Shahen (Sassanian General) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Shahen or Shahin (
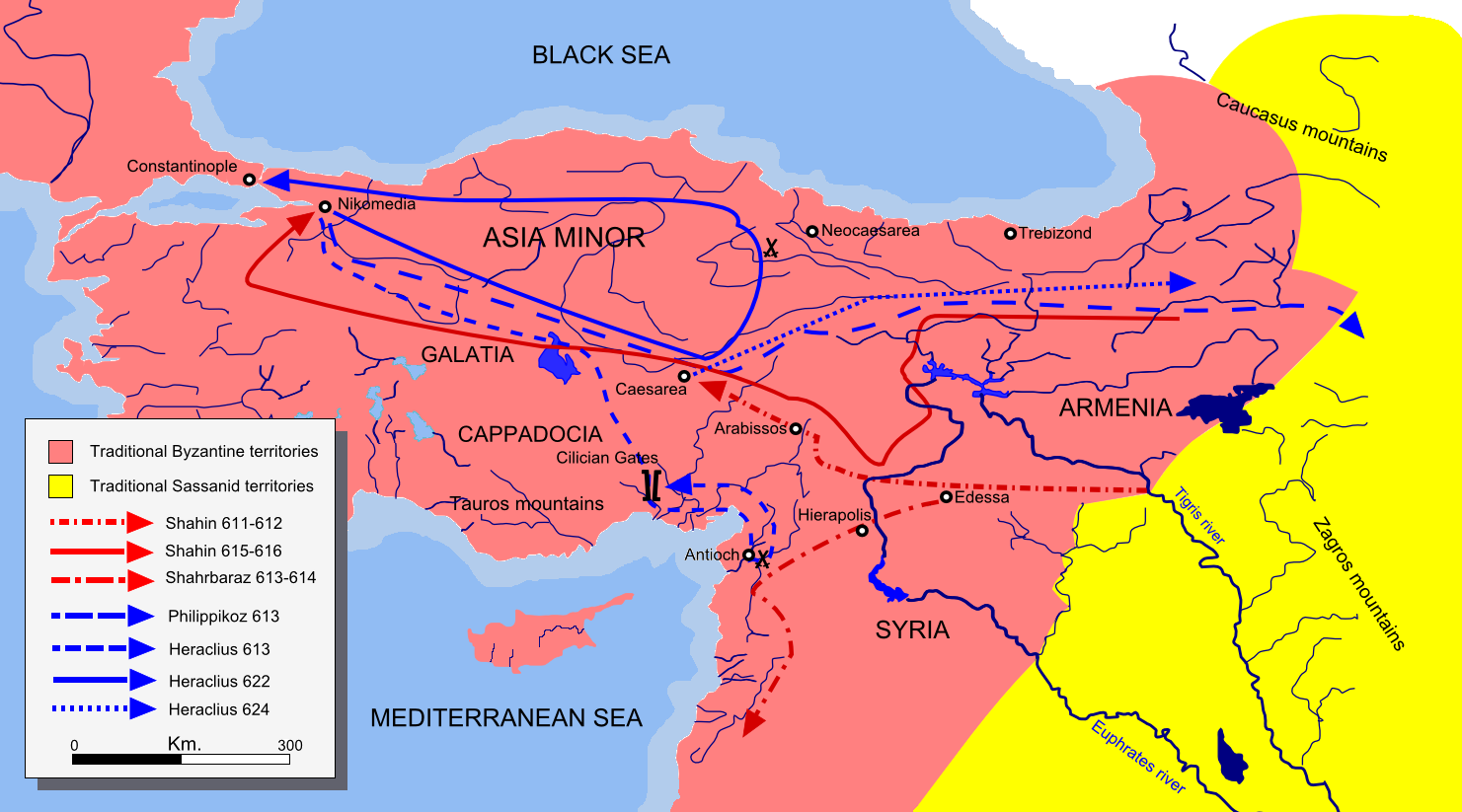 Shahin is first mentioned in 602, after the outbreak of the
Shahin is first mentioned in 602, after the outbreak of the
Middle Persian
Middle Persian or Pahlavi, also known by its endonym Pārsīk or Pārsīg () in its later form, is a Western Middle Iranian language which became the literary language of the Sasanian Empire. For some time after the Sasanian collapse, Middle Per ...
: ''Shāhēn Vahūmanzādagān'', in Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
sources: ; died ca. 626) was a senior Sasanian
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the History of Iran, last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th cen ...
general (''spahbed
''Spāhbed'' (also spelled ''spahbod'' and ''spahbad'') is a Middle Persian title meaning "army chief" used chiefly in the Sasanian Empire. Originally there was a single ''spāhbed'', called the , who functioned as the generalissimo of the Sasa ...
