|
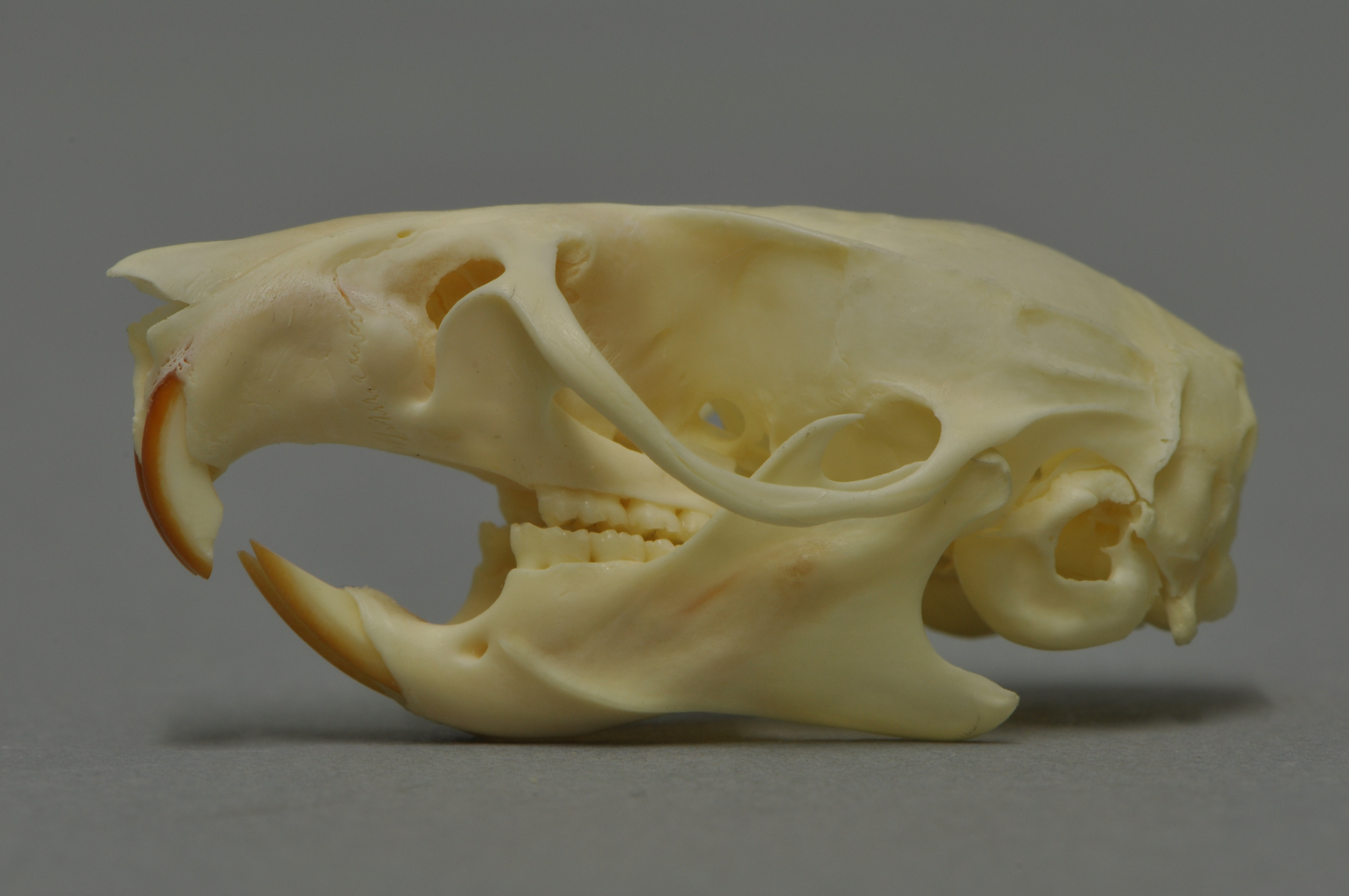
Cuban Solenodon
The Cuban solenodon or ''almiquí'' (''Atopogale cubana'') is a small, furry, shrew-like mammal endemic to Cuban moist forests, mountainous forests on Cuba. It is the monotypic taxon, only species in the genus ''Atopogale''. An elusive animal, it lives in burrows and is only active at night when it uses its unusual toxic saliva to feed on insects. The solenodons (family Solenodontidae), native to the Caribbean, are one of venomous mammal, only a few mammals that are venomous. The Cuban solenodon is Endangered species, endangered and was once considered Extinction, extinct due to its rarity. It and the Hispaniolan solenodon (''Solenodon paradoxus'') are the only surviving solenodon species; the others are Extinction, extinct. Taxonomy Although formerly classified in the genus ''Solenodon (genus), Solenodon'', phylogenetic evidence supports it being in its own genus, ''Atopogale''. Rediscovery Since its discovery in 1861 by the German naturalist Wilhelm Peters, only 36 had ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronx Zoo
The Bronx Zoo (also historically the Bronx Zoological Park and the Bronx Zoological Gardens) is a zoo within Bronx Park in the Bronx, New York City. It is one of the largest zoos in the United States by area and the largest Metropolis, metropolitan zoo, comprising of park lands and naturalistic habitats separated by the Bronx River. The zoo has 2.1 million average yearly visitors . The zoo's original buildings, known as Astor Court, were designed as a series of Beaux-Arts architecture, Beaux-Arts pavilions grouped around the large circular sea lion pool. The Rainey Memorial Gates were designed by sculptor Paul Manship in 1934 and listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1972. The zoo opened on November 8, 1899, featuring 843 animals in 22 exhibits. Its first director was William Temple Hornaday, who served for 30 years. From its inception the zoo has played a vital role in animal conservation. In 1905, the American Bison Society was created in an attempt to save th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shrew
Shrews ( family Soricidae) are small mole-like mammals classified in the order Eulipotyphla. True shrews are not to be confused with treeshrews, otter shrews, elephant shrews, West Indies shrews, or marsupial shrews, which belong to different families or orders. Although its external appearance is generally that of a long-nosed mouse, a shrew is not a rodent, as mice are. It is, in fact, a much closer relative of hedgehogs and moles; shrews are related to rodents only in that both belong to the Boreoeutheria magnorder. Shrews have sharp, spike-like teeth, whereas rodents have gnawing front incisor teeth. Shrews are distributed almost worldwide. Among the major tropical and temperate land masses, only New Guinea, Australia, New Zealand, and South America have no native shrews. However, as a result of the Great American Interchange, South America does have a relatively recently naturalised population, present only in the northern Andes. The shrew family has 385 kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
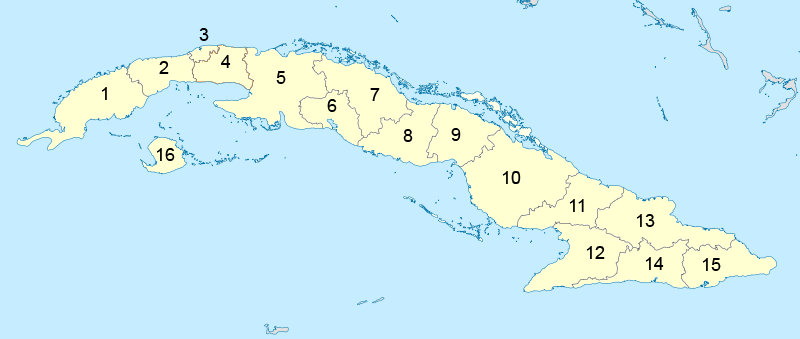
Holguín Province
Holguín () is one of the provinces of Cuba, the third most populous after Havana and Santiago de Cuba. It lies in the southeast of the country. Its major cities include Holguín (the capital), Banes, Antilla, Mayarí, and Moa. The province has a population of slightly over one million people. Its territory exceeds , 25 percent of which is covered by forest. History Christopher Columbus landed in what is believed to have been today's Holguín province on October 27, 1492. He declared that it was "the most beautiful land human eyes had ever seen". The Holguín province was established in 1978, when it was split from the Oriente region. Economy Like much of Cuba, Holguín's economy is based around sugarcane, though other crops such as corn and coffee, as well as mining, are also large earners for the province. A large nickel plus cobalt processing plant with shipping facilities was built in Moa, using foreign investment, much of it from Canada. Chromium, iron and stee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of Cuba
Administrative division, Administratively, Cuba is divided into 15 provinces and one special municipality (the Isla de la Juventud). The current structure has been in place since August 2010, when the La Habana Province (1976–2010), then-La Habana Province was divided into Artemisa Province and Mayabeque Province. List of provinces From west to east, Cuba's provinces are: # Pinar del Río Province, Pinar del Río # Artemisa Province, Artemisa # La Habana Province, La Habana # Mayabeque Province, Mayabeque # Matanzas Province, Matanzas # Cienfuegos Province, Cienfuegos # Villa Clara Province, Villa Clara # Sancti Spíritus Province, Sancti Spíritus # Ciego de Ávila Province, Ciego de Ávila # Camagüey Province, Camagüey # Las Tunas Province, Las Tunas # Granma Province, Granma # Holguín Province, Holguín # Santiago de Cuba Province, Santiago de Cuba # Guantánamo Province, Guantánamo # Isla de la Juventud ("special municipality") History 1879–1976 The province ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nipe-Sagua-Baracoa
Nipe-Sagua-Baracoa, also known as Macizo Nipe Sagua Baracoa ("Nipe Sagua Baracoa Massif"), is a mountain range of eastern Cuba. Geography The range is located in Holguín Province, Holguín and Guantánamo Province, Guantánamo provinces, and a small portion in northeastern Santiago de Cuba Province. The Nipe-Sagua-Baracoa massif extends for a length of 187 km and a width of 50 km, from the central-eastern part of the Holguín Province (near Nipe Bay, Mayarí) to Cuba's easternmost point at Maisí in Guantánamo Province. Lowlands and hills separate the massif from the Sierra Maestra to the southwest. The massif includes Pico Cristal (1,231 m), the second highest Cuban peak after Pico Turquino (1,974 m) in the Sierra Maestra. The massif is crossed by the rivers Toa River, Toa, Mayarí River, Mayarí, and Sagua de Tánamo River, Sagua de Tánamo. The massif is made up of several smaller ranges. * The Sierra de Nipe is the westernmost range, a plateau of approximately 600 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feral Dog
