Southern cooking on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The cuisine of the Southern United States encompasses diverse food traditions of several subregions, including
 The
The
"The Surprising Ways That Chickens Changed the World"
. ''National Geographic'': "When slaves were brought here from West Africa, they came with a deep knowledge of the chicken, because in West Africa the chicken was a common farm animal and also a very sacred animal. The knowledge that African-Americans brought served them very well, because white plantation owners for the most part didn't care much about chicken. In colonial times there were so many other things to eat that chicken was not high on the list." Scottish fried chicken was battered with seasonings and cooked in German immigrants came to colonial America beginning in 1608 and helped to start the colony of
German immigrants came to colonial America beginning in 1608 and helped to start the colony of
 Hardtack was not available to many Confederates because it was made from wheat, and wheat was not grown in many Southern states except for Georgia and Virginia. Cornbread replaced the hardtack rations in the Confederate army. Confederate soldiers made Johnnie cakes and "corn dodgers" that was similar to hardtack. In addition, they made fried flatbread and balls of cornmeal called "flapjacks" cooked over an open fire, and ate bacon, imitation coffee, and
Hardtack was not available to many Confederates because it was made from wheat, and wheat was not grown in many Southern states except for Georgia and Virginia. Cornbread replaced the hardtack rations in the Confederate army. Confederate soldiers made Johnnie cakes and "corn dodgers" that was similar to hardtack. In addition, they made fried flatbread and balls of cornmeal called "flapjacks" cooked over an open fire, and ate bacon, imitation coffee, and
 Since the 20th century into present day, immigrants from Asia, the Middle East, Africa, and other European countries brought their cuisines to the South and influenced southern cuisine. An article from ''
Since the 20th century into present day, immigrants from Asia, the Middle East, Africa, and other European countries brought their cuisines to the South and influenced southern cuisine. An article from ''
 Chains serving Southern foods—often along with American
Chains serving Southern foods—often along with American
 A traditional Southern meal may include pan-
A traditional Southern meal may include pan-
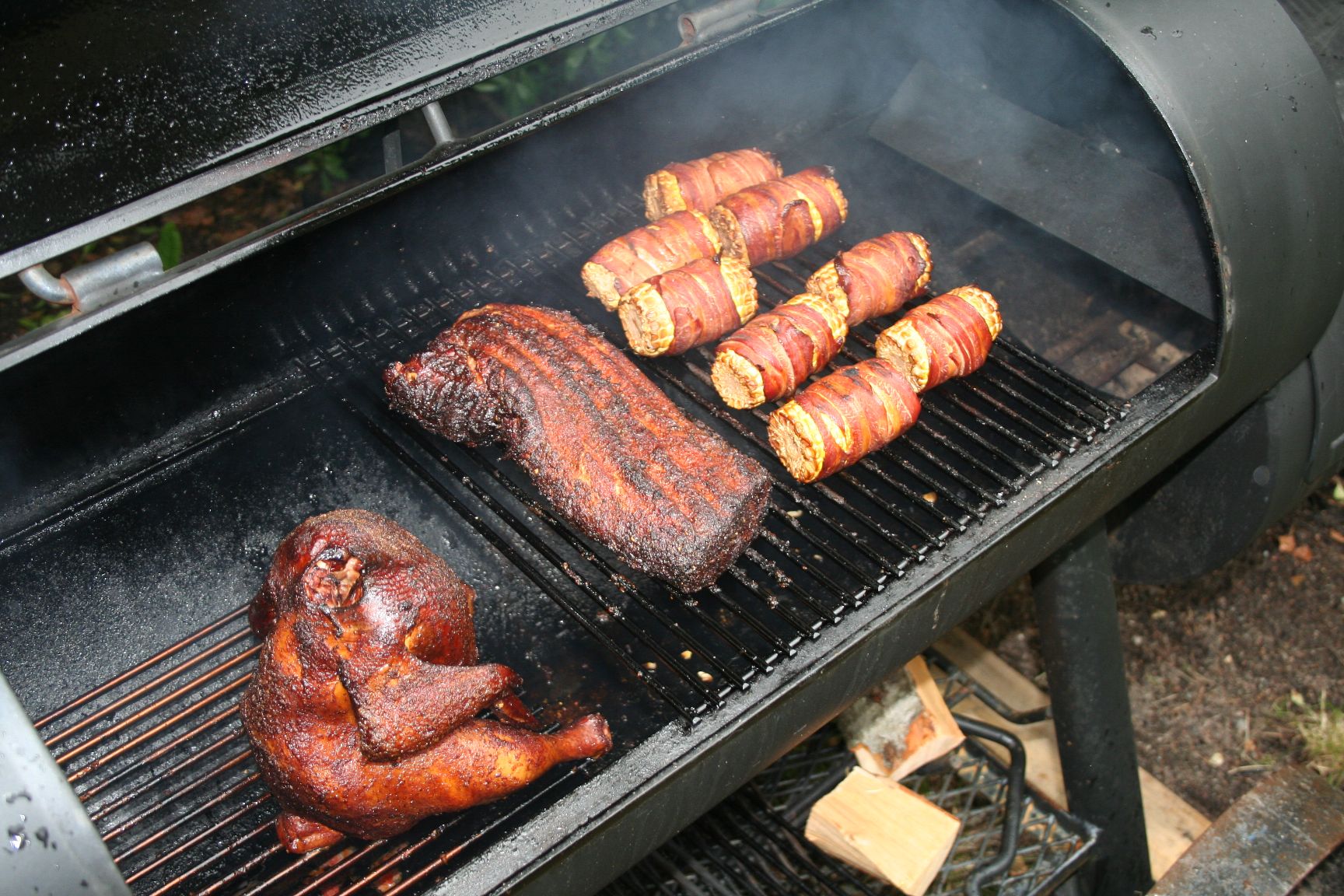 "White barbecue sauce" made with
"White barbecue sauce" made with
 Southern meals sometimes consist only of vegetables, with a little meat (especially salt pork) used in cooking but with no meat dish served. "Beans and greens"—white or brown beans served alongside a "mess" of greens stewed with a little bacon—is a traditional meal in many parts of the South ( Turnip greens are the typical greens for such a meal; they're cooked with some diced turnip and a piece of
Southern meals sometimes consist only of vegetables, with a little meat (especially salt pork) used in cooking but with no meat dish served. "Beans and greens"—white or brown beans served alongside a "mess" of greens stewed with a little bacon—is a traditional meal in many parts of the South ( Turnip greens are the typical greens for such a meal; they're cooked with some diced turnip and a piece of
 Southern cuisine varies widely by region. Generally speaking:
* Appalachian areas have many ramps (a variety of wild onion) and berries. Appalachia uses butter extensively but makes little use of cheese, and eats more wild game (as well as wild fruits and vegetables) than the rest of the South; apples, oats, and potatoes are also common in Appalachian cuisine, since the mountains are cooler and drier than the lowlands.
* The Upper South favors pork and whiskey; the Low Country (the coast, especially coastal Georgia and coastal South Carolina) favors seafood, rice, and grits.
* Texas and Oklahoma tend to prefer beef; the rest of the South prefers pork.
*
Southern cuisine varies widely by region. Generally speaking:
* Appalachian areas have many ramps (a variety of wild onion) and berries. Appalachia uses butter extensively but makes little use of cheese, and eats more wild game (as well as wild fruits and vegetables) than the rest of the South; apples, oats, and potatoes are also common in Appalachian cuisine, since the mountains are cooler and drier than the lowlands.
* The Upper South favors pork and whiskey; the Low Country (the coast, especially coastal Georgia and coastal South Carolina) favors seafood, rice, and grits.
* Texas and Oklahoma tend to prefer beef; the rest of the South prefers pork.
*
 Southern
Southern
 Because of its geographic location, Appalachia cuisine offers a wide range of ingredients and products that can be transformed using traditional methods and contemporary applications.Ronni Lundy, Staples of Appalachian cuisine that are common in other regional cuisines of the south include coconut cream cake,
Because of its geographic location, Appalachia cuisine offers a wide range of ingredients and products that can be transformed using traditional methods and contemporary applications.Ronni Lundy, Staples of Appalachian cuisine that are common in other regional cuisines of the south include coconut cream cake,
Why The Story Of Southern Food Is As Much About People As Dishes
from South Carolina Public Radio NPR
Southern Foodways Alliance
Southern Food & Beverage Museum
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cuisine Of The Southern United States Cuisine of the Southern United States, American cuisine by region Southern United States, Cuisine
cuisine
A cuisine is a style of cooking characterized by distinctive ingredients, List of cooking techniques, techniques and Dish (food), dishes, and usually associated with a specific culture or geographic region. Regional food preparation techniques, ...
of Southeastern Native American tribes, Tidewater, Appalachian, Ozarks
The Ozarks, also known as the Ozark Mountains, Ozark Highlands or Ozark Plateau, is a physiographic region in the U.S. states of Missouri, Arkansas, and Oklahoma, as well as a small area in the southeastern corner of Kansas. The Ozarks cover ...
, Lowcountry
The Lowcountry (sometimes Low Country or just low country) is a geographic and cultural region along South Carolina's coast, including the Sea Islands. The region includes significant salt marshes and other coastal waterways, making it an impor ...
, Cajun
The Cajuns (; French: ''les Cadjins'' or ''les Cadiens'' ), also known as Louisiana ''Acadians'' (French: ''les Acadiens''), are a Louisiana French ethnicity mainly found in the US state of Louisiana and surrounding Gulf Coast states.
Whi ...
, Creole, African American cuisine and Floribbean, Spanish, French, British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
, Ulster-Scots and German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
cuisine. In recent history, elements of Southern cuisine have spread to other parts of the United States, influencing other types of American cuisine
American cuisine consists of the cooking style and traditional dishes prepared in the United States. It has been significantly influenced by Europeans, Indigenous Americans, Africans, Latin Americans, Asians, Pacific Islanders, and many other ...
.
Many elements of Southern cooking—tomato
The tomato (, ), ''Solanum lycopersicum'', is a plant whose fruit is an edible Berry (botany), berry that is eaten as a vegetable. The tomato is a member of the nightshade family that includes tobacco, potato, and chili peppers. It originate ...
es, squash, corn
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout Poaceae, grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples of Mexico, indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago ...
(and its derivatives, such as hominy
Hominy is a food item produced from dried maize (corn) kernels that have been treated with an alkali, in a process called nixtamalization ( is the Nahuatl word for "hominy"). "Lye hominy" is a type of hominy made with lye.
History
The process ...
and grits
Grits (stylized as GRITS) is an American Christian hip hop group from Nashville, Tennessee. Their name is an acronym, which stands for "Grammatical Revolution In the Spirit". GRITS is made up of Stacey "Coffee" Jones and Teron "Bonafide" Carter ...
), and deep-pit barbecuing—are borrowings from Indigenous peoples of the region (e.g., Cherokee
The Cherokee (; , or ) people are one of the Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, they were concentrated in their homelands, in towns along river valleys of what is now southwestern ...
, Caddo
The Caddo people comprise the Caddo Nation of Oklahoma, a federally recognized tribe headquartered in Binger, Oklahoma. They speak the Caddo language.
The Caddo Confederacy was a network of Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands, who ...
, Choctaw
The Choctaw ( ) people are one of the Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States, originally based in what is now Louisiana, Mississippi and Alabama. The Choctaw language is a Western Muskogean language. Today, Choct ...
, and Seminole
The Seminole are a Native American people who developed in Florida in the 18th century. Today, they live in Oklahoma and Florida, and comprise three federally recognized tribes: the Seminole Nation of Oklahoma, the Seminole Tribe of Florida, ...
). From the Old World
The "Old World" () is a term for Afro-Eurasia coined by Europeans after 1493, when they became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia in the Eastern Hemisphere, previously ...
, European colonists introduced sugar, flour, milk, eggs, and livestock, along with a number of vegetables; meanwhile, enslaved West Africans trafficked to the North American colonies through the Atlantic slave trade
The Atlantic slave trade or transatlantic slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of Slavery in Africa, enslaved African people to the Americas. European slave ships regularly used the triangular trade route and its Middle Pass ...
introduced black-eyed pea
The black-eyed pea or black-eyed bean is a legume grown around the world for its medium-sized, edible bean. It is a subspecies of the cowpea, an Old World plant domesticated in Africa, and is sometimes simply called a cowpea.
The common commerci ...
s, okra
Okra (, ), ''Abelmoschus esculentus'', known in some English-speaking countries as lady's fingers, is a flowering plant in the Malvaceae, mallow family native to East Africa. Cultivated in tropical, subtropical, and warm temperate regions aro ...
, eggplant
Eggplant (American English, US, Canadian English, CA, Australian English, AU, Philippine English, PH), aubergine (British English, UK, Hiberno English, IE, New Zealand English, NZ), brinjal (Indian English, IN, Singapore English, SG, Malays ...
, sesame
Sesame (; ''Sesamum indicum'') is a plant in the genus '' Sesamum'', also called benne. Numerous wild relatives occur in Africa and a smaller number in India. It is widely naturalized in tropical regions around the world and is cultivated for ...
, sorghum
''Sorghum bicolor'', commonly called sorghum () and also known as great millet, broomcorn, guinea corn, durra, imphee, jowar, or milo, is a species in the Poaceae, grass genus ''Sorghum (genus), Sorghum'' cultivated for its grain. The grain i ...
, melon
A melon is any of various plants of the family Cucurbitaceae with sweet, edible, and fleshy fruit. It can also specifically refer to ''Cucumis melo'', commonly known as the "true melon" or simply "melon". The term "melon" can apply to both the p ...
s, and various spices. Rice also became prominent in many dishes in the Lowcountry
The Lowcountry (sometimes Low Country or just low country) is a geographic and cultural region along South Carolina's coast, including the Sea Islands. The region includes significant salt marshes and other coastal waterways, making it an impor ...
region of South Carolina because the enslaved people who settled the region (now known as the Gullah
The Gullah () are a subgroup of the African Americans, African American ethnic group, who predominantly live in the South Carolina Lowcountry, Lowcountry region of the U.S. states of North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia, and Florida within ...
people), were already quite familiar with the crop.