'') during the reign of Khosrow II
Khosrow II (spelled Chosroes II in classical sources; pal, 𐭧𐭥𐭮𐭫𐭥𐭣𐭩, Husrō), also known as Khosrow Parviz (New Persian: , "Khosrow the Victorious"), is considered to be the last great Sasanian king (shah) of Iran, ruling f ...
(590–628). He was a member of the House of Spandiyadh.
Biography
Byzantine–Sasanian War of 602–628
The Byzantine–Sasanian War of 602–628 was the final and most devastating of the series of wars fought between the Byzantine / Roman Empire and the Sasanian Empire of Iran. The previous war between the two powers had ended in 591 after ...
, where he commanded the forces invading Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
territory in the Transcaucasia
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and Western Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Arme ...
, winning a battle against Domentziolus near Theodosiopolis in 607/8. Following the expulsion of Roman forces from that region, in 611 Shahin led an advance into Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The r ...
, capturing Caesarea
Caesarea () ( he, קֵיסָרְיָה, ), ''Keysariya'' or ''Qesarya'', often simplified to Keisarya, and Qaysaria, is an affluent town in north-central Israel, which inherits its name and much of its territory from the ancient city of Caesare ...
. There, Phocas
Phocas ( la, Focas; grc-gre, Φωκάς, Phōkás; 5475 October 610) was Eastern Roman emperor from 602 to 610. Initially, a middle-ranking officer in the Eastern Roman army, Phocas rose to prominence as a spokesman for dissatisfied soldie ...
' son-in-law Priscus, started a year-long siege to trap them inside the city. However, Shahin's troops escaped Priscus' blockade and burned Caesarea, much to Heraclius
Heraclius ( grc-gre, Ἡράκλειος, Hērákleios; c. 575 – 11 February 641), was Eastern Roman emperor from 610 to 641. His rise to power began in 608, when he and his father, Heraclius the Elder, the exarch of Africa, led a revolt ...
' displeasure. In 613 the Roman offensive pressed on into Syria, but the combined Persian armies under Shahin and Shahrbaraz crushingly defeated Heraclius near Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου, ''Antiókheia hē epì Oróntou'', Learned ; also Syrian Antioch) grc-koi, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου; or Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπ� ...
. After this victory the Persians looted the city, slew the Patriarch of Antioch and deported many citizens. Roman forces lost again while attempting to defend the area just to the north of Antioch at the Cilician Gates
The Cilician Gates or Gülek Pass is a pass through the Taurus Mountains connecting the low plains of Cilicia to the Anatolian Plateau, by way of the narrow gorge of the Gökoluk River. Its highest elevation is about 1000m.
The Cilician Gates ...
, despite some initial success. The Persians then captured Tarsus and the Cilician plain. This defeat cut the Byzantine empire in half, severing Constantinople and Anatolia's land link to Syria, Palestine, Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Med ...
, and the Exarchate of Carthage.
In 614 Shahin was able to campaign all the way across Anatolia to Chalcedon
Chalcedon ( or ; , sometimes transliterated as ''Chalkedon'') was an ancient maritime town of Bithynia, in Asia Minor. It was located almost directly opposite Byzantium, south of Scutari (modern Üsküdar) and it is now a district of the c ...
on the shore of the Bosphoros opposite Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth ( Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
. On the shore of Chalcedon, Heraclius held a conference with Shahin, who, before Heraclius descended from his galley, saluted with reverence and pity the majesty of the purple. The friendly offer of Shahin to conduct an embassy to the presence of the great king, was accepted with the warmest gratitude, and the prayer for pardon and peace was humbly presented by the praetorian prefect
The praetorian prefect ( la, praefectus praetorio, el, ) was a high office in the Roman Empire. Originating as the commander of the Praetorian Guard, the office gradually acquired extensive legal and administrative functions, with its holders be ...
, the prefect of the city, and one of the first ecclesiastics of the patriarchal church. But the lieutenant of Chosroes had fatally mistaken the intentions of his master:
According to the history of the Patriarch Nicephorus, Shahin, for his presumption, was flayed alive and his skin was used to make a bag. However this is inconsistent with the account of Theophanes the Confessor
Theophanes the Confessor ( el, Θεοφάνης Ὁμολογητής; c. 758/760 – 12 March 817/818) was a member of the Byzantine aristocracy who became a monk and chronicler. He served in the court of Emperor Leo IV the Khazar before takin ...
, who claims that Shahin fought against Byzantine forces in the following years.
Despite overwhelming Persian successes spanning almost two decades of war, from 622 Heraclius
Heraclius ( grc-gre, Ἡράκλειος, Hērákleios; c. 575 – 11 February 641), was Eastern Roman emperor from 610 to 641. His rise to power began in 608, when he and his father, Heraclius the Elder, the exarch of Africa, led a revolt ...
led a fresh counter-offensive in the Transcaucasus which brought about a remarkable revival of Byzantine fortunes. By 624, Heraclius wintered in Caucasian Albania
Caucasian Albania is a modern exonym for a former state located in ancient times in the Caucasus: mostly in what is now Azerbaijan (where both of its capitals were located). The modern endonyms for the area are ''Aghwank'' and ''Aluank'', amon ...
, gathering forces for the next year. Khosrau was not content to let Heraclius quietly rest in Albania. He sent three armies, commanded by Shahin, Shahrbaraz, and Shahraplakan, to try to trap and destroy Heraclius' forces. Shahraplakan retook lands up as far as Siwnik, aiming to capture the mountain passes. Shahrbaraz was sent to block Heraclius' retreat through Caucasian Iberia
In Greco-Roman geography, Iberia (Ancient Greek: ''Iberia''; la, Hiberia) was an exonym for the Georgian kingdom of Kartli ( ka, ქართლი), known after its core province, which during Classical Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages ...
, and Shahin was sent to block the Bitlis Pass. Heraclius, planning to engage the Persian armies separately, spoke to his worried Lazic, Abasgian, and Iberian allies and soldiers, saying: "Do not let the number of our enemies disturb us. For, God willing, one will pursue ten thousand."
Two soldiers who feigned desertion were sent to Shahrbaraz, claiming that the Byzantines were fleeing before Shahin. Due to jealousy between the Persian commanders, Shahrbaraz hurried with his army to take part in the glory of the victory. Heraclius met them at Tigranakert and routed the forces of Shahraplakan and Shahin one after the other. Shahin lost his baggage train, and Shahraplakan (according to one source) was killed, though he re-appears later. After this victory, Heraclius crossed the Araxes and camped in the plains on the other side. Shahin, with the remnants of both his and Shahraplakan's armies joined Shahrbaraz in the pursuit of Heraclius, but marshes slowed them down. At Aliovit, Shahrbaraz split his forces, sending some 6,000 troops to ambush Heraclius while the remainder of the troops stayed at Aliovit. Heraclius instead launched a surprise night attack on the Persian main camp in February 625, destroying it. Shahrbaraz only barely escaped, naked and alone, having lost his harem
Harem ( Persian: حرمسرا ''haramsarā'', ar, حَرِيمٌ ''ḥarīm'', "a sacred inviolable place; harem; female members of the family") refers to domestic spaces that are reserved for the women of the house in a Muslim family. A har ...
, baggage, and men.
Death
Shahin then regrouped with Shahrbaraz, shadowing Heraclius through Armenia in an inconclusive campaign for the remainder of that year. In 626 Khosrau ordered an exceptional levy of troops from across his empire to revive the faltering war effort. Shahin was put in charge of these new recruits, called the New Army, together with a large number of veterans, and sent against Heraclius, but was heavily defeated by the emperor's brother Theodore. The dejected Shahin fell ill and Khosrau, enraged at Shahin's failure, mistreated the general's corpse, which had been sent to him preserved in salt.References
Sources
* *Edward Gibbon
Edward Gibbon (; 8 May 173716 January 1794) was an English historian, writer, and member of parliament. His most important work, '' The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire'', published in six volumes between 1776 and 1788, is ...
, ''The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire
''The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire'' is a six-volume work by the English historian Edward Gibbon. It traces Western civilization (as well as the Islamic and Mongolian conquests) from the height of the Roman Empire to t ...
'', chapter 46
* Geoffrey Greatrex, Samuel N. C. Lieu, ''The Roman Eastern Frontier and the Persian Wars, (Part II, 363–630)'' (London 2002)
*
* Virasp Mehta, ''Causes of the Downfall of the Sassanian Empire'' (Palo Alto 2007)
*
* Theophanes the Confessor
Theophanes the Confessor ( el, Θεοφάνης Ὁμολογητής; c. 758/760 – 12 March 817/818) was a member of the Byzantine aristocracy who became a monk and chronicler. He served in the court of Emperor Leo IV the Khazar before takin ...
, ''The Chronicle of Theophanes — Anni mundi 6095–6305 (A.D. 602–813)'', ed. Harry Turtledove
Harry Norman Turtledove (born June 14, 1949) is an American author who is best known for his work in the genres of alternate history, historical fiction, fantasy, science fiction, and mystery fiction. He is a student of history and completed ...
(Philadelphia 1982)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Shahin
626 deaths
People of the Byzantine–Sasanian War of 602–628
7th-century Iranian people
Year of birth unknown
House of Spandiyadh
Generals of Khosrow II