 A compound engine is an
A compound engine is an engine
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert one or more forms of energy into mechanical energy.
Available energy sources include potential energy (e.g. energy of the Earth's gravitational field as exploited in hydroelectric power ge ...
that has more than one stage for recovering energy from the same working fluid
For fluid power, a working fluid is a gas or liquid that primarily transfers force, motion, or mechanical energy. In hydraulics, water or hydraulic fluid transfers force between hydraulic components such as hydraulic pumps, hydraulic cylinders, a ...
, with the exhaust from the first stage passing through the second stage, and in some cases then on to another subsequent stage or even stages. Originally invented as a means of making steam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs Work (physics), mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a Cylinder (locomotive), cyl ...
s more efficient, the compounding of engines by use of several stages has also been used on internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal comb ...
s and continues to have niche markets there.
The stages of a compound engine may be either of differing or of similar technologies, for example:
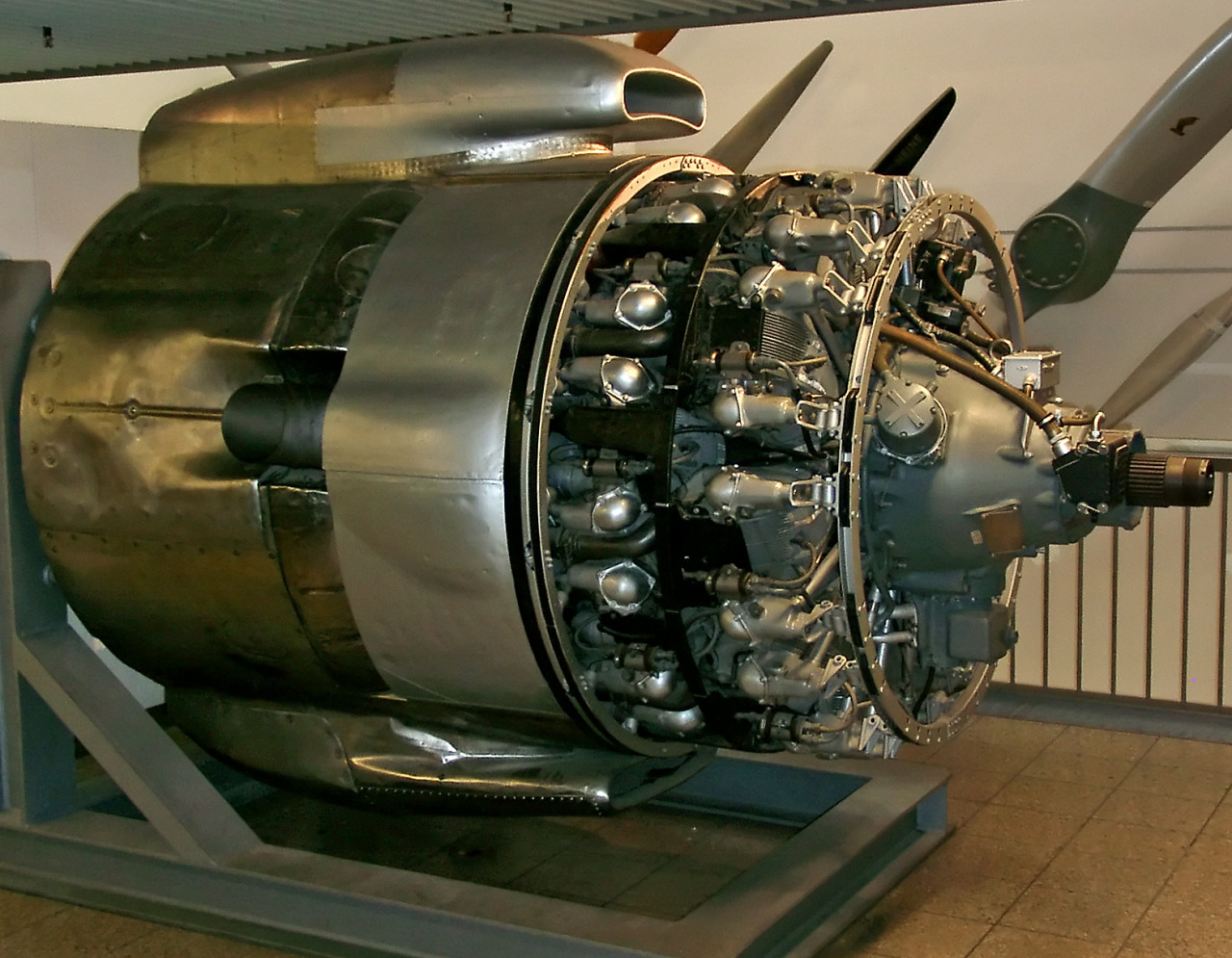
* In a turbo-compound engine
A turbo-compound engine is a reciprocating engine that employs a turbine to recover energy from the exhaust gases. Instead of using that energy to drive a turbocharger as found in many high-power aircraft engines, the energy is instead sent to ...