Many Southern foodways are local adaptations of Old World
The "Old World" () is a term for Afro-Eurasia coined by Europeans after 1493, when they became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia in the Eastern Hemisphere, previously ...
traditions. In Appalachia, many Southern dishes are Scottish or British Border in origin. For instance, the South's fondness for a full breakfast
A full breakfast or fry-up is a substantial cooked breakfast meal often served in Britain and Ireland. Depending on the region, it may also be referred to as a full English, a full Irish, full Scottish, full Welsh or Ulster fry. The fried br ...
derives from the British full breakfast or fry-up. Pork, once considered informally taboo in Scotland, has taken the place of lamb and mutton. Instead of chopped oats, Southerners have traditionally eaten grits
Grits (stylized as GRITS) is an American Christian hip hop group from Nashville, Tennessee. Their name is an acronym, which stands for "Grammatical Revolution In the Spirit". GRITS is made up of Stacey "Coffee" Jones and Teron "Bonafide" Carter ...
, a porridge normally made from coarsely ground, nixtamalized maize
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native American ...
, also known as hominy
Hominy is a food item produced from dried maize (corn) kernels that have been treated with an alkali, in a process called nixtamalization ( is the Nahuatl word for "hominy"). "Lye hominy" is a type of hominy made with lye.
History
The process ...
.
Certain regions have been infused with different Old World traditions. Louisiana Creole cuisine
Louisiana Creole cuisine (, , ) is a style of cooking originating in Louisiana, United States, which blends African cuisine, West African, French cuisine, French, Spanish cuisine, Spanish, and Native American cuisine, Native American influenc ...
draws upon vernacular French cuisine
French cuisine is the cooking traditions and practices of France. In the 14th century, Guillaume Tirel, a Court (royal), court chef known as "Taillevent", wrote ''Le Viandier'', one of the earliest recipe collections of medieval France. In ...
, West African cuisine
West African cuisine encompasses a diverse range of foods that are split between its 16 countries. In West Africa, many families grow and raise their own food, and within each there is a division of labor. Indigenous foods consist of a number of ...
, and Spanish cuisine
Spanish cuisine () consists of the traditions and practices of Spanish cooking. It features considerable regional diversity, with significant differences among the traditions of each of Spain's regional cuisines.
Olive oil (of which Spain is ...
; Floribbean cuisine is Spanish-based with obvious Caribbean
The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America ...
influences; and Tex-Mex
Tex-Mex cuisine (derived from the words ''Texas'' and ''Mexico'') is a regional American cuisine that originates from the culinary creations of Tejanos, Tejano people. It has spread from border states such as Texas and others in the Southwestern ...
has considerable Mexican and Indigenous influences with its abundant use of New World vegetables (e.g. corn, tomatoes, squash, and peppers) and barbecued meat. In Southern Louisiana, West African influences have persisted in dishes such as gumbo
Gumbo () is a stew that is popular among the U.S. Gulf Coast community, the New Orleans stew variation being the official state cuisine of the U.S. state of Louisiana. Gumbo consists primarily of a strongly flavored stock, meat or shellfis ...
, jambalaya, and red beans and rice.
History
Indigenous cuisine before colonization
Native Americans utilized a number of cooking methods in early American cuisine that have been blended with the methods of early Europeans to form the basis of what is now Southern cuisine. Prior to the 1600s, native peoples lived off the land in very diverse bioregions and had done so for thousands of years, often living a nomadic life where their diet changed with the season. Many practiced a form of agriculture revolving around the Three Sisters, the rotation ofbean
A bean is the seed of some plants in the legume family (Fabaceae) used as a vegetable for human consumption or animal feed. The seeds are often preserved through drying (a ''pulse''), but fresh beans are also sold. Dried beans are traditi ...
s, maize
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native American ...
, and squash as staples of their diet. Wild game was equally a staple of nearly every tribe: generally, deer, elk, and bison were staples, as were rabbits and hare. The Cherokee
The Cherokee (; , or ) people are one of the Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, they were concentrated in their homelands, in towns along river valleys of what is now southwestern ...
of the Southern Appalachians used blowguns made of an indigenous type of bamboo to hunt squirrels.
Native Americans introduced the first non-Native American Southerners to many other vegetables still familiar on southern tables. Squash, pumpkin
A pumpkin is a cultivar, cultivated winter squash in the genus ''Cucurbita''. The term is most commonly applied to round, orange-colored squash varieties, but does not possess a scientific definition. It may be used in reference to many dif ...
, many types of bean
A bean is the seed of some plants in the legume family (Fabaceae) used as a vegetable for human consumption or animal feed. The seeds are often preserved through drying (a ''pulse''), but fresh beans are also sold. Dried beans are traditi ...
s, many types of peppers, and sassafras all came to the settlers via Indigenous peoples. The Virginia Algonquian word ''pawcohiccora'' means hickory
Hickory is a common name for trees composing the genus ''Carya'', which includes 19 species accepted by ''Plants of the World Online''.
Seven species are native to southeast Asia in China, Indochina, and northeastern India (Assam), and twelve ...
-nut meat or a nut milk drink made from it.
Many fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants (angiosperms) that is formed from the ovary after flowering.
Fruits are the means by which angiosperms disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particular have long propaga ...
s are available in this region. Muscadine
''Vitis rotundifolia'', or muscadine, is a grapevine species native to the southern United States, southeastern and south-central United States. The growth range extends from Florida to New Jersey coast, and west to eastern Texas and Oklahoma. I ...
s, blackberries
BlackBerry is a discontinued brand of handheld devices and related mobile services, originally developed and maintained by the Canadian company Research In Motion (RIM, later known as BlackBerry Limited) until 2016. The first BlackBerry device ...
, raspberries, and many other wild berries were part of Southern Native Americans' diet.
Colonial era 1513 to 1776 and Antebellum era 1776 to 1861
Southern food have influences from Native American, European, andWest African
West Africa, also known as Western Africa, is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Ma ...
cuisines and foods. From corn
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout Poaceae, grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples of Mexico, indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago ...
Southeastern Native American tribes made grits, cornmeal mush, corn chowder, hush puppies, and cornbread that were adapted by European settlers and enslaved Africans cuisine called soul food
Soul food is the ethnic cuisine of African Americans. Originating in the Southern United States, American South from the cuisines of Slavery in the United States, enslaved Africans transported from Africa through the Atlantic slave trade, sou ...
. Another Native American influence in Southern cuisine is fried green tomatoes. Squash was (and continues to be cooked) by Native Americans and has a long shelf life when not cooked, and because of its long shelf-life African Americans and European Americans placed it in their kitchens. An additional Native American influence in Southern cuisine is the use of maple syrup
Maple syrup is a sweet syrup made from the sap of maple trees. In cold climates, these trees store starch in their trunks and roots before winter; the starch is then converted to sugar that rises in the sap in late winter and early spring. Ma ...
. Indigenous people used maple syrup to sweeten and add flavor to dishes; this influenced the foodways of enslaved Africans and European settlers as they used maple syrup to sweeten their dishes and poured syrup over pancakes and other breakfast foods.
Other Indigenous influences are dried meats, smoked fish, and preparing meals with deer, rabbit, turtle, catfish, and eating local strawberries, blueberries, blackberries, raspberries, and cranberries. Foods cultivated by Indigenous people
There is no generally accepted definition of Indigenous peoples, although in the 21st century the focus has been on self-identification, cultural difference from other groups in a state, a special relationship with their traditional territ ...
in the Western Hemisphere
The Western Hemisphere is the half of the planet Earth that lies west of the Prime Meridian (which crosses Greenwich, London, United Kingdom) and east of the 180th meridian.- The other half is called the Eastern Hemisphere. Geopolitically, ...
influenced Southern and global cuisine.
The first European nation to colonize the mainland portion of North America was Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
in the early 16th century in the year 1513 under Juan Ponce de León
Juan Ponce de León ( – July 1521) was a Spanish explorer and ''conquistador'' known for leading the first official European expedition to Puerto Rico in 1508 and Florida in 1513. He was born in Santervás de Campos, Valladolid, Spain, in ...
. In the year 1565, Spanish explorer Pedro Menéndez de Avilés
Pedro Menéndez de Avilés (; ; 15 February 1519 – 17 September 1574) was a Spanish admiral, explorer and conquistador from Avilés, in Asturias, Spain. He is notable for planning the first regular trans-oceanic convoys, which became known as ...
established a settlement in St. Augustine, Florida
St. Augustine ( ; ) is a city in and the county seat of St. Johns County, Florida, United States. Located 40 miles (64 km) south of downtown Jacksonville, the city is on the Atlantic coast of northeastern Florida. Founded in 1565 by Spani ...
and was accompanied by free and enslaved Africans. Two Spanish expeditions encountered the Apalachee in the first half of the 16th century. The expedition of Pánfilo de Narváez entered the Apalachee domain in 1528, and arrived at a village, which Narváez believed was the main settlement in Apalachee. The Apalachee
The Apalachee were an Indigenous people of the Southeastern Woodlands, specifically an Indigenous people of Florida, who lived in the Florida Panhandle until the early 18th century. They lived between the Aucilla River and Ochlockonee River,Bobby ...
Indigenous people influenced the foodways of Spanish colonists in Florida. Apalachee people prepared meals with hunted animals such as deer, rabbit, raccoon, and turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
(a bird indigenous to North America). They grew in their gardens corn, beans, squash, and sunflowers, and foraged for wild berries and nuts. From these food sources the Apalachee made stews and sweet flavored dishes. Spanish colonists enjoyed Native American cacina tea and turkey.
New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( ; Nahuatl: ''Yankwik Kaxtillan Birreiyotl''), originally the Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain. It was one of several ...
was in the present-day southern states of Florida and Louisiana. An article from the Florida Department of State explains the influence of the Spaniards in Southern cuisine: "The Spanish brought many foods to Florida (and the Americas) that are commonly eaten today. One major change to the landscape of Florida was the Spanish introduction of domesticated animals to provide favored meats, like beef, pork, and chicken! Olive oil and wine (brought over to the colonies in large earthenware jars) were essential staples for any Spanish kitchen. Fruits (like peaches, figs, and watermelons), nuts and beans (like almonds, field peas, and garbanzo beans) and spices (like saffron, cinnamon, and different types of peppers) were brought to Florida from all over the world."
 The
The British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
established a permanent settlement in Jamestown, Virginia
The Jamestown settlement in the Colony of Virginia was the first permanent British colonization of the Americas, English settlement in the Americas. It was located on the northeast bank of the James River, about southwest of present-day Willia ...
in 1607. They brought their food traditions from London that influenced Southern cuisine. British cuisine
British cuisine consists of the cooking traditions and practices associated with the United Kingdom, including the regional cuisines of English cuisine, England, Scottish cuisine, Scotland, Welsh cuisine, Wales, and Northern Irish cuisine, Nort ...
has cured and aged ham
Ham is pork from a leg cut that has been preserved by wet or dry curing, with or without smoking."Bacon: Bacon and Ham Curing" in '' Chambers's Encyclopædia''. London: George Newnes, 1961, Vol. 2, p. 39. As a processed meat, the term '' ...
and English bread. These foods were augmented in colonial Jamestown with North American ingredients. For example, the ham dishes in Britain became Virginia hams, and English breads became hot breads and other sweets. However, the predominant cooks in Virginia's kitchens were enslaved African Americans. Enslaved cooks in white plantation homes combined food traditions from West Africa with Native American and European cooking methods and prepared new dishes that influenced Southern cuisine, such as fried okra.
The origin of fried chicken in the southern states of America has been traced to precedents in Scottish quoted at . and West African cuisine
West African cuisine encompasses a diverse range of foods that are split between its 16 countries. In West Africa, many families grow and raise their own food, and within each there is a division of labor. Indigenous foods consist of a number of ...
.Worral, Simon (December 21, 2014"The Surprising Ways That Chickens Changed the World"
. ''National Geographic'': "When slaves were brought here from West Africa, they came with a deep knowledge of the chicken, because in West Africa the chicken was a common farm animal and also a very sacred animal. The knowledge that African-Americans brought served them very well, because white plantation owners for the most part didn't care much about chicken. In colonial times there were so many other things to eat that chicken was not high on the list." Scottish fried chicken was battered with seasonings and cooked in
lard
Lard is a Quasi-solid, semi-solid white fat product obtained by rendering (animal products), rendering the adipose tissue, fatty tissue of a domestic pig, pig.
, later West African fried chicken added different seasonings, and was battered and cooked in palm oil
Palm oil is an edible vegetable oil derived from the mesocarp (reddish pulp) of the fruit of oil palms. The oil is used in food manufacturing, in beauty products, and as biofuel. Palm oil accounted for about 36% of global oils produced from o ...
. Scottish frying and seasoning techniques and African seasoning techniques were used in the American South by enslaved Africans. At Monticello
Monticello ( ) was the primary residence and plantation of Thomas Jefferson, a Founding Father, author of the Declaration of Independence, and the third president of the United States. Jefferson began designing Monticello after inheriting l ...
in Virginia, President Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (, 1743July 4, 1826) was an American Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809. He was the primary author of the United States Declaration of Indepe ...
noted how the enslaved prepared meals with the African crop sesame seeds. Enslaved people ate sesame raw, toasted, or boiled and prepared stews, baked breads, boiled their greens with sesame seeds, and made sesame pudding. European colonists used sesame seeds to make baked breads.
In the 17th and 18th centuries, English colonists in Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
came into contact with Powhatan
Powhatan people () are Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands who belong to member tribes of the Powhatan Confederacy, or Tsenacommacah. They are Algonquian peoples whose historic territories were in eastern Virginia.
Their Powh ...
Indigenous people and adapted corn into their cuisine and Johnny cakes, corn pone, and fry bread became a part of their diet. English settlers at Jamestown were not prepared on how to survive in Virginia's wilderness. Settlers experienced the " starving time" in the winter of 1609 to 1610. Powhatan people taught the English how to hunt, fish and grow corn to survive. The food and survival skills English settlers learned from Natives became a part of their diet and cuisine. However, most Jamestown's residents did not survive that winter because of dwindling food supplies.
