Sicilian People on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sicilians () are a European
 All three tribes lived both a sedentary
All three tribes lived both a sedentary
Technological and cultural change among the last Hunter-Gatherers of the Maghreb: the Capsian (10,000 B.P. to 6000 B.P.)
''Journal of World Prehistory'' 18(1): 57–105. Another archaeological site, originally identified by
 In the 11th century, the mainland southern Italian powers were hiring Norman conquest of southern Italy, Norman mercenaries, who were Christians, Christian descendants of the Vikings; it was the Normans under Roger I of Sicily, Roger I (of the Hauteville dynasty) who conquered Sicily from the Muslims Battle of Cerami, over a period of thirty years until finally controlling the entire island by 1091 as the County of Sicily. In 1130, Roger II of Sicily, Roger II founded the Norman Kingdom of Sicily as an independent state with its own Sicilian Parliament, Parliament, language, schooling, army and currency, while the Sicilian culture evolved distinct traditions, clothing, linguistic changes, Sicilian cuisine, cuisine and customs not found in mainland
In the 11th century, the mainland southern Italian powers were hiring Norman conquest of southern Italy, Norman mercenaries, who were Christians, Christian descendants of the Vikings; it was the Normans under Roger I of Sicily, Roger I (of the Hauteville dynasty) who conquered Sicily from the Muslims Battle of Cerami, over a period of thirty years until finally controlling the entire island by 1091 as the County of Sicily. In 1130, Roger II of Sicily, Roger II founded the Norman Kingdom of Sicily as an independent state with its own Sicilian Parliament, Parliament, language, schooling, army and currency, while the Sicilian culture evolved distinct traditions, clothing, linguistic changes, Sicilian cuisine, cuisine and customs not found in mainland
 In 1735, the Spanish Empire, Spanish era ended when Charles V of Sicily, Charles V from the House of Bourbon-Two Sicilies, House of Bourbon was crowned king. For the better part of the next century-and-a-half, Sicily was in personal union with the other Southern Italian Kingdom of Naples, with the official residence located in Naples, under the House of Bourbon-Two Sicilies, Bourbon dynasty. After the Napoleonic Wars, King Ferdinand I of the Two Sicilies, Ferdinand I, who had just recently been restored back to the throneship of Kingdom of Naples, Southern Italy in 1815, made a decision to administratively and politically merged the two separate Kingdoms of Naples and Sicily, which ended up forming the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies in 1816. In 1861, however, Sicily became part of the Kingdom of Italy as a result of the Italian unification, Risorgimento. Prior to the Risorgimento, the Two Sicilies were conquered by the Kingdom of Sardinia (1720–1861), Kingdom of Sardinia during the Expedition of the Thousand (led by general Giuseppe Garibaldi) in 1860, and subsequently brought under the monarchial realm of
In 1735, the Spanish Empire, Spanish era ended when Charles V of Sicily, Charles V from the House of Bourbon-Two Sicilies, House of Bourbon was crowned king. For the better part of the next century-and-a-half, Sicily was in personal union with the other Southern Italian Kingdom of Naples, with the official residence located in Naples, under the House of Bourbon-Two Sicilies, Bourbon dynasty. After the Napoleonic Wars, King Ferdinand I of the Two Sicilies, Ferdinand I, who had just recently been restored back to the throneship of Kingdom of Naples, Southern Italy in 1815, made a decision to administratively and politically merged the two separate Kingdoms of Naples and Sicily, which ended up forming the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies in 1816. In 1861, however, Sicily became part of the Kingdom of Italy as a result of the Italian unification, Risorgimento. Prior to the Risorgimento, the Two Sicilies were conquered by the Kingdom of Sardinia (1720–1861), Kingdom of Sardinia during the Expedition of the Thousand (led by general Giuseppe Garibaldi) in 1860, and subsequently brought under the monarchial realm of
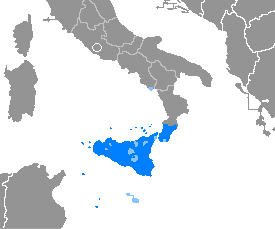 Sicily has experienced the presence of a number of different cultures and ethnicities in its vast history, including the aboriginal peoples of differing Ethnolinguistic group, ethnolinguistic origins (
Sicily has experienced the presence of a number of different cultures and ethnicities in its vast history, including the aboriginal peoples of differing Ethnolinguistic group, ethnolinguistic origins (
 In Sicily, there are three ''metropolitan areas'':
# Palermo, which has a Larger Urban Zone of 1,044,169 people
# Catania, whose Larger Urban Zones, LUZ's populous numbers some 801,280 people
#
In Sicily, there are three ''metropolitan areas'':
# Palermo, which has a Larger Urban Zone of 1,044,169 people
# Catania, whose Larger Urban Zones, LUZ's populous numbers some 801,280 people
#
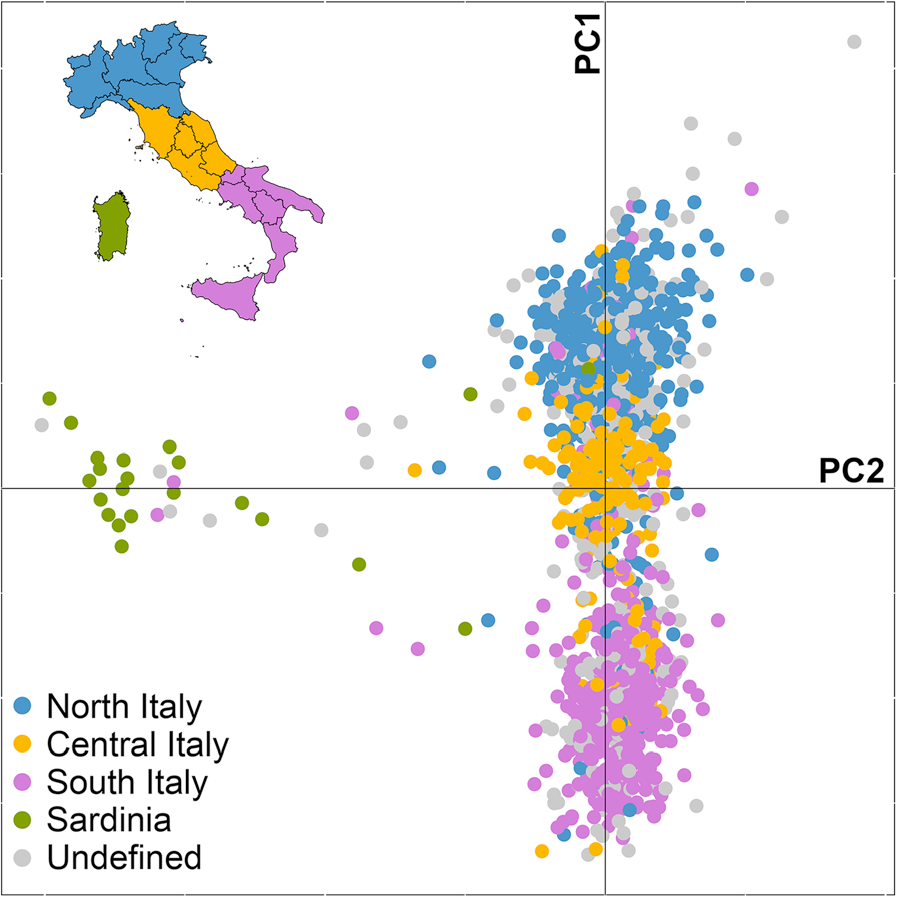 Several studies involving Genome-wide association study, whole genome analysis of mainland Italians and Sicilians have found that samples from Northern Italy,
Several studies involving Genome-wide association study, whole genome analysis of mainland Italians and Sicilians have found that samples from Northern Italy,
 Today in Sicily most people are bilingual and speak both Italian language, Italian and Sicilian language, Sicilian, a distinct Romance languages, Romance language. Many Sicilian language, Sicilian words are of
Today in Sicily most people are bilingual and speak both Italian language, Italian and Sicilian language, Sicilian, a distinct Romance languages, Romance language. Many Sicilian language, Sicilian words are of
 Historically, Sicily has been home to many religions, including Islam, Native religions, Judaism, Classical antiquity, Classical Paganism, Punic religion, Carthaginian religions, and Eastern Orthodox Church, Byzantine Orthodoxy, the coexistence of which has been historically seen as an ideal example of religious multiculturalism. Most Sicilians today are baptized as Catholic. Catholicism and Liturgical Latinization, Latinization in Sicily originated from the islands Norman occupiers and forced conversion continued under the Spanish invaders, where the majority of Sicily's population were forced to convert from their former religions. Despite the historical push for Catholicism in Sicily, a minority of other religious communities thrive in Sicily.
Sicilian Catholics
For Catholics in Sicily, the Hodegetria, Virgin Hodegetria is the patroness of Sicily. The Sicilian people are also known for their deep devotion to some Sicilian female saints: the martyrs Agatha of Sicily, Agatha and Saint Lucy, Lucy, who are the patron saints of Catania and Syracuse respectively, and the hermit Saint Rosalia, patroness of Palermo. Sicilian people have significantly contributed to the history of many religions. There have been four Sicilian Popes (Pope Agatho, Agatho, Pope Leo II, Leo II, Pope Sergius I, Sergius I, and Pope Stephen III, Stephen III) and a Sicilian Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople (Methodios I of Constantinople, Methodios I). Sicily is also mentioned in the New Testament in the Acts of the Apostles, 28:11–13, in which Saint Paul briefly visits Sicily for three days before leaving the Island. It is believed he was the first Christian to ever set foot in Sicily.
Sicilian Muslims
During the Emirate of Sicily, period of Muslim rule, many Sicilians converted to Islam. Many Islamic scholars were born on the island, including Al-Maziri, a prominent jurist of the Maliki school of Sunni Islamic Law. Under the rule of Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor, Frederick II, all Muslims were expelled from the Island following a rebellion of local Saracens who wished to keep their local independence in Western Sicily but were not allowed to due to Pope Gregory IX's demands. Any remaining Muslim was eventually expelled by the Spanish inquisition.
In more recent years, many immigrants from predominantly Muslim countries like Pakistan, Albania, Bangladesh, Morocco, Egypt, and Tunisia have arrived on Sicily. In 1980, Catania, a city on the eastern coast of Sicily, became home to Italy's first modern mosque. Also known as the Omar Mosque, it was financed by Libya.
Sicilian Jewish community
There is a legend that the Jews were first brought to Sicily as captive slaves in the 1st century after the Fall of Jerusalem, AD 70, Fall of Jerusalem in 70 CE by the Romans. However, it is generally presumed that Sicily's Jewish population was ceded before the destruction of the Temple of Jerusalem. Rabbi Akiva visited the city of Syracuse during one of his trips abroad. Judaism in Sicily was the first monotheistic religion to appear on the Island. The Jewish Sicilian community remained until the Aragonese rulers' Queen Isabella I of Castile and Ferdinand II of Aragon, expelled them in the year 1493 with the Alhambra Decree. On 3 February 1740, the Neapolitan Charles III of Spain, King Charles III – hailed as an Enlightenment King, issued a proclamation containing 37 paragraphs, in which Jews for the first time were formally invited to return to Sicily. However, the effort was generally unsuccessful.
The Sicilian Jewish community still has several active members and has made a limited recovery in recent years. In the year 2005, for the first time since the Expulsion, a Passover Seder was conducted in Sicily (in Palermo), held by a Milanese Rabbi. The Jewish community in Sicily is led in part by Rabbi Stefano Di Mauro, a Sicilian American descendant of Sicilian ''neofiti''. He opened a small synagogue in 2008, but he has not yet set up a full-time Jewish congregation in Sicily. Services are held weekly on Shabbat and the High Holy Days. Also, Shavei Israel has expressed interest in helping to facilitate the return of the Sicilian Bnei Anusim to Judaism.
Historically, Sicily has been home to many religions, including Islam, Native religions, Judaism, Classical antiquity, Classical Paganism, Punic religion, Carthaginian religions, and Eastern Orthodox Church, Byzantine Orthodoxy, the coexistence of which has been historically seen as an ideal example of religious multiculturalism. Most Sicilians today are baptized as Catholic. Catholicism and Liturgical Latinization, Latinization in Sicily originated from the islands Norman occupiers and forced conversion continued under the Spanish invaders, where the majority of Sicily's population were forced to convert from their former religions. Despite the historical push for Catholicism in Sicily, a minority of other religious communities thrive in Sicily.
Sicilian Catholics
For Catholics in Sicily, the Hodegetria, Virgin Hodegetria is the patroness of Sicily. The Sicilian people are also known for their deep devotion to some Sicilian female saints: the martyrs Agatha of Sicily, Agatha and Saint Lucy, Lucy, who are the patron saints of Catania and Syracuse respectively, and the hermit Saint Rosalia, patroness of Palermo. Sicilian people have significantly contributed to the history of many religions. There have been four Sicilian Popes (Pope Agatho, Agatho, Pope Leo II, Leo II, Pope Sergius I, Sergius I, and Pope Stephen III, Stephen III) and a Sicilian Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople (Methodios I of Constantinople, Methodios I). Sicily is also mentioned in the New Testament in the Acts of the Apostles, 28:11–13, in which Saint Paul briefly visits Sicily for three days before leaving the Island. It is believed he was the first Christian to ever set foot in Sicily.
Sicilian Muslims
During the Emirate of Sicily, period of Muslim rule, many Sicilians converted to Islam. Many Islamic scholars were born on the island, including Al-Maziri, a prominent jurist of the Maliki school of Sunni Islamic Law. Under the rule of Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor, Frederick II, all Muslims were expelled from the Island following a rebellion of local Saracens who wished to keep their local independence in Western Sicily but were not allowed to due to Pope Gregory IX's demands. Any remaining Muslim was eventually expelled by the Spanish inquisition.
