|
Belgian Revolution
The Belgian Revolution (, ) was a conflict which led to the secession of the southern provinces (mainly the former Southern Netherlands) from the United Kingdom of the Netherlands and the establishment of an independent Kingdom of Belgium. The people of the south were mainly Flemish people, Flemings and Walloons. Both peoples were traditionally Roman Catholic as contrasted with Protestant-dominated (Dutch Reformed) people of the north. Many outspoken liberals regarded William I of the Netherlands, King William I's rule as despotic. There were high levels of unemployment and industrial unrest among the working classes. On 25 August 1830, riots erupted in Brussels and shops were looted. Theatergoers who had just watched the nationalistic opera ''La muette de Portici'' joined the mob. Uprisings followed elsewhere in the country. Factories were occupied and machinery destroyed. Order was restored briefly after William committed troops to the Southern Provinces but rioting continued ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
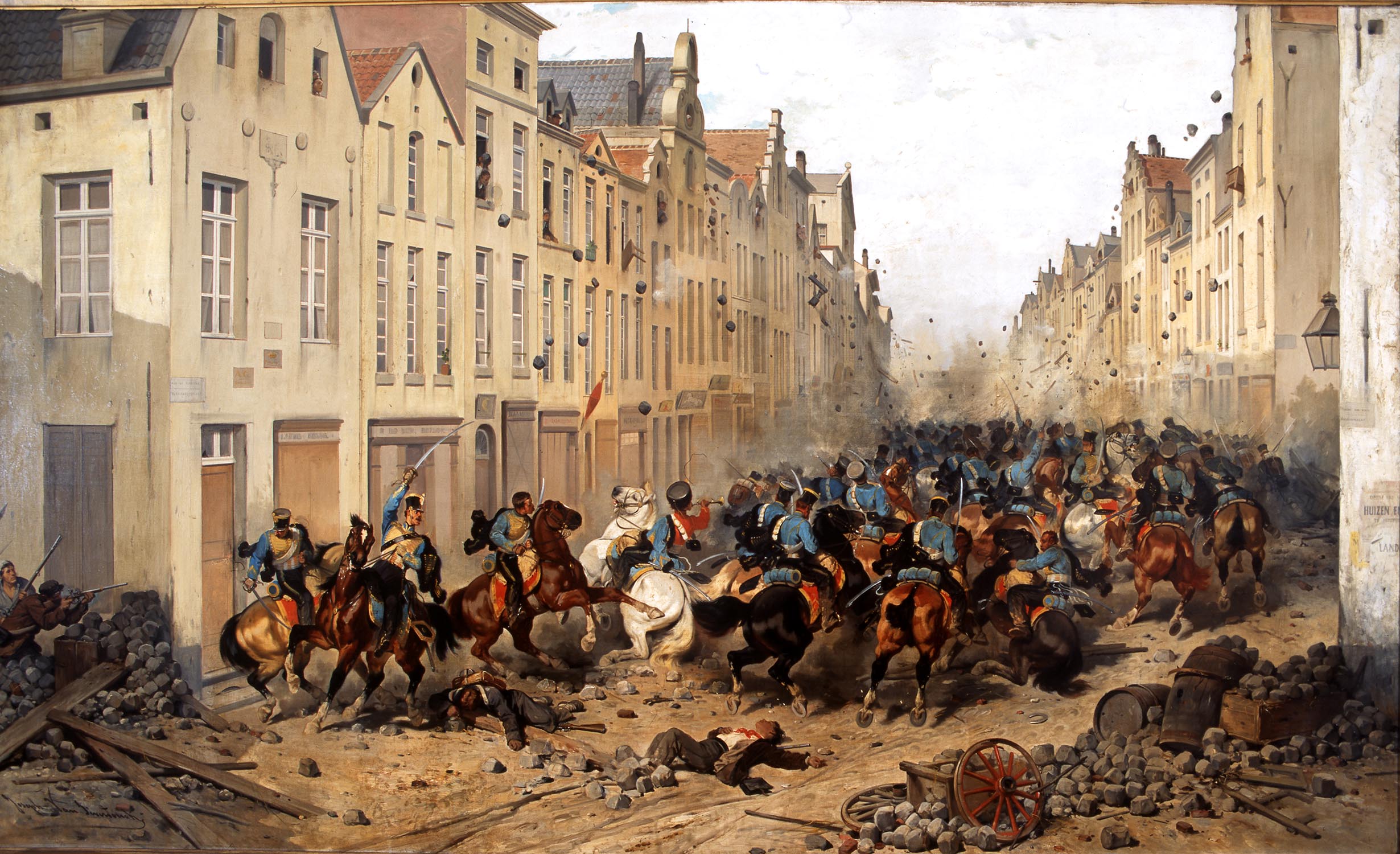
Episode Of The Belgian Revolution Of 1830
''Episode of the Belgian revolution of 1830'' is an oil painting by Belgian artist Gustaaf Wappers, completed in 1835. It is a romantic depiction of the moment when the Belgian Declaration of Independence was read to the people of Brussels during the Belgian Revolution. The work is now in the Oldmasters Museum in Brussels, Belgium. Background Following the Congress of Vienna in 1815, the territory of the then Southern Netherlands was ceded from the remains of the First French Empire to form part of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. Inspired by Liberalism, Catholic anti-Protestantism, recent food crises, and Francophone interests, the people of the then Southern Netherlands engaged in open revolt in August 1830, eventually declaring independence in October of that same year and establishing the Kingdom of Belgium in 1831. Gustaaf Wappers (1803 1874) was a Belgian professor at the Royal Academy of Fine Arts of Antwerp in 1833 who gained fame for his paintings of patriotic the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
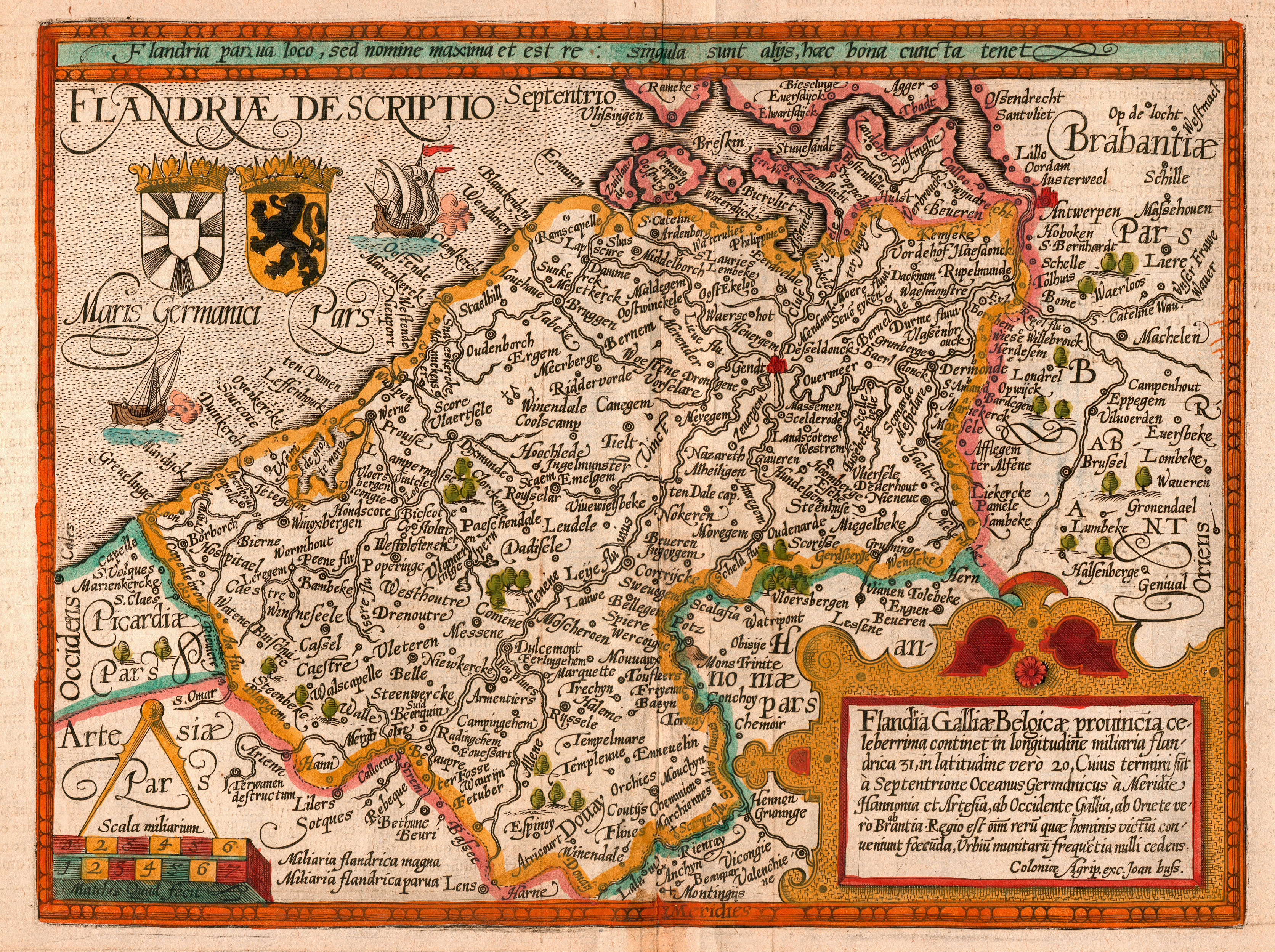
Flemish People
Flemish people or Flemings ( ) are a Germanic peoples, Germanic ethnic group native to Flanders, Belgium, who speak Flemish Dutch. Flemish people make up the majority of Belgians, at about 60%. ''Flemish'' was historically a geographical term, as all inhabitants of the medieval County of Flanders in modern-day Belgium, France and the Netherlands were referred to as "Flemings" irrespective of their ethnicity or language. The contemporary region of Flanders comprises a part of this historical county, as well as parts of the medieval Duchy of Brabant and the medieval County of Loon, where the modern national identity and Flemish culture, culture gradually formed. History The sense of "Flemish" identity increased significantly after the Belgian Revolution. Prior to this, the term "" in the Dutch language was in first place used for the inhabitants of the former County of Flanders. Flemish, however, had been used since the 14th century to refer to the language and dialects of both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Orange-Nassau
