Shah Dheri on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Taxila or Takshashila () is a city in the
''The Rise of Civilization in India and Pakistan''.
Cambridge University Press, 1982 p.127 it was possibly founded around 1000 BCE. Takshashila and
Other scholars do not consider it to have been a university in the modern sense, in that the teachers living there may not have had official membership of particular colleges, and there did not seem to have existed purpose-built lecture halls and residential quarters in the city. In a 2010 report, the
 In ancient times, Taxila was known as in
In ancient times, Taxila was known as in
Pothohar
The Pothohar Plateau (, : ''Pо̄ṭhoā̀r Paṭhār''; , ''Satāh Murtafā Pо̄ṭhohār''), also spelled Pothwar, is a plateau in the Sind Sagar Doab of northern Punjab, Pakistan, located between the Indus and Jhelum rivers.
Etymology
A l ...
region of Punjab
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panjāb or Panj-Āb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
, Pakistan. Located in the Taxila Tehsil
The Taxila Tehsil, with its administrative centre in Taxila, is one of the eight sub-districts of the Rawalpindi District in the province of Punjab, Pakistan. It is neighboured by the Attock District to the west, Rawalpindi Tehsil to the south, t ...
of Rawalpindi District
Rawalpindi District (Punjabi language, Punjabi and ) is a Districts of Pakistan, district located in the northernmost part of the Punjab (Pakistan), Punjab province of Pakistan. Parts of the district form part of the Islamabad Rawalpindi metropo ...
, it lies approximately northwest of the Islamabad–Rawalpindi metropolitan area
The Islamabad–Rawalpindi metropolitan area (Urdu:) is the fourth-largest metropolitan area of Pakistan, after Karachi, Lahore, and Faisalabad. It consists of the twin cities of Islamabad and Rawalpindi.
The area includes the Pothohar Plateau ...
and is just south of the Haripur District
Haripur District (Hindko, ) is a district in the Hazara Division of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. Before obtaining the status of a district in 1991, Haripur was a tehsil of Abbottabad District Its headquarters are the city of Haripur. Accor ...
of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa
Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (; ; , ; abbr. KP or KPK), formerly known as the North West Frontier Province (NWFP), is a Administrative units of Pakistan, province of Pakistan. Located in the Northern Pakistan, northwestern region of the country, Khyber ...
.
Established during the Vedic period, Old Taxila was for a time the capital city of ancient Gandhāra. It was situated on the eastern shore of the Indus River
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayas, Himalayan river of South Asia, South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northw ...
—the pivotal junction of the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
and Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Pers ...
;Raymond Allchin, Bridget Allchin''The Rise of Civilization in India and Pakistan''.
Cambridge University Press, 1982 p.127 it was possibly founded around 1000 BCE. Takshashila and
Pushkalavati
Pushkalavati, was the capital of the ancient region of Gāndhāra, situated in present day's Pakistan. Its ruins are located on the outskirts of the modern city of Charsadda, in Charsadda District, in the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, 35-42 kilometres ...
remained prominent cities in Gandhāra during the Mahajanapadas
The Mahājanapadas were sixteen Realm, kingdoms and aristocracy, aristocratic republics that existed in ancient India from the sixth to fourth centuries BCE, during the History of India#Second urbanisation (c. 600 – 200 BCE), second urbanis ...
. The city was later conquered
Conquest involves the annexation or control of another entity's territory through war or coercion. Historically, conquests occurred frequently in the international system, and there were limited normative or legal prohibitions against conquest ...
by the Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian peoples, Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, i ...
and incorporated into the Hindush
Hindush ( ) was an administrative division of the Achaemenid Empire in modern-day Pakistan. According to the Greek historian Herodotus, it was the "easternmost province" governed by the Achaemenid dynasty. Established through the Persian conqu ...
satrap, between 550 – 326 BCE. In 326 BCE, the city was claimed by Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
, after overthrowing the Achaemenids. He gained control of the city without a battle since it immediately surrendered to his Macedonian Empire
Macedonia ( ; , ), also called Macedon ( ), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, which later became the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by the royal ...
. This was followed successively by the Mauryans (~317 – ~200 BCE), the Indo-Greeks
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, also known as the Yavana Kingdom, was a Hellenistic-era Greek kingdom covering various parts of modern-day Afghanistan, Pakistan and northwestern India.
The term "Indo-Greek Kingdom" loosely describes a number of var ...
(~200 BCE – ~55 BCE), the Indo-Scythians
The Indo-Scythians, also known as Indo-Sakas, were a group of nomadic people of Iranic Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into the present-day regions of Afghanistan, Eastern Iran and the northwestern Indian subcontinent: p ...
(~80 BCE – ~30 CE), and the Kushan Empire
The Kushan Empire (– CE) was a Syncretism, syncretic empire formed by the Yuezhi in the Bactrian territories in the early 1st century. It spread to encompass much of what is now Afghanistan, Eastern Iran, India, Pakistan, Tajikistan and Uzbe ...
(~30 CE – ~375 CE), who destroyed the existing city, in the first century CE, to build their own on a site to the north of the ruins. Owing to its strategic location, Taxila has changed hands many times over the centuries, with many polities vying for its control. When the great ancient trade routes connecting these regions ceased to be important, the city sank into insignificance and was finally destroyed in the 5th century by the invading Hunas
Hunas or Huna (Middle Brahmi script: ''Hūṇā'') was the name given by the ancient Indians to a group of Central Asian tribes who, via the Khyber Pass, entered the Indian subcontinent at the end of the 5th or early 6th century. The Hunas occu ...
. In mid-19th century British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance in South Asia. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another ...
, ancient Taxila's ruins were rediscovered by British archaeologist Alexander Cunningham
Major General Sir Alexander Cunningham (23 January 1814 – 28 November 1893) was a British Army engineer with the Bengal Sappers who later took an interest in the history and archaeology of India. In 1861, he was appointed to the newly crea ...
and extensively excavated by Sir John Marshall
Sir John Hubert Marshall (19 March 1876, Chester, England – 17 August 1958, Guildford, England) was an English archaeologist who was Director-General of the Archaeological Survey of India from 1902 to 1928. He oversaw the excavations of H ...
. In 1980, UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
designated Taxila as a World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
.
By some accounts, the University of ancient Taxila is considered to be one of the earliest universities or education centre in South Asia.Balakrishnan Muniapan
Bala Krishna (). Present day Krishna worship is an amalgam of various elements. According to historical testimonies Krishna-Vasudeva worship already flourished in and around Mathura several centuries before Christ. A second important element is ...
, Junaid M. Shaikh Junayd or Junaid or Junayed () and sometimes Jounaid is a male given name which means soldier or warrior.
Persons with the given name Junaid
*Junaid (born 1975), Pakistani politician
* Junaid Babunagari (1953-2021), Bangladeshi Islamic scholar
* ...
(2007), "Lessons in corporate governance from Kautilya's Arthashastra
''Kautilya's Arthashastra'' (, ; ) is an Ancient Indian Sanskrit treatise on statecraft, politics, economic policy and military strategy. The text is likely the work of several authors over centuries, starting as a compilation of ''Arthashas ...
in ancient India", ''World Review of Entrepreneurship, Management and Sustainable Development'' 3 (1):Other scholars do not consider it to have been a university in the modern sense, in that the teachers living there may not have had official membership of particular colleges, and there did not seem to have existed purpose-built lecture halls and residential quarters in the city. In a 2010 report, the
Global Heritage Fund
Global Heritage Fund is a non-profit organization that operates internationally.
Founded in California in 2002, its mission is to "transform local communities by investing in global heritage."
To date, it has partnered with over 100 public and ...
identified Taxila as one of 12 worldwide sites that were "on the verge" of irreparable loss and damage, citing insufficient management, development pressure, looting, and armed conflict as primary threats. However, significant preservation efforts have since been carried out by the Pakistani government
The Government of Pakistan () (abbreviated as GoP), constitutionally known as the Federal Government, commonly known as the Centre, is the national authority of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, a federal republic located in South Asia
...
, which has resulted in the site's recategorization as "well-preserved" by different international publications. Because of the extensive preservation efforts and upkeep, Taxila is one of Punjab's popular tourist spots, attracting up to one million tourists every year.
Etymology
 In ancient times, Taxila was known as in
In ancient times, Taxila was known as in Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
(per IAST
The International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration (IAST) is a transliteration scheme that allows the lossless romanisation of Brahmic family, Indic scripts as employed by Sanskrit and related Indic languages. It is based on a scheme that ...
) and as in Pali
Pāli (, IAST: pāl̤i) is a Classical languages of India, classical Middle Indo-Aryan languages, Middle Indo-Aryan language of the Indian subcontinent. It is widely studied because it is the language of the Buddhist ''Pali Canon, Pāli Can ...
. The city's Sanskrit name translates to "City of Cut Stone" or "Rock of Taksha" in reference to a story in the ''Ramayana
The ''Ramayana'' (; ), also known as ''Valmiki Ramayana'', as traditionally attributed to Valmiki, is a smriti text (also described as a Sanskrit literature, Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epic) from ancient India, one of the two important epics ...
'' that states that the city was founded by Bharata, the younger brother of the Hindu
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also be ...
deity Rama
Rama (; , , ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the seventh and one of the most popular avatars of Vishnu. In Rama-centric Hindu traditions, he is considered the Supreme Being. Also considered as the ideal man (''maryāda' ...
, and named in honour of Bharata's son, Taksha.
The city's modern name, however, is derived from the ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
rendering noted in Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzant ...
's ''Geography
Geography (from Ancient Greek ; combining 'Earth' and 'write', literally 'Earth writing') is the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding o ...
''. The Greek-language transcription of ''Taxila'' became universally favoured over time, and both the Sanskrit and Pali names fell out of use.
Faxian
Faxian (337–), formerly romanization of Chinese, romanized as Fa-hien and Fa-hsien, was a Han Chinese, Chinese Chinese Buddhism, Buddhist bhikkhu, monk and translator who traveled on foot from Eastern Jin dynasty, Jin China to medieval India t ...
, a Chinese Buddhist
Chinese Buddhism or Han Buddhism ( zh, s=汉传佛教, t=漢傳佛教, first=t, poj=Hàn-thoân Hu̍t-kàu, j=Hon3 Cyun4 Fat6 Gaau3, p=Hànchuán Fójiào) is a Chinese form of Mahayana Buddhism. The Chinese Buddhist canonJiang Wu, "The Chin ...
pilgrim who visited the city via the Silk Road
The Silk Road was a network of Asian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over , it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and religious interactions between the ...
, had given its name's meaning as "cut-off head". With the help of a ''Jataka'', he had interpreted it to be the place where Gautama Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha (),*
*
*
was a śramaṇa, wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism. According to Buddhist lege ...