In more recent years, many immigrants from predominantly Muslim countries like Pakistan, Albania, Bangladesh, Morocco, Egypt, and Tunisia have arrived on Sicily. In 1980, Catania, a city on the eastern coast of Sicily, became home to Italy's first modern mosque. Also known as the Omar Mosque, it was financed by Libya.
Sicilian Jewish community
There is a legend that the Jews were first brought to Sicily as captive slaves in the 1st century after the Fall of Jerusalem, AD 70, Fall of Jerusalem in 70 CE by the Romans. However, it is generally presumed that Sicily's Jewish population was ceded before the destruction of the Temple of Jerusalem. Rabbi Akiva visited the city of Syracuse during one of his trips abroad. Judaism in Sicily was the first monotheistic religion to appear on the Island. The Jewish Sicilian community remained until the Aragonese rulers' Queen Isabella I of Castile and Ferdinand II of Aragon, expelled them in the year 1493 with the Alhambra Decree. On 3 February 1740, the Neapolitan Charles III of Spain, King Charles III – hailed as an Enlightenment King, issued a proclamation containing 37 paragraphs, in which Jews for the first time were formally invited to return to Sicily. However, the effort was generally unsuccessful.
The Sicilian Jewish community still has several active members and has made a limited recovery in recent years. In the year 2005, for the first time since the Expulsion, a Passover Seder was conducted in Sicily (in Palermo), held by a Milanese Rabbi. The Jewish community in Sicily is led in part by Rabbi Stefano Di Mauro, a Sicilian American descendant of Sicilian ''neofiti''. He opened a small synagogue in 2008, but he has not yet set up a full-time Jewish congregation in Sicily. Services are held weekly on Shabbat and the High Holy Days. Also, Shavei Israel has expressed interest in helping to facilitate the return of the Sicilian Bnei Anusim to Judaism.
File:Bruno, Giuseppe (1836-1904) - Ragazzo siciliano - Da Artnet.jpg, Sicilian youth in traditional attire - c. 1890s
File:Sicilian monk (39322503152).jpg, Sicilian friar - 2012
File:Reprofotografi av bild från resealbum, i samband med utställningen Samtida venetianskt konstglas - Hallwylska museet - 87765.tif, Sicilian family - 1888
File:Il Carretto Siciliano - panoramio (1).jpg, Sicilian cart
File:Sicilian Collection (39362073261).jpg, Modern-day Sicilian men - 2012
File:Marco Castelli Captured at the Cannes Film Festival.jpg, Marco Castelli, Sicilian Model - 2021
File:Sergio Mattarella Presidente della Repubblica Italiana.jpg, Sergio Mattarella, President of Italy - 2021
File:Giorgio Avola teams 2014 CIP t132130.jpg, Giorgio Avola, Olympian Fencer - 2014
File:Bruno, Giuseppe (1836-1904) - n. 003.jpg, Sicilian man, c. 1890–1899
ethnographic group
An ethnographic group or ethnocultural group is a group that has cultural traits that make it stand out from the larger ethnic group it is a part of. In other words, members of an ethnographic group will also consider themselves to be members of a ...
who are indigenous to Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
, the largest island in the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
, as well as the largest and most populous of the autonomous regions of Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
.
History
The Sicilian people are indigenous to the island of Sicily, which was first populated beginning in thePaleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic ( years ago) ( ), also called the Old Stone Age (), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone tools, and which represents almost the entire period of human prehist ...
and Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
periods. According to the famous Italian historian Carlo Denina, the origin of the first inhabitants of Sicily is no less obscure than that of the first Italians; however, there is no doubt that a large part of these early individuals traveled to Sicily from Southern Italy
Southern Italy (, , or , ; ; ), also known as () or (; ; ; ), is a macroregion of Italy consisting of its southern Regions of Italy, regions.
The term "" today mostly refers to the regions that are associated with the people, lands or cultu ...
—others from the Islands of Greece
Greece has many islands, with estimates ranging from somewhere around 1,200 to 6,000, depending on the minimum size to take into account. The number of inhabited islands is variously cited as between 166 and 227.
The largest Greek island by ...
, and the coasts of Iberia
The Iberian Peninsula ( ), also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in south-western Europe. Mostly separated from the rest of the European landmass by the Pyrenees, it includes the territories of peninsular Spain and Continental Portugal, compri ...
and Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's extent varies depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the Western half of the ancient Mediterranean ...
.
Prehistory
The aboriginal inhabitants of Sicily, long absorbed into the population, were tribes known to the ancient Greek writers as theElymians
The Elymians () were an ancient tribe, tribal people who inhabited the western part of Sicily during the Bronze Age and Classical antiquity.
Origins
According to Thucydides, the Elymians were refugees coming from the destroyed Troy. Instead for ...
, the Sicanians, and the Sicels
The Sicels ( ; or ''Siculī'') were an Indo-European tribe who inhabited eastern Sicily, their namesake, during the Iron Age. They spoke the Siculian language. After the defeat of the Sicels at the Battle of Nomae in 450 BC and the death of ...
, the last being an Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the northern Indian subcontinent, most of Europe, and the Iranian plateau with additional native branches found in regions such as Sri Lanka, the Maldives, parts of Central Asia (e. ...
-speaking people of possible Italic affiliation, who migrated from the Italian mainland (likely from the Amalfi Coast
The Amalfi Coast ( or ) is a stretch of coastline in southern Italy overlooking the Tyrrhenian Sea and the Gulf of Salerno. It is located south of the Sorrentine Peninsula and north of the Cilentan Coast.
Attracting international tourists o ...
or Calabria
Calabria is a Regions of Italy, region in Southern Italy. It is a peninsula bordered by the region Basilicata to the north, the Ionian Sea to the east, the Strait of Messina to the southwest, which separates it from Sicily, and the Tyrrhenian S ...
via the Strait of Messina
The Strait of Messina (; ) is a narrow strait between the eastern tip of Sicily (Punta del Faro) and the western tip of Calabria (Punta Pezzo) in Southern Italy. It connects the Tyrrhenian Sea to the north with the Ionian Sea to the south, with ...
) during the second millennium BC, after whom the island was named. The Elymian tribes have been speculated to be a Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the northern Indian subcontinent, most of Europe, and the Iranian plateau with additional native branches found in regions such as Sri Lanka, the Maldives, parts of Central Asia (e. ...
people who migrated to Sicily from either Central Anatolia, Southern-Coastal Anatolia, Calabria, or one of the Aegean Islands, or perhaps were a collection of native migratory maritime-based tribes from all previously mentioned regions, and formed a common "Elymian" tribal identity/basis after settling down in Sicily. When the Elymians migrated to Sicily is unknown, however scholars of antiquity considered them to be the second oldest inhabitants, while the Sicanians, thought to be the oldest inhabitants of Sicily by scholars of antiquity, were speculated to also be a pre-Indo-European tribe, who migrated via boat
A boat is a watercraft of a large range of types and sizes, but generally smaller than a ship, which is distinguished by its larger size or capacity, its shape, or its ability to carry boats.
Small boats are typically used on inland waterways s ...
from the Xúquer river basin in Castellón, Cuenca, Valencia
Valencia ( , ), formally València (), is the capital of the Province of Valencia, province and Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Valencian Community, the same name in Spain. It is located on the banks of the Turia (r ...
and Alicante
Alicante (, , ; ; ; officially: ''/'' ) is a city and municipalities of Spain, municipality in the Valencian Community, Spain. It is the capital of the province of Alicante and a historic Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean port. The population ...
. Before the Sicanians lived in the easternmost part of the Iberian peninsula. The name 'Sicanus' has been asserted to have a possible link to the modern river known in Valencian Valencian can refer to:
* Something related to the Valencian Community ( Valencian Country) in Spain
* Something related to the city of Valencia
* Something related to the province of Valencia in Spain
* Something related to the old Kingdom of ...
as the Xúquer and in Castilian as the Júcar. The Beaker was introduced in Sicily from Sardinia and spread mainly in the north-west and south-west of the island. In the northwest and in the Palermo kept almost intact its cultural and social characteristics, while in the south-west there was a strong integration with local cultures. The only known single bell-shaped glass in eastern Sicily was found in Syracuse.The basic study is Joshua Whatmough in R.S. Conway, J. Whatmough and S.E. Johnson, ''The Prae-Italic Dialects of Italy'' (London 1933) vol. 2:431–500; a more recent study is A. Zamponi, "Il Siculo" in A.L. Prosdocimi, ed., ''Popoli e civiltà dell'Italia antica'', vol. 6 "Lingue e dialetti" (1978949-1012.)
pastoral
The pastoral genre of literature, art, or music depicts an idealised form of the shepherd's lifestyle – herding livestock around open areas of land according to the seasons and the changing availability of water and pasture. The target au ...
and orchard farming lifestyle, and a semi-nomadic fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment (Freshwater ecosystem, freshwater or Marine ecosystem, marine), but may also be caught from Fish stocking, stocked Body of water, ...
, transhumance
Transhumance is a type of pastoralism or Nomad, nomadism, a seasonal movement of livestock between fixed summer and winter pastures. In montane regions (''vertical transhumance''), it implies movement between higher pastures in summer and low ...
and mixed farming lifestyle. Prior to the Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution, also known as the First Agricultural Revolution, was the wide-scale transition of many human cultures during the Neolithic period in Afro-Eurasia from a lifestyle of hunter-gatherer, hunting and gathering to one of a ...
, Paleolithic Sicilians would have lived a hunter-gatherer
A hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living in a community, or according to an ancestrally derived Lifestyle, lifestyle, in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local naturally occurring sources, esp ...
lifestyle, just like most human cultures before the Neolithic. The river Salsu was the territorial boundary between the Sicels and Sicanians. They wore basic clothing made of wool
Wool is the textile fiber obtained from sheep and other mammals, especially goats, rabbits, and camelids. The term may also refer to inorganic materials, such as mineral wool and glass wool, that have some properties similar to animal w ...
, plant fibre, papyrus
Papyrus ( ) is a material similar to thick paper that was used in ancient times as a writing surface. It was made from the pith of the papyrus plant, ''Cyperus papyrus'', a wetland sedge. ''Papyrus'' (plural: ''papyri'' or ''papyruses'') can a ...
, esparto grass, animal skins, palm leaves, leather
Leather is a strong, flexible and durable material obtained from the tanning (leather), tanning, or chemical treatment, of animal skins and hides to prevent decay. The most common leathers come from cattle, sheep, goats, equine animals, buffal ...
and fur
A fur is a soft, thick growth of hair that covers the skin of almost all mammals. It consists of a combination of oily guard hair on top and thick underfur beneath. The guard hair keeps moisture from reaching the skin; the underfur acts as an ...
, and created everyday tools
A tool is an object that can extend an individual's ability to modify features of the surrounding environment or help them accomplish a particular task. Although many animals use simple tools, only human beings, whose use of stone tools dates ...
, as well as weapons
A weapon, arm, or armament is any implement or device that is used to deter, threaten, inflict physical damage, harm, or kill. Weapons are used to increase the efficacy and efficiency of activities such as hunting, crime (e.g., murder), law ...
, using metal forging, woodworking
Woodworking is the skill of making items from wood, and includes cabinetry, furniture making, wood carving, joinery, carpentry, and woodturning.
History
Along with stone, clay and animal parts, wood was one of the first materials worked b ...
and pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other raw materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. The place where such wares are made by a ''potter'' is al ...
. They typically lived in a nuclear family
A nuclear family (also known as an elementary family, atomic family, or conjugal family) is a term for a family group consisting of parents and their children (one or more), typically living in one home residence. It is in contrast to a single ...
unit, with some extended family
An extended family is a family that extends beyond the nuclear family of parents and their children to include aunts, uncles, grandparents, cousins or other relatives, all living nearby or in the same household. Particular forms include the stem ...
members as well, usually within a drystone hut, a neolithic long house or a simple hut made of mud, stones, wood, palm leaves or grass. Their main methods of transportation were horseback, donkeys and chariots. Evidence of pet wildcats, cirneco dogs and children's toys Children's toys and games may refer to:
* Boys' toys and games
* Girls' toys and games
* Toys and games in ancient Rome
See also
* List of children's games
* List of toys
{{disambiguation ...
have been discovered in archaeological digs, especially in cemetery tombs. Their diet was a typical Mediterranean diet
The Mediterranean diet is a concept first proposed in 1975 by the American biologist Ancel Keys and chemist Margaret Keys. The diet took inspiration from the eating habits and traditional food typical of Crete, much of the rest of Greece, and s ...
, including unique food varieties such as Gaglioppo, Acitana and Diamante citron, while in modern times the Calabrian Salami, which is also produced in Sicily, and sometimes used to make spicy 'Nduja spreadable paste/sauce, is a popular type of salami sold in Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
and the Anglosphere
The Anglosphere, also known as the Anglo-American world, is a Western-led sphere of influence among the Anglophone countries. The core group of this sphere of influence comprises five developed countries that maintain close social, cultura ...
. All 3 tribes also specialised in building megalith
A megalith is a large stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. More than 35,000 megalithic structures have been identified across Europe, ranging geographically f ...
ic single-chambered dolmen tombs, a tradition which dates back to the Neolithic. "An important archaeological site, located in Southeast Sicily, is the Necropolis of Pantalica
The Necropolis of Pantalica is a collection of cemeteries with rock-cut chamber tombs in southeast Sicily, Italy. Dating from the 13th to the 7th centuries BC, there was thought to be over 5,000 tombs, although the most recent estimate suggests ...
, a collection of cemeteries with rock-cut chamber tombs. Dating
Dating is a stage of Romance (love), romantic relationships in which individuals engage in activity together, often with the intention of evaluating each other's suitability as a partner in a future intimate relationship. It falls into the cate ...
from the 13th to the 7th centuries BC., recent estimates suggest a figure of just under 4,000 tombs. They extend around the flanks of a large promontory located at the junction of the Anapo river with its tributary, the Calcinara
The Calcinara is a river in southeastern Sicily in Italy. It flows into the Anapo near the archaeological site of Pantalica
The Necropolis of Pantalica is a collection of cemeteries with rock-cut chamber tombs in southeast Sicily, Italy. Dating ...