Colonial Williamsburg, Virginia
Williamsburg is an Independent city (United States), independent city in Virginia, United States. It had a population of 15,425 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. Located on the Virginia Peninsula, Williamsburg is in the northern par ...
was founded in 1632 by the English. Historians at Colonial Williamsburg
Colonial Williamsburg is a living-history museum and private foundation presenting a part of the historic district in Williamsburg, Virginia. Its historic area includes several hundred restored or recreated buildings from the 18th century, wh ...
researched colonial records and found what colonists in Williamsburg ate. The dishes colonial cooks prepared for Williamsburg's upper class were roast pigeon, fried ox tongue, mince pies, made meat dishes from beef, lamb, pork, chicken, and fish with vegetables, and made baked breads. For beverages they drank coffee, tea and chocolate. An article in the newspaper, ''The Warren Record,'' explains the influence of the English and Scottish on Southern American food: "English settlers in the South baked yeast bread, made savory puddings and drank beer...." "Settlers from lowland Scotland brought with them a tradition of cooking a kale soup and drinking distilled beverages."
English and Scottish settlers introduced biscuits
A biscuit is a Flour, flour-based baked food item. Biscuits are typically hard, flat, and Unleavened bread, unleavened. They are usually sweet and may be made with sugar, chocolate, icing (food), icing, jam, ginger, or cinnamon. They can also ...
into Southern breakfast. In England and Ireland people ate biscuits as part of a meal and were taken aboard ships during long voyages because they lasted longer and did not spoil like other foods. In the Southern United States, Americans evolved the recipe and made fluffier biscuits and poured gravy, honey and jam over them which became a popular breakfast item. Biscuits were an economical food for Southerners after the mid-19th century as they were made with simple ingredients of flour, baking powder
Baking powder is a dry chemical leavening agent, a mixture of a carbonate or bicarbonate and a weak acid. The base and acid are prevented from reacting prematurely by the inclusion of a buffer such as cornstarch. Baking powder is used to increas ...
, salt, butter, and milk.
In 1614, the Dutch established several settlements in Maryland and other Northern colonies. Dutch colonists introduced pancake
A pancake, also known as a hotcake, griddlecake, or flapjack, is a flat type of batter bread like cake, often thin and round, prepared from a starch-based Batter (cooking), batter that may contain eggs, milk, and butter, and then cooked on a ...
s, waffle
A waffle is a dish made from leavened Batter (cooking), batter or dough that is cooked between two plates that are patterned to give a characteristic size, shape, and surface impression. There are many variations based on the type of waffle iron ...
s, doughnut
A doughnut or donut () is a type of pastry made from leavened fried dough. It is popular in many countries and is prepared in various forms as a sweet snack that can be homemade or purchased in bakeries, supermarkets, food stalls, and fran ...
s, cookie
A cookie is a sweet biscuit with high sugar and fat content. Cookie dough is softer than that used for other types of biscuit, and they are cooked longer at lower temperatures. The dough typically contains flour, sugar, egg, and some type of ...
s, coleslaw
Coleslaw or cole slaw (from the Dutch term , meaning 'cabbage salad'), also widely known within North America simply as slaw, is a side dish consisting primarily of finely shredded raw cabbage with a salad dressing or condiment, commonly eithe ...
and pretzel
A pretzel ( ; from or , ) is a type of baking, baked pastry made from dough that is commonly shaped into a knot. The traditional pretzel shape is a distinctive symmetrical form, with the ends of a long strip of dough intertwined and then twi ...
s into the cuisine of the Thirteen Colonies. Colonial records showed Dutch people brought their waffle iron
A waffle iron or waffle maker is a kitchen utensil used to cook waffles between two hinged metal plates. Both plates have gridded indentations to shape the waffle from the batter or dough placed between them. The plates are heated and the iron ...
s from the Netherlands to colonial America. The English and Dutch introduced pie
A pie is a baked dish which is usually made of a pastry dough casing that contains a filling of various sweet or savoury ingredients. Sweet pies may be filled with fruit (as in an apple pie), nuts ( pecan pie), fruit preserves ( jam tart ...
s and Dutch settlers introduced deep-dish crust pie
A pie is a baked dish which is usually made of a pastry dough casing that contains a filling of various sweet or savoury ingredients. Sweet pies may be filled with fruit (as in an apple pie), nuts ( pecan pie), fruit preserves ( jam tart ...
recipes which enslaved African Americans and other Southerners adapted into their cuisine. The first documented pie recipe in Colonial America
The colonial history of the United States covers the period of European colonization of North America from the late 15th century until the unifying of the Thirteen British Colonies and creation of the United States in 1776, during the Re ...
was in 1675; it was a pumpkin pie recipe modified from British spiced and boiled squash. European settlers prepared pies because they preserved food. They made meat and sweet pies using local ingredients and other ingredients from foreign countries. An article from Southern Living Magazine explains the history of the Southern American pie tradition: "The mixture of eggs, butter, sugar, vanilla, and flour made its way to the American South from England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
. It became popular in Virginia and has had many incarnations, from the Classic Chess Pie
Chess pie is a dessert with a filling composed mainly of flour, butter, sugar, eggs, and sometimes milk, characteristic of Cuisine of the Southern United States, Southern United States cuisine.
Jefferson Davis pie is similar to chess pie, but J ...
to fruity versions, like Lemon Chess Pie."
Enslaved Africans influence in Southern cuisine are food items from West Africa such as okra, black-eyed peas, one-pot rice cooking methods to make stews that influenced the making of gumbo
Gumbo () is a stew that is popular among the U.S. Gulf Coast community, the New Orleans stew variation being the official state cuisine of the U.S. state of Louisiana. Gumbo consists primarily of a strongly flavored stock, meat or shellfis ...
and jambalaya, and adding a variety of spices and hot and sweet sauces to Southern dishes. West-Central Africans were trafficked to the South as early as 1526 under Spanish explorers to the colonies of South Carolina and Georgia called San Miguel de Gualdape, and enslaved people from Angola
Angola, officially the Republic of Angola, is a country on the west-Central Africa, central coast of Southern Africa. It is the second-largest Portuguese-speaking world, Portuguese-speaking (Lusophone) country in both total area and List of c ...
were brought to colonial Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
in 1619. Other foods brought from West Africa during the slave trade that influenced Southern cuisine were guinea pepper, gherkin
A pickled cucumber – commonly known as a pickle in the United States, Canada and Australia and a gherkin ( ) in Britain, Ireland, South Africa, and New Zealand – is a usually small or miniature cucumber that has been pickled in a brine, ...
, sesame seeds, kola nut
The kola nut ( Yoruba: ''obi'', Dagbani: ''guli'', Hausa: goro, Igbo: ''ọjị'', Sängö: ''gôro,'' Swahili: ''mukezu'') is the seed of certain species of plant of the genus ''Cola'', placed formerly in the cocoa family Sterculiaceae and ...
s, eggplant, watermelon
The watermelon (''Citrullus lanatus'') is a species of flowering plant in the family Cucurbitaceae, that has a large, edible fruit. It is a Glossary of botanical terms#scandent, scrambling and trailing vine-like plant, and is plant breeding ...
, rice, and cantaloupe.
Gullah Geechee people in the Sea Islands
The Sea Islands are a chain of over a hundred tidal and barrier islands on the Atlantic Ocean coast of the Southeastern United States, between the mouths of the Santee and St. Johns rivers along South Carolina, Georgia and Florida. The la ...
of South Carolina and Georgia influenced some of the Southern rice-based dishes. West Africans in the rice growing regions of present-day Senegal
Senegal, officially the Republic of Senegal, is the westernmost country in West Africa, situated on the Atlantic Ocean coastline. It borders Mauritania to Mauritania–Senegal border, the north, Mali to Mali–Senegal border, the east, Guinea t ...
, Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone, officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It is bordered to the southeast by Liberia and by Guinea to the north. Sierra Leone's land area is . It has a tropical climate and envi ...
, and Liberia
Liberia, officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to Guinea–Liberia border, its north, Ivory Coast to Ivory Coast–Lib ...
cultivated African rice for about 3,000 years. African rice is a species related to, yet distinct from, Asian rice. It was originally domesticated in the inland delta of the Upper Niger River
The Niger River ( ; ) is the main river of West Africa, extending about . Its drainage basin is in area. Its source is in the Guinea Highlands in south-eastern Guinea near the Sierra Leone border. It runs in a crescent shape through Mali, Nige ...
. Once Carolinian and Georgian planters in the American South discovered that African rice would grow in that region, they often sought enslaved Africans from rice-growing regions because they had the skills and knowledge needed to develop and build irrigation, dams and earthworks. The rice-based dished created by Gullah people are Charleston red rice and Hoppin' John
Hoppin' John, also known as Carolina peas and rice, is a rice and beans dish of legendary origins associated with the cuisine of the Southern United States. Similar dishes are found in regions with a significant African-origin demographic like Lo ...
. Enslaved African Americans grew collard greens in their gardens. They incorporated collards in their soups and stews a tradition that came from West Africa. As the National Museum of African American History and Culture explained that African Americans in the American South spread the recipe of collard greens to other parts of the United States when they left the South during the Great Migration.
The French established a permanent settlement in the South in present-day New Orleans
New Orleans (commonly known as NOLA or The Big Easy among other nicknames) is a Consolidated city-county, consolidated city-parish located along the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Louisiana. With a population of 383,997 at the 2020 ...
, Louisiana in 1718. French colonists relied on Indigenous people to survive. As historian Gwendolyn Midlo Hall explained how the French learned from the Chitimacha and other Indigenous people about the flora and fauna, topography of the land, how to build boats and navigate the waters, how to preserve food, and cultivate corn, squash, potatoes, and other indigenous crops. The first enslaved Africans to arrive in Louisiana came in 1719 aboard two slave ships that brought several barrels of rice seeds. African rice became a staple in Louisiana cuisine cultivated by enslaved people from West Africa's rice growing regions.
French people incorporated roux
Roux () is a mixture of flour and fat cooked together and used to thicken sauces. Roux is typically made from equal parts of flour and fat by weight. The flour is added to the melted fat or Cooking oil, oil on the stove top, blended until smoo ...
into Louisiana cuisine that influenced the making of gumbo
Gumbo () is a stew that is popular among the U.S. Gulf Coast community, the New Orleans stew variation being the official state cuisine of the U.S. state of Louisiana. Gumbo consists primarily of a strongly flavored stock, meat or shellfis ...
. Another French influence is mirepoix
A mirepoix ( , ) is a mixture of diced vegetables cooked with fat (usually butter) for a long time on low heat without coloring or browning. The ingredients are not sautéed or otherwise hard-cooked, because the intention is to sweeten rather t ...
made with carrots, celery, and onion that became a Creole and Cajun version in Louisiana called the "holy trinity" made with bell peppers, celery and onions. Indigenous peoples of Louisiana during the colonial period (and into present day) made fry bread and Indian tacos. They also prepared meals with hunted animals such as turkey and deer and caught fish. Native Americans in Louisiana influenced the foodways of African Americans and European Americans as non-Natives prepared their meals with turkey, cornbread, and other Indigenous staples.
Spaniards and enslaved West Africans influenced the making of jambalaya in New Orleans. Some historians suggest jambalaya has its roots in West African cuisine. The French introduced the tomato
The tomato (, ), ''Solanum lycopersicum'', is a plant whose fruit is an edible Berry (botany), berry that is eaten as a vegetable. The tomato is a member of the nightshade family that includes tobacco, potato, and chili peppers. It originate ...
(a food native to the Americas) to West Africans, and they incorporated the food into their one-pot rice cooking meals and enhanced jollof rice
Jollof (), or jollof rice, is a rice dish from West Africa. The dish is typically made with long-grain rice, tomatoes, chilis, onions, spices, and sometimes other vegetables and/or meat in a single pot, although its ingredients and preparatio ...
and created jambalaya. Author Ibraham Seck, director of research at the Whitney Plantation Slave Museum in St. John the Baptist Parish, suggests jambalaya originated on the Senegalese
Demographic features of the population of Senegal include population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.
About 42% of Senegal's population i ...
coast of West Africa. Senegalese people had knowledge of rice cultivation and created dishes using rice and meats that were brought to Louisiana during the era of the slave trade. About sixty percent of enslaved Africans brought to Louisiana came from Senegambia
The Senegambia (other names: Senegambia region or Senegambian zone,Barry, Boubacar, ''Senegambia and the Atlantic Slave Trade'', (Editors: David Anderson, Carolyn Brown; trans. Ayi Kwei Armah; contributors: David Anderson, American Council of Le ...
. Senegambians had knowledge of rice cultivation and prepared meals using rice and other grains adding meat and vegetables into one pot. An article from the United Nations states that the cuisines of Nigeria, Senegal, Guinea, and Benin influenced the development of jambalaya: "Jambalaya (mixed rice, meat and vegetables), feijoada (black beans and meat), gombo(okra), and hopping johns (peas) are all dishes that have been re-adapted from Senegal, Nigeria, Guinea and Benin. You will find variations of these dishes in America and the Caribbean region."
Jamestown, Virginia
The Jamestown settlement in the Colony of Virginia was the first permanent British colonization of the Americas, English settlement in the Americas. It was located on the northeast bank of the James River, about southwest of present-day Willia ...
and established settlements in the Shenandoah Valley
The Shenandoah Valley () is a geographic valley and cultural region of western Virginia and the eastern panhandle of West Virginia in the United States. The Valley is bounded to the east by the Blue Ridge Mountains, to the west by the east ...
. They brought their food traditions from Germany and influenced cuisine in America. The classic southern dish chicken and dumplings have origins in German cuisine
The cuisine of Germany consists of many different local or regional cuisines, reflecting the country's federal history. Germany itself is part of the larger cultural region of Central Europe, sharing many culinary traditions with neighbouring c ...
