Southern Netherlands on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Southern Netherlands, also called the Catholic Netherlands, were the parts of the
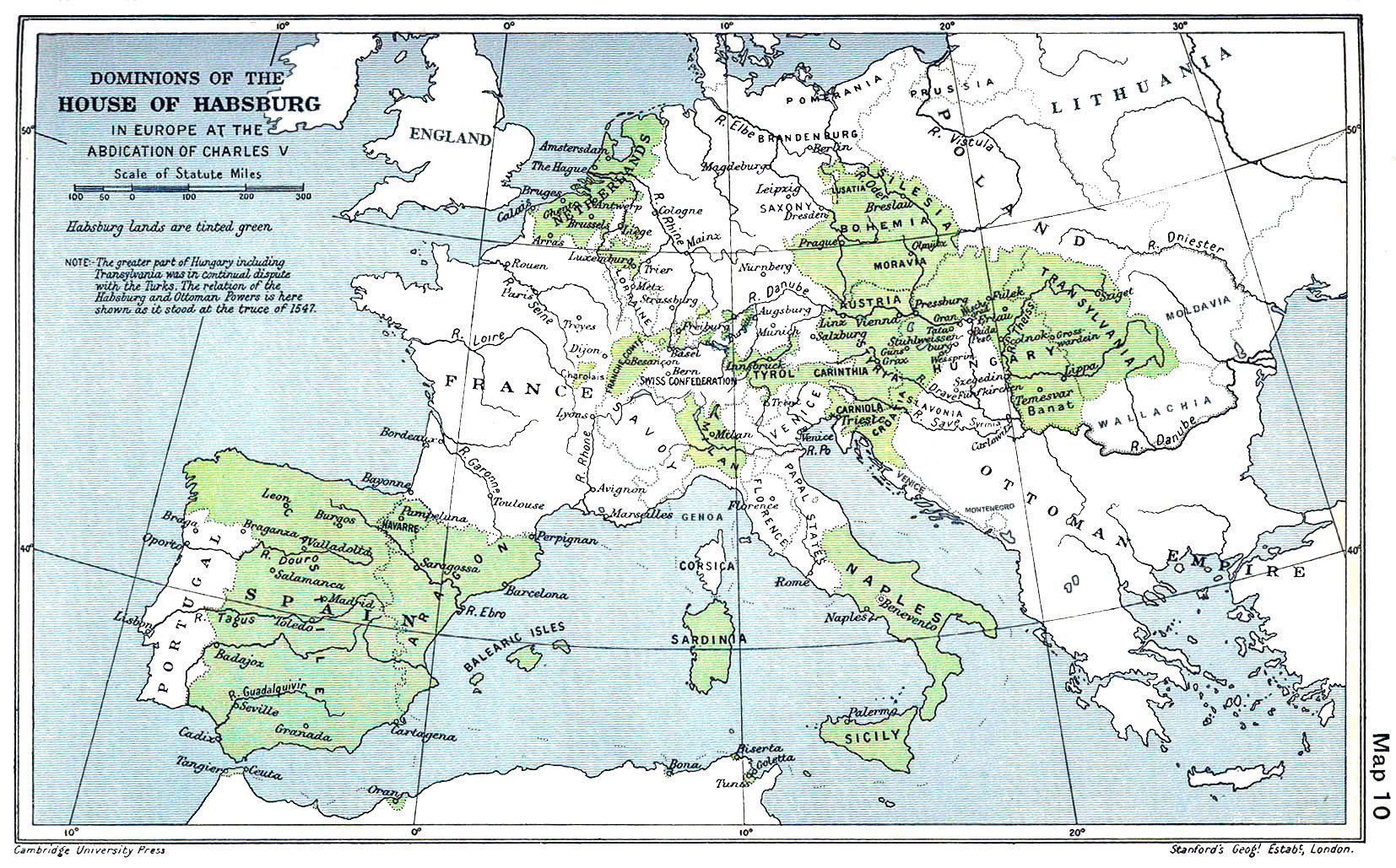 As they were very wealthy, the Netherlands in general were an important territory of the Habsburg crown which also ruled Spain and Austria among other places. But unlike the other Habsburg dominions, they were led by a merchant class. It was the merchant economy which made them wealthy, and the Habsburg attempts at increasing taxation to finance their wars was a major factor in the population’s (merchants') efforts to defend their privileges. This, added to resistance to penal laws enforced by the
As they were very wealthy, the Netherlands in general were an important territory of the Habsburg crown which also ruled Spain and Austria among other places. But unlike the other Habsburg dominions, they were led by a merchant class. It was the merchant economy which made them wealthy, and the Habsburg attempts at increasing taxation to finance their wars was a major factor in the population’s (merchants') efforts to defend their privileges. This, added to resistance to penal laws enforced by the
 The
The

 Under the Treaty of Rastatt (1714), following the
Under the Treaty of Rastatt (1714), following the
excerpt and text search
als
complete edition online
* Cammaerts, Émile. ''A History of Belgium from the Roman Invasion to the Present Day'' (1921) 357 pages
complete text online
* Cook, Bernard A. ''Belgium: a history'', 3rd ed. New York, 2004 * Kossmann, E. H. ''The Low Countries 1780–1940'' (1978
excerpt and text search
Low Countries
The Low Countries (; ), historically also known as the Netherlands (), is a coastal lowland region in Northwestern Europe forming the lower Drainage basin, basin of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta and consisting today of the three modern "Bene ...