, about 23 km (14 mi) northwest of Syracuse
Syracuse most commonly refers to:
* Syracuse, Sicily, Italy; in the province of Syracuse
* Syracuse, New York, USA; in the Syracuse metropolitan area
Syracuse may also refer to:
Places
* Syracuse railway station (disambiguation)
Italy
* Provi ...
. Together with the city of Syracuse, Pantalica was listed as a UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
World Heritage Site in 2005. The site was mainly excavated between 1895 and 1910 by the Italian archeologist, Paolo Orsi
Paolo Orsi (Rovereto, October 17, 1859 – November 8, 1935) was an Italian archaeologist and classicist.
Life
Orsi was born in Rovereto, then part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire and now in the province of Trento in Italy. After studying at a gy ...
, although most of the tombs had already been looted long before his time. Items found within the tombs of Pantalica, some now on display at the Archaeology Museum in Syracuse, were the characteristic red-burnished pottery vessels, and metal objects, including weaponry (small knives and daggers) and clothing, such as bronze fibulae (brooches) and rings, which were placed with the deceased in the tombs. Most of the tombs contained between one and seven individuals of all ages and both sexes. Many tombs were evidently re-opened periodically for more burials. The average human life span at this time was probably around 30 years of age, although the size of the prehistoric population is hard to estimate from the available data, but might have been around 1000 people."
Nuragic
The nuraghe, or nurhag, is the main type of ancient megalithic edifice found in Sardinia, Italy, developed during the Nuragic Age between 1900 and 730 BC. Today it has come to be the symbol of Sardinia and its distinctive culture known a ...
ceramic remains, (from Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; ; ) is the Mediterranean islands#By area, second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, and one of the Regions of Italy, twenty regions of Italy. It is located west of the Italian Peninsula, north of Tunisia an ...
), carbon dated to the 13th century BC, have been found in Lipari
Lipari (; ) is a ''comune'' including six of seven islands of the Aeolian Islands (Lipari, Vulcano, Panarea, Stromboli, Filicudi and Alicudi) and it is located in the Tyrrhenian Sea off the northern coast of Sicily, Southern Italy; it is ...
. The prehistoric Thapsos culture, associated with the Sicani, shows noticeable influences from Mycenaean Greece
Mycenaean Greece (or the Mycenaean civilization) was the last phase of the Bronze Age in ancient Greece, spanning the period from approximately 1750 to 1050 BC.. It represents the first advanced and distinctively Greek civilization in mainla ...
.''Pantalica e i suoi monumenti'' di Paolo Orsi The type of burial found in the necropolis
A necropolis (: necropolises, necropoles, necropoleis, necropoli) is a large, designed cemetery with elaborate tomb monuments. The name stems from the Ancient Greek ''nekropolis'' ().
The term usually implies a separate burial site at a distan ...
of the Thapsos culture, is characterized by large rock-cut chamber tombs, and often of ''tholos-type'' that some scholars believe to be of Mycenaean derivation, while others believe it to be the traditional shape of the hut. The housing are made up of mostly circular huts bounded by stone walls, mainly in small numbers. Some huts have rectangular shape, particularly the roof. The economy was based on farming, herding, hunting and fishing. There are numerous evidences of trading networks, in particular of bronze vessels and weapons of Mycenaean and Nuragic (Sardinian) production. There were close trading relationships/networks established with the ''Milazzo Culture'' of the Aeolian Islands
The Aeolian Islands ( ; ; ), sometimes referred to as the Lipari Islands or Lipari group ( , ) after their largest island, are a volcanic archipelago in the Tyrrhenian Sea north of Sicily, said to be named after Aeolus, the mythical ruler of ...
, and with the Apennine culture
The Apennine culture is a technology complex in central and southern Italy from the Italian Middle Bronze Age (15th–14th centuries BC). In the mid-20th century the Apennine was divided into Proto-, Early, Middle and Late , but now archaeolog ...
of mainland southern Italy. In Sicily's earlier prehistory
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use ...
, there is also evidence of trade with the Capsian and Iberomaurusian
The Iberomaurusian is a backed bladelet lithic industry found near the coasts of Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia. It is also known from a single major site in Libya, the Haua Fteah, where the industry is known as the Eastern Oranian.The "Weste ...
mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Ancient Greek language, Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic i ...
cultures from Tunisia
Tunisia, officially the Republic of Tunisia, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered by Algeria to the west and southwest, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Tunisia also shares m ...
, with some lithic stone sites attested in certain parts of the island.2005 D. Lubell. Continuité et changement dans l'Epipaléolithique du Maghreb. In, M. Sahnouni (ed.) ''Le Paléolithique en Afrique: l’histoire la plus longue'', pp. 205–226. Paris: Guides de la Préhistoire Mondiale, Éditions Artcom’/Errance.2004 N. RahmaniTechnological and cultural change among the last Hunter-Gatherers of the Maghreb: the Capsian (10,000 B.P. to 6000 B.P.)
''Journal of World Prehistory'' 18(1): 57–105. Another archaeological site, originally identified by
Paolo Orsi
Paolo Orsi (Rovereto, October 17, 1859 – November 8, 1935) was an Italian archaeologist and classicist.
Life
Orsi was born in Rovereto, then part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire and now in the province of Trento in Italy. After studying at a gy ...
on the basis of a particular ceramic style, is the Castelluccio culture
Castelluccio culture is an archaeological feature dating to Ancient Bronze Age (2000 B.C. approximately) of the prehistoric civilization of Sicily, originally identified by Paolo Orsi on the basis of a particular ceramic style, in the homonymous v ...
which dates back to the Ancient Bronze Age (2000 B.C. approximately), and is seen as sort of a "prehistoric proto-civilization", located between Noto
Noto (; ) is a city and in the Province of Syracuse, Sicily, Italy. It is southwest of the city of Syracuse at the foot of the Iblean Mountains. It lends its name to the surrounding area Val di Noto. In 2002 Noto and its church were decl ...
and Siracusa. The discovery of a prehistoric village in Castelluccio di Noto, next to the remains of prehistoric circular huts, led to finds of Ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant, and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcela ...
glass
Glass is an amorphous (non-crystalline solid, non-crystalline) solid. Because it is often transparency and translucency, transparent and chemically inert, glass has found widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in window pane ...
decorated with brown lines on a yellow-reddish background, and tri-color with the use of white. The weapons used in the days of Castelluccio culture were green stone and basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial ...
axes and, in the most recent settlements, bronze axes, and frequently carved bones, considered idols similar to those of Malta
Malta, officially the Republic of Malta, is an island country in Southern Europe located in the Mediterranean Sea, between Sicily and North Africa. It consists of an archipelago south of Italy, east of Tunisia, and north of Libya. The two ...
, and of Troy II and III. Burials were made in rounded tombs carved into the rock, with doors with relief carving of spiral symbols and motifs that evoke the sexual act. The Castelluccio culture is dated to a period between 2200 BC and 1800 BC, although some believe it to be contemporary to the Middle-Late Helladic period
Helladic chronology is a relative dating system used in archaeology and art history. It complements the Minoan chronology scheme devised by Sir Arthur Evans for the categorisation of Bronze Age artefacts from the Minoan civilization within a his ...
(1800/1400 BC)." "Sites related to the Castelluccio culture were present in the villages of south-east Sicily, including Monte Casale
Monte Casale is a mountainous elevation on Sicily in Italy, reaching 910m above sea level, which (with the neighbouring Monte Lauro) formed part of the oldest volcanic formation of the Hyblaean Mountains. Their peaks form the boundary between ...
, Cava/Quarry d'Ispica, Pachino
Pachino (; ) is a town and ''comune'' in the Province of Syracuse, Sicily (Italy). The name derives from the Latin word ''bacchus,'' which is the Roman god of wine, and the word ''vinum'', which means wine in Latin; originally the town was name ...
, Niscemi
Niscemi is a little town and ''comune'' in the province of Caltanissetta, Sicily, Italy. It has a population of 27,558. It is located not far from Gela and Caltagirone and 90 km from Catania.
Etymology
The name Niscemi is derived from the ...
, Cava/Quarry Lazzaro, near Noto
Noto (; ) is a city and in the Province of Syracuse, Sicily, Italy. It is southwest of the city of Syracuse at the foot of the Iblean Mountains. It lends its name to the surrounding area Val di Noto. In 2002 Noto and its church were decl ...
, of Rosolini
Rosolini () is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Syracuse,
Sicily, southern Italy. It is about southeast of Palermo and about southwest of Syracuse, Italy, Syracuse. Rosolini was a town in feudal times, and was a settlement in th ...
, in the rocky Byzantine district of coastal Santa Febronia in Palagonia
Palagonia ( Sicilian: ''Palaunìa'', Latin: ''Palica'') is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Catania in the Italian region Sicily, located about southeast of Palermo and about southwest of Catania. Palagonia borders the f ...
, in Cuddaru d' Crastu (Tornabé-Mercato d'Arrigo) near Pietraperzia
Pietraperzia ( Sicilian: ''Petrapirzia'') is a ''comune'' in the province of Enna, in Sicilian region of southern Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe ...
, where there are remains of a fortress partly carved in stone, and – with different ceramic forms – also near Agrigento
Agrigento (; or ) is a city on the southern coast of Sicily, Italy and capital of the province of Agrigento.
Founded around 582 BC by Greek colonists from Gela, Agrigento, then known as Akragas, was one of the leading cities during the golden ...
in Monte Grande
Monte Grande is a city which forms part of the urban agglomeration of Greater Buenos Aires. It is the administrative seat of Esteban Echeverría Partido in Buenos Aires Province, Argentina.
It was founded in 1824 as an agricultural colony. The ...
. The discovery of a cup of 'Etna type' in the area of Comiso
Comiso () is a ''comune'' of the Province of Ragusa, Sicily, Southern Italy. As of 2017, its population was 29,857.
History
In the past Comiso has been incorrectly identified with the ancient Greek colony of Casmene in Magna Graecia.
Under the B ...
, among local ceramic objects led to the discovery of commercial trades with the Castelluccio sites of Paternò
Paternò () is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Catania, in the Italy, Italian region of Sicily. With a population (2016) of 48,009, it is the third municipality of the province after Catania and Acireale.
Geography
Pa ...
, Adrano
Adrano (; Adernò until 1929; ), ancient '' Adranon'', is a town and in the Metropolitan City of Catania on the east coast of Sicily.
It is situated around northwest of Catania, which was also the capital of the province to which Adrano belo ...
and Biancavilla
Biancavilla () is a town and ''comune'' in the Metropolitan City of Catania, Sicily, southern Italy. It is located between the towns of Adrano and S. Maria di Licodia, northwest of Catania. The town was founded and historically inhabited by th ...
, whose graves differ in making due to the hard basaltic terrain and also for the utilization of the lava cave
A lava cave is any cave formed in volcanic rock, though it typically means caves formed by volcanic processes, which are more properly termed volcanic caves. Sea caves, and other sorts of erosional and crevice caves, may be formed in volcanic rock ...
s as chamber tombs. In the area around Ragusa Ragusa may refer to:
Places Croatia
* Ragusa, Dalmatia, the historical name of the city of Dubrovnik
* the Republic of Ragusa (or Republic of Dubrovnik), the maritime city-state of Ragusa
* Ragusa Vecchia, historical Italian name of Cavtat, a t ...
, there have been found evidences of mining among the ancient residents of Castelluccio; tunnels excavated by the use of basalt bats allowed the extraction and production of highly sought flint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Historically, flint was widely used to make stone tools and start ...
s. Some dolmens
A dolmen, () or portal tomb, is a type of single-chamber megalithic tomb, usually consisting of two or more upright megaliths supporting a large flat horizontal capstone or "table". Most date from the Late Neolithic period (40003000 BCE) and w ...
, dated back to this same period, with sole funeral function, are found in different parts of Sicily and attributable to a people not belonging to the Castelluccio Culture."
The Sicelian polytheistic
Polytheism is the belief in or worship of more than one Deity, god. According to Oxford Reference, it is not easy to count gods, and so not always obvious whether an apparently polytheistic religion, such as Chinese folk religions, is really so, ...
worship of the ancient and native chthonic
In Greek mythology, deities referred to as chthonic () or chthonian () were gods or spirits who inhabited the underworld or existed in or under the earth, and were typically associated with death or fertility. The terms "chthonic" and "chthonian" ...
, animistic
Animism (from meaning 'breath, Soul, spirit, life') is the belief that objects, places, and creatures all possess a distinct Spirituality, spiritual essence. Animism perceives all things—animals, plants, Rock (geology), rocks, rivers, Weather, ...
-cult deities associated with geysers known as the Palici, as well as the worship of the volcano-fire god by the name of Adranos
Adranus or Adranos () was a fire god worshipped by the Sicels, an ancient population of the island of Sicily. His worship occurred all over the island, but particularly in the town of Adranus, modern Adrano, near Mount Etna. According to Aelian, ...
, were also worshiped throughout Sicily by the Elymians and Sicanians. Their (Palici) centre of worship was originally based on three small lakes that emitted sulphur
Sulfur (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphur (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth spelling) is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundance of the chemical ...
ous vapors in the Palagonia
Palagonia ( Sicilian: ''Palaunìa'', Latin: ''Palica'') is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Catania in the Italian region Sicily, located about southeast of Palermo and about southwest of Catania. Palagonia borders the f ...
n plains, and as a result these twin brothers were associated with geysers and the underworld
The underworld, also known as the netherworld or hell, is the supernatural world of the dead in various religious traditions and myths, located below the world of the living. Chthonic is the technical adjective for things of the underworld.
...
. There was also a shrine to the Palici in Palacia, where people could subject themselves or others to tests of reliability through divine judgement; passing meant that an oath could be trusted. The mythological lineage of the Palici is uncertain. According to Macrobius
Macrobius Ambrosius Theodosius, usually referred to as Macrobius (fl. AD 400), was a Roman provincial who lived during the early fifth century, during late antiquity, the period of time corresponding to the Later Roman Empire, and when Latin was ...
, the nymph Thalia gave birth to the divine twins while living underneath the Earth. They were most likely either the sons of the native fire god Adranos, or, as Polish historian "Krzysztof Tomasz Witczak" suggests, the Palici may derive from the old Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. No direct record of Proto-Indo-European exists; its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-Euro ...
mytheme
In structuralism-influenced studies of mythology, a mytheme is a fundamental generic unit of narrative structure (typically involving a relationship between a character, an event, and a theme) from which myths are thought to be constructed—a m ...
of the divine twins
The Divine Twins are youthful horsemen, either gods or demigods, who serve as rescuers and healers in Proto-Indo-European mythology.
Like other Proto-Indo-European divinities, the Divine Twins are not directly attested by archaeological or writte ...
. Mount Etna
Mount Etna, or simply Etna ( or ; , or ; ; or ), is an active stratovolcano on the east coast of Sicily, Italy, in the Metropolitan City of Catania, between the cities of Messina, Italy, Messina and Catania. It is located above the Conve ...
is named after the mythological
Myth is a genre of folklore consisting primarily of narratives that play a fundamental role in a society. For scholars, this is very different from the vernacular usage of the term "myth" that refers to a belief that is not true. Instead, the ...
Sicilian nymph
A nymph (; ; sometimes spelled nymphe) is a minor female nature deity in ancient Greek folklore. Distinct from other Greek goddesses, nymphs are generally regarded as personifications of nature; they are typically tied to a specific place, land ...
called Aetna
Aetna Inc. ( ) is an American managed health care company that sells traditional and consumer directed health care insurance and related services, such as medical, pharmaceutical, dental, behavioral health, long-term care, and disability plans, ...
, who might have been the possible mother to the Palici twins. Mount Etna was also believed to have been the region where Zeus
Zeus (, ) is the chief deity of the List of Greek deities, Greek pantheon. He is a sky father, sky and thunder god in ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, who rules as king of the gods on Mount Olympus.
Zeus is the child ...
buried the Serpentine giant Typhon
Typhon (; , ), also Typhoeus (; ), Typhaon () or Typhos (), was a monstrous serpentine giant and one of the deadliest creatures in Greek mythology. According to Hesiod, Typhon was the son of Gaia and Tartarus. However, one source has Typhon as t ...
, and the humanoid giant Enceladus
Enceladus is the sixth-largest moon of Saturn and the 18th-largest in the Solar System. It is about in diameter, about a tenth of that of Saturn's largest moon, Titan. It is covered by clean, freshly deposited snow hundreds of meters thick, ...
in classical mythology. The Cyclopes
In Greek mythology and later Roman mythology, the Cyclopes ( ; , ''Kýklōpes'', "Circle-eyes" or "Round-eyes"; singular Cyclops ; , ''Kýklōps'') are giant one-eyed creatures. Three groups of Cyclopes can be distinguished. In Hesiod's ''The ...
, giant one-eyed humanoid creatures in classical Greco-Roman mythology, known as the maker of Zeus' thunderbolts, were traditionally associated with Sicily and the Aeolian Islands
The Aeolian Islands ( ; ; ), sometimes referred to as the Lipari Islands or Lipari group ( , ) after their largest island, are a volcanic archipelago in the Tyrrhenian Sea north of Sicily, said to be named after Aeolus, the mythical ruler of ...
. The Cyclopes were said to have been assistants to the Greek blacksmith God Hephaestus
Hephaestus ( , ; wikt:Hephaestus#Alternative forms, eight spellings; ) is the Greek god of artisans, blacksmiths, carpenters, craftsmen, fire, metallurgy, metalworking, sculpture and volcanoes.Walter Burkert, ''Greek Religion'' 1985: III.2. ...
, at his forge in Sicily, underneath Mount Etna, or perhaps on one of the nearby Aeolian Islands. The Aeolian Islands, off the coast of Northwestern Sicily, were themselves named after the mythological king and "keeper of the heavy winds" known as Aeolus
In Greek mythology, Aiolos, transcribed as Aeolus (; ; ) refers to three characters. These three are often difficult to tell apart, and even the ancient mythographers appear to have been perplexed about which Aeolus was which. Diodorus Siculus m ...
. In his ''Hymn to Artemis
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, Artemis (; ) is the goddess of the hunting, hunt, the wilderness, wild animals, transitions, nature, vegetation, childbirth, Kourotrophos, care of children, and chastity. In later tim ...
'', Cyrene poet Callimachus
Callimachus (; ; ) was an ancient Greek poet, scholar, and librarian who was active in Alexandria during the 3rd century BC. A representative of Ancient Greek literature of the Hellenistic period, he wrote over 800 literary works, most of which ...
states that the Cyclopes on the Aeolian island of Lipari
Lipari (; ) is a ''comune'' including six of seven islands of the Aeolian Islands (Lipari, Vulcano, Panarea, Stromboli, Filicudi and Alicudi) and it is located in the Tyrrhenian Sea off the northern coast of Sicily, Southern Italy; it is ...
, working "at the anvils of Hephaestus
Hephaestus ( , ; wikt:Hephaestus#Alternative forms, eight spellings; ) is the Greek god of artisans, blacksmiths, carpenters, craftsmen, fire, metallurgy, metalworking, sculpture and volcanoes.Walter Burkert, ''Greek Religion'' 1985: III.2. ...
", make the bows and arrows used by Apollo
Apollo is one of the Twelve Olympians, Olympian deities in Ancient Greek religion, ancient Greek and Ancient Roman religion, Roman religion and Greek mythology, Greek and Roman mythology. Apollo has been recognized as a god of archery, mu ...
and Artemis
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, Artemis (; ) is the goddess of the hunting, hunt, the wilderness, wild animals, transitions, nature, vegetation, childbirth, Kourotrophos, care of children, and chastity. In later tim ...
. The Hesiod
Hesiod ( or ; ''Hēsíodos''; ) was an ancient Greece, Greek poet generally thought to have been active between 750 and 650 BC, around the same time as Homer.M. L. West, ''Hesiod: Theogony'', Oxford University Press (1966), p. 40.Jasper Gr ...
ic Latin poet Ovid
Publius Ovidius Naso (; 20 March 43 BC – AD 17/18), known in English as Ovid ( ), was a Augustan literature (ancient Rome), Roman poet who lived during the reign of Augustus. He was a younger contemporary of Virgil and Horace, with whom he i ...
names three Cyclopes "Brontes, Steropes and Acmonides" working as forge
A forge is a type of hearth used for heating metals, or the workplace (smithy) where such a hearth is located. The forge is used by the smith to heat a piece of metal to a temperature at which it becomes easier to shape by forging, or to the ...
rs inside Sicilian caves.
Besides Demeter
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, Demeter (; Attic Greek, Attic: ''Dēmḗtēr'' ; Doric Greek, Doric: ''Dāmā́tēr'') is the Twelve Olympians, Olympian goddess of the harvest and agriculture, presiding over cro ...
(the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
goddess of agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
and law
Law is a set of rules that are created and are enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior, with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. It has been variously described as a science and as the ar ...
), and Persephone
In ancient Greek mythology and Ancient Greek religion, religion, Persephone ( ; , classical pronunciation: ), also called Kore ( ; ) or Cora, is the daughter of Zeus and Demeter. She became the queen of the Greek underworld, underworld afte ...
(the Greek personified
Personification is the representation of a thing or abstraction as a person, often as an embodiment or incarnation. In the arts, many things are commonly personified, including: places, especially cities, countries, and continents; elements of ...
goddess of vegetation
Vegetation is an assemblage of plants and the ground cover they provide. It is a general term, without specific reference to particular Taxon, taxa, life forms, structure, Spatial ecology, spatial extent, or any other specific Botany, botanic ...
), The Phoenicia
Phoenicians were an Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient Semitic group of people who lived in the Phoenician city-states along a coastal strip in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily modern Lebanon and the Syria, Syrian ...
n bull god Moloch
Moloch, Molech, or Molek is a word which appears in the Hebrew Bible several times, primarily in the Book of Leviticus. The Greek Septuagint translates many of these instances as "their king", but maintains the word or name ''Moloch'' in others, ...
(a significant deity also mentioned in the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
. '' moon goddess A lunar deity or moon deity is a deity who represents the Moon, or an aspect of it. These deities can have a variety of functions and traditions depending upon the culture, but they are often related. Lunar deities and Moon worship can be foun ...
of . '' moon goddess A lunar deity or moon deity is a deity who represents the Moon, or an aspect of it. These deities can have a variety of functions and traditions depending upon the culture, but they are often related. Lunar deities and Moon worship can be foun ...
fertility
Fertility in colloquial terms refers the ability to have offspring. In demographic contexts, fertility refers to the actual production of offspring, rather than the physical capability to reproduce, which is termed fecundity. The fertility rate ...
and prosperity
Prosperity is the flourishing, thriving, good fortune and successful social status. Prosperity often produces profuse wealth including other factors which can be profusely wealthy in all degrees, such as happiness and health.
Competing notions ...
Astarte
Astarte (; , ) is the Greek language, Hellenized form of the Religions of the ancient Near East, Ancient Near Eastern goddess ʿAṯtart. ʿAṯtart was the Northwest Semitic languages, Northwest Semitic equivalent of the East Semitic language ...
(with her Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
equivalent being Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is often called Earth's "twin" or "sister" planet for having almost the same size and mass, and the closest orbit to Earth's. While both are rocky planets, Venus has an atmosphere much thicker ...
), the Punic
The Punic people, usually known as the Carthaginians (and sometimes as Western Phoenicians), were a Semitic people who migrated from Phoenicia to the Western Mediterranean during the Early Iron Age. In modern scholarship, the term ''Punic'' ...
goddess Tanit
Tanit or Tinnit (Punic language, Punic: 𐤕𐤍𐤕 ''Tīnnīt'' (JStor)) was a chief deity of Ancient Carthage; she derives from a local Berber deity and the consort of Baal Hammon. As Ammon is a local Libyan deity, so is Tannit, who represents ...
, and the weather
Weather is the state of the atmosphere, describing for example the degree to which it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloud cover, cloudy. On Earth, most weather phenomena occur in the lowest layer of the planet's atmo ...
& war god
A war god in mythology associated with war, combat, or bloodshed. They occur commonly in polytheistic religions.
Unlike most gods and goddesses in polytheistic religions, monotheistic deities have traditionally been portrayed in their mythologies ...
Baal
Baal (), or Baʻal, was a title and honorific meaning 'owner' or 'lord
Lord is an appellation for a person or deity who has authority, control, or power (social and political), power over others, acting as a master, chief, or ruler. The ...
(which later evolved into the Carthaginian The term Carthaginian ( ) usually refers to the civilisation of ancient Carthage.
It may also refer to:
* Punic people, the Semitic-speaking people of Carthage
* Punic language
The Punic language, also called Phoenicio-Punic or Carthaginian, i ...
god Baal Hammon
Baal Hammon, properly Baʿal Ḥamon ( Phoenician and ), meaning "Lord Hammon", was the chief god of ancient Carthage. He was a weather god considered responsible for the fertility of vegetation and esteemed as king of the gods. He was depicte ...
), as well as the Carthaginian chief god Baal Hammon, also had centres of cultic-worship throughout Sicily. The river Anapus was viewed as the personification of the river god Anapus
In Greek mythology, Anapus () was god of the river Anapus in eastern Sicily.''Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography'', vol. I, p. 130 ("Anapus"). He was worshiped by the Syracusans, who depicted him as a young man. Anapus was husband to the ...
in Greek-Sicilian mythology. The Elymians inhabited the western parts of Sicily, while the Sicanians inhabited the central parts, and the Sicels inhabited the eastern
Eastern or Easterns may refer to:
Transportation
Airlines
*China Eastern Airlines, a current Chinese airline based in Shanghai
* Eastern Air, former name of Zambia Skyways
*Eastern Air Lines, a defunct American airline that operated from 192 ...
parts.
Ancient history
From the 11th century BC,Phoenicians
Phoenicians were an ancient Semitic group of people who lived in the Phoenician city-states along a coastal strip in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily modern Lebanon and the Syrian coast. They developed a maritime civi ...
began to settle in western Sicily, having already started colonies on the nearby parts of North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of t ...
and Malta
Malta, officially the Republic of Malta, is an island country in Southern Europe located in the Mediterranean Sea, between Sicily and North Africa. It consists of an archipelago south of Italy, east of Tunisia, and north of Libya. The two ...
. Sicily was later colonized and heavily settled by Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
, beginning in the 8th century BC. Initially, this was restricted to the eastern
Eastern or Easterns may refer to:
Transportation
Airlines
*China Eastern Airlines, a current Chinese airline based in Shanghai
* Eastern Air, former name of Zambia Skyways
*Eastern Air Lines, a defunct American airline that operated from 192 ...
and southern parts of the island. As the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
and Phoenician communities grew more populous and more powerful, the Sicels and Sicanians were pushed further into the centre of the island. The independent Phoenician colonial settlements were eventually absorbed by Carthage
Carthage was an ancient city in Northern Africa, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classic ...
during the 6th century BC. By the 3rd century BC, Syracuse
Syracuse most commonly refers to:
* Syracuse, Sicily, Italy; in the province of Syracuse
* Syracuse, New York, USA; in the Syracuse metropolitan area
Syracuse may also refer to:
Places
* Syracuse railway station (disambiguation)
Italy
* Provi ...
was the most populous Greek city state in the world. Sicilian politics was intertwined with politics in Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
itself, leading Athens
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
, for example, to mount the disastrous Sicilian Expedition
The Sicilian Expedition was an Classical Athens, Athenian military expedition to Sicily, which took place from 415–413 BC during the Peloponnesian War between Classical Athens, Athens on one side and Sparta, Syracuse, Sicily, Syracuse and Co ...
against Syracuse in 415–413 BC during the Peloponnesian War
The Second Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), often called simply the Peloponnesian War (), was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek war fought between Classical Athens, Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Ancien ...
, which ended up severely affecting a defeated Athens, both politically and economically, in the following years to come. Another battle which Syracuse took part in, this time under the Tyrant Hiero I of Syracuse
Hiero I (; also Hieron ; ) was the son of Deinomenes, the brother of Gelon and tyrant of Syracuse in Sicily, from 478 to 467 BC. In succeeding Gelon, he conspired against a third brother, Polyzelos.
Life
During his reign, he greatly increased ...
, was the Battle of Cumae
The Battle of Cumae is the name given to at least two battles between Cumae and the Etruscans:
* In 524 BC an invading army of Umbrians, Daunians, Etruscans, and others were defeated by the Greeks of Cumae.
* The naval battle in 474 BC was be ...
, where the combined navies
A navy, naval force, military maritime fleet, war navy, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operation ...
of Syracuse and Cumae
Cumae ( or or ; ) was the first ancient Greek colony of Magna Graecia on the mainland of Italy and was founded by settlers from Euboea in the 8th century BCE. It became a rich Roman city, the remains of which lie near the modern village of ...
defeated an Etruscan force, resulting in significant territorial loses for the Etruscans. The constant warfare between Ancient Carthage
Ancient Carthage ( ; , ) was an Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient Semitic civilisation based in North Africa. Initially a settlement in present-day Tunisia, it later became a city-state, and then an empire. Founded by the Phoenicians ...
and the Greek city-states
Polis (: poleis) means 'city' in Ancient Greek. The ancient word ''polis'' had socio-political connotations not possessed by modern usage. For example, Modern Greek πόλη (polē) is located within a (''khôra''), "country", which is a πατ ...
eventually opened the door to an emerging third power
In arithmetic and algebra, the cube of a number is its third power, that is, the result of multiplying three instances of together.
The cube of a number is denoted , using a superscript 3, for example . The cube operation can also be defi ...
. In the 3rd century BC, the Messanan Crisis, caused by Mamertine mercenaries
A mercenary is a private individual who joins an War, armed conflict for personal profit, is otherwise an outsider to the conflict, and is not a member of any other official military. Mercenaries fight for money or other forms of payment rath ...
from Campania
Campania is an administrative Regions of Italy, region of Italy located in Southern Italy; most of it is in the south-western portion of the Italian Peninsula (with the Tyrrhenian Sea to its west), but it also includes the small Phlegraean Islan ...
, when the city-states of Messina
Messina ( , ; ; ; ) is a harbour city and the capital city, capital of the Italian Metropolitan City of Messina. It is the third largest city on the island of Sicily, and the 13th largest city in Italy, with a population of 216,918 inhabitants ...
( Carthaginian-owned) and Syracuse
Syracuse most commonly refers to:
* Syracuse, Sicily, Italy; in the province of Syracuse
* Syracuse, New York, USA; in the Syracuse metropolitan area
Syracuse may also refer to:
Places
* Syracuse railway station (disambiguation)
Italy
* Provi ...
( Dorian-owned) were being constantly raided and pillaged by Mamertines
The Mamertines (, "sons of Mars", ) were mercenaries of Italian origin who had been hired from their home in Campania by Agathocles (361–289 BC), Tyrant of Syracuse and self-proclaimed King of Sicily. After Syracuse lost the Seventh Sicilia ...
, during the period (282–240 BC) when Central, Western and Northeast Sicily were put under Carthaginian rule, motivated the intervention of the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establis ...
into Sicilian affairs, and led to the First Punic War
The First Punic War (264–241 BC) was the first of three wars fought between Rome and Carthage, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the early 3rd century BC. For 23 years, in the longest continuous conflict and grea ...
between Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
and Carthage
Carthage was an ancient city in Northern Africa, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classic ...
. By the end of the war
War is an armed conflict between the armed forces of states, or between governmental forces and armed groups that are organized under a certain command structure and have the capacity to sustain military operations, or between such organi ...
in 242 BC, and with the death of Hiero II
Hiero II (; also Hieron ; ; c. 308 BC – 215 BC) was the Greek tyrant of Syracuse, Greek Sicily, from 275 to 215 BC, and the illegitimate son of a Syracusan noble, Hierocles, who claimed descent from Gelon. He was a former general of Pyrrhus o ...
, all of Sicily except Syracuse was in Roman hands, becoming Rome's first province outside of the Italian peninsula. For the next 600 years, Sicily would be a province of the Roman Republic and later Empire
An empire is a political unit made up of several territories, military outpost (military), outposts, and peoples, "usually created by conquest, and divided between a hegemony, dominant center and subordinate peripheries". The center of the ...
. Prior to Roman rule, there were three native Elymian
The Elymians () were an ancient tribal people who inhabited the western part of Sicily during the Bronze Age and Classical antiquity.
Origins
According to Thucydides, the Elymians were refugees coming from the destroyed Troy. Instead for Hellan ...
towns by the names of Segesta
Segesta (, ''Egesta'', or , ''Ségesta'', or , ''Aígesta''; ) was one of the major cities of the Elymians, one of the three indigenous peoples of Sicily. The other major cities of the Elymians were Eryx and Entella. It is located in the no ...
, Eryx Eryx may refer to:
* Eryx (Sicily), an ancient city in Sicily, the modern Erice, Italy
* Mount Eryx, upon which the city stood, the modern Mount Erice
* Eryx (mythology), a mythological king of the Sicilian city of Eryx, and boxer killed by Herac ...
and Entella
Éntella (Greek language, Greek: ), was an ancient city in the interior of Sicily, situated on the left bank of the river Hypsas (modern Belice), and nearly midway between the two seas, being about 40 km from the mouth of the Hypsas, and ...
, as well as several Siculian
Siculian (or Sicel) is an extinct Indo-European language spoken in central and eastern Sicily by the Sicels. It is attested in fewer than thirty inscriptions in eastern Sicily from the late 6th century to 4th century BCE, and in around twenty-five ...
towns called Agyrion, Kale Akte
Kale (), also called leaf cabbage, belongs to a group of cabbage (''Brassica oleracea'') cultivars primarily grown for their Leaf vegetable, edible leaves; it has also been used as an ornamental plant. Its multiple different cultivars vary quite ...
(founded by the Sicel leader Ducetius
Ducetius () (died 440 BCE) was a Hellenized leader of the Sicels and founder of a united Sicilian state and numerous cities.LiviusDucetius of Sicily Retrieved on 25 April 2006. It is thought he may have been born around the town of Mineo. His s ...
), Enna
Enna ( or ; ; , less frequently ), known from the Middle Ages until 1926 as Castrogiovanni ( ), is a city and located roughly at the center of Sicily, southern Italy, in the province of Enna, towering above the surrounding countryside. It has e ...
and Pantalica
The Necropolis of Pantalica is a collection of cemeteries with rock-cut chamber tombs in southeast Sicily, Italy. Dating from the 13th to the 7th centuries BC, there was thought to be over 5,000 tombs, although the most recent estimate suggests ...
, and one Sicani
The Sicani or Sicanians were one of three ancient peoples of Sicily present at the time of Phoenician and Greek colonization. The Sicani dwelt east of the Elymians and west of the Sicels, having, according to Diodorus Siculus, the boundary with ...
an town known as Thapsos
Thapsos () was a prehistoric village in Sicily of the middle Bronze Age. It was found by the Italian archaeologist Paolo Orsi on the small peninsula of Magnisi, near Priolo Gargallo. In its vicinity was born the Thapsos culture, one of the mo ...
. (Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
: Θάψος)
Sometime after Carthage conquered most of Sicily except for the Southeast which was still controlled by Syracuse, Pyrrhus of Epirus
Pyrrhus ( ; ; 319/318–272 BC) was a Greeks, Greek king and wikt:statesman, statesman of the Hellenistic period.Plutarch. ''Parallel Lives'',Pyrrhus... He was king of the Molossians, of the royal Aeacidae, Aeacid house, and later he became ki ...
, the Molossian
The Molossians () were a group of ancient Greek tribes which inhabited the region of Epirus in classical antiquity. Together with the Chaonians and the Thesprotians, they formed the main tribal groupings of the northwestern Greek group. On th ...
king of Epirus
Epirus () is a Region#Geographical regions, geographical and historical region, historical region in southeastern Europe, now shared between Greece and Albania. It lies between the Pindus Mountains and the Ionian Sea, stretching from the Bay ...
, was installed as King/Tyrant of Sicily from 278 to 275 BC, even capturing the native Elymian
The Elymians () were an ancient tribal people who inhabited the western part of Sicily during the Bronze Age and Classical antiquity.
Origins
According to Thucydides, the Elymians were refugees coming from the destroyed Troy. Instead for Hellan ...
mountain-city of Eryx Eryx may refer to:
* Eryx (Sicily), an ancient city in Sicily, the modern Erice, Italy
* Mount Eryx, upon which the city stood, the modern Mount Erice
* Eryx (mythology), a mythological king of the Sicilian city of Eryx, and boxer killed by Herac ...
, which was previously under Carthaginian fortification & protection before he captured it. Pyrrhus even attempted to capture Lilybaeum
Marsala (, ; ) is an Italian comune located in the Province of Trapani in the westernmost part of Sicily. Marsala is the most populated town in its province and the fifth largest in Sicily.The town is famous for the docking of Giuseppe Garibald ...
( Siege of Lilybaeum) from the Punics
The Punic people, usually known as the Carthaginians (and sometimes as Western Phoenicians), were a Semitic people who migrated from Phoenicia to the Western Mediterranean during the Early Iron Age. In modern scholarship, the term ''Punic'', ...
, which didn't succeed. A couple years later (275 BC), Envoys from Southern Italy
Southern Italy (, , or , ; ; ), also known as () or (; ; ; ), is a macroregion of Italy consisting of its southern Regions of Italy, regions.
The term "" today mostly refers to the regions that are associated with the people, lands or cultu ...
had notified him that of all the Greek cities in Italy, only Tarentum hadn't fallen to the Romans. Upon hearing this, coinciding with the fact that the Sicilian city-states had started becoming hostile towards him, due to him trying to force Sicily into becoming a martial state, Pyrrhus made his decision to depart from the island and dethrone himself, leaving Syracuse and Carthage in charge of the island again. As his ship left the island, he turned and, foreshadowing the Punic Wars
The Punic Wars were a series of wars fought between the Roman Republic and the Ancient Carthage, Carthaginian Empire during the period 264 to 146BC. Three such wars took place, involving a total of forty-three years of warfare on both land and ...
, said to his companions: "What a wrestling ground we are leaving, my friends, for the Carthaginians and the Romans." While his army was being transported by ship to mainland Italy, Pyrrhus' navy was destroyed by the Carthaginians at the Battle of the Strait of Messina
The Battle of the Strait of Messina was fought in 276 BC when a Carthaginian fleet attacked the Sicilian fleet of Pyrrhus of Epirus, who was crossing the strait to Italy. Pyrrhus had left Italy for Sicily on the Autumn of 278 BC and scored s ...
, with 98 warships sunk or disabled out of 110. After Pyrrhus of Epirus landed on Mainland Italy, his Roman opponents had mastered up a large army under Roman consul
The consuls were the highest elected public officials of the Roman Republic ( to 27 BC). Romans considered the consulship the second-highest level of the ''cursus honorum''an ascending sequence of public offices to which politicians aspire ...
Manius Curius Dentatus
Manius Curius Dentatus (died 270 BC) was a Roman general and statesman noted for ending the Samnite War and for his military exploits during the Pyrrhic War. According to Pliny, he was born with teeth, thus earning the surname Dentatus, "toothed ...
, while he was still Tyrant of Sicily. After Pyrrhus was defeated at the Battle of Beneventum (275 BC)
The Battle of Beneventum (275 BC) was the last battle of the Pyrrhic War. It was fought near Beneventum, in southern Italy, between the forces of Pyrrhus, king of Epirus in Greece, and the Romans, led by consul Manius Curius Dentatus. The ...
by the Romans, he decided to end his campaigns against Southern Italy, and return to Epirus
Epirus () is a Region#Geographical regions, geographical and historical region, historical region in southeastern Europe, now shared between Greece and Albania. It lies between the Pindus Mountains and the Ionian Sea, stretching from the Bay ...
, resulting in the loss of all his territorial gains in Italy. The city of Tarentum however still remained under Epirote control.
The ancient historian Diodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus or Diodorus of Sicily (; 1st century BC) was an ancient Greece, ancient Greek historian from Sicily. He is known for writing the monumental Universal history (genre), universal history ''Bibliotheca historica'', in forty ...
who wrote and recorded the monumental universal history Universal history may refer to:
* Universal history (genre), a literary genre
**''Jami' al-tawarikh'', 14th-century work of literature and history, produced by the Mongol Ilkhanate in Persia
** Universal History (Sale et al), ''Universal History'' ...
Bibliotheca historica
''Bibliotheca historica'' (, ) is a work of Universal history (genre), universal history by Diodorus Siculus. It consisted of forty books, which were divided into three sections. The first six books are geographical in theme, and describe the h ...
, and the ancient Doric-Greek revolutionary scientist, inventor and mathematician Archimedes
Archimedes of Syracuse ( ; ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek Greek mathematics, mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and Invention, inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse, Sicily, Syracuse in History of Greek and Hellenis ...
who anticipated modern calculus
Calculus is the mathematics, mathematical study of continuous change, in the same way that geometry is the study of shape, and algebra is the study of generalizations of arithmetic operations.
Originally called infinitesimal calculus or "the ...