—during a previous birth as ''Pusa'' or ''Chandaprabha''—cut off his head to feed a hungry lion. This tradition still persists with the area in front of Sirkap
Sirkap (Urdu and ) is the name of an archaeological site on the bank opposite to the city of Taxila, Punjab, Pakistan.
The city of Sirkap was built by the Greco-Bactrian king Demetrius after he invaded modern-day Pakistan around 180 BC. Demetr ...
(also meaning "cut-off head"), which was known in the 19th century as ''Babur Khana'' ('House of Tiger'), alluding to the place where Gautama Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha (),*
*
*
was a śramaṇa, wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism. According to Buddhist lege ...
had offered his head. In addition, a hill range to south of the Taxila Valley is called ''Margala'' ().
In traditional sources
In Vedic texts such as theShatapatha Brahmana
The Shatapatha Brahmana (, , abbreviated to 'SB') is a commentary on the Yajurveda, Śukla Yajurveda. It is attributed to the Vedic sage Yajnavalkya. Described as the most complete, systematic, and important of the Brahmanas (commentaries on the ...
, it is mentioned that the Vedic philosopher Uddalaka Aruni (c. 7th century BCE) had travelled to the region of Gandhara. In later Buddhist texts, the 4th - 3rd century BCE Jatakas
The ''Jātaka'' (Sanskrit for "Birth-Related" or "Birth Stories") are a voluminous body of literature native to the Indian subcontinent which mainly concern the previous births of Gautama Buddha in both human and animal form. Jataka stories we ...
, it is specified that Taxila was the city where Aruni and his son Shvetaketu each had received their education.
One of the earliest mentions of Taxila is in Pāṇini
(; , ) was a Sanskrit grammarian, logician, philologist, and revered scholar in ancient India during the mid-1st millennium BCE, dated variously by most scholars between the 6th–5th and 4th century BCE.
The historical facts of his life ar ...
's , a Sanskrit grammar treatise dated to the 4th century BCE.
Much of the Hindu epic, the Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; , , ) is one of the two major Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epics of ancient India revered as Smriti texts in Hinduism, the other being the ''Ramayana, Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the events and aftermath of the Kuru ...
, is a conversation between Vaishampayana
Vaishampayana (, ) is the traditional narrator of the ''Mahabharata'', one of the two major Sanskrit epics of India.
He was one of Vyasa's four main disciples. His nephew and disciple, Yajnavalkya, who was also a well-known sage.
Legend
Vai ...
(a pupil of the sage, Vyasa
Vyasa (; , ) or Veda Vyasa (, ), also known as Krishna Dvaipayana Veda Vyasa (, ''Vedavyāsa''), is a ''rishi'' (sage) with a prominent role in most Hindu traditions. He is traditionally regarded as the author of the epic Mahabharata, Mah� ...
) and King Janamejaya
Janamejaya () was a Kuru king who reigned during the Middle Vedic period. Along with his father and predecessor Parikshit, he played a decisive role in the consolidation of the Kuru state, the arrangement of Vedic hymns into collections, and ...
. It is traditionally believed that the story was first recited by Vaishampayana at the behest of Vyasa during the snake sacrifice performed by Janamejaya at Takshashila. The audience also included Ugrashravas
Ugrashravas Sauti (Sanskrit: उग्रश्रवस् सौती, also Ugraśravas, Sauti, Sūta, Śri Sūta, Suta Gosvāmī) is a character in Hindu literature, featured as the narrator of the ''Mahābhārata'' and several Puranas inclu ...
, an itinerant bard, who would later recite the story to a group of priests at an ashram
An ashram (, ) is a spiritual hermitage or a monastery in Indian religions, not including Buddhism.
Etymology
The Sanskrit noun is a thematic nominal derivative from the root 'toil' (< Naimisha Forest from where the story was further disseminated. The Kuru Kingdom's heir,
"Taxila"
in D. K. Chakrabarti and M. Lal (eds.), ''History of Ancient India III: The Texts, and Political History and Administration till c. 200 BC'', Vivekananda International Foundation, Aryan Books International, Delhi, p. 654. Periods IA and II at Sarai Khola seem to show continuity from Period I, with the appearance of red burnished wares. However,
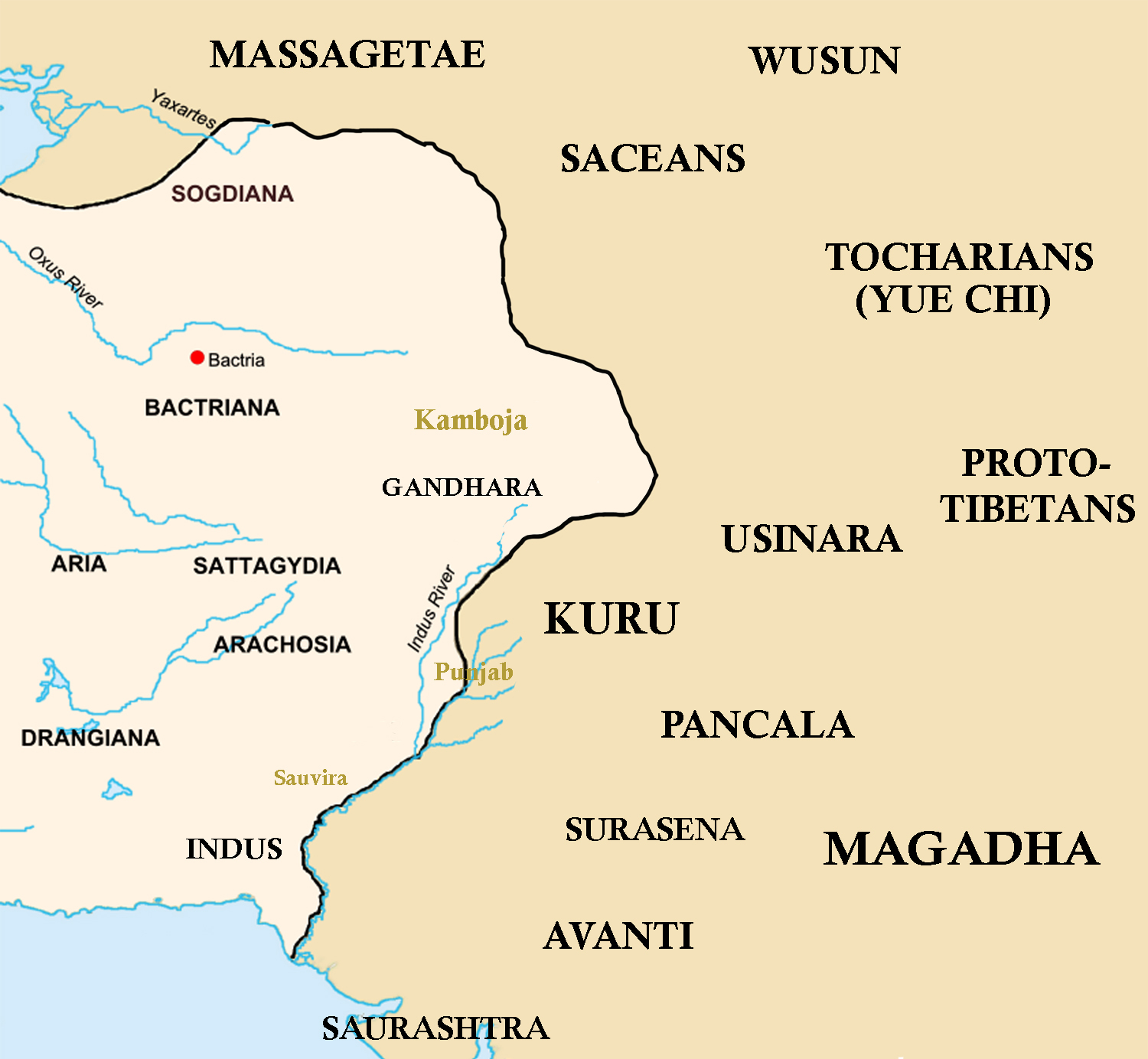
 During his invasion of the
During his invasion of the
 By some accounts, Taxila was considered to be one of the earliest (or the earliest) universities in the world. The school consisted of several monasteries without large dormitories or lecture halls where the religious instruction was provided on an individualistic basis. Others do not consider it a university in the modern sense, in that the teachers living there may not have had official membership of particular colleges, and there did not seem to have existed purpose-built lecture halls and residential quarters in Taxila,:
By some accounts, Taxila was considered to be one of the earliest (or the earliest) universities in the world. The school consisted of several monasteries without large dormitories or lecture halls where the religious instruction was provided on an individualistic basis. Others do not consider it a university in the modern sense, in that the teachers living there may not have had official membership of particular colleges, and there did not seem to have existed purpose-built lecture halls and residential quarters in Taxila,:
F. W. Thomas (1944), in :
in contrast to the later
 The vast archaeological site includes neolithic remains dating to 3360 BCE, and Early Harappan remains dating to 2900–2600 BCE at ''Sarai Kala''. Taxila, however, is most famous for ruins of several settlements, the earliest dating from around 1000 BCE. It is also known for its collection of Buddhist religious monuments, including the
The vast archaeological site includes neolithic remains dating to 3360 BCE, and Early Harappan remains dating to 2900–2600 BCE at ''Sarai Kala''. Taxila, however, is most famous for ruins of several settlements, the earliest dating from around 1000 BCE. It is also known for its collection of Buddhist religious monuments, including the
 Taxila is one of northern Pakistan's most important tourist destinations and is home to the
Taxila is one of northern Pakistan's most important tourist destinations and is home to the
 The ancient
The ancient
 Taxila is home to many secondary educational institutes including CIIT Wah Campus, and
Taxila is home to many secondary educational institutes including CIIT Wah Campus, and
Image:TaxilaCoinBM.JPG, A coin from 2nd century BCE Taxila.
Image:Coin of Antialcidas.jpg, The
File:CrystalGoose.JPG, Reliquary in the form of a crystal goose dating to the 1st Century AD in the British Museum.
File:SirkapJainTemple.JPG, Jain Temple at
Explore Taxila with Google Earth
on
''Guide to Historic Taxila'' by Ahmad Hasan Dani in 10 chapters
* ttps://www.srikanta-sastri.org/taxila-an-ancient-indian-university Taxila: An Ancient Indian Universityby S. Srikanta Sastri
John Marshall, ''A guide to Taxila'' (1918)
on
''Telapatta Jataka''
also known as the ''Takkasila Jataka'' {{Authority control Taxila Tehsil Places in Hindu mythology Archaeological sites in Punjab, Pakistan World Heritage Sites in Pakistan Ancient Greek archaeological sites in Pakistan Hinduism in Pakistan Buddhism in Pakistan Gandhara Former populated places in Pakistan Buddhist sites in Pakistan Indo-Parthian kingdom Populated places in Taxila Tehsil Cities in Rawalpindi District Populated places established in the 1st millennium BC Ancient cities
Parikshit
Parīkṣit (, ) was a Kuru king who reigned during the Middle Vedic period (12th–9th centuries BCE). Along with his son and successor, Janamejaya, he played a decisive role in the consolidation of the Kuru state, the arrangement of Vedic ...