belonging to the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
which were at first largely controlled by Habsburg Spain
Habsburg Spain refers to Spain and the Hispanic Monarchy (political entity), Hispanic Monarchy, also known as the Rex Catholicissimus, Catholic Monarchy, in the period from 1516 to 1700 when it was ruled by kings from the House of Habsburg. In t ...
(Spanish Netherlands
The Spanish Netherlands (; ; ; ) (historically in Spanish: , the name "Flanders" was used as a '' pars pro toto'') was the Habsburg Netherlands ruled by the Spanish branch of the Habsburgs from 1556 to 1714. They were a collection of States of t ...
, 1556–1714) and later by the Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
n Habsburgs (Austrian Netherlands
The Austrian Netherlands was the territory of the Burgundian Circle of the Holy Roman Empire between 1714 and 1797. The period began with the acquisition by the Austrian Habsburg monarchy of the former Spanish Netherlands under the Treaty of Ras ...
, 1714–1794) until occupied and annexed by Revolutionary France (1794–1815).
The region also included a number of smaller states that were never ruled by Spain or Austria: the Prince-Bishopric of Liège, the Imperial Abbey of Stavelot-Malmedy, the County of Bouillon, the County of Horne and the Princely Abbey of Thorn.
The Southern Netherlands comprised most of modern-day Belgium
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. Situated in a coastal lowland region known as the Low Countries, it is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeas ...
and Luxembourg
Luxembourg, officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, is a landlocked country in Western Europe. It is bordered by Belgium to the west and north, Germany to the east, and France on the south. Its capital and most populous city, Luxembour ...
, small parts of the modern Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
and Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
(the Upper Guelders {{unreferenced, date=November 2011
Upper Guelders or Spanish Guelders was one of the four quarters in the Imperial Guelders, Duchy of Guelders. In the Dutch Revolt, it was the only quarter that did not secede from the Habsburg monarchy to become pa ...
region, as well as the Bitburg
Bitburg (; ; ) is a city in Germany, in the state of Rhineland-Palatinate approximately 25 km (16 mi.) northwest of Trier and 50 km (31 mi.) northeast of Luxembourg (city), Luxembourg city. The American Spangdahlem Air Base i ...
area in Germany, then part of Luxembourg), in addition to (until 1678) most of the present Nord-Pas-de-Calais
Nord-Pas-de-Calais (; ; West Flemish: ''Nôord-Nauw van Kales'') was a former regions of France, administrative region of France. Since 1 January 2016, it has been part of the new Regions of France, region Hauts-de-France. It consisted of the ...
region, and Longwy area in northern France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
. The (southern) Upper Guelders region consisted of what is now divided between Germany and the modern Dutch Province of Limburg (in 1713 largely ceded to Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, ...
).
