Solenodon on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Solenodons (from , 'channel' or 'pipe' and , 'tooth') are venomous,
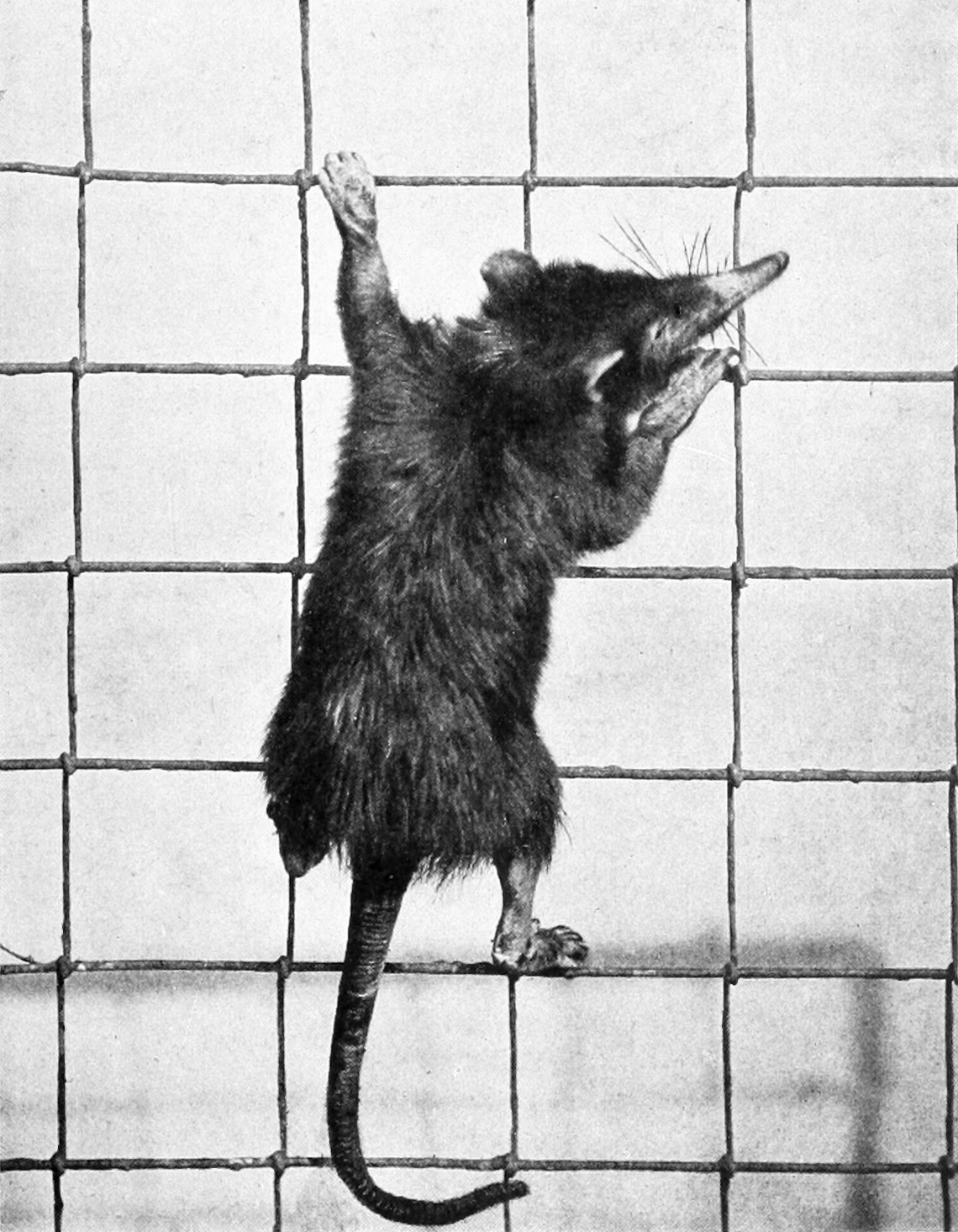

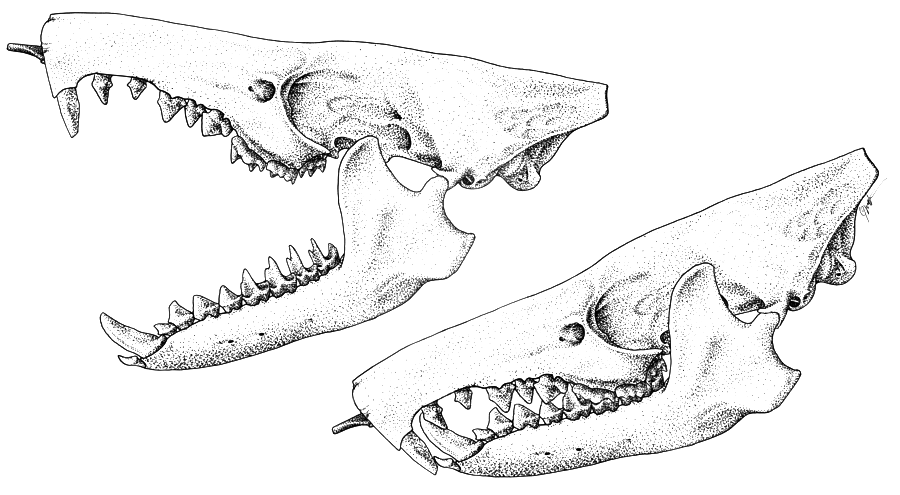 Traditionally, solenodons' closest relatives were considered to be the giant water shrew of Africa and Tenrecidae of Madagascar, though they are now known to be more closely related to true shrews ( Eulipotyphla). Solenodons resemble very large shrews, and are often compared to them; with extremely elongated cartilaginous snouts, long, naked, scaly tails, hairless feet, and small eyes. The Cuban solenodon is generally smaller than its Hispaniolan counterpart. It is also a rusty brown with black on its throat and back. The Hispaniolan solenodon is a darker brown with yellowish tint to the face. The snout is flexible and, in the Hispaniolan solenodon, actually has a ball-and-socket joint at the base to increase its mobility. This allows the animal to investigate narrow crevices where potential prey may be hiding.
Solenodons are also noted for the glands in their inguinal and groin areas that secrete what is described as a musky, goat-like odor. Solenodons range from from nose to rump, and weigh between .
Solenodons have a few unusual traits, one of them being the position of the two teats on the female, almost on the buttocks of the animal, and another being the
Traditionally, solenodons' closest relatives were considered to be the giant water shrew of Africa and Tenrecidae of Madagascar, though they are now known to be more closely related to true shrews ( Eulipotyphla). Solenodons resemble very large shrews, and are often compared to them; with extremely elongated cartilaginous snouts, long, naked, scaly tails, hairless feet, and small eyes. The Cuban solenodon is generally smaller than its Hispaniolan counterpart. It is also a rusty brown with black on its throat and back. The Hispaniolan solenodon is a darker brown with yellowish tint to the face. The snout is flexible and, in the Hispaniolan solenodon, actually has a ball-and-socket joint at the base to increase its mobility. This allows the animal to investigate narrow crevices where potential prey may be hiding.
