Soviet Central Asia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
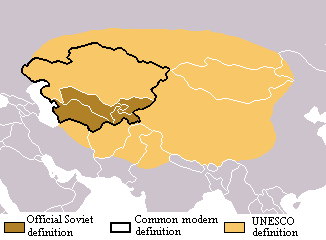 Soviet Central Asia () was the part of
Soviet Central Asia () was the part of
 By the end of the 19th century, Russian
By the end of the 19th century, Russian
 The Khorezm People's Soviet Republic was created as the successor to the
The Khorezm People's Soviet Republic was created as the successor to the
 Kazakhstan had started to produce and refine sizable amounts of
Kazakhstan had started to produce and refine sizable amounts of
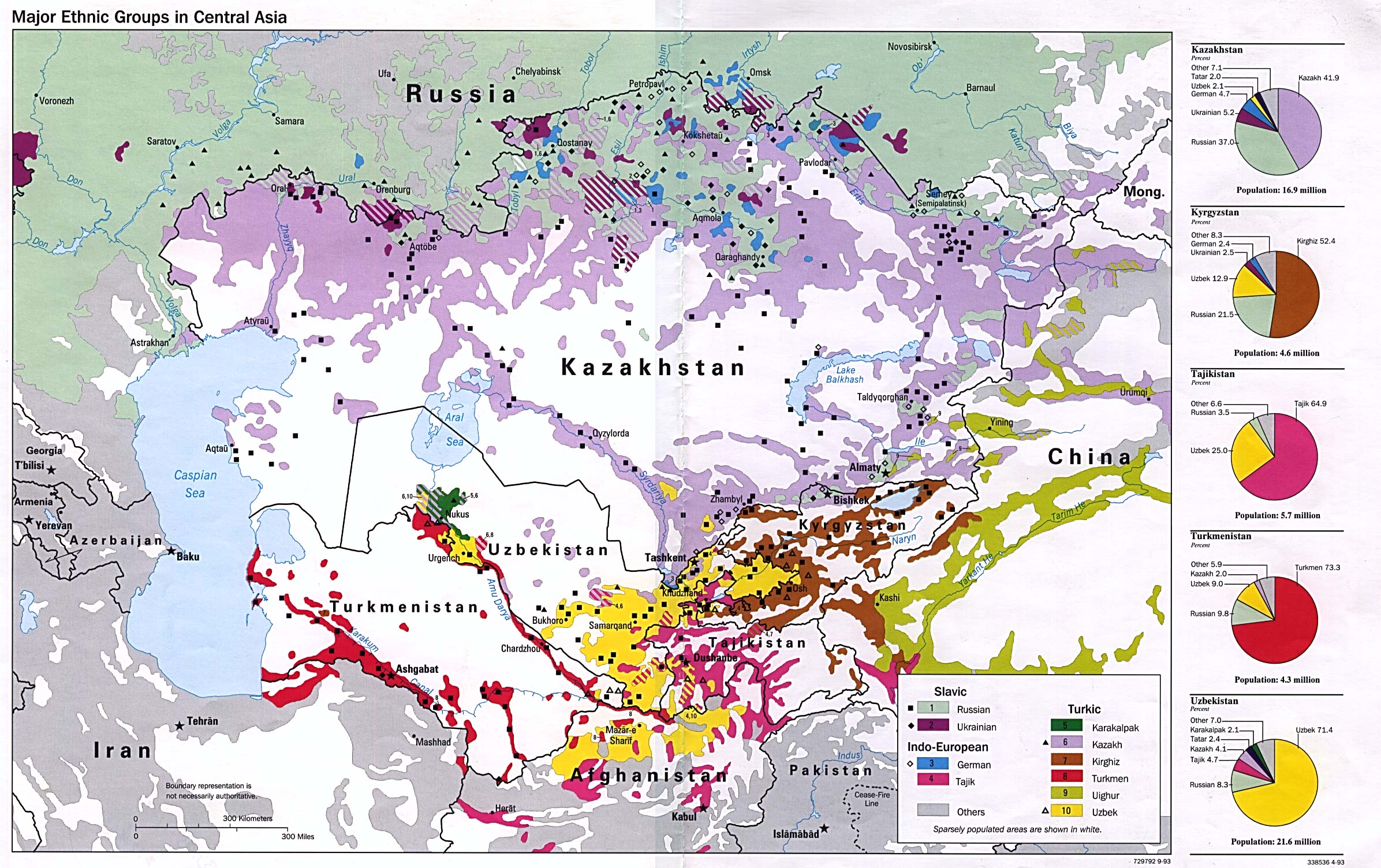 Following a series of migrations, mostly predating Soviet rule, that displaced the autochthonous
Following a series of migrations, mostly predating Soviet rule, that displaced the autochthonous
10_1
/ref> (sample size is 331) is the following: C (25.3%), J (18.2%), N (15.2%), R (10.1%).
The Strange State of Soviet Central Asia
Alicia Patterson Foundation Reporter * Keller, Bill (1989).
, The New York Times. * ttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=b0_U44QBbz8 Kazakh SSR AnthemYouTube
Uzbek SSR Anthem
YouTube
* *
Alec Rasizade. Dictators, Islamists, big powers and ordinary people: the new 'great game' in Central Asia. = Internationale Politik und Gesellschaft (Bonn: F.Ebert Stiftung), July 2002, number 3, pages 90–106.
{{Navboxes, , list1 = {{Autonomous Oblasts of the Soviet Union {{Autonomous republics of the Soviet Union {{Kazakhstan topics {{Kyrgyzstan topics {{Republics of the Soviet Union {{Tajikistan topics {{Turkmenistan topics {{Uzbekistan topics Post–Russian Empire states Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic Turkmen Soviet Socialist Republic Tajik Soviet Socialist Republic Kirghiz Soviet Socialist Republic Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic Communist states Early Soviet republics Former empires in Asia
 Soviet Central Asia () was the part of
Soviet Central Asia () was the part of Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Pers ...
administered by the Russian SFSR
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (Russian SFSR or RSFSR), previously known as the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic and the Russian Soviet Republic, and unofficially as Soviet Russia,Declaration of Rights of the labo ...
and then the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
between 1918 and 1991, when the Central Asian Soviet republics declared independence. It is nearly synonymous with Russian Turkestan
Russian Turkestan () was a colony of the Russian Empire, located in the western portion of the Central Asian region of Turkestan. Administered as a Krai or Governor-Generalship, it comprised the oasis region to the south of the Kazakh Steppe, b ...
in the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
. Soviet Central Asia went through many territorial divisions before the current borders were created in the 1920s and 1930s.
Administrative divisions
Former divisions
Turkestan Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic
tsar
Tsar (; also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar''; ; ; sr-Cyrl-Latn, цар, car) is a title historically used by Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word '' caesar'', which was intended to mean ''emperor'' in the Euro ...
s effectively ruled over most of the territory that later would constitute Soviet Central Asia. Russia annexed Lake Issyk Kul in north east Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan, officially the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia lying in the Tian Shan and Pamir Mountains, Pamir mountain ranges. Bishkek is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Kyrgyzstan, largest city. Kyrgyz ...
from China in the early 1860s, lands of Turkmens
Turkmens (, , , ) are a Turkic ethnic group native to Central Asia, living mainly in Turkmenistan, northern and northeastern regions of Iran and north-western Afghanistan. Sizeable groups of Turkmens are found also in Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, ...
, Khanate of Khiva
The Khanate of Khiva (, , uz-Latn-Cyrl, Xiva xonligi, Хива хонлиги, , ) was a Central Asian polity that existed in the historical region of Khwarazm, Khorezm from 1511 to 1920, except for a period of Afsharid Iran, Afsharid occupat ...
, Emirate of Bukhara
The Emirate of Bukhara (, ) was a Muslims, Muslim-Uzbeks, Uzbek polity in Central Asia that existed from 1785 to 1920 in what is now Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan and Kazakhstan. It occupied the land between the Amu Darya and Syr Darya rive ...
in the second half of 1800s.
Emerging from the Russian Empire following the Russian Revolution of 1917 and the Russian Civil War of 1918–1921, the USSR was a union of several Soviet republics, but the synecdoche Russia – after its largest and dominant constituent state – continued to be commonly used throughout the state's existence. ''Turkestan Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic'' (initially Turkestan Socialist Federative Republic) (30 April 1918 – 27 October 1924) was created from the Turkestan Krai of Imperial Russia
Imperial is that which relates to an empire, emperor/empress, or imperialism.
Imperial or The Imperial may also refer to:
Places
United States
* Imperial, California
* Imperial, Missouri
* Imperial, Nebraska
* Imperial, Pennsylvania
* ...
. Its capital was Tashkent
Tashkent (), also known as Toshkent, is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Uzbekistan, largest city of Uzbekistan. It is the most populous city in Central Asia, with a population of more than 3 million people as of April 1, 2024. I ...
, population about 500,000.
British and Persian forces briefly tried to reach Baku
Baku (, ; ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Azerbaijan, largest city of Azerbaijan, as well as the largest city on the Caspian Sea and in the Caucasus region. Baku is below sea level, which makes it the List of capital ci ...
in Azerbaijan and the Turkmen port of Krasnovodsk. Bukhara
Bukhara ( ) is the List of cities in Uzbekistan, seventh-largest city in Uzbekistan by population, with 280,187 residents . It is the capital of Bukhara Region.