(grandson of Arjuna) is said to have been enthroned at Takshashila.
The Ramayana describes Takshashila as a magnificent city famed for its wealth which was founded by Bharata, the younger brother of Rama
Rama (; , , ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the seventh and one of the most popular avatars of Vishnu. In Rama-centric Hindu traditions, he is considered the Supreme Being. Also considered as the ideal man (''maryāda' ...
. Bharata, who also founded nearby Pushkalavati
Pushkalavati, was the capital of the ancient region of Gāndhāra, situated in present day's Pakistan. Its ruins are located on the outskirts of the modern city of Charsadda, in Charsadda District, in the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, 35-42 kilometres ...
, installed his two sons, Taksha and Pushkala, as the rulers of the two cities.
In the Buddhist Jatakas, Taxila is described as the capital of the kingdom of Gandhara and a great centre of learning with world-famous teachers. The Jatakas mention non-Buddhist institutions and teachers in Taxila. They show the predominance of Vedic
upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the '' Atharvaveda''.
The Vedas ( or ; ), sometimes collectively called the Veda, are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed ...
and technical disciplines including law, medicine, and military science. The Takkasila Jataka, more commonly known as the Telapatta Jataka, tells the tale of a prince of Benares
Varanasi (, also Benares, Banaras ) or Kashi, is a city on the Ganges, Ganges river in North India, northern India that has a central place in the traditions of pilgrimage, death, and mourning in the Hinduism, Hindu world.*
*
*
* The city ...
who is told that he would become the king of Takkasila if he could reach the city within seven days without falling prey to the yakshini
Yakshinis or Yakshis (, , Prakrit languages, Prakrit: ) are a class of female nature spirits in Hinduism, Hindu, Buddhism, Buddhist, and Jainism, Jain religious mythologies that are different from Hindu deities, Devas and Asuras and Gandharva ...
s who waylaid travellers in the forest. According to the Dipavamsa, one of Taxila's early kings was a Kshatriya
Kshatriya () (from Sanskrit ''kṣatra'', "rule, authority"; also called Rajanya) is one of the four varnas (social orders) of Hindu society and is associated with the warrior aristocracy. The Sanskrit term ''kṣatriyaḥ'' is used in the con ...
named Dipankara who was succeeded by twelve sons and grandsons. , mentioned in the Avadanakalpalata, is another king associated with the city.
In Jainism
Takshashila was closely associated withJainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religions, Indian religion whose three main pillars are nonviolence (), asceticism (), and a rejection of all simplistic and one-sided views of truth and reality (). Jainism traces its s ...
. According to the Jaina tradition, Rishabhanatha
Rishabhanatha (Devanagari: ऋषभनाथ), also Rishabhadeva (Devanagari: ऋषभदेव, ), Rishabha (Devanagari: ऋषभ, ) or Ikshvaku (Devanagari: इक्ष्वाकु, ''Ikṣvāku''), is the first (Supreme preacher) ...
, the first Tirthankara
In Jainism, a ''Tirthankara'' (; ) is a saviour and supreme preacher of the ''Dharma (Jainism), dharma'' (righteous path). The word ''tirthankara'' signifies the founder of a ''Tirtha (Jainism), tirtha'', a fordable passage across ''Saṃsā ...
, entrusted the region of Ayodhya
Ayodhya () is a city situated on the banks of the Sarayu river in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is the administrative headquarters of the Ayodhya district as well as the Ayodhya division of Uttar Pradesh, India. Ayodhya became th ...
to his son Bharata and the region of Takshashila to his son Bahubali
Bahubali (, ) was the son of Rishabhanatha (the first ''tirthankara'' of Jainism) and the brother of the ''Chakravarti (Sanskrit term), chakravartin'' Bharata (Jainism), Bharata. He is a revered figure in Jainism. He is said to have meditated ...
.
As per canonical Śvetāmbara
The Śvetāmbara (; also spelled Shwetambara, Shvetambara, Svetambara or Swetambara) is one of the two main branches of Jainism, the other being the Digambara. ''Śvetāmbara'' in Sanskrit means "white-clad", and refers to its ascetics' practi ...
Jaina
Jaina can refer to:
* Jain/Jaina, a follower of Jainism, an ancient classical religion of India
** List of Jains, a list of various notable Jains
** Federation of Jain Associations in North America (JAINA)
* Jaina Island, an archaeological site ...
texts ''Āvaśyaka Cūrṇi'' and ''Āvaśyaka Niryukti'', Tirthankara
In Jainism, a ''Tirthankara'' (; ) is a saviour and supreme preacher of the ''Dharma (Jainism), dharma'' (righteous path). The word ''tirthankara'' signifies the founder of a ''Tirtha (Jainism), tirtha'', a fordable passage across ''Saṃsā ...
Rishabhanatha
Rishabhanatha (Devanagari: ऋषभनाथ), also Rishabhadeva (Devanagari: ऋषभदेव, ), Rishabha (Devanagari: ऋषभ, ) or Ikshvaku (Devanagari: इक्ष्वाकु, ''Ikṣvāku''), is the first (Supreme preacher) ...
visited Takshashila while wandering after initiation as a monk millions of years ago. Upon learning of his arrival, Bahubali
Bahubali (, ) was the son of Rishabhanatha (the first ''tirthankara'' of Jainism) and the brother of the ''Chakravarti (Sanskrit term), chakravartin'' Bharata (Jainism), Bharata. He is a revered figure in Jainism. He is said to have meditated ...
, who was not in the city at that moment, rushed to the city, but the Rishabhanatha had already departed before Bahubali arrived. His footprints were subsequently consecrated by Bahubali who erected a throne and a dharmachakra
The dharmachakra (Sanskrit: धर्मचक्र, ) or wheel of dharma is a symbol used in the Dharmic religions. It has a widespread use in Buddhism.John C. Huntington, Dina Bangdel, ''The Circle of Bliss: Buddhist Meditational Art,'' p. ...
('wheel of the law') over them several miles in height and circumference. The 14th century Vividha Tirtha Kalpa
''Vividha Tirtha Kalpa'', originally named ''Kalpa-pradeepa'', is a widely cited Jain text composed by Jinaprabha Suri in the 14th century CE. It is a compilation of about 60 Kalpas (sections), most of them give the accounts of major Jain Tirth ...
mentions this establishment, stating:
"तक्षशिलायां बाहुबलीविनिर्मितं धर्मचक्रम् ॥"
- Ācārya Jinaprabhāsūri in "''Vividha Tirtha Kalpa"'' (p. 85)
As per the canonical Jaina text ''Mahanishith Sutra'', the ''Dharmachakra Tirtha'' established by Bahubali is recognized as the abode of Chandraprabha
Chandraprabha () or Chandranatha is the eighth Tirthankara of of Jainism in the present age (). According to traditional accounts, he was born to King Mahasena and Queen Lakshmana Devi at Chandrapuri to the Ikshvaku dynasty. According to Jain ...
, and Takshashila is also referred to as ''"Dharmachakra Bhumi,"'' marking its significance as a center of Jainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religions, Indian religion whose three main pillars are nonviolence (), asceticism (), and a rejection of all simplistic and one-sided views of truth and reality (). Jainism traces its s ...
.
While there is limited information about the subsequent period, it is noted that during the medieval era, Takshashila faced challenges due to the proliferation of fraudulent ascetics and a lack of proper sustenance, leading to restrictions on Jaina ascetics' wandering in the region, as documented in six ancient Jaina texts known as the '' Chedasūtras''.
Emperor Samprati built a Jaina temple known as ''"Kunala Stupa
Kunala Stupa is a Kushan-era Buddhist stupa and monastery complex to the south-east of Taxila, on a hill about 200 meters just south of Sirkap, Punjab, Pakistan, thought to date to the 2nd century CE. It is located on a hill overlooking the ancien ...
"'' in honor of his father Kunala
Kunala (IAST: ) (263 BC – ?) was the Crown Prince and second son of 3rd Mauryan Emperor Ashoka and Queen Padmavati and the presumptive heir to Ashoka, thus the heir to the Mauryan Empire which once ruled almost all of the Indian subcontinen ...
. During Samprati's rule, the extent of the wandering of Jaina monks developed multifold times, and later also included this region.
According to the Prabhavakacharita, by the second to third century CE, there were approximately 500 Jaina temples in Takshashila, and it was occupied by a significant number of Jainas. However, a devastating plague struck the city, leading to widespread death and chaos. The Jaina community sent a Sravaka named Virchand to Nadol
Nadol is a census town in Desuri tehsil of Pali district, India. Ashapura Mataji temple and Shri Nadol Tirth attract pilgrims.
History
Nadol was originally called Naddula. The Chahamanas of Naddula (called Chauhans of Nadol in vernacular le ...
, who conveyed their suffering to Acharya Manadevasuri. Suri gave "''Laghu Shanti Stava''," stating that reciting it would alleviate the plague. Following the recitation, the plague subsided within a few days. However, in the third year, the Turks devastated the city.
According to Acharya Dhaneswarasuri's "''Shatrunjaya Mahatmya''," Javad Shah, a merchant from Mahuva, renovated Palitana temples in Vikrama Samvat
Vikram Samvat (ISO: ''Vikrama Saṁvata''; abbreviated VS), also known as the Vikrami calendar is a Hindu calendar historically used in the Indian subcontinent and still also used in several Indian states and Nepal. It is a lunisolar calendar, ...
108. He retrieved an image of Rishabhanatha
Rishabhanatha (Devanagari: ऋषभनाथ), also Rishabhadeva (Devanagari: ऋषभदेव, ), Rishabha (Devanagari: ऋषभ, ) or Ikshvaku (Devanagari: इक्ष्वाकु, ''Ikṣvāku''), is the first (Supreme preacher) ...
from Takshashila and established it as the principal deity at the principal shrine amongst Shatrunjaya temples.
Excavations in Takshashila support these traditions. Dr. Sir John Marshall noted that Indo-Greek kings displaced the city from its fortified position and settled it in Sirkap
Sirkap (Urdu and ) is the name of an archaeological site on the bank opposite to the city of Taxila, Punjab, Pakistan.
The city of Sirkap was built by the Greco-Bactrian king Demetrius after he invaded modern-day Pakistan around 180 BC. Demetr ...
during the early years of the second century BCE. The city remained inhabited through the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
, Shaka
Shaka kaSenzangakhona (–24 September 1828), also known as Shaka (the) Zulu () and Sigidi kaSenzangakhona, was the king of the Zulu Kingdom from 1816 to 1828. One of the most influential monarchs of the Zulu, he ordered wide-reaching reform ...
, Pahlava
The Pahlavas are a people mentioned in ancient Indian texts. According to Patrick Carnegy, a Raj-era ethnographer, the 4th-century BCE ''Vartika'' of Katyayana mentions the ''Sakah-Parthavah'', demonstrating an awareness of these Saka-Parthians, ...
, and Kushan ''Kushan'' or Kushana may refer to:
* Kushan Empire
The Kushan Empire (– CE) was a Syncretism, syncretic empire formed by the Yuezhi in the Bactrian territories in the early 1st century. It spread to encompass much of what is now Afghanistan ...
periods. Numerous small and large temples have been discovered along the main road of Sirkap. Dr. Marshall concluded that the temples in blocks 'F' and 'G' of Sirkap are Jaina temples due to their architectural similarities with Kankali Tila
''Kankali Tila'' (also Kankali mound or Jaini mound) is a mound located at Mathura in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. The name of the mound is derived from a modern temple of Hindu goddess Kankali. The famous Jain stupa was excavated here ...
, a Jaina stupa, found in Mathura
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the states and union territories of India, Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located south-east of Delhi; and about from the town of Vrindavan. In ancient ti ...
. In block 'G,' located on the right side of the main road, numerous ruins of large buildings have been found, characterized by the presence of small temples alongside these structures, which were accessible to devotees. This evidence strongly supports claims by the Jaina tradition that Takshashila was a significant center for Jainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religions, Indian religion whose three main pillars are nonviolence (), asceticism (), and a rejection of all simplistic and one-sided views of truth and reality (). Jainism traces its s ...
.
History
Early settlement
The region around Taxila was settled by theNeolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
era, with some ruins at Taxila dating to 1000 BCE. Ruins dating from the Early Harappan period around 1300 BCE have also been discovered in the Taxila area, though the area was eventually abandoned after the collapse of the Indus Valley civilisation.
The earliest settled occupation in Taxila Valley was found at Sarai Khola, located 2 km to the south-west of Taxila Museum
Taxila Museum (Punjabi language, Punjabi, ) is located at Taxila (modern), Taxila, Punjab (Pakistan), Punjab, Pakistan. The museum is home to a significant and comprehensive collection of Greco-Buddhist art, Gandharan art dating from the 1st to ...
, where three radiocarbon dates from Period I suggest the site was first occupied between the late 4th and early 3rd millennium BCE, with deposits of polished stone celts, chert blades and a distinctive type of highly burnished pottery that shows clear signs of the use of woven baskets in the manufacturing process and the application of a slurry to the exterior surface.Petrie, Cameron, (2013)"Taxila"
in D. K. Chakrabarti and M. Lal (eds.), ''History of Ancient India III: The Texts, and Political History and Administration till c. 200 BC'', Vivekananda International Foundation, Aryan Books International, Delhi, p. 654. Periods IA and II at Sarai Khola seem to show continuity from Period I, with the appearance of red burnished wares. However,
Kot Diji
Kot Diji (; ) is an ancient site which was part of the Indus Valley Civilization, estimated to have been occupied around 3300 BCE. Located about south of Khairpur in the modern-day province of Sindh, India, it is on the east bank of the Indus R ...
-style wares were found in greater numbers, and the Kot Diji-style forms show signs of having been wheel-thrown, marking a clear technological change from the Period I material. Seven radiocarbon dates were also taken from the earlier and later Period II/Kot Diji, and seem to show this phase dates from the mid-late 3rd to early 2nd millennium BCE.
Gandhāra kingdom
Gandhara was an ancient Indo-Aryan kingdom of westernSouth Asia
South Asia is the southern Subregion#Asia, subregion of Asia that is defined in both geographical and Ethnicity, ethnic-Culture, cultural terms. South Asia, with a population of 2.04 billion, contains a quarter (25%) of the world's populatio ...
whose existence was attested during the Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
. The capital of the kingdom was in Taxila. The first major settlement at Taxila, in Hathial
Hathial is an ancient archaeological site next to Bhir Mound, just south of Sirkap, in the area of Taxila in Pakistan. It is quite a large site, in which red burnished ware and various materials were discovered similar to those of Charsadda. ...
mound, was established around 1000 BCE. By 900 BCE, the city was already involved in regional commerce, as the discovered pottery shards reveal trading ties between the city and Puṣkalāvatī
Pushkalavati, was the capital of the ancient region of Gāndhāra, situated in present day's Pakistan. Its ruins are located on the outskirts of the modern city of Charsadda, in Charsadda District, in the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, 35-42 kilometres ...
.
Later, Taxila was inhabited at Bhir Mound
The Bhir Mound () is an archaeological site in Taxila in the Punjab province of Pakistan. It contains some of the oldest ruins of Ancient Taxila, dated to sometime around the period 800–525 BC as its earliest layers bear "grooved" Red Burni ...
, dated to some time around the period 800-525 BCE with these early layers bearing grooved red burnished ware.

Achaemenid Empire
Archaeological excavations show that the city may have grown significantly during the rule of the PersianAchaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian peoples, Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, i ...
in the 6th century BCE. In 516 BCE, Darius I
Darius I ( ; – 486 BCE), commonly known as Darius the Great, was the third King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 522 BCE until his death in 486 BCE. He ruled the empire at its territorial peak, when it included much of West A ...
embarked on a campaign to conquer Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Pers ...
, ''Ariana
In the Greco-Roman world, Ariana was a geographical term referring to a general area of land between Central Asia and the Indus River. Situated far to the east in the Achaemenid Empire, it covered a number of satrapies spanning what is today th ...
'' and ''Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian language, Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient Iranian peoples, Iranian civilization in Central Asia based in the area south of the Oxus River (modern Amu Darya) and north of the mountains of the Hindu Kush, an area ...
'', before marching onto what is now Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran borde ...
and northern Pakistan. Emperor Darius spent the winter of 516-515 BCE in the Gandhara region surrounding Taxila, and prepared to conquer the Indus Valley
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans- Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northwest through the disp ...
, which he did in 515 BCE, after which he appointed Scylax of Caryanda
Scylax of Caryanda (; ) was a Greek explorer and writer during the late 6th and early 5th centuries BCE of the Achaemenid Empire. His own writings are lost, though occasionally cited or quoted by later Greek and Roman authors. The periplus sometim ...
to explore the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or approximately 20% of the water area of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia (continent), ...
from the mouth of the Indus to the Suez
Suez (, , , ) is a Port#Seaport, seaport city with a population of about 800,000 in north-eastern Egypt, located on the north coast of the Gulf of Suez on the Red Sea, near the southern terminus of the Suez Canal. It is the capital and largest c ...
. Darius then returned to Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
via the Bolan Pass
Bolan Pass () is a valley and a natural gateway through the Toba Kakar range in Balochistan province of Pakistan. It is situated south of Pakistan's border with Afghanistan. The pass is an stretch of the Bolan River valley from Rindli in the ...
. The region continued under Achaemenid suzerainty under the reign of Xerxes I, and continued under Achaemenid rule for over a century.
Taxila was sometimes ruled as part of the Gandhara kingdom (whose capital was Pushkalavati), particularly after the Achaemenid period, but Taxila sometimes formed its own independent district or city-state.
Hellenistic
 During his invasion of the
During his invasion of the Indus Valley
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans- Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northwest through the disp ...
, Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
was able to gain control of Taxila () in 326 BCE without a battle, as the city was surrendered by its ruler, king Omphis (Āmbhi). Greek historians accompanying Alexander described Taxila as "wealthy, prosperous, and well governed". Arrian
Arrian of Nicomedia (; Greek: ''Arrianos''; ; )
was a Greek historian, public servant, military commander, and philosopher of the Roman period.
'' The Anabasis of Alexander'' by Arrian is considered the best source on the campaigns of ...
writes that Alexander was welcomed by the citizens of the city, and he offered sacrifices and celebrated a gymnastic and equestrian contest there.
On Alexander's death, in 323 BCE, the province and much of the once Achaemenid territories would pass to his general Seleucus I Nicator
Seleucus I Nicator (; Ancient Greek, Greek: Σέλευκος Νικάτωρ, ''Séleukos Nikátōr'', "Seleucus the Victorious"; ) was a Ancient Macedonians, Macedonian Greek general, officer and successor of Alexander the Great who went on to fo ...
and founder of the successor Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire ( ) was a Greek state in West Asia during the Hellenistic period. It was founded in 312 BC by the Macedonian general Seleucus I Nicator, following the division of the Macedonian Empire founded by Alexander the Great ...
.
Mauryan Empire
By 303 BCE, theSeleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire ( ) was a Greek state in West Asia during the Hellenistic period. It was founded in 312 BC by the Macedonian general Seleucus I Nicator, following the division of the Macedonian Empire founded by Alexander the Great ...
's satrap
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median kingdom, Median and Achaemenid Empire, Persian (Achaemenid) Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic period, Hellenistic empi ...
s in South Asia had been formally annexed by the expanding Mauryan empire, following the Seleucid–Mauryan war
The Seleucid–Mauryan War was a confrontation between the Seleucid and Mauryan empires that took place somewhere between 305 and 303 BCE, when Seleucus I Nicator of the Seleucid Empire crossed the Indus river into the former Indian satrapies ...
, with the provincial capital and center of higher education at Taxila under the control of Chandragupta Maurya
Chandragupta Maurya (Sanskrit: elp:IPA/Sanskrit, t̪͡ɕɐn̪d̪ɾɐgupt̪ɐ mɐʊɾjɐ (reigned 320 BCE – c. 298 BCE) was the founder and the first emperor of the Maurya Empire, based in Magadha (present-day Bihar) in the Indian ...
. His advisor, Kautilya/Chanakya, was said to have taught at Taxila's university. Under the reign of Ashoka the Great
Ashoka, also known as Asoka or Aśoka ( ; , ; – 232 BCE), and popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was List of Mauryan emperors, Emperor of Magadha from until #Death, his death in 232 BCE, and the third ruler from the Mauryan dynast ...
, Chandragupta's grandson, the city was made a great seat of Buddhist learning, though the city was home to a minor rebellion during this time.
Taxila was founded in a strategic location along the ancient "Royal Highway" that connected the Mauryan capital at Pataliputra
Pataliputra (IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, Bihar, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE, as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliput ...
in Bihar
Bihar ( ) is a states and union territories of India, state in Eastern India. It is the list of states and union territories of India by population, second largest state by population, the List of states and union territories of India by are ...
, with ancient Peshawar, Puṣkalāvatī, and onwards towards Central Asia via Kashmir
Kashmir ( or ) is the Northwestern Indian subcontinent, northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term ''Kashmir'' denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir P ...
, Bactria, and Kāpiśa. Taxila thus changed hands many times over the centuries, with many empires vying for its control.
Indo-Greek, Indo-Scythian, and Indo-Parthian Kingdoms
In the 2nd century BCE, Taxila was annexed by theIndo-Greek kingdom
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, also known as the Yavana Kingdom, was a Hellenistic period, Hellenistic-era Ancient Greece, Greek kingdom covering various parts of modern-day Afghanistan, Pakistan and northwestern India.
The term "Indo-Greek Kingdom" ...
of Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian language, Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient Iranian peoples, Iranian civilization in Central Asia based in the area south of the Oxus River (modern Amu Darya) and north of the mountains of the Hindu Kush, an area ...
. Indo-Greeks built a new capital, Sirkap, on the opposite bank of the river from Taxila. During this new period of Bactrian Greek rule, several dynasties (like Antialcidas
Antialcidas Nikephoros (; epithet means "the Bearer of Victory" or "the Victorious", Brahmi: 𑀅𑀁𑀢𑀮𑀺𑀓𑀺𑀢𑀲 ''Aṃtalikitasa'', in the Heliodorus Pillar) was a king of the Indo-Greek Kingdom, who reigned from his capital at ...
) likely ruled from the city as their capital. During lulls in Greek rule, the city managed profitably on its own, to independently control several local trade guilds, who also minted most of the city's autonomous coinage. In about the 1st century BCE or 1st century CE, an Indo-Scythian
The Indo-Scythians, also known as Indo-Sakas, were a group of nomadic people of Iranian peoples, Iranic Scythians, Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into the present-day regions of Afghanistan, Eastern Iran and the northwe ...
king named Azilises
Azilises (Greek: , (epigraphic); Kharosthi: , ) was an Indo-Scythian king who ruled in the area of Gandhara circa 57-35 BCE.
Name
Azes's name is attested on his coins in the Greek form () and the Kharosthi form (), which are both derived fro ...
had three mints, one of which was at Taxila, and struck coins with obverse legends in Greek and Kharoṣṭhī
Kharosthi script (), also known as the Gandhari script (), was an ancient script originally developed in the Gandhara, Gandhara Region of modern-day Pakistan, between the 5th and 3rd century BCE. used primarily by the people of Gandhara along ...
.
The last Greek king of Taxila was overthrown by the Indo-Scythian chief Maues
Maues (Greek language, Greek: ; (epigraphic); Kharosthi: , , called , on the Taxila copper plate; also called , in the Mathura lion capital inscription,) was the first Indo-Scythian king, ruling from 98/85 to 60/57 BCE. He invaded Indi ...
around 90 BCE. Gondophares
Gondophares I ( Greek: Γονδοφαρης ''Gondopharēs'', Υνδοφερρης ''Hyndopherrēs''; Kharosthi: 𐨒𐨂𐨡𐨥𐨪 ', '; 𐨒𐨂𐨡𐨥𐨪𐨿𐨣 ', '; 𐨒𐨂𐨡𐨂𐨵𐨪 ', ') was the founder of the Indo-Parthian K ...
, founder of the Indo-Parthian Kingdom
The Indo-Parthian kingdom was a Parthian kingdom founded by Gondophares, and active from 19 CE to c. 226 CE. At their zenith, they ruled an area covering parts of eastern Iran, various parts of Afghanistan and the northwest regions of the Indian ...
, conquered Taxila around 20 BCE, and made Taxila his capital. According to early Christian legend, Thomas the Apostle
Thomas the Apostle (; , meaning 'the Twin'), also known as Didymus ( 'twin'), was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus according to the New Testament. Thomas is commonly known as "doubting Thomas" because he initially doubted the resurrection of ...
visited Gondophares IV around 46 CE, possibly at Taxila given that city was Gondophares' capital city.
Kushan Empire
Around the year 50 CE, the GreekNeopythagorean
Neopythagoreanism (or neo-Pythagoreanism) was a school of Hellenistic and Roman philosophy which revived Pythagorean doctrines. Neopythagoreanism was influenced by middle Platonism and in turn influenced Neoplatonism. It originated in the 1st ce ...
philosopher Apollonius of Tyana
Apollonius of Tyana (; ; ) was a Greek philosopher and religious leader from the town of Tyana, Cappadocia in Roman Anatolia, who spent his life travelling and teaching in the Middle East, North Africa and India. He is a central figure in Ne ...
allegedly visited Taxila, which was described by his biographer, Philostratus
Philostratus or Lucius Flavius Philostratus (; ; 170s – 240s AD), called "the Athenian", was a Greek sophist of the Roman imperial period. His father was a minor sophist of the same name. He flourished during the reign of Septimius Severus ...
, writing some 200 years later, as a fortified city laid out on a symmetrical plan, similar in size to Nineveh
Nineveh ( ; , ''URUNI.NU.A, Ninua''; , ''Nīnəwē''; , ''Nīnawā''; , ''Nīnwē''), was an ancient Assyrian city of Upper Mesopotamia, located in the modern-day city of Mosul (itself built out of the Assyrian town of Mepsila) in northern ...
''.'' Modern archaeology confirms this description. Inscriptions dating to 76 CE demonstrate that the city had come under Kushan ''Kushan'' or Kushana may refer to:
* Kushan Empire
The Kushan Empire (– CE) was a Syncretism, syncretic empire formed by the Yuezhi in the Bactrian territories in the early 1st century. It spread to encompass much of what is now Afghanistan ...
rule by that time, after the city was captured from the Parthians
Parthia ( ''Parθava''; ''Parθaw''; ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Medes during the 7th century BC, was incorporated into the subsequent Achaemen ...
by Kujula Kadphises
Kujula Kadphises (Kushan language: Κοζουλου Καδφιζου, also Κοζολα Καδαφες; Kharosthi: 𐨐𐨂𐨗𐨂𐨫 𐨐𐨯, International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration, IAST: ', '; ; r. 30–80 CE, or 40–90 CE accor ...
, founder of the Kushan Empire
The Kushan Empire (– CE) was a Syncretism, syncretic empire formed by the Yuezhi in the Bactrian territories in the early 1st century. It spread to encompass much of what is now Afghanistan, Eastern Iran, India, Pakistan, Tajikistan and Uzbe ...
. The great Kushan ruler Kanishka
Kanishka I, also known as Kanishka the Great, was an emperor of the Kushan dynasty, under whose reign (–150 CE) the empire reached its zenith. He is famous for his military, political, and spiritual achievements. A descendant of Kujula Kadp ...
later founded Sirsukh
Sirsukh () is an ancient city that forms part of the ruins at Taxila, near the modern day city of Taxila, Punjab, Pakistan.
City
The city of Sirsukh is said to have been founded during the Kushan era after 80 CE, and is the last of the great a ...
, the most recent of the ancient settlements at Taxila.
Gupta Empire
In the mid-fourth century CE, the Gupta Empire occupied the territories in Eastern Gandhara, establishing a Kumaratya's post at Taxila. The city became well known for its trade links, including silk, sandalwood, horses, cotton, silverware, pearls, and spices. It is during this time that the city heavily features in classical Indian literature – both as a centre of culture as well as a militarised border city. Taxila's university remained in existence during the travels of Chinese pilgrim Faxian, who visited Taxila around 400 CE. He wrote that Taxila's name translated as "the Severed Head", and was the site of a story in the life of Buddha "where he gave his head to a man".Decline
TheKidarites
The Kidarites, or Kidara Huns, were a dynasty that ruled Bactria and adjoining parts of Central Asia and South Asia in the 4th and 5th centuries. The Kidarites belonged to a complex of peoples known collectively in India as the Huna people, Huna, ...
, vassals of the Hephthalite Empire
The Hephthalites (), sometimes called the White Huns (also known as the White Hunas, in Iranian as the ''Spet Xyon'' and in Sanskrit and Prakrit as the ''Sveta-huna''), were a people who lived in Central Asia during the 5th to 8th centuries CE, ...
are known to have invaded Taxila in c. 450 CE. Though repelled by the Gupta Emperor Skandagupta
Skandagupta (Gupta script: ''Ska-nda-gu-pta'', r. –467) was a Gupta Empire, Gupta Emperor of India. His Bhitari pillar inscription of Skandagupta, Bhitari pillar inscription suggests that he restored the Gupta power by defeating his enemies, ...
, the city would not recover- probably on account of the strong Hunnic presence in the area, breakdown of trade as well as the three-way war among Persia, the Kidarite State, and the Huns in Western Gandhara.
The White Huns
The Hephthalites (), sometimes called the White Huns (also known as the White Hunas, in Iranian as the ''Spet Xyon'' and in Sanskrit and Prakrit as the ''Sveta-huna''), were a people who lived in Central Asia during the 5th to 8th centuries CE, ...
and Alchon Huns
The Alchon Huns, ( Bactrian: ''Alkhon(n)o'' or ''Alkhan(n)o'') also known as the Alkhan, Alchono, Alxon, Alkhon, Alakhana, and Walxon, were a nomadic people who established states in Central Asia and South Asia during the 4th and 6th centurie ...
swept over Gandhāra
Gandhara () was an ancient Indo-Aryan civilization in present-day northwest Pakistan and northeast Afghanistan. The core of the region of Gandhara was the Peshawar (Pushkalawati) and Swat valleys extending as far east as the Pothohar Platea ...
and Punjab
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panjāb or Panj-Āb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
around 470 CE, causing widespread devastation and destruction of Taxila's famous Buddhist monasteries and stupa
In Buddhism, a stupa (, ) is a domed hemispherical structure containing several types of sacred relics, including images, statues, metals, and '' śarīra''—the remains of Buddhist monks or nuns. It is used as a place of pilgrimage and m ...
s, a blow from which the city would never recover. From 500 CE to 540 CE, the city languished after falling under the control of the Hunnic Empire ruled by Mihirakula
Mihirakula (Gupta script: , ''Mi-hi-ra-ku-la'', Chinese: 摩酰逻矩罗 ''Mo-hi-lo-kiu-lo''), sometimes referred to as Mihiragula or Mahiragula, was the second and last Alchon Huns, Alchon Hun king of northwestern region of the Indian subcont ...