The House of Orange-Nassau (, ), also known as the House of Orange because of the prestige of the princely title of Orange, also referred to as the Fourth House of Orange in comparison with the other noble houses that held the Principality of Orange, is the current dynasty, reigning house of the Netherlands. A branch of the European House of Nassau, the house has played a central role in the Politics and government of the Netherlands (1581–1795), politics and government of the Netherlands and elsewhere in Europe, particularly since William the Silent organised the Dutch Revolt against Spain, Spanish rule, which after the Eighty Years' War (1568–1648) led to an Dutch Republic, independent Dutch state. William III of Orange led the resistance of the Netherlands and Europe to Louis XIV of France and orchestrated the Glorious Revolution in England that established parliamentary rule. Similarly, Queen Wilhelmina of the Netherlands was instrumental in the Dutch resistance during W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congress Of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon, Napoleon Bonaparte. Participants were representatives of all European powers (other than the Ottoman Empire) and other stakeholders. The Congress was chaired by Austrian Empire, Austrian statesman Klemens von Metternich, and was held in Vienna from September 1814 to June 1815. The objective of the Congress was to provide a long-term peace plan for Europe by settling critical issues arising from the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars through negotiation. The goal was not simply to restore old boundaries, but to resize the main powers so they could European balance of power, balance each other and remain at peace, being at the same time shepherds for the smaller powers. More generally, conservative leaders like Metternich also soug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Waterloo
The Battle of Waterloo was fought on Sunday 18 June 1815, near Waterloo, Belgium, Waterloo (then in the United Kingdom of the Netherlands, now in Belgium), marking the end of the Napoleonic Wars. The French Imperial Army (1804–1815), French Imperial Army under the command of Napoleon, Napoleon I was defeated by two armies of the Seventh Coalition. One was a United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, British-led force with units from the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom, the United Kingdom of the