People have inhabited the region around Bukhara for at least five millennia, and t ...
, Khiva
Khiva ( uz-Latn-Cyrl, Xiva, Хива, ; other names) is a district-level city of approximately 93,000 people in Khorazm Region, Uzbekistan. According to archaeological data, the city was established around 2,500 years ago.
In 1997, Khiva celebr ...
, Samarkand
Samarkand ( ; Uzbek language, Uzbek and Tajik language, Tajik: Самарқанд / Samarqand, ) is a city in southeastern Uzbekistan and among the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities in Central As ...
, Kokand, Dushanbe
Dushanbe is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Tajikistan. , Dushanbe had a population of 1,564,700, with this population being largely Tajiks, Tajik. Until 1929, the city was known in Russian as Dyushambe, and from 1929 to 1961 as St ...
and the former Trans-Caspian Province would see various anti-Bolshevik risings over the next few years.
In 1924, it was split into Karakalpak Autonomous Oblast (now Karakalpakstan
Karakalpakstan, officially the Republic of Karakalpakstan, is an autonomous republic and part of Uzbekistan. It spans the northwestern portion of Uzbekistan. Its capital is Nukus (' / ). Karakalpakstan has an area of , and has a population of a ...
), Kara-Kirghiz Autonomous Oblast
The Kara-Kirghiz Autonomous Oblast, abbreviated as Kara-Kirghiz AO or KAO in the former region of Soviet Central Asia, was created on 14 October 1924 within the Russian SFSR from the predominantly Kyrgyz part of the Turkestan Autonomous Soviet ...
(now Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan, officially the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia lying in the Tian Shan and Pamir Mountains, Pamir mountain ranges. Bishkek is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Kyrgyzstan, largest city. Kyrgyz ...
), Tajik ASSR (now Tajikistan
Tajikistan, officially the Republic of Tajikistan, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Dushanbe is the capital city, capital and most populous city. Tajikistan borders Afghanistan to the Afghanistan–Tajikistan border, south, Uzbekistan to ...
), Turkmen SSR
The Turkmen Soviet Socialist Republic, also known as Soviet Turkmenistan, the Turkmen SSR, TuSSR, Turkmenistan, or Turkmenia, was one of the Republics of the Soviet Union, constituent republics of the Soviet Union located in Soviet Central Asia, ...
(now Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan is a landlocked country in Central Asia bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the south and southwest and the Caspian Sea to the west. Ash ...
), and Uzbek SSR
The Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic (, ), also known as Soviet Uzbekistan, the Uzbek SSR, UzSSR, or simply Uzbekistan and rarely Uzbekia, was a union republic of the Soviet Union. It was governed by the Uzbek branch of the Soviet Communist P ...
(now Uzbekistan
, image_flag = Flag of Uzbekistan.svg
, image_coat = Emblem of Uzbekistan.svg
, symbol_type = Emblem of Uzbekistan, Emblem
, national_anthem = "State Anthem of Uzbekistan, State Anthem of the Republ ...
).
Bukharan People's Soviet Republic
In March 1918, activists of the Young Bukharian Movement informed theBolsheviks
The Bolsheviks, led by Vladimir Lenin, were a radical Faction (political), faction of the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) which split with the Mensheviks at the 2nd Congress of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party, ...
that the Bukhara
Bukhara ( ) is the List of cities in Uzbekistan, seventh-largest city in Uzbekistan by population, with 280,187 residents . It is the capital of Bukhara Region.
People have inhabited the region around Bukhara for at least five millennia, and t ...
ns were ready for the revolution and that the people were awaiting liberation. The Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People ...
marched to the gates of Bukhara and demanded that the emir
Emir (; ' (), also Romanization of Arabic, transliterated as amir, is a word of Arabic language, Arabic origin that can refer to a male monarch, aristocratic, aristocrat, holder of high-ranking military or political office, or other person po ...
surrender the city to the Young Bukharans. As Russian sources report, the emir responded by murdering the Bolshevik delegation, along with several hundred Russian inhabitants of Bukhara and the surrounding territories. The majority of Bukharans did not support an invasion and the ill-equipped and ill-disciplined Bolshevik army fled back to the Soviet stronghold at Tashkent.
However, the emir had won only a temporary respite. As the civil war in Russia wound down, Moscow sent reinforcements to Central Asia. On 2 September 1920, an army of well-disciplined and well equipped Red Army troops under the command of Bolshevik general Mikhail Frunze
Mikhail Vasilyevich Frunze (; ; 2 February 1885 – 31 October 1925) was a Soviet revolutionary, politician, army officer and military theory, military theorist.
Born to a Bessarabian father and a Russian mother in Russian Turkestan, Frunze at ...
attacked the city. After four days of fighting, the emir's citadel (Arc) was destroyed, the Red flag was raised from the top of Kalyan Minaret
The Kalyan Minaret (Uzbek: Minorai Kalon, Persian/Tajik: Minâra-i Kalân, Kalon Minor, Kalon Minaret) is a minaret of the Po-i-Kalyan mosque complex in Bukhara, Uzbekistan and one of the most prominent landmarks in the city.
The minaret, desig ...
, and the Emir Alim Khan was forced to flee to his base at Dushanbe
Dushanbe is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Tajikistan. , Dushanbe had a population of 1,564,700, with this population being largely Tajiks, Tajik. Until 1929, the city was known in Russian as Dyushambe, and from 1929 to 1961 as St ...
in Eastern Bukharan, and finally to Kabul
Kabul is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province. The city is divided for administration into #Districts, 22 municipal districts. A ...
, Afghanistan.
A nearby anti-Bolshevik stronghold in the Tadjik/Moslem village of Khangir (qingir) declared its independence shortly afterwards, but soon surrendered after a 14-day siege by Russian and Bokhkori Bolsheviks. It was then quickly re-integrated back into Communist Bokhorah.
The Bukharan People's Republic was proclaimed on 8 October 1920 under Faizullah Khojaev. The overthrow of the Emir was the impetus for the Basmachi Revolt, an anti-Russian rebellion. In 1922, most of the territory of the republic was controlled by Basmachi
The Basmachi movement (, derived from ) was an uprising against Imperial Russian and Soviet rule in Central Asia by rebel groups inspired by Islamic beliefs. It has been called "probably the most important movement of opposition to Soviet rul ...
, surrounding the city of Bukhara. Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Dzhugashvili; 5 March 1953) was a Soviet politician and revolutionary who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until Death and state funeral of Joseph Stalin, his death in 1953. He held power as General Secret ...
would later purge
In history, religion and political science, a purge is a position removal or execution of people who are considered undesirable by those in power from a government, another, their team leaders, or society as a whole. A group undertaking such an ...
and exile many of the local Bukhori people as well as most of the local Jewish community from the former Bukharan People's Soviet Republic
The Bukharan People's Soviet Republic was a Soviet state that governed the former Emirate of Bukhara during the years immediately following the Russian Revolution. In 1924, its name was changed to the Bukharan Socialist Soviet Republic (Bukhara ...
.
Prior to the establishment of the state of Israel, the Bukharian Jews
Bukharan Jews, also known as Bukharian Jews, are the Mizrahi Jews, Mizrahi Jewish sub-group of Central Asia that dwelt predominantly in what is today Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Afghanistan. The group's name is derived from the E ...
were one of the most isolated Jewish communities in the world.
Khorezm People's Soviet Republic and SSR
Khanate of Khiva
The Khanate of Khiva (, , uz-Latn-Cyrl, Xiva xonligi, Хива хонлиги, , ) was a Central Asian polity that existed in the historical region of Khwarazm, Khorezm from 1511 to 1920, except for a period of Afsharid Iran, Afsharid occupat ...
in February 1920 and officially declared on 26 April 1920. On 20 October 1923, it was transformed into the Khorezm Socialist Soviet Republic. The Khorezm SSR only survived until 17 February 1925, when it was divided between Karakalpak Autonomous Oblast, the Turkmen SSR
The Turkmen Soviet Socialist Republic, also known as Soviet Turkmenistan, the Turkmen SSR, TuSSR, Turkmenistan, or Turkmenia, was one of the Republics of the Soviet Union, constituent republics of the Soviet Union located in Soviet Central Asia, ...
, and the Uzbek SSR
The Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic (, ), also known as Soviet Uzbekistan, the Uzbek SSR, UzSSR, or simply Uzbekistan and rarely Uzbekia, was a union republic of the Soviet Union. It was governed by the Uzbek branch of the Soviet Communist P ...
as part of the reorganization of Central Asia by Moscow according to nationalities.
Kara-Kirghiz Autonomous Oblast
The Kara-Kyrgyz Autonomous Oblast (Кара-Киргизская АО) was created on 14 October 1924 within theRussian SFSR
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (Russian SFSR or RSFSR), previously known as the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic and the Russian Soviet Republic, and unofficially as Soviet Russia,Declaration of Rights of the labo ...
from the predominantly Kazakh and Kyrgyz parts of the Turkestan Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic. On 15 May 1925 it was renamed into the Kyrgyz Autonomous Oblast. On 11 February 1926 it was reorganized into the Kyrgyz ASSR. On 5 December 1936 it became the Kyrgyz SSR
The Kirghiz Soviet Socialist Republic (Kirghiz SSR), also known as the Kyrgyz Soviet Socialist Republic (Kyrgyz SSR), KySSR or Kirgiz Soviet Socialist Republic (Kirgiz SSR), was one of the Republics of the Soviet Union, constituent republics of ...