. "...the famous southern dish, Chicken and Dumplings, received its birth from the German influence of Spaetzel, which are small potato dumplings, even smaller than its Italian cousin, gnocchi." Other German influences are liver beef dishes, German sausages
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
, and liver dumplings. German people
Germans (, ) are the natives or inhabitants of Germany, or sometimes more broadly any people who are of German descent or native speakers of the German language. The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, constitution of Germany, imple ...
also influenced cuisine in Louisiana after their arrival to the colony in 1722. For example, "German sausage making is called andouille. Andouille sausage is a combination of pork, pork fat, salt, garlic, red pepper and black pepper, all packed into a sausage casing, which is smoked over sugar cane and pecan logs. When smoked, the sausage becomes very dark in color." This method of preparation of sausage is found in between St. Charles and St. John Baptist parishes. German foods such as marinated meats, pastries, sour flavors, and wursts were assimilated into the Southern diet and they became classic American foods that are eaten today in the form of hot dog
A hot dog is a grilled, steamed, or boiled sausage served in the slit of a partially sliced bun. The term ''hot dog'' can also refer to the sausage itself. The sausage used is a wiener ( Vienna sausage) or a frankfurter ( Frankfurter Würs ...
s and hamburger
A hamburger (or simply a burger) consists of fillings—usually a patty of ground meat, typically beef—placed inside a sliced bun or bread roll. The patties are often served with cheese, lettuce, tomato, onion, pickles, bacon, or chilis ...
s.
The Southern side dish potato salad
Potato salad is a salad dish made from boiled potatoes, usually containing a dressing and a variety of other ingredients such as boiled eggs and raw vegetables. It is usually served as a side dish.
History and varieties
Potato salad is foun ...
have German influences. An article from South Carolina National Public Radio (NPR) explains:
Culinary historians do not know who added mayonnaise to potato salad. Mayonnaise became available to purchase in the early 1900s. By the 1920s and 1930s, people were adding mayonnaise to potato salad.
American Civil War (1861 to 1865)
During theAmerican Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
, food supplies were limited for Union and Confederate soldiers. Civil War soldiers received limited food rations which consisted of bread, coffee, salt pork, hard bread, a pound of beef or pork and a pound of bread or flour, and sometimes extras which included dried beans or peas, rice, vinegar, and molasses
Molasses () is a viscous byproduct, principally obtained from the refining of sugarcane or sugar beet juice into sugar. Molasses varies in the amount of sugar, the method of extraction, and the age of the plant. Sugarcane molasses is usuall ...
. Historians found that a lot of food was fried during the Civil War. An article from the Florida Department of State explains the soldier's diet: "The most common form of hard bread, was called hardtack
Hardtack (or hard tack) is a type of dense Cracker (food), cracker made from flour, water, and sometimes salt. Hardtack is inexpensive and long-lasting. It is used for sustenance in the absence of perishable foods, commonly during long sea voyage ...
, a basic wheat biscuit that did not easily decay and could survive a rough march. It was extremely hard, and was often soaked in water, coffee, or in meat fat to soften it enough to eat. Other items, such as beans, peas, rice, coffee, sugar, or salt, were also issued, but not on a daily basis." Enslaved African Americans prepared meals for wealthy Confederate soldiers. In Union camps, contraband of war (Freedmen) and other cooks prepared meals for the Union army. Over time, rations between Union and Confederate armies varied as Confederate rations were reduced in wheat and livestock because of a Union blockade that prevented the Confederates from obtaining food and supplies.
 Hardtack was not available to many Confederates because it was made from wheat, and wheat was not grown in many Southern states except for Georgia and Virginia. Cornbread replaced the hardtack rations in the Confederate army. Confederate soldiers made Johnnie cakes and "corn dodgers" that was similar to hardtack. In addition, they made fried flatbread and balls of cornmeal called "flapjacks" cooked over an open fire, and ate bacon, imitation coffee, and
Hardtack was not available to many Confederates because it was made from wheat, and wheat was not grown in many Southern states except for Georgia and Virginia. Cornbread replaced the hardtack rations in the Confederate army. Confederate soldiers made Johnnie cakes and "corn dodgers" that was similar to hardtack. In addition, they made fried flatbread and balls of cornmeal called "flapjacks" cooked over an open fire, and ate bacon, imitation coffee, and molasses
Molasses () is a viscous byproduct, principally obtained from the refining of sugarcane or sugar beet juice into sugar. Molasses varies in the amount of sugar, the method of extraction, and the age of the plant. Sugarcane molasses is usuall ...
. In some Southern hospitals patients ate dried fruit, potatoes, mush, beef, chicken soup, and bread. Despite limited rations, some Union soldiers were able to make hearty meals. The meals prepared were "...chicken fricassee, mushroom ketchup (a condiment made by boiling mushrooms), a beef-and-potato stew, cornish game hens and ham and beans." Union and Confederates foraged for food when rations were low and cooked the fresh food they found. They also ate desiccated
Desiccation is the state of extreme dryness, or the process of extreme drying. A desiccant is a hygroscopic (attracts and holds water) substance that induces or sustains such a state in its local vicinity in a moderately sealed container. ...
vegetables which were dehydrated and compressed vegetables into one inch by one-foot rectangular bricks that were made from string beans, turnips, carrots, beets, and onions. Other vegetables were packed into cakes, dried, and boiled for consumption.
Post antebellum era
Interest in American regional cooking continued to grow after the Civil War, especially concerning the traditions of the Southern United States. Many new cookbooks were added to the existing body of literature. Some of these fell within the scope of domestic manuals offering instruction to southern homemakers to the maintenance of homes in the new post-Slavery era. Some of these works like Mary Stuart Smith's ''Virginia Cookery Book'' (1885) aimed to preserve the culinary heritage of the South. Recipes made by former slaves were published in African-American cookbooks after the Civil War. The earliest such cookbook was self-published in 1866 by Malinda Russell as a pamphlet titled, ''A Domestic Cookbook: Containing a Careful Selection of Useful Receipts for the Kitchen''. A cookbook published in 1900 in the city ofCharleston, South Carolina
Charleston is the List of municipalities in South Carolina, most populous city in the U.S. state of South Carolina. The city lies just south of the geographical midpoint of South Carolina's coastline on Charleston Harbor, an inlet of the Atla ...
had recipes used by formerly enslaved Gullah people. Benne seeds from ''sesame'', a plant native to West Africa, were eaten raw with sugar or milk. Enslaved people also made cakes, wafers, and brittles from them for white plantation families.
In the Appalachian region, 19th-century meals included greens fried in bear grease, elk backstrap steaks and venison
Venison refers primarily to the meat of deer (or antelope in South Africa). Venison can be used to refer to any part of the animal, so long as it is edible, including the internal organs. Venison, much like beef or pork, is categorized into spe ...
stew. Ashcakes were cornbread cooked directly on hearth coals. Cornbread
Cornbread is a quick bread made with cornmeal, associated with the cuisine of the Southern United States, with origins in Native American cuisine. It is an example of batter bread. Dumplings and pancakes made with finely ground cornmeal are st ...
was the most common bread in the mountains, and still remains a staple. As wheat
Wheat is a group of wild and crop domestication, domesticated Poaceae, grasses of the genus ''Triticum'' (). They are Agriculture, cultivated for their cereal grains, which are staple foods around the world. Well-known Taxonomy of wheat, whe ...
flour
Flour is a powder made by Mill (grinding), grinding raw grains, List of root vegetables, roots, beans, Nut (fruit), nuts, or seeds. Flours are used to make many different foods. Cereal flour, particularly wheat flour, is the main ingredie ...
and baking powder
Baking powder is a dry chemical leavening agent, a mixture of a carbonate or bicarbonate and a weak acid. The base and acid are prevented from reacting prematurely by the inclusion of a buffer such as cornstarch. Baking powder is used to increas ...
/baking soda
Sodium bicarbonate (IUPAC name: sodium hydrogencarbonate), commonly known as baking soda or bicarbonate of soda (or simply “bicarb” especially in the UK) is a chemical compound with the formula NaHCO3. It is a salt (chemistry), salt compose ...
became available in the late 19th century, buttermilk
Buttermilk is a fermented dairy drink. Traditionally, it was the liquid left behind after churning butter out of cultured cream. As most modern butter in Western countries is not made with cultured cream but uncultured sweet cream, most mode ...
biscuit
A biscuit is a flour-based baked food item. Biscuits are typically hard, flat, and unleavened. They are usually sweet and may be made with sugar, chocolate, icing, jam, ginger, or cinnamon. They can also be savoury, similar to crackers.
...
s became popular. Today, buttermilk biscuits and sausage gravy
Sausage gravy is a traditional Southern cuisine, Southern breakfast dish in the United States. After loose pork sausage is cooked in a pan and removed, a roux is formed by browning flour in the residual fat. Milk and seasonings, such as salt an ...
are the classic Appalachian breakfast; they are also a common breakfast everywhere where Appalachian people have emigrated. Both North Carolina
North Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, South Carolina to the south, Georgia (U.S. stat ...
and West Virginia
West Virginia is a mountainous U.S. state, state in the Southern United States, Southern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States.The United States Census Bureau, Census Bureau and the Association of American ...
have statewide biscuit chain restaurants; many Southern or originally-Southern chains offer biscuits and gravy, and when McDonald's introduced a new breakfast menu selling either Egg McMuffins (with English muffins) or a variant with biscuits, the biscuit zone was practically a map of the South with the exception of Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
, Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east ...
, and Florida
Florida ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders the Gulf of Mexico to the west, Alabama to the northwest, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the north, the Atlantic ...
.
The American hot dog
A hot dog is a grilled, steamed, or boiled sausage served in the slit of a partially sliced bun. The term ''hot dog'' can also refer to the sausage itself. The sausage used is a wiener ( Vienna sausage) or a frankfurter ( Frankfurter Würs ...
originated from German sausages called "frankfurts" in Frankfurt-am-Main, Germany. Sausages in Germany were served without bread. Charles L Feltman was a German immigrant and came to Coney Island, New York in 1856 and served sausages wrapped in a bun beginning in 1867. This method of eating sausages later spread across America making its way into the Southern states and are eaten at baseball games. Southerners make different versions of hot dogs, giving them a southern flavor. Some Southern hot dogs have brown sugar mustard as a topping. In Huntsville, Alabama
Huntsville is the List of municipalities in Alabama, most populous city in the U.S. state of Alabama. The population of the city is estimated to be 241,114 in 2024, making it the List of United States cities by population, 100th-most populous ...
, hot dogs are served with chili and ketchup-slaw. In Mobile, Alabama
Mobile ( , ) is a city and the county seat of Mobile County, Alabama, United States. The population was 187,041 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. After a successful vote to annex areas west of the city limits in July 2023, Mobil ...
, hot dogs are served on a toasted bun with a mustard-based coleslaw.
Other cultural influences
 Since the 20th century into present day, immigrants from Asia, the Middle East, Africa, and other European countries brought their cuisines to the South and influenced southern cuisine. An article from ''
Since the 20th century into present day, immigrants from Asia, the Middle East, Africa, and other European countries brought their cuisines to the South and influenced southern cuisine. An article from ''Time Magazine
''Time'' (stylized in all caps as ''TIME'') is an American news magazine based in New York City. It was published weekly for nearly a century. Starting in March 2020, it transitioned to every other week. It was first published in New York Cit ...
'' explains: "...immigrants and their American-born sons and daughters have helped transform the perception of Southern cuisine into something beyond biscuits and gravy and mint juleps. Southern food is now kebabs in Nashville's Little Kurdistan, one of the largest enclaves of Kurds in the U.S. It's Greek diners across Alabama and Ethiopian restaurants standing next to Salvadoran pupuserías in Virginia. In rural towns that have seen their populations decline, it's the Chinese or Mexican restaurant that took over former greasy spoons while preserving them as de facto community centers. And in reborn urban centers, it's the Michelin-approved fine-dining restaurants where chefs have fused techniques from India, Laos and Nigeria with the staples of the Southern canon."
Mexican food
Mexican cuisine consists of the cuisines and associated traditions of the modern country of Mexico. Its earliest roots lie in Mesoamerican cuisine. Mexican cuisine's ingredients and methods arise from the area's first agricultural communities ...
culture influence on Southern cuisine is taco
A taco (, , ) is a traditional Mexican cuisine, Mexican dish consisting of a small hand-sized corn tortilla, corn- or Flour tortilla, wheat-based tortilla topped with a Stuffing, filling. The tortilla is then folded around the filling and fing ...
s. Texas
Texas ( , ; or ) is the most populous U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the we ...
was once a part of Mexico until it declared independence on March 2, 1836, and became a US state in 1845. Tex-Mex
Tex-Mex cuisine (derived from the words ''Texas'' and ''Mexico'') is a regional American cuisine that originates from the culinary creations of Tejanos, Tejano people. It has spread from border states such as Texas and others in the Southwestern ...
food is a fusion of Texas cuisine with Northern Mexican. Tacos in Texas have barbecued meats from pork, chicken, brisket
Brisket is a cut of meat from the breast or lower chest of beef or veal. The beef brisket is one of the nine beef primal cuts, though the definition of the cut differs internationally. The brisket muscles include the Pectoralis major, superficial ...
, vegetables, and Mexican salsa. Indigenous people of Texas hunted pronghorn, deer, rabbits, turkeys, and quail. They made flour from ground acorns and mesquite pods. The Indigenous nations of the Antelope Creek in the Panhandle, the Caddo
The Caddo people comprise the Caddo Nation of Oklahoma, a federally recognized tribe headquartered in Binger, Oklahoma. They speak the Caddo language.
The Caddo Confederacy was a network of Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands, who ...
in East Texas, and the Jornada Mogollon near El Paso influenced Southern foodways as venison, catfish, and pecans are staples in Texas cuisine. The Tejanos
Tejanos ( , ) are descendants of Texas Creoles and Mestizos who settled in Texas before its admission as an American state. The term is also sometimes applied to Texans of Mexican descent.
Etymology
The word ''Tejano'', with a ''J'' instead o ...
are a multiethnic people of Spanish and Native American heritage, and their food influenced Texas cuisine. A common dish in Texas is chili con carne made with cumin, black pepper, garlic, onion, and beef are all foreign imported foods, and the chiles come from Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
. Tamale
A tamale, in Spanish language, Spanish , is a traditional Mesoamerican dish made of ''masa'', a dough made from nixtamalization, nixtamalized maize, corn, which is steaming, steamed in a corn husk or Banana leaf, banana leaves. The wrapping ...
is a dish native to Central America and Mexico. The Tejanos' Indigenous ancestors brought tamales to Texas.