Netherlands, Netherlands, Kingdom of Hanover, Hanover, Duchy of Brunswick, Brunswick, and Duchy of Nassau, Nassau, under the command of field marshal Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, Arthur Wellesley, Duke of Wellington. The other comprised three corps of the Kingdom of Prussia, Prussian army under Field Marshal Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher, Blücher. The battle was known contemporaneously as the ''Battle of Mont-Saint-Jean, Belgium, Mont Saint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
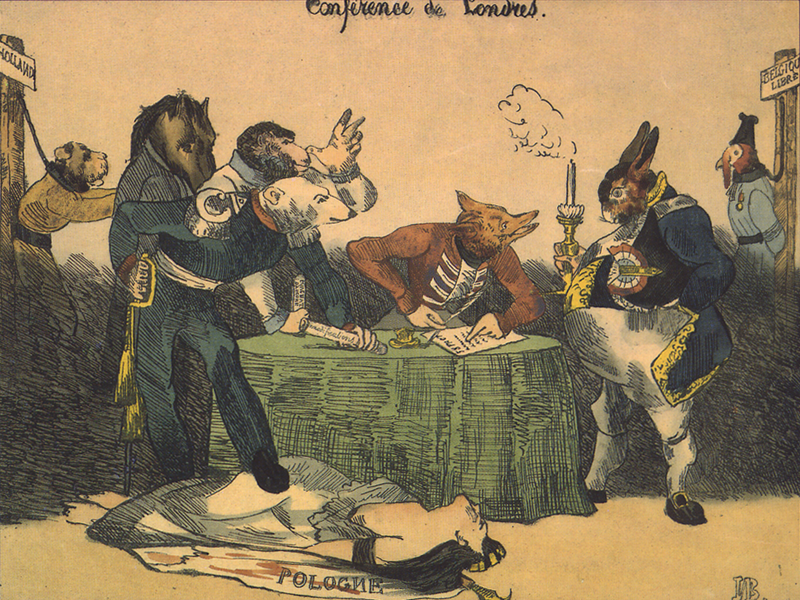
London Conference Of 1830
The London Conference of 1830 brought together representatives of the five major European powers Austrian Empire, Austria, United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, Britain, July monarchy, France, Prussia and Russian Empire, Russia. At the conference, which began on 20 December, they recognized the success of the Belgian revolution, Belgian secession from the United Kingdom of the Netherlands and permanently guaranteed History of Belgium#Independence, Belgian independence. Dutch response The History of the Netherlands#Belgium breaks away, Dutch were strongly opposed to Belgian independence, Ten days' campaign, launching an unsuccessful invasion in 1831. Not until 1839 did the Dutch accept the decision of the London Conference and recognize Belgian independence. Winners and losers Fishman says that the London Conference was "an extraordinarily successful conference" because it "provided the institutional framework through which the leading powers of the time safeguarded the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Powers
A great power is a sovereign state that is recognized as having the ability and expertise to exert its influence on a global scale. Great powers characteristically possess military and economic strength, as well as diplomatic and soft power influence, which may cause middle or small powers to consider the great powers' opinions before taking actions of their own. International relations theorists have posited that great power status can be characterized into power capabilities, spatial aspects, and status dimensions. While some nations are widely considered to be great powers, there is considerable debate on the exact criteria of great power status. Historically, the status of great powers has been formally recognized in organizations such as the Congress of Vienna of 1814–1815Danilovic, Vesna. "When the Stakes Are High – Deterrence and Conflict among Major Powers", University of Michigan Press (2002), pp 27, 225–22(PDF chapter downloads) [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Congress Of Belgium