, one of the constituent republics of the Soviet Union.
Karakalpak Autonomous Oblast
The Karakalpak Autonomous Oblast was created on 19 February 1925 by separating lands of the ethnicKarakalpaks
The Karakalpaks or Qaraqalpaqs (; ), are a Kipchak languages, Kipchak-Nogai Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group native to Karakalpakstan in Northwestern Uzbekistan. During the 18th century, they settled in the lower reaches of the Amu Darya a ...
from the Turkestan Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic and Khorezm People's Soviet Republic
The Khorezm People's Soviet Republic was the state created as the successor to the Khanate of Khiva in February 1920, when the Khan abdicated in response to pressure. It was officially declared by the First Khorezm Kurultay (Assembly) on 26 Apri ...
.
Initially located within the Kazakh Autonomous Socialist Soviet Republic, the Karakalpak A.O. was transferred to the RSFSR
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (Russian SFSR or RSFSR), previously known as the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic and the Russian Soviet Republic, and unofficially as Soviet Russia,Declaration of Rights of the labo ...
from 20 July 1930 to 20 March 1932, at which time it was elevated to the Karakalpak Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic. The Karakalpak ASSR was joined to the Uzbek SSR
The Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic (, ), also known as Soviet Uzbekistan, the Uzbek SSR, UzSSR, or simply Uzbekistan and rarely Uzbekia, was a union republic of the Soviet Union. It was governed by the Uzbek branch of the Soviet Communist P ...
on 5 December 1936.
Kazakh Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic
The Kazakh ASSR was an autonomous republic of theSoviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
. It became the Kazakh SSR on 5 December 1936.
Its original name was the Kirgiz Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic. This ASSR was established on 26 August 1920, and was a part of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (Russian SFSR or RSFSR), previously known as the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic and the Russian Soviet Republic, and unofficially as Soviet Russia,Declaration of Rights of the labo ...
(RSFSR)
In 1925 it was renamed the Kazakh Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic. In 1929 the city of Almaty
Almaty, formerly Alma-Ata, is the List of most populous cities in Kazakhstan, largest city in Kazakhstan, with a population exceeding two million residents within its metropolitan area. Located in the foothills of the Trans-Ili Alatau mountains ...
(Alma-Ata) was designated as the capital of the ASSR.
Soviet Republics
Kazakhstan
TheKazakh Soviet Socialist Republic
The Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic, also known as Soviet Kazakhstan, the Kazakh SSR, KSSR, or simply Kazakhstan, was one of the transcontinental country, transcontinental Republics of the Soviet Union, constituent republics of the Soviet Un ...
, also known as Kazakhstan, was established on 5 December 1936. It was initially called Kyrgyz ASSR (Kirghiz Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic) and was a part of the Russian SFSR. On 15–19 April 1925, it was renamed Kazakh ASSR and on 5 December 1936 it became a Union Republic of the USSR
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
called Kazakh SSR in the culminating act of the national delimitation in the Soviet Union. During the 1950s and 1960s Soviet citizens were urged to settle in the " Virgin Lands" of the Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic. The influx of immigrants (mostly Russians
Russians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Eastern Europe. Their mother tongue is Russian language, Russian, the most spoken Slavic languages, Slavic language. The majority of Russians adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church ...
and Ukrainians
Ukrainians (, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. Their native tongue is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and the majority adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, forming the List of contemporary eth ...
, but also some forcibly resettled ethnic minorities, such as the Volga Germans
The Volga Germans (, ; ) are ethnic Germans who settled and historically lived along the Volga River in the region of southeastern European Russia around Saratov and close to Ukraine nearer to the south.
Recruited as immigrants to Russia in the ...
and the Chechens
The Chechens ( ; , , Old Chechen: Нахчой, ''Naxçoy''), historically also known as ''Kistin, Kisti'' and ''Durdzuks'', are a Northeast Caucasian languages, Northeast Caucasian ethnic group of the Nakh peoples native to the North Caucasus. ...
) skewed the ethnic mixture and enabled non-Kazakhs
The Kazakhs (Kazakh language, Kazakh: , , , ) are a Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group native to Central Asia and Eastern Europe. They share a common Culture of Kazakhstan, culture, Kazakh language, language and History of Kazakhstan, history ...
to outnumber natives. The influx also deprived the Kazakhs of much pasture land, making it increasingly difficult to sustain the nomadic way of life. Industry, and especially mining, developed. Russian and European culture began to influence Kazakh society.
In 1924, the borders of political units in Central Asia were changed along ethnic lines determined by Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov ( 187021 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin, was a Russian revolutionary, politician and political theorist. He was the first head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 until Death and state funeral of ...
's Commissar
Commissar (or sometimes ''Kommissar'') is an English transliteration of the Russian (''komissar''), which means ' commissary'. In English, the transliteration ''commissar'' often refers specifically to the political commissars of Soviet and ...
for Nationalities, Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Dzhugashvili; 5 March 1953) was a Soviet politician and revolutionary who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until Death and state funeral of Joseph Stalin, his death in 1953. He held power as General Secret ...
. The Turkestan ASSR, the Bukharan People's Republic, and the Khorezm People's Republic were abolished and their territories were divided into eventually five separate Soviet Socialist Republics, one of which was the Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic. The next year the Uzbek SSR became one of the republics of the Soviet Union.
Almaty
Almaty, formerly Alma-Ata, is the List of most populous cities in Kazakhstan, largest city in Kazakhstan, with a population exceeding two million residents within its metropolitan area. Located in the foothills of the Trans-Ili Alatau mountains ...
is the largest city in Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
, with a population of 1,226,000 (as of 1 August 2005). The ethnic group
An ethnicity or ethnic group is a group of people with shared attributes, which they collectively believe to have, and long-term endogamy. Ethnicities share attributes like language, culture, common sets of ancestry, traditions, society, re ...
s in a 2003 census were: Kazakh 43.6%, Russian 40.2%, Uyghur 5.7%, Tatar 2.1%, Korean 1.8%, Ukrainian 1.7%, German 0.7%.
Kyzil Orda / Kyzylorda
Kyzylorda ( , formerly known as Kzyl-Orda (), Ak-Mechet (Ак-Мечеть), Perovsk (Перовск), and Fort-Perovsky (Форт-Перовский), is a city in south-central Kazakhstan, capital of Kyzylorda Region and former capital of the ...
was founded in 1820 as a Kokand fortress of Ak-Mechet (also spelt Aq Masjid, Aq Mechet, 'white mosque'). The name comes from the Kazakh for 'Red center'.
Uralsk / Oral
The word oral may refer to:
Relating to the mouth
* Relating to the mouth, the first portion of the alimentary canal that primarily receives food and liquid
**Oral administration of medicines
** Oral examination (also known as an oral exam or ora ...
was founded in 1613 by Cossacks, was originally named Yaitsk, after the Yaik River. The city was put under siege during the Russian Civil War. It has a population of 210,600. It is the capital of the West Kazakhstan Province. Ethnic composition is dominated by Russians (54%), Kazakhs (34%), along with a few Ukrainians and Germans.
Kirghizia
TheKirghiz Soviet Socialist Republic
The Kirghiz Soviet Socialist Republic (Kirghiz SSR), also known as the Kyrgyz Soviet Socialist Republic (Kyrgyz SSR), KySSR or Kirgiz Soviet Socialist Republic (Kirgiz SSR), was one of the constituent republics of the Soviet Union (USSR) from 1 ...
(sometimes spelled Kyrgyz), also known as Kirghizia, was one of fifteen constituent republics of the Soviet Union. Established on 14 October 1924 as the Kara-Kyrgyz Autonomous Oblast of the Russian SFSR
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (Russian SFSR or RSFSR), previously known as the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic and the Russian Soviet Republic, and unofficially as Soviet Russia,Declaration of Rights of the labo ...
, it was transformed into the Kyrgyz ASSR ( Kyrgyz Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic) on 1 February 1926, still being a part of the Russian SFSR. Today it is the independent state of Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan, officially the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia lying in the Tian Shan and Pamir Mountains, Pamir mountain ranges. Bishkek is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Kyrgyzstan, largest city. Kyrgyz ...
in Central Asia. Kyrgyz Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic (Kyrgyz ASSR) was the name of two different national entities within Russian SFSR, in the territories of modern Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan.
On 5 December 1936, it became a separate constituent republic of the USSR as the Kyrgyz Soviet Socialist Republic during the final stages of the national delimitation in the Soviet Union
In the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), national delimitation was the process of specifying well-defined national territorial units (Soviet socialist republics SR autonomous Soviet socialist republics SSR autonomous oblasts ro ...
.
