Shringasaurus Indicus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Shringasaurus'' (meaning "horned lizard", from
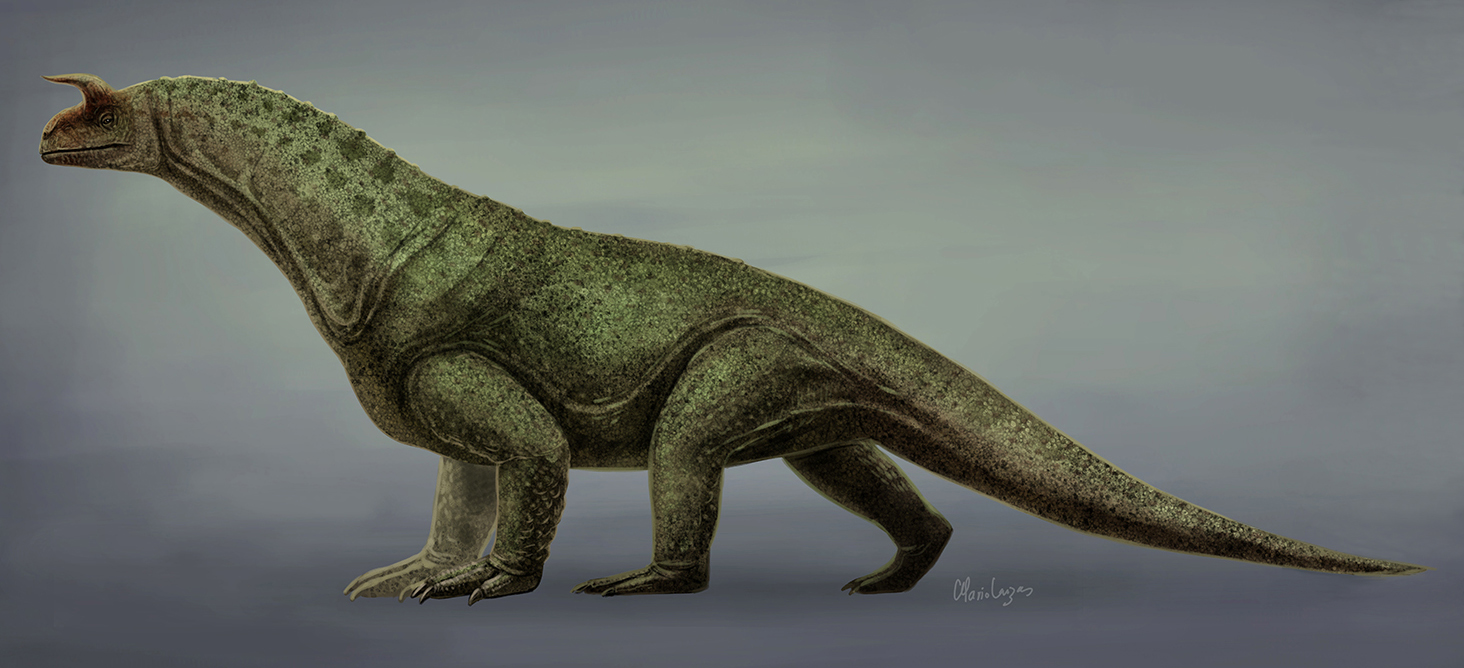
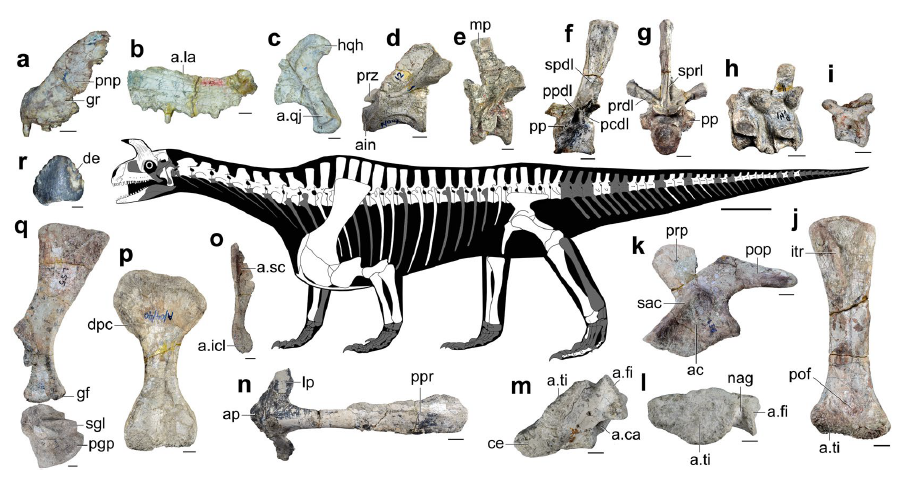 ''Shringasaurus'' was a large-bodied quadruped, with an estimated body length of . It closely resembles the related ''Azendohsaurus'', with its small, boxy head on a long neck and a large, barrel-shaped body with deep shoulders and ribs, sprawled to semi-sprawled limbs and a short tail. Aside from being notably larger than ''Azendohsaurus'', ''Shringasaurus'' is most recognisable for its long curving brow horns, as well as for having a proportionately shorter and thicker neck than other azendohsaurids and much taller
''Shringasaurus'' was a large-bodied quadruped, with an estimated body length of . It closely resembles the related ''Azendohsaurus'', with its small, boxy head on a long neck and a large, barrel-shaped body with deep shoulders and ribs, sprawled to semi-sprawled limbs and a short tail. Aside from being notably larger than ''Azendohsaurus'', ''Shringasaurus'' is most recognisable for its long curving brow horns, as well as for having a proportionately shorter and thicker neck than other azendohsaurids and much taller
 The teeth of ''Shringasaurus'' are low and leaf-shaped (lanceolate) with large denticles on either side, similar in shape to those of ''Azendohsaurus'' but lacking the prominent expansion above the root, like the teeth of ''
The teeth of ''Shringasaurus'' are low and leaf-shaped (lanceolate) with large denticles on either side, similar in shape to those of ''Azendohsaurus'' but lacking the prominent expansion above the root, like the teeth of ''
 The
The
 The ''Shringasaurus'' bone bed consists of mostly disarticulated bones (although one partial skeleton was found in articulation) scattered within a 5 m X 5 m () area of red mudstone with fine, sandy laminations. The bonebed is monodominant, only containing fossils of ''Shringasaurus'', and preserves eight individuals based on the minimum number of unique right femora, left humeri, skull roofs and horns discovered. The specimens also represent a variety of different ontogenetic stages of growth with a wide range of body sizes, from juveniles to adults. Of these individuals, only one or two lacked horns, and it's suggested that the bone bed was taphonomically biased towards the heavier, solidly built skulls of horned individuals while being transported and preserved.
