Royal Palace of Barcelona, constructed from 1303 to 1310, exhibits double windows, polished contours, and refined proportions. Similar to other Gothic cathedrals, the Chapel of Agueda displays stained glass
Stained glass refers to coloured glass as a material or art and architectural works created from it. Although it is traditionally made in flat panels and used as windows, the creations of modern stained glass artists also include three-dimensio ...
windows as well as religious iconography
Iconography, as a branch of art history, studies the identification, description and interpretation of the content of images: the subjects depicted, the particular compositions and details used to do so, and other elements that are distinct fro ...
. These features highlight the artistry of Spanish Gothic architecture that can still be seen in architectural design today. The Ace Hotel
Ace Hotel is a chain of hotels headquartered in Los Angeles and New York City. Founded in 1999 in Seattle, it operates hotels Internationally in 4 continents, with locations in; Brooklyn, New York City; Palm Springs, California; Seattle, Washing ...
in Los Angeles is an example of Spanish Gothic influence in contemporary time.
Key Spanish Gothic Architectural Elements
 *
* nave
The nave () is the central part of a church, stretching from the (normally western) main entrance or rear wall, to the transepts, or in a church without transepts, to the chancel. When a church contains side aisles, as in a basilica-type ...
* aisles
** double ambulatory
* flying buttresses
The flying buttress (''arc-boutant'', arch buttress) is a specific form of buttress composed of a ramping arch that extends from the upper portion of a wall to a pier of great mass, to convey to the ground the lateral forces that push a wall out ...
** double flying buttresses
* Arches
An arch is a curved vertical structure span (engineering), spanning an open space underneath it. Arches may support the load above them, or they may perform a purely decorative role. As a decorative element, the arch dates back to the 4th mill ...
:
** pointed arch
** pier arches
* Vaults:
** diamond vaults
** cross-ribbed vaulting
* Windows:
** clerestory windows
** rose window
Rose window is often used as a generic term applied to a circular window, but is especially used for those found in Gothic cathedrals and churches. The windows are divided into segments by stone mullions and tracery. The term ''rose window'' wa ...
* Sequence of Gothic styles in Spain
 The designations of styles in Spanish Gothic architecture are as follows. Dates are approximate.
* Early Gothic (12th century)
* High Gothic (13th century)
*
The designations of styles in Spanish Gothic architecture are as follows. Dates are approximate.
* Early Gothic (12th century)
* High Gothic (13th century)
* Mud├®jar
Mud├®jar were Muslims who remained in Iberia in the late medieval period following the Christian reconquest. It is also a term for Mud├®jar art, which was greatly influenced by Islamic art, but produced typically by Christian craftsmen for C ...
Gothic (from the 13th to the 15th centuries)
* Levantino Gothic (14th century)
* Valencian Gothic (14th and 15th century)
* Catalan Gothic
* Flamboyant/Late Gothic (15th century)
* Isabelline Gothic
The Isabelline style, also called the Isabelline Gothic (), or Castilian late Gothic, was the dominant architectural style of the Crown of Castile during the reign of the Catholic Monarchs, Queen Isabella I of Castile and King Ferdinand II of A ...
(15th century)
* Plateresque Gothic (15th century)
Examples
Early Gothic
* Cathedral of ├üvila * Cathedral of Cuenca * Cathedral of Sig├╝enza *Abbey of Santa Mar├Ła la Real de Las Huelgas
The Abbey of Santa Mar├Ła la Real de Las Huelgas is a monastery of Cistercian nuns located approximately 1.5 km west of the city of Burgos in Spain. The word , which usually refers to "labour strikes" in modern Spanish, refers in this case ...
in Burgos
Burgos () is a city in Spain located in the autonomous community of Castile and Le├│n. It is the capital and most populous municipality of the province of Burgos.
Burgos is situated in the north of the Iberian Peninsula, on the confluence of th ...
High Gothic
*Cathedral of Burgos
The Cathedral of Saint Mary of Burgos () is a Catholic church dedicated to the Virgin Mary located in the historical center of the Spain, Spanish city of Burgos. Its official name is the Holy Metropolitan Cathedral Basilica Church of St Mary of ...
* Cathedral of Burgo de Osma
* Cathedral of Le├│n
* Cathedral of Toledo
* Palace of the Kings of Navarre in Olite
* San Pablo Church, Valladolid
Valladolid ( ; ) is a Municipalities of Spain, municipality in Spain and the primary seat of government and ''de facto'' capital of the Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Castile and Le├│n. It is also the capital of the pr ...
Mud├®jar Gothic
* Cathedral of San Salvador, inZaragoza
Zaragoza (), traditionally known in English as Saragossa ( ), is the capital city of the province of Zaragoza and of the autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Aragon, Spain. It lies by the Ebro river and its tributaries, the ...