Bishkek was the capital and the largest city of Kyrgyzstan and the Kirghiz ASSR, with a population of approximately 900,000 in 2005. In 1862, the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
destroyed the local fort and began to settle the area with Russian migrants. Over the years many fertile black soil farms were developed by the Tsarists and, later, the process carried on by the USSR. In 1926, the city became the capital of the newly established Kirghiz Autonomous Socialist Soviet Republic (1926–1936), Kirghiz ASSR and was renamed Frunze after the Bolshevik hero Mikhail Frunze
Mikhail Vasilyevich Frunze (; ; 2 February 1885 – 31 October 1925) was a Soviet revolutionary, politician, army officer and military theory, military theorist.
Born to a Bessarabian father and a Russian mother in Russian Turkestan, Frunze at ...
, one of Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov ( 187021 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin, was a Russian revolutionary, politician and political theorist. He was the first head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 until Death and state funeral of ...
's close associates who was born in Bishkek, until Kirghiz independence in 1991.
Tajikistan
TheTajik Soviet Socialist Republic
The Tajik Soviet Socialist Republic, also commonly known as Soviet Tajikistan, the Tajik SSR, TaSSR, or simply Tajikistan, was one of the constituent republics of the Soviet Union which existed from 1929 to 1991 in Central Asia.
The Tajik Rep ...
, also named Tajikistan (or by its Russian spelling, Tadzhikistan), was one of the new states created in Central Asia in 1924 was Uzbekistan
, image_flag = Flag of Uzbekistan.svg
, image_coat = Emblem of Uzbekistan.svg
, symbol_type = Emblem of Uzbekistan, Emblem
, national_anthem = "State Anthem of Uzbekistan, State Anthem of the Republ ...
, which had the status of a Soviet socialist republic. In 1929 Tajikistan
Tajikistan, officially the Republic of Tajikistan, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Dushanbe is the capital city, capital and most populous city. Tajikistan borders Afghanistan to the Afghanistan–Tajikistan border, south, Uzbekistan to ...
was detached from Uzbekistan
, image_flag = Flag of Uzbekistan.svg
, image_coat = Emblem of Uzbekistan.svg
, symbol_type = Emblem of Uzbekistan, Emblem
, national_anthem = "State Anthem of Uzbekistan, State Anthem of the Republ ...
and given full status as a Soviet socialist republic. The city of Dushanbe would become an important regional hub on the border with Afghanistan.
Tajikistan has 3 exclaves
An enclave is a territory that is entirely surrounded by the territory of only one other state or entity. An enclave can be an independent territory or part of a larger one. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is s ...
, all of them located in the Fergana Valley region where Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan meet. The largest is Vorukh (with an area between 95 – 130 km2/37 – 50 sq mi, population estimated between 23,000 and 29,000, 95% Tajiks and 5% Kyrgyz, distributed among 17 villages), located south of Isfara
Isfara (; ) is a city in Sughd Region in northern Tajikistan, situated on the border with Kyrgyzstan. The city was the seat of the former Isfara District.
There are currently territorial disputes between Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan over the area ...
on the right bank of the river Karavshin, in Kyrgyz territory. Another exclave in Kyrgyzstan is a small settlement near the Kyrgyz railway station of Kairagach. The last is the village of Sarvan, which includes a narrow, long strip of land (about long by 1 km (over ½ mi) wide) alongside the road from Angren to Kokand; it is surrounded by Uzbek territory. There are no foreign enclaves within Tajikistan.
In 1931, the city formerly known as "Dyushambe" was renamed "Stalinabad" (after Joseph Stalin), but in 1961, as part of Nikita Khrushchev
Nikita Sergeyevich Khrushchev (– 11 September 1971) was the General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, First Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1953 to 1964 and the Premier of the Soviet Union, Chai ...
's de-Stalinization
De-Stalinization () comprised a series of political reforms in the Soviet Union after Death and state funeral of Joseph Stalin, the death of long-time leader Joseph Stalin in 1953, and Khrushchev Thaw, the thaw brought about by ascension of Nik ...
initiative, the city was renamed ''Dushanbe
Dushanbe is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Tajikistan. , Dushanbe had a population of 1,564,700, with this population being largely Tajiks, Tajik. Until 1929, the city was known in Russian as Dyushambe, and from 1929 to 1961 as St ...
''. The Soviets
The Soviet people () were the citizens and nationals of the Soviet Union. This demonym was presented in the ideology of the country as the "new historical unity of peoples of different nationalities" ().
Nationality policy in the Soviet Union ...
transformed the area into a centre for cotton and silk production, and relocated tens of thousands of people to the city from around the Soviet Union. The population also increased with thousands of ethnic Tajiks migrating to Tajikistan
Tajikistan, officially the Republic of Tajikistan, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Dushanbe is the capital city, capital and most populous city. Tajikistan borders Afghanistan to the Afghanistan–Tajikistan border, south, Uzbekistan to ...
following the transfer of Bukhara and Samarkand to the Uzbek SSR
The Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic (, ), also known as Soviet Uzbekistan, the Uzbek SSR, UzSSR, or simply Uzbekistan and rarely Uzbekia, was a union republic of the Soviet Union. It was governed by the Uzbek branch of the Soviet Communist P ...
. Dushanbe
Dushanbe is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Tajikistan. , Dushanbe had a population of 1,564,700, with this population being largely Tajiks, Tajik. Until 1929, the city was known in Russian as Dyushambe, and from 1929 to 1961 as St ...
later became the home to a university and the Tajik Academy of Sciences. Dushanbe also had a relatively high military population during the war with Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran borde ...
.
Turkmenia
TheTurkmen Soviet Socialist Republic
The Turkmen Soviet Socialist Republic, also known as Soviet Turkmenistan, the Turkmen SSR, TuSSR, Turkmenistan, or Turkmenia, was one of the constituent republics of the Soviet Union located in Central Asia existed as a republic from 1925 to 199 ...
which is also known as Turkmenia (or sometimes known as Turkmenistan) was one of fifteen constituent republics of the Soviet Union. It was initially established on 7 August 1921 as Turkmen Oblast of the Turkestan ASSR. On 13 May 1925 it was transformed into Turkmen SSR and became a separate republic of the Soviet Union. Today it is the independent state of Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan is a landlocked country in Central Asia bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the south and southwest and the Caspian Sea to the west. Ash ...
in Central Asia.
The Communist Party of the Turkmen SSR was the ruling communist party of the Turkmen SSR, and a part of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union
The Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU),. Abbreviated in Russian as КПСС, ''KPSS''. at some points known as the Russian Communist Party (RCP), All-Union Communist Party and Bolshevik Party, and sometimes referred to as the Soviet ...
. From 1985 it was led by Mr Saparmurat Niyazov
Saparmurat Atayevich Niyazov (19 February 1940 – 21 December 2006) was a Turkmenistani politician who led Turkmenistan from 1985 until his death in 2006. He was the Secretary (title), first secretary of the Communist Party of Turkmenist ...
, who in 1991 renamed the party to the Democratic Party of Turkmenistan, which is no longer a communist party . The current Communist Party of Turkmenistan is illegal.
Ashkhabad has a population of 695,300 (2001 census estimate) and has a primarily Turkmen population, with minorities of ethnic Russians
Russians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Eastern Europe. Their mother tongue is Russian language, Russian, the most spoken Slavic languages, Slavic language. The majority of Russians adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church ...
, Armenians
Armenians (, ) are an ethnic group indigenous to the Armenian highlands of West Asia.Robert Hewsen, Hewsen, Robert H. "The Geography of Armenia" in ''The Armenian People From Ancient to Modern Times Volume I: The Dynastic Periods: From Antiq ...
, and Azeris. It is 920 km from the second largest city in Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
, Mashhad
Mashhad ( ; ), historically also known as Mashad, Meshhed, or Meshed in English, is the List of Iranian cities by population, second-most-populous city in Iran, located in the relatively remote north-east of the country about from Tehran. ...
. The principal industries are cotton textiles and metal working.
Merv
Merv (, ', ; ), also known as the Merve Oasis, was a major Iranian peoples, Iranian city in Central Asia, on the historical Silk Road, near today's Mary, Turkmenistan. Human settlements on the site of Merv existed from the 3rd millennium& ...
/ Mary is an ancient city. Its population was 123,000 in 1999. It has an interesting regional museum and lies near the remains of the ancient city of Merv, which, through its corrupted form, gives its name to the modern town. Carpets
A carpet is a textile floor covering typically consisting of an upper layer of Pile (textile), pile attached to a backing. The pile was traditionally made from wool, but since the 20th century synthetic fiber, synthetic fibres such as polyprop ...
from the region of Merv are sometimes considered superior to the Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
n ones.
Uzbekistan
TheUzbek Soviet Socialist Republic
The Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic (, ), also known as Soviet Uzbekistan, the Uzbek SSR, UzSSR, or simply Uzbekistan and rarely Uzbekia, was a Republics of the Soviet Union, union republic of the Soviet Union. It was governed by the Communist ...
, also referred to as Uzbekistan, was created in 1924 when the new national boundaries separating the Uzbek and Kirghiz Soviet Socialist Republics cut off the eastern end of the Fergana Valley, as well as the slopes surrounding it. This was compounded in 1928 when the Tajik ASSR became a fully-fledged republic, the Tajik SSR
The Tajik Soviet Socialist Republic, also commonly known as Soviet Tajikistan, the Tajik SSR, TaSSR, or simply Tajikistan, was one of the constituent republics of the Soviet Union which existed from 1929 to 1991 in Central Asia.
The Tajik Re ...