Southern food in restaurants
 Chains serving Southern foods—often along with American
Chains serving Southern foods—often along with American comfort food
Comfort food is food that provides a nostalgic or sentimental value to someone and may be characterized by its high caloric nature associated with childhood or home cooking. The nostalgia may be specific to an individual or it may apply to a ...
—have had great success; many have spread across the country or across the world, while others have chosen to stay in the South. Pit barbecue is popular all over the American South; unlike the rest of the country, most of the rural South has locally owned, non-franchise pit-barbecue restaurants, many serving the regional style of barbecue instead of the nationally predominant Kansas City style. Family-style restaurants serving Southern cuisine are common throughout the South, and range from the humble and down-home to the decidedly upscale.
During the civil rights movement, soul food
Soul food is the ethnic cuisine of African Americans. Originating in the Southern United States, American South from the cuisines of Slavery in the United States, enslaved Africans transported from Africa through the Atlantic slave trade, sou ...
restaurants were places where civil rights leaders and activists met to discuss and strategize civil rights protests and ideas for implementing social and political change. Paschal's Restaurant in Atlanta, like Georgia Gilmore's eatery in Montgomery, had an important part in the civil rights movement. Upon returning to Atlanta from Montgomery, Martin Luther King Jr.
Martin Luther King Jr. (born Michael King Jr.; January 15, 1929 – April 4, 1968) was an American Baptist minister, civil and political rights, civil rights activist and political philosopher who was a leader of the civil rights move ...
got permission "to bring his team members and guests to Paschal's to eat, meet, rest, plan, and strategize."
Traditional Southern dishes
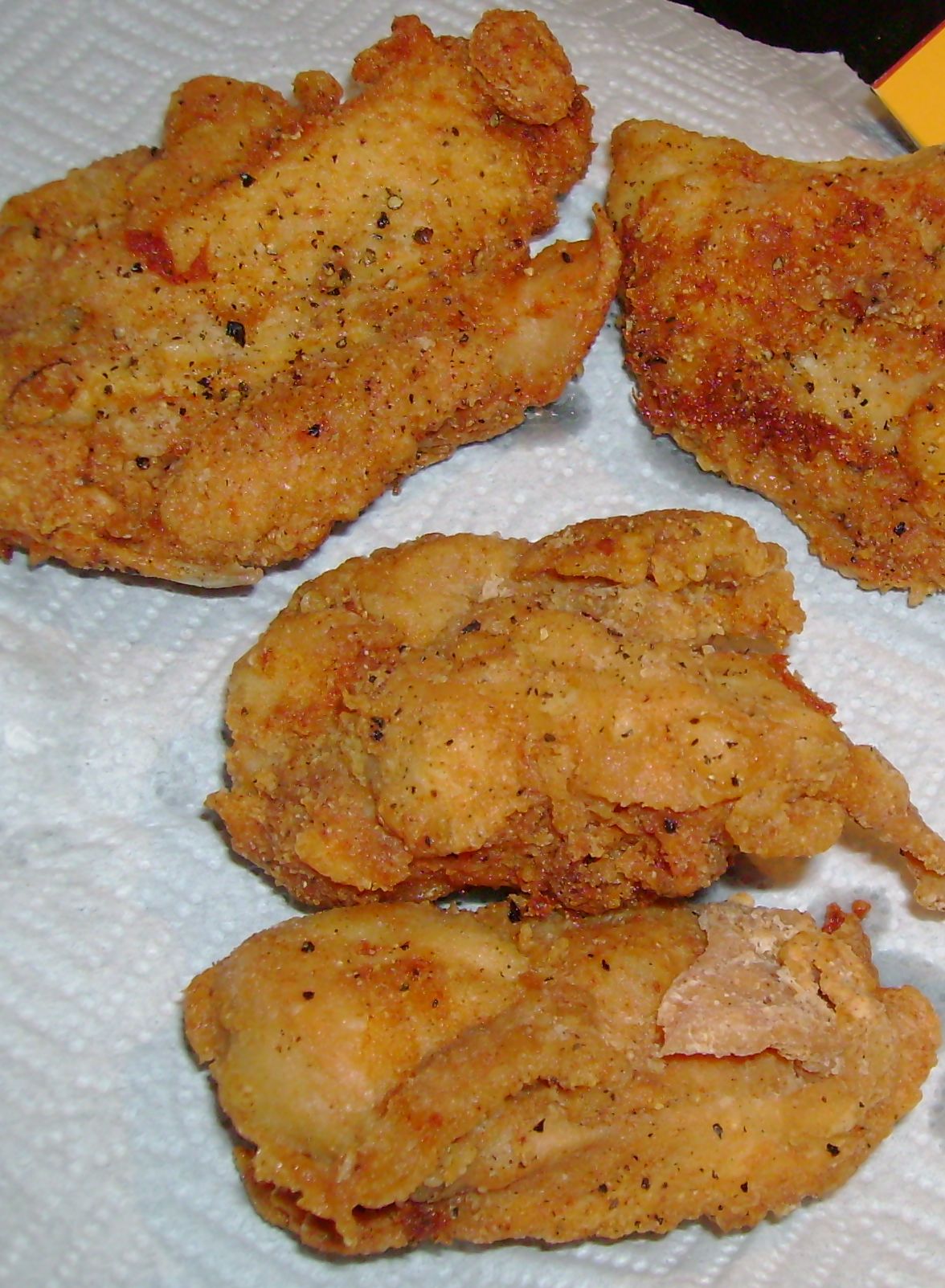
 A traditional Southern meal may include pan-
A traditional Southern meal may include pan-fried chicken
Fried chicken, also called Southern fried chicken, is a dish consisting of chicken pieces that have been coated with seasoned flour or batter and pan-fried, deep fried, pressure fried, or air fried. The breading adds a crisp coating or ...
, field peas (such as black-eyed pea
The black-eyed pea or black-eyed bean is a legume grown around the world for its medium-sized, edible bean. It is a subspecies of the cowpea, an Old World plant domesticated in Africa, and is sometimes simply called a cowpea.
The common commerci ...
s), greens (such as collard greens
Collard is a group of loose-leafed cultivars of ''Brassica oleracea'' (the same species as many common vegetables like cabbage and broccoli). Part of the acephala cultivar group (or kale group), collard is also classified as the variety ''B.& ...
, mustard greens, turnip greens, or poke sallet), mashed potatoes, cornbread
Cornbread is a quick bread made with cornmeal, associated with the cuisine of the Southern United States, with origins in Native American cuisine. It is an example of batter bread. Dumplings and pancakes made with finely ground cornmeal are st ...
or corn pone, sweet tea
Sweet tea, also known as sweet iced tea, is a popular style of iced tea commonly consumed in the United States (especially the South) and Indonesia. Sweet tea is most commonly made by adding sugar or simple syrup to black tea while the tea is ...
, and dessert—typically a pie (sweet potato
The sweet potato or sweetpotato (''Ipomoea batatas'') is a dicotyledonous plant in the morning glory family, Convolvulaceae. Its sizeable, starchy, sweet-tasting tuberous roots are used as a root vegetable, which is a staple food in parts of ...
, chess
Chess is a board game for two players. It is an abstract strategy game that involves Perfect information, no hidden information and no elements of game of chance, chance. It is played on a square chessboard, board consisting of 64 squares arran ...
, shoofly, pecan
The pecan ( , , ; ''Carya illinoinensis'') is a species of hickory native to the Southern United States and northern Mexico in the region of the Mississippi River.
The tree is cultivated for its seed primarily in the U.S. states of Georgia ( ...
, and peach
The peach (''Prunus persica'') is a deciduous tree first domesticated and Agriculture, cultivated in China. It bears edible juicy fruits with various characteristics, most called peaches and the glossy-skinned, non-fuzzy varieties called necta ...
are the most common), or a cobbler
Cobbler(s) may refer to:
*A person who repairs shoes
* Cobbler (food), a type of pie
Places
* The Cobbler, a mountain located near the head of Loch Long in Scotland
* Mount Cobbler, Australia
Art, entertainment and media
* ''The Cobbler' ...
(peach, blackberry, sometimes apple in Kentucky or Appalachia).
Other Southern foods include grits
Grits (stylized as GRITS) is an American Christian hip hop group from Nashville, Tennessee. Their name is an acronym, which stands for "Grammatical Revolution In the Spirit". GRITS is made up of Stacey "Coffee" Jones and Teron "Bonafide" Carter ...
, country ham
A country is a distinct part of the Earth, world, such as a state (polity), state, nation, or other polity, political entity. When referring to a specific polity, the term "country" may refer to a sovereign state, List of states with limited r ...
, hushpuppies, beignet
Beignet ( , also , ; ) is a type of deep-fried pastry of French origin. It is commonly made from choux pastry, pâte à choux, but can also be made using rice flour (rice beignets) or yeast-leavened batters. Beignets can be served in a variety o ...
s (in the Gulf South), Southern styles of succotash, brisket
Brisket is a cut of meat from the breast or lower chest of beef or veal. The beef brisket is one of the nine beef primal cuts, though the definition of the cut differs internationally. The brisket muscles include the Pectoralis major, superficial ...
, meatloaf, chicken fried steak, buttermilk biscuits (may be served with butter
Butter is a dairy product made from the fat and protein components of Churning (butter), churned cream. It is a semi-solid emulsion at room temperature, consisting of approximately 81% butterfat. It is used at room temperature as a spread (food ...
, jelly, fruit preserves
Fruit preserves are preparations of fruits whose main preserving agent is sugar and sometimes acid, often stored in glass jars and used as a condiment or spread.
There are many varieties of fruit preserves globally, distinguished by the meth ...
, honey
Honey is a sweet and viscous substance made by several species of bees, the best-known of which are honey bees. Honey is made and stored to nourish bee colonies. Bees produce honey by gathering and then refining the sugary secretions of pl ...
, gravy
Gravy is a sauce made from the juices of meats and vegetables that run naturally during cooking and often thickened with thickeners for added texture. The gravy may be further coloured and flavoured with gravy salt (a mix of salt and caramel food ...
or sorghum molasses), pimento cheese, boiled or baked sweet potato
The sweet potato or sweetpotato (''Ipomoea batatas'') is a dicotyledonous plant in the morning glory family, Convolvulaceae. Its sizeable, starchy, sweet-tasting tuberous roots are used as a root vegetable, which is a staple food in parts of ...
es, pit barbecue, fried catfish
Catfish (or catfishes; order (biology), order Siluriformes or Nematognathi) are a diverse group of ray-finned fish. Catfish are common name, named for their prominent barbel (anatomy), barbels, which resemble a cat's whiskers, though not ...
, fried green tomatoes
''Fried Green Tomatoes'' is a 1991 American comedy-drama film directed by Jon Avnet and based on Fannie Flagg's 1987 novel '' Fried Green Tomatoes at the Whistle Stop Cafe''. Written by Flagg and Carol Sobieski, and starring Kathy Bates, J ...
, macaroni and cheese, bread pudding
Bread pudding is a popular bread-based United Kingdom, British dessert. It is made with stale bread and milk or cream, generally containing egg (food), eggs, a form of fat such as oil, butter or suet and, depending on whether the pudding is swe ...
, okra
Okra (, ), ''Abelmoschus esculentus'', known in some English-speaking countries as lady's fingers, is a flowering plant in the Malvaceae, mallow family native to East Africa. Cultivated in tropical, subtropical, and warm temperate regions aro ...
(principally fried okra that has been dredged in cornmeal
Maize meal is a meal (coarse flour) ground from dried maize. It is a common staple food and is ground to coarse, medium, and fine consistencies, but it is not as fine as wheat flour can be.Herbst, Sharon, ''Food Lover's Companion'', Third Editi ...
, but also steamed, stewed, sauteed, or pickled), butter beans, and pinto bean
The pinto bean () is a variety of Phaseolus vulgaris, common bean (''Phaseolus vulgaris''). In Spanish language, Spanish they are called . It is the most popular bean by crop production in Northern Mexico and the Southwestern United States, South ...
s.
Barbecue
 "White barbecue sauce" made with
"White barbecue sauce" made with mayonnaise
Mayonnaise (), colloquially referred to as "mayo" (), is a thick, creamy sauce with a rich and tangy taste that is commonly used on sandwiches, hamburgers, Salad#Bound salads, bound salads, and French fries. It also forms the base for various o ...
, pepper and vinegar is a specialty of Alabama barbecue usually served with smoked barbecue chicken.
"Yellow barbecue sauce" made with a mustard
Mustard may refer to:
Food and plants
* Mustard (condiment), a paste or sauce made from mustard seeds used as a condiment
* Mustard plant, one of several plants, having seeds that are used for the condiment
** Mustard seed, small, round seeds of ...
base is unique to South Carolina barbecue and has roots in the mass immigration of Germans to the area in the mid-1700s.
For barbecue in the United States
Barbecue is a tradition often considered a quintessential part of Culture of the United States, American culture, especially the Southern United States.
First introduced to the lands which would become the United States by the Taíno to Christ ...
, each Southern locale has its own variety of barbecue, particularly sauces. In recent years, the regional variations have blurred as restaurants and consumers experiment and adapt the styles of other regions. South Carolina
South Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders North Carolina to the north and northeast, the Atlantic Ocean to the southeast, and Georgia (U.S. state), Georg ...
is the only state that traditionally features all four recognized barbecue sauce
Barbecue sauce (also abbreviated as BBQ sauce) is a sauce used as a marinade, basting, condiment, or topping for meat cooked in the barbecue cooking style, including pork, beef, and chicken. It is a ubiquitous condiment in the Southern United ...
s, including mustard-based, vinegar-based, and light and heavy tomato-based sauces. North Carolina
North Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, South Carolina to the south, Georgia (U.S. stat ...
sauces vary by region; eastern North Carolina uses a vinegar-based sauce, the center of the state uses Lexington-style barbecue, with a combination of ketchup
Ketchup or catsup is a table condiment with a sweet and sour flavor. "Ketchup" now typically refers to tomato ketchup, although early recipes for different varieties contained mushrooms, oysters, mussels, egg whites, grapes, or walnuts, amon ...
and vinegar as its base, and western North Carolina uses a heavier ketchup base. Memphis barbecue is best known for tomato- and vinegar-based sauces. In some Memphis establishments and in Kentucky, meat is rubbed with dry seasoning ( dry rubs) and smoked over hickory
Hickory is a common name for trees composing the genus ''Carya'', which includes 19 species accepted by ''Plants of the World Online''.