However, the retention of bones rapidly lost in transport (such as ribs and limb bones), as well as minimal abrasion to many of the bones, indicates they were not transported a great distance after death. Although the bones were later disarticulated after transportation (apart from a single series of six dorsal vertebrae and ribs), they remained in closely associated clusters. They also show little weathering, indicating that most of the bones only remained exposed on the surface for perhaps only 1–3 years, with only a few exposed for longer (3–15 years). The articulated vertebrae, found lowest in the bonebed, was likely buried immediately, while the remaining bones higher in the bonebed were buried by subsequent floods. Similarly, the bones show now signs of trampling or marks from scavenging and plant growth, indicative of their short exposure before burial.
The fossils were excavated and prepared by Professor Saswati Bandyopadhyay, Dhurjati Sengupta and Shiladri Das of the
The ''Shringasaurus'' bone bed consists of mostly disarticulated bones (although one partial skeleton was found in articulation) scattered within a 5 m X 5 m () area of red mudstone with fine, sandy laminations. The bonebed is monodominant, only containing fossils of ''Shringasaurus'', and preserves eight individuals based on the minimum number of unique right femora, left humeri, skull roofs and horns discovered. The specimens also represent a variety of different ontogenetic stages of growth with a wide range of body sizes, from juveniles to adults. Of these individuals, only one or two lacked horns, and it's suggested that the bone bed was taphonomically biased towards the heavier, solidly built skulls of horned individuals while being transported and preserved.
However, the retention of bones rapidly lost in transport (such as ribs and limb bones), as well as minimal abrasion to many of the bones, indicates they were not transported a great distance after death. Although the bones were later disarticulated after transportation (apart from a single series of six dorsal vertebrae and ribs), they remained in closely associated clusters. They also show little weathering, indicating that most of the bones only remained exposed on the surface for perhaps only 1–3 years, with only a few exposed for longer (3–15 years). The articulated vertebrae, found lowest in the bonebed, was likely buried immediately, while the remaining bones higher in the bonebed were buried by subsequent floods. Similarly, the bones show now signs of trampling or marks from scavenging and plant growth, indicative of their short exposure before burial.
The fossils were excavated and prepared by Professor Saswati Bandyopadhyay, Dhurjati Sengupta and Shiladri Das of the
 ''Shringasaurus'' and other azendohsaurids share several features, including confluent nares, leaf-shaped teeth and a long neck, as well as a few other minor details of the skeleton. It is particularly similar to ''Azendohsaurus'' in features of the parietals, the lower jaw, shoulder, hip, femur and vertebrae, but can be distinguished by teeth that are not expanded above the roots, the lack of a groove on the inside surface of the maxilla, tall neural spines, and of course the horns.
''Shringasaurus'' and other azendohsaurids share several features, including confluent nares, leaf-shaped teeth and a long neck, as well as a few other minor details of the skeleton. It is particularly similar to ''Azendohsaurus'' in features of the parietals, the lower jaw, shoulder, hip, femur and vertebrae, but can be distinguished by teeth that are not expanded above the roots, the lack of a groove on the inside surface of the maxilla, tall neural spines, and of course the horns.
 The horns of ''Shringasaurus'' are its most prominent feature, and so some focus was placed on their role and function in its initial description. Its describers considered its horns to be likely products of
The horns of ''Shringasaurus'' are its most prominent feature, and so some focus was placed on their role and function in its initial description. Its describers considered its horns to be likely products of
 In the upper Denwa Formation, ''Shringasaurus'' coexisted with the
In the upper Denwa Formation, ''Shringasaurus'' coexisted with the
Indian Statistical Institute's director's report, September 16th 2017
– A report by Prof. Sanghamitra Bandyopadhyay for the ISI that includes several photos of the ''Shringasaurus'' bone bed during its excavation. {{Portalbar, Paleontology, Reptiles, India Azendohsauridae Prehistoric reptile genera Anisian genera Middle Triassic reptiles of Asia Triassic India Fossils of India Fossil taxa described in 2017
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
शृङ्ग (''śṛṅga),'' "horn", and Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
(''sauros),'' "lizard") is an extinct
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and ...
genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
of archosauromorph
Archosauromorpha (Greek for "ruling lizard forms") is a clade of diapsid reptiles containing all reptiles more closely related to archosaurs (such as crocodilians and dinosaurs, including birds) than to lepidosaurs (such as tuataras, lizards, a ...
reptile
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocepha ...
from the Middle Triassic
In the geologic timescale, the Middle Triassic is the second of three epoch (geology), epochs of the Triassic period (geology), period or the middle of three series (stratigraphy), series in which the Triassic system (stratigraphy), system is di ...