Place in the broader Netherlands
 As they were very wealthy, the Netherlands in general were an important territory of the Habsburg crown which also ruled Spain and Austria among other places. But unlike the other Habsburg dominions, they were led by a merchant class. It was the merchant economy which made them wealthy, and the Habsburg attempts at increasing taxation to finance their wars was a major factor in the population’s (merchants') efforts to defend their privileges. This, added to resistance to penal laws enforced by the
As they were very wealthy, the Netherlands in general were an important territory of the Habsburg crown which also ruled Spain and Austria among other places. But unlike the other Habsburg dominions, they were led by a merchant class. It was the merchant economy which made them wealthy, and the Habsburg attempts at increasing taxation to finance their wars was a major factor in the population’s (merchants') efforts to defend their privileges. This, added to resistance to penal laws enforced by the Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy, also known as Habsburg Empire, or Habsburg Realm (), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities (composite monarchy) that were ruled by the House of Habsburg. From the 18th century it is ...
that made heresy
Heresy is any belief or theory that is strongly at variance with established beliefs or customs, particularly the accepted beliefs or religious law of a religious organization. A heretic is a proponent of heresy.
Heresy in Heresy in Christian ...
a capital crime, led to a general rebellion of the Netherlands against Habsburg rule towards 1570 (protests and hostilities started the Eighty Years' War
The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt (; 1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and the Spanish Empire, Spanish government. The Origins of the Eighty Years' War, causes of the w ...
–1568). Although the northern seven provinces, led by Holland
Holland is a geographical regionG. Geerts & H. Heestermans, 1981, ''Groot Woordenboek der Nederlandse Taal. Deel I'', Van Dale Lexicografie, Utrecht, p 1105 and former provinces of the Netherlands, province on the western coast of the Netherland ...
and Zeeland
Zeeland (; ), historically known in English by the Endonym and exonym, exonym Zealand, is the westernmost and least populous province of the Netherlands. The province, located in the southwest of the country, borders North Brabant to the east ...
, established their independence as the United Provinces after 1581, the ten southern Netherlands were reconquered by the Spanish general Alexander Farnese, Duke of Parma. Liège, Stavelot-Malmédy and Bouillon maintained their independence.
The Habsburg Netherlands passed to the Austrian Habsburgs after the War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict fought between 1701 and 1714. The immediate cause was the death of the childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700, which led to a struggle for control of the Spanish E ...
in 1714. Under Austrian rule, the ten provinces' defence of their privileges proved as troublesome to the reforming Emperor Joseph II, Holy Roman Emperor
Joseph II (13 March 1741 – 20 February 1790) was Holy Roman Emperor from 18 August 1765 and sole ruler of the Habsburg monarchy from 29 November 1780 until his death. He was the eldest son of Empress Maria Theresa and her husband, Francis I, ...
as it had to his ancestor Philip II two centuries earlier, leading to a major rebellion in 1789–1790. The Austrian Netherlands were ultimately lost to the French Revolutionary armies, and annexed to France in 1794. Following the war, Austria's loss of the territories was confirmed, and they were joined with the northern Netherlands as a single kingdom under the House of Orange at the 1815 Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon, Napol ...
. The southeastern third of Luxembourg Province was made into the autonomous Grand Duchy of Luxembourg
Luxembourg, officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, is a landlocked country in Western Europe. It is bordered by Belgium to the west and north, Germany to the east, and France on the south. Its capital and most populous city, Luxembour ...
, because it was claimed by both the Netherlands and Prussia.
In 1830 the predominantly Roman Catholic southern half became independent as the Kingdom of Belgium
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. Situated in a coastal lowland region known as the Low Countries, it is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southe ...
(the northern half being predominantly Calvinist
Reformed Christianity, also called Calvinism, is a major branch of Protestantism that began during the 16th-century Protestant Reformation. In the modern day, it is largely represented by the Continental Reformed Protestantism, Continenta ...
). In 1839 the final border between the kingdom of the Netherlands
The Kingdom of the Netherlands (, ;, , ), commonly known simply as the Netherlands, is a sovereign state consisting of a collection of constituent territories united under the monarch of the Netherlands, who functions as head of state. The re ...
and Belgium was determined and the eastern part of Limburg went to the Netherlands as the province of Limburg. The autonomy of Luxembourg was recognised in 1839, but an instrument to that effect was not signed until 1867. The King of the Netherlands was Grand Duke of Luxembourg until 1890, when William III was succeeded by his daughter, Wilhelmina of the Netherlands
Wilhelmina (; Wilhelmina Helena Pauline Maria; 31 August 1880 – 28 November 1962) was List of monarchs of the Netherlands, Queen of the Netherlands from 1890 until her abdication in 1948. She reigned for nearly 58 years, making her the longest- ...
– but Luxembourg still followed the Salic law
The Salic law ( or ; ), also called the was the ancient Frankish Civil law (legal system), civil law code compiled around AD 500 by Clovis I, Clovis, the first Frankish King. The name may refer to the Salii, or "Salian Franks", but this is deba ...
at the time, which forbade a woman to rule in her own right; so the union of the Dutch and Luxembourgish crowns then ended. The northwestern two-thirds of the original Luxembourg remains a province of Belgium.
Spanish Netherlands
 The
The Spanish Netherlands
The Spanish Netherlands (; ; ; ) (historically in Spanish: , the name "Flanders" was used as a '' pars pro toto'') was the Habsburg Netherlands ruled by the Spanish branch of the Habsburgs from 1556 to 1714. They were a collection of States of t ...
(Dutch: ''Spaanse Nederlanden'', Spanish: ''Países Bajos españoles'') was a portion of the Low Countries
The Low Countries (; ), historically also known as the Netherlands (), is a coastal lowland region in Northwestern Europe forming the lower Drainage basin, basin of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta and consisting today of the three modern "Bene ...
controlled by Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
from 1556 to 1714, inherited from the Dukes of Burgundy. Although the territory of the Duchy of Burgundy itself remained in the hands of France, the Habsburgs remained in control of the title of Duke of Burgundy and the other parts of the Burgundian inheritance, notably the Low Countries and the Free County of Burgundy in the Holy Roman Empire. They often used the term Burgundy to refer to it (e.g. in the name of the Imperial Circle it was grouped into), until 1794, when the Austrian Netherlands were lost to the French Republic.
When part of the Netherlands separated from Spanish rule and became the United Provinces in 1581 the remainder of the area became known as the Spanish Netherlands and remained under Spanish control. This region comprised modern Belgium, Luxembourg as well as part of northern France.
The Spanish Netherlands originally consisted of:
*County of Flanders
The County of Flanders was one of the most powerful political entities in the medieval Low Countries, located on the North Sea coast of modern-day Belgium and north-eastern France. Unlike the neighbouring states of Duchy of Brabant, Brabant and ...
, including Walloon Flanders
* County of Artois
*City of Tournai
Tournai ( , ; ; ; , sometimes Anglicisation (linguistics), anglicised in older sources as "Tournay") is a city and Municipalities in Belgium, municipality of Wallonia located in the Hainaut Province, Province of Hainaut, Belgium. It lies by ...
*Cambrai
Cambrai (, ; ; ), formerly Cambray and historically in English Camerick or Camericke, is a city in the Nord department and in the Hauts-de-France region of France on the Scheldt river, which is known locally as the Escaut river.
A sub-pref ...
(roughly the département Nord and the northern half of Pas-de-Calais
The Pas-de-Calais (, ' strait of Calais'; ; ) is a department in northern France named after the French designation of the Strait of Dover, which it borders. It has the most communes of all the departments of France, with 890, and is the ...
in modern France)
*Duchy of Luxembourg
The Duchy of Luxembourg (; ; ; ) was a Imperial state, state of the Holy Roman Empire, the ancestral homeland of the noble House of Luxembourg. The House of Luxembourg became one of the most important political forces in the 14th century, comp ...
* Duchy of Limburg
*County of Hainaut
The County of Hainaut ( ; ; ; ), sometimes spelled Hainault, was a territorial lordship within the medieval Holy Roman Empire that straddled the present-day border of Belgium and France. Its most important towns included Mons, Belgium, Mons (), n ...
* County of Namur
* Lordship of Mechelen (officially a county since 1490)
*Duchy of Brabant
The Duchy of Brabant, a Imperial State, state of the Holy Roman Empire, was established in 1183. It developed from the Landgraviate of Brabant of 1085–1183, and formed the heart of the historic Low Countries. The Duchy comprised part of the Bu ...
, including the Margraviate of Antwerp
*the Upper Quarter (''Bovenkwartier'') of the duchy of Guelders (around Venlo
Venlo () is a List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in southeastern Netherlands, close to the border with Germany. It is situated in the province of Limburg (Netherlands), ...
and Roermond
Roermond (; or ) is a city, municipality, and diocese in the Limburg (Netherlands), Limburg province of the Netherlands. Roermond is a historically important town on the lower Roer on the east bank of the river Meuse. It received City rights i ...
, in the present province of Dutch Limburg, and the town of Geldern in the present German district Kleve
Kleve (; traditional ; ; ; ; ; Low Rhenish: ''Kleff'') is a town in the Lower Rhine region of northwestern Germany near the Netherlands, Dutch border and the River Rhine. From the 11th century onwards, Cleves was capital of a county and lat ...
)
The capital, Brussels
Brussels, officially the Brussels-Capital Region, (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) is a Communities, regions and language areas of Belgium#Regions, region of Belgium comprising #Municipalit ...
, was in Brabant. In the early 17th century, there was a flourishing court at Brussels, which was under the government of King Philip III's half-sister Archduchess Isabella and her husband, Archduke Albert of Austria. Among the artists who emerged from the court of the "Archdukes", as they were known, was Peter Paul Rubens
Sir Peter Paul Rubens ( ; ; 28 June 1577 – 30 May 1640) was a Flemish painting, Flemish artist and diplomat. He is considered the most influential artist of the Flemish Baroque painting, Flemish Baroque tradition. Rubens' highly charged comp ...
. Under the Archdukes, the Spanish Netherlands actually had formal independence from Spain, but always remained unofficially within the Spanish sphere of influence, and with Albert's death in 1621 they returned to formal Spanish control, although the childless Isabella remained on as Governor until her death in 1633.
The failing wars intended to regain the 'heretical' northern Netherlands meant significant loss of (still mainly Catholic) territories in the north, which was consolidated in 1648 in the Peace of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia (, ) is the collective name for two peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and brought peace to the Holy Roman Empire ...
, and given the peculiar, inferior status of '' Generality Lands'' (jointly ruled by the United Republic, not admitted as member provinces): Zeelandic Flanders (south of the river Scheldt
The Scheldt ( ; ; ) is a river that flows through northern France, western Belgium, and the southwestern part of Netherlands, the Netherlands, with its mouth at the North Sea. Its name is derived from an adjective corresponding to Old Englis ...
), the present Dutch province of North Brabant and Maastricht
Maastricht ( , , ; ; ; ) is a city and a Municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the southeastern Netherlands. It is the capital city, capital and largest city of the province of Limburg (Netherlands), Limburg. Maastricht is loca ...
(in the present Dutch province of Limburg).
As Spanish power waned in the latter decades of the 17th century, the territory of the Spanish Netherlands was repeatedly invaded by the French and an increasing portion of the territory came under French control in successive wars. By the Treaty of the Pyrenees of 1659 the French annexed Artois while Dunkirk
Dunkirk ( ; ; ; Picard language, Picard: ''Dunkèke''; ; or ) is a major port city in the Departments of France, department of Nord (French department), Nord in northern France. It lies from the Belgium, Belgian border. It has the third-larg ...
was ceded to the English. By the Treaties of Aix-la-Chapelle (ending the War of Devolution
The War of Devolution took place from May 1667 to May 1668. In the course of the war, Kingdom of France, France occupied large parts of the Spanish Netherlands and County of Burgundy, Franche-Comté, both then provinces of the Holy Roman Empire ...
in 1668) and Nijmegen
Nijmegen ( , ; Nijmeegs: ) is the largest city in the Dutch province of Gelderland and the ninth largest of the Netherlands as a whole. Located on the Waal River close to the German border, Nijmegen is one of the oldest cities in the ...
(ending the Franco-Dutch War
The Franco-Dutch War, 1672 to 1678, was primarily fought by Kingdom of France, France and the Dutch Republic, with both sides backed at different times by a variety of allies. Related conflicts include the 1672 to 1674 Third Anglo-Dutch War and ...
in 1678), further territory up to the current Franco-Belgian border was ceded, including Cambrai
Cambrai (, ; ; ), formerly Cambray and historically in English Camerick or Camericke, is a city in the Nord department and in the Hauts-de-France region of France on the Scheldt river, which is known locally as the Escaut river.
A sub-pref ...
, Walloon Flanders (the area around Lille
Lille (, ; ; ; ; ) is a city in the northern part of France, within French Flanders. Positioned along the Deûle river, near France's border with Belgium, it is the capital of the Hauts-de-France Regions of France, region, the Prefectures in F ...