, and analysis
Analysis (: analyses) is the process of breaking a complex topic or substance into smaller parts in order to gain a better understanding of it. The technique has been applied in the study of mathematics and logic since before Aristotle (38 ...
by applying methods of infinitesimal
In mathematics, an infinitesimal number is a non-zero quantity that is closer to 0 than any non-zero real number is. The word ''infinitesimal'' comes from a 17th-century Modern Latin coinage ''infinitesimus'', which originally referred to the " ...
s and exhaustion
Exhaust, exhaustive, or exhaustion may refer to:
Law
*Exhaustion of intellectual property rights, limits to intellectual property rights in patent and copyright law
**Exhaustion doctrine, in patent law
** Exhaustion doctrine under U.S. law, in ...
to rigorously derive and prove the range of geometric
Geometry (; ) is a branch of mathematics concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. Geometry is, along with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. A mathematician w ...
theorems
In mathematics and formal logic, a theorem is a statement (logic), statement that has been Mathematical proof, proven, or can be proven. The ''proof'' of a theorem is a logical argument that uses the inference rules of a deductive system to esta ...
, and invented the innovative Archimedean screw
The Archimedes' screw, also known as the Archimedean screw, hydrodynamic screw, water screw or Egyptian screw, is one of the earliest documented hydraulic machines. It was so-named after the Greek mathematician Archimedes who first described it ...
, compound pulleys, and defensive war machines to protect his native town of Syracuse from invasions, were both born, grew up in, lived and died in Sicily.
Middle Ages
As the Roman Empire was falling apart, a Germanic tribe known as theVandals
The Vandals were a Germanic people who were first reported in the written records as inhabitants of what is now Poland, during the period of the Roman Empire. Much later, in the fifth century, a group of Vandals led by kings established Vand ...
along with a Scythian
The Scythians ( or ) or Scyths (, but note Scytho- () in composition) and sometimes also referred to as the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic people who had migrated during the 9th to 8th centuries BC fr ...
tribe originating from the European Steppe known as the Alans
The Alans () were an ancient and medieval Iranian peoples, Iranic Eurasian nomads, nomadic pastoral people who migrated to what is today North Caucasus – while some continued on to Europe and later North Africa. They are generally regarded ...
took over Sicily for a relatively brief period beginning in 440 AD under the rule of their king Geiseric
Gaiseric ( – 25 January 477), also known as Geiseric or Genseric (; reconstructed Vandalic language, Vandalic: ) was king of the Vandals and Alans from 428 to 477. He ruled over Vandal Kingdom, a kingdom and played a key role in the Fall of th ...
, forming the Kingdom of the Vandals. The Vandals and Alans gained a monopoly on the Mediterranean grain trade
The grain trade refers to the local and international trade in cereals such as wheat, barley, maize, rice, and other food grains. Grain is an important trade item because it is easily stored and transported with limited spoilage, unlike other agri ...
during their monarchical reign, with all grain taxes being monitored by them. Due to the Western Roman Empire
In modern historiography, the Western Roman Empire was the western provinces of the Roman Empire, collectively, during any period in which they were administered separately from the eastern provinces by a separate, independent imperial court. ...
being too preoccupied with war in Gaul
Gaul () was a region of Western Europe first clearly described by the Roman people, Romans, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, and parts of Switzerland, the Netherlands, Germany, and Northern Italy. It covered an area of . Ac ...
, when the Vandals & Alans started invading Sicily in 440, the Romans could not respond. Eastern Roman Emperor Theodosius II
Theodosius II ( ; 10 April 401 – 28 July 450), called "the Calligraphy, Calligrapher", was Roman emperor from 402 to 450. He was proclaimed ''Augustus (title), Augustus'' as an infant and ruled as the Eastern Empire's sole emperor after the ...
sent a failed expeditionary force to deal with them in 441, which ended in a Vandal-Alan counter-victory. However, they soon lost these newly acquired possessions, except for one toehold in Lilybaeum
Marsala (, ; ) is an Italian comune located in the Province of Trapani in the westernmost part of Sicily. Marsala is the most populated town in its province and the fifth largest in Sicily.The town is famous for the docking of Giuseppe Garibald ...
, to Odoacer
Odoacer ( – 15 March 493 AD), also spelled Odovacer or Odovacar, was a barbarian soldier and statesman from the Middle Danube who deposed the Western Roman child emperor Romulus Augustulus and became the ruler of Italy (476–493). Odoacer' ...
(an Arian Christian
Arianism (, ) is a Christological doctrine which rejects the traditional notion of the Trinity and considers Jesus to be a creation of God, and therefore distinct from God. It is named after its major proponent, Arius (). It is considered he ...
Barbarian
A barbarian is a person or tribe of people that is perceived to be primitive, savage and warlike. Many cultures have referred to other cultures as barbarians, sometimes out of misunderstanding and sometimes out of prejudice.
A "barbarian" may ...
statesman & general of possible East Germanic
East is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fact that eas ...
& Hunnic descent, and client king
A client state in the context of international relations is a state that is economically, politically, and militarily subordinated to a more powerful controlling state. Alternative terms for a ''client state'' are satellite state, associated state ...
under Zeno
Zeno may refer to:
People
* Zeno (name), including a list of people and characters with the given name
* Zeno (surname)
Philosophers
* Zeno of Elea (), philosopher, follower of Parmenides, known for his paradoxes
* Zeno of Citium (333 – 264 B ...
whose reign over Italy marked the Fall of the Western Roman Empire
The fall of the Western Roman Empire, also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Rome, was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rule, and its vast ...
) in 476 and completely to the Ostrogothic
The Ostrogoths () were a Roman-era Germanic peoples, Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Goths, Gothic kingdoms within the Western Roman Empire, drawing upon the large Gothic populatio ...
conquest of Sicily by Theodoric the Great
Theodoric (or Theoderic) the Great (454 – 30 August 526), also called Theodoric the Amal, was king of the Ostrogoths (475–526), and ruler of the independent Ostrogothic Kingdom of Italy between 493 and 526, regent of the Visigoths (511–526 ...
which began in 488; although the Goths
The Goths were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe. They were first reported by Graeco-Roman authors in the 3rd century AD, living north of the Danube in what is ...
were Germanic, Theodoric sought to revive Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
culture and government and allowed freedom of religion. In contrast to the prior Carthaginian, Syracusan (Dorian) and Roman Empires which ruled Sicily in the past, Sicily did not serve as a distinct province or administrative region under Germanic control, although it did retain a certain amount of autonomy. The Gothic War took place between the Ostrogoths
The Ostrogoths () were a Roman-era Germanic peoples, Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Goths, Gothic kingdoms within the Western Roman Empire, drawing upon the large Gothic populatio ...
and the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
(with its capital-city based at Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
, modern Istanbul
Istanbul is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, constituting the country's economic, cultural, and historical heart. With Demographics of Istanbul, a population over , it is home to 18% of the Demographics ...
), and during the reign of Justinian I
Justinian I (, ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was Roman emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign was marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovatio imperii'', or "restoration of the Empire". This ambition was ...
, Sicily was brought back under Greco-Roman rule under the military expeditions of Byzantine generals Flavius Belisarius
BelisariusSometimes called Flavius Belisarius. The name became a courtesy title by the late 4th century, see (; ; The exact date of his birth is unknown. March 565) was a military commander of the Byzantine Empire under Emperor Justinian I. B ...
and Narses
Narses (also spelled Nerses; ; ; ; c. 478–573) was a distinguished Byzantine general and statesman of Armenian heritage, renowned for his critical role in Emperor Justinian I’s military campaigns. Alongside the famed Belisarius, Narses was ...
, resulting in Byzantine-Greek language and religion
Religion is a range of social system, social-cultural systems, including designated religious behaviour, behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, religious text, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics in religion, ethics, or ...
being embraced by the majority of the population. It was Syracuse where the Byzantine Emperor Constans II
Constans II (; 7 November 630 – 15 July 668), also called "the Bearded" (), was the Byzantine emperor from 641 to 668. Constans was the last attested emperor to serve as Roman consul, consul, in 642, although the office continued to exist unti ...
desired to move his capital in 663 AD, a decision which eventually led to his assassination. Sicily remained under autonomous
In developmental psychology and moral, political, and bioethical philosophy, autonomy is the capacity to make an informed, uncoerced decision. Autonomous organizations or institutions are independent or self-governing. Autonomy can also be defi ...
stable Byzantine rule as the Theme/Province of Sicily (Theme (Byzantine district)
The themes or (, , singular: , ) were the main military and administrative divisions of the middle Byzantine Empire. They were established in the mid-7th century in the aftermath of the Slavic migrations to Southeastern Europe and Muslim conq ...
) for several peaceful centuries, until an invasion by Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
Muslims
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
(Aghlabids
The Aghlabid dynasty () was an Arab dynasty centered in Ifriqiya (roughly present-day Tunisia) from 800 to 909 that conquered parts of Sicily, Southern Italy, and possibly Sardinia, nominally as vassals of the Abbasid Caliphate. The Aghlabids ...
from the Banu Tamim Clan) in the 9th century.
Besides Sicily, the Theme or province of Sicily also included the adjacent region of Calabria
Calabria is a Regions of Italy, region in Southern Italy. It is a peninsula bordered by the region Basilicata to the north, the Ionian Sea to the east, the Strait of Messina to the southwest, which separates it from Sicily, and the Tyrrhenian S ...
in Mainland Italy. The capital city of Byzantine Sicily
The history of Sicily has been influenced by numerous ethnic groups. It has seen Sicily controlled by powers, including Phoenicians, Phoenician and Carthage, Carthaginian, Magna Grecia, Greek, Roman Empire, Roman, Kingdom of the Vandals, Vandal a ...
was Syracuse
Syracuse most commonly refers to:
* Syracuse, Sicily, Italy; in the province of Syracuse
* Syracuse, New York, USA; in the Syracuse metropolitan area
Syracuse may also refer to:
Places
* Syracuse railway station (disambiguation)
Italy
* Provi ...
. The province was looked after by the imperial governor known as a Praetor
''Praetor'' ( , ), also ''pretor'', was the title granted by the government of ancient Rome to a man acting in one of two official capacities: (i) the commander of an army, and (ii) as an elected ''magistratus'' (magistrate), assigned to disch ...
, and was militarily protected under a general by the title of Dux
''Dux'' (, : ''ducēs'') is Latin for "leader" (from the noun ''dux, ducis'', "leader, general") and later for duke and its variant forms (doge, duce, etc.). During the Roman Republic and for the first centuries of the Roman Empire, ''dux'' coul ...
. Sicily itself was divided into many districts known as a Turma
A ''turma'' (; plural ''turmae''; ) was a cavalry unit in the Roman army of the Republic and Empire. In the Byzantine Empire, it became applied to the larger, regiment-sized military-administrative divisions of a '' thema''. The word is often tran ...
. The Byzantine Exarch of Ravennan Italy named Theophylact, between 702 and 709, originally came from Sicily. After he got promoted into the Exarchate, Theophylact marched from Sicily to Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
for unknown reasons, a decision which angered the local Roman soldiers living there, however the newly elected Pope John VI
Pope John VI (; 65511 January 705) was the bishop of Rome from 30 October 701 to his death on 11 January 705. John VI was a Greeks, Greek from Ephesus who reigned during the Byzantine Papacy. His papacy was noted for military and political break ...
, was able to calm them down. While Theophylact was still Exarch, Byzantine Emperor Justinian II
Justinian II (; ; 668/69 – 4 November 711), nicknamed "the Slit-Nosed" (), was the last Byzantine emperor of the Heraclian dynasty, reigning from 685 to 695 and again from 705 to 711. Like his namesake, Justinian I, Justinian II was an ambitio ...
seized all the leading citizens and officials of Ravenna at a local banquet, and dragged them abroad a ship to Constantinople. He sentenced all but one of the Ravennan captives to death, the exception being Archbishop Felix, who was permanently blinded instead. This was due to a recent rebellion which Ravenna
Ravenna ( ; , also ; ) is the capital city of the Province of Ravenna, in the Emilia-Romagna region of Northern Italy. It was the capital city of the Western Roman Empire during the 5th century until its Fall of Rome, collapse in 476, after which ...
took part in, in 695. Justinian II later sacked Ravenna, weakening the Exarchate in charge of it. Theophylact was not a victim of the catastrophe, but was the first Exarch to experience a weakened Ravenna. Theophylact possibly moved back to Sicily after he retired from the Exarchate in 709. Theophylact might have also been the Strategos
''Strategos'' (), also known by its Linguistic Latinisation, Latinized form ''strategus'', is a Greek language, Greek term to mean 'military General officer, general'. In the Hellenistic world and in the Byzantine Empire, the term was also use ...
of Sicily from 700 to 710. The Strategos of Sicily was also able to exercise some control over the autonomous duchies of Naples
Naples ( ; ; ) is the Regions of Italy, regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 908,082 within the city's administrative limits as of 2025, while its Metropolitan City of N ...
, Gaeta
Gaeta (; ; Southern Latian dialect, Southern Laziale: ''Gaieta'') is a seaside resort in the province of Latina in Lazio, Italy. Set on a promontory stretching towards the Gulf of Gaeta, it is from Rome and from Naples.
The city has played ...
and Amalfi
Amalfi (, , ) is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Salerno, in the region of Campania, Italy, on the Gulf of Salerno. It lies at the mouth of a deep ravine, at the foot of Monte Cerreto (1,315 metres, 4,314 feet), surrounded by dramatic c ...
, depending on the local political situation or faction at the time.
The Aghlabid invasions were in part caused by the Byzantine-Sicilian military commander Euphemius (Sicily), Euphemius, who invited the Aghlabids to aid him in his rebellion against the imperial governor of Sicily in 826 AD. A similar situation happened a century prior, when the imperial governor of Sicily (Sergios), had declared a Byzantine official from Istanbul, Constantinople by the name of Basil Onomagoulos (regnal name Tiberius (praenomen), Tiberius) as rival emperor, when false news reached Sicily that Constantinople had fallen to the Umayyad Caliphate, Umayyads. When Leo III the Isaurian, Emperor Leo the Syrian sent an Chartoularios, administrative official named Paul (exarch), Paul to Sicily, the people and army of Syracuse surrendered Basil and his rebels up to him, leading to the beheading of Basil, while the former governor Sergios was able to escape to Kingdom of the Lombards, the parts of Mainland Italy controlled by the Lombards. Another rebellion took place between the years 781–793, when the aristocratic governor of Sicily, Elpidius (rebel), Elpidius, was accused of conspiring against Irene of Athens, Empress Irene in favour of Nikephoros (Caesar), Nikephoros. After Elpidius's forces were militarily defeated by Empress Irene's large fleet dispatched in Sicily, he, along with his lieutenant, the dux of Calabria
Calabria is a Regions of Italy, region in Southern Italy. It is a peninsula bordered by the region Basilicata to the north, the Ionian Sea to the east, the Strait of Messina to the southwest, which separates it from Sicily, and the Tyrrhenian S ...
named Nikephoros, defected to the Abbasid Caliphate, where he was posthumously acknowledged as rival emperor. After losing another military expedition, this time against Anatolia, Asia Minor with the help of the Abbasids, he advised the Banu Abbas, Abbasid Emir of Upper Mesopotamia, Mesopotamia, Abd al-Malik ibn Salih, to "throw away his silk and put on his armour", warning him against the aggressive new reign of Nikephoros I. Muslim conquest of Sicily, The Muslim conquest was a see-saw affair; the local population resisted fiercely and the Aghlabids, Arabs suffered considerable dissension and infighting among themselves during this process. Not until 965 was the island's conquest successfully completed by the Fatimid Caliphate, with Syracuse in particular resisting almost to the end (Siege of Syracuse (877-878)). Jawhar (general), Jawhar the Sicilian, the Fatimid general of Saqaliba, Slavic origins that led the Fatimid conquest of Egypt, conquest of Egypt, under Caliph Al-Mu'izz li-Din Allah, was born and grew up in Ragusa, Sicily. Jawhar served as viceroy of Egypt until 973, consolidating Fatimid control over North Africa, and laying the foundations for Cairo.
The first phase of Muslim rule began with the conquests of the third Aghlabid Emir Ziyadat Allah I of Ifriqiya, and consolidated with the reign of the ninth Emir Ibrahim II of Ifriqiya after the conquest of Taormina. The first attempt to Siege of Syracuse (827-828), capture Syracuse was under general Asad ibn al-Furat, although it ended in a Byzantine victory. A combination of Persian and Andalusian troops helped to capture the Island between 830 and 831. After a revolt was suppressed, the Fatimid Caliph Al-Mansur Billah appointed a member of the Kalbids, Kalbid dynasty, Al-Hasan ibn Ali al-Kalbi, as First Emir of Sicily. The Kalbids ruled Sicily from 948 to 1053. Al-Mu'izz ibn Badis, fourth ruler of the Zirid dynasty, Zirid Sanhaja dynasty in North Africa, attempted to annex the island for the Zirids, but his attempts failed. The new Arab rulers initiated Arab Agricultural Revolution, land reforms, which in turn increased productivity and encouraged the growth of smallholdings, a dent to the dominance of the landed estates. The Arabs further improved irrigation systems through Qanats, introducing oranges, lemons, pistachio, and sugarcane to Sicily. Ibn Hawqal, a Baghdadi merchant who visited Sicily in 950, commented that a walled suburb called the Kasr (the palace) was the center of Palermo, with the great Friday mosque on the site of the later Roman Catholic cathedral. The suburb of Al-Khalisa (Kalsa) contained the Sultan's palace, baths, a mosque, government offices, and a private prison. Ibn Hawqual reckoned there were 7,000 individual butchers trading in 150 shops. By 1050, Palermo had a population of 350,000, making it one of the largest cities in Europe, behind Moorish-Spain's capital Córdoba and the Byzantine capital of Constantinople, which had populations over 450–500,000. Palermo's population dropped to 150,000 under Norman rule. By 1330 Palermo's population had declined to 51,000, possibly due to the inhabitants of the region being deported to other regions of County of Sicily, Norman Sicily, or to the Norman County of Apulia and Calabria. The local population conquered by the Muslims were Greek-speaking Byzantine Christians, but there were also a significant number of Jews. Christians and Jews were tolerated in Muslim Sicily as dhimmis, and had to pay the Jizya poll tax, and Kharaj land tax, but were exempt from the Zakat alms-giving tax Muslims had to pay. Many Jews immigrated to Sicily during Muslim rule, but left after the Normans arrived.
 In the 11th century, the mainland southern Italian powers were hiring Norman conquest of southern Italy, Norman mercenaries, who were Christians, Christian descendants of the Vikings; it was the Normans under Roger I of Sicily, Roger I (of the Hauteville dynasty) who conquered Sicily from the Muslims Battle of Cerami, over a period of thirty years until finally controlling the entire island by 1091 as the County of Sicily. In 1130, Roger II of Sicily, Roger II founded the Norman Kingdom of Sicily as an independent state with its own Sicilian Parliament, Parliament, language, schooling, army and currency, while the Sicilian culture evolved distinct traditions, clothing, linguistic changes, Sicilian cuisine, cuisine and customs not found in mainland
In the 11th century, the mainland southern Italian powers were hiring Norman conquest of southern Italy, Norman mercenaries, who were Christians, Christian descendants of the Vikings; it was the Normans under Roger I of Sicily, Roger I (of the Hauteville dynasty) who conquered Sicily from the Muslims Battle of Cerami, over a period of thirty years until finally controlling the entire island by 1091 as the County of Sicily. In 1130, Roger II of Sicily, Roger II founded the Norman Kingdom of Sicily as an independent state with its own Sicilian Parliament, Parliament, language, schooling, army and currency, while the Sicilian culture evolved distinct traditions, clothing, linguistic changes, Sicilian cuisine, cuisine and customs not found in mainland Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
. A great number of families from Kingdom of Italy (Holy Roman Empire), northern Italy began settling in Sicily during this time, with some of their descendants forming distinct communities that survive to the present day, such as the Lombards of Sicily. Other migrants arrived from County of Apulia and Calabria, southern Italy, as well as Duchy of Normandy, Normandy, County of Provence, southern France, England and other parts of northern Europe.
The Siculo-Norman rule of the Hauteville dynasty continued until 1198, when Frederick I of Sicily, Frederick II of Sicily, the son of a Siculo-Norman queen and a Hohenstaufen dynasty, Swabian-German emperor ascended the throne. In fact, it was during the reign of this Hohenstaufen king Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor, Frederick II, that the poetic form known as a sonnet was invented by Giacomo da Lentini, the head Poet, Teacher and Notary of the Sicilian School, Sicilian School for Poetry. Frederick II was also responsible for the Muslim settlement of Lucera. His descendants governed Sicily until the Papal States, Papacy invited a Capetian dynasty, French prince to take the throne, which led to a decade-and-a-half of Kingdom of France, French rule under Charles I of Sicily; he was later deposed in the War of the Sicilian Vespers against County of Anjou, French rule, which put the daughter of Manfred of Sicily – Constance of Sicily, Queen of Aragon, Constance II and her husband Peter III of Aragon, a member of the House of Barcelona, on the throne. Their House of Barcelona, descendants ruled the Kingdom of Sicily until 1401. Following the Compromise of Caspe in 1412 the Sicilian throne passed to the Iberian Peninsula, Iberian monarchs from Crown of Aragon, Aragon and Crown of Castile, Castile.
Modern and contemporary history
 In 1735, the Spanish Empire, Spanish era ended when Charles V of Sicily, Charles V from the House of Bourbon-Two Sicilies, House of Bourbon was crowned king. For the better part of the next century-and-a-half, Sicily was in personal union with the other Southern Italian Kingdom of Naples, with the official residence located in Naples, under the House of Bourbon-Two Sicilies, Bourbon dynasty. After the Napoleonic Wars, King Ferdinand I of the Two Sicilies, Ferdinand I, who had just recently been restored back to the throneship of Kingdom of Naples, Southern Italy in 1815, made a decision to administratively and politically merged the two separate Kingdoms of Naples and Sicily, which ended up forming the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies in 1816. In 1861, however, Sicily became part of the Kingdom of Italy as a result of the Italian unification, Risorgimento. Prior to the Risorgimento, the Two Sicilies were conquered by the Kingdom of Sardinia (1720–1861), Kingdom of Sardinia during the Expedition of the Thousand (led by general Giuseppe Garibaldi) in 1860, and subsequently brought under the monarchial realm of
In 1735, the Spanish Empire, Spanish era ended when Charles V of Sicily, Charles V from the House of Bourbon-Two Sicilies, House of Bourbon was crowned king. For the better part of the next century-and-a-half, Sicily was in personal union with the other Southern Italian Kingdom of Naples, with the official residence located in Naples, under the House of Bourbon-Two Sicilies, Bourbon dynasty. After the Napoleonic Wars, King Ferdinand I of the Two Sicilies, Ferdinand I, who had just recently been restored back to the throneship of Kingdom of Naples, Southern Italy in 1815, made a decision to administratively and politically merged the two separate Kingdoms of Naples and Sicily, which ended up forming the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies in 1816. In 1861, however, Sicily became part of the Kingdom of Italy as a result of the Italian unification, Risorgimento. Prior to the Risorgimento, the Two Sicilies were conquered by the Kingdom of Sardinia (1720–1861), Kingdom of Sardinia during the Expedition of the Thousand (led by general Giuseppe Garibaldi) in 1860, and subsequently brought under the monarchial realm of Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; ; ) is the Mediterranean islands#By area, second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, and one of the Regions of Italy, twenty regions of Italy. It is located west of the Italian Peninsula, north of Tunisia an ...
. After the unification of Italy and the Fascism, Fascist era, a wave of Sicilian nationalism led to the adoption of the Statute of Sicily, under which the island has become an autonomous region. Since 1946, the island enjoys the most advanced special status of all the Autonomous regions with special statute, autonomous regions.
Demographics
Sicani
The Sicani or Sicanians were one of three ancient peoples of Sicily present at the time of Phoenician and Greek colonization. The Sicani dwelt east of the Elymians and west of the Sicels, having, according to Diodorus Siculus, the boundary with ...
, Siculi and Elymians
The Elymians () were an ancient tribe, tribal people who inhabited the western part of Sicily during the Bronze Age and Classical antiquity.
Origins
According to Thucydides, the Elymians were refugees coming from the destroyed Troy. Instead for ...
), Bruttians, Morgetes, Oenotrians, List of Phoenician cities, Phoenicians and Punics, Carthaginians, Ancient Greeks (Magna Graecia), Mamertines
The Mamertines (, "sons of Mars", ) were mercenaries of Italian origin who had been hired from their home in Campania by Agathocles (361–289 BC), Tyrant of Syracuse and self-proclaimed King of Sicily. After Syracuse lost the Seventh Sicilia ...
, Roman people, Romans and Jews during the ancient history, ancient and classical antiquity, classical periods.
In the early medieval era, Sicily experienced the brief rule of Germanic Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic people who were first reported in the written records as inhabitants of what is now Poland, during the period of the Roman Empire. Much later, in the fifth century, a group of Vandals led by kings established Vand ...
and Iranian peoples, Iranic Alans
The Alans () were an ancient and medieval Iranian peoples, Iranic Eurasian nomads, nomadic pastoral people who migrated to what is today North Caucasus – while some continued on to Europe and later North Africa. They are generally regarded ...
during the Kingdom of the Vandals and Alans, while under Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Emirate of Sicily, Saracen and Kingdom of Sicily, Norman rule, there were Byzantine Greeks, Arabs and Normans. From the late medieval period into the modern era, Crown of Aragon, Aragonese, Spaniards and French people, French ruled over and left a minor impact on the island, while Albanians settled and formed communities which still exist today known as the Arbereshe people, Arbereshe.
About five million people live in Sicily, making it the List of regions of Italy#List of regions, fourth most populated region in Italy. However, in the first century after the Italian unification, Sicily had one of the most negative net migration rates among the regions of Italy because of millions of people moving to the Italian mainland and countries like Germany, Sweden, Belgium, the United States, Canada, Australia, Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
, Argentina, the United Kingdom, France, New Zealand, Singapore and South Africa. Many Sicilian communities, including those formed by the descendants of the Sicilian migrants, are all over the world. It is estimated that the number of people of Sicilian descent in the world is more than six million. The most famous community is represented by the Sicilian Americans.
Like the other parts of Southern Italy, immigration to the island is relatively low compared to other regions of Italy because workers tend to head to Northern Italy instead, in search of better employment and industrial opportunities. The most recent Istituto Nazionale di Statistica, ISTAT figures show around 175,000 immigrants out of the total of almost 5.1 million population (nearly 3.5% of the population); Romanians with more than 50,000 make up the most immigrants, followed by Tunisians, Moroccans, Sri Lankan Tamil diaspora, Sri Lankans, Albanians, and others mostly from Eastern Europe. As in the rest of Italy, the primary religion is Roman Catholicism (but with combined Latin liturgical rites, Latin & Byzantine Rites) and the official language is Italian language, Italian; Sicilian language, Sicilian is currently not a recognised language in Italy.
Major settlements
Messina
Messina ( , ; ; ; ) is a harbour city and the capital city, capital of the Italian Metropolitan City of Messina. It is the third largest city on the island of Sicily, and the 13th largest city in Italy, with a population of 216,918 inhabitants ...
and its Larger Urban Zones, LUZ, with a total of 418,916 people.
Overall, there are fifteen cities and towns with a population above 50,000 people, these are:
# Palermo (677,854)
# Catania (315,576)
# Messina
Messina ( , ; ; ; ) is a harbour city and the capital city, capital of the Italian Metropolitan City of Messina. It is the third largest city on the island of Sicily, and the 13th largest city in Italy, with a population of 216,918 inhabitants ...