(Anisian
In the geologic timescale, the Anisian is the lower stage (stratigraphy), stage or earliest geologic age, age of the Middle Triassic series (stratigraphy), series or geologic epoch, epoch and lasted from million years ago until million years ag ...
) of India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
. It is known from the type
Type may refer to:
Science and technology Computing
* Typing, producing text via a keyboard, typewriter, etc.
* Data type, collection of values used for computations.
* File type
* TYPE (DOS command), a command to display contents of a file.
* ...
and only known species, ''S. indicus''. ''Shringasaurus'' is known from the Denwa Formation in the state of Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (; ; ) is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal and the largest city is Indore, Indore. Other major cities includes Gwalior, Jabalpur, and Sagar, Madhya Pradesh, Sagar. Madhya Pradesh is the List of states and union te ...
. ''Shringasaurus'' was an allokotosaur
Allokotosauria is a clade of early archosauromorph reptiles from the Middle to Late Triassic known from Asia, Africa, North America and Europe. Allokotosauria was first described and named when a new monophyletic grouping of specialized herbivoro ...
, a group of unusual herbivorous reptiles from the Triassic, and is most closely related to the smaller and better known ''Azendohsaurus
''Azendohsaurus'' is an extinct genus of Herbivore, herbivorous archosauromorph reptile from roughly the late Middle Triassic, Middle to early Late Triassic, Late Triassic Period of Morocco and Madagascar. The type species, ''Azendohsaurus laarou ...
'' in the family
Family (from ) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). It forms the basis for social order. Ideally, families offer predictabili ...
Azendohsauridae
Azendohsauridae is a family of allokotosaurian archosauromorphs that lived during the Middle to Late Triassic period, around 242-216 million years ago. The family was originally named solely for the eponymous ''Azendohsaurus'', marking out its di ...
. Like some ceratopsid
Ceratopsidae (sometimes spelled Ceratopidae) is a family of ceratopsian dinosaurs including ''Triceratops'', '' Centrosaurus'', and '' Styracosaurus''. All known species were quadrupedal herbivores from the Upper Cretaceous. All but one species are ...
dinosaurs
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic Geological period, period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the #Evolutio ...
, ''Shringasaurus'' had two large horns over its eyes
An eye is a sensory organ that allows an organism to perceive visual information. It detects light and converts it into electro-chemical impulses in neurons (neurones). It is part of an organism's visual system.
In higher organisms, the ey ...
that faced up and forwards from its skull
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate.
In the human, the skull comprises two prominent ...
. ''Shringasaurus'' also bears convergent physical similarities to sauropodomorph
Sauropodomorpha ( ; from Greek, meaning "lizard-footed forms") is an extinct clade of long-necked, herbivorous, saurischian dinosaurs that includes the sauropods and their ancestral relatives. Sauropods generally grew to very large sizes, had lo ...
dinosaurs, such as its long neck, its shoulders and forelimbs, and the shape of its teeth. ''Shringasaurus'' possibly occupied a similar ecological niche
In ecology, a niche is the match of a species to a specific environmental condition.
Three variants of ecological niche are described by
It describes how an organism or population responds to the distribution of Resource (biology), resources an ...
as a large browsing herbivore
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically evolved to feed on plants, especially upon vascular tissues such as foliage, fruits or seeds, as the main component of its diet. These more broadly also encompass animals that eat ...
before such dinosaurs had evolved.
Description
 ''Shringasaurus'' was a large-bodied quadruped, with an estimated body length of . It closely resembles the related ''Azendohsaurus'', with its small, boxy head on a long neck and a large, barrel-shaped body with deep shoulders and ribs, sprawled to semi-sprawled limbs and a short tail. Aside from being notably larger than ''Azendohsaurus'', ''Shringasaurus'' is most recognisable for its long curving brow horns, as well as for having a proportionately shorter and thicker neck than other azendohsaurids and much taller
''Shringasaurus'' was a large-bodied quadruped, with an estimated body length of . It closely resembles the related ''Azendohsaurus'', with its small, boxy head on a long neck and a large, barrel-shaped body with deep shoulders and ribs, sprawled to semi-sprawled limbs and a short tail. Aside from being notably larger than ''Azendohsaurus'', ''Shringasaurus'' is most recognisable for its long curving brow horns, as well as for having a proportionately shorter and thicker neck than other azendohsaurids and much taller neural spine
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal ...
s in the neck and over the shoulders.
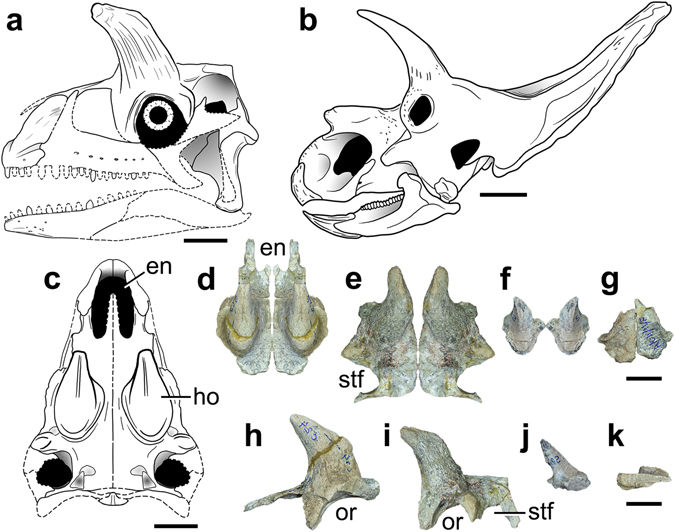
Skull
The skull of ''Shringasaurus'' is not completely known, but what's preserved indicates that the skull was small and boxy, with a short, deep snout with rounded jaw tips and bony nostrils fused into a single, confluent opening at the front of the snout. This is broadly similar to the completely known skull of ''Azendohsaurus'', but the lower jaw of ''Shringasaurus'' has a more conspicuous taper towards the tip compared to the deep, down-turneddentary
In jawed vertebrates, the mandible (from the Latin ''mandibula'', 'for chewing'), lower jaw, or jawbone is a bone that makes up the lowerand typically more mobilecomponent of the mouth (the upper jaw being known as the maxilla).