, the exhaust gas
Exhaust gas or flue gas is emitted as a result of the combustion of fuels such as natural gas, gasoline (petrol), diesel fuel, fuel oil, biodiesel blends, or coal. According to the type of engine, it is discharged into the atmosphere through ...
from the cylinders passes through a turbine, the two stages being dissimilar.
* In a compound steam locomotive, the steam passes from the high-pressure cylinder or cylinders to the low-pressure cylinder or cylinders, the two stages being similar.
* In a triple-expansion steam engine, the steam passes through three successive cylinders of increasing size and decreasing pressure. Such engines were the most common marine engines in the golden age of steam.
These examples and compound turbine
In steam turbine design, compounding is a method of extracting steam energy in multiple stages rather than a single one. Each stage of a compounded steam turbine has its own set of nozzles and Turbines, rotors. These are arranged in series, eithe ...
s are the main but not the only uses of compounding in engines, see below.
Terminology
A compound engine uses several stages to produce its output. Not all engines that use multiple stages are called ''compound engines''. In particular, if an engine uses a later stage purely to extract energy from the exhaust for some other purpose, and notably for turbo charging, is not called a ''compound engine''. Similarly, proposed engines that use a free piston engine to drive a turbine would not be called ''compound engines'', as only the second stage produces output power. However, if a turbo compound engine is alsosupercharged
In an internal combustion engine, a supercharger compresses the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement. It is a form of forced induction that is mechanically powered (usually by ...
by feeding some of the shaft power back to the supercharger, as in some aircraft engines, it is still a compound engine. Usage of the terms ''supercharged'' and ''turbosupercharged'' has varied with time, for example the makers of the Wright R-3350 Duplex-Cyclone compound engine described it at the time as ''turbosupercharged''. It is however a compound engine, and a similar engine produced today would be described as ''supercharged'' rather than ''turbocharged''.
The term compounding is a little less restrictive than ''compound engine''. Large compound turbine
In steam turbine design, compounding is a method of extracting steam energy in multiple stages rather than a single one. Each stage of a compounded steam turbine has its own set of nozzles and Turbines, rotors. These are arranged in series, eithe ...
s are an application of compounding, as are the multiple rows of blades used in many gas turbine
A gas turbine or gas turbine engine is a type of Internal combustion engine#Continuous combustion, continuous flow internal combustion engine. The main parts common to all gas turbine engines form the power-producing part (known as the gas gene ...
s, but neither is normally referred to as a compound engine. The several sets of blades in a single turbine are perhaps better thought of as similar in principle to the uniflow steam engine
The uniflow type of steam engine uses steam that flows in one direction only in each half of the cylinder. Thermal efficiency is increased by having a temperature gradient along the cylinder. Steam always enters at the hot ends of the cylinder an ...
than to compounding. Unlike the uniflow steam engine, which has found niche uses only, multiple row turbines have found enormous practical application.
An engine that does not use compounding is referred to as a simple engine, particularly in the case of a steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, Fuel oil, oil or, rarely, Wood fuel, wood) to heat ...
, or more precisely as a simple expansion engine, particularly in the case of a marine steam engine
A marine steam engine is a steam engine that is used to power a ship or boat. This article deals mainly with marine steam engines of the reciprocating type, which were in use from the inception of the steamboat in the early 19th century to thei ...
.
Note however that in the case of any steam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs Work (physics), mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a Cylinder (locomotive), cyl ...
, ''simple engine'' can also be used to mean one that does not use a condenser to generate negative pressure and so improve efficiency. Use of separate condensers for this purpose is one of the key features that distinguishes the Watt steam engine
The Watt steam engine design was an invention of James Watt that became synonymous with steam engines during the Industrial Revolution, and it was many years before significantly new designs began to replace the basic Watt design.
The Newcomen ...
of 1765 from the Newcomen steam engine
The atmospheric engine was invented by Thomas Newcomen in 1712, and is sometimes referred to as the Newcomen fire engine (see below) or Newcomen engine. The engine was operated by condensing steam being drawn into the cylinder, thereby creating ...
of 1712.
No ambiguity arises in the case of a steam locomotive, as in a condensing steam locomotive the condenser is not there to increase efficiency, and may even reduce efficiency in order to conserve water and reduce emissions. So for example the Metropolitan Railway A Class is in every sense a ''simple'' locomotive despite its condensers, and the term ''simple engine'' applied to steam locomotives always in practice means one that does not use compounding, again irrespective of its use of condensers. The terms ''simple expansion locomotive'' and ''simple expansion engine'' are sometimes applied to locomotives to remove any possible confusion.