Seven species are native to southeast Asia in China, Indochina, and northeastern India (Assam), and twelve ...
wood without sauce. The finished barbecue is then served with barbecue sauce on the side.
Fried chicken
Fried chicken
Fried chicken, also called Southern fried chicken, is a dish consisting of chicken pieces that have been coated with seasoned flour or batter and pan-fried, deep fried, pressure fried, or air fried. The breading adds a crisp coating or ...
is among the region's best-known exports. It is believed that the Scots, and later Scottish immigrants to many southern states had a tradition of deep frying chicken in batter with seasonings fat, unlike their English counterparts who baked or boiled chicken. However, some sources trace the origin of fried chicken to Southern and Western England where most of the Early settlers to the South came from. They conclude that Southern and Western England had a strong tradition of frying, simmering, and sautéing meats in a skillet as opposed to East Anglia which favored baking and boiling meats.
The importance of fried chicken to southern cuisine is apparent through the multiple traditions and different adaptations of fried chicken, such as KFC
KFC Corporation, doing business as KFC (an abbreviation of Kentucky Fried Chicken), is an American fast food restaurant chain specializing in fried chicken and chicken sandwiches. Headquartered in Louisville, Kentucky, it is the world's se ...
; Nashville's Prince's Hot Chicken Shack; or the Cajun-inspired Bojangles' Famous Chicken 'n Biscuits and Popeyes Chicken.Ugly Delicious. "Fried Chicken." Episode 6. Directed by Eddie Schmidt. Written by Danny Breen. Netflix, February 23, 2018.
Pork and ham
Pork is an integral part of the cuisine. Stuffed ham is served inSouthern Maryland
Southern Maryland, also referred to as SoMD, is a geographical, cultural and historic region in Maryland composed of the state's southernmost counties on the Western Shore of the Chesapeake Bay. According to the state of Maryland, the region incl ...
. A traditional holiday get-together featuring whole hog barbecue is known in Virginia and the Carolinas as a " pig pickin'".
Green beans are often flavored with bacon
Bacon is a type of Curing (food preservation), salt-cured pork made from various cuts of meat, cuts, typically the pork belly, belly or less fatty parts of the back. It is eaten as a side dish (particularly in breakfasts), used as a central in ...
and salt pork
Salt pork is salt-cured pork. It is usually prepared from pork belly, or, less commonly, fatback. Salt pork typically resembles uncut side bacon, but is fattier, being made from the lowest part of the belly, and saltier, as the cure is stronge ...
, turnip greens are stewed with pork and served with vinegar, ham biscuits (biscuits
A biscuit is a Flour, flour-based baked food item. Biscuits are typically hard, flat, and Unleavened bread, unleavened. They are usually sweet and may be made with sugar, chocolate, icing (food), icing, jam, ginger, or cinnamon. They can also ...
cut in half with slices of salt ham served between the halves) often accompany breakfast, and ham with red-eye gravy or country gravy is a common dinner dish.
Country ham, a heavily salt-cured ham, is common across the Southern United States, with the most well-known being the Virginia-originating Smithfield ham.
Pig feet, often called trotters, are perhaps less common because they are considered a southern delicacy, but can be prepared in a variety of ways. They are most often either pickled in white vinegar or braised in a mixture of sweet and smoky flavors, but can also be deep-fried, grilled, and stewed. They are usually served among other soul dishes such as yams, cornbread, and collard greens.
Vegetables
 Southern meals sometimes consist only of vegetables, with a little meat (especially salt pork) used in cooking but with no meat dish served. "Beans and greens"—white or brown beans served alongside a "mess" of greens stewed with a little bacon—is a traditional meal in many parts of the South ( Turnip greens are the typical greens for such a meal; they're cooked with some diced turnip and a piece of
Southern meals sometimes consist only of vegetables, with a little meat (especially salt pork) used in cooking but with no meat dish served. "Beans and greens"—white or brown beans served alongside a "mess" of greens stewed with a little bacon—is a traditional meal in many parts of the South ( Turnip greens are the typical greens for such a meal; they're cooked with some diced turnip and a piece of fatback
Fatback is a layer of subcutaneous fat taken from under the skin of the back of a domestic pig, with or without the skin (referred to as pork rind).
In cuisine
Fatback is a preferred fat for various forms of charcuterie, particularly sau ...
).
Other low-meat Southern meals include beans and cornbread
Cornbread is a quick bread made with cornmeal, associated with the cuisine of the Southern United States, with origins in Native American cuisine. It is an example of batter bread. Dumplings and pancakes made with finely ground cornmeal are st ...
—the beans being pinto beans stewed with ham or bacon—and Hoppin' John
Hoppin' John, also known as Carolina peas and rice, is a rice and beans dish of legendary origins associated with the cuisine of the Southern United States. Similar dishes are found in regions with a significant African-origin demographic like Lo ...
(black-eyed pea
The black-eyed pea or black-eyed bean is a legume grown around the world for its medium-sized, edible bean. It is a subspecies of the cowpea, an Old World plant domesticated in Africa, and is sometimes simply called a cowpea.
The common commerci ...
s, rice, onions, red or green pepper, and bacon).
Cabbage is largely used as the basis of coleslaw
Coleslaw or cole slaw (from the Dutch term , meaning 'cabbage salad'), also widely known within North America simply as slaw, is a side dish consisting primarily of finely shredded raw cabbage with a salad dressing or condiment, commonly eithe ...
, both as a side dish and on a variety of barbecued and fried meats. Sauteéd red cabbage, flavored with vinegar and sugar, is popular in German-influenced areas of the South such as central Texas
Central Texas is a region in the U.S. state of Texas roughly bordered on the west by San Saba, to the southeast by Bryan- College Station, the south by San Marcos and to the north by Hillsboro. Central Texas overlaps with and includes part ...
.
Butternut squash
Butternut squash (a variety of ''Cucurbita moschata''), known in Australia and New Zealand as butternut pumpkin or gramma, is a type of winter squash that grows on a vine. It has a Sweetness, sweet, Nut (fruit), nutty taste similar to that of a ...
is common in winter, often prepared as a roasted casserole
A casserole (French language, French: diminutive of , from Provençal dialect, Provençal , meaning 'saucepan') is a kind of large, deep cookware and bakeware, pan or bowl used for cooking a variety of dishes in the oven; it is also a categor ...
with butter and honey. Other typical vegetable sides include collard greens
Collard is a group of loose-leafed cultivars of ''Brassica oleracea'' (the same species as many common vegetables like cabbage and broccoli). Part of the acephala cultivar group (or kale group), collard is also classified as the variety ''B.& ...
and congealed salads. Double stuffed potatoes with barbecue pork, cheddar cheese, cream cheese, mayonnaise and chives are served at barbecue restaurants throughout the South.
The tomato sandwich is associated with Southern cuisine and according to ''Yahoo News'' is considered an important part of the cuisine. According to Chuck Reece, editor of '' Georgia Public Radio''grits
Grits (stylized as GRITS) is an American Christian hip hop group from Nashville, Tennessee. Their name is an acronym, which stands for "Grammatical Revolution In the Spirit". GRITS is made up of Stacey "Coffee" Jones and Teron "Bonafide" Carter ...
as the true dividing line." According to ''Garden & Gun'' it is "the south's most beloved sandwich".
Though usually considered a snack, boiled peanuts are often sold throughout sports games and roadside stands as a southern favorite. This practice was adapted from West African culture and was recorded as early as 1899. It also has cultural significance drawn from the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
with a song titled “ Goober peas” from 1866 that reflected its purpose as a ration food.
Rice
Country Captain is a regional dish of curry chicken and rice that dates back to at least the 1920s. It became well known after aColumbus, Georgia
Columbus is a consolidated city-county located on the west-central border of the U.S. state of Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia. Columbus lies on the Chattahoochee River directly across from Phenix City, Alabama. It is the county seat of Muscogee ...
cook served the dish to then President Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), also known as FDR, was the 32nd president of the United States, serving from 1933 until his death in 1945. He is the longest-serving U.S. president, and the only one to have served ...
. George Patton once said "If you can't give me a party and have Country Captain, meet me at the train with a bucket of it."
Red Rice is another staple of Low Country southern cuisine, which is a rice dish simmered in tomato paste, usually cooked with bacon, onion, and other spices
Sweets and pastries
Georgia is known for peach cultivation and variations of Peach melba are commonly served as desserts.Chess pie
Chess pie is a dessert with a filling composed mainly of flour, butter, sugar, eggs, and sometimes milk, characteristic of Cuisine of the Southern United States, Southern United States cuisine.
Jefferson Davis pie is similar to chess pie, but J ...
is a traditional pastry made with eggs, butter and sugar or molasses. Bananas foster is a specialty of New Orleans.
Seafood
Gulf seafood like black grouper, shrimp andswordfish
The swordfish (''Xiphias gladius''), also known as the broadbill in some countries, are large, highly migratory predatory fish characterized by a long, flat, pointed bill. They are the sole member of the Family (biology), family Xiphiidae. They ...
can be found, and "channel catfish
Catfish (or catfishes; order (biology), order Siluriformes or Nematognathi) are a diverse group of ray-finned fish. Catfish are common name, named for their prominent barbel (anatomy), barbels, which resemble a cat's whiskers, though not ...
" ('' Ictalurus punctatus'') farmed locally in the Mississippi Delta
The Mississippi Delta, also known as the Yazoo–Mississippi Delta, or simply the Delta, is the distinctive northwest section of the U.S. state of Mississippi (and portions of Arkansas and Louisiana) that lies between the Mississippi and Yazo ...
region is especially popular in Oxford, Mississippi
Oxford is the List of municipalities in Mississippi, 14th most populous city in Mississippi, United States, and the county seat of Lafayette County, Mississippi, Lafayette County, southeast of Memphis, Tennessee, Memphis. A college town, Oxford ...
. Fried catfish battered in cornmeal is commonly served at local establishments with hot sauce and a side of fries and coleslaw. Oysters Rockefeller
Oysters Rockefeller is a dish consisting of oysters on the half-shell that have been topped with a rich sauce of butter, parsley and other green herbs, bread crumbs, and then baked or broiled. Lemon wedges are the typical garnish. Many contempora ...
is a New Orleans specialty, believed to have originated in the state. Creole dishes like gumbo
Gumbo () is a stew that is popular among the U.S. Gulf Coast community, the New Orleans stew variation being the official state cuisine of the U.S. state of Louisiana. Gumbo consists primarily of a strongly flavored stock, meat or shellfis ...
and jambalaya often feature crawfish
Crayfish are freshwater crustaceans belonging to the infraorder Astacidea, which also contains lobsters. Taxonomically, they are members of the superfamilies Astacoidea and Parastacoidea. They breathe through feather-like gills. Some spe ...
, oysters, blue crab Blue crab may refer to:
* Blue Crab 11, an American sailboat design
* ''Callinectes sapidus
''Callinectes sapidus'' (from the Ancient Greek language, Ancient Greek ,"beautiful" + , "swimmer", and Latin , "savory"), the blue crab, Atlantic blue ...
and shrimp.
By region

 Southern cuisine varies widely by region. Generally speaking:
* Appalachian areas have many ramps (a variety of wild onion) and berries. Appalachia uses butter extensively but makes little use of cheese, and eats more wild game (as well as wild fruits and vegetables) than the rest of the South; apples, oats, and potatoes are also common in Appalachian cuisine, since the mountains are cooler and drier than the lowlands.
* The Upper South favors pork and whiskey; the Low Country (the coast, especially coastal Georgia and coastal South Carolina) favors seafood, rice, and grits.
* Texas and Oklahoma tend to prefer beef; the rest of the South prefers pork.
*
Southern cuisine varies widely by region. Generally speaking:
* Appalachian areas have many ramps (a variety of wild onion) and berries. Appalachia uses butter extensively but makes little use of cheese, and eats more wild game (as well as wild fruits and vegetables) than the rest of the South; apples, oats, and potatoes are also common in Appalachian cuisine, since the mountains are cooler and drier than the lowlands.
* The Upper South favors pork and whiskey; the Low Country (the coast, especially coastal Georgia and coastal South Carolina) favors seafood, rice, and grits.
* Texas and Oklahoma tend to prefer beef; the rest of the South prefers pork.
* Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the West South Central region of the Southern United States. It borders Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, Texas to the southwest, and Oklahoma ...
is the top rice-producing state in the nation. It produces Riceland rice and sweet corn, both of which are staples of the cuisine of Southeastern Arkansas. Arkansas is also noted for catfish, pork barbecue at restaurants, and chicken.
* Florida
Florida ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders the Gulf of Mexico to the west, Alabama to the northwest, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the north, the Atlantic ...
is home of the Key lime pie
Key lime pie is an American dessert pie. It is made of Key lime juice, egg yolks, and sweetened condensed milk. It may be served with no topping, with a meringue topping made from egg whites, or with whipped cream. Traditionally, Key lime pie i ...
and swamp cabbage. Orange juice is the well-known beverage of the state. It has a large beef industry, as well as a seafood industry, and both are reflected in local cuisine. Rock shrimp is beloved on the coast, while beef is common in the state's interior. Due to its long-term economic and trading relationship with the rest of the Caribbean, a particular form of fusion cuisine known as Floribbean cuisine
Floribbean cuisine refers to a fusion cuisine found in Florida with an emphasis on fresh regional ingredients and complex medleys of spices, especially strong flavors offset by milder ones. Floribbean-style cooking incorporates an exotic spic ...
has developed in the state, a fusion of traditional southern food with Caribbean cuisine, often relying on both peppers and fruit to flavor meat dishes.
* Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
is known for its peaches, pecans, peanuts, and Vidalia onion
A Vidalia onion () is one of several varieties of sweet onion grown in a production area defined by law of the U.S. state of Georgia since 1986 and the United States Code of Federal Regulations (CFR). Varieties include the hybrid Yellow Granex ...
s.
* In Southern Louisiana, there is Cajun
The Cajuns (; French: ''les Cadjins'' or ''les Cadiens'' ), also known as Louisiana ''Acadians'' (French: ''les Acadiens''), are a Louisiana French ethnicity mainly found in the US state of Louisiana and surrounding Gulf Coast states.
Whi ...
and Creole cuisine
Creole cuisine (; ; ) is a cuisine style born in colonial times, from the fusion between African, European and pre-Columbian traditions. ''Creole'' is a term that refers to those of European origin who were born in the New World and have adap ...
. Louisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25 ...
is the largest supplier of crawfish
Crayfish are freshwater crustaceans belonging to the infraorder Astacidea, which also contains lobsters. Taxonomically, they are members of the superfamilies Astacoidea and Parastacoidea. They breathe through feather-like gills. Some spe ...
in the US.
* Kentucky
Kentucky (, ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north, West Virginia to the ...
is famous for Burgoo, beer cheese, and the Hot Brown
A Hot Brown sandwich (sometimes known as a Louisville Hot Brown or Kentucky Hot Brown) is an American hot sandwich originally created at the Brown Hotel in Louisville, Kentucky, by Fred K. Schmidt in 1926. It is a variation of traditional Wels ...
. Kentucky is also known for KFC
KFC Corporation, doing business as KFC (an abbreviation of Kentucky Fried Chicken), is an American fast food restaurant chain specializing in fried chicken and chicken sandwiches. Headquartered in Louisville, Kentucky, it is the world's se ...
and fried chicken
Fried chicken, also called Southern fried chicken, is a dish consisting of chicken pieces that have been coated with seasoned flour or batter and pan-fried, deep fried, pressure fried, or air fried. The breading adds a crisp coating or ...
.
* Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east ...
and Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
are known for their blue and soft-shell crabs, and Smith Island Cake
Smith Island is a collection of three distinct island communities – Tylerton, Rhodes Point, and Ewell, Maryland – on the Chesapeake Bay, on the border of Maryland and Virginia territorial waters in the United States. The island is the last ...
.
* Mississippi and Alabama produce the most catfish in the United States.
* Oklahoma
Oklahoma ( ; Choctaw language, Choctaw: , ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Texas to the south and west, Kansas to the north, Missouri to the northea ...
has an official state meal which consists of barbecued pork, chicken fried steak, sausage with biscuits and gravy, fried okra, squash, grits, corn, black-eyed peas, corn bread, strawberries and a slice of pecan pie.
* Carolina-style barbecue is common in North Carolina, South Carolina, and Virginia, and is made traditionally from pulled-pork and a vinegar based sauce.
* Southwest Virginia
Southwest Virginia, often abbreviated as SWVA, is a mountainous region of Virginia in the westernmost part of the commonwealth. Located within the broader region of western Virginia, Southwest Virginia has been defined alternatively as all V ...
has a reputation for many grain- and bean-based dishes, such as "cornbread and beans" or the breakfast dish biscuits and gravy. Mississippi specializes in farm-raised catfish, found in traditional "fish houses" throughout the state.
* In the coastal areas of South Carolina
South Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders North Carolina to the north and northeast, the Atlantic Ocean to the southeast, and Georgia (U.S. state), Georg ...
, rice was an important crop, leading to local specialties like "Hoppin' John
Hoppin' John, also known as Carolina peas and rice, is a rice and beans dish of legendary origins associated with the cuisine of the Southern United States. Similar dishes are found in regions with a significant African-origin demographic like Lo ...
" (a mixture of rice and black-eyed pea
The black-eyed pea or black-eyed bean is a legume grown around the world for its medium-sized, edible bean. It is a subspecies of the cowpea, an Old World plant domesticated in Africa, and is sometimes simply called a cowpea.
The common commerci ...
s flavored with salt pork) and Charleston red rice.
* Tennessee
Tennessee (, ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders Kentucky to the north, Virginia to the northeast, North Carolina t ...
is known for its country ham and Memphis is known for several famous barbecue restaurants and a major barbecue cooking competition held in May. Memphis barbecue usually consists of pork and is distinct for its dry rub. No sauce is applied during the cooking process instead flavor is gained from the rub when cooking. Nashville
Nashville, often known as Music City, is the capital and List of municipalities in Tennessee, most populous city in the U.S. state of Tennessee. It is the county seat, seat of Davidson County, Tennessee, Davidson County in Middle Tennessee, locat ...
is known for its famous hot chicken from places like Prince's Hot Chicken Shack, Bolton's Hot Chicken, Hattie B's, and Biscuit Love. Nashville is also home to the restaurant Husk run by world-class chef Sean Brock.
* Texas
Texas ( , ; or ) is the most populous U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the we ...
specializes in barbecue, chili, and Southern cuisine as well as a regional variation of Mexican food unique to Texas called Tex-Mex
Tex-Mex cuisine (derived from the words ''Texas'' and ''Mexico'') is a regional American cuisine that originates from the culinary creations of Tejanos, Tejano people. It has spread from border states such as Texas and others in the Southwestern ...
.
* Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
produces Smithfield ham and Virginia peanuts. Brunswick stew, which originated in the town of Brunswick, Virginia is also popular. The state's proximity to the Chesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula, including parts of the Ea ...
and the ideal conditions of the Rappahannock River
The Rappahannock River is a river in eastern Virginia, in the United States, approximately in length.U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed April 1, 2011 It traverses the enti ...
, makes oysters a popular dish in Virginia, be they served fried, raw, or in a cream-based oyster stew.
* West Virginia
West Virginia is a mountainous U.S. state, state in the Southern United States, Southern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States.The United States Census Bureau, Census Bureau and the Association of American ...
is the area where pepperoni rolls are most popular, which typically consists of a white bread roll with pepperoni baked in the middle. The fats in the pepperoni melt into the bread, giving the bread an extra dimension of flavor. Other ingredients are sometimes added, such as cheese, peppers, or melted butter on top. The state also has Tudor's Biscuit World restaurants specializing in biscuits and sausage gravy.
Louisiana Creole cuisine
 Southern
Southern Louisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25 ...
is geographically part of the South, but its cuisine is probably best understood as having only mild Southern influences. Creole cuisine
Creole cuisine (; ; ) is a cuisine style born in colonial times, from the fusion between African, European and pre-Columbian traditions. ''Creole'' is a term that refers to those of European origin who were born in the New World and have adap ...
makes good use of many coastal animals—crawfish (commonly called crayfish
Crayfish are freshwater crustaceans belonging to the infraorder Astacidea, which also contains lobsters. Taxonomically, they are members of the superfamilies Astacoidea and Parastacoidea. They breathe through feather-like gills. Some spe ...
outside the region), crab
Crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura (meaning "short tailed" in Greek language, Greek), which typically have a very short projecting tail-like abdomen#Arthropoda, abdomen, usually hidden entirely under the Thorax (arthropo ...
, oysters, shrimp, and saltwater fish. Mirliton (chayote
Chayote (; previously placed in the obsolete genus ''Sechium''), also known as christophine, mirliton, güisquil, and choko, is an edible plant belonging to the gourd family, Cucurbitaceae. This fruit was first cultivated in Mesoamerica between ...
squash), is popular in Louisiana. Coffee blended with Chicory is sometimes preferred over pure ground—especially as an accompaniment to beignet
Beignet ( , also , ; ) is a type of deep-fried pastry of French origin. It is commonly made from choux pastry, pâte à choux, but can also be made using rice flour (rice beignets) or yeast-leavened batters. Beignets can be served in a variety o ...
s.
Lowcountry cuisine
TheLowcountry
The Lowcountry (sometimes Low Country or just low country) is a geographic and cultural region along South Carolina's coast, including the Sea Islands. The region includes significant salt marshes and other coastal waterways, making it an impor ...
region of the coastal Carolinas and Georgia shares many of the same food resources as the Upper Gulf Coast: fish, shrimp, oysters, rice, and okra. It also displays some similarities to Creole and Cajun cuisines.
Appalachian cuisine
 Because of its geographic location, Appalachia cuisine offers a wide range of ingredients and products that can be transformed using traditional methods and contemporary applications.Ronni Lundy, Staples of Appalachian cuisine that are common in other regional cuisines of the south include coconut cream cake,
Because of its geographic location, Appalachia cuisine offers a wide range of ingredients and products that can be transformed using traditional methods and contemporary applications.Ronni Lundy, Staples of Appalachian cuisine that are common in other regional cuisines of the south include coconut cream cake, peanut brittle
Brittle is a type of confection consisting of flat broken pieces of hard sugar candy embedded with nuts such as pecans, almonds, or peanuts, and which are usually less than 1 cm thick.
Types
It has many variations around the world, such as:
* ' ...
, sweet potato casserole
A casserole (French language, French: diminutive of , from Provençal dialect, Provençal , meaning 'saucepan') is a kind of large, deep cookware and bakeware, pan or bowl used for cooking a variety of dishes in the oven; it is also a categor ...
, pork chops, biscuits and gravy, and chicken and dumplings. Basic soul food
Soul food is the ethnic cuisine of African Americans. Originating in the Southern United States, American South from the cuisines of Slavery in the United States, enslaved Africans transported from Africa through the Atlantic slave trade, sou ...
dishes like collard greens
Collard is a group of loose-leafed cultivars of ''Brassica oleracea'' (the same species as many common vegetables like cabbage and broccoli). Part of the acephala cultivar group (or kale group), collard is also classified as the variety ''B.& ...
, hominy
Hominy is a food item produced from dried maize (corn) kernels that have been treated with an alkali, in a process called nixtamalization ( is the Nahuatl word for "hominy"). "Lye hominy" is a type of hominy made with lye.
History
The process ...
, cracklings
Cracklings (American English), crackling (British English), also known as scratchings, are the solid material that remains after Rendering (animal products), rendering animal fat and skin to produce lard, tallow, or schmaltz, or as the result of ro ...
and ham hocks are also common to the Appalachian kitchen.Mark F. Sohn, Appalachian home cooking. pp. 8–15.
European fruits—especially apple
An apple is a round, edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus'' spp.). Fruit trees of the orchard or domestic apple (''Malus domestica''), the most widely grown in the genus, are agriculture, cultivated worldwide. The tree originated ...
s and pear
Pears are fruits produced and consumed around the world, growing on a tree and harvested in late summer into mid-autumn. The pear tree and shrub are a species of genus ''Pyrus'' , in the Family (biology), family Rosaceae, bearing the Pome, po ...
s—can grow in the mountains, and sweet fried apples are a common side dish. Appalachian cuisine also makes use of berries
A berry is a small, pulpy, and often edible fruit. Typically, berries are juicy, rounded, brightly colored, sweet, sour or tart, and do not have a stone fruit, stone or pit (fruit), pit although many wikt:pip#Etymology 2, pips or seeds may be p ...
, both native and European, and some parts of the mountains are high enough or far enough north that sugar maple
''Acer saccharum'', the sugar maple, is a species of flowering plant in the soapberry and lychee family Sapindaceae. It is native to the hardwood forests of eastern Canada and the eastern United States. Sugar maple is best known for being the ...
grows there—allowing for maple syrup
Maple syrup is a sweet syrup made from the sap of maple trees. In cold climates, these trees store starch in their trunks and roots before winter; the starch is then converted to sugar that rises in the sap in late winter and early spring. Ma ...
and maple sugar
Maple sugar is a traditional sweetener in Canada and the Northeastern United States, prepared from the sap of the maple tree ("maple syrup, maple sap").
Sources
Three species of maple trees in the genus ''Acer (plant), Acer'' are predomina ...
production. Wild morel mushrooms and ramps (similar to scallion
Scallions (also known as green onions and spring onions) are edible vegetables of various species in the genus ''Allium''. Scallions generally have a milder taste than most onions. Their close relatives include garlic, shallots, leeks, chive ...
s and leek
A leek is a vegetable, a cultivar of ''Allium ampeloprasum'', the broadleaf wild leek (synonym (taxonomy), syn. ''Allium porrum''). The edible part of the plant is a bundle of Leaf sheath, leaf sheaths that is sometimes erroneously called a "s ...
s) are often collected; there are even festivals dedicated to ramps, and they figure in some Appalachian fairy tales. The diet included corn, beans, squash, mixed pickles, milk, cheeses, butter, cream, tea, and coffee.
Salt
In common usage, salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl). When used in food, especially in granulated form, it is more formally called table salt. In the form of a natural crystalline mineral, salt is also known as r ...
, a necessity for life, was always available (much of it coming from Saltville
Saltville is a town in Smyth and Washington counties in the U.S. state of Virginia. The population was 1,824 at the 2020 census. It is part of the Kingsport– Bristol (TN)– Bristol (VA) Metropolitan Statistical Area, which is a co ...
, Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
), and local seasonings like spicebush were certainly known and used; but the only other seasonings used in the mountains are black pepper and flaked red pepper, along with a little use of cinnamon, nutmeg, and cloves around Christmas. Gunpowder seasoning is also popular in the Appalachian region, often made from activated charcoal, dehydrated onion and garlic, paprika, salt, sugar, corn starch, and sunflower oil. Its ‘smoky’ flavor is commonly used as a dry rub, making it perfect for regional game as well as a variety of grilled vegetables such as bell peppers, white onion, and yellow squash.
Coffee, drunk without milk and only lightly sweetened, is a basic drink in Appalachia, often consumed with every meal; in wartime, chicory was widely used as a coffee substitute.
Rice and cane sugar, grown further south, were not easy to come by in Appalachia and generally sorghum
''Sorghum bicolor'', commonly called sorghum () and also known as great millet, broomcorn, guinea corn, durra, imphee, jowar, or milo, is a species in the Poaceae, grass genus ''Sorghum (genus), Sorghum'' cultivated for its grain. The grain i ...
