Soviet Belarus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic (BSSR, Byelorussian SSR or Byelorussia; ; ), also known as Soviet Belarus or simply Belarus, was a

 On 11 September 1918, the
On 11 September 1918, the
 The western winter offensive was not limited to Byelorussia; Soviet forces similarly moved to the north into
The western winter offensive was not limited to Byelorussia; Soviet forces similarly moved to the north into  In the ''
In the ''
 In April 1920, Poland initiated its major offensive on Kiev, which although was initially successful, ended in a Polish defeat. The Soviet Red Army was much more organised than it was a year earlier, and though Polish troops managed to make several gains in Ukraine, notably the capture of
In April 1920, Poland initiated its major offensive on Kiev, which although was initially successful, ended in a Polish defeat. The Soviet Red Army was much more organised than it was a year earlier, and though Polish troops managed to make several gains in Ukraine, notably the capture of
 As the negotiations between the Polish Republic and the Russian Bolshevik government took place in
As the negotiations between the Polish Republic and the Russian Bolshevik government took place in
 In February 1921, the delegations of the Second Polish Republic and the Russian SFSR finally signed the
In February 1921, the delegations of the Second Polish Republic and the Russian SFSR finally signed the
 According to its entry in the
According to its entry in the
/ref> however, continued to consider herself part of the USSR. On 19 September the republic was renamed the
 Until 1990, Byelorussia was a
Until 1990, Byelorussia was a
 Whilst part of the Union, the cuisine of Byelorussia consisted mainly of vegetables, meat (particularly pork), and bread. Foods are usually either slowly cooked or stewed. Typically, Byelorussians eat a light breakfast and two hearty meals, with dinner being the largest meal of the day. Wheat and
Whilst part of the Union, the cuisine of Byelorussia consisted mainly of vegetables, meat (particularly pork), and bread. Foods are usually either slowly cooked or stewed. Typically, Byelorussians eat a light breakfast and two hearty meals, with dinner being the largest meal of the day. Wheat and
online review
* * * * * * * Vakar, Nicholas Platonovich. ''Belorussia: the making of a nation: a case study'' (Harvard UP, 1956). * Vakar, Nicholas Platonovich. ''A bibliographical guide to Belorussia'' (Harvard UP, 1956). * * *
''Byelorussia : speeding towards abundance''
by Tikhon Kiselev. {{Coord, 54.0000, N, 29.0000, E, source:wikidata, display=title States and territories disestablished in 1991 Communism in Belarus * Former socialist republics Countries and territories where Russian is an official language 1941 disestablishments in Belarus 1944 establishments in Belarus States and territories established in 1919 States and territories disestablished in 1941 States and territories established in 1944
republic
A republic, based on the Latin phrase ''res publica'' ('public affair' or 'people's affair'), is a State (polity), state in which Power (social and political), political power rests with the public (people), typically through their Representat ...
of the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
(USSR). It existed between 1920 and 1922 as an independent state, and afterwards as one of fifteen constituent republics of the USSR from 1922 to 1991, with its own legislation from 1990 to 1991. The republic was ruled by the Communist Party of Byelorussia
Communism () is a sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology within the socialist movement, whose goal is the creation of a communist society, a socioeconomic order centered on common ownership of the means of production, ...
. It was also known as the ''White Russian Soviet Socialist Republic''.
Following the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk was a separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Soviet Russia and the Central Powers (Germany, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and Bulgaria), by which Russia withdrew from World War I. The treaty, whi ...
in March 1918, which ended Russia's involvement in World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, the Belarusian Democratic Republic
The Belarusian People's Republic (BNR; , ), also known as the Belarusian Democratic Republic, was a state proclaimed by the Council of the Belarusian Democratic Republic in its Second Constituent Charter on 9 March 1918 during World War I. The ...
(BDR) was proclaimed under German occupation; however, as German troops left, the Socialist Soviet Republic of Byelorussia
The Socialist Soviet Republic of Byelorussia (SSRB; ; ) was an early republic in the historical territory of Belarus for only one month in 1919 after the collapse of the Russian Empire as a result of the October Revolution.
First establishmen ...
was established in its place by the Bolsheviks
The Bolsheviks, led by Vladimir Lenin, were a radical Faction (political), faction of the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) which split with the Mensheviks at the 2nd Congress of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party, ...
in December, and it was later merged with the Lithuanian Soviet Socialist Republic
The Lithuanian Soviet Socialist Republic (Lithuanian SSR; ; ), also known as Soviet Lithuania or simply Lithuania, was ''de facto'' one of the Republics of the Soviet Union, constituent republics of the Soviet Union between 1940–1941 and 1944 ...
in 1919 to form the Socialist Soviet Republic of Lithuania and Belorussia
The Socialist Soviet Republic of Lithuania and Belorussia (SSR LiB), alternatively referred to as the Socialist Soviet Republic of Lithuania and White Russia or simply Litbel, was a Soviet republic that existed within the parts of the territori ...
, which ceased to exist as a result of the Polish occupation during the Polish–Soviet War
The Polish–Soviet War (14 February 1919 – 18 March 1921) was fought primarily between the Second Polish Republic and the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, following World War I and the Russian Revolution.
After the collapse ...
. Following a peace treaty with Lithuania, the Socialist Soviet Republic of Byelorussia was re-founded on 31 July 1920 and later became known as the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic.
The BSSR became one of the four founding members of the Soviet Union in December 1922, together with the republics of Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
, Transcaucasia
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and West Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Armenia, ...
, and Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
. Byelorussia was one of several Soviet republics occupied by Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
. Towards the final years of the Soviet Union's existence, the Supreme Soviet of the Byelorussian SSR
The Supreme Soviet of the Byelorussian SSR (Belarusian language, Belarusian: Вярхоўны Савет Беларускай ССР, ''Vyarkhowny Savyet Byelaruskay SSR''; Russian language, Russian: Верховный Совет Белорус ...
adopted the Declaration of State Sovereignty in 1990. On 25 August 1991, the Byelorussian SSR declared independence, and on 19 September it was renamed the Republic of Belarus
A republic, based on the Latin phrase ''res publica'' ('public affair' or 'people's affair'), is a state in which political power rests with the public (people), typically through their representatives—in contrast to a monarchy. Although a ...
. The Soviet Union was formally dissolved on 26 December 1991.
Terminology
The term ''Byelorussia'' (), derives from the term ''Belaya Rus' '', i.e., '' White Rus'''. There are several claims to the origin of the name ''White Rus'.'' An ethno-religious theory suggests that the name used to describe the part of oldRuthenia
''Ruthenia'' is an exonym, originally used in Medieval Latin, as one of several terms for Rus'. Originally, the term ''Rus' land'' referred to a triangular area, which mainly corresponds to the tribe of Polans in Dnieper Ukraine. ''Ruthenia' ...
n lands within the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a sovereign state in northeastern Europe that existed from the 13th century, succeeding the Kingdom of Lithuania, to the late 18th century, when the territory was suppressed during the 1795 Partitions of Poland, ...
that had been populated mostly by early Christianized Slavs
The Slavs or Slavic people are groups of people who speak Slavic languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout the northern parts of Eurasia; they predominantly inhabit Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, and ...
, as opposed to Black Ruthenia, which was predominantly inhabited by pagan Balts.
The latter part similar but spelled and stressed differently from Росси́я (''Russia''), first rose in the days of the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
, and the Russian Tsar was usually styled "the Tsar of All the Russias", as ''Russia'' or the ''Russian Empire'' was formed by three parts of Russia—the Great
Great may refer to:
Descriptions or measurements
* Great, a relative measurement in physical space, see Size
* Greatness, being divine, majestic, superior, majestic, or transcendent
People
* List of people known as "the Great"
* Artel Great (bo ...
, Little, and White
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no chroma). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully (or almost fully) reflect and scatter all the visible wa ...
. This asserted that the territories are all Russian and all the peoples are also Russian; in the case of the Belarusians, that they were variants of the Russian people.
Following the Bolshevik Revolution
The October Revolution, also known as the Great October Socialist Revolution (in Soviet historiography), October coup, Bolshevik coup, or Bolshevik revolution, was the second of two revolutions in Russia in 1917. It was led by Vladimir L ...
in 1917, the term "White Russia" caused some confusion as it became the name of the so-called White military force that opposed the Red Bolsheviks. During the period of the Byelorussian SSR, the term ''Byelorussia'' was embraced as part of a national consciousness. In western Belarus
Western Belorussia or Western Belarus (; ; ) is a historical region of modern-day Belarus which belonged to the Second Polish Republic during the interwar period. For twenty years before the 1939 invasion of Poland, it was the northern part of th ...
, under Polish control until World War II, ''Byelorussia'' became commonly used in the regions of Białystok
Białystok is the largest city in northeastern Poland and the capital of the Podlaskie Voivodeship. It is the List of cities and towns in Poland, tenth-largest city in Poland, second in terms of population density, and thirteenth in area.
Biał ...
and Grodno
Grodno, or Hrodna, is a city in western Belarus. It is one of the oldest cities in Belarus. The city is located on the Neman, Neman River, from Minsk, about from the Belarus–Poland border, border with Poland, and from the Belarus–Lithua ...
. Upon the establishment of the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic in 1920, the term ''Byelorussia'' (its names in other languages such as English being based on the Russian form) was only used officially. In 1936, with the proclamation of the 1936 Soviet Constitution
The 1936 Constitution of the Soviet Union, also known as the Stalin Constitution, was the constitution of the Soviet Union adopted on 5 December 1936.
The 1936 Constitution was the second constitution of the Soviet Union and replaced the 1924 ...
, the republic was renamed to the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic. In English, it was also known as the ''White Russian Soviet Socialist Republic''.
On 19 September 1991 the Supreme Soviet of the Byelorussian SSR
The Supreme Soviet of the Byelorussian SSR (Belarusian language, Belarusian: Вярхоўны Савет Беларускай ССР, ''Vyarkhowny Savyet Byelaruskay SSR''; Russian language, Russian: Верховный Совет Белорус ...
renamed the Soviet republic to the Republic of Belarus, with the short form "Belarus". Conservative forces in the newly independent Belarus did not support the name change and opposed its inclusion in the 1991 draft of the Constitution of Belarus
The Constitution of the Republic of Belarus (; ) is the supreme basic law of Belarus. The Constitution is composed of a preamble and nine sections divided into 148 articles.
Adopted in 1994, three years after the country declared its independen ...
.
History

Beginning
Prior to theFirst World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, the territories of modern-day Belarus were part of the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
, which it gained from the Partitions of Poland
The Partitions of Poland were three partition (politics), partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that took place between 1772 and 1795, toward the end of the 18th century. They ended the existence of the state, resulting in the eli ...
more than a century earlier. During the war, the Great Retreat
The Great Retreat (), also known as the retreat from Mons, was the long withdrawal to the River Marne in August and September 1914 by the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) and the French Fifth Army. The Franco-British forces on the Western F ...
in the Western Front in August–September 1915 ended with the lands of Grodno Governorate
Grodno Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (''guberniya'') of the Northwestern Krai of the Russian Empire, with its capital in Grodno. It encompassed in area and consisted of a population of 1,603,409 inhabitants by 1897. Gro ...
and most of Vilna Governorate
The Vilna Governorate was a province ('' guberniya'') of the Northwestern Krai of the Russian Empire. In 1897, the governorate covered an area of and had a population of 1,591,207 inhabitants. The governorate was defined by the Minsk Governo ...
being occupied by Germany. The resulting front, passing at 100 kilometres to the west of Minsk, remained static towards the end of the conflict, despite Russian attempts to break it at the Lake Naroch offensive in late spring 1916, and General Alexei Evert's inconclusive thrust around the city of Baranovichi in the summer of that year, during the Brusilov offensive further south, in western Ukraine.
The abdication of Nicholas II
Nicholas II (Nikolai Alexandrovich Romanov; 186817 July 1918) or Nikolai II was the last reigning Emperor of Russia, King of Congress Poland, and Grand Duke of Finland from 1 November 1894 until his abdication on 15 March 1917. He married ...
in light of the February Revolution
The February Revolution (), known in Soviet historiography as the February Bourgeois Democratic Revolution and sometimes as the March Revolution or February Coup was the first of Russian Revolution, two revolutions which took place in Russia ...
in Russia in February 1917, activated a rather dormant political life in Belarus. As central authority waned, different political and ethnic groups strived for greater self-determination and even secession from the increasingly ineffective Russian Provisional Government
The Russian Provisional Government was a provisional government of the Russian Empire and Russian Republic, announced two days before and established immediately after the abdication of Nicholas II on 2 March, O.S. New_Style.html" ;"title="5 ...
. The momentum picked up after the incompetent actions of the 10th Army during the ill-fated Kerensky offensive during the summer. Representatives of Belarusian regions and of different (mostly left-wing) newly established political powers, including the Belarusian Socialist Assembly, the Christian democratic movement
The Christian Democratic Movement (, KDH) is a Christian democratic political party in Slovakia that is a member of the European People's Party (EPP) and an observer of the Centrist Democrat International
The Centrist Democrat International ...
and the General Jewish Labour Bund
The General Jewish Labour Bund in Lithuania, Poland and Russia (), generally called The Bund (, cognate to , ) or the Jewish Labour Bund (), was a Jewish secularism, secular Jewish Socialism, socialist party initially formed in the Russian Empire ...
, formed a Belarusian Central Council. However, the national parties in Belarus were unable to secure mass support, and the nationalist movement was confined to a small, divided and ineffective intelligentsia
The intelligentsia is a status class composed of the university-educated people of a society who engage in the complex mental labours by which they critique, shape, and lead in the politics, policies, and culture of their society; as such, the i ...
.
Towards the autumn, political stability continued to shake, and countering the rising nationalist tendencies, were the soviets
The Soviet people () were the citizens and nationals of the Soviet Union. This demonym was presented in the ideology of the country as the "new historical unity of peoples of different nationalities" ().
Nationality policy in the Soviet Union ...
led by Bolsheviks
The Bolsheviks, led by Vladimir Lenin, were a radical Faction (political), faction of the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) which split with the Mensheviks at the 2nd Congress of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party, ...
when the October Revolution
The October Revolution, also known as the Great October Socialist Revolution (in Historiography in the Soviet Union, Soviet historiography), October coup, Bolshevik coup, or Bolshevik revolution, was the second of Russian Revolution, two r ...
hit Russia; that same day, on 25 October (7 November) 1917, the Minsk Soviet of Workers' and Soldiers' Deputies took over the administration of the city. The Bolshevik All-Russian Council of Soviets declared the creation of the Western Oblast, which unified the Vilna, Vitebsk
Vitebsk or Vitsyebsk (, ; , ; ) is a city in northern Belarus. It serves as the administrative center of Vitebsk Region and Vitebsk District, though it is administratively separated from the district. As of 2025, it has 358,927 inhabitants, m ...
, Mogilev
Mogilev (; , ), also transliterated as Mahilyow (, ), is a city in eastern Belarus. It is located on the Dnieper, Dnieper River, about from the Belarus–Russia border, border with Russia's Smolensk Oblast and from Bryansk Oblast. As of 2024, ...
and Minsk
Minsk (, ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Belarus, located on the Svislach (Berezina), Svislach and the now subterranean Nyamiha, Niamiha rivers. As the capital, Minsk has a special administrative status in Belarus and is the administra ...
governorates that were not occupied by the German army, to administer the Belarusian lands in the frontal zone. On 26 November (6 December), the executive committee of Workers', Peasants' and Soldiers' Deputies for the Western Oblast was merged with the Western front's executive committee, creating a single '' Obliskomzap''. During the autumn of 1917 and winter of 1918, the Western Oblast was headed by Aleksandr Myasnikyan as the head of the Western Oblast's Military Revolutionary Committee
The Military Revolutionary Committee (Milrevcom; , ) was the name for military organs created by the Bolsheviks under the soviets in preparation for the October Revolution (October 1917 – March 1918).
, who passed this duty on to Kārlis Landers. Myasnikyan took over as chair of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party
The Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP), also known as the Russian Social Democratic Workers' Party (RSDWP) or the Russian Social Democratic Party (RSDP), was a socialist political party founded in 1898 in Minsk, Russian Empire. The ...
's (RSDRP(b)) committee for the Western Oblast and as the chair of the ''Obliskomzap''.
Countering this, the Belarusian Central Council reorganised itself as the Belarusian National Council (''Rada''), and started working on establishing governmental institutions, and discarded the ''Obliskomzap'' as a military formation, rather than governmental. As a result, on 7 (20) December, when the first All-Belarusian Congress convened, the Minsk Bolsheviks commanded the pro-Soviet troops to disbanded it. Following this, they proclaimed the rule of soviets dominated by the Bolsheviks. The first Soviet government in Belarus was established at the end of December by communist organs in Minsk with the support of Russian troops of the Western Front. However, its authority only extended to the regions occupied by pro-communist forces and the major cities, where the local soviets followed Bolshevik leadership.
German involvement
The Russo-German front in Belarus remained static since 1915 and formal negotiations began only on 19 November (2 December N.S.), when the Soviet delegation traveled to the German-occupied city ofBrest-Litovsk
Brest, formerly Brest-Litovsk and Brest-on-the-Bug, is a city in south-western Belarus at the border with Poland opposite the Polish town of Terespol, where the Bug and Mukhavets rivers meet, making it a border town. It serves as the admini ...
. A cease-fire was quickly agreed and proper peace negotiations began in December.
However, the German party soon went back on its word and took full advantage of the situation, and the Bolsheviks' demand of a treaty "without annexations or indemnities" was unacceptable to the Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,; ; , ; were one of the two main coalitions that fought in World War I (1914–1918). It consisted of the German Empire, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Bulga ...
, and on 18 February, hostilities resumed. The German Operation Faustschlag
The Operation Faustschlag or (), also known as the Eleven Days' War, was a Central Powers offensive in World War I. It was the last major offensive on the Eastern Front.
Russian forces were unable to put up any serious resistance due to the ...
was of immediate success, and within 11 days, they were able to make a serious advance eastward, taking over Ukraine, the Baltic region, and occupying eastern Belarus. This forced the ''Obliskomzap'' to evacuate to Smolensk
Smolensk is a city and the administrative center of Smolensk Oblast, Russia, located on the Dnieper River, west-southwest of Moscow.
First mentioned in 863, it is one of the oldest cities in Russia. It has been a regional capital for most of ...
. The Smolensk Governorate
Smolensk Governorate () was an administrative-territorial unit ('' guberniya'') of the Tsardom of Russia, the Russian Empire, and the Russian SFSR. It existed, with interruptions, between 1708 and 1929.
Smolensk Governorate, together with seven o ...
was passed to the Western Oblast. At the end of February, the Germans entered Minsk, which the Soviet authorities had already cleared a few days prior.
Faced with the German demands, the Bolsheviks accepted their terms at the final Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk was a separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Soviet Russia and the Central Powers (Germany, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and Bulgaria), by which Russia withdrew from World War I. The treaty, whi ...
, which was signed on 3 March 1918. For the German Empire, Operation Faustschlag achieved one of their strategic plans for World War I, to create a German-centered hegemony of buffer states, called ''Mitteleuropa
(), meaning Middle Europe, is one of the German terms for Central Europe. The term has acquired diverse cultural, political and historical connotations. University of Warsaw, Johnson, Lonnie (1996) ''Central Europe: Enemies, Neighbors, Friends' ...
''. On the eve of Germany's occupation of Minsk, some members of the disbanded Belarusian National Council emerged from hiding and formed a provisional government, hoping to achieve German recognition. However, the Germans did not recognise it as another assembly in Vilna was created under their auspices. The Minsk and Vilna organisations issued a joint proclamation on 25 March establishing the Belarusian Democratic Republic
The Belarusian People's Republic (BNR; , ), also known as the Belarusian Democratic Republic, was a state proclaimed by the Council of the Belarusian Democratic Republic in its Second Constituent Charter on 9 March 1918 during World War I. The ...
(BDR) with German approval. The new government also sought material aid from Germany. The more radical nationalists who disapproved of collaboration with the Germans went to the communists and fled to Russia. The communists who did not escape to the east during the German occupation were driven underground.
In the spring of 1918, the Germans disapproved of the socialist inclinations of the nationalists in the Belarusian government and forced a change in leadership of the puppet government; however, the Germans were also displeased with him and removed him. As a result, the Germans permitted the government less jurisdiction compared to the one in Ukraine. An increase in repression by the Germans also led to an agrarian revolt, although not as violent as the one in Ukraine, which benefitted the communists. The communist underground were directed by the party's Northwestern Regional Committee in Smolensk, which aimed for an alliance with the peasantry.
Creation
Revolutionary Military Council
The Revolutionary Military Council (), sometimes called the Revolutionary War Council Brian PearceIntroductionto Fyodor Raskolnikov s "Tales of Sub-lieutenant Ilyin." or ''Revvoyensoviet'' (), was the supreme military authority of Soviet Rus ...
ordered the creation of the Western Defence region in the Western Oblast out of Curtain forces
Curtain forces () were military forces, created soon after the signing of the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk by Soviet Russia in 1918, to protect the inner regions of the state and initially served as border troops. They were created by the directive No.7 ...
which were stationed there. Simultaneously the Council reorganised the Western Oblast as a ''Western Commune''. After Germany was defeated in the First World War, it announced its evacuation from the occupied territories. The Germans began to depart in November 1918; however, there was no nationalist organisation in Belarus that was capable of assuming political authority, unlike in Ukraine. On 13 November, Moscow annulled the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk was a separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Soviet Russia and the Central Powers (Germany, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and Bulgaria), by which Russia withdrew from World War I. The treaty, whi ...
. Two days later, it transformed the Defence region into a Western army. It began an initial advance westward on 17 November. The Belarusian National Republic barely resisted, evacuating Minsk on 3 December. The Soviets maintained a distance of about between the two armies, and took Minsk on 10 December. As the Red Army re-occupied Belarus, the soviets in the country were dominated by Russian and Jewish parties sympathetic to the communists.
Encouraged by their success, in Smolensk on 30–31 December 1918, the Sixth Western Oblast Party conference met and announced its split from the Russian Communist Party, proclaiming itself as the first congress of the Communist Party of Byelorussia (KP(b)B). The next day, the Soviet Socialist Republic of Byelorussia was proclaimed in Smolensk, terminating the Western Commune, and on 7 January, it was moved to Minsk. Aleksandr Myasnikyan emerged as head of the All-Byelorussian Central Executive Committee and Zmicier Zhylunovich as head of the provisional government.
The new Soviet republic initially consisted of seven districts: Baranovichi, Vitebsk
Vitebsk or Vitsyebsk (, ; , ; ) is a city in northern Belarus. It serves as the administrative center of Vitebsk Region and Vitebsk District, though it is administratively separated from the district. As of 2025, it has 358,927 inhabitants, m ...
, Gomel
Gomel (, ) or Homyel (, ) is a city in south-eastern Belarus. It serves as the administrative centre of Gomel Region and Gomel District, though it is administratively separated from the district. As of 2025, it is the List of cities and largest ...
, Grodno
Grodno, or Hrodna, is a city in western Belarus. It is one of the oldest cities in Belarus. The city is located on the Neman, Neman River, from Minsk, about from the Belarus–Poland border, border with Poland, and from the Belarus–Lithua ...
, Mogilev
Mogilev (; , ), also transliterated as Mahilyow (, ), is a city in eastern Belarus. It is located on the Dnieper, Dnieper River, about from the Belarus–Russia border, border with Russia's Smolensk Oblast and from Bryansk Oblast. As of 2024, ...
and Smolensk
Smolensk is a city and the administrative center of Smolensk Oblast, Russia, located on the Dnieper River, west-southwest of Moscow.
First mentioned in 863, it is one of the oldest cities in Russia. It has been a regional capital for most of ...
. On 30 January, the republic announced its separation from the Russian SFSR
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (Russian SFSR or RSFSR), previously known as the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic and the Russian Soviet Republic, and unofficially as Soviet Russia,Declaration of Rights of the labo ...
and renaming as the ''Soviet Socialist'' Republic of Byelorussia (SSRB). This was conferred by the First Congress of deputies, composed of workers, soldiers and Red Army soldiers, which met on 2–3 February 1919, to adopt a new socialist constitution. The Red Army continued its westward advance, capturing the city of Grodno on New Year's Day 1919, Pinsk
Pinsk (; , ; ; ; ) is a city in Brest Region, Belarus. It serves as the administrative center of Pinsk District, though it is administratively separated from the district. It is located in the historical region of Polesia, at the confluence of t ...
on 21 January, and Baranovichi on 6 February 1919, thereby enlarging the SSRB.
Litbel
Lithuania
Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, P ...
, as the newly created Soviet republic had hoped to include Lithuania. On 16 December, the Lithuanian Socialist Soviet Republic (LSSR) was proclaimed in Vilnius
Vilnius ( , ) is the capital of and List of cities in Lithuania#Cities, largest city in Lithuania and the List of cities in the Baltic states by population, most-populous city in the Baltic states. The city's estimated January 2025 population w ...
.
The Lithuanian operation and continuing conquest of Byelorussia were threatened by the rise of the Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland, was a country in Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 7 October 1918 and 6 October 1939. The state was established in the final stage of World War I ...
after the withdrawal of German forces. However, the conflict with Poland did not break out and the Soviet High Command's 12 January directive was to cease advance on the Neman
Neman, Nemunas or Niemen is a river in Europe that rises in central Belarus and flows through Lithuania then forms Lithuania–Russia border, the northern border of Kaliningrad Oblast, Russia's western exclave, which specifically follows its s ...
- Bug rivers. However, the region to the east of those lines was historically mixed among a population of Belarusians, Poles and Lithuanians, with a sizeable Jewish minority. The local communities of each respective group wanted to be part of the respective states that were establishing themselves.
 In the ''
In the ''Kresy
Eastern Borderlands (), often simply Borderlands (, ) was a historical region of the eastern part of the Second Polish Republic. The term was coined during the interwar period (1918–1939). Largely agricultural and extensively multi-ethnic with ...
'' ("borderland") areas of Lithuania, Belarus and western Ukraine, self-organized militias, the ''Samoobrona Litwy i Białorusi'' numbering approximately 2,000 soldiers under General Wejtko, began to fight against the local communist and advancing Bolshevik forces. Each side was trying to secure the territories for its own government. The newly formed Polish Army began sending its organised units to reinforce the militias. On 14 February, the first clash between regular armies took place and a front emerged. The operations in Lithuania brought the front close to East Prussia
East Prussia was a Provinces of Prussia, province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1772 to 1829 and again from 1878 (with the Kingdom itself being part of the German Empire from 1871); following World War I it formed part of the Weimar Republic's ...
, and the German units that had withdrawn there began to assist the Lithuanian forces to defeat the Soviets; they repelled the Red offensive against Kaunas
Kaunas (; ) is the second-largest city in Lithuania after Vilnius, the fourth largest List of cities in the Baltic states by population, city in the Baltic States and an important centre of Lithuanian economic, academic, and cultural life. Kaun ...
in February 1919.
Eager to win support, the Bolshevik government decided to merge the Lithuanian and Byelorussian republics into the Lithuanian–Belorussian Soviet Socialist Republic (''Litbel'') on 28 February 1919. Its capital was proclaimed as Vilna
Vilnius ( , ) is the capital of and List of cities in Lithuania#Cities, largest city in Lithuania and the List of cities in the Baltic states by population, most-populous city in the Baltic states. The city's estimated January 2025 population w ...
, with five governorates: Vilna
Vilnius ( , ) is the capital of and List of cities in Lithuania#Cities, largest city in Lithuania and the List of cities in the Baltic states by population, most-populous city in the Baltic states. The city's estimated January 2025 population w ...
, Grodno
Grodno, or Hrodna, is a city in western Belarus. It is one of the oldest cities in Belarus. The city is located on the Neman, Neman River, from Minsk, about from the Belarus–Poland border, border with Poland, and from the Belarus–Lithua ...
, Kovno
Kaunas (; ) is the second-largest city in Lithuania after Vilnius, the fourth largest List of cities in the Baltic states by population, city in the Baltic States and an important centre of Lithuanian economic, academic, and cultural life. Kaun ...
, Suwalki and Minsk
Minsk (, ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Belarus, located on the Svislach (Berezina), Svislach and the now subterranean Nyamiha, Niamiha rivers. As the capital, Minsk has a special administrative status in Belarus and is the administra ...
. The Vitebsk and Mogilev governorates were transferred to the Russian SFSR, and were soon joined by the Gomel Governorate, which was created on 26 April. The two parties of the republics were also combined. The republic was headed by Vincas Mickevičius-Kapsukas
Vincas Mickevičius, known under his pen name ''Kapsukas'' ( – 17 February 1935), was a Lithuanian Communism, communist political activist, Opinion journalism, publicist, and revolutionary.
As an active member of the Lithuanian National Reviv ...
and the combined party was headed by nationalist Zmicier Zhylunovich. However, the Belarusian nationalists disapproved that the republic was being expanded, and Zhylunovich resigned shortly after, followed by other nationalists.
In March 1919, Polish units opened an offensive: forces under General Stanisław Szeptycki captured the city of Slonim
Slonim is a town in Grodno Region, in western Belarus. It serves as the administrative center of Slonim District. It is located at the junction of the Shchara and Isa (river), Isa rivers, southeast of Grodno. As of 2025, it has a population of ...
(2 March) and crossed the Neman, whilst Lithuanian advances forced the Soviets out of Panevėžys
Panevėžys () is the fifth-largest List of cities in Lithuania, city in Lithuania and the List of cities in the Baltic states by population, eighth-most-populous city in the Baltic States. it occupies with 89,100 inhabitants. As defined by Eu ...
. A final Soviet counter-offensive retook Panevėžys
Panevėžys () is the fifth-largest List of cities in Lithuania, city in Lithuania and the List of cities in the Baltic states by population, eighth-most-populous city in the Baltic States. it occupies with 89,100 inhabitants. As defined by Eu ...
and Grodno
Grodno, or Hrodna, is a city in western Belarus. It is one of the oldest cities in Belarus. The city is located on the Neman, Neman River, from Minsk, about from the Belarus–Poland border, border with Poland, and from the Belarus–Lithua ...
in early April, but the Western Army was too thinly spread to fight both the Polish and Lithuanian troops, and the German units assisting them. The Polish offensive quickly gained momentum, and Vilna offensive in April 1919, forced Litbel to evacuate the capital first to Dvinsk (28 April), then to Minsk (28 April), then to Bobruysk (19 May). As the Litbel lost territory, its powers were quickly stripped by Moscow. For example, on 1 June, Vtsik
The All-Russian Central Executive Committee () was (June – November 1917) a permanent body formed by the First All-Russian Congress of Soviets of Workers' and Soldiers' Deputies (held from June 16 to July 7, 1917 in Saint Petersburg, Petrograd), ...
's decree put all of Litbel's armed forces under the command of the Red Army. On 17 July, the Defence Soviet was liquidated, and its function was passed to Minsk's Milrevcom. When on 8 August Polish forces captured Minsk, that same day the capital was evacuated to Smolensk
Smolensk is a city and the administrative center of Smolensk Oblast, Russia, located on the Dnieper River, west-southwest of Moscow.
First mentioned in 863, it is one of the oldest cities in Russia. It has been a regional capital for most of ...
. On 28 August, Lithuanian forces took Zarasai
Zarasai () is a city in northeastern Lithuania, surrounded by many lakes and rivers: to the southwest of the city is Lake Zarasas, to the northLake Zarasaitis, to the southeastLake Baltas, and the eastLake Griežtas. Lakes Zarasaitis and Griežtas ...
(the last Lithuanian town held by Litbel) and the same day Bobruysk fell to the Poles.
By late summer of 1919, the Polish advance was also exhausted. The defeat of the Red Army allowed the outbreak of another historic disagreement over territory between Poland and Lithuania; their competition to control the city of Vilna soon erupted into a military conflict
War is an armed conflict between the armed forces of states, or between governmental forces and armed groups that are organized under a certain command structure and have the capacity to sustain military operations, or between such organize ...
, with Poland winning. Facing Denikin and Kolchak, Soviet Russia could not spare men for the western front. A stalemate with localised skirmishes developed between Poland and Lithuania.
The Polish Sejm had also declared that the territories of Belarus were an inalienable part of the Polish Commonwealth. As the Sejm was voting for annexation, Józef Piłsudski
Józef Klemens Piłsudski (; 5 December 1867 – 12 May 1935) was a Polish statesman who served as the Chief of State (Poland), Chief of State (1918–1922) and first Marshal of Poland (from 1920). In the aftermath of World War I, he beca ...
offered the Belarusians federal ties instead; however, the Polish occupation authorities disregarded the social radicalism of the masses and nationalist sentiments among parts of the Belarusian intelligentsia, with the Poles ordering for the lands confiscated by the communists to be returned to the landowners, and Polish being introduced as an official language.
Pawn on a chessboard
The stalemate and the occasional, though fruitless, negotiations gave Russia a much needed pause to concentrate on other regions. During the latter half of 1919, the Red Army successfully defeated Denikin in the south, taking over the Don, North Caucasus and eastern Ukraine, and pushed Kolchak from the Volga, beyond the Ural mountains intoSiberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states ...
. In the autumn of 1919, Nikolai Yudenich
Nikolai Nikolayevich Yudenich ( Russian: Николай Николаевич Юденич; – 5 October 1933) was a commander of the Russian Imperial Army during World War I. He was a leader of the anti-communist White movement in northweste ...
's advance on Petrograd
Saint Petersburg, formerly known as Petrograd and later Leningrad, is the second-largest city in Russia after Moscow. It is situated on the River Neva, at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea. The city had a population of 5,601, ...
was checked, whilst in the far north the Evgeny Miller's army was pushed into the Arctic. On the diplomatic front, on 11 September 1919, the People's Commissar of Foreign Affairs of Soviet Russia, Georgy Chicherin, sent a note to Lithuania with a proposal for a peace treaty
A peace treaty is an treaty, agreement between two or more hostile parties, usually country, countries or governments, which formally ends a declaration of war, state of war between the parties. It is different from an armistice, which is an ag ...
. It was a ''de facto'' recognition of the Lithuanian state. Similar negotiations with Estonia
Estonia, officially the Republic of Estonia, is a country in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Ru ...
and Latvia
Latvia, officially the Republic of Latvia, is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is one of the three Baltic states, along with Estonia to the north and Lithuania to the south. It borders Russia to the east and Belarus to t ...
, gave way for a peace treaty with the former on 2 February 1920 and a cease-fire agreement with the latter a day earlier.
Lenin feared that a Polish offensive was incoming, and offered to accept the current frontline as a permanent border between Poland and Russia, which would include nearly all of Belarus going to Poland. However, Piłsudski had greater ambitions, and he also made an agreement with Symon Petliura in Ukraine to exchange Galicia in return for a promise to force out communists in right-bank Ukraine.
War continues
 In April 1920, Poland initiated its major offensive on Kiev, which although was initially successful, ended in a Polish defeat. The Soviet Red Army was much more organised than it was a year earlier, and though Polish troops managed to make several gains in Ukraine, notably the capture of
In April 1920, Poland initiated its major offensive on Kiev, which although was initially successful, ended in a Polish defeat. The Soviet Red Army was much more organised than it was a year earlier, and though Polish troops managed to make several gains in Ukraine, notably the capture of Kiev
Kyiv, also Kiev, is the capital and most populous List of cities in Ukraine, city of Ukraine. Located in the north-central part of the country, it straddles both sides of the Dnieper, Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2022, its population was 2, ...
, in Byelorussia, both of its offensives towards Zhlobin and Orsha
Orsha (; , ; ) is a city in Vitebsk Region, Belarus. It is situated on the fork of the Dnieper, Dnieper River and Arshytsa River, and it serves as the administrative center of Orsha District. As of 2025, it has a population of 101,662.
History
...
were thrown back in May.
In June, the RSFSR was finally ready to open its major Western advance. To preserve the neutrality of Lithuania (though the peace treaty was still being negotiated), on 6 June the exiled government of Litbel was disbanded. Within a few days, the 3rd Cavalry Corps under command of Hayk Bzhishkyan
Hayk Bzhishkian (, , also known as Guy Dmitrievich Guy, Gai Dmitrievich Gai (Гай Дмитриевич Гай), Gaya Gai (Гая Гай), – 11 December 1937), was a Soviet military commander of Armenian origin who fought in the Russian Civi ...
broke the Polish front, causing a collapse and a retreat. On 11 July Minsk was re-taken, and on 31 July 1920 once again the Soviet Socialist Republic of Belorussia was re-established in Minsk.
As the front moved west, and more Belarusian lands were adjoined to the new republic, the first administrative decrees were issued. The entity was divided into seven uyezd
An uezd (also spelled uyezd or uiezd; rus, уе́зд ( pre-1918: уѣздъ), p=ʊˈjest), or povit in a Ukrainian context () was a type of administrative subdivision of the Grand Duchy of Moscow, the Tsardom of Russia, the Russian Empire, the R ...
s: Bobruysk, Borisov, Igumen, Minsk, Mozyr and Slutsk
Slutsk is a town in Minsk Region, in central Belarus. It serves as the administrative center of Slutsk District, and is located on the Sluch (Belarus), Sluch River south of the capital Minsk. As of 2025, it has a population of 59,450.
Geography ...
. (Vitebsk, Gomel and Mogilev remained part of the RSFSR.) This time the leaders were Aleksandr Chervyakov (head of Minsk's milrevcom) and Wilhelm Knorin (as chairmen of the Central Committee of the Belarusian Communist Party). The SSRB sought to join further territories, as the Red Army crossed into Poland, but the decisive Polish victory at the Battle of Warsaw in August ended these ambitions. Once again, the Red Army found itself on the defensive in Belorussia. The Poles were able to successfully break the Russian lines at the Battle of the Niemen River in September 1920. As a result, the Soviets were not only forced to abandon their World Revolution
World revolution is the Marxist concept of overthrowing capitalism in all countries through the conscious revolutionary action of the organized working class. For theorists, these revolutions will not necessarily occur simultaneously, but whe ...
targets, but Western Belarus
Western Belorussia or Western Belarus (; ; ) is a historical region of modern-day Belarus which belonged to the Second Polish Republic during the interwar period. For twenty years before the 1939 invasion of Poland, it was the northern part of th ...
too. However early autumn rains halted the Polish advance, which exhausted itself by October. A cease-fire agreed on 12 October, came into effect on 18 October.
Slutsk uprising
 As the negotiations between the Polish Republic and the Russian Bolshevik government took place in
As the negotiations between the Polish Republic and the Russian Bolshevik government took place in Riga
Riga ( ) is the capital, Primate city, primate, and List of cities and towns in Latvia, largest city of Latvia. Home to 591,882 inhabitants (as of 2025), the city accounts for a third of Latvia's total population. The population of Riga Planni ...
, the Soviet side saw the armistice as only a temporary setback in its western advance. Seeing the failure of overcoming the Polish nationalist rhetoric with Communist propaganda, the Soviet government chose a different tactic, by appealing to the minorities of the Polish state, creating a fifth column
A fifth column is a group of people who undermine a larger group or nation from within, usually in favor of an enemy group or another nation. The activities of a fifth column can be overt or clandestine. Forces gathered in secret can mobilize ...
element out of Belarusians
Belarusians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Belarus. They natively speak Belarusian language, Belarusian, an East Slavic language. More than 9 million people proclaim Belarusian ethnicity worldwide. Nearly 7.99&n ...
and Ukrainians
Ukrainians (, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. Their native tongue is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and the majority adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, forming the List of contemporary eth ...
. During the negotiations, RSFSR offered all of BSSR to Poland in return for concessions in Ukraine, which were rejected by the Polish side. Eventually a compromising armistice line was agreed, which would see the Belarusian city of Slutsk
Slutsk is a town in Minsk Region, in central Belarus. It serves as the administrative center of Slutsk District, and is located on the Sluch (Belarus), Sluch River south of the capital Minsk. As of 2025, it has a population of 59,450.
Geography ...
handed over to the Bolsheviks.
News of Belarus' upcoming permanent division angered the population, and using the town's Polish occupation, the local population began self-organising into a militia and associating itself with the Belarusian Democratic Republic
The Belarusian People's Republic (BNR; , ), also known as the Belarusian Democratic Republic, was a state proclaimed by the Council of the Belarusian Democratic Republic in its Second Constituent Charter on 9 March 1918 during World War I. The ...
. On 24 November the Polish units left the town, and for nearly a month the Slutsk partisans resisted Soviet attempts to re-gain control of the area. Eventually the Red Army had to mobilise two divisions to overcome the resistance, when the last units of Slutsk militia crossed the Moroch River and interned by the Polish border guards.
Early Soviet years
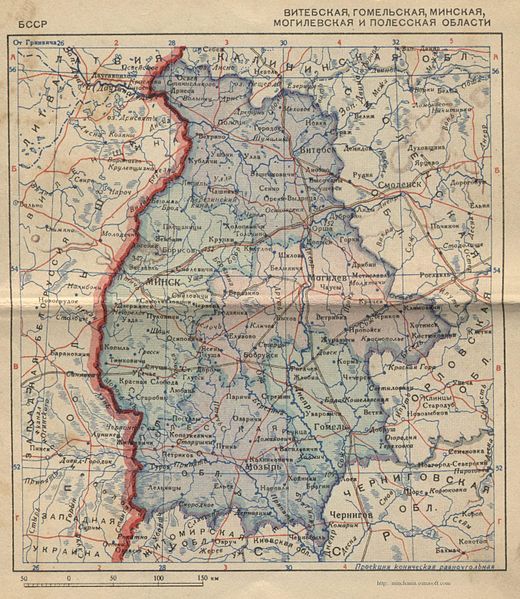
 In February 1921, the delegations of the Second Polish Republic and the Russian SFSR finally signed the
In February 1921, the delegations of the Second Polish Republic and the Russian SFSR finally signed the Treaty of Riga
The Treaty of Riga was signed in Riga, Latvia, on between Poland on one side and Soviet Russia (acting also on behalf of Soviet Belarus) and Soviet Ukraine on the other, ending the Polish–Soviet War (1919–1921). The chief negotiators of ...
putting an end of hostilities in Europe, and Belarus in particular. Six years of war had left the land neglected and looted, and the endless change of occupying regimes, each worse than the previous, left their mark on the Belarusian people, who were now divided. Almost half (Western Belarus
Western Belorussia or Western Belarus (; ; ) is a historical region of modern-day Belarus which belonged to the Second Polish Republic during the interwar period. For twenty years before the 1939 invasion of Poland, it was the northern part of th ...
) now belonged to Poland. Eastern Belarus (Gomel, Vitebsk and parts of Smolensk guberniyas) were administered by the RSFSR. The rest was the SSRB, a republic with 52,400 square kilometres and a population of a mere 1.544 million people.
An interesting paradox arose in the status of SSRB within the future Bolshevik state. On one hand its small geographic, population and almost negligent economic indicators did not warrant it much political weight on Soviet affairs. In fact the leader of the Communist Party of Byelorussia (Bolshevik), Alexander Chervyakov
Alexander Grigoryevich Chervyakov (Aliaksandr Charviakou, , ''Aliaksandr Ryhoravič Čarviakoŭ'' , ''Aleksandr Grigor'evič Červjakov''; 25 February 1892 — 16 June 1937) was a Soviet Union, Soviet Politician and revolutionary and one of the f ...
would represent Byelorussian communists at seven party congresses in Moscow, but not once be elected into the party's Central Committee. Moreover, the weak national sentiment of the Belarusian people would easily have allowed SSRB to be disbanded and annexed to the RSFSR, unlike for example Ukraine.
On the other hand, the region's strategic role decided its fate, as a full Union republic within the negotiations upon forming the future state. For one Leon Trotsky
Lev Davidovich Bronstein ( – 21 August 1940), better known as Leon Trotsky,; ; also transliterated ''Lyev'', ''Trotski'', ''Trockij'' and ''Trotzky'' was a Russian revolutionary, Soviet politician, and political theorist. He was a key figure ...
and his supporters within the Soviet leadership still supported its World Revolution
World revolution is the Marxist concept of overthrowing capitalism in all countries through the conscious revolutionary action of the organized working class. For theorists, these revolutions will not necessarily occur simultaneously, but whe ...
concept, and as said above, viewed the Treaty of Riga as only a temporary setback to the process, and a future advance would require a prepared bridgehead. This justified giving the SSRB the status of a full union republic within the Treaty on the Creation of the USSR
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between sovereign states and/or international organizations that is governed by international law. A treaty may also be known as an international agreement, protocol, covenant, conventio ...
that was signed on 30 December 1922. SSR Byelorussia became a founding member of the Soviet Union in 1922 and became known as BSSR.
However the politics in Moscow took a different course of events, and eventually the accession of Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Dzhugashvili; 5 March 1953) was a Soviet politician and revolutionary who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until Death and state funeral of Joseph Stalin, his death in 1953. He held power as General Secret ...
saw a new policy adopted: Socialism in One Country. In accordance with which, expansionist and irredentist claims were removed from Soviet ideology, which instead would focus on making regions economically viable. Thus in March 1924, by decree of the All-Russian Central Executive Committee
The All-Russian Central Executive Committee () was (June – November 1917) a permanent body formed by the First All-Russian Congress of Soviets of Workers' and Soldiers' Deputies (held from June 16 to July 7, 1917 in Petrograd), then became the ...
, Russia returned most of territories that made up the Vitebsk and Mogilev Governorates, as well as parts of Smolensk. The passing of land that largely survived the destruction of war not only doubled the SSRB's area to 110,600 square kilometres, but also raised the population to 4.2 million people.
SSRB in the mid-1920s
 According to its entry in the
According to its entry in the Great Soviet Encyclopedia
The ''Great Soviet Encyclopedia'' (GSE; , ''BSE'') is one of the largest Russian-language encyclopedias, published in the Soviet Union from 1926 to 1990. After 2002, the encyclopedia's data was partially included into the later ''Great Russian Enc ...
,Great Soviet Encyclopedia
The ''Great Soviet Encyclopedia'' (GSE; , ''BSE'') is one of the largest Russian-language encyclopedias, published in the Soviet Union from 1926 to 1990. After 2002, the encyclopedia's data was partially included into the later ''Great Russian Enc ...
1st edition, Volume 5, p.378-413, 1927 in 1925 SSRB was a largely rural country. Out of the 4,342,800 people that inhabited it, only 14.5% lived in urban areas. Administratively it was split into ten okrugs: Bobruysk, Borisov, Vitebsk
Vitebsk or Vitsyebsk (, ; , ; ) is a city in northern Belarus. It serves as the administrative center of Vitebsk Region and Vitebsk District, though it is administratively separated from the district. As of 2025, it has 358,927 inhabitants, m ...
, Kalinin, Minsk
Minsk (, ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Belarus, located on the Svislach (Berezina), Svislach and the now subterranean Nyamiha, Niamiha rivers. As the capital, Minsk has a special administrative status in Belarus and is the administra ...
, Mogilev
Mogilev (; , ), also transliterated as Mahilyow (, ), is a city in eastern Belarus. It is located on the Dnieper, Dnieper River, about from the Belarus–Russia border, border with Russia's Smolensk Oblast and from Bryansk Oblast. As of 2024, ...
, Mozyr, Orsha
Orsha (; , ; ) is a city in Vitebsk Region, Belarus. It is situated on the fork of the Dnieper, Dnieper River and Arshytsa River, and it serves as the administrative center of Orsha District. As of 2025, it has a population of 101,662.
History
...
, Polotsk
Polotsk () or Polatsk () is a town in Vitebsk Region, Belarus. It is situated on the Dvina River and serves as the administrative center of Polotsk District. Polotsk is served by Polotsk Airport and Borovitsy air base. As of 2025, it has a pop ...
and Slutsk
Slutsk is a town in Minsk Region, in central Belarus. It serves as the administrative center of Slutsk District, and is located on the Sluch (Belarus), Sluch River south of the capital Minsk. As of 2025, it has a population of 59,450.
Geography ...
; all of which contained a total of 100 raion
A raion (also spelt rayon) is a type of administrative unit of several post-Soviet states. The term is used for both a type of subnational entity and a division of a city. The word is from the French (meaning 'honeycomb, department'), and is c ...
s and 1,229 selsoviet
A selsoviet (; , ; ) is the shortened name for Selsky soviet, i.e., rural council (; ; ). It has three closely related meanings:
*The administration (''soviet (council), soviet'') of a certain rural area.
*The territorial subdivision administered ...
s. Only 25 towns and cities and an additional 49 urban settlements.
Trotsky's plan for the SSRB to act as a future magnet for the minorities in the Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland, was a country in Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 7 October 1918 and 6 October 1939. The state was established in the final stage of World War I ...
is clearly evidenced in the national policies. The republic initially had four official languages: Belarusian, Russian, Yiddish
Yiddish, historically Judeo-German, is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated in 9th-century Central Europe, and provided the nascent Ashkenazi community with a vernacular based on High German fused with ...
, and Polish, despite the fact that the Russians
Russians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Eastern Europe. Their mother tongue is Russian language, Russian, the most spoken Slavic languages, Slavic language. The majority of Russians adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church ...
and the Poles
Pole or poles may refer to:
People
*Poles (people), another term for Polish people, from the country of Poland
* Pole (surname), including a list of people with the name
* Pole (musician) (Stefan Betke, born 1967), German electronic music artist
...
made up only around 2% of the total population (most of the latter lived next to the state border in the Minsk and Borisov districts). The most important minority was the Jewish population of Belarus, which had a long history of targeted oppression under the Tsars, and in 1925 made up almost 44% of the urban population and began to be aided by affirmative action
Affirmative action (also sometimes called reservations, alternative access, positive discrimination or positive action in various countries' laws and policies) refers to a set of policies and practices within a government or organization seeking ...
programmes. In 1924 the government created a committee – ''Belkomzet'' – to allocate land to Jewish families, in 1926 a total of 32,700 hectares were given for 6,860 Jewish families. Jews would continue to play a major role in Byelorussian politics, society and economy right up to the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
; in fact, between 1928 and 1930, the first secretary of the Communist Party of Byelorussia
Communism () is a sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology within the socialist movement, whose goal is the creation of a communist society, a socioeconomic order centered on common ownership of the means of production, ...
, Yakov Gamarnik, was a Jew.
Yet, the titular nation of the SSRB were the Belarusians
Belarusians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Belarus. They natively speak Belarusian language, Belarusian, an East Slavic language. More than 9 million people proclaim Belarusian ethnicity worldwide. Nearly 7.99&n ...
, which made up 82% of the rural population, but less than half of the urban one (40.1%). The Belarusian national sentiment was a lot weaker than that of neighbouring Ukraine, this was greatly exploited by the Bolshevik-Polish power struggle in the Polish–Soviet War
The Polish–Soviet War (14 February 1919 – 18 March 1921) was fought primarily between the Second Polish Republic and the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, following World War I and the Russian Revolution.
After the collapse ...
. (In fact to avoid being annexed to Poland, at the census of 1920, many chose to be label themselves as Russians
Russians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Eastern Europe. Their mother tongue is Russian language, Russian, the most spoken Slavic languages, Slavic language. The majority of Russians adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church ...
.). To appeal to the Belarusians
Belarusians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Belarus. They natively speak Belarusian language, Belarusian, an East Slavic language. More than 9 million people proclaim Belarusian ethnicity worldwide. Nearly 7.99&n ...
of Western Belarus
Western Belorussia or Western Belarus (; ; ) is a historical region of modern-day Belarus which belonged to the Second Polish Republic during the interwar period. For twenty years before the 1939 invasion of Poland, it was the northern part of th ...
and also to prevent the nationalist element of the exiled Belarusian Democratic Republic
The Belarusian People's Republic (BNR; , ), also known as the Belarusian Democratic Republic, was a state proclaimed by the Council of the Belarusian Democratic Republic in its Second Constituent Charter on 9 March 1918 during World War I. The ...
from having any influence on the population (i.e. to avoid another Slutsk uprising), a policy of Korenizatsiya
Korenizatsiia (, ; ) was an early policy of the Soviet Union for the integration of non-Russian nationalities into the governments of their specific Soviet republics. In the 1920s, the policy promoted representatives of the titular nation, and ...
was widely implemented. Belarusian language, folklore and culture was put at front of everything else. This went on par with the Soviet policy of liquidation of illiteracy (likbez
Likbez (, ; a portmanteau of , , meaning "elimination of illiteracy") was a campaign of eradication of illiteracy in Soviet Russia and the Soviet Union in the 1920s and 1930s. The term was also used for various schools and courses established dur ...
).
Economically the republic remained largely self-centred, and most of the effort was put into restoring and repairing the war-damaged industry (if in 1923 there was only 226 different fabrics and factories, then by 1926 the number climbed to 246. However, the employed manpower jumped from 14 thousand to 21.3 thousand workers). The majority was food industry followed by metal and wood working combines. A lot more was centred in local and private sector, as allowed by the New Economic Policy
The New Economic Policy (NEP) () was an economic policy of the Soviet Union proposed by Vladimir Lenin in 1921 as a temporary expedient. Lenin characterized the NEP in 1922 as an economic system that would include "a free market and capitalism, ...
of the USSR, in 1925 these number 38.5 thousand who employed almost 50 thousand people. Most being textile workshops and lumber yards and blacksmiths.
On 6 December 1926, the SSRB was once again enlarged, in order to make the republic prosperous and continue the creating of well-defined national territorial units. This time, parts of RSFSR's Gomel Governorate were added, including the cities of Gomel
Gomel (, ) or Homyel (, ) is a city in south-eastern Belarus. It serves as the administrative centre of Gomel Region and Gomel District, though it is administratively separated from the district. As of 2025, it is the List of cities and largest ...
and Rechytsa. This increased the area to 126,300 square kilometres and the 1926 Soviet census that was held at the same time reported a population of 4,982,623. Of the latter 83% was rural, and Belarusians made up 80.6% (though only 39.2% of urban, yet 89% of rural).
On 11 April 1927, the republic adopted its new Constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organization or other type of entity, and commonly determines how that entity is to be governed.
When these pri ...
, bringing its laws in tie with those of the USSR and changing the name from the ''Soviet Socialist Republic of Byelorussia'' to the ''Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic.'' The head of government (chairman of the Soviet of People's Commissars) was by now then newly appointed Nikolay Goloded, whilst Vilhelm Knorin
Vilhelm Georgiyevich Knorin (, Latvian: ''Vilhelms "Vilis" Knoriņš''; (29 August 1890 – 29 July 1939) was a Latvian Bolshevik revolutionary, Soviet politician, publicist and historian.
Biography
Knorin was born in to a Latvian peasant fami ...
remained the first secretary of the Communist Party.
Stalinist years
The 1930s marked the peak ofSoviet repressions in Belarus
Soviet repression in Belarus () refers to cases of persecution of people in Belarus under Soviet rule.
Number of victims
According to researchers, the exact number of people who became victims of Soviet repression in Belarus is hard to determin ...
. According to incomplete calculations, about 600,000 people fell victim to Soviet repressions in Belarus between 1917 and 1953.В. Ф. Кушнер. ''Грамадска-палітычнае жыццё ў БССР у 1920—1930–я гг.'' Гісторыя Беларусі (у кантэксьце сусьветных цывілізацыяў) p. 370. Other estimates put the number at higher than 1.4 million persons., of which 250,000 were sentenced by judicial or executed by extrajudicial bodies (''dvoikas'', '' troikas'', special commissions of the OGPU
The Joint State Political Directorate ( rus, Объединённое государственное политическое управление, p=ɐbjɪdʲɪˈnʲɵn(ː)əjə ɡəsʊˈdarstvʲɪn(ː)əjə pəlʲɪˈtʲitɕɪskəjə ʊprɐˈv ...
, NKVD
The People's Commissariat for Internal Affairs (, ), abbreviated as NKVD (; ), was the interior ministry and secret police of the Soviet Union from 1934 to 1946. The agency was formed to succeed the Joint State Political Directorate (OGPU) se ...
, MGB). Excluding those sentenced in the 1920s–1930s, over 250,000 Belarusians were deported as kulak
Kulak ( ; rus, кула́к, r=kulák, p=kʊˈɫak, a=Ru-кулак.ogg; plural: кулаки́, ''kulakí'', 'fist' or 'tight-fisted'), also kurkul () or golchomag (, plural: ), was the term which was used to describe peasants who owned over ...
s or kulak family members to regions outside the Belarusian Soviet Republic. The scale of Soviet terror in Belarus was higher than in Russia or Ukraine which resulted in a much stronger extent of Russification
Russification (), Russianisation or Russianization, is a form of cultural assimilation in which non-Russians adopt Russian culture and Russian language either voluntarily or as a result of a deliberate state policy.
Russification was at times ...
in the republic.
A Polish Autonomous District was founded in 1932 and disbanded in 1935.
In September 1939, the Soviet Union, following the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact
The Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, officially the Treaty of Non-Aggression between Germany and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, and also known as the Hitler–Stalin Pact and the Nazi–Soviet Pact, was a non-aggression pact between Nazi Ge ...
with Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
, occupied eastern Poland after the 1939 invasion of Poland
The invasion of Poland, also known as the September Campaign, Polish Campaign, and Polish Defensive War of 1939 (1 September – 6 October 1939), was a joint attack on the Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany, the Slovak Republic, and the Soviet ...
. The former Polish territories referred to as West Belarus were incorporated into the Belarusian SSR, with an exception of the city of Vilnius
Vilnius ( , ) is the capital of and List of cities in Lithuania#Cities, largest city in Lithuania and the List of cities in the Baltic states by population, most-populous city in the Baltic states. The city's estimated January 2025 population w ...
and its surroundings that were transferred to Lithuania
Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, P ...
. The annexation was internationally recognized after the end of World War II.
Nazi German occupation
In the summer of 1941, Belarus was occupied by Nazi Germany. A large part of the territory of Belarus became the ''General District Belarus'' within theReichskommissariat Ostland
The (RKO; ) was an Administrative division, administrative entity of the Reich Ministry for the Occupied Eastern Territories of Nazi Germany from 1941 to 1945. It served as the German Civil authority, civilian occupation regime in Lithuania, La ...
.
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
imposed a brutal regime, deporting some 380,000 people for slave labour
Slavery is the ownership of a person as property, especially in regards to their labour. Slavery typically involves compulsory work, with the slave's location of work and residence dictated by the party that holds them in bondage. Enslavemen ...
, and killing hundreds of thousands of civilians more. 800,000 Belarusian Jews
The history of the Jews in Belarus begins as early as the 8th century. Jews lived in all parts of the lands of modern Belarus. In 1897, the Jewish population of Belarus reached 910,900, or 14.2% of the total population. Following the Poli ...
(about 90 percent of the Jewish population) were killed during the Holocaust
The Holocaust (), known in Hebrew language, Hebrew as the (), was the genocide of History of the Jews in Europe, European Jews during World War II. From 1941 to 1945, Nazi Germany and Collaboration with Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy ...
. At least 5,295 Belarusian settlements were destroyed by the Germans and some or all their inhabitants killed (out of 9,200 settlements that were burned or otherwise destroyed in Belarus during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
). More than 600 villages like Khatyn were totally annihilated. Altogether, over 2,000,000 people were killed in Belarus during the three years of German occupation, almost a quarter of the region's population.
After World War II, the Byelorussian SSR was given a seat in the United Nations General Assembly
A general assembly or general meeting is a meeting of all the members of an organization or shareholders of a company.
Specific examples of general assembly include:
Churches
* General Assembly (presbyterian church), the highest court of presby ...
together with the Soviet Union and Ukrainian SSR, becoming one of the founding members of the UN. This was part of a deal with the United States to ensure a degree of balance in the General Assembly
A general assembly or general meeting is a meeting of all the members of an organization or shareholders of a company.
Specific examples of general assembly include:
Churches
* General Assembly (presbyterian church), the highest court of presby ...
, which, the USSR opined, was unbalanced in favor of the Western Bloc. A Byelorussian, G.G. Chernushchenko, served as President of the United Nations Security Council
The presidency of the United Nations Security Council is responsible for leading the United Nations Security Council. It rotates among the fifteen member-states of the council monthly. The head of the country's delegation is known as the president ...
from January–February 1975.
Dissolution
In its last years during ''perestroika
''Perestroika'' ( ; rus, перестройка, r=perestrojka, p=pʲɪrʲɪˈstrojkə, a=ru-perestroika.ogg, links=no) was a political reform movement within the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU) during the late 1980s, widely associ ...
'' under Mikhail Gorbachev
Mikhail Sergeyevich Gorbachev (2 March 1931 – 30 August 2022) was a Soviet and Russian politician who served as the last leader of the Soviet Union from 1985 to dissolution of the Soviet Union, the country's dissolution in 1991. He served a ...
, the Supreme Soviet of Byelorussian SSR declared sovereignty on 27 July 1990 over Soviet laws.
On 25 August 1991, after the failure of the coup in Moscow, the republic proclaimed its political and economic independence from the Soviet Union,ПОСТАНОВЛЕНИЕ ВЕРХОВНОГО СОВЕТА БЕЛОРУССКОЙ ССР от 25 августа 1991 г. № 1019-XII «Об обеспечении политической и экономической самостоятельности Белорусской ССР»/ref> however, continued to consider herself part of the USSR. On 19 September the republic was renamed the
Republic of Belarus
A republic, based on the Latin phrase ''res publica'' ('public affair' or 'people's affair'), is a state in which political power rests with the public (people), typically through their representatives—in contrast to a monarchy. Although a ...
. On 8 December 1991 it was a signatory, along with Russia and Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
, of the Belovezha Accords
The Agreement on the creation of the Commonwealth of Independent States (officially), or unofficially the Minsk Agreement and best known as the Belovezha Accords, is the agreement declaring that the Soviet Union (USSR) had Dissolution of the So ...
, which replaced the Soviet Union with the Commonwealth of Independent States
The Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) is a regional organization, regional intergovernmental organization in Eurasia. It was formed following the dissolution of the Soviet Union, dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. It covers an ar ...
. Belarus received independence on 25 December 1991. A day later the Soviet Union ceased to exist. However, the Constitution (Fundamental Law) of the Republic of Belarus of 1978, was retained after independence.
Politics and government
 Until 1990, Byelorussia was a
Until 1990, Byelorussia was a one-party
A one-party state, single-party state, one-party system or single-party system is a governance structure in which only a single political party controls the ruling system. In a one-party state, all opposition parties are either outlawed or en ...
socialist republic, governed by the Communist Party of Byelorussia
Communism () is a sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology within the socialist movement, whose goal is the creation of a communist society, a socioeconomic order centered on common ownership of the means of production, ...
, a branch within the Communist Party of the Soviet Union
The Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU),. Abbreviated in Russian as КПСС, ''KPSS''. at some points known as the Russian Communist Party (RCP), All-Union Communist Party and Bolshevik Party, and sometimes referred to as the Soviet ...
(CPSU/KPSS). Like all other Soviet republics, it was one of the 15 constituent republics composing the Soviet Union from its entry into the union in 1922 until its dissolution in 1991. Executive power
The executive branch is the part of government which executes or enforces the law.
Function
The scope of executive power varies greatly depending on the political context in which it emerges, and it can change over time in a given country. In ...
was exercised by the Byelorussian Communist Party authorities, at its top sits the Chairman of the Council of Ministers. Legislative power
A legislature (, ) is a deliberative assembly with the legal authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country, nation or city on behalf of the people therein. They are often contrasted with the executive and judicial powers o ...
was vested in the unicameral parliament, the Supreme Soviet of the Byelorussian SSR
The Supreme Soviet of the Byelorussian SSR (Belarusian language, Belarusian: Вярхоўны Савет Беларускай ССР, ''Vyarkhowny Savyet Byelaruskay SSR''; Russian language, Russian: Верховный Совет Белорус ...
, also dominated by the Communist Party.
Belarus is the legal successor of the Byelorussian SSR and in its Constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organization or other type of entity, and commonly determines how that entity is to be governed.
When these pri ...
it states, "Laws, decrees and other acts which were applied in the territory of the Republic of Belarus prior to the entry into force of the present Constitution shall apply in the particular parts thereof that are not contrary to the Constitution of the Republic of Belarus."Constitution of Belarus
The Constitution of the Republic of Belarus (; ) is the supreme basic law of Belarus. The Constitution is composed of a preamble and nine sections divided into 148 articles.
Adopted in 1994, three years after the country declared its independen ...
, Art. 142.
Foreign relations
On the international stage, Byelorussia (along with Ukraine) was one of only tworepublics of the Soviet Union
In the Soviet Union, a Union Republic () or unofficially a Republic of the USSR was a Federated state, constituent federated political entity with a List of forms of government, system of government called a Soviet republic (system of governm ...
to be separate members of the United Nations. Both republics and the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
joined the UN when the organization was founded with the other 50 states on 24 October 1945. In effect, this provided the Soviet Union (a permanent Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, an ...
member with veto powers) with another 2 votes in the General Assembly
A general assembly or general meeting is a meeting of all the members of an organization or shareholders of a company.
Specific examples of general assembly include:
Churches
* General Assembly (presbyterian church), the highest court of presby ...
.
Apart from the UN, the Byelorussian SSR was a member of the UN Economic and Social Council
The United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) is one of six principal organs of the United Nations, responsible for coordinating the economic and social fields of the organization, specifically in regards to the fifteen specialized ...
, UNICEF
UNICEF ( ), originally the United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund, officially United Nations Children's Fund since 1953, is an agency of the United Nations responsible for providing Humanitarianism, humanitarian and Development a ...
, International Labour Organization
The International Labour Organization (ILO) is a United Nations agency whose mandate is to advance social and economic justice by setting international labour standards. Founded in October 1919 under the League of Nations, it is one of the firs ...
, Universal Postal Union
The Universal Postal Union (UPU, ) is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) that coordinates postal policies among member nations and facilitates a uniform worldwide postal system. It has 192 member states and is headquartered in Be ...
, World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
, UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
, International Telecommunication Union
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU)In the other common languages of the ITU:
*
* is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for many matters related to information ...
, United Nations Economic Commission for Europe
The United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (ECE or UNECE) is an intergovernmental organization or a specialized body of the United Nations. The UNECE is one of five regional commissions under the jurisdiction of the United Nations Econom ...
, World Intellectual Property Organization
The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO; (OMPI)) is one of the 15 specialized agencies of the United Nations (UN). Pursuant to the 1967 Convention Establishing the World Intellectual Property Organization, WIPO was created to pr ...
and the International Atomic Energy Agency
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) is an intergovernmental organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear technology, nuclear energy and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons. It was ...
. Byelorussia was excluded separately from the Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Pact (WP), formally the Treaty of Friendship, Co-operation and Mutual Assistance (TFCMA), was a Collective security#Collective defense, collective defense treaty signed in Warsaw, Polish People's Republic, Poland, between the Sovi ...
, Comecon
The Council for Mutual Economic Assistance, often abbreviated as Comecon ( ) or CMEA, was an economic organization from 1949 to 1991 under the leadership of the Soviet Union that comprised the countries of the Eastern Bloc#List of states, Easter ...
, the World Federation of Trade Unions
The World Federation of Trade Unions (WFTU) is an international federation of trade union, trade unions established on October 3, 1945. Founded in the immediate aftermath of World War Two, the organization built on the pre-war legacy of the Int ...
and the World Federation of Democratic Youth
The world is the totality of entities, the whole of reality, or everything that exists. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the world as unique, while others talk of a "plu ...
. In 1949, it joined the International Olympic Committee
The International Olympic Committee (IOC; , CIO) is the international, non-governmental, sports governing body of the modern Olympic Games. Founded in 1894 by Pierre de Coubertin and Demetrios Vikelas, it is based i ...
as a Union Republic.
Demographics
According to the 1959 Soviet Census, the population of the republic were made up as follows: Ethnicities (1959): *Belarusians
Belarusians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Belarus. They natively speak Belarusian language, Belarusian, an East Slavic language. More than 9 million people proclaim Belarusian ethnicity worldwide. Nearly 7.99&n ...
– 81%
*Poles
Pole or poles may refer to:
People
*Poles (people), another term for Polish people, from the country of Poland
* Pole (surname), including a list of people with the name
* Pole (musician) (Stefan Betke, born 1967), German electronic music artist
...
– 16%
*Lithuanians
Lithuanians () are a Balts, Baltic ethnic group. They are native to Lithuania, where they number around 2,378,118 people. Another two million make up the Lithuanian diaspora, largely found in countries such as the Lithuanian Americans, United Sta ...
– 5%
*Ukrainians
Ukrainians (, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. Their native tongue is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and the majority adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, forming the List of contemporary eth ...
– about 1%
*Jews – about 1%
*Russians
Russians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Eastern Europe. Their mother tongue is Russian language, Russian, the most spoken Slavic languages, Slavic language. The majority of Russians adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church ...
– <1%
The largest cities were:
*Minsk
Minsk (, ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Belarus, located on the Svislach (Berezina), Svislach and the now subterranean Nyamiha, Niamiha rivers. As the capital, Minsk has a special administrative status in Belarus and is the administra ...
* Brest
*Gomel
Gomel (, ) or Homyel (, ) is a city in south-eastern Belarus. It serves as the administrative centre of Gomel Region and Gomel District, though it is administratively separated from the district. As of 2025, it is the List of cities and largest ...
*Grodno
Grodno, or Hrodna, is a city in western Belarus. It is one of the oldest cities in Belarus. The city is located on the Neman, Neman River, from Minsk, about from the Belarus–Poland border, border with Poland, and from the Belarus–Lithua ...
*Mogilev
Mogilev (; , ), also transliterated as Mahilyow (, ), is a city in eastern Belarus. It is located on the Dnieper, Dnieper River, about from the Belarus–Russia border, border with Russia's Smolensk Oblast and from Bryansk Oblast. As of 2024, ...
*Vitebsk
Vitebsk or Vitsyebsk (, ; , ; ) is a city in northern Belarus. It serves as the administrative center of Vitebsk Region and Vitebsk District, though it is administratively separated from the district. As of 2025, it has 358,927 inhabitants, m ...
*Bobruisk
Babruysk (, ) or Bobruysk (, ; , ) is a city in Mogilev Region, Belarus. It serves as the administrative center of Babruysk District, though it is administratively separated from the district. It is situated on the Berezina River. Babruysk o ...
Culture
Cuisine
 Whilst part of the Union, the cuisine of Byelorussia consisted mainly of vegetables, meat (particularly pork), and bread. Foods are usually either slowly cooked or stewed. Typically, Byelorussians eat a light breakfast and two hearty meals, with dinner being the largest meal of the day. Wheat and
Whilst part of the Union, the cuisine of Byelorussia consisted mainly of vegetables, meat (particularly pork), and bread. Foods are usually either slowly cooked or stewed. Typically, Byelorussians eat a light breakfast and two hearty meals, with dinner being the largest meal of the day. Wheat and rye
Rye (''Secale cereale'') is a grass grown extensively as a grain, a cover crop and a forage crop. It is grown principally in an area from Eastern and Northern Europe into Russia. It is much more tolerant of cold weather and poor soil than o ...
breads are consumed in Belarus, but rye is more plentiful because conditions are too harsh for growing wheat. Many of the cuisines within Byelorussia also shared its cuisine with Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
and Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
.
See also
* Captive Nations *Belarusization
Belarusization () was a policy of protection and advancement of the Belarusian language and recruitment and promotion of Belarusian nationalists within the government of the Belarusian SSR (BSSR) and the Belarusian Communist Party, conducted by ...
* Russification of Belarus
Notes
References
Bibliography
*Further reading
* * Bekus, Nelly. ''Struggle over Identity: The Official and the Alternative "Belarussianness" '' (Budapest: Central European University Press, 2010); * Bemporad, Elissa. ''Becoming Soviet Jews: The Bolshevik Experiment in Minsk'' (Indiana UP, 2013). * Epstein, Barbara. ''The Minsk Ghetto 1941–1943: Jewish Resistance and Soviet Internationalism'' (U of California Press, 2008). * * * * * * * * * Rudling, Pers Anders. ''The Rise and Fall of Belarusian Nationalism, 1906–1931'' (University of Pittsburgh Press; 2014) 436ponline review
* * * * * * * Vakar, Nicholas Platonovich. ''Belorussia: the making of a nation: a case study'' (Harvard UP, 1956). * Vakar, Nicholas Platonovich. ''A bibliographical guide to Belorussia'' (Harvard UP, 1956). * * *
External links
''Byelorussia : speeding towards abundance''
by Tikhon Kiselev. {{Coord, 54.0000, N, 29.0000, E, source:wikidata, display=title States and territories disestablished in 1991 Communism in Belarus * Former socialist republics Countries and territories where Russian is an official language 1941 disestablishments in Belarus 1944 establishments in Belarus States and territories established in 1919 States and territories disestablished in 1941 States and territories established in 1944