*Castillo de Coca
The Castle of Coca is a castle located in the Coca, Segovia, Coca Municipalities of Spain, municipality, central Spain. The castle was constructed in the 15th century and has been considered to be one of the best examples of Spanish Mud├®jar, Mud ...
in Coca
Coca is any of the four cultivated plants in the family Erythroxylaceae, native to western South America. Coca is known worldwide for its psychoactive alkaloid, cocaine. Coca leaves contain cocaine which acts as a mild stimulant when chewed or ...
* St. Mart├Łn's Tower in Teruel
Teruel () is a city in Aragon, located in eastern Spain, and is also the capital of Teruel (province), Teruel Province. It had a population of 35,900 as of 2022, making it the least populated provincial capital in Spain. It is noted for its har ...
Valencian Gothic
*Valencia Cathedral
Valencia Cathedral, at greater length the Metropolitan CathedralŌĆōBasilica of the Assumption of Our Lady of Valencia (, ), also known as St Mary's Cathedral, is a Catholic church in Valencia, Spain.
The cathedral was consecrated in 1238 by ...
* Lonja de la Seda, in Valencia
Valencia ( , ), formally Val├©ncia (), is the capital of the Province of Valencia, province and Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Valencian Community, the same name in Spain. It is located on the banks of the Turia (r ...
* Torres de Serranos
* Palace of the Borgias
* Monastery of Sant Jeroni de Cotalba, in Alfauir.
* Monastery of Santa Mar├Ła de la Valldigna, in Simat de la Valldigna.
* Basilica of Santa Maria, in Alicante
Alicante (, , ; ; ; officially: ''/'' ) is a city and municipalities of Spain, municipality in the Valencian Community, Spain. It is the capital of the province of Alicante and a historic Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean port. The population ...
.
* Orihuela Cathedral, in Orihuela
Orihuela (; ''Corpus Topon├Łmic Valenci├Ā''. Acad├©mia Valenciana de la Llengua. 2009, Val├©ncia.) is a city and municipality located at the foot of the Sierra de Orihuela mountains in the province of Alicante, Valencian Community, Spain. The c ...
.
* Castell├│ Cathedral and El Fadr├Ł, in Castell├│n de la Plana
Castell├│n de la Plana (in ), or simply Castell├│n (), is the capital city of the province of Castell├│n, in the Valencian Community, Spain. It is located in the east of the Iberian Peninsula, on the Costa del Azahar by the Mediterranean Sea. Th ...
* Segorbe Cathedral in Segorbe
Segorbe is a municipality in the mountainous coastal province of Castell├│, Valencia (autonomous community), autonomous community of Valencia, Spain. The former Palace of the Dukes of Medinaceli now houses the city's mayor. Segorbe's bull-running ...
.
Balearic Gothic
* La Seu (cathedral) ofPalma de Mallorca
Palma (, ; ), also known as Palma de Mallorca (officially between 1983 and 1988, 2006ŌĆō2008, and 2012ŌĆō2016), is the capital and largest city of the Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of the Balearic Islands in Spain. It is ...
Catalan Gothic
* Santa Maria del Mar ofBarcelona
Barcelona ( ; ; ) is a city on the northeastern coast of Spain. It is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, as well as the second-most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within c ...
* Barcelona Royal Shipyard
* Royal Palace in Barcelona
* Cathedral of Girona
Flamboyant/Late Gothic
*Cathedral of Oviedo
The Metropolitan Cathedral Basilica of the Holy Saviour or Cathedral of San Salvador (, ) is a Roman Catholic church and minor basilica in the centre of Oviedo, in the Asturias region of northern Spain.
The Cathedral of San Salvador of Oviedo to ...
*Cathedral of Sevilla
The Cathedral of Saint Mary of the See (), better known as Seville Cathedral (), is a Catholic cathedral and former mosque in Seville, Andalusia, Spain. It was registered in 1987 by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site, along with the adjoining Alc├ ...
* Cathedral of Segovia
* Chapel of the Condestable, Cathedral of Burgos
* New Cathedral in Salamanca
Isabelline Gothic
* Monastery of San Juan de los Reyes in Toledo *Royal Chapel of Granada
The Royal Chapel of Granada () is an Isabelline style building in Granada, Spain. Constructed between 1505 and 1517, it was originally integrated in the complex of the neighbouring Granada Cathedral. It is the burial place of the Spanish monarchs ...
in Granada
Granada ( ; ) is the capital city of the province of Granada, in the autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Andalusia, Spain. Granada is located at the foot of the Sierra Nevada (Spain), Sierra Nevada mountains, at the confluence ...