Solenodons are also noted for the glands in their inguinal and groin areas that secrete what is described as a musky, goat-like odor. Solenodons range from from nose to rump, and weigh between .
Solenodons have a few unusual traits, one of them being the position of the two teats on the female, almost on the buttocks of the animal, and another being the
nocturnal
Nocturnality is a ethology, behavior in some non-human animals characterized by being active during the night and sleeping during the day. The common adjective is "nocturnal", versus diurnality, diurnal meaning the opposite.
Nocturnal creatur ...
, burrowing, insectivorous mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
s belonging to the family
Family (from ) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). It forms the basis for social order. Ideally, families offer predictabili ...
Solenodontidae . The two living solenodon species are the Cuban solenodon (''Atopogale cubana'') and the Hispaniolan solenodon
The Hispaniolan solenodon (''Solenodon paradoxus''), also known as the agouta, is a small, furry, shrew-like mammal endemic to the Caribbean island of Hispaniola (in the Dominican Republic and Haiti). Like other solenodons, it is a venomous, in ...
(''Solenodon paradoxus''). Threats to both species include habitat destruction
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss or habitat reduction) occurs when a natural habitat is no longer able to support its native species. The organisms once living there have either moved elsewhere, or are dead, leading to a decrease ...
and predation by non-native cats
The cat (''Felis catus''), also referred to as the domestic cat or house cat, is a small domesticated carnivorous mammal. It is the only domesticated species of the family Felidae. Advances in archaeology and genetics have shown that the ...
, dogs, and mongooses, introduced by humans to the solenodons' home islands to control snakes and rodents.
The Hispaniolan solenodon covers a wide range of habitats on the island of Hispaniola
Hispaniola (, also ) is an island between Geography of Cuba, Cuba and Geography of Puerto Rico, Puerto Rico in the Greater Antilles of the Caribbean. Hispaniola is the most populous island in the West Indies, and the second-largest by List of C ...
from lowland dry forest to highland pine forest. Two other described species became extinct during the Quaternary period. Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch (geology), epoch of the Paleogene Geologic time scale, Period that extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that defin ...
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
n genera, such as '' Apternodus'', have been suggested as relatives of ''Solenodon'', but the origins of the animal remain obscure.
Taxonomy
Two genera, '' Atopogale'' and '' Solenodon'', are known, each with one extant species. Other genera have been erected, but are now regarded as junior synonyms. Solenodontidae show retention of primitive mammal characteristics. In 2016, solenodons were confirmed by genetic analysis as belonging to an evolutionary branch that split from the lineage leading tohedgehog
A hedgehog is a spiny mammal of the subfamily Erinaceinae, in the eulipotyphlan family Erinaceidae. There are 17 species of hedgehog in five genera found throughout parts of Europe, Asia, and Africa, and in New Zealand by introduction. The ...
s, moles, and shrew
Shrews ( family Soricidae) are small mole-like mammals classified in the order Eulipotyphla. True shrews are not to be confused with treeshrews, otter shrews, elephant shrews, West Indies shrews, or marsupial shrews, which belong to dif ...
s before the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event. They are one of two families of Caribbean soricomorphs. The other family, Nesophontidae, became extinct during the Holocene
The Holocene () is the current geologic time scale, geological epoch, beginning approximately 11,700 years ago. It follows the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene to ...
. Molecular data suggest they diverged from solenodons roughly 57 million years ago. The solenodon is estimated to have diverged from other living mammals about 73 million years ago.
Extant species
In addition, 2 extinct species, the giant solenodon (''S. arredondoi'') andMarcano's solenodon
Marcano's solenodon (''Solenodon marcanoi'') is an extinct species of mammal in the family Solenodontidae known only from skeletal remains found on the island of Hispaniola (today the Dominican Republic and Haiti).
Etymology
The Specific epithe ...
(''S. marcanoi'') are both thought to have gone extinct during the last 500 years, both presumably due to predation by introduced rats.
Characteristics

 Traditionally, solenodons' closest relatives were considered to be the giant water shrew of Africa and Tenrecidae of Madagascar, though they are now known to be more closely related to true shrews ( Eulipotyphla). Solenodons resemble very large shrews, and are often compared to them; with extremely elongated cartilaginous snouts, long, naked, scaly tails, hairless feet, and small eyes. The Cuban solenodon is generally smaller than its Hispaniolan counterpart. It is also a rusty brown with black on its throat and back. The Hispaniolan solenodon is a darker brown with yellowish tint to the face. The snout is flexible and, in the Hispaniolan solenodon, actually has a ball-and-socket joint at the base to increase its mobility. This allows the animal to investigate narrow crevices where potential prey may be hiding.
Solenodons are also noted for the glands in their inguinal and groin areas that secrete what is described as a musky, goat-like odor. Solenodons range from from nose to rump, and weigh between .
Solenodons have a few unusual traits, one of them being the position of the two teats on the female, almost on the buttocks of the animal, and another being the
Traditionally, solenodons' closest relatives were considered to be the giant water shrew of Africa and Tenrecidae of Madagascar, though they are now known to be more closely related to true shrews ( Eulipotyphla). Solenodons resemble very large shrews, and are often compared to them; with extremely elongated cartilaginous snouts, long, naked, scaly tails, hairless feet, and small eyes. The Cuban solenodon is generally smaller than its Hispaniolan counterpart. It is also a rusty brown with black on its throat and back. The Hispaniolan solenodon is a darker brown with yellowish tint to the face. The snout is flexible and, in the Hispaniolan solenodon, actually has a ball-and-socket joint at the base to increase its mobility. This allows the animal to investigate narrow crevices where potential prey may be hiding.
Solenodons are also noted for the glands in their inguinal and groin areas that secrete what is described as a musky, goat-like odor. Solenodons range from from nose to rump, and weigh between .
Solenodons have a few unusual traits, one of them being the position of the two teats on the female, almost on the buttocks of the animal, and another being the venom
Venom or zootoxin is a type of toxin produced by an animal that is actively delivered through a wound by means of a bite, sting, or similar action. The toxin is delivered through a specially evolved ''venom apparatus'', such as fangs or a sti ...
ous saliva
Saliva (commonly referred as spit or drool) is an extracellular fluid produced and secreted by salivary glands in the mouth. In humans, saliva is around 99% water, plus electrolytes, mucus, white blood cells, epithelial cells (from which ...
that flows from modified salivary glands in the mandible
In jawed vertebrates, the mandible (from the Latin ''mandibula'', 'for chewing'), lower jaw, or jawbone is a bone that makes up the lowerand typically more mobilecomponent of the mouth (the upper jaw being known as the maxilla).