History
Steam
compound steam engine
A compound steam engine unit is a type of steam engine where steam is expanded in two or more stages.
A typical arrangement for a compound engine is that the steam is first expanded in a high-pressure (HP) cylinder, then having given up heat ...
s. In 1805 Arthur Woolf
Arthur Woolf (1766, Camborne, Cornwall – 16 October 1837, Guernsey) was a Cornish engineer, most famous for inventing a high-pressure compound steam engine. In this way he made an outstanding contribution to the development and perfection ...
patented the ''Woolf high pressure compound engine'' which used this principle.
Compounding was particularly used on stationary steam engine
Stationary steam engines are fixed steam engines used for pumping or driving mills and factories, and for power generation. They are distinct from locomotive engines used on railways, traction engines for heavy steam haulage on roads, steam car ...
s, marine steam engine
A marine steam engine is a steam engine that is used to power a ship or boat. This article deals mainly with marine steam engines of the reciprocating type, which were in use from the inception of the steamboat in the early 19th century to thei ...
s, and on some steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, Fuel oil, oil or, rarely, Wood fuel, wood) to heat ...
s starting from the 1850s, largely in continental Europe.
Three stage or triple expansion
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be trans ...
reciprocating steam engines, with three cylinders of increasing bore in line, were quite popular for steamship
A steamship, often referred to as a steamer, is a type of steam-powered vessel, typically ocean-faring and seaworthy, that is propelled by one or more steam engines that typically move (turn) propellers or paddlewheels. The first steamships ...
propulsion. "Doctor" Alexander Carnegie Kirk, experimentally fitted his first triple expansion engine to a ship called ''Propontis'' in 1874. In 1881, Kirk installed a refined version of his engine in SS ''Aberdeen'' on Clydeside, Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjac ...
. This ship proved the advantages of power and economy of the new engine, in commercial service between the United Kingdom and the Far East
The Far East is the geographical region that encompasses the easternmost portion of the Asian continent, including North Asia, North, East Asia, East and Southeast Asia. South Asia is sometimes also included in the definition of the term. In mod ...
. The first warship
A warship or combatant ship is a naval ship that is used for naval warfare. Usually they belong to the navy branch of the armed forces of a nation, though they have also been operated by individuals, cooperatives and corporations. As well as b ...
to be so equipped was the Spanish warship ''Destructor'', which was also built on Clydeside, and the first engine of this type used in ships of the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom ...
was designed by J. W. Reed, who also created the Reed water tube boiler. Other navies and commercial shipowners soon followed. Four-stage, or quadruple, expansion engines were also used.
Several classes of steam locomotive have existed in both simple and compound form, most commonly when locomotives originally built as compound were converted to simple in order to gain power at the expense of efficiency, for example the majority of the NZR X class. Other conversions involved redesigning the details of the compounding, for example many compound locomotives designed by Alfred de Glehn and state of the art in their day were modified by André Chapelon to use his later scheme.
Internal combustion
Somecompound internal combustion engine
A compound internal combustion engine is a type of internal combustion engine (ICE) where gasses of combustion are expanded in two or more stages. A typical arrangement for a compound ICE is that the fuel/air is first combusted and expanded in one ...
s have been patented, but these have not met with much commercial success. these engines use a three-cylinder arrangement with alternating high-pressure cylinders exhaust into a central low-pressure cylinder.
Examples include: Deutz 1879, Forest-Gallice 1888, Connelly 1888, Diesel 1897, Bales 1897, Babled 1903, Butler 1904, Eisenhuth 1904–7, Abbot 1910. The concept was "re-invented" and patented as the five-stroke engine
The five-stroke engine is a compound internal combustion engine patented by Gerhard Schmitz in 2000.
Concept
The goal of the five-stroke engine is to achieve higher efficiency than a four-stroke engine. In order to increase efficiency, a secon ...
in 2000 by Gerhard Schmitz, which was experimented with by Ilmor.
Turbo-compounding has been applied to internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal comb ...
s. Turbo compound engines were extensively used as aircraft engine
An aircraft engine, often referred to as an aero engine, is the power component of an aircraft propulsion system. Aircraft using power components are referred to as powered flight. Most aircraft engines are either piston engines or gas turbin ...
s immediately after the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
.
Diesel turbo compound engines remain in use in trucks and agricultural machinery.http://www.demanddetroit.com/pdf/engines/2007-dd15-brochure.pdf retrieved 7 December 2012 ''Fifty free horsepower'' customer brochure
Examples
 *
* Turbo-compound engine
A turbo-compound engine is a reciprocating engine that employs a turbine to recover energy from the exhaust gases. Instead of using that energy to drive a turbocharger as found in many high-power aircraft engines, the energy is instead sent to ...
s
** Truck and machinery engines
** Aircraft engines
*** Napier Nomad
The Napier Nomad is a British diesel engine, diesel aircraft engine designed and built by Napier & Son in 1949. They combined a piston engine with a turbine to recover energy from the exhaust and thereby improve fuel efficiency, fuel economy. T ...
*** Wright R-3350 Duplex-Cyclone which was produced in both simple and compound versions and which in compound configuration powered many post World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
aircraft including the Lockheed Constellation
The Lockheed Constellation ("Connie") is a propeller-driven, four-engined airliner built by Lockheed Corporation starting in 1943. The Constellation series was the first civil airliner family to enter widespread use equipped with a pressurized cab ...
http://www.enginehistory.org/Wright/Kuhns/CurtissWrightTC18/TurboCompounds.shtml retrieved 9 December 2012http://www.superconstellation.org/TechnicalInformation/motor/motor-en.html retrieved 9 December 2012
*** Dobrynin VD-4K aircraft engine
* Compound steam engine
A compound steam engine unit is a type of steam engine where steam is expanded in two or more stages.
A typical arrangement for a compound engine is that the steam is first expanded in a high-pressure (HP) cylinder, then having given up heat ...
s
** Compound locomotive
A compound locomotive is a steam locomotive which is powered by a compound steam engine, compound engine, a type of steam engine where steam is expanded in two or more stages. The locomotive was only one application of compounding. Two and three ...
s (see also :Compound locomotives)
*** LMS Compound 4-4-0
The London, Midland and Scottish Railway Compound 4-4-0 was a class of steam locomotive designed for passenger work.
Overview
One hundred and ninety five engines were built by the LMS, adding to the 45 Midland Railway 1000 Class, to which ...
*** NZR A class (1906)
*** LMS 6399 Fury
*** Württemberg Tssd
*** Bavarian S 3/6
*** Some Mallet locomotive
A Mallet locomotive is a type of compound locomotive, compound articulated locomotive, articulated steam locomotive, invented by the Swiss engineer Anatole Mallet (1837–1919).
The front of the locomotive is articulated on a bogie. The Compou ...
s, particularly the original designs
*** Nilgiri Mountain Railway X class
** Cross-compound steam-driven air compressor, e.g. Westinghouse 8 1/2" 150-D, used on many large American locomotives
**Many traction engine
A traction engine is a steam engine, steam-powered tractor used to move heavy loads on roads, plough ground or to provide power at a chosen location. The name derives from the Latin ''tractus'', meaning 'drawn', since the prime function of any ...
s
**Most reciprocating marine steam engine
A marine steam engine is a steam engine that is used to power a ship or boat. This article deals mainly with marine steam engines of the reciprocating type, which were in use from the inception of the steamboat in the early 19th century to thei ...
s
*** Two triple-expansion steam engines were fitted to each of the three ''Olympic''-class ocean liners including RMS ''Titanic'' (1912), driving the wing propellers. These engines were typical of the era. In the ''Olympic'' class, further compounding was achieved by using the exhaust steam from these engines to drive a low-pressure steam turbine
A steam turbine or steam turbine engine is a machine or heat engine that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam and uses it to do mechanical work utilising a rotating output shaft. Its modern manifestation was invented by Sir Charles Par ...
driving a smaller central propeller. This scheme had been pioneered by SS ''Laurentic'' (1908).
* Rolls Royce R6 compound Wankel engine
The Wankel engine (, ) is a type of internal combustion engine using an eccentric (mechanism), eccentric Pistonless rotary engine, rotary design to convert pressure into rotating motion. The concept was proven by German engineer Felix Wankel, f ...
http://www.der-wankelmotor.de/Motoren/Rolls-Royce/rolls-royce.html (in German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
) retrieved 7 December 2012
See also
Theory
* *Inventors and designers
*Arthur Woolf
Arthur Woolf (1766, Camborne, Cornwall – 16 October 1837, Guernsey) was a Cornish engineer, most famous for inventing a high-pressure compound steam engine. In this way he made an outstanding contribution to the development and perfection ...
* Anatole Mallet
* Alfred de Glehn
* Joseph Anton Maffei
* Gaston du Bousquet
* André Chapelon
Similar technology
*Compound turbine
In steam turbine design, compounding is a method of extracting steam energy in multiple stages rather than a single one. Each stage of a compounded steam turbine has its own set of nozzles and Turbines, rotors. These are arranged in series, eithe ...
* Compounding of steam turbines
* Pressure compounding in turbines
References
{{steam engine configurations Engine technology