, and the area around Khodjend was made a part of it. This blocked the valley's natural outlet and the routes to Samarkand and Bukhara, but none of these borders was of any great significance so long as Soviet rule lasted.
The Uzbek SSR included the Tajik ASSR until 1929, when the Tajik ASSR was upgraded to an equal status. In 1930, the Uzbek SSR capital was relocated from Samarkand
Samarkand ( ; Uzbek language, Uzbek and Tajik language, Tajik: Самарқанд / Samarqand, ) is a city in southeastern Uzbekistan and among the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities in Central As ...
to Tashkent
Tashkent (), also known as Toshkent, is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Uzbekistan, largest city of Uzbekistan. It is the most populous city in Central Asia, with a population of more than 3 million people as of April 1, 2024. I ...
. In 1936, the Uzbek SSR was enlarged with the addition of the Karakalpak ASSR taken from the Kazakh SSR in the last stages of the national delimitation in the Soviet Union
In the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), national delimitation was the process of specifying well-defined national territorial units (Soviet socialist republics SR autonomous Soviet socialist republics SSR autonomous oblasts ro ...
. Further bits and pieces of territory were transferred several times between the Kazakh SSR and the Uzbek SSR after World War II. During the Great Purges of Joseph Stalin, many thousands of Chechens
The Chechens ( ; , , Old Chechen: Нахчой, ''Naxçoy''), historically also known as ''Kistin, Kisti'' and ''Durdzuks'', are a Northeast Caucasian languages, Northeast Caucasian ethnic group of the Nakh peoples native to the North Caucasus. ...
, Koreans
Koreans are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Korean Peninsula. The majority of Koreans live in the two Korean sovereign states of North and South Korea, which are collectively referred to as Korea. As of 2021, an estimated 7.3 m ...
and Crimean Tatars were exiled to the Uzbek SSR.
The State Anthem of the Uzbek SSR was the national anthem of Uzbekistan
, image_flag = Flag of Uzbekistan.svg
, image_coat = Emblem of Uzbekistan.svg
, symbol_type = Emblem of Uzbekistan, Emblem
, national_anthem = "State Anthem of Uzbekistan, State Anthem of the Republ ...
when it was a republic of the Soviet Union and known as the Uzbek SSR
The Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic (, ), also known as Soviet Uzbekistan, the Uzbek SSR, UzSSR, or simply Uzbekistan and rarely Uzbekia, was a union republic of the Soviet Union. It was governed by the Uzbek branch of the Soviet Communist P ...
.
The city of Tashkent
Tashkent (), also known as Toshkent, is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Uzbekistan, largest city of Uzbekistan. It is the most populous city in Central Asia, with a population of more than 3 million people as of April 1, 2024. I ...
began to industrialize in the 1920s and 1930s, but industry increased tremendously during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, with the relocation of factories from western Russia to preserve the Soviet industrial capacity from the hostile invading Nazis
Nazism (), formally named National Socialism (NS; , ), is the far-right politics, far-right Totalitarianism, totalitarian socio-political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Germany. During H ...
. The Russian population increased dramatically as well, with evacuees from the war zones increasing the population to well over a million. (The Russian community would eventually comprise more than half of the total residents of Tashkent by the 1980s.) On 26 April 1966, Tashkent was destroyed by an earthquake
An earthquakealso called a quake, tremor, or tembloris the shaking of the Earth's surface resulting from a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those so weak they ...
and over 300,000 were left homeless. At the time of the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991, Tashkent was the fourth largest Soviet city and a major center of learning in the fields of science and engineering.
As the nation's capital, Tashkent is still a fairly prosperous city and the capital of Uzbekistan and has a population of the city in 2006 was 2.1 million. The city has been the target of several terrorist acts since gaining independence. These have been attributed by the Uzbek the government to Islamic insurgents aided by the Afghan Taliban
, leader1_title = Supreme Leader of Afghanistan, Supreme leaders
, leader1_name = {{indented plainlist,
* Mullah Omar{{Natural Causes{{nbsp(1994–2013)
* Akhtar Mansour{{Assassinated (2015–2016)
* Hibatullah Akhundzada (2016–present) ...
.
Samarkand
Samarkand ( ; Uzbek language, Uzbek and Tajik language, Tajik: Самарқанд / Samarqand, ) is a city in southeastern Uzbekistan and among the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities in Central As ...
is one of the oldest inhabited cities in the world, prospering from its location on the trade route between China and Europe (Silk Road
The Silk Road was a network of Asian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over , it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and religious interactions between the ...
). In 1370, Timur the Lame, or Tamerlane
Timur, also known as Tamerlane (1320s17/18 February 1405), was a Turco-Mongol tradition, Turco-Mongol conqueror who founded the Timurid Empire in and around modern-day Afghanistan, Iran, and Central Asia, becoming the first ruler of the Timuri ...
, decided to make Samarkand
Samarkand ( ; Uzbek language, Uzbek and Tajik language, Tajik: Самарқанд / Samarqand, ) is a city in southeastern Uzbekistan and among the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities in Central As ...
the capital of his empire, which extended from India to Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
. Despite its status as the second city of Uzbekistan
, image_flag = Flag of Uzbekistan.svg
, image_coat = Emblem of Uzbekistan.svg
, symbol_type = Emblem of Uzbekistan, Emblem
, national_anthem = "State Anthem of Uzbekistan, State Anthem of the Republ ...
, the majority of the city's inhabitants are Persian-speaking Tajiks
Tajiks (; ; also spelled ''Tadzhiks'' or ''Tadjiks'') is the name of various Persian-speaking Eastern Iranian groups of people native to Central Asia, living primarily in Afghanistan, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan. Even though the term ''Tajik'' ...
. The city a became rich trading center as a major capital of the Silk Road
The Silk Road was a network of Asian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over , it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and religious interactions between the ...
between China and the West. The Timurid dynasty
The Timurid dynasty, self-designated as Gurkani (), was the ruling dynasty of the Timurid Empire (1370–1507). It was a Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslim dynasty or Barlās clan of Turco-Mongol originB.F. Manz, ''"Tīmūr Lang"'', in Encyclopaedia of I ...
's extensive building in Samarkand produced monuments that rank amongst some of the most striking in the Islamic world.
Nationalist rebellions
Turkestan Autonomy
Kokand is a city in Fergana Province in easternUzbekistan
, image_flag = Flag of Uzbekistan.svg
, image_coat = Emblem of Uzbekistan.svg
, symbol_type = Emblem of Uzbekistan, Emblem
, national_anthem = "State Anthem of Uzbekistan, State Anthem of the Republ ...
, at the southwestern edge of the Fergana Valley
The Fergana Valley (also commonly spelled the Ferghana Valley) in Central Asia crosses eastern Uzbekistan, southern Kyrgyzstan and northern Tajikistan.
Encompassing three former Republics of the Soviet Union, Soviet republics, the valley is e ...
. By 1999 it had a population of 192,500. Kokand is 228 km southeast of Tashkent
Tashkent (), also known as Toshkent, is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Uzbekistan, largest city of Uzbekistan. It is the most populous city in Central Asia, with a population of more than 3 million people as of April 1, 2024. I ...
, 115 km west of Andijan
Andijan ( ), also spelt Andijon () and formerly romanized as Andizhan ( ), is a city in Uzbekistan. It is the administrative, economic, and cultural center of Andijan Region. Andijan is a district-level city with an area of . Andijan is the most ...
, and 88 km west of Fergana
Fergana ( uz-Latn-Cyrl, Fargʻona, Фарғона, ), () or Ferghana, also Farghana is a district-level city and the capital of Fergana Region in eastern Uzbekistan. Fergana is about 320 km east of Tashkent, about 75 km southwest of A ...
. It is nicknamed "City of Winds", or sometimes "Town of the Boar". It is at an altitude of 409 meters.
Kokand is on the crossroads of the ancient trade routes, at the junction of two main routes into the Fergana Valley, one leading northwest over the mountains to Tashkent, and the other west through Khujand
Khujand, sometimes spelled Khodjent and formerly known as Leninabad from 1936 to 1991, is the second-largest city of Tajikistan and the capital of Tajikistan's northernmost Sughd province.
Khujand is one of the oldest cities in Central Asia, d ...
. As a result, Kokand is the main transportation junction in the Fergana Valley.
Russian imperial forces under Mikhail Skobelev captured the city in 1876 which then became part of Russian Turkistan. With the fall of the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
, a provisional government
A provisional government, also called an interim government, an emergency government, a transitional government or provisional leadership, is a temporary government formed to manage a period of transition, often following state collapse, revoluti ...
attempted to maintain control in Tashkent. It was quickly overthrown and local Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
opposition crushed. In April 1918, Tashkent became the capital of the Turkestan Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic ( Turkestan ASSR). It was the capital of the short-lived (1917–18) Anti-Bolshevik Provisional Government of Autonomous Turkistan (also known as the Turkestan Autonomy).
Alash Autonomy
The ''Alash Autonomy'' (, ; , ) was astate
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
that existed between 13 December 1917 and 26 August 1920, located roughly on the territory of present-day Republic of Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
. The capital city was Semey
Semey (; , formerly known as Semipalatinsk ( ) until 2007 and as Alash-Qala ( ) from 1917 to 1920, is a city in eastern Kazakhstan, in the Kazakh part of Siberia. When Abai Region was created in 2022, Semey became its administrative centre. I ...