, honey
Honey is a sweet and viscous substance made by several species of bees, the best-known of which are honey bees. Honey is made and stored to nourish bee colonies. Bees produce honey by gathering and then refining the sugary secretions of pl ...
and maple syrup
Maple syrup is a sweet syrup made from the sap of maple trees. In cold climates, these trees store starch in their trunks and roots before winter; the starch is then converted to sugar that rises in the sap in late winter and early spring. Ma ...
were used as sweetener in local dishes. Travel distances, conditions, and poor roads limited most early settlements to foods that could be grown or produced locally.
For farmers, pigs and chicken
The chicken (''Gallus gallus domesticus'') is a domesticated subspecies of the red junglefowl (''Gallus gallus''), originally native to Southeast Asia. It was first domesticated around 8,000 years ago and is now one of the most common and w ...
s were the primary source of meat
Meat is animal Tissue (biology), tissue, often muscle, that is eaten as food. Humans have hunted and farmed other animals for meat since prehistory. The Neolithic Revolution allowed the domestication of vertebrates, including chickens, sheep, ...
, with many farmers maintaining their own smokehouse
A smokehouse (North American) or smokery (British) is a building where meat or fish is curing (food preservation), cured with Smoking (cooking), smoke. The finished product might be stored in the building, sometimes for a year or more.ham
Ham is pork from a leg cut that has been preserved by wet or dry curing, with or without smoking."Bacon: Bacon and Ham Curing" in '' Chambers's Encyclopædia''. London: George Newnes, 1961, Vol. 2, p. 39. As a processed meat, the term '' ...
s, bacon
Bacon is a type of Curing (food preservation), salt-cured pork made from various cuts of meat, cuts, typically the pork belly, belly or less fatty parts of the back. It is eaten as a side dish (particularly in breakfasts), used as a central in ...
, and sausage
A sausage is a type of meat product usually made from ground meat—often pork, beef, or poultry—along with salt, spices and other flavourings. Other ingredients, such as grains or breadcrumbs, may be included as fillers or extenders.
...
s. Seafood, beyond the occasionally locally caught fresh-water fish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ...
(pan-fried catfish
Catfish (or catfishes; order (biology), order Siluriformes or Nematognathi) are a diverse group of ray-finned fish. Catfish are common name, named for their prominent barbel (anatomy), barbels, which resemble a cat's whiskers, though not ...
is much loved, as is trout
Trout (: trout) is a generic common name for numerous species of carnivorous freshwater ray-finned fishes belonging to the genera '' Oncorhynchus'', ''Salmo'' and ''Salvelinus'', all of which are members of the subfamily Salmoninae in the ...
in the mountains of western North Carolina
North Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, South Carolina to the south, Georgia (U.S. stat ...
, East Tennessee
East Tennessee is one of the three Grand Divisions of Tennessee defined in state law. Geographically and socioculturally distinct, it comprises approximately the eastern third of the U.S. state of Tennessee. East Tennessee consists of 33 coun ...
, and Southwest Virginia
Southwest Virginia, often abbreviated as SWVA, is a mountainous region of Virginia in the westernmost part of the commonwealth. Located within the broader region of western Virginia, Southwest Virginia has been defined alternatively as all V ...
) and crawfish
Crayfish are freshwater crustaceans belonging to the infraorder Astacidea, which also contains lobsters. Taxonomically, they are members of the superfamilies Astacoidea and Parastacoidea. They breathe through feather-like gills. Some spe ...
, were unavailable until modern times.
However, Appalachia
Appalachia ( ) is a geographic region located in the Appalachian Mountains#Regions, central and southern sections of the Appalachian Mountains in the east of North America. In the north, its boundaries stretch from the western Catskill Mountai ...
did offer a wide variety of wild game, with venison
Venison refers primarily to the meat of deer (or antelope in South Africa). Venison can be used to refer to any part of the animal, so long as it is edible, including the internal organs. Venison, much like beef or pork, is categorized into spe ...
, rabbit
Rabbits are small mammals in the family Leporidae (which also includes the hares), which is in the order Lagomorpha (which also includes pikas). They are familiar throughout the world as a small herbivore, a prey animal, a domesticated ...
and squirrel
Squirrels are members of the family Sciuridae (), a family that includes small or medium-sized rodents. The squirrel family includes tree squirrels, ground squirrels (including chipmunks and prairie dogs, among others), and flying squirrel ...
particularly common, thus helping to compensate for distance from major cities and transportation networks. The popularity of hunting and fishing in Appalachia means that game and fresh-water fish were often staples of the table. Deer, wild turkey, grouse and other game birds are hunted and utilized in many recipes from barbecue to curing and jerky.
Home canning
Canning is a method of food preservation in which food is processed and sealed in an airtight container (jars like Mason jars, and steel and tin cans). Canning provides a shelf life that typically ranges from one to five years, although under ...
, of both garden and foraged foods, is a strong tradition in Appalachia as well; mason jar
A Mason jar, also known as a canning jar, preserves jar or fruit jar, is a glass jar used in home canning to food preservation, preserve food. It was named after American tinsmith John Landis Mason, who patented it in 1858. The jar's mouth has a ...
s are an everyday sight in mountain life; the most common canned foods are savory vegetables: green bean
Green beans are young, unripe fruits of various cultivars of the common bean ('' Phaseolus vulgaris''), although immature or young pods of the runner bean ('' Phaseolus coccineus''), yardlong bean ( ''Vigna unguiculata'' subsp. ''sesquipedali ...
s (half-runners, snaps), shelly beans (green beans that were more mature and had ripe beans along with the green husks), and tomatoes, as well as jam, jelly and local fruits.
Dried pinto bean
The pinto bean () is a variety of Phaseolus vulgaris, common bean (''Phaseolus vulgaris''). In Spanish language, Spanish they are called . It is the most popular bean by crop production in Northern Mexico and the Southwestern United States, South ...
s are a major staple food during the winter months, used to make the ubiquitous ham-flavored bean soup usually called soup beans. Kieffer pears and apple
An apple is a round, edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus'' spp.). Fruit trees of the orchard or domestic apple (''Malus domestica''), the most widely grown in the genus, are agriculture, cultivated worldwide. The tree originated ...
varietals are used to make pear butter and apple butter.
Also popular are bread and butter pickles, fried mustard greens with vinegar
Vinegar () is an aqueous solution of diluted acetic acid and trace compounds that may include flavorings. Vinegar typically contains from 5% to 18% acetic acid by volume. Usually, the acetic acid is produced by a double fermentation, converting ...
, pickled beet
The beetroot (British English) or beet (North American English) is the taproot portion of a '' Beta vulgaris'' subsp. ''vulgaris'' plant in the Conditiva Group. The plant is a root vegetable also known as the table beet, garden beet, dinner ...
s, chow-chow (commonly called "chow"), a relish
A relish (a pickle-based condiment) is a cooking, cooked and pickling, pickled culinary dish made of chopped vegetables, fruits or herbs, typically used as a condiment to enhance a staple. Examples are chutneys and the North American relish, a p ...
known as corn ketchup and fried green tomatoes
''Fried Green Tomatoes'' is a 1991 American comedy-drama film directed by Jon Avnet and based on Fannie Flagg's 1987 novel '' Fried Green Tomatoes at the Whistle Stop Cafe''. Written by Flagg and Carol Sobieski, and starring Kathy Bates, J ...
; tomatoes are also used in tomato gravy, a variant of sausage gravy with a thinner, lighter roux
Roux () is a mixture of flour and fat cooked together and used to thicken sauces. Roux is typically made from equal parts of flour and fat by weight. The flour is added to the melted fat or Cooking oil, oil on the stove top, blended until smoo ...
. A variety of wild fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants (angiosperms) that is formed from the ovary after flowering.
Fruits are the means by which angiosperms disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particular have long propaga ...
s like pawpaws, wild blackberries
BlackBerry is a discontinued brand of handheld devices and related mobile services, originally developed and maintained by the Canadian company Research In Motion (RIM, later known as BlackBerry Limited) until 2016. The first BlackBerry device ...
, and persimmon
The persimmon () is the edible fruit of a number of species of trees in the genus '' Diospyros''. The most widely cultivated of these is the Chinese and Japanese kaki persimmon, ''Diospyros kaki''. In 2022, China produced 77% of the world's p ...
s are also commonly available in Appalachia as well.
The gravy for biscuits and gravy is typically sausage or sawmill, not the red-eye gravy (made with coffee) used in the lowland South. Pork
Pork is the culinary name for the meat of the pig (''Sus domesticus''). It is the most commonly consumed meat worldwide, with evidence of pig animal husbandry, husbandry dating back to 8000–9000 BCE.
Pork is eaten both freshly cooke ...
drippings from frying sausage
A sausage is a type of meat product usually made from ground meat—often pork, beef, or poultry—along with salt, spices and other flavourings. Other ingredients, such as grains or breadcrumbs, may be included as fillers or extenders.
...
, bacon
Bacon is a type of Curing (food preservation), salt-cured pork made from various cuts of meat, cuts, typically the pork belly, belly or less fatty parts of the back. It is eaten as a side dish (particularly in breakfasts), used as a central in ...
, and other types of pan-fried pork are collected and saved, used for making gravy
Gravy is a sauce made from the juices of meats and vegetables that run naturally during cooking and often thickened with thickeners for added texture. The gravy may be further coloured and flavoured with gravy salt (a mix of salt and caramel food ...
and in greasing cast-iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content of more than 2% and silicon content around 1–3%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloying elements determine the form in which its car ...
cookware. (Appalachia is overwhelmingly Protestant, the Catholic prohibition on meat-eating during Lent had no impact on Appalachian cuisine.)
Chicken and dumplings and fried chicken
Fried chicken, also called Southern fried chicken, is a dish consisting of chicken pieces that have been coated with seasoned flour or batter and pan-fried, deep fried, pressure fried, or air fried. The breading adds a crisp coating or ...
remain much-loved dishes. Cornbread
Cornbread is a quick bread made with cornmeal, associated with the cuisine of the Southern United States, with origins in Native American cuisine. It is an example of batter bread. Dumplings and pancakes made with finely ground cornmeal are st ...
, corn pone, hominy grits, mush, cornbread pudding and hominy
Hominy is a food item produced from dried maize (corn) kernels that have been treated with an alkali, in a process called nixtamalization ( is the Nahuatl word for "hominy"). "Lye hominy" is a type of hominy made with lye.
History
The process ...
stew are also quite common foods, as corn
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout Poaceae, grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples of Mexico, indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago ...
is the primary grain grown in the Appalachian hills and mountains, but are less common than in the past.
See also
*Bahamian cuisine
Bahamian cuisine refers to the foods and beverages of The Bahamas. It includes seafood such as fish, shellfish, lobster, crab, and conch, as well as tropical fruits, rice, peas, pigeon peas, and pork. Popular seasonings commonly used in dishes i ...
* Barbecue
Barbecue or barbeque (often shortened to BBQ worldwide; barbie or barby in Australia and New Zealand) is a term used with significant regional and national variations to describe various cooking methods that employ live fire and smoke to coo ...
* Cuisine of the Southwestern United States
* Cuisine of the United States
American cuisine consists of the cooking style and traditional dishes prepared in the United States. It has been significantly influenced by Europeans, Indigenous Americans, Africans, Latin Americans, Asians, Pacific Islanders, and many other ...
* Liberian cuisine
Liberian cuisine refers to the cuisine of Liberia. It is centered on unique dishes of rice, cassava, plantain, yam, tropical fruits and vegetables (potatoes, greens, cassava leaf, okra, cabbage), as well as fish, meat and more. Liberian cuisine ...
* List of foods of the Southern United States
* Soul food
Soul food is the ethnic cuisine of African Americans. Originating in the Southern United States, American South from the cuisines of Slavery in the United States, enslaved Africans transported from Africa through the Atlantic slave trade, sou ...
* Southern Food and Beverage Museum
* Tex-Mex cuisine
Tex-Mex cuisine (derived from the words ''Texas'' and ''Mexico'') is a regional American cuisine that originates from the culinary creations of Tejano people. It has spread from border states such as Texas and others in the Southwestern United ...
* Memphis-style barbecue
* Texan cuisine
* Cuisine of New Orleans
* Cuisine of Kentucky
* Cuisine of Houston
* Cuisine of Atlanta
References
* Bowen, Carl. ''Southern-Recipes''. 2010. . * Domine, David. ''111 Fabulous Food Finds: Best Bites in the Bluegrass''. McClanahan Publishing House, 2011. . * Domine, David. ''Adventures in New Kentucky Cooking with the Bluegrass Peasant''. McClanahan Publishing House, 2007. . * Domine, David. ''Splash of Bourbon, Kentucky's Spirit''. McClanahan Publishing House, 2010. * Harris, Jessica. ''On the Side: More than 100 Recipes for the Sides, Salads, and Condiments That Make the Meal''. Simon & Schuster, 2004. . * The Junior League of Charleston. ''Charleston Receipts''. Wimmer Brothers, 1950. . * Lewis, Edna and Peacock, Scott. ''The Gift of Southern Cooking: Recipes and Revelations from Two Great American Cook''. Knopf, 2003. . * Neal, Bill. ''Bill Neal's Southern Cooking''. University of North Carolina Press, 1989. . * Neal, Bill. ''Biscuits, Spoonbread, and Sweet Potato Pie''. University of North Carolina Press, 2003. . * Neal, Bill. ''Good Old Grits Cookbook''. Workman Publishing Company, 1991. . * Snow, Constance. ''Gulf Coast Kitchens''. Clarkson Potter/Publishers, 2003. . *Sohn, Mark F. Appalachian Home Cooking History, Culture, & Recipes Lexington: University Press of Kentucky. 2005. * Taylor, John. ''Hoppin' John's Lowcountry Cooking''. 1992. . * Walter, Eugene. ''American Cooking: Southern Style''. New York: Time Life Books, 1971.Further reading
* * Ferris, Marcie Cohen (2014). ''The Edible South: The Power of Food and the Making of an American Region.'' Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Press.External links
Why The Story Of Southern Food Is As Much About People As Dishes
from South Carolina Public Radio NPR
Southern Foodways Alliance
Southern Food & Beverage Museum
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cuisine Of The Southern United States Cuisine of the Southern United States, American cuisine by region Southern United States, Cuisine