The National Congress (, ) was a temporary legislature, legislative assembly in Belgium, convened in 1830 in the aftermath of the Belgian Revolution. Its purpose was to devise a Constitution of Belgium, national constitution for the new state, whose independence had been proclaimed on 4 October 1830 by the self-declared Provisional Government of Belgium, Provisional Government. History The National Congress was 1830 Belgian general election, elected by approximately 30,000 voters on 3 November 1830 and consisted of 200 members. Its president was Baron Erasme Louis Surlet de Chokier. The assembly chose a constitutional monarchy, constitutional popular monarchy as the form of government for Belgium and chose the son of the July Monarchy, French King Louis-Philippe, Prince Louis, Duke of Nemours, Louis, Duke of Nemours, as the new head of state. Other candidates included Auguste de Beauharnais, 2nd Duke of Leuchtenberg, Auguste de Beauharnais and Archduke Charles, Duke of Teschen, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Muette De Portici
''La muette de Portici'' (''The Mute Girl of Portici'', or ''The Dumb Girl of Portici''), also called ''Masaniello'' () in some versions, is an opera in five acts by Daniel Auber, with a libretto by Germain Delavigne, revised by Eugène Scribe. The work has an important place in music history as the earliest French grand opera. It is also known for its alleged role in the Belgian Revolution of 1830. Background The opera was first given at the Salle Le Peletier of the Paris Opéra on 29 February 1828. The role of Masaniello was taken by the famous tenor Adolphe Nourrit and Princess Elvire was sung by Laure Cinti-Damoreau. The dancer Lise Noblet played the mute title role, a part later taken by other dancers such as Marie Taglioni, Fanny Elssler and Pauline Leroux, also the actress Harriet Smithson (the future wife of Hector Berlioz). Alphonse was created by Alexis Dupont, who was Lise Noblet's brother-in-law. The conductor at the premiere was Henri Valentino.; ; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brussels
Brussels, officially the Brussels-Capital Region, (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) is a Communities, regions and language areas of Belgium#Regions, region of Belgium comprising #Municipalities, 19 municipalities, including the City of Brussels, which is the capital of Belgium. The Brussels-Capital Region is located in the central portion of the country. It is a part of both the French Community of Belgium and the Flemish Community, and is separate from the Flemish Region (Flanders), within which it forms an enclave, and the Walloon Region (Wallonia), located less than to the south. Brussels grew from a small rural settlement on the river Senne (river), Senne to become an important city-region in Europe. Since the end of the Second World War, it has been a major centre for international politics and home to numerous international organisations, politicians, Diplomacy, diplomats and civil servants. Brussels is the ''de facto' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |