snapshot hyperspectral imaging on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Snapshot hyperspectral imaging is a method for capturing hyperspectral images during a single integration time of a detector array. No scanning is involved with this method, in contrast to push broom and whisk broom scanning techniques. The lack of moving parts means that motion artifacts should be avoided. This instrument typically features detector arrays with a high number of pixels.
Snapshot hyperspectral imaging is a method for capturing hyperspectral images during a single integration time of a detector array. No scanning is involved with this method, in contrast to push broom and whisk broom scanning techniques. The lack of moving parts means that motion artifacts should be avoided. This instrument typically features detector arrays with a high number of pixels.
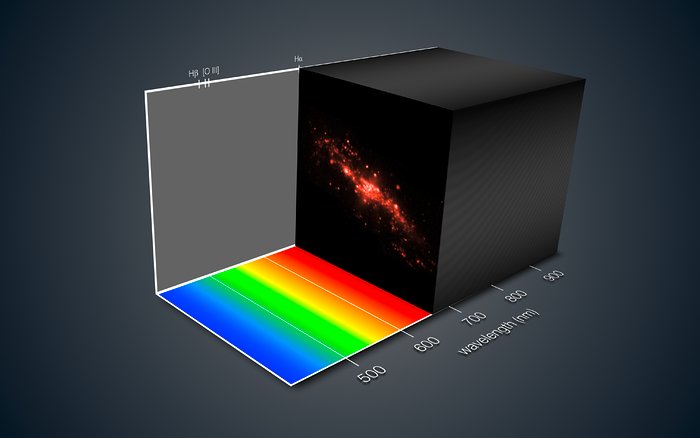 While snapshot instruments are featured prominently in the research literature, none of these instruments have seen wide adoption in commercial use (i.e. outside the professional
While snapshot instruments are featured prominently in the research literature, none of these instruments have seen wide adoption in commercial use (i.e. outside the professional
 Snapshot hyperspectral imaging is a method for capturing hyperspectral images during a single integration time of a detector array. No scanning is involved with this method, in contrast to push broom and whisk broom scanning techniques. The lack of moving parts means that motion artifacts should be avoided. This instrument typically features detector arrays with a high number of pixels.
Snapshot hyperspectral imaging is a method for capturing hyperspectral images during a single integration time of a detector array. No scanning is involved with this method, in contrast to push broom and whisk broom scanning techniques. The lack of moving parts means that motion artifacts should be avoided. This instrument typically features detector arrays with a high number of pixels.
Development
Although the first known reference to a snapshot hyperspectral imaging device—the Bowen "image slicer"—dates from 1938, the concept was not successful until a larger amount of spatial resolution was available. With the arrival of large-format detector arrays in the late 1980s and early 1990s, a series of new snapshot hyperspectral imaging techniques were developed to take advantage of the new technology: a method which uses afiber
Fiber (spelled fibre in British English; from ) is a natural or artificial substance that is significantly longer than it is wide. Fibers are often used in the manufacture of other materials. The strongest engineering materials often inco ...
bundle at the image plane and reformatting the fibers in the opposite end of the bundle to a long line, viewing a scene through a 2D grating
A grating is any regularly spaced collection of essentially identical, parallel, elongated elements. Gratings usually consist of a single set of elongated elements, but can consist of two sets, in which case the second set is usually perpendicu ...
and reconstructing the multiplexed data with computed tomography
Tomography is imaging by sections or sectioning that uses any kind of penetrating wave. The method is used in radiology, archaeology, biology, atmospheric science, geophysics, oceanography, plasma physics, materials science, cosmochemistry, ast ...
mathematics, the (lenslet-based) integral field spectrograph, a modernized version of Bowen's image slicer. More recently, a number of research groups have attempted to advance the technology in order to create devices capable of commercial use. These newer devices include the HyperPixel Array imager a derivative of the integral field spectrograph, a multiaperture spectral filter approach, a compressive-sensing–based approach using a coded aperture
Coded apertures or coded-aperture masks are grids, gratings, or other patterns of materials opaque to various wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation. The wavelengths are usually high-energy radiation such as X-rays and gamma rays. A coded "shad ...
, a microfaceted-mirror-based approach, a generalization of the Lyot filter, and a generalization of the Bayer filter
A Bayer filter mosaic is a color filter array (CFA) for arranging RGB color model, RGB color filters on a square grid of photosensors. Its particular arrangement of color filters is used in most single-chip digital image sensors used in digit ...
approach to multispectral filtering.
Slitless spectroscopy can be considered a basic snapshot hyperspectral imaging technique. Spaced point-like sources, such as a sparse field of stars, is a requirement to avoid spectrum overlap on the detector.
Applications
 While snapshot instruments are featured prominently in the research literature, none of these instruments have seen wide adoption in commercial use (i.e. outside the professional
While snapshot instruments are featured prominently in the research literature, none of these instruments have seen wide adoption in commercial use (i.e. outside the professional astronomical
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest include ...
community) due to manufacturing limitations. Thus, their primary venue continues to be astronomical telescope
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption, or Reflection (physics), reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally, it was an optical instrument using len ...
s. One of the main reasons for the popularity of snapshot devices in the astronomical community is that they offer large increases in the light collection capacity of a telescope when performing hyperspectral imaging. Recent applications have been in soil spectroscopy and vegetation sciences.
See also
* Chemical imaging *Computed tomography imaging spectrometer
The computed tomography imaging spectrometer (CTIS) is a snapshot hyperspectral imaging, snapshot imaging spectrometer which can produce ''in fine'' the three-dimensional (i.e. spatial and spectral) Hyperspectral imaging, hyperspectral datacube of ...
*Imaging spectrometer
An imaging spectrometer is an instrument used in hyperspectral imaging and imaging spectroscopy to acquire a spectrally-resolved image of an object or scene, usually to support analysis of the composition the object being imaged. The spectral data ...
*Imaging spectroscopy
Imaging is the representation or reproduction of an object's form; especially a visual representation (i.e., the formation of an image).
Imaging technology is the application of materials and methods to create, preserve, or duplicate images.
...
*Multi-spectral image
Multispectral imaging captures image data within specific wavelength ranges across the electromagnetic spectrum. The wavelengths may be separated by Filter (optics), filters or detected with the use of instruments that are sensitive to partic ...
* Spectral imaging
* Video spectroscopy
References
{{Reflist Satellite meteorology Remote sensing Infrared imaging Infrared spectroscopy