The jawbone i ...
through grooves on the second lower incisors ("solenodon" derives from the Greek "grooved tooth"). Solenodons are among a handful of venomous mammals. Fossil records show that some other now-extinct mammal groups also had the dental venom delivery system, indicating that the solenodon's most distinct characteristic may have been a more general ancient mammalian characteristic that has been lost in most modern mammals and is only retained in a couple of very ancient lineages. The solenodon has often been called a "living fossil" because it has endured virtually unchanged for the past 76 million years.
It is not known exactly how long solenodons can live in the wild. However, certain individuals of the Cuban species have been recorded to have lived for up to five years in captivity and individuals of the Hispaniolan species for up to eleven years.
West Indian natives have long known about the venomous character of the solenodon bite. Early studies on the nature of the tiny mammal's saliva suggested that it was very similar to the neurotoxic
Neurotoxicity is a form of toxicity in which a biological, chemical, or physical agent produces an adverse effect on the structure or function of the central and/or peripheral nervous system. It occurs when exposure to a substance – specifical ...
venom of certain snakes. More recently, the venom has been found to be related to that of the northern short-tailed shrew and it is mostly composed of kallikreins ''KLK1'', serine proteases that prevent blood clotting, cause hypotension
Hypotension, also known as low blood pressure, is a cardiovascular condition characterized by abnormally reduced blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps out blood and is ...
and ultimately end up being fatal to the prey. The KLK1 in solenodon venom is very similar to serine protease found in venomous snakes like vipers, and has evolved in parallel in both lineages from an ancient toxin precursor. Solenodons create venom in enlarged submaxillary glands, and only inject venom through their bottom set of teeth. The symptoms of a solenodon bite include general depression, breathing difficulty, paralysis, and convulsions; large enough doses have resulted in death in lab studies on mice.
Their diets consist largely of insects, earthworm
An earthworm is a soil-dwelling terrestrial invertebrate that belongs to the phylum Annelida. The term is the common name for the largest members of the class (or subclass, depending on the author) Oligochaeta. In classical systems, they we ...
s, and other invertebrate
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordata, chordate s ...
s, but they also eat vertebrate carrion
Carrion (), also known as a carcass, is the decaying flesh of dead animals.
Overview
Carrion is an important food source for large carnivores and omnivores in most ecosystems. Examples of carrion-eaters (or scavengers) include crows, vultures ...
, and perhaps even some living vertebrate prey, such as small reptile
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocepha ...
s or amphibian
Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniote, anamniotic, tetrapod, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class (biology), class Amphibia. In its broadest sense, it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all Tetrapod, tetrapods, but excl ...
s. They have also been known to feed on fruits, roots, and vegetables. Based on observation of the solenodon in captivity, they have only been known to drink while bathing. Solenodons have a relatively unspecialised, and almost complete dentition, with a dental formula of: .
Solenodons find food by sniffing the ground until they come upon their prey. If the prey is small enough, the solenodon will consume it immediately. After coming across the prey, the solenodon will bring the forelimbs up to either side of the prey and then move the head forward, opening the jaw and properly catching its prey. While sniffing for food, the solenodon can get through physical barriers with the help of its sharp claws.
There has been research that suggests that males and females of the two species have different eating habits. The female has a habit of scattering the food to make sure that no morsel of food is missed as it is foraging. The male was noted to use its tongue to lap up the food and using the lower jaw as a scoop. However, these specimens were studied in captivity, so these habits may not be found in the wild.