(242,121)
# Syracuse
Syracuse most commonly refers to:
* Syracuse, Sicily, Italy; in the province of Syracuse
* Syracuse, New York, USA; in the Syracuse metropolitan area
Syracuse may also refer to:
Places
* Syracuse railway station (disambiguation)
Italy
* Provi ...
(123,248)
# Marsala (82,812)
# Gela (77,295)
# Ragusa Ragusa may refer to:
Places Croatia
* Ragusa, Dalmatia, the historical name of the city of Dubrovnik
* the Republic of Ragusa (or Republic of Dubrovnik), the maritime city-state of Ragusa
* Ragusa Vecchia, historical Italian name of Cavtat, a t ...
(73,756)
# Trapani (70,642)
# Vittoria, Sicily, Vittoria (63,393)
# Caltanissetta (60,221)
# Agrigento
Agrigento (; or ) is a city on the southern coast of Sicily, Italy and capital of the province of Agrigento.
Founded around 582 BC by Greek colonists from Gela, Agrigento, then known as Akragas, was one of the leading cities during the golden ...
(59,190)
# Bagheria (56,421)
# Modica (55,294)
# Acireale (53,205)
# Mazara del Vallo (51,413).
Names and surnames
The most common Sicilian names are ''Giuseppe'', ''Maria'' and ''Salvatore''. The most common Sicilian surnames are ''Russo'', ''Messina'' and ''Lombardo''.Diaspora
In 2008, the number of Sicilians abroad was well over 1 million. The countries in which they are most numerous on this date are: United States, Germany, Belgium, Switzerland, Argentina, Uruguay, Brazil, France and Canada. The population of the Diaspora without including those in the United States is 629,114 individuals. In the United States, the Sicilian-Americans are a large subset of Americans whose ancestors came from Sicily. This group is perhaps the largest part of the Sicilian diaspora. The entire autochthonous population ofMalta
Malta, officially the Republic of Malta, is an island country in Southern Europe located in the Mediterranean Sea, between Sicily and North Africa. It consists of an archipelago south of Italy, east of Tunisia, and north of Libya. The two ...
is of Sicilian origin, but the Maltese people, Maltese generally do not consider themselves Sicilian due to centuries of cultural and geographical separation, and the fact that Maltese language, their native language evolved from Siculo-Arabic instead of Italo-Dalmatian like the modern Sicilian language.
Genetics
Autosomal studies
 Several studies involving Genome-wide association study, whole genome analysis of mainland Italians and Sicilians have found that samples from Northern Italy,
Several studies involving Genome-wide association study, whole genome analysis of mainland Italians and Sicilians have found that samples from Northern Italy, Southern Italy
Southern Italy (, , or , ; ; ), also known as () or (; ; ; ), is a macroregion of Italy consisting of its southern Regions of Italy, regions.
The term "" today mostly refers to the regions that are associated with the people, lands or cultu ...
and Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
belong to their own unique/distinct separate clusters, while a genetic gap is filled by an intermediate Central Italy, Central Italian cluster, creating a continuous cline of variation that mirrors geography. Genetically, Sicilians cluster the closest to other Southern Italy, South Italians, and especially to Calabria
Calabria is a Regions of Italy, region in Southern Italy. It is a peninsula bordered by the region Basilicata to the north, the Ionian Sea to the east, the Strait of Messina to the southwest, which separates it from Sicily, and the Tyrrhenian S ...
ns. Other studies have also demonstrated that the population of Sicily is genetically very similar to that of Malta
Malta, officially the Republic of Malta, is an island country in Southern Europe located in the Mediterranean Sea, between Sicily and North Africa. It consists of an archipelago south of Italy, east of Tunisia, and north of Libya. The two ...
, and to Greeks, Greek speaking ethnic group, groups from the Ionian Islands, the Aegean Islands, Crete and the Peloponnese while the rest of Geography of Greece, mainland Greece appears as slightly differentiated, by clustering with the other Balkans, Southern Balkan populations such as Albanians of Albania, Kosovo and the Arbëreshë people.
mtDNA and Y-DNA studies
According to one study, Human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup, Y-DNA haplogroups were found at the following frequencies in Sicily: Haplogroup R1 (Y-DNA), R1 (36.76%), Haplogroup J (Y-DNA), J (29.65%), Haplogroup E1b1b (Y-DNA), E1b1b (18.21%), Haplogroup I (Y-DNA), I (7.62%), Haplogroup G (Y-DNA), G (5.93%), Haplogroup T (Y-DNA), T (5.51%), Haplogroup Q-M242 (Y-DNA), Q (2.54%). R1 and I haplogroups are typical in Western Europe, West European and Northern Europe, North European populations while J, T, G, Q and E1b1b (and their various subclades) consist of lineages with differential distribution across Europe and theMediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
. The five main Human mitochondrial DNA haplogroup, MtDNA haplogroups present in Sicily are Haplogroup H (mtDNA), haplogroups H, haplogroup K (mtDNA), K, haplogroup X (mtDNA), X, haplogroup W (mtDNA), W and Haplogroup U (mtDNA), U, which are also the five most commonly found MtDNA-haplogroups in Europe and the Caucasus.
The Norman Kingdom of Sicily was created in 1130, with Palermo as its capital, 70 years after the initial Norman invasion and 40 after the conquest of the last town, Noto
Noto (; ) is a city and in the Province of Syracuse, Sicily, Italy. It is southwest of the city of Syracuse at the foot of the Iblean Mountains. It lends its name to the surrounding area Val di Noto. In 2002 Noto and its church were decl ...
in 1091, and would last until 1198. Today, it is in north-west Sicily, around Trapani, Palermo and Agrigento
Agrigento (; or ) is a city on the southern coast of Sicily, Italy and capital of the province of Agrigento.
Founded around 582 BC by Greek colonists from Gela, Agrigento, then known as Akragas, was one of the leading cities during the golden ...
where Italo-Normans, Norman Y-DNA is the most common, with 8% to 20% of the lineages belonging to haplogroup I1. Ancient and medieval Greeks, Greek genetic paternal legacy is estimated at 37% in Sicily. Sicilians are of European genetic origin, with modern genetic profiles that are closely similar to people who lived in the region of Magna Graecia during the Classical antiquity period, these people were a mix of Italic Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
and Greeks, Greek genetic ancestry. Sicilians closely resemble mainland Italians and Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
genetically.
It is a misconception that Sicilians are of primarily Moors, Moorish or otherwise Sub-Saharan Africa, African origin, but this has been entirely disproven by genetic analysis of Sicilian genomes. The falsified myth that Sicilian DNA was of Moorish origin was fabricated by Anti-Italianism, Anti-Italian Xenophobia, xenophobic Nativism (politics), nativists from primarily English-speaking world, anglophonic nations. Overall the estimated Balkans, Balkan and Northwestern European paternal contributions in Sicily are about 63% and 34% respectively.
Paleogenetics
Fernandes et al. (2019), The Arrival of Steppe and Iranian Related Ancestry in the Islands of the Western Mediterranean, found that in Sicily, Western Steppe Herders ancestry arrived by ~2200 BCE and likely came at least in part from Spain. 4 of the 5 Early Bronze Age Sicilian males had Steppe-associated Y-haplogroup R1b1a1a2a1a2 (R-P312). Two of these were Y-haplogroup R1b1a1a2a1a2a1 (Z195) which today is largely restricted to Iberia and has been hypothesized to have originated there 2500–2000 BCE. A 2022 genome-wide study of more than 700 individuals from the South Mediterranean area (102 from Southern Italy), combined with ancient DNA from neighbouring areas, found high affinities of South-Eastern Italians with modern Eastern Peloponnese, Peloponnesians, and a closer affinity of ancient Greek genomes with those from specific regions of South Italy than modern Greek genomes. The study also discovered common genetic sources shared between South Italy and Peloponnese, which can be modeled as a mixture of Anatolian Neolithic and Iranian Chalcolithic ancestries. Monnereau et al (2024) analyzed burials at the site of Calatafimi-Segesta, Segesta to investigate the interactions between Muslims, Muslim and Christians, Christian communities during the Middle Ages in Sicily. The biomolecular and Isotopic results suggest the Christians remained genetically distinct from the Muslim community at Segesta while following a substantially similar diet. Based on these results, the authours suggest that the two communities at Segesta could have followed endogamy rules.Culture
Languages
 Today in Sicily most people are bilingual and speak both Italian language, Italian and Sicilian language, Sicilian, a distinct Romance languages, Romance language. Many Sicilian language, Sicilian words are of
Today in Sicily most people are bilingual and speak both Italian language, Italian and Sicilian language, Sicilian, a distinct Romance languages, Romance language. Many Sicilian language, Sicilian words are of Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
origin, while smaller numbers of other loan words are from Norman language, Norman, Arabic language, Arabic, Catalan language, Catalan, Occitan language, Occitan, Spanish language, Spanish and other languages. Other dialects of Sicilian, or those very closely related to it, are also spoken in Languages of Calabria#Central-Southern Calabrian, southern Calabria, Salentino, Salento and Lower Cilentano, Cilento.
Sicilian was an early influence in the development of standard Italian, although its use remained confined to an intellectual elite. This was a literary language in Sicily created under the auspices of Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor, Frederick II and his court of notaries or ''Magna Curia'' which, headed by Giacomo da Lentini, also gave birth to the Sicilian School, widely inspired by troubadour literature. It is in this language that appeared the first sonnet, whose invention is attributed to Giacomo da Lentini himself. Sicilian was also the official language of the Kingdom of Sicily from 1300 to 1543.
Prior to the 20th century, large numbers of Sicilian people spoke only Sicilian as their mother tongue, with little or no fluent knowledge of Italian. Today, although not officially recognized by the Italian Republic, the Sicilian language is described as "a stable indigenous language of Italy" by ''Ethnologue'' and is recognized as a minority language by UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
. It has also been identified as a language by the Sicilian Region. Even so, Italian continues to be the sole official language recognized by the Italian Republic and predominates in the public arena, being used as everyday language in the daily lives of many Sicilians.
The Siculo-Arabic dialect was a vernacular Varieties of Arabic, variety of Arabic once spoken in Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
and neighbouring Malta
Malta, officially the Republic of Malta, is an island country in Southern Europe located in the Mediterranean Sea, between Sicily and North Africa. It consists of an archipelago south of Italy, east of Tunisia, and north of Libya. The two ...
between the end of the ninth century and the mid to late thirteenth century. The language became extinct in Sicily, but in Malta it eventually evolved into what is now the Maltese language.
The Siculish dialect is the Macaronic language, macaronic "Sicilianization" of English language words and phrases by immigrants from Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
to the United States in the early 20th century. Forms of Siculish are also to be found in other Sicilian immigrant communities of Anglosphere, English-speaking countries, namely Canada and Australia. A surprising similarity can often be found between these forms, through either coincidence, trans-national movements of Sicilian immigrants, or more likely, through the logical adaptation of English language, English using linguistic norms from the Sicilian language.
Ethno-linguistic minorities
There are two main historical Ethnolinguistics, ethno-linguistic minorities in Sicily, the Lombards of Sicily and the Arbëreshë people, Arbëreshë: * The Lombards of Sicily are a linguistic minority living in Sicily who speak Gallo-Italic of Sicily, an isolated group of Gallo-Italic languages found in about 15 isolated communities of central easternSicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
. Forming a language island within the Sicilian language, it dates back to migrations from Northern Italy to central and eastern
Eastern or Easterns may refer to:
Transportation
Airlines
*China Eastern Airlines, a current Chinese airline based in Shanghai
* Eastern Air, former name of Zambia Skyways
*Eastern Air Lines, a defunct American airline that operated from 192 ...
Sicily about 900 years ago, during the Norman conquest of Sicily. Because of linguistic differences among the Gallo-Italic dialects of Sicily, it is supposed that there were different immigration routes. From Piedmont, Liguria, Emilia-Romagna, Emilia, and Lombardy they began to spread south between the 11th and 14th centuries. The most important areas where the Gallo-Italic of Sicily is spoken are Acquedolci, Montalbano Elicona, Novara di Sicilia, Fondachelli-Fantina San Fratello and San Piero Patti (Province of Messina), Aidone, Nicosia, Sicily, Nicosia, Piazza Armerina and Sperlinga (Province of Enna).
* The Arbëreshë people settled in Southern Italy in the 15th to 18th centuries in several waves of migrations. They are the descendants of mostly Tosk Albanian refugees of Christian faith who fled to Italy after the conquest and subsequent Islamisation of Albania by the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Turks in the Balkans. They speak their own variant of the Arbëresh language. There are three identified Arbëreshë communities in the province of Palermo. The areas are: Contessa Entellina, Piana degli Albanesi and Santa Cristina Gela; while the varieties of Piana and Santa Cristina Gela are similar enough to be entirely mutually intelligible, the variety of Contessa Entellina is not entirely intelligible. The largest centre is Piana degli Albanesi which, besides being the hub of Eparchy of Piana degli Albanesi, religious and socio-cultural communities, has kept their unique features intact over time. There are two other communities with a strong historical and linguistic heritage.
* The community of the Griko people, Greeks of Messina (or Siculo-Greeks) speaks modern Greek with some elements of the Ancient Greek, ancient Greek language spoken in the island, and Calabrian Greek. The Greek community was reconstituted in 2003 with the name of ''"Comunità Hellenica dello Stretto"'' (Hellenic Community of the Strait).
Religion
Art and architecture
Cuisine
Gallery
See also
*List of people from Sicily *Sicilian Wars *Normans of Sicily *Griko people *Maltese people *Kingdom of AfricaReferences
.137 Valenza, Giuseppe. ELAMITI ELIMIOTI ELIMI ''Il teatro genealogico degli Elimi nel crocevia del Mediterraneo''. Prefazione Vaccarella, Ilaria.2022. ISBN 978-88-908854-2-6External links
{{Sicily Ethnic groups in Italy People from Sicily, Romance peoples