, Douai
Douai ( , , ; ; ; formerly spelled Douay or Doway in English) is a city in the Nord (French department), Nord département in northern France. It is a Subprefectures in France, sub-prefecture of the department. Located on the river Scarpe (rive ...
and Orchies), as well as half of the county of Hainaut (including Valenciennes
Valenciennes (, also , , ; ; or ; ) is a communes of France, commune in the Nord (French department), Nord Departments of France, department, Hauts-de-France, France.
It lies on the Scheldt () river. Although the city and region experienced ...
). Later, in the War of the Reunions and the Nine Years' War
The Nine Years' War was a European great power conflict from 1688 to 1697 between Kingdom of France, France and the Grand Alliance (League of Augsburg), Grand Alliance. Although largely concentrated in Europe, fighting spread to colonial poss ...
, France temporarily annexed other parts of the region that were returned in the 1697 Peace of Ryswick.
Austrian Netherlands
 Under the Treaty of Rastatt (1714), following the
Under the Treaty of Rastatt (1714), following the War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict fought between 1701 and 1714. The immediate cause was the death of the childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700, which led to a struggle for control of the Spanish E ...
, what was left of the Spanish Netherlands
The Spanish Netherlands (; ; ; ) (historically in Spanish: , the name "Flanders" was used as a '' pars pro toto'') was the Habsburg Netherlands ruled by the Spanish branch of the Habsburgs from 1556 to 1714. They were a collection of States of t ...
was ceded to Austria and thus became known as the Austrian Netherlands or ''Belgium Austriacum''. However, the Austrians themselves generally had little interest in the region (aside from a short-lived attempt by Emperor Charles VI to compete with British and Dutch trade through the Ostend Company), and the fortresses along the border (the Barrier Fortresses) were, by treaty, garrisoned with Dutch troops. The area had, in fact, been given to Austria largely at British and Dutch insistence, as these powers feared potential French domination of the region.
Throughout the latter part of the eighteenth century, the principal foreign policy goal of the Habsburg rulers was to exchange the Austrian Netherlands for Bavaria
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a States of Germany, state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the list of German states by area, largest German state by land area, comprising approximately 1/5 of the total l ...
, which would round out Habsburg possessions in southern Germany. In the 1757 Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was a peace treaty signed on 28 June 1919. As the most important treaty of World War I, it ended the state of war between Germany and most of the Allies of World War I, Allied Powers. It was signed in the Palace ...
, Austria agreed to the creation of an independent state in the Southern Netherlands ruled by Philip, Duke of Parma and garrisoned by French troops in exchange for French help in recovering Silesia
Silesia (see names #Etymology, below) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at 8, ...
. However the agreement was unimplemented and revoked by the Third Treaty of Versailles (1785) and Austrian rule continued.
In 1784, its ruler, Emperor Joseph II, took up the long-standing grudge of Antwerp
Antwerp (; ; ) is a City status in Belgium, city and a Municipalities of Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of Antwerp Province, and the third-largest city in Belgium by area at , after ...
, whose once-flourishing trade was destroyed by the permanent closing of the Scheldt
The Scheldt ( ; ; ) is a river that flows through northern France, western Belgium, and the southwestern part of Netherlands, the Netherlands, with its mouth at the North Sea. Its name is derived from an adjective corresponding to Old Englis ...
, and he demanded for the Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, commonly referred to in historiography as the Dutch Republic, was a confederation that existed from 1579 until the Batavian Revolution in 1795. It was a predecessor state of the present-day Netherlands ...
to open the river to navigation. However, his stance was far from militant, and he called off hostilities after the so-called Kettle War, so called because its only "casualty" was a kettle. Though Joseph secured in the 1785 Treaty of Fontainebleau that the territory's rulers would be compensated by the Dutch Republic for the continued closing the Scheldt
The Scheldt ( ; ; ) is a river that flows through northern France, western Belgium, and the southwestern part of Netherlands, the Netherlands, with its mouth at the North Sea. Its name is derived from an adjective corresponding to Old Englis ...
, this failed to gain him much popularity.
The people of the Austrian Netherlands rebelled against Austria in 1788 as a result of Joseph II's centralizing policies. The different provinces established the United States of Belgium (January 1790). However, waylaying Joseph's intended concessions to the Belgians to restore the height of their autonomy and privileges, Austrian imperial power had been restored by Joseph's brother and successor, Leopold II, by the end of 1790.