Reproduction
Solenodons give birth in a nesting burrow to one or two young. The young remain with the mother for several months and initially follow the mother by hanging on to her elongated teats. Once they reach adulthood solenodons are solitary animals and rarely interact except to breed. The reproductive rate of solenodons is relatively low, producing only two litters per year. Breeding can occur at any time. Males will not aid in the care for the young. The mother will nurse her offspring using her two nipples, which are placed toward the back of the animal. If the litter consists of three offspring, one will become malnourished and die. The nursing period can last for up to seventy-five days. In their nesting burrows, solenodons give birth to one or two pups, displaying a distinctive reproductive behavior. For several months, the mother tends to them, and the young follow her, clinging on lengthy teats. Breeding can take place at any time, with a comparatively low reproductive rate of two litters annually, and males do not participate in the upbringing of their offspring. Up to 75 days of breastfeeding are dedicated to showcasing the interesting function that mothers play in solenodon reproduction.Behavior
Solenodons make their homes in bushy areas in forests. During the daytime they seek refuge in caves, burrows, or hollow logs. They are easily provoked and can fly into a frenzy of squealing and biting with no warning. They run and climb quite fast, despite only ever touching the ground with toes. Solenodons are said to give off grunts similar to that of a pig or bird-call when feeling threatened. Solenodons generate clicking noises similar to those of shews; the sound waves bounce off objects in their vicinity. This form of echolocation helps a solenodon navigate as well as find food. This well developed auditory ability combined with its above average sense of smell helps the solenodon survive despite its extremely small eyes and poor vision. Solenodons have been described as both omnivorous and insectivorous. Their natural diet largely consists of insects including ants and roaches, grubs, vegetation, and fruit. However, they have also been observed to eat small vertebrates like mice and chicks, meat of large animals, as well as animal products such as eggs and milk, when fed these food items in captivity.Status
Cuba
The Cuban solenodon is consideredEndangered
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching, inv ...
due to predation by the small Indian mongoose (''Urva auropunctata''), which was introduced in colonial times to hunt snakes and rats, as well as by feral cats and dogs. The Cuban solenodon was thought to have been extinct until a live specimen was found in 2003.
Haiti
The Hispaniolan solenodon was also once thought to be extinct, more due to its secretive and elusive behavior than to low population numbers. Recent studies have proven that the species is widely distributed through the island of Hispaniola, but it does not tolerate habitat degradation. A 1981 study of the Hispaniolan solenodon in Haiti found that the species was "functionally extinct", with the exception of a small population in the area of Massif de la Hotte. A follow-up study, in 2007, noted that the solenodon was still thriving in the area, even though the region has had an increase in human population density in recent years.Dominican Republic
The Sierra de Bahoruco, a mountain range in the southwest of the Dominican Republic that straddles the border with Haiti, was examined by conservation teams looking for solenodons. The work occurred during the day when the animals were asleep in burrows so that they could be viewed with an infrared camera. When researchers search for solenodons in daylight, they look for the following clues to their presence: * nearby nose-poke holes that the creatures make in the ground with their long noses to probe the earth, as they look for insects they can hunt and eat. After a relatively long period of time they will be covered in leaves, but a fresh hole will be covered in moist soil. * nearby scratches in logs that were made with their long claws. * a strong musty goat-like smell seeping out of a burrow. The pungent odor indicates that the burrow is active, and a solenodon may be present sleeping. A solenodon was captured in 2008 during a month-long expedition in the Dominican Republic, thereby allowing researchers the rare opportunity to examine it in daylight. The Durrell Wildlife Conservation Trust and the Ornithological Society of Hispaniola were able to take measurements and DNA from the creature before it was released. It was the only trapping made from the entire month-long expedition. The new information gathered was significant because little information was known about the solenodon's ecology, behavior, population status, and genetics, and without that knowledge it is difficult for researchers to design effective conservation. In a 2020 assessment from the IUCN, the Hispaniolan solenodon was found to be much more common on Hispaniola than previously thought, warranting its downlisting from "Endangered" to a "Least Concern
A least-concern species is a species that has been evaluated and categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as not being a focus of wildlife conservation because the specific species is still plentiful in the wil ...
" species.
Conservation
After the arrival of Europeans to the Caribbean, the existence of both species of solenodon has been threatened by introduced species, like dogs, cats, rats, and mongooses, as well as more dense human settlement. These factors were possibly the catalyst for the relatively recent extinction of two species, the giant solenodon (''S. arredondoi'') and the Marcano's solenodon (''S. marcanoi''). Native snakes and birds of prey are also threats. Solenodons have no known negative effects on human populations; in fact, they serve as both pest control, helping ecosystems by keeping down the population of invertebrates, and a means of spreading fruit seeds. Human activity has also had an adverse effect on the solenodon population. Human development on both Cuba and Hispaniola has resulted in fragmentation and habitat loss, further contributing to the reduction of the solenodon's range and numbers.See also
* List of eulipotyphlans of the CaribbeanReferences
External links
* * * * {{Taxonbar, from=Q266725 Venomous mammals Extant Pleistocene first appearances Mammals of the Caribbean