The jawbone ...
of the ''Azendohsaurus''.
The horns of ''Shringasaurus'' closely resemble those seen in ceratopsid dinosaurs, despite azendohsaurids and ceratopsids being totally unrelated to each other. The horns are attached to the frontal bone
In the human skull, the frontal bone or sincipital bone is an unpaired bone which consists of two portions.'' Gray's Anatomy'' (1918) These are the vertically oriented squamous part, and the horizontally oriented orbital part, making up the bo ...
s on the roof of the skull over the eyes, and sit across almost the entire breadth of the skull. They are pointed up and curve forwards from the skull, with slight variation in size and orientation existing among large individuals. Smaller and younger individuals had smaller, more gracile horns, indicating that the horns did not fully develop until the animals were mature. Intriguingly, at least one small specimen lacks horns entirely, whereas another similarly small specimen has small but well developed horns. It is suggested then that ''Shringasaurus'' was sexually dimorphic
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where sexes of the same species exhibit different Morphology (biology), morphological characteristics, including characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most dioecy, di ...
, and that possibly the females lacked horns.
The horns themselves have a rough, grooved texture that implies they were covered with a keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. It is the key structural material making up Scale (anatomy), scales, hair, Nail (anatomy), nails, feathers, horn (anatomy), horns, claws, Hoof, hoove ...
ous sheath of horn in life, also like ceratopsid horns, and so would have likely been longer than the bony cores indicate. The bones of the skull beneath the horns are unusually thick, and in the larger individuals the bones of roof of the skull (the nasal
Nasal is an adjective referring to the nose, part of human or animal anatomy. It may also be shorthand for the following uses in combination:
* With reference to the human nose:
** Nasal administration, a method of pharmaceutical drug delivery
* ...
, prefrontal Prefrontal may refer to:
*Prefrontal bone, a skull bone in some tetrapods
*Prefrontal cortex, a region of the brain of a mammal
*Prefrontal scales
The prefrontal scales on snakes and other reptiles are the scales adjacent and anterior to the fr ...
, frontal and postfrontal) are fused together on each side.
 The teeth of ''Shringasaurus'' are low and leaf-shaped (lanceolate) with large denticles on either side, similar in shape to those of ''Azendohsaurus'' but lacking the prominent expansion above the root, like the teeth of ''
The teeth of ''Shringasaurus'' are low and leaf-shaped (lanceolate) with large denticles on either side, similar in shape to those of ''Azendohsaurus'' but lacking the prominent expansion above the root, like the teeth of ''Pamelaria
''Pamelaria'' is an extinct genus of allokotosaurian archosauromorph reptile known from a single species, ''Pamelaria dolichotrachela'', from the Middle Triassic of India. ''Pamelaria'' has sprawling legs, a long neck, and a pointed skull with no ...
''. Because the skull and jaws are incompletely known, the total tooth count of ''Shringasaurus'' is unknown, but like ''Azendohsaurus'' it had four teeth in each premaxilla
The premaxilla (or praemaxilla) is one of a pair of small cranial bones at the very tip of the upper jaw of many animals, usually, but not always, bearing teeth. In humans, they are fused with the maxilla. The "premaxilla" of therian mammals h ...
. ''Shringasaurus'' also had numerous palatal
The palate () is the roof of the mouth in humans and other mammals. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity.
A similar structure is found in crocodilians, but in most other tetrapods, the oral and nasal cavities are not truly sepa ...
teeth (though known only from the vomer
The vomer (; ) is one of the unpaired facial bones of the skull. It is located in the midsagittal line, and articulates with the sphenoid, the ethmoid, the left and right palatine bones, and the left and right maxillary bones. The vomer forms ...
thus far), and like ''Azendohsaurus'' they are uniquely as well developed as the marginal teeth along the edge of the jaw. Like them, they were leaf-shaped and serrated, but in ''Shringasaurus'' the palatal teeth are even more lanceolate than the marginal rows. Such palatal teeth are unusual, as most other herbivorous reptiles with them have much simpler, domed palatal teeth, and palatal teeth identical to those of the jaw margins are otherwise only found in the related allokotosaurs ''Azendohsaurus'' and ''Teraterpeton
''Teraterpeton'' (meaning "wonderful creeping thing" in Greek (language), Greek) is an extinct genus of trilophosaurid archosauromorphs. It is known from a partial skeleton from the Late Triassic Wolfville Formation of Nova Scotia, described in ...
''.
Skeleton
 The
The vertebral column
The spinal column, also known as the vertebral column, spine or backbone, is the core part of the axial skeleton in vertebrates. The vertebral column is the defining and eponymous characteristic of the vertebrate. The spinal column is a segmente ...
is well known in ''Shringasaurus'', including the whole cervical series, various dorsal vertebrae
In vertebrates, thoracic vertebrae compose the middle segment of the vertebral column, between the cervical vertebrae and the lumbar vertebrae. In humans, there are twelve thoracic vertebra (anatomy), vertebrae of intermediate size between the ce ...
, both sacral vertebrae
The sacrum (: sacra or sacrums), in human anatomy, is a triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1S5) between ages 18 and 30.
The sacrum situates at the upper, back part of the pelvic cavity, ...
and some caudal vertebrae
Caudal vertebrae are the vertebrae of the tail in many vertebrates. In birds, the last few caudal vertebrae fuse into the pygostyle, and in apes, including humans, the caudal vertebrae are fused into the coccyx.
In many reptiles, some of the caud ...
. Like other azendohsaurids, the first-through-middle cervical vertebrae are characteristically elongated, giving ''Shringasaurus'' a long, raised neck, although it is proportionately shorter than in ''Azendohsaurus'' and ''Pamelaria''. The neck is also much taller than in other azendohsaurids, with tall, prominent neural spines. This trend continues into the dorsals of the back, which although are not as long as the cervicals have neural spines twice the height of their centra
Centra is a convenience shop chain that operates throughout Ireland. The chain operates as a symbol group owned by Musgrave Group, the food wholesaler, meaning the individual shops are all owned by individual franchisees.
The chain has three ...
. The 2nd–5th cervicals of ''Shringasaurus'' sport prominent epipophyses
Epipophyses are bony projections of the cervical vertebrae found in archosauromorphs, particularly dinosaurs (including some basal birds). These paired processes sit above the postzygapophyses on the rear of the vertebral neural arch. Their m ...
, structures for supporting neck musculature. The first twelve dorsals are also marked by various well-defined laminae that bound deep fossae (depressions in the bone), similar to those found on the vertebrae of sauropod
Sauropoda (), whose members are known as sauropods (; from '' sauro-'' + '' -pod'', 'lizard-footed'), is a clade of saurischian ('lizard-hipped') dinosaurs. Sauropods had very long necks, long tails, small heads (relative to the rest of their b ...
s. Like ''Azendohsaurus'', ''Shringasaurus'' has two sacral vertebrae with well-developed ribs that articulate with the ilia.
The shoulder
The human shoulder is made up of three bones: the clavicle (collarbone), the scapula (shoulder blade), and the humerus (upper arm bone) as well as associated muscles, ligaments and tendons.
The articulations between the bones of the shoulder m ...
and forelimb are broadly similar to those of ''Azendohsaurus'', with a tall scapula
The scapula (: scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side ...
that is concave along the front with an expanded tip, and an interclavicle
An interclavicle is a bone which, in most tetrapods, is located between the clavicles. Therian mammals ( marsupials and placentals) are the only tetrapods which never have an interclavicle, although some members of other groups also lack one. In ...
with a long paddle-like process on the back and a short forward-pointing process (an unusual feature for archosauromorphs but also found in ''Azendohsaurus''). The coracoid
A coracoid is a paired bone which is part of the shoulder assembly in all vertebrates except therian mammals (marsupials and placentals). In therian mammals (including humans), a coracoid process is present as part of the scapula, but this is n ...
articulates with the scapula to form a glenoid (shoulder socket) that faces out to the sides and back. The humerus
The humerus (; : humeri) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius (bone), radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extrem ...
is likewise similar, with broad ends and a narrow midshaft, and a very well-developed deltopectoral crest half as long as the whole bone, indicating powerful forelimbs. The ulna
The ulna or ulnar bone (: ulnae or ulnas) is a long bone in the forearm stretching from the elbow to the wrist. It is on the same side of the forearm as the little finger, running parallel to the Radius (bone), radius, the forearm's other long ...
, however, can be distinguished by a lower olecranon process
The olecranon (, ), is a large, thick, curved bony process on the proximal, posterior end of the ulna. It forms the protruding part of the elbow and is opposite to the cubital fossa or elbow pit (trochlear notch). The olecranon serves as a lever ...
below the elbow than in ''Azendohsaurus''.
The hips
In vertebrate anatomy, the hip, or coxaLatin ''coxa'' was used by Celsus in the sense "hip", but by Pliny the Elder in the sense "hip bone" (Diab, p 77) (: ''coxae'') in medical terminology, refers to either an anatomical region or a joint ...
and hind limbs are very similar to those of ''Azendohsaurus''. The ilium has a prominent, semi-circular process at the front while the rear process is longer and thinner, and the acetabulum (hip socket) is also solid, unlike the perforated hip socket of dinosaurs. The femur
The femur (; : femurs or femora ), or thigh bone is the only long bone, bone in the thigh — the region of the lower limb between the hip and the knee. In many quadrupeds, four-legged animals the femur is the upper bone of the hindleg.
The Femo ...
is robust and slightly s-shaped, held out to the sides in a sprawl, with a robust tibia
The tibia (; : tibiae or tibias), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two Leg bones, bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outsi ...
and a fibula
The fibula (: fibulae or fibulas) or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. ...
only half as wide in the lower leg. The foot is typical for early archosauromorphs, including ''Azendohsaurus''.
Discovery and naming
''Shringasaurus'' is known from a singlebone bed
A bone bed is any Geology, geological stratum or deposition (geology), deposit that contains bones of whatever kind. Inevitably, such deposits are Sedimentary rock, sedimentary in nature. Not a formal term, it tends to be used more to describe esp ...
of fossils in the upper Denwa Formation, India. The formation is part of the Satpura Gondwana Basin, located in the Hoshangabad district
Hoshangabad district (), officially Narmadapuram district (), is one of the districts of Madhya Pradesh States and territories of India, state of India, and Hoshangabad city is the district headquarters.
Geography
The district has an area of ...
in the state of Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (; ; ) is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal and the largest city is Indore, Indore. Other major cities includes Gwalior, Jabalpur, and Sagar, Madhya Pradesh, Sagar. Madhya Pradesh is the List of states and union te ...
. The precise age of the Denwa Formation is not known, but vertebrate biostratigraphy
Biostratigraphy is the branch of stratigraphy which focuses on correlating and assigning relative ages of rock strata by using the fossil assemblages contained within them.Hine, Robert. "Biostratigraphy." ''Oxford Reference: Dictionary of Biology ...
has been used to narrow it down to a range in the early Middle Triassic with conflicting opinions on an early or late Anisian
In the geologic timescale, the Anisian is the lower stage (stratigraphy), stage or earliest geologic age, age of the Middle Triassic series (stratigraphy), series or geologic epoch, epoch and lasted from million years ago until million years ag ...
age. The upper Denwa Formation is characteristically dominated by red mudstone
Mudstone, a type of mudrock, is a fine-grained sedimentary rock whose original constituents were clays or muds. Mudstone is distinguished from ''shale'' by its lack of fissility.Blatt, H., and R.J. Tracy, 1996, ''Petrology.'' New York, New York, ...
s with ribbon-shaped sandstone
Sandstone is a Clastic rock#Sedimentary clastic rocks, clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of grain size, sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate mineral, silicate grains, Cementation (geology), cemented together by another mineral. Sand ...
sheets encased within them. The bonebed itself was preserved in a crevasse splay
A crevasse splay is a sedimentary fluvial deposit which forms when a stream breaks its natural or artificial levees and deposits sediment on a floodplain. A breach that forms a crevasse splay deposits sediments in similar pattern to an alluvial ...
deposit composed of cross-bedded
In geology, cross-bedding, also known as cross-stratification, is layering within a stratum and at an angle to the main bedding plane. The sedimentary structures which result are roughly horizontal units composed of inclined layers. The original ...
, dipped sandstone with irregular boundaries that breached along the south edge of an ancient filled river channel. This flooding event was unlikely to be an isolated event, as the size of the crevasse splay suggests multiple phases of flooding that cumulatively buried the remains of the herd.
 The ''Shringasaurus'' bone bed consists of mostly disarticulated bones (although one partial skeleton was found in articulation) scattered within a 5 m X 5 m () area of red mudstone with fine, sandy laminations. The bonebed is monodominant, only containing fossils of ''Shringasaurus'', and preserves eight individuals based on the minimum number of unique right femora, left humeri, skull roofs and horns discovered. The specimens also represent a variety of different ontogenetic stages of growth with a wide range of body sizes, from juveniles to adults. Of these individuals, only one or two lacked horns, and it's suggested that the bone bed was taphonomically biased towards the heavier, solidly built skulls of horned individuals while being transported and preserved.
However, the retention of bones rapidly lost in transport (such as ribs and limb bones), as well as minimal abrasion to many of the bones, indicates they were not transported a great distance after death. Although the bones were later disarticulated after transportation (apart from a single series of six dorsal vertebrae and ribs), they remained in closely associated clusters. They also show little weathering, indicating that most of the bones only remained exposed on the surface for perhaps only 1–3 years, with only a few exposed for longer (3–15 years). The articulated vertebrae, found lowest in the bonebed, was likely buried immediately, while the remaining bones higher in the bonebed were buried by subsequent floods. Similarly, the bones show now signs of trampling or marks from scavenging and plant growth, indicative of their short exposure before burial.
The fossils were excavated and prepared by Professor Saswati Bandyopadhyay, Dhurjati Sengupta and Shiladri Das of the
The ''Shringasaurus'' bone bed consists of mostly disarticulated bones (although one partial skeleton was found in articulation) scattered within a 5 m X 5 m () area of red mudstone with fine, sandy laminations. The bonebed is monodominant, only containing fossils of ''Shringasaurus'', and preserves eight individuals based on the minimum number of unique right femora, left humeri, skull roofs and horns discovered. The specimens also represent a variety of different ontogenetic stages of growth with a wide range of body sizes, from juveniles to adults. Of these individuals, only one or two lacked horns, and it's suggested that the bone bed was taphonomically biased towards the heavier, solidly built skulls of horned individuals while being transported and preserved.
However, the retention of bones rapidly lost in transport (such as ribs and limb bones), as well as minimal abrasion to many of the bones, indicates they were not transported a great distance after death. Although the bones were later disarticulated after transportation (apart from a single series of six dorsal vertebrae and ribs), they remained in closely associated clusters. They also show little weathering, indicating that most of the bones only remained exposed on the surface for perhaps only 1–3 years, with only a few exposed for longer (3–15 years). The articulated vertebrae, found lowest in the bonebed, was likely buried immediately, while the remaining bones higher in the bonebed were buried by subsequent floods. Similarly, the bones show now signs of trampling or marks from scavenging and plant growth, indicative of their short exposure before burial.
The fossils were excavated and prepared by Professor Saswati Bandyopadhyay, Dhurjati Sengupta and Shiladri Das of the Indian Statistical Institute
The Indian Statistical Institute (ISI) is a public research university headquartered in Kolkata, India with centers in New Delhi, Bengaluru, Chennai and Tezpur. It was declared an Institute of National Importance by the Government of India und ...
, Kolkata
Kolkata, also known as Calcutta ( its official name until 2001), is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of West Bengal. It lies on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River, west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary ...
, where the fossils are also stored. It was then described and named in August 2017 by Sarandee Sengupta and Bandyopadhyay, as well as by Martín D. Ezcurra of the Bernardino Rivadavia Natural Sciences Argentine Museum in Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
. The holotype
A holotype (Latin: ''holotypus'') is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of s ...
specimen, ISIR 780, consists of a partial skull roof including the prefrontal, frontal, postfrontal and parietal bones, along with a pair of large supra-orbital horns. The various other specimens from the bone bed have been designated as paratype
In zoology and botany, a paratype is a specimen of an organism that helps define what the scientific name of a species and other taxon actually represents, but it is not the holotype (and in botany is also neither an isotype (biology), isotype ...
s and consist of multiple cranial and postcranial bones from much of the skeleton. The genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
was named using the ancient Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
word for "horn", 'Śṛṅga' (शृङ्ग), for the unique horns on its skull, combined with the Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
''σαῦρος'' (''sauros'') for "lizard". The specific name Specific name may refer to:
* in Database management systems, a system-assigned name that is unique within a particular database
In taxonomy, either of these two meanings, each with its own set of rules:
* Specific name (botany), the two-part (bino ...
''indicus'' is Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
for "Indian", to refer to its country of discovery.
Classification
''Shringasaurus'' is recognised as a member of the familyAzendohsauridae
Azendohsauridae is a family of allokotosaurian archosauromorphs that lived during the Middle to Late Triassic period, around 242-216 million years ago. The family was originally named solely for the eponymous ''Azendohsaurus'', marking out its di ...
, and as the closest relative of ''Azendohsaurus'' itself. The family is typically grouped within the recently recognised clade
In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach t ...
Allokotosauria
Allokotosauria is a clade of early archosauromorph reptiles from the Middle to Late Triassic known from Asia, Africa, North America and Europe. Allokotosauria was first described and named when a new monophyletic grouping of specialized herbivor ...
, along with the trilophosaurids, as was recovered by Sengupta and colleagues when they described ''Shringasaurus'' and analysed its phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical dat ...
relationships in 2017. Another analysis of archosauromorph relationships in 2019 that used a different dataset from Sengupta ''et al.'' (2017)—that of Pritchard ''et al.'' (2018)—was updated to include ''Shringasaurus'', and similarly recovered it and ''Azendohsaurus'' as each other's closest relatives within Allokotosauria, further supporting an azendohsaurid affinity for ''Shringasaurus''.
The results found by Sengupta and colleagues in 2017 is shown below as an excerpt of the full cladogram, simplified and focused on the relationships of ''Shringasaurus'' to other allokotosaurs:
 ''Shringasaurus'' and other azendohsaurids share several features, including confluent nares, leaf-shaped teeth and a long neck, as well as a few other minor details of the skeleton. It is particularly similar to ''Azendohsaurus'' in features of the parietals, the lower jaw, shoulder, hip, femur and vertebrae, but can be distinguished by teeth that are not expanded above the roots, the lack of a groove on the inside surface of the maxilla, tall neural spines, and of course the horns.
''Shringasaurus'' and other azendohsaurids share several features, including confluent nares, leaf-shaped teeth and a long neck, as well as a few other minor details of the skeleton. It is particularly similar to ''Azendohsaurus'' in features of the parietals, the lower jaw, shoulder, hip, femur and vertebrae, but can be distinguished by teeth that are not expanded above the roots, the lack of a groove on the inside surface of the maxilla, tall neural spines, and of course the horns.
Palaeobiology
The ''Shringasaurus'' bonebed suggests that it was agregarious
Sociality is the degree to which individuals in an animal population tend to associate in social groups (gregariousness) and form cooperative societies.
Sociality is a survival response to evolutionary pressures. For example, when a mother was ...
animal that lived in herds. The herd appears to have died in a mass mortality event
A mass mortality event (MME) is an incident that kills a vast number of individuals of a single species in a short period of time. The event may put a species at risk of extinction or upset an ecosystem. This is distinct from the mass die-off asso ...
and was buried in a short span of time, possibly drowned by a breached levee. The bonebed includes juveniles, sub-adults and adults, further suggesting that ''Shringasaurus'' lived in mixed-age herds. The herd was also mixed-sex, based on the presence of both purported males and females, although it is unclear if they lived mixed-sex year round or if they only did so during part of the year, namely the breeding season (as observed in domestic sheep
Sheep (: sheep) or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are a domesticated, ruminant mammal typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus '' Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to ...
and related herbivores where males similarly spar with their horns). The herd was likely congregating around a nearby river channel during a period of environmental stress such as a drought, as occurs in living herbivores and has also been inferred for some dinosaurs.
Function of the horns
 The horns of ''Shringasaurus'' are its most prominent feature, and so some focus was placed on their role and function in its initial description. Its describers considered its horns to be likely products of
The horns of ''Shringasaurus'' are its most prominent feature, and so some focus was placed on their role and function in its initial description. Its describers considered its horns to be likely products of sexual selection
Sexual selection is a mechanism of evolution in which members of one sex mate choice, choose mates of the other sex to mating, mate with (intersexual selection), and compete with members of the same sex for access to members of the opposite sex ...
, not primarily for defence or species recognition
Intra-species recognition is the recognition by a member of an animal species of a conspecific (another member of the same species). In many species, such recognition is necessary for procreation.
Different species may employ different methods, ...
(as has been proposed for the head ornaments of dinosaurs). The horns grow notably larger and more robust in large adults, while smaller individuals have shorter and more graceful horns. The possibility that ''Shringasaurus'' was sexually dimorphic, with probable females lacking horns, further supports this interpretation. This would be similar to modern horned bovid
The Bovidae comprise the family (biology), biological family of cloven-hoofed, ruminant mammals that includes Bos, cattle, bison, Bubalina, buffalo, antelopes (including Caprinae, goat-antelopes), Ovis, sheep and Capra (genus), goats. A member o ...
s, but unlike ceratopsid
Ceratopsidae (sometimes spelled Ceratopidae) is a family of ceratopsian dinosaurs including ''Triceratops'', '' Centrosaurus'', and '' Styracosaurus''. All known species were quadrupedal herbivores from the Upper Cretaceous. All but one species are ...
dinosaurs, and indeed other archosauromorphs, which do not appear to have been dimorphic.
Palaeopathology
One specimen of ''Shringasaurus'' is known to have had a pair of malformed vertebrae in its neck. The two cervicals are partially fused together, interpreted as either the result of abirth defect
A birth defect is an abnormal condition that is present at birth, regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can range from mild to severe. Birth de ...
, spondyloarthropathy
Spondyloarthritis (SpA), also known as spondyloarthropathy, is a collection of syndromes connected by genetic predisposition and clinical symptoms. The best-known subtypes are enteropathic arthritis (EA), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), ankylosing ...
(a type of arthritis
Arthritis is a general medical term used to describe a disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, Joint effusion, swelling, and decreased range of motion of ...
), or possibly a bacterial or fungal disc
Disc or disk may refer to:
* Disk (mathematics), a two dimensional shape, the interior of a circle
* Disk storage
* Optical disc
* Floppy disk
Music
* Disc (band), an American experimental music band
* ''Disk'' (album), a 1995 EP by Moby
Other ...
infection. The vertebrae belonged to a large adult animal, so it is unlikely that the quality of life for the individual was severely affected by the disorder, and it was probably not fatal to the animal. One of the vertebrae also preserves a healed fracture, although the cause for this injury is unknown.
Palaeoecology
 In the upper Denwa Formation, ''Shringasaurus'' coexisted with the
In the upper Denwa Formation, ''Shringasaurus'' coexisted with the lungfish
Lungfish are freshwater vertebrates belonging to the class Dipnoi. Lungfish are best known for retaining ancestral characteristics within the Osteichthyes, including the ability to breathe air, and ancestral structures within Sarcopterygii, inc ...
''Ceratodus
''Ceratodus'' (from , 'horn' and 'tooth') is an extinct genus of freshwater lungfish that was found worldwide during the Mesozoic Era. It has been described as a "catch all", and a " form genus" used to refer to the remains (typically tooth ...
'' sp. and a variety of temnospondyl
Temnospondyli (from Greek language, Greek τέμνειν, ''temnein'' 'to cut' and σπόνδυλος, ''spondylos'' 'vertebra') or temnospondyls is a diverse ancient order (biology), order of small to giant tetrapods—often considered Labyrinth ...
amphibians, including the capitosaurid ''Paracyclotosaurus crookshanki
''Paracyclotosaurus'' (meaning "Near Wheeled Lizard") is an extinct genus of temnospondyl, which would have appeared similar to today's salamander – but much larger, measuring up to long and weighing between . It lived in the Middle Triassic ...
'', the mastodonsaurid
Mastodonsauridae is a family of capitosauroid temnospondyls. Fossils belonging to this family have been found in North America, Greenland, Europe, Asia, and Australia. The family Capitosauridae is synonymous with Mastodonsauridae.
Description S ...
''Cherninia denwai
''Cherninia'' is an extinct genus of mastodonsaurid temnospondyl known from the Denwa Formation of India and the Ntawere Formation of Zambia.
Discovery and species
The type species, ''Cherninia denwai'', is known from the Denwa Formation. ...
'', a lonchorhynchine trematosaurid, and a brachyopid. Other terrestrial vertebrates include a large undescribed rhynchosaur
Rhynchosaurs are a group of extinct herbivorous Triassic archosauromorph reptiles, belonging to the order Rhynchosauria. Members of the group are distinguished by their triangular skulls and elongated, beak like premaxillary bones. Rhynchosaurs ...
and two species of dicynodonts
Dicynodontia is an extinct clade of anomodonts, an extinct type of non-mammalian therapsid. Dicynodonts were herbivores that typically bore a pair of tusks, hence their name, which means 'two dog tooth'. Members of the group possessed a horny, t ...
, a mid-sized species similar to ''Kannemeyeria
''Kannemeyeria'' is a genus of dicynodont that lived during the Anisian age of Middle Triassic period in what is now Africa and South America. The generic name is given in honor of Daniel Rossouw Kannemeyer, the South African fossil collector w ...
'' and a larger species interpreted as similar to ''Stahleckeria
''Stahleckeria'' is an extinct genus of Middle Triassic (Ladinian) dicynodonts.''Stahle ...
''. The environment is interpreted as representing a dry, semi-arid floodplain with slow moving, anabranch
An anabranch is a section of a river or stream that diverts from the main channel or stem of the watercourse and rejoins the main stem downstream. Local anabranches can be the result of small islands in the watercourse. In larger anabranches, ...
ing rivers that periodically burst their banks. Rainfall was seasonal, and the environment experienced droughts that dried up ephemeral rivers and ponds. The large body size of ''Shringasaurus'' and its convergent similarity to sauropodomorphs—including its jaws and teeth as well as a superficially similar body shape—suggests that it possibly occupied the role of a large, relatively high-browsing herbivore in its environment.
References
External links
Indian Statistical Institute's director's report, September 16th 2017
– A report by Prof. Sanghamitra Bandyopadhyay for the ISI that includes several photos of the ''Shringasaurus'' bone bed during its excavation. {{Portalbar, Paleontology, Reptiles, India Azendohsauridae Prehistoric reptile genera Anisian genera Middle Triassic reptiles of Asia Triassic India Fossils of India Fossil taxa described in 2017