(referred to at the time as ''Alash-qala'').
The ''Alash Orda'' (, ) was the name of the provisional Kazakh government between 13 December 1917 and 26 August 1920. It was led by Akhmet Baytursinuli, Alikhan Bokeikhanov and Mirjaqip Dulatuli amongst others.
The Alash Party proclaimed the autonomy of the Kazakh people in December 1917. Membership consists from 25 members (10 positions reserved for non-Kazakhs) and 15 member candidates. They formed special educational commission and established militia regiments as their armed forces.
Basmachi revolt
In 1897, the railway reachedTashkent
Tashkent (), also known as Toshkent, is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Uzbekistan, largest city of Uzbekistan. It is the most populous city in Central Asia, with a population of more than 3 million people as of April 1, 2024. I ...
, and finally in 1906 a direct rail link with European Russia was opened across the steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without closed forests except near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the tropical and subtropica ...
from Orenburg
Orenburg (, ), formerly known as Chkalov (1938–1957), is the administrative center of Orenburg Oblast, Russia. It lies in Eastern Europe, along the banks of the Ural River, being approximately southeast of Moscow.
Orenburg is close to the ...
to Tashkent
Tashkent (), also known as Toshkent, is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Uzbekistan, largest city of Uzbekistan. It is the most populous city in Central Asia, with a population of more than 3 million people as of April 1, 2024. I ...
. This led to much larger numbers of Slavic settlers flowing into Turkestan
Turkestan,; ; ; ; also spelled Turkistan, is a historical region in Central Asia corresponding to the regions of Transoxiana and East Turkestan (Xinjiang). The region is located in the northwest of modern day China and to the northwest of its ...
than had hitherto been the case, and their settlement was overseen by a specially created Migration
Migration, migratory, or migrate may refer to: Human migration
* Human migration, physical movement by humans from one region to another
** International migration, when peoples cross state boundaries and stay in the host state for some minimum le ...
Department in St. Petersburg (Переселенческое Управление). This caused considerable discontent amongst the local population, Kyrgyz, Kazakhs
The Kazakhs (Kazakh language, Kazakh: , , , ) are a Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group native to Central Asia and Eastern Europe. They share a common Culture of Kazakhstan, culture, Kazakh language, language and History of Kazakhstan, history ...
and Sart
Sart is a name for the settled inhabitants of Central Asia which has had shifting meanings over the centuries. According to Great Soviet Encyclopedia, before the October Revolution of 1917, the name “Sart” was used in ...
s, as these settlers took scarce land and water resources away from them. In 1916 discontent boiled over in the Basmachi Revolt, sparked by a decree conscripting the natives into Labour battalions (they had previously been exempt from military service). Thousands of settlers were killed, and this was matched by Russian reprisals, particularly against the nomadic
Nomads are communities without fixed habitation who regularly move to and from areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the population of nomadic pa ...
population. The competition for land and water which ensued between the Kazakhs and the newcomers caused great resentment against colonial rule during the final years of Tsarist
Tsarist autocracy (), also called Tsarism, was an autocracy, a form of absolute monarchy in the Grand Duchy of Moscow and its successor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire. In it, the Tsar possessed in principle authority and ...
Russia, with the most serious uprising, the Central Asian Revolt, occurring in 1916. The Kazakhs attacked Russian and Cossack
The Cossacks are a predominantly East Slavic Eastern Christian people originating in the Pontic–Caspian steppe of eastern Ukraine and southern Russia. Cossacks played an important role in defending the southern borders of Ukraine and Rus ...
villages, killing indiscriminately. The Russians' revenge
Revenge is defined as committing a harmful action against a person or group in response to a grievance, be it real or perceived. Vengeful forms of justice, such as primitive justice or retributive justice, are often differentiated from more fo ...
was merciless. A military force drove 300,000 Kazakhs to flee into the mountains or to China. When approximately 80,000 of them returned the next year, many of them were slaughtered by Tsarist forces. Order had not really been restored by the time the February Revolution
The February Revolution (), known in Soviet historiography as the February Bourgeois Democratic Revolution and sometimes as the March Revolution or February Coup was the first of Russian Revolution, two revolutions which took place in Russia ...
took place in 1917. This would usher in a still bloodier chapter in Turkestan's history, as the Bolsheviks
The Bolsheviks, led by Vladimir Lenin, were a radical Faction (political), faction of the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) which split with the Mensheviks at the 2nd Congress of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party, ...
of the Tashkent Soviet (made up entirely of Russian soldiers and railway workers, with no Muslim members) launched an attack on the autonomous Jadid
The Jadid movement or Jadidism was an Turco-Islamic modernist political, religious, and cultural movement in the Russian Empire in the late 19th and early 20th century. They normally referred to themselves by the Tatar terms ''Taraqqiparvarlar ...
government in Kokand early in 1918, which left 14,000 dead. Resistance to the Bolsheviks
The Bolsheviks, led by Vladimir Lenin, were a radical Faction (political), faction of the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) which split with the Mensheviks at the 2nd Congress of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party, ...
by the local population (dismissed as 'Basmachi
The Basmachi movement (, derived from ) was an uprising against Imperial Russian and Soviet rule in Central Asia by rebel groups inspired by Islamic beliefs. It has been called "probably the most important movement of opposition to Soviet rul ...
' or 'Banditry
Banditry is a type of organized crime committed by outlaws typically involving the threat or use of violence. A person who engages in banditry is known as a bandit and primarily commits crimes such as extortion, robbery, kidnapping, and murder, ...
' by Soviet historians
This list of Russian historians includes historians, as well as archaeologists, paleographers, genealogists and other representatives of auxiliary historical disciplines from the Russian Federation, the Soviet Union, the Russian Empire and other p ...
) continued well into the 1920s.
Kengir uprising
During the rule of Joseph Stalin, a prison labour camp of the Steplag division of theGulag
The Gulag was a system of Labor camp, forced labor camps in the Soviet Union. The word ''Gulag'' originally referred only to the division of the Chronology of Soviet secret police agencies, Soviet secret police that was in charge of runnin ...
was set up adjacent to the village of Kengir, near the River Kengir in central Kazakhstan. It was mentioned in Aleksandr Solzhenitsyn
Aleksandr Isayevich Solzhenitsyn. (11 December 1918 – 3 August 2008) was a Soviet and Russian author and Soviet dissidents, dissident who helped to raise global awareness of political repression in the Soviet Union, especially the Gulag pris ...
's book, ''The Gulag Archipelago
''The Gulag Archipelago: An Experiment in Literary Investigation'' () is a three-volume nonfiction series written between 1958 and 1968 by Russian writer Aleksandr Solzhenitsyn, a Soviet dissident. It was first published in 1973 by the Parisian ...
''. The location of the camp was near the city of Dzhezkazgan. Russian actor Oleg Yankovsky
Oleg Ivanovich Yankovsky (; 23 February 1944 – 20 May 2009) was a Soviet Union, Soviet and Russian actor who excelled in psychologically sophisticated roles of modern intellectuals. In 1991, he became, together with , the last person to be nam ...
is the most famous of the city's natives. There was a prison revolt in 1954, by political prisoner
A political prisoner is someone imprisoned for their political activity. The political offense is not always the official reason for the prisoner's detention.
There is no internationally recognized legal definition of the concept, although ...
s, criminals, and other inmates.
Exiles
Dissident Islamist and anti-Soviet Central Asians fled to Afghanistan, British India, and to the Hijaz in Saudi Arabia. The last Emir of BukharaMohammed Alim Khan
Emir Sayyid Mir Muhammad Alim Khan ( Chagatai and , 3 January 1880 – 28 April 1944) was the last emir of the Uzbek Manghit dynasty, rulers of the Emirate of Bukhara in Central Asia. Although Bukhara was a protectorate of the Russian Empire ...
fled to Afghanistan. The Islamist Uzbek As-Sayyid Qāsim bin Abd al-Jabbaar Al-Andijaani(السيد قاسم بن عبد الجبار الأنديجاني) was born in Fergana valley's Andijan city in Turkestan (Central Asia). He went to British India was educated at Darul Uloom Deoband, and then returned to Turkestan where he preached against Communist Russian rule. He then fled to Afghanistan, then to British India and then to Hijaz where he continued his education in Mecca and Medina and wrote several works on Islam and engaged in anti-Soviet activities.
Uzbek exiles in Saudi Arabia from Soviet ruled Central Asia also adopted the identity "Turkistani". A lot of them are also called "Bukhari". A number of Saudi "Uzbeks" do not consider themselves as Uzbek and instead consider themselves as Muslim Turkestanis. Many Uzbeks in Saudi Arabia adopted the Arabic nisba of their home city in Uzbekistan, such as Al Bukhari from Bukhara, Al Samarqandi from Samarqand, Al Tashkandi from Tashkent, Al Andijani from Andijan, Al Kokandi from Kokand, Al Turkistani from Turkistan.
Bukhari and Turkistani were labels for all the Uzbeks in general while specific names for Uzbeks from different places were Farghani, Marghilani, Namangani, and Kokandi. Kokandi was used to refer to Uzbeks from Ferghana.
Shami Domullah introduced Salafism to Soviet Central Asia.
Mosques in Uzbekistan are funded by Saudi-based Uzbeks.
Saudis have tried to propagate their version of Islam into Uzbekistan following the collapse of the Soviet Union.
Saudi Arabia's "Bukharian brethren" were led by Nuriddin al-Bukhari as of 1990.
Industry
Oil and gas
AfterWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
the Soviet Union rapidly industrialized Kazakhstan and started prospecting for oil in the whole of Soviet Central Asia. Oil was found in Uzbekistan and both oil and gas
A fossil fuel is a flammable carbon compound- or hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the buried remains of prehistoric organisms (animals, plants or microplanktons), a process that occurs within geologi ...
were found in Turkmenistan. These fuel supplies would prove invaluable to the region over the coming years.
The central part of the geological depression
In geology, a depression is a landform sunken or depressed below the surrounding area. Depressions form by various mechanisms.
Types
Erosion-related:
* Blowout: a depression created by wind erosion typically in either a partially vegetated sa ...
that forms the Ferghana Valley is characterized by block subsidence, originally to depths estimated at 6–7 km, largely filled with sediments
Sediment is a solid material that is transported to a new location where it is deposited. It occurs naturally and, through the processes of weathering and erosion, is broken down and subsequently sediment transport, transported by the action of ...
that range in age as far back as the Permian-Triassic boundary. Some of the sediments are marine carbonates and clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolinite, ). Most pure clay minerals are white or light-coloured, but natural clays show a variety of colours from impuriti ...
s. The faults are upthrusts and overthrusts. Anticline
In structural geology, an anticline is a type of Fold (geology), fold that is an arch-like shape and has its oldest Bed (geology), beds at its core, whereas a syncline is the inverse of an anticline. A typical anticline is convex curve, c ...
s associated with these faults form traps for petroleum and natural gas, which has been discovered in 52 small fields.
Kazakhstan's Mangystau Province has an area of 165,600 square kilometers and a population of 316,847. It is a major oil- and gas-producing region. The city of Aktau was built in Kazakhstan's Mangyshlak Peninsula as a small village to house the region's oil workers in 1961. Over the years a large influx of Russian and Ukrainian oil and chemical
A chemical substance is a unique form of matter with constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Chemical substances may take the form of a single element or chemical compounds. If two or more chemical substances can be combin ...
workers arrived. Engineers discovered large amounts of crude oil
Petroleum, also known as crude oil or simply oil, is a naturally occurring, yellowish-black liquid chemical mixture found in geological formations, consisting mainly of hydrocarbons. The term ''petroleum'' refers both to naturally occurring u ...
and petroleum in the area in the days of the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
, and when drilling commenced, much of the area was built up around the industry. Aktau is Kazakhstan's only seaport on the Caspian Sea.
From 1964 to 1991 Aktau, which had become a city, bore the name "Shevchenko" in honour of the Ukrainian poet Taras Shevchenko
Taras Hryhorovych Shevchenko (; ; 9 March 1814 – 10 March 1861) was a Ukrainian poet, writer, artist, public and political figure, folklorist, and ethnographer. He was a fellow of the Imperial Academy of Arts and a member of the Brotherhood o ...
(1814–1861), who had been assigned to the area on military work. The average temperature on January is −3 °C, on July +26 °C. Annual rainfall averages 150 mm. Aktau had a population of 154,500 .
Transport
Much of the road and railway infrastructure that exists across Central Asia was developed when the areas was in the Soviet Union. As a result, it often disregards existing national borders. After the dissolution of the Soviet Union, this infrastructure has faced decline and degradation.Metallurgy
 Kazakhstan had started to produce and refine sizable amounts of
Kazakhstan had started to produce and refine sizable amounts of tin
Tin is a chemical element; it has symbol Sn () and atomic number 50. A silvery-colored metal, tin is soft enough to be cut with little force, and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, a bar of tin makes a sound, the ...
and uranium
Uranium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Ura ...
by the early 1970s. Vanadium
Vanadium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol V and atomic number 23. It is a hard, silvery-grey, malleable transition metal. The elemental metal is rarely found in nature, but once isolated artificially, the formation of an ...
and cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. ...
were, and still are also mined in the south of the country. Uranium was also first produced in Uzbekistan in the 1970s.
The city of Zhezkazgan was created in 1938 in connection with the exploitation of the rich local copper deposits. In 1973 a large mining and metallurgical complex was constructed to the southeast to smelt the copper that until then had been sent elsewhere for processing. Other metal ores mined and processed locally are manganese
Manganese is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese was first isolated in the 1770s. It is a transition m ...
, iron and gold. It is on a reservoir of the Kara-Kengir River and has a population of 90,000 (1999 census).
Its urban area includes the neighbouring mining town of Satpayev, total population 148,700. 55% of the population are Kazakhs
The Kazakhs (Kazakh language, Kazakh: , , , ) are a Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group native to Central Asia and Eastern Europe. They share a common Culture of Kazakhstan, culture, Kazakh language, language and History of Kazakhstan, history ...
, 30% Russians
Russians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Eastern Europe. Their mother tongue is Russian language, Russian, the most spoken Slavic languages, Slavic language. The majority of Russians adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church ...
, with smaller minorities of Ukrainians
Ukrainians (, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. Their native tongue is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and the majority adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, forming the List of contemporary eth ...
, Germans
Germans (, ) are the natives or inhabitants of Germany, or sometimes more broadly any people who are of German descent or native speakers of the German language. The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, constitution of Germany, imple ...
, Chechens
The Chechens ( ; , , Old Chechen: Нахчой, ''Naxçoy''), historically also known as ''Kistin, Kisti'' and ''Durdzuks'', are a Northeast Caucasian languages, Northeast Caucasian ethnic group of the Nakh peoples native to the North Caucasus. ...
and Koreans
Koreans are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Korean Peninsula. The majority of Koreans live in the two Korean sovereign states of North and South Korea, which are collectively referred to as Korea. As of 2021, an estimated 7.3 m ...
. Dzhezkazgan has an extreme continental climate
Continental climates often have a significant annual variation in temperature (warm to hot summers and cold winters). They tend to occur in central and eastern parts of the three northern-tier continents (North America, Europe, and Asia), typi ...
. The average temperature ranges from +24 °C (75 °F) in July to −16 °C (3 °F) in January.
Today the city is the headquarters of the copper conglomerate Kazakhmys, the city's main employer. The company has subsidiaries in China, Russia, France and the UK and is listed on the London Stock Exchange
The London Stock Exchange (LSE) is a stock exchange based in London, England. the total market value of all companies trading on the LSE stood at US$3.42 trillion. Its current premises are situated in Paternoster Square close to St Paul's Cath ...
.
Cement
Cement was a major product in both the cities ofShymkent
Shymkent (, ; ) is a city in southern Kazakhstan, located near the border with Uzbekistan. It holds the status of a city of republican significance, one of only three cities in Kazakhstan with this distinction, alongside Almaty and Astana. As of ...
and Dushanbe
Dushanbe is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Tajikistan. , Dushanbe had a population of 1,564,700, with this population being largely Tajiks, Tajik. Until 1929, the city was known in Russian as Dyushambe, and from 1929 to 1961 as St ...
in the south of the region.
Hydro-electricity
By the early 1970s, the Soviets had started to build some of theirhydroelectric
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is Electricity generation, electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies 15% of the world's electricity, almost 4,210 TWh in 2023, which is more than all other Renewable energ ...
power stations in Eastern Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan as part of an overall development strategy. The waters of the Ili River
The Ili River (, , ; ; ; zh, 伊犁河, ; , ; , ) is a river in Northwest China and Southeastern Kazakhstan. It flows from the Ili Kazakh Autonomous Prefecture of the Xinjiang Uighur Autonomous Region to the Almaty Region in Kazakhstan.
It ...
and of Lake Balkhash are considered to be of a vital economic importance to Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
. The Ili river is dammed for hydroelectric power at Kaptchagayskoye, and the river waters are heavily diverted for agricultural irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering of plants) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has bee ...
and for industrial purposes. In Tajikistan, the Vakhsh River, main tributary of the Amu Darya, is dammed multiple times, including the Nurek Dam (highest dam in the world at time of construction) and the still-under-construction Rogun Dam.
Cotton
The Soviets began to grow cotton in Uzbekistan after the '' Virgin Lands'' project and the mass use of the isolated and now shrinkingAral Sea
The Aral Sea () was an endorheic lake lying between Kazakhstan to its north and Uzbekistan to its south, which began shrinking in the 1960s and had largely dried up into desert by the 2010s. It was in the Aktobe and Kyzylorda regions of Kazakhst ...
for desert irrigation in the early 1960s. A massive expansion of irrigation canals during the Soviet period, to irrigate cotton fields, wrought ecological carnage to the area, with the river drying up long before reaching the Aral Sea which, as a result, has shrunk to a small remnant of its former size.
Baikonur Cosmodrome
TheBaikonur Cosmodrome
The Baikonur Cosmodrome is a spaceport operated by Russia within Kazakhstan. Located in the Kazakh city of Baikonur, it is the largest operational space launch facility in terms of area. All Russian Human spaceflight, crewed spaceflights are l ...
was founded in Kazakhstan on 2 June 1955, during the Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
, as one of many long-range nuclear missile
Nuclear weapons delivery is the technology and systems used to place a nuclear weapon at the position of detonation, on or near its target. All nine nuclear states have developed some form of medium- to long-range delivery system for their nuc ...
bases in the region, but diverged into space travel.