A free-ranging dog is a dog that is not confined to a yard or house. Free-ranging dogs include street dogs, village dogs, stray dogs, feral dogs, etc., and may be owned or unowned. The global dog population is estimated to be 900 million, of which around 20% are regarded as owned pets and therefore restrained. Free-ranging dogs are common in developing countries. It is estimated that there are about 62 million free-ranging dogs in India. In Western countries free-ranging dogs are rare; in Europe they are primarily found in parts of Eastern Europe, and, to a lesser extent, in parts of Southern Europe. Various human organizations work to manage free-ranging dogs, citing concerns about the spread of rabies, the animals' welfare, and other areas. These include governments, animal rights organizations and other non-governmental organizations, and veterinarians. Some governments have dog-management policies, including trap–neuter–return, the permanent removal of dogs from the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feral Cat
A feral cat or a stray cat is an unowned domestic cat (''Felis catus'') that lives outdoors and avoids human contact; it does not allow itself to be handled or touched, and usually remains hidden from humans. Feral cats may breed over dozens of generations and become a local apex predator in urban, savannah and bushland environments, and especially on islands where native animals did not evolve alongside predators. Some feral cats may become more comfortable with people who regularly feed them, but even with long-term attempts at socialization of animals, socialization, they usually remain aloof and reject human touch. Of the 700 million cats in the world, an estimated 480 million are feral. Feral cats are devastating to wildlife, and conservation biologists consider them to be one of the worst invasive species on Earth. They are included in the list of 100 of the World's Worst Invasive Alien Species, the world's 100 worst invasive alien species. Attempts to control feral cat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Rat
The black rat (''Rattus rattus''), also known as the roof rat, ship rat, or house rat, is a common long-tailed rodent of the stereotypical rat genus ''Rattus'', in the subfamily Murinae. It likely originated in the Indian subcontinent, but is now found worldwide. The black rat is black to light brown in colour with a lighter underside. It is a generalist omnivore and a serious Pest (organism), pest to farmers because it feeds on a wide range of agricultural crops. It is sometimes kept as a pet. In parts of India, it is considered sacred and respected in the Karni Mata Temple in Deshnoke. Taxonomy ''Mus rattus'' was the scientific name proposed by Carl Linnaeus in 1758 for the black rat. Three subspecies were once recognized, but today are considered invalid and are now known to be actually Morph (zoology), color morphs: *''Rattus rattus rattus'' – roof rat *''Rattus rattus alexandrinus'' – Alexandrine rat *''Rattus rattus frugivorus'' – fruit rat Characteristics A ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Indian Mongoose
The small Indian mongoose (''Urva auropunctata'') is a mongoose species native to Iraq and northern India; it has also been introduced to several Caribbean and Pacific islands. Taxonomy ''Mangusta auropunctata'' was the scientific name proposed by Brian Houghton Hodgson in 1836 for a mongoose specimen collected in central Nepal. In the 19th and 20th centuries, several zoological specimens were described: *''Mangusta pallipes'' proposed by Edward Blyth in 1845 was based on mongooses observed in Kandahar, Afghanistan. *''Herpestes palustris'' proposed by R. K. Ghose in 1965 was an adult male mongoose collected in a swamp on the eastern fringe of Kolkata, India. The small Indian mongoose was later classified in the genus '' Herpestes''; all Asian mongooses are now classified the genus '' Urva''. The small Indian mongoose was once considered a subspecies of the Javan mongoose (''H. javanicus''). Genetic analysis of hair and tissue samples from 18 small Indian and Javan mongooses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invasive Species
An invasive species is an introduced species that harms its new environment. Invasive species adversely affect habitats and bioregions, causing ecological, environmental, and/or economic damage. The term can also be used for native species that become harmful to their native environment after human alterations to its food web. Since the 20th century, invasive species have become serious economic, social, and environmental threats worldwide. Invasion of long-established ecosystems by organisms is a natural phenomenon, but human-facilitated introductions have greatly increased the rate, scale, and geographic range of invasion. For millennia, humans have served as both accidental and deliberate dispersal agents, beginning with their earliest migrations, accelerating in the Age of Discovery, and accelerating again with the spread of international trade. Notable invasive plant species include the kudzu vine, giant hogweed (''Heracleum mantegazzianum''), Japanese knotw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predation
Predation is a biological interaction in which one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common List of feeding behaviours, feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill the Host (biology), host) and parasitoidism (which always does, eventually). It is distinct from Scavenger, scavenging on dead prey, though many predators also scavenge; it overlaps with Herbivore, herbivory, as Seed predation, seed predators and destructive frugivores are predators. Predation behavior varies significantly depending on the organism. Many predators, especially carnivores, have evolved distinct hunting strategy, hunting strategies. Pursuit predation involves the active search for and pursuit of prey, whilst ambush predation, ambush predators instead wait for prey to present an opportunity for capture, and often use stealth or aggressive mimicry. Other predators are opportunism, opportunistic or om ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endangered Species
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching, invasive species, and climate change. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List lists the global conservation status of many species, and various other agencies assess the status of species within particular areas. Many nations have laws that protect conservation-reliant species which, for example, forbid hunting, restrict land development, or create protected areas. Some endangered species are the target of extensive conservation efforts such as captive breeding and habitat restoration. Human activity is a significant cause in causing some species to become endangered. Conservation status The conservation status of a species indicates the likelihood that it will become extinct. Multiple factors are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |