Shot (pellet) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Shot is a collective term for small spheres or pellets, often made of
Shot is a collective term for small spheres or pellets, often made of
 Producing lead shot from a shot tower was pioneered in the late 18th century by William Watts of
Producing lead shot from a shot tower was pioneered in the late 18th century by William Watts of

 When used as a pourable/mouldable weight, lead shot may be left loose, or mixed with a bonding agent such as
When used as a pourable/mouldable weight, lead shot may be left loose, or mixed with a bonding agent such as
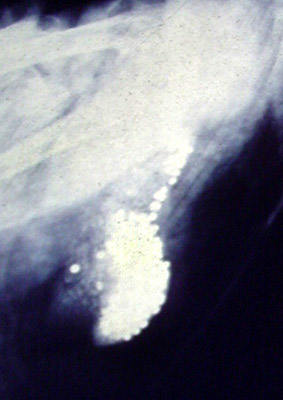 Lead shot-related waterfowl poisonings were first documented in the US in the 1880s; by 1919, the spent lead pellets from waterfowl hunting were positively identified as a major source of deaths of bottom-feeding waterfowl.Federal Cartridge Company Waterfowl and Steel Shot Guide. Volume I; 1988. Once ingested, stomach acids and mechanical action cause the lead to break down and be absorbed into the body and bloodstream, resulting in death. "If a bird swallows only one pellet, it usually survives, although its immune system and fertility are likely to be affected. Even low concentrations of lead have a negative impact on energy storage, which affects the ability to prepare for migration."
Lead shot-related waterfowl poisonings were first documented in the US in the 1880s; by 1919, the spent lead pellets from waterfowl hunting were positively identified as a major source of deaths of bottom-feeding waterfowl.Federal Cartridge Company Waterfowl and Steel Shot Guide. Volume I; 1988. Once ingested, stomach acids and mechanical action cause the lead to break down and be absorbed into the body and bloodstream, resulting in death. "If a bird swallows only one pellet, it usually survives, although its immune system and fertility are likely to be affected. Even low concentrations of lead have a negative impact on energy storage, which affects the ability to prepare for migration."
 Shot is a collective term for small spheres or pellets, often made of
Shot is a collective term for small spheres or pellets, often made of lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleabl ...
. These have been projected from slings since ancient times and were the original projectile
A projectile is an object that is propelled by the application of an external force and then moves freely under the influence of gravity and air resistance. Although any objects in motion through space are projectiles, they are commonly found ...
s for shotguns and are still fired primarily from shotgun
A shotgun (also known as a scattergun, peppergun, or historically as a fowling piece) is a long gun, long-barreled firearm designed to shoot a straight-walled cartridge (firearms), cartridge known as a shotshell, which discharges numerous small ...
s and grenade launcher
A grenade launcher is a weapon that fires a specially designed, large caliber projectile, often with an explosive, Smoke screen, smoke, or tear gas, gas warhead. Today, the term generally refers to a class of dedicated firearms firing unitary gre ...
s, while they are less commonly used in riot gun
In current usage, a riot gun or less-lethal launcher is a type of firearm used to fire Non-lethal weapon, "non-lethal" or "less-lethal" ammunition for the purpose of suppressing riots or apprehending suspects with minimal harm or risk. Less-leth ...
s. Shot shells are also available in many handgun
A handgun is a firearm designed to be usable with only one hand. It is distinguished from a long gun, long barreled gun (i.e., carbine, rifle, shotgun, submachine gun, or machine gun) which typically is intended to be held by both hands and br ...
calibers in a configuration known as " birdshot", " rat shot", or " snake shot".
Lead shot is also used for a variety of other purposes such as filling cavities with dense material for weight and/or balance. Some versions may be plated with other metals. Lead shot was originally made by pouring molten lead through screens into water, forming what was known as "swan shot", and, later, more economically mass-produced at higher quality using a shot tower. The ''Bliemeister method'' has supplanted the shot tower method since the early 1960s.
Manufacture
 Producing lead shot from a shot tower was pioneered in the late 18th century by William Watts of
Producing lead shot from a shot tower was pioneered in the late 18th century by William Watts of Bristol
Bristol () is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city, unitary authority area and ceremonial county in South West England, the most populous city in the region. Built around the River Avon, Bristol, River Avon, it is bordered by t ...
who adapted his house on Redcliffe Hill by adding a three-storey
A storey (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English) or story (American English), is any level part of a building with a floor that could be used by people (for living, work, storage, recreation, etc.). Plurals for the wor ...
tower and digging a shaft under the house through the caves underneath to achieve the required drop. The process was patented in 1782. The process was later brought above ground through the building of shot towers.
Molten lead would be dropped from the top of the tower. Like most liquids, surface tension
Surface tension is the tendency of liquid surfaces at rest to shrink into the minimum surface area possible. Surface tension (physics), tension is what allows objects with a higher density than water such as razor blades and insects (e.g. Ge ...
makes drops of molten lead become near-spherical as they fall. When the tower is high enough, the lead droplets will solidify during the fall and thus retain their spherical form. Water is usually placed at the bottom of the tower, cooling the lead immediately upon landing.
Roundness of manufactured shot produced from the shot tower process is graded by forcing the newly produced shot to roll accurately down inclined planes. Unround shot will naturally roll to the side, for collection. The unround shot was either re-processed in another attempt to make round shot using the shot tower again, or used for applications which did not require round shot (e.g., split shot for fishing).
The hardness of lead shot is controlled through adding variable amounts of tin
Tin is a chemical element; it has symbol Sn () and atomic number 50. A silvery-colored metal, tin is soft enough to be cut with little force, and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, a bar of tin makes a sound, the ...
, antimony
Antimony is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Sb () and atomic number 51. A lustrous grey metal or metalloid, it is found in nature mainly as the sulfide mineral stibnite (). Antimony compounds have been known since ancient t ...
and arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol As and atomic number 33. It is a metalloid and one of the pnictogens, and therefore shares many properties with its group 15 neighbors phosphorus and antimony. Arsenic is not ...
, forming alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which in most cases at least one is a metal, metallic element, although it is also sometimes used for mixtures of elements; herein only metallic alloys are described. Metallic alloys often have prop ...
s. This also affects its melting point. Hardness is also controlled by the rate of cooling that is used in manufacturing lead shot.
The ', named after inventor Louis W. Bliemeister of Los Angeles, California, (, dated April 11, 1961) is a process for making lead shot in small sizes from about #7 to about #9. In this process, molten lead is dripped from small orifices and dropped approximately into a hot liquid, where it is then rolled along an incline and then dropped another . The temperature of the liquid controls the cooling rate of the lead, while the surface tension of the liquid and the inclined surface(s) work together to bring the small droplets of lead into highly regular balls of lead in spherical form. The size of the lead shot that is produced is determined by the diameter of the orifice used to drip the lead, ranging from approximately for #9 lead shot to about for #6 or #7.0 shot, while also depending on the specific lead alloy that is used.
The roundness of the lead shot depends on the angle of the inclined surfaces as well as the temperature of the liquid coolant. Various coolants have successfully been used, ranging from diesel fuel to antifreeze and water-soluble oil. After the lead shot cools, it is washed, then dried, and small amounts of graphite are finally added to prevent clumping of the lead shot. Lead shot larger than about #5 tends to clump badly when fed through tubes, even when graphite is used, whereas lead shot smaller than about #6 tends not to clump when fed through tubes when graphite is used.
Lead shot dropped quickly into liquid cooling baths when being produced from molten lead is known as "chilled lead shot", in contrast to "soft lead shot" which is produced by molten lead not being dropped as quickly into a liquid cooling bath. The process of rapidly chilling lead shot during its manufacturing process causes the shot to become harder than it would otherwise be if allowed to cool more slowly. Hence, chilled lead shot, being harder and less likely to deform during firing, is preferred by shotgunners for improving shot pattern densities at longer (> ) ranges, whereas soft lead shot, being softer and more likely to deform during firing, is preferred for improving shot pattern densities at very close (< ) ranges as the softer and now deformed shot scatters more quickly when fired. Soft lead shot is also more readily deformed during the firing process by the effects of chokes.
The manufacture of non-lead shot differs from that of lead, with compression molding
Compression molding is a method of molding (process), molding in which the molding material, generally preheated, is first placed in an open, heated Molding (process), mold cavity. The mold is closed with a top force or plug member, pressure ...
used to create some alloys.
Sizes
Shot is available in many sizes for different applications. The size of numbered shot decreases as the number increases. In hunting, some sizes are traditionally used for certain game, or certain shooting situations, although there is overlap and subjective preference. The range at which game is typically encountered and the penetration needed to assure a clean kill must both be considered. Local hunting regulations may also specify a size range for certain game. Shot loses its velocity very quickly due to its lowsectional density
Sectional density (often abbreviated SD) is the ratio of an object's mass to its cross sectional area with respect to a given axis. It conveys how well an object's mass is distributed (by its shape) to overcome resistance along that axis.
Secti ...
and ballistic coefficient
In ballistics, the ballistic coefficient (BC, ''C'') of a body is a measure of its ability to overcome air resistance in flight. It is inversely proportional to the negative acceleration: a high number indicates a low negative acceleration—the ...
(see external ballistics
External ballistics or exterior ballistics is the part of ballistics that deals with the behavior of a projectile in flight. The projectile may be powered or un-powered, guided or unguided, spin or fin stabilized, flying through an atmosphere or ...
). Generally, larger shot carries farther, and does not spread out as much as smaller shot.
Buckshot
Buckshot is a shot formed to larger diameters so that it can be used against bigger game such asdeer
A deer (: deer) or true deer is a hoofed ruminant ungulate of the family Cervidae (informally the deer family). Cervidae is divided into subfamilies Cervinae (which includes, among others, muntjac, elk (wapiti), red deer, and fallow deer) ...
, moose
The moose (: 'moose'; used in North America) or elk (: 'elk' or 'elks'; used in Eurasia) (''Alces alces'') is the world's tallest, largest and heaviest extant species of deer and the only species in the genus ''Alces''. It is also the tal ...
, or caribou
The reindeer or caribou (''Rangifer tarandus'') is a species of deer with circumpolar distribution, native to Arctic, subarctic, tundra, boreal, and mountainous regions of Northern Europe, Siberia, and North America. It is the only represe ...
. Sizes range in ascending order from size #B (0.17 in, 4.32 mm) to Tri-Ball. It is usually referred by the size, followed by "buck", e.g. "#000" is referred to as "triple-aught buck" in the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
or "triple-o buck" in other English speaking countries. Buckshot is traditionally swaged (in high volume production) or cast (in small volume production). The Bliemeister method does not work for shot larger than #5 (0.12 in, 3.05 mm), and works progressively poorly for shot sizes larger than about #6.
Lead shot comparison chart
Below is a chart with diameters per pellet and weight for idealized lead spheres for U.S. Standard Designations with a comparison to English shot sizes.Applications outside firearms

 When used as a pourable/mouldable weight, lead shot may be left loose, or mixed with a bonding agent such as
When used as a pourable/mouldable weight, lead shot may be left loose, or mixed with a bonding agent such as epoxy
Epoxy is the family of basic components or Curing (chemistry), cured end products of epoxy Resin, resins. Epoxy resins, also known as polyepoxides, are a class of reactive prepolymers and polymers which contain epoxide groups. The epoxide fun ...
to contain and stabilize the pellets after they are poured.
Some applications of lead shot are:
* As ballast
Ballast is dense material used as a weight to provide stability to a vehicle or structure. Ballast, other than cargo, may be placed in a vehicle, often a ship or the gondola of a balloon or airship, to provide stability. A compartment within ...
in various situations, especially where a dense, pourable weight is required. Generally, small shot is best for these applications, as it can be poured more like a liquid. Completely round shot is not required.
* Stress testing: Providing variable weights in strength-of-materials stress-testing systems. Shot pours from a hopper into a basket, which is connected to the test item. When the test item fracture
Fracture is the appearance of a crack or complete separation of an object or material into two or more pieces under the action of stress (mechanics), stress. The fracture of a solid usually occurs due to the development of certain displacemen ...
s, the chute closes and the mass of the lead shot in the basket is used to calculate the fracture stress of the item.
* Hydrometer
A hydrometer or lactometer is an instrument used for measuring density or relative density of liquids based on the concept of buoyancy. They are typically Calibration, calibrated and Graduation (instrument), graduated with one or more scales suc ...
s: use a weight made of shot, since the weight has to be poured into a narrow glass vessel.
* Split shot, a larger type of lead shot where each pellet is cut part-way through the diameter. This type of shot was formerly commonly used as a line weight in angling
Angling (from Old English ''angol'', meaning "hook") is a fishing technique that uses a fish hook attached to a fishing line to tether individual fish in the mouth. The fishing line is usually manipulated with a fishing rod, although rodless te ...
. They are no longer solely manufactured from lead but instead are often made from softer materials that can be easily pressed onto the fishing line instead of being closed in a crimp using pliers, as was once common.
* The heads of some dead blow hammer
A dead-blow hammer is a specialized mallet helpful in minimizing damage to the struck surface and in controlling striking force, with minimal rebound from the struck surface. The minimal rebound is helpful in avoiding accidental damage to precis ...
s are filled with shot to minimize rebound off the struck surface.
* Shot belt: some scuba diving
Scuba diving is a Diving mode, mode of underwater diving whereby divers use Scuba set, breathing equipment that is completely independent of a surface breathing gas supply, and therefore has a limited but variable endurance. The word ''scub ...
weight belts contain pouches filled with lead shot.
* Many blackjacks and saps use lead shot as a flexible weight to deliver high energy blows while minimizing damage from sharp impact force (similar to the way it is used in dead blow hammers).
* Loudspeaker
A loudspeaker (commonly referred to as a speaker or, more fully, a speaker system) is a combination of one or more speaker drivers, an enclosure, and electrical connections (possibly including a crossover network). The speaker driver is an ...
stands can be filled with lead shot for additional acoustic decoupling, as well as stability.
* Model rocketry
A model rocket is a small rocket designed to reach low altitudes (e.g., for a model) and #Model rocket recovery methods, be recovered by a variety of means.
According to the United States National Association of Rocketry, National Associati ...
: to add weight to the nose of the rocket, increasing the stability factor.
* Due to its heat capacity and low thermal conductivity at low temperatures, lead shot has been used as a suitable material for a regenerator in Stirling engine
A Stirling engine is a heat engine that is operated by the cyclic expansion and contraction of air or other gas (the ''working fluid'') by exposing it to different temperatures, resulting in a net conversion of heat energy to mechanical Work (ph ...
s and thermoacoustic cryocoolers
A cryocooler is a refrigerator designed to reach cryogenic temperatures (below 120 K, -153 °C, -243.4 °F). The term is most often used for smaller systems, typically table-top size, with input powers less than about 20 kW. Some can have inpu ...
.
* Due to lead's high density, it is used to attenuate radiation
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or a material medium. This includes:
* ''electromagnetic radiation'' consisting of photons, such as radio waves, microwaves, infr ...
, especially X-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
s and gamma ray
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol ), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from high energy interactions like the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei or astronomical events like solar flares. It consists o ...
s. Lead shot may be enclosed in a vest, blanket, or bag that is placed around a point source
A point source is a single identifiable ''localized'' source of something. A point source has a negligible extent, distinguishing it from other source geometries. Sources are called point sources because, in mathematical modeling, these sources ...
for radiation shielding.
Bird lead poisoning
 Lead shot-related waterfowl poisonings were first documented in the US in the 1880s; by 1919, the spent lead pellets from waterfowl hunting were positively identified as a major source of deaths of bottom-feeding waterfowl.Federal Cartridge Company Waterfowl and Steel Shot Guide. Volume I; 1988. Once ingested, stomach acids and mechanical action cause the lead to break down and be absorbed into the body and bloodstream, resulting in death. "If a bird swallows only one pellet, it usually survives, although its immune system and fertility are likely to be affected. Even low concentrations of lead have a negative impact on energy storage, which affects the ability to prepare for migration."
Lead shot-related waterfowl poisonings were first documented in the US in the 1880s; by 1919, the spent lead pellets from waterfowl hunting were positively identified as a major source of deaths of bottom-feeding waterfowl.Federal Cartridge Company Waterfowl and Steel Shot Guide. Volume I; 1988. Once ingested, stomach acids and mechanical action cause the lead to break down and be absorbed into the body and bloodstream, resulting in death. "If a bird swallows only one pellet, it usually survives, although its immune system and fertility are likely to be affected. Even low concentrations of lead have a negative impact on energy storage, which affects the ability to prepare for migration." Upland game bird
Upland game bird is an American term which refers to non-waterfowl game birds in groundcover-rich terrestrial ecosystems above wetlands and riparian zones (i.e. "uplands"), which are commonly hunted with gun dogs (pointing breeds, flushing spaniel ...
s such as mourning doves, ring-necked pheasant
The common pheasant (''Phasianus colchicus''), ring-necked pheasant, or blue-headed pheasant, is a bird in the pheasant family (Phasianidae). The genus name comes from Latin ''phasianus'' 'pheasant'. The species name ''colchicus'' is Latin for ...
s, wild turkey
The wild turkey (''Meleagris gallopavo'') is an upland game bird native to North America, one of two extant species of Turkey (bird), turkey and the heaviest member of the order Galliformes. It is the ancestor to the domestic turkey (''M. g. dom ...
, northern bobwhite quail
Quail is a collective name for several genera of mid-sized birds generally placed in the order Galliformes. The collective noun for a group of quail is a flock, covey, or bevy.
Old World quail are placed in the family Phasianidae, and New ...
and chukars can also ingest lead and thus be poisoned when they feed on seeds.
Lead from spent ammunition also impacts scavenging bird species such as vultures, ravens, eagles and other birds of prey. Foraging studies of the endangered Californian condor have shown that avian scavengers consume lead fragments in gut piles left in the field from harvested big game animals, as well as by the consumption of small game, or "pest animal," carcasses that have been shot with lead-core ammo, but not retrieved. Not all lead exposure in these circumstances leads to immediate mortality, but multiple sub-lethal exposures result in secondary poisoning impacts, which eventually lead to death. Among condors around the Grand Canyon
The Grand Canyon is a steep-sided canyon carved by the Colorado River in Arizona, United States. The Grand Canyon is long, up to wide and attains a depth of over a mile ().
The canyon and adjacent rim are contained within Grand Canyon Nati ...
, lead poisoning because of eating lead shot is the most frequently diagnosed cause of death.
Restrictions on the use of lead
Alternatives to lead shot are mandated for use by hunters in certain locations or when hunting migratorywaterfowl
Anseriformes is an order of birds also known as waterfowl that comprises about 180 living species of birds in three families: Anhimidae (three species of screamers), Anseranatidae (the magpie goose), and Anatidae, the largest family, which i ...
and migratory birds
Bird migration is a seasonal movement of birds between breeding and wintering grounds that occurs twice a year. It is typically from north to south or from south to north. Migration is inherently risky, due to predation and mortality.
The ...
or when hunting
Hunting is the Human activity, human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, and killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to obtain the animal's body for meat and useful animal products (fur/hide (sk ...
within federal waterfowl production areas, wildlife refuges, or some state wildlife management areas. Shot pellets used in waterfowl hunting
Waterfowl hunting is the practice of hunting aquatic birds such as ducks, geese and other waterfowls or shorebirds for sport and meat. Waterfowl are hunted in crop fields where they feed, or in areas with bodies of water such as rivers, lakes ...
must be lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleabl ...
-free in the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
, and in the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
.
Lead shot is also banned within an eight-county area in California designated as the condor
Condor is the common name for two species of New World vultures, each in a monotypic genus. The name derives from the Quechua language, Quechua ''kuntur''. They are the largest flying land birds in the Western Hemisphere.
One species, the And ...
's range. As of 2011, thirty-five states prohibited lead shot use in such specially-specified areas when hunting.
In an effort to protect the condor, the use of projectiles containing lead has been banned for hunting wild boar, deer, antelope, elk, pronghorn, antelope, coyote, squirrel, and other non-game wildlife in areas of California designated as its habitat range. The bald eagle
The bald eagle (''Haliaeetus leucocephalus'') is a bird of prey found in North America. A sea eagle, it has two known subspecies and forms a species pair with the white-tailed eagle (''Haliaeetus albicilla''), which occupies the same niche ...
has similarly been shown to be affected by lead originating from dead or wounded waterfowl—the requirement to protect this species was one of the biggest factors behind laws being introduced in 1991 by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service
The United States Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS or FWS) is a List of federal agencies in the United States, U.S. federal government agency within the United States Department of the Interior which oversees the management of fish, wildlife, ...
to ban lead shot in migratory waterfowl hunting.
Hunting restrictions have also banned the use of lead shot while hunting migratory waterfowl in at least 29 countries across by international agreement, for example the Agreement on the Conservation of African-Eurasian Migratory Waterbirds. Depending on hunting laws, alternatives to lead shot are mandated for use by hunters in some locations when hunting migratory birds, notably waterfowl. In the US, the restrictions are limited to migratory waterfowl, while Canadian restrictions are wider and apply (with some exceptions) to all migratory birds. The hunting of upland migratory birds such as mourning doves was specifically excluded from the 1991 US restrictions as scientific evidence did not support their contribution to the poisoning of bald eagles. In 1985, Denmark banned the use of lead in wetlands covered by the Ramsar Convention
The Ramsar Convention on Wetlands of International Importance Especially as Waterfowl Habitat is an international treaty for the conservation and sustainable use of Ramsar site, Ramsar sites (wetlands). It is also known as the Convention on We ...
, later expanding this restriction to the whole country. The use of lead has been banned for all hunting activities in the Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
as of 1992.
The Missouri Department of Conservation
The Missouri Department of Conservation (MDC) and the Missouri Conservation Commission were created by Article IV Sections 40-42 of the Missouri Constitution, which were adopted by the voters of the state in 1936 as Amendment 4 to the constitut ...
introduced regulations in 2007 in some hunting areas requiring the use of non-toxic shot to protect upland birds. Some clay pigeon ranges in the US have banned the use of lead after elevated levels of lead were found in waterfowl, small birds, mammals and frogs in their vicinity.
Non-toxic alternatives to lead shot
Approved alternatives while hunting migratory waterfowl include pellets manufactured fromsteel
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon that demonstrates improved mechanical properties compared to the pure form of iron. Due to steel's high Young's modulus, elastic modulus, Yield (engineering), yield strength, Fracture, fracture strength a ...
, tungsten-iron, tungsten-polymer, tungsten
Tungsten (also called wolfram) is a chemical element; it has symbol W and atomic number 74. It is a metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively in compounds with other elements. It was identified as a distinct element in 1781 and first ...
-nickel
Nickel is a chemical element; it has symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive, but large pieces are slo ...
-iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
, and bismuth
Bismuth is a chemical element; it has symbol Bi and atomic number 83. It is a post-transition metal and one of the pnictogens, with chemical properties resembling its lighter group 15 siblings arsenic and antimony. Elemental bismuth occurs nat ...
-tin
Tin is a chemical element; it has symbol Sn () and atomic number 50. A silvery-colored metal, tin is soft enough to be cut with little force, and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, a bar of tin makes a sound, the ...
in place of lead shot. In Canada, the United States, the United Kingdom, and many western European countries (France as of 2006), all shot used for hunting migratory waterfowl
Anseriformes is an order of birds also known as waterfowl that comprises about 180 living species of birds in three families: Anhimidae (three species of screamers), Anseranatidae (the magpie goose), and Anatidae, the largest family, which i ...
must now be non-toxic, and therefore may not contain any lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleabl ...
.
Steel was one of the first widely used lead alternatives that the ammunition industry turned to. But steel is one hundred times harder than lead, with only two-thirds its density, resulting in undesirable ballistic properties compared to lead. Steel shot can be as hard as some barrels, and may therefore damage chokes on older firearms that were designed only for use with softer lead shot. The higher pressures required to compensate for the lower density of steel may exceed the design limits of a barrel.
Within recent years, several companies have created non-toxic shot out of bismuth
Bismuth is a chemical element; it has symbol Bi and atomic number 83. It is a post-transition metal and one of the pnictogens, with chemical properties resembling its lighter group 15 siblings arsenic and antimony. Elemental bismuth occurs nat ...
, tungsten
Tungsten (also called wolfram) is a chemical element; it has symbol W and atomic number 74. It is a metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively in compounds with other elements. It was identified as a distinct element in 1781 and first ...
, or other elements or alloys
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which in most cases at least one is a metallic element, although it is also sometimes used for mixtures of elements; herein only metallic alloys are described. Metallic alloys often have properties ...
with a density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the ratio of a substance's mass to its volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' (or ''d'') can also be u ...
similar to or greater than lead, and with a shot softness that results in ballistic properties that are comparable to lead. These shells provide more consistent patterns and greater range than steel shot. They are also generally safe to use in older shotguns with barrels and chokes not rated for use with steel shot, such as for bismuth and tungsten-polymer (although not tungsten-iron) shot. Unfortunately, all non-lead shot other than steel is far more expensive than lead, which has diminished in its acceptance by hunters.
See also
*Slug (projectile)
A slug is a term used for a bulky solid ballistic projectile. It is "solid" in the sense of being composed of one piece; the shape can vary widely, including partially hollowed shapes. The term is occasionally applied to bullets (just the pro ...
* Bullet
A bullet is a kinetic projectile, a component of firearm ammunition that is shot from a gun barrel. They are made of a variety of materials, such as copper, lead, steel, polymer, rubber and even wax; and are made in various shapes and constru ...
* Pellet (air gun)
A pellet is a non-spherical projectile designed to be shot from an air gun, and an airgun that shoots such pellets is commonly known as a pellet gun. Air gun pellets differ from bullets and shot (pellet), shot used in firearms in terms of the pre ...
References
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Shot (pellet) Ammunition Lead Shotgun cartridges