On 8 June 2005 the Russian Federation Council ratified an agreement between Russia and Kazakhstan extending Russia's rent term of the spaceport until 2050.
Culture, religion and ethnicity
 Following a series of migrations, mostly predating Soviet rule, that displaced the autochthonous
Following a series of migrations, mostly predating Soviet rule, that displaced the autochthonous Iranian peoples
Iranian peoples, or Iranic peoples, are the collective ethnolinguistic groups who are identified chiefly by their native usage of any of the Iranian languages, which are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages within the Indo-European langu ...
, most of the inhabitants of Soviet Central Asia were speakers of either Kipchak languages
The Kipchak languages (also known as the Kypchak, Qypchaq, Qypshaq or the Northwestern Turkic languages) are a sub-branch of the Turkic language family spoken by approximately 30 million people in much of Central Asia and Eastern Europe, spanni ...
(such as Kazakhs), Uyghuric languages (Uzbeks) or Oghuz languages
The Oghuz languages are a sub-branch of the Turkic language family, spoken by approximately 108 million people. The three languages with the largest number of speakers are Turkish, Azerbaijani and Turkmen, which, combined, account for more ...
(Turkmens). Those populations were nomadic and settled, respectively. There remained traces of some settled farming and urban Iranian communities like the Tajiks
Tajiks (; ; also spelled ''Tadzhiks'' or ''Tadjiks'') is the name of various Persian-speaking Eastern Iranian groups of people native to Central Asia, living primarily in Afghanistan, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan. Even though the term ''Tajik'' ...
and Bukhara in the south, and nomadic
Nomads are communities without fixed habitation who regularly move to and from areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the population of nomadic pa ...
Mongol
Mongols are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, China (Inner Mongolia and other 11 autonomous territories), as well as the republics of Buryatia and Kalmykia in Russia. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family of M ...
ic Kyrgiz on the border with China.
In Kazakh ɑzɑqtɑr Russian: Казахи; the English name 'Kazakh' is transliterated from Russian) are Turkic people
Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West Asia, West, Central Asia, Central, East Asia, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose members ...
of the northern parts of Central Asia (largely Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
, but also found in parts of Uzbekistan
, image_flag = Flag of Uzbekistan.svg
, image_coat = Emblem of Uzbekistan.svg
, symbol_type = Emblem of Uzbekistan, Emblem
, national_anthem = "State Anthem of Uzbekistan, State Anthem of the Republ ...
, China, Russia, and Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south and southeast. It covers an area of , with a population of 3.5 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by po ...
).
According to Robert G. Gordon Jr., editor of the Ethnologue: Languages of the World, classifies Kalmyk- Oirat under the Oirat-Khalkha group, since he contends that Kalmyk-Oirat is related to Khalkha Mongolian – the national language of Mongolia. The descent of the Kyrgyz from the autochthonous Siberian population is confirmed on the other hand by recent genetic studies.
The Slavic community would grow very rapidly under communism and Russians would eventually become a major ethnic group in the region. The Slavic population followed Orthodox Christianity, while the rest were mostly Sunni
Sunni Islam is the largest branch of Islam and the largest religious denomination in the world. It holds that Muhammad did not appoint any successor and that his closest companion Abu Bakr () rightfully succeeded him as the caliph of the Mu ...
Muslims. Various nationality, such as the Meskhetian Turks and Volga Germans
The Volga Germans (, ; ) are ethnic Germans who settled and historically lived along the Volga River in the region of southeastern European Russia around Saratov and close to Ukraine nearer to the south.
Recruited as immigrants to Russia in the ...
would get banished to the region. Over the years ethnic groups changed. Uralsk and Oral
The word oral may refer to:
Relating to the mouth
* Relating to the mouth, the first portion of the alimentary canal that primarily receives food and liquid
**Oral administration of medicines
** Oral examination (also known as an oral exam or ora ...
are now Russians (54%) and Kazakhs (34%), while it's also Kazakh 43.6% and Russian 40.2% in Almaty
Almaty, formerly Alma-Ata, is the List of most populous cities in Kazakhstan, largest city in Kazakhstan, with a population exceeding two million residents within its metropolitan area. Located in the foothills of the Trans-Ili Alatau mountains ...
.
Religion
The Bolsheviks would quickly set about closing mosques and churches throughout the USSR. This became particularly prevalent in the 1930s, but had been fully abandoned by the 1980s.Veil
In Uzbekistan and Tajikistan women wore veils which covered their entire face and body like theParanja
Paranja , paranji, or faranji (from ; , , ; ; ) is a traditional Central Asian robe for women and girls that covers the head and body. It is also known as "burqa" in Arabic. It is similar in basic style and function to other regional styles such ...
and faranji.
The traditional veil in Central Asia worn before modern times was the faranji but it was banned by the Soviet Communists.
Y-haplogroups
According to the interim results of Kazach mitochondrial DNA studies (where sample consisted of only 246 individuals), the main maternal lineages of Kazakhs are: D (17.9%), C (16%), G (16%), A (3.25%), F (2.44%), which is of eastern-Eurasian origin (58%), and haplogroups H (13%), T (4.07%), J (4.07%), K (4.07%), U5 (3.25%), I (0.41%), V (0.81%), W (1.63%), of western Eurasian origin (41%). The on a similar level, the distribution of Y-DNA haplogroups, according to E.K. Husnutdinova,/ref> (sample size is 331) is the following: C (25.3%), J (18.2%), N (15.2%), R (10.1%).
R1a
The descent of the Kyrgyz from the autochthonousSiberian
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states si ...
population is confirmed on the other hand by the recent genetic studies (The Eurasian Heartland: A continental perspective on Y-chromosome diversity). Remarkably, 63% of modern Kyrgyz men share Haplogroup R1a1 (Y-DNA) with Tajiks
Tajiks (; ; also spelled ''Tadzhiks'' or ''Tadjiks'') is the name of various Persian-speaking Eastern Iranian groups of people native to Central Asia, living primarily in Afghanistan, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan. Even though the term ''Tajik'' ...
(64%), Ruthenians
A ''Ruthenian'' and ''Ruthene'' are exonyms of Latin language, Latin origin, formerly used in Eastern and Central Europe as common Ethnonym, ethnonyms for East Slavs, particularly during the late medieval and early modern periods. The Latin term ...
(54%), Poles
Pole or poles may refer to:
People
*Poles (people), another term for Polish people, from the country of Poland
* Pole (surname), including a list of people with the name
* Pole (musician) (Stefan Betke, born 1967), German electronic music artist
...
and Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are an Ethnicity, ethnic group native to Hungary (), who share a common Culture of Hungary, culture, Hungarian language, language and History of Hungary, history. They also have a notable presence in former pa ...
(≈60%), and even Icelanders
Icelanders () are an ethnic group and nation who are native to the island country of Iceland. They speak Icelandic, a North Germanic language.
Icelanders established the country of Iceland in mid 930 CE when the (parliament) met for th ...
(25%). Haplogroup R1a1 (Y-DNA) is believed to be a marker of the Proto-Indo-European language
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. No direct record of Proto-Indo-European exists; its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-Eu ...
speakers.
R-Z93 (R1a1a1b2)
This large subclade appears to encompass most of the R1a1a found in Asia .See also
*Hujum
Hujum ( ; , ) refers to a broad campaign undertaken by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union to remove all manifestations of gender inequality within the Union Republics of Central Asia. Beginning in the Stalinist era, it particularly ta ...
* Bamboo Curtain
* Russian Turkestan
Russian Turkestan () was a colony of the Russian Empire, located in the western portion of the Central Asian region of Turkestan. Administered as a Krai or Governor-Generalship, it comprised the oasis region to the south of the Kazakh Steppe, b ...
* Soviet–Afghan War
The Soviet–Afghan War took place in the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan from December 1979 to February 1989. Marking the beginning of the 46-year-long Afghan conflict, it saw the Soviet Union and the Armed Forces of the Democratic Republic o ...
* Greater Central Asia
References
* * *Further reading
External links
The Strange State of Soviet Central Asia
Alicia Patterson Foundation Reporter * Keller, Bill (1989).
, The New York Times. * ttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=b0_U44QBbz8 Kazakh SSR AnthemYouTube
Uzbek SSR Anthem
YouTube
* *
Alec Rasizade. Dictators, Islamists, big powers and ordinary people: the new 'great game' in Central Asia. = Internationale Politik und Gesellschaft (Bonn: F.Ebert Stiftung), July 2002, number 3, pages 90–106.
{{Navboxes, , list1 = {{Autonomous Oblasts of the Soviet Union {{Autonomous republics of the Soviet Union {{Kazakhstan topics {{Kyrgyzstan topics {{Republics of the Soviet Union {{Tajikistan topics {{Turkmenistan topics {{Uzbekistan topics Post–Russian Empire states Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic Turkmen Soviet Socialist Republic Tajik Soviet Socialist Republic Kirghiz Soviet Socialist Republic Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic Communist states Early Soviet republics Former empires in Asia