*Colegio de San Gregorio
The Colegio de San Gregorio is an Isabelline style building located in the city of Valladolid, in Castile and Le├│n, Spain, it was formerly a college and now is housing the National Museum of Sculpture. This building is one of the best examples ...
in Valladolid
Valladolid ( ; ) is a Municipalities of Spain, municipality in Spain and the primary seat of government and ''de facto'' capital of the Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Castile and Le├│n. It is also the capital of the pr ...
* Palace of Infantado in Guadalajara
* Palace of Jabalquinto in Baeza, Ja├®n
* San Pablo Church in Valladolid
Modern Spanish Gothic
* Ace Hotel Los AngelesGallery
Toledo Cathedral
The Primatial Metropolitan Cathedral of Saint Mary of the Assumption (), is a Roman Catholic cathedral in Toledo, Spain. It is the seat of the Metropolitan Archdiocese of Toledo. Since 1088, it holds the honorific title of Primatial, granted by ...
, Exterior
File:Cathedral of Toledo, Spain - interior 1.JPG, Toledo Cathedral
The Primatial Metropolitan Cathedral of Saint Mary of the Assumption (), is a Roman Catholic cathedral in Toledo, Spain. It is the seat of the Metropolitan Archdiocese of Toledo. Since 1088, it holds the honorific title of Primatial, granted by ...
, Interior
File:Catedral del Salvador de Zaragoza (ATHA-BAR-NV-006-061).jpg, Cathedral of San Salvador, in Zaragoza
File:Catedral de Valencia, Valencia, Espa├▒a, 2014-06-30, DD 160.JPG, Valencia Cathedral
Valencia Cathedral, at greater length the Metropolitan CathedralŌĆōBasilica of the Assumption of Our Lady of Valencia (, ), also known as St Mary's Cathedral, is a Catholic church in Valencia, Spain.
The cathedral was consecrated in 1238 by ...
, Exterior
File:Catedral de Valencia, Valencia, Espa├▒a, 2014-06-30, DD 157-159 HDR.JPG, Valencia Cathedral
Valencia Cathedral, at greater length the Metropolitan CathedralŌĆōBasilica of the Assumption of Our Lady of Valencia (, ), also known as St Mary's Cathedral, is a Catholic church in Valencia, Spain.
The cathedral was consecrated in 1238 by ...
, Interior
File:Orihuela 2022 - west facade.jpg, Orihuela Cathedral
File:Palma Cathedral.jpg, Palma Cathedral
The Cathedral of Santa Maria of Palma, more commonly referred to as La Seu (a title also used by many other churches), is a Gothic Roman Catholic cathedral located in Palma, Mallorca, Spain. It is the Cathedral of the diocese of Mallorca, and is ...
File:Cathedral of Girona (17).jpg, Girona Cathedral
The Cathedral of Saint Mary, (Catalan language, Catalan: ''Catedral de Santa Maria''), is a Catholic Church, Roman Catholic cathedral located in Girona, Catalonia, Spain. It is the seat of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Girona.
The cathedral's in ...
File:Pinnacles Cathedral Seville Spain.jpg, Seville Cathedral
The Cathedral of Saint Mary of the See (), better known as Seville Cathedral (), is a Catholic cathedral and former mosque in Seville, Andalusia, Spain. It was registered in 1987 by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site, along with the adjoining Alc├ ...
File:B├│veda del crucero de la Catedral de Sevilla.jpg, Crossing vault of Seville Cathedral
The Cathedral of Saint Mary of the See (), better known as Seville Cathedral (), is a Catholic cathedral and former mosque in Seville, Andalusia, Spain. It was registered in 1987 by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site, along with the adjoining Alc├ ...
by Juan Gil de Honta├▒├│n
Juan Gil de Honta├▒├│n (1480 in As├│n-Ag├╝era, Rasines, Cantabria ŌĆō 11 May 1531 in Salamanca) was a master builder and Trasmiera#Master masons of Trasmiera, Trasmeran mason of Spain during the 16th century. His first work was associated with Seg ...
File:WLM14ES - Catedral Nueva de Salamanca. - julianrdc edited.jpg, New Cathedral of Salamanca
The Catedral de la Asunci├│n de la Virgen (Cathedral of the Assumption of the Virgin Mary), popularly known as New Cathedral () is, together with the Old Cathedral, Salamanca, Old Cathedral, one of the two cathedrals of Salamanca, Castile and Le ...
File:San Pablo Church, Valladolid (3).JPG, San Pablo Church, Valladoild
See also
*Gothic architecture
Gothic architecture is an architectural style that was prevalent in Europe from the late 12th to the 16th century, during the High Middle Ages, High and Late Middle Ages, surviving into the 17th and 18th centuries in some areas. It evolved f ...
* Romanesque architecture
Romanesque architecture is an architectural style of medieval Europe that was predominant in the 11th and 12th centuries. The style eventually developed into the Gothic style with the shape of the arches providing a simple distinction: the Ro ...
* Cathedral architecture of Western Europe
* gothicmed
References