French annexation
In the course of the French Revolution, the entire region (including territories that were never under Habsburg rule, like the Prince-Bishopric of Liège) was overrun by French armies after they won the Battle of Sprimont in 1794. The territory was then annexed to the Republic (October 1, 1795). Only a minority of the population – mostly the localJacobin
The Society of the Friends of the Constitution (), renamed the Society of the Jacobins, Friends of Freedom and Equality () after 1792 and commonly known as the Jacobin Club () or simply the Jacobins (; ), was the most influential political cl ...
s and other members of "Societies of Friends of Liberty and Equality" in urban areas – supported the annexation. The majority were hostile to the French regime, above all because of the imposition of the assignat, wholesale conscription, and the ferocious antireligious policies of the French revolutionaries. The opposition was first led by the Catholic clergy, which became an irreducible enemy of the French Republic after it dissolved convents and monasteries and confiscated ecclesiastical properties, ordered the separation of Church and State, shut down the University of Louvain and other Catholic educational institutions, regulated church attendance and introduced divorce. In 1797, nearly 8000 priests refused to swear the newly introduced Oath of Hatred of Kings ("serment de haine à la royauté"), and went into hiding to escape arrest and deportation. The situation, particularly in the religious field, eased with the rise to power of Bonaparte in 1799, but soon, the intensification of conscription, the police state and the Continental System, which brought ruin to Ostend
Ostend ( ; ; ; ) is a coastal city and municipality in the province of West Flanders in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It comprises the boroughs of Mariakerke, Raversijde, Stene and Zandvoorde, and the city of Ostend proper – the la ...
and Antwerp, reignited opposition to French rule. During that period Belgium was divided into nine départements: Deux-Nèthes, Dyle, Escaut, Forêts, Jemmape, Lys, Meuse-Inférieure, Ourthe and Sambre-et-Meuse.
Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
confirmed the loss of its territories by the Treaty of Campo Formio
The Treaty of Campo Formio (today Campoformido) was signed on 17 October 1797 (26 Vendémiaire VI) by Napoleon Bonaparte and Count Philipp von Cobenzl as representatives of the French Republic and the Austrian monarchy, respectively. The trea ...
, in 1797.
In anticipation of Napoleon's defeat in 1814, it was hotly debated inside Austrian ruling circles whether Austria should get the Southern Netherlands back or, in view of the experience gained after the War of the Spanish Succession about the difficulty of defending non contiguous possessions, whether she should not instead obtain contiguous territorial compensations in Northern Italy. This latter viewpoint won and the Congress of Vienna allotted the Southern Netherlands to the new United Kingdom of the Netherlands. After the Belgian Revolution
The Belgian Revolution (, ) was a conflict which led to the secession of the southern provinces (mainly the former Southern Netherlands) from the United Kingdom of the Netherlands and the establishment of an independent Kingdom of Belgium.
The ...
of 1830, the region separated to become the independent Kingdom of Belgium
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. Situated in a coastal lowland region known as the Low Countries, it is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeas ...
.
See also
* Catholic Church in the Netherlands, in Belgium and in Luxembourg *Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy, also known as Habsburg Empire, or Habsburg Realm (), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities (composite monarchy) that were ruled by the House of Habsburg. From the 18th century it is ...
* History of Belgium
* List of governors of the Habsburg Netherlands
* List of plenipotentiaries of Austrian Netherlands
* Seventeen Provinces
The Seventeen Provinces were the Imperial states of the Habsburg Netherlands in the 16th century. They roughly covered the Low Countries, i.e., what is now the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, and most of the France, French Departments of Franc ...
* Spanish Armada
The Spanish Armada (often known as Invincible Armada, or the Enterprise of England, ) was a Spanish fleet that sailed from Lisbon in late May 1588, commanded by Alonso de Guzmán, Duke of Medina Sidonia, an aristocrat without previous naval ...
* Union of Atrecht (Including map, 1579)
Notes
References
Sources
* *Further reading
* Blom, J. C. H. and E. Lamberts, eds. ''History of the Low Countries'' (2006) 504pexcerpt and text search
als
complete edition online
* Cammaerts, Émile. ''A History of Belgium from the Roman Invasion to the Present Day'' (1921) 357 pages
complete text online
* Cook, Bernard A. ''Belgium: a history'', 3rd ed. New York, 2004 * Kossmann, E. H. ''The Low Countries 1780–1940'' (1978
excerpt and text search
External links
* {{Authority control Early modern history of Luxembourg