. Mihirakula presided over some destruction of Buddhist sites, monasteries and Hindu temples across northwestern regions of the Indian subcontinent.Li Rongxi (1996), ''The Great Tang Dynasty Record of the Western Regions'', Bukkyo Dendo Kyokai and Numata Center for Buddhist Translation and Research, Berkeley, pp. 97–100
Xuanzang
Xuanzang (; ; 6 April 6025 February 664), born Chen Hui or Chen Yi (), also known by his Sanskrit Dharma name Mokṣadeva, was a 7th-century Chinese Bhikkhu, Buddhist monk, scholar, traveller, and translator. He is known for the epoch-making ...
visited India between 629 and 645 CE. Taxila which was desolate and half-ruined was visited by him in 630 CE, and found most of its sangharama
Sangharama (Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor langu ...
s still ruined and desolate. Only a few monks remained there. He adds that the kingdom had become a dependency of Kashmir with the local leaders fighting amongst themselves for power. He noted that it had some time previously been a subject of Kapisa. By the ninth century, it became a dependency of the Kabul Shahis. The Turki Shahi dynasty of Kabul was replaced by the Hindu Shahi
The Hindu Shahis, also referred to as the Kabul Shahis and Uḍi Śāhis, were a dynasty established between 843 CE and 1026 CE. They endured multiple waves of conquests for nearly two centuries and their core territory was described as having c ...
dynasty which was overthrown by Mahmud of Ghazni
Abu al-Qasim Mahmud ibn Sabuktigin (; 2 November 971 – 30 April 1030), usually known as Mahmud of Ghazni or Mahmud Ghaznavi (), was Sultan of the Ghaznavid Empire, ruling from 998 to 1030. During his reign and in medieval sources, he is usuall ...
with the defeat of Trilochanpala
The Hindu Shahis, also referred to as the Kabul Shahis and Uḍi Śāhis, were a dynasty established between 843 CE and 1026 CE. They endured multiple waves of conquests for nearly two centuries and their core territory was described as having c ...
.
Al-Usaifan's king during the reign of Al-Mu'tasim
Abū Isḥāq Muḥammad ibn Hārūn al-Rashīd (; October 796 – 5 January 842), better known by his laqab, regnal name al-Muʿtaṣim biʾllāh (, ), was the eighth Abbasid Caliphate, Abbasid caliph, ruling from 833 until his death in 842. ...
is said to have converted to Islam by Al-Biladhuri
ʾAḥmad ibn Yaḥyā ibn Jābir al-Balādhurī () was a 9th-century West Asian historian. One of the eminent Middle Eastern historians of his age, he spent most of his life in Baghdad and enjoyed great influence at the court of the caliph al-M ...
and abandoned his old faith due to the death of his son despite having priests of a temple pray for his recovery. Said to be located between Kashmir, Multan and Kabul, al-Usaifan is identified with kingdom of Taxila by some authors.
Centre of learning
F. W. Thomas (1944), in :
in contrast to the later
Nalanda
Nalanda (International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration, IAST: , ) was a renowned Buddhism, Buddhist ''mahavihara'' (great monastery) in medieval Magadha (Mahajanapada), Magadha (modern-day Bihar), eastern India. Widely considered to be am ...
university in eastern India."Nalanda" (2007). ''Encarta''."Nalanda" (2001). ''Columbia Encyclopedia
The ''Columbia Encyclopedia'' is a one-volume encyclopedia produced by Columbia University Press and, in the last edition, sold by the Gale Group. First published in 1935, and continuing its relationship with Columbia University
Columbi ...
''.
Taxila became a noted centre of learning (including the religious teachings of Historical Vedic Religion
The historical Vedic religion, also called Vedism or Brahmanism, and sometimes ancient Hinduism or Vedic Hinduism, constituted the religious ideas and practices prevalent amongst some of the Indo-Aryan peoples of the northwest Indian subcontin ...
and Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
) at least several centuries BCE, and continued to attract students from around the old world until the destruction of the city in the 5th century. It has been suggested that at its height, Taxila exerted a sort of "intellectual suzerainty
A suzerain (, from Old French "above" + "supreme, chief") is a person, state (polity)">state or polity who has supremacy and dominant influence over the foreign policy">polity.html" ;"title="state (polity)">state or polity">state (polity)">st ...
" over other centres of learning in India and its primary concern was not with elementary, but higher education. Generally, a student entered Taxila at the age of sixteen. The ancient and the most revered scriptures, and the Eighteen ''Silpas'' or Arts, which included skills such as archery, hunting, and elephant lore, were taught, in addition to its law school, medical school, and school of military science
Military science is the study of military processes, institutions, and behavior, along with the study of warfare, and the theory and application of organized coercive force. It is mainly focused on theory, method, and practice of producing mi ...
. Students came to Taxila from far-off places such as Kashi
Kashi or Kaashi most commonly refers to:
* Varanasi (historically known as "Kashi"), a holy city in India
Kashi may also refer to:
Places
**Kingdom of Kashi, an ancient kingdom in the same place, one of the sixteen Mahajanapadas
**Kashi Vishwana ...
, Kosala
Kosala, sometimes referred to as Uttara Kosala () was one of the Mahajanapadas of ancient India. It emerged as a small state during the Late Vedic period and became (along with Magadha) one of the earliest states to transition from a lineage ...
and Magadha, in spite of the long and arduous journey they had to undergo, on account of the excellence of the learned teachers there, all recognised as authorities on their respective subjects. The admission to Takshashila
was not only limited to the students belonging to the elite
class, some evidence mentions the sons of kings, nobles,
merchants, tailors, and even fishermen getting education at
Takshashila.
Notable students and teachers
Taxila had great influence on Hindu culture and the Sanskrit language. It is perhaps best known for its association with Chanakya, also known asKautilya
''Kautilya's Arthashastra'' (, ; ) is an Ancient Indian Sanskrit treatise on statecraft, politics, economic policy and military strategy. The text is likely the work of several authors over centuries, starting as a compilation of ''Arthashas ...
, the strategist who guided Chandragupta Maurya and assisted in the founding of the Mauryan
The Maurya Empire was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in South Asia with its power base in Magadha. Founded by Chandragupta Maurya around c. 320 BCE, it existed in loose-knit fashion until 185 BCE. The primary sourc ...
empire. The Ayurvedic
Ayurveda (; ) is an alternative medicine system with historical roots in the Indian subcontinent. It is heavily practised throughout India and Nepal, where as much as 80% of the population report using ayurveda. The theory and practice of ayur ...
healer Charaka
Charaka was one of the principal contributors to Ayurveda, a system of medicine and lifestyle developed in ancient India. He is known as a physician who edited the medical treatise entitled ''Charaka Samhita'', one of the foundational texts of ...
also studied at Taxila. He also started teaching at Taxila in the later period. Pāṇini, the grammarian who codified the rules that would define Classical Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest ...
, has also been part of the community at Taxila.
Jīvaka
Jīvaka (; ) was the personal physician () of the Buddha and the Indian King Bimbisara, Bimbisāra. He lived in Rājagṛha, present-day Rajgir, in the 5th century BCE. Sometimes described as the "Medicine King" () and "Thrice Crowned physician ...
, the court physician of the Magadha emperor Bimbisara
Bimbisāra (in Buddhist tradition) or Shrenika () and Seniya () in the Jain histories ( or ) was
the King of Magadha (V. K. Agnihotri (ed.), ''Indian History''. Allied Publishers, New Delhi 262010p. 166f. or ) and belonged to the Haryanka d ...
who once cured the Buddha, and the Buddhism-supporting ruler of Kosala, Prasenajit, are some important personalities mentioned in Pali texts who studied at Taxila.
No external authorities like kings or local leaders subjected the scholastic activities at Taxila to their control. Each teacher formed his own institution, enjoying complete autonomy in work, teaching as many students as he liked and teaching subjects he liked without conforming to any centralised syllabus. Study terminated when the teacher was satisfied with the student's level of achievement. In general, specialisation in a subject took around eight years, though this could be lengthened or shortened in accordance with the intellectual abilities and dedication of the student in question. In most cases the "schools" were located within the teachers' private houses, and at times students were advised to quit their studies if they were unable to fit into the social, intellectual and moral atmosphere there.
Knowledge was considered too sacred to be bartered for money, and hence any stipulation that fees ought to be paid was vigorously condemned. Financial support came from the society at large, as well as from rich merchants and wealthy parents. Though the number of students studying under a single Guru sometimes numbered in the hundreds, teachers did not deny education even if the student was poor; free boarding and lodging was provided, and students had to do manual work in the household. Paying students, such as princes, were taught during the day, while non-paying ones were taught at night. Gurudakshina was usually expected at the completion of a student's studies, but it was essentially a mere token of respect and gratitude - many times being nothing more than a turban, a pair of sandals, or an umbrella. In cases of poor students being unable to afford even that, they could approach the king, who would then step in and provide something. Not providing a poor student a means to supply his Guru's Dakshina was considered the greatest slur on a King's reputation.
Examinations were treated as superfluous, and not considered part of the requirements to complete one's studies. The process of teaching was critical and thorough- unless one unit was mastered completely, the student was not allowed to proceed to the next. No convocations were held upon completion, and no written "degrees" were awarded, since it was believed that knowledge was its own reward. Using knowledge for earning a living or for any selfish end was considered sacrilegious.
Students arriving at Taxila usually had completed their primary education at home (until the age of eight), and their secondary education in the Ashrams (between the ages of eight and twelve), and therefore came to Taxila chiefly to reach the ends of knowledge in specific disciplines.
Ruins
The sites of a number of important cities noted in ancient Indian texts were identified by scholars early in the 19th century. The lost city of Taxila, however, was not identified until later, in 1863-64. Its identification was made difficult partly due to errors in the distances recorded by Pliny in hisNaturalis Historia
The ''Natural History'' () is a Latin work by Pliny the Elder. The largest single work to have survived from the Roman Empire to the modern day, the ''Natural History'' compiles information gleaned from other ancient authors. Despite the work' ...
which pointed to a location somewhere on the Haro river
The Haro () is a river in Pakistan that flows through Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and parts of Punjab. It is a left tributary of the Indus. Its main valley is in Abbottabad District, in the Hazara Division of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Province, northern Pakist ...
, two days march from the Indus. Alexander Cunningham
Major General Sir Alexander Cunningham (23 January 1814 – 28 November 1893) was a British Army engineer with the Bengal Sappers who later took an interest in the history and archaeology of India. In 1861, he was appointed to the newly crea ...
, the founder and the first director-general of the Archaeological Survey of India
The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) is an Indian government agency that is responsible for archaeological research and the conservation and preservation of cultural historical monuments in the country. It was founded in 1861 by Alexander ...
, noticed that this position did not agree with the descriptions provided in the itineraries of Chinese pilgrims and in particular, that of Xuanzang, the 7th-century Buddhist monk. Unlike Pliny, these sources noted that the journey to Taxila from the Indus took three days and not two. Cunningham's subsequent explorations in 1863–64 of a site at Shah-dheri convinced him that his hypothesis was correct.
Taxila's archaeological sites lie near modern Taxila about northwest of the city of Rawalpindi. The sites were first excavated by John Marshall
John Marshall (September 24, 1755July 6, 1835) was an American statesman, jurist, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the fourth chief justice of the United States from 1801 until his death in 1835. He remai ...
, who worked at Taxila over a period of twenty years from 1913.
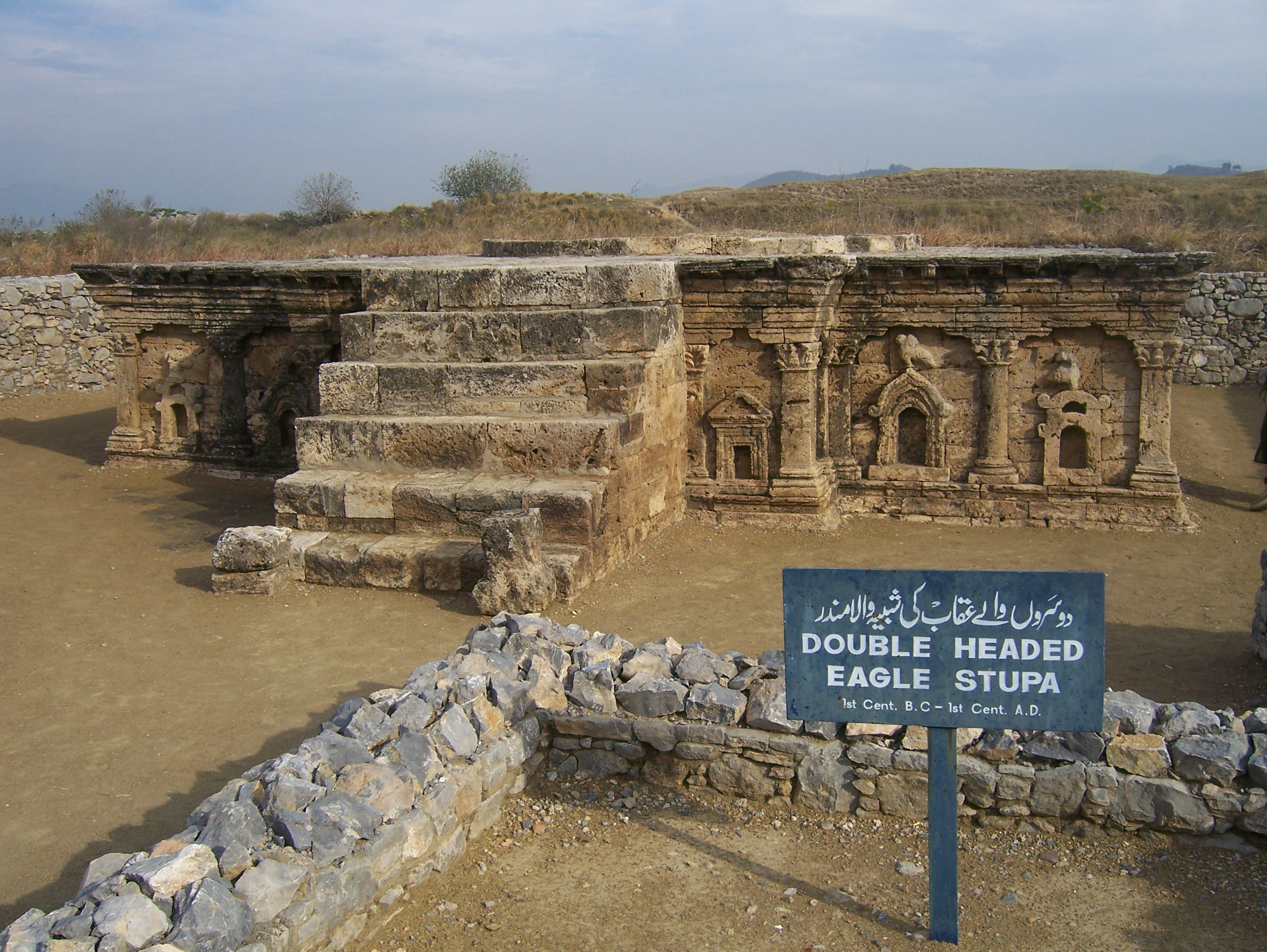
 The vast archaeological site includes neolithic remains dating to 3360 BCE, and Early Harappan remains dating to 2900–2600 BCE at ''Sarai Kala''. Taxila, however, is most famous for ruins of several settlements, the earliest dating from around 1000 BCE. It is also known for its collection of Buddhist religious monuments, including the
The vast archaeological site includes neolithic remains dating to 3360 BCE, and Early Harappan remains dating to 2900–2600 BCE at ''Sarai Kala''. Taxila, however, is most famous for ruins of several settlements, the earliest dating from around 1000 BCE. It is also known for its collection of Buddhist religious monuments, including the Dharmarajika stupa
The Dharmarajika Stupa (Punjabi language, Punjabi, ), also referred to as the Great Stupa of Taxila, is a Buddhist stupa near Taxila (modern), Taxila, Pakistan. It was built over the relics of the Buddha by Ashoka, the Emperor of Magadha, in ...
, the Jaulian
Jaulian (; meaning ''Seat of Saints'') is a ruined Buddhist monastery dating from the 2nd century CE, located in Taxila, in Pakistan.
Jaulian, along with the nearby monastery at Mohra Muradu, form part of the Ruins of Taxila – a collecti ...
monastery, and the Mohra Muradu
Mohra Muradu () is the place of an ancient Buddhist stupa and monastery near the ruins of Taxila, in the Punjab province of Pakistan. The ancient monastery is located in a valley and has views of the surrounding mountains. The monks could medi ...
monastery.
The main ruins of Taxila include four major cities, each belonging to a distinct time period, at three different sites. The earliest settlement at Taxila is found in the Hathial section, which yielded pottery shards that date from as early as the late 2nd millennium BCE to the 6th century BCE. The Bhir Mound ruins at the site date from the 6th century BCE, and are adjacent to Hathial. The ruins of Sirkap date to the 2nd century BCE, and were built by the region's Greco-Bactrian
The Greco-Bactrian Kingdom () was a Greek state of the Hellenistic period located in Central-South Asia. The kingdom was founded by the Seleucid satrap Diodotus I Soter in about 256 BC, and continued to dominate Central Asia until its fall a ...
kings who ruled in the region following Alexander the Great's invasion of the region in 326 BCE. The third and most recent settlement is that of Sirsukh
Sirsukh () is an ancient city that forms part of the ruins at Taxila, near the modern day city of Taxila, Punjab, Pakistan.
City
The city of Sirsukh is said to have been founded during the Kushan era after 80 CE, and is the last of the great a ...
, which was built by rulers of the Kushan ''Kushan'' or Kushana may refer to:
* Kushan Empire
The Kushan Empire (– CE) was a Syncretism, syncretic empire formed by the Yuezhi in the Bactrian territories in the early 1st century. It spread to encompass much of what is now Afghanistan ...
empire, who ruled from nearby Purushapura (modern Peshawar).
World Heritage Site
Taxila was designated aUNESCO World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
in 1980 in particular for the ruins of the four settlement sites which "reveal the pattern of urban evolution on the Indian subcontinent through more than five centuries". The serial site includes a number of monuments and other historical places of note in the area besides the four settlements at Bhir, Saraikala, Sirkap, and Sirsukh. They number 18 in all:
In a 2010 report, Global Heritage Fund
Global Heritage Fund is a non-profit organization that operates internationally.
Founded in California in 2002, its mission is to "transform local communities by investing in global heritage."
To date, it has partnered with over 100 public and ...
identified Taxila as one of 12 worldwide sites most "on the Verge" of irreparable loss and damage, citing insufficient management, development pressure, looting, and war and conflict as primary threats. In 2017, it was announced that Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
would assist in conservation efforts at Taxila, as well as at Buddhist sites in the Swat Valley
Swat District (), also known as the Swat Valley, is a district in the Malakand Division of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. Known for its stunning natural beauty, the district is a popular tourist destination. With a population of 2,687,384 per th ...
.
Demographics
Population
According to 2023 census, Taxila had a population of 136,900.Geography
Taxila is located north-west of the Pakistani capital Islamabad. The city is located approximately abovesea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an mean, average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal Body of water, bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical ...
.
Climate
Taxila features ahumid subtropical climate
A humid subtropical climate is a subtropical -temperate climate type, characterized by long and hot summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between ...
(Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (1951–2014), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author ...
: Cwa)
Economy
Tourism
 Taxila is one of northern Pakistan's most important tourist destinations and is home to the
Taxila is one of northern Pakistan's most important tourist destinations and is home to the Taxila Museum
Taxila Museum (Punjabi language, Punjabi, ) is located at Taxila (modern), Taxila, Punjab (Pakistan), Punjab, Pakistan. The museum is home to a significant and comprehensive collection of Greco-Buddhist art, Gandharan art dating from the 1st to ...
which holds a large number of artifacts from Taxila's excavations. Though the number of foreign visitors to the site drastically declined following the start of an Islamist insurgency in Pakistan in 2007, visitor numbers began to noticeably improve by 2017, after the law and order situation in the region had greatly improved following the start of the 2014 ''Zarb-e-Azb
Operation Zarb-e-Azb (Pashto/ ALA-LC: ; ) was a joint military offensive conducted by the Pakistan Armed Forces against various militant groups, including the Tehrik-i-Taliban Pakistan (TTP), the Islamic Movement of Uzbekistan, the East Tur ...
'' campaign launched by the Pakistani Army
The Pakistan Army (, ), commonly known as the Pak Army (), is the Land warfare, land service branch and the largest component of the Pakistan Armed Forces. The president of Pakistan is the Commander-in-chief, supreme commander of the army. The ...
against radical Islamist militants.
In 2017, the Pakistani government announced its intention to develop Taxila into a site for Buddhist religious pilgrimage. As part of the efforts, it announced that an exhibition on the Buddhist heritage of the region would be held in Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
, and that the Thai government would assist in conservation efforts at the site. Relics from Taxila were also sent to Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
for the 2017 ''Vesak
Vesak (; Sanskrit: '), also known as Buddha Jayanti, Buddha Purnima, Visak Bochea and Buddha Day, is a holiday traditionally observed by Buddhism, Buddhists in South Asia and Southeast Asia, as well as in Tibet and Mongolia. It is among the ...
'' holiday as part of an effort to showcase the region's Buddhist heritage. The Pakistan Tourism Development Corporation
Pakistan Tourism Development Corporation (PTDC; ) is an organization of the Government of Pakistan. The PTDC is governed by a Board of Directors and for promoting and developing tourism provides transportation to various areas and owns and runs ...
also announced in 2017 that a tour bus service would be launched between the Taxila Museum and Islamabad.
In addition to the ruins of ancient Taxila, relics of Mughal garden
A Mughal garden is a type of garden built by the Mughal Empire, Mughals. This style was influenced by the Persian gardens particularly the Charbagh structure, which is intended to create a representation of an earthly utopia in which humans c ...
s and vestiges of historical Grand Trunk Road
Grand Trunk Road (formerly known as Uttarapath, Sadak-e-Azam, Shah Rah-e-Azam, Badshahi Sadak, and Long Walk) is one of Asia's oldest and longest major roads. For at least 2,500 years it has linked Central Asia to the Indian subcontinent. It r ...
are also found in Taxila. Nicholson's Obelisk
Nicholson's Obelisk (), or Nicholson's Memorial, is a monument in Pakistan, erected in 1868 in honour of Brigadier-General John Nicholson (East India Company officer), John Nicholson, a famous military figure of the British Empire.
It is situated ...
, named in honor of Brigadier John Nicholson who died during the Sepoy Mutiny
The Indian Rebellion of 1857 was a major uprising in India in 1857–58 against the rule of the British East India Company, which functioned as a sovereign power on behalf of the British Crown. The rebellion began on 10 May 1857 in the form ...
of 1857, is a monument from the British era that welcomes travelers arriving from Rawalpindi/Islamabad.
Industry
Taxila is home toHeavy Industries Taxila
Heavy Industries Taxila (Reporting name: HIT), () is a Pakistani state-owned enterprise and defense contractor working under the Ministry of Defence Production, located in Taxila (modern), Taxila, Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab.
, a major Pakistani defence
Defense or defence may refer to:
Tactical, martial, and political acts or groups
* Defense (military), forces primarily intended for warfare
* Civil defense, the organizing of civilians to deal with emergencies or enemy attacks
* Defense indust ...
, military contractor, engineering
Engineering is the practice of using natural science, mathematics, and the engineering design process to Problem solving#Engineering, solve problems within technology, increase efficiency and productivity, and improve Systems engineering, s ...
conglomerate. The city's economy is also closely linked to the large Pakistan Ordnance Factories
The Pakistan Ordnance Factories (POF) is a major firearms and a defence contractor headquartered in Wah Cantt, Punjab, Pakistan. Described as "the largest defence industrial complex under the Ministry of Defence Production, producing convent ...
at nearby Wah Cantt, which employs 27,000 people. Cottage and household industries include stoneware
Stoneware is a broad class of pottery fired at a relatively high temperature, to be impervious to water. A modern definition is a Vitrification#Ceramics, vitreous or semi-vitreous ceramic made primarily from stoneware clay or non-refractory fire ...
, pottery and footwear. Heavy Mechanical Complex is also located in Taxila city.
Transportation
Rail
Taxila is served by theTaxila Cantonment Junction railway station
Taxila Cantonment Junction Railway Station (Urdu and ) is located in Taxila Cantonment, Taxila cantonment area near Taxila (modern), Taxila, Rawalpindi district of Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab province, Pakistan. It serves as a junction for Havelian ...
. Taxila Junction is served by the Karachi–Peshawar Railway Line, and is the southern terminus of the Khunjerab Railway
Khunjerab Railway (), also known as the China–Pakistan railway and ML-5, is a semi-planned railway line in Pakistan, passing through the region of Kashmir. The current active line begins from Taxila Junction station and ends at Havelian stat ...
, which connects Taxila to the Havelian railway station
Havelian Railway Station () is located in Havelian, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan.
See also
* List of railway stations in Pakistan
* Pakistan Railways
Pakistan Railways is the state-owned railway operator in Pakistan. Founded in 1861 as th ...
. A planned extension of the railway will eventually connect Taxila to China's Southern Xinjiang Railway in Kashgar
Kashgar () or Kashi ( zh, c=喀什) is a city in the Tarim Basin region of southern Xinjiang, China. It is one of the westernmost cities of China, located near the country's border with Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan. For over 2,000 years, Kashgar ...
, as part of the China–Pakistan Economic Corridor
China–Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC; zh, c=中巴经济走廊, p=Zhōng bā jīngjì zǒuláng; ) is a 3,000 km Chinese infrastructure network project currently under construction in Pakistan. This sea-and-land-based corridor aims to ...
.
Road
 The ancient
The ancient Grand Trunk Road
Grand Trunk Road (formerly known as Uttarapath, Sadak-e-Azam, Shah Rah-e-Azam, Badshahi Sadak, and Long Walk) is one of Asia's oldest and longest major roads. For at least 2,500 years it has linked Central Asia to the Indian subcontinent. It r ...
is designated as N-5 National Highway
The N-5 or National Highway 5 (Urdu: ) is a 1819 km national highway in Pakistan, which extends from Karachi in Sindh to Torkham in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa.
Route
The N-5 is the longest national highway in Pakistan and serves as an impor ...
, and connects the city to the Afghan border, and northern Punjab
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panjāb or Panj-Āb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
. The Karakoram Highway
The Karakoram Highway (, ), also known as the KKH, National Highway 35 (), N-35, and the ChinaPakistan Friendship Highway, is a National Highways of Pakistan, national highway which extends from Hasan Abdal in the Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab p ...
's southern terminus is in nearby Hasan Abdal
Hasan Abdal ( Punjabi; ) is a city in the Attock District of Punjab Province in Pakistan. Located 40 km northwest of the country's capital city, Islamabad, Hassan Abdal is the headquarters of Hasan Abdal Tehsil (sub-district).
As home of ...
, and connects Taxila to the Chinese border near the Hunza Valley
The Hunza Valley (; ) is a mountainous valley located in the northern region of the Gilgit-Baltistan, Pakistan.
Geography
The valley stretches along the Hunza River and shares borders with Ishkoman Valley, Ishkoman to the northwest, Shigar Val ...
.
The city is linked to Peshawar and Islamabad by the M-1 Motorway, which in turn offers wider motorway access to Lahore
Lahore ( ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the Administrative units of Pakistan, Pakistani province of Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab. It is the List of cities in Pakistan by population, second-largest city in Pakistan, after Karachi, and ...
via the M-2 Motorway, and Faisalabad
Faisalabad, formerly known as Lyallpur, is the List of cities in Punjab, Pakistan by population, second-largest city and primary List of cities in Punjab, Pakistan by population, industrial center of the Pakistani province of Punjab, Pakistan ...
via the M-4 Motorway.
Air
The nearest airport to Taxila isIslamabad International Airport
Islamabad International Airport () () is an international airport serving Islamabad, the capital city of Pakistan and Rawalpindi. It is located south-west of the city, and is directly connected to the Lahore and Peshawar motorways as well to ...
located 36.5 kilometers away. Peshawar's Bacha Khan International Airport
Bacha Khan International Airport , formerly known as Peshawar International Airport, is an international airport located in Peshawar, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. Located in the southwestern end of the city of Peshawar, it is the fourth-busies ...
is 155 kilometers away.
Education
 Taxila is home to many secondary educational institutes including CIIT Wah Campus, and
Taxila is home to many secondary educational institutes including CIIT Wah Campus, and HITEC University
HITEC University is a private university located in Taxila Cantonment, Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab, Pakistan.
Taxila, a historic seat of learning and an important archaeological site, is about 30 km north-west of Islamabad and Rawalpindi. HIT ...
. The University of Engineering and Technology, Taxila was established in 1975 as a campus of the University of Engineering and Technology, Lahore
A university () is an institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". Uni ...
,
and offers bachelor, master, and doctoral degrees in engineering.
Ancient ruins
TheRuins of Taxila
Taxila or Takshashila () is a city in the Pothohar region of Punjab, Pakistan. Located in the Taxila Tehsil of Rawalpindi District, it lies approximately northwest of the Islamabad–Rawalpindi metropolitan area and is just south of the Harip ...
include four major cities, each belonging to a distinct time period, at three different sites. The earliest settlement at Taxila is found in the Hathial section, which yielded pottery shards that date from as early as the late 2nd millennium BCE to the 6th century BCE. The Bhir Mound
The Bhir Mound () is an archaeological site in Taxila in the Punjab province of Pakistan. It contains some of the oldest ruins of Ancient Taxila, dated to sometime around the period 800–525 BC as its earliest layers bear "grooved" Red Burni ...
ruins at the site date from the 6th century BCE, and are adjacent to ''Hathial''. The ruins of Sirkap
Sirkap (Urdu and ) is the name of an archaeological site on the bank opposite to the city of Taxila, Punjab, Pakistan.
The city of Sirkap was built by the Greco-Bactrian king Demetrius after he invaded modern-day Pakistan around 180 BC. Demetr ...
date to the 2nd century BCE, and were built by the region's Greco-Bactrian
The Greco-Bactrian Kingdom () was a Greek state of the Hellenistic period located in Central-South Asia. The kingdom was founded by the Seleucid satrap Diodotus I Soter in about 256 BC, and continued to dominate Central Asia until its fall a ...
kings who ruled in the region following Alexander the Great's invasion of the region in 326 BCE. The third and most recent settlement is that of Sirsukh
Sirsukh () is an ancient city that forms part of the ruins at Taxila, near the modern day city of Taxila, Punjab, Pakistan.
City
The city of Sirsukh is said to have been founded during the Kushan era after 80 CE, and is the last of the great a ...
, which was built by rulers of the Kushan empire, who ruled from nearby ''Purushapura'' (modern Peshawar).
Culture
Modern Taxila is a mix of relatively wealthy urban, and poorer rural environs. Urban residential areas are general in the form of planned housing colonies populated by workers of the heavy mechanical complex & heavy industries, educational institutes and hospitals that are located in the area.Museums
Taxila Museum
Taxila Museum (Punjabi language, Punjabi, ) is located at Taxila (modern), Taxila, Punjab (Pakistan), Punjab, Pakistan. The museum is home to a significant and comprehensive collection of Greco-Buddhist art, Gandharan art dating from the 1st to ...
has one of the most significant and comprehensive collections of stone Buddhist sculpture from the first to the seventh centuries in Pakistan (known as Gandharan art
The Greco-Buddhist art or Gandhara art is the artistic manifestation of Greco-Buddhism, a cultural syncretism between Ancient Greek art and Buddhism. It had mainly evolved in the ancient region of Gandhara, located in the northwestern fringe of t ...
. The core of the collection comes from excavated sites in the Taxila Valley, particularly the excavations of Sir John Marshall. Other objects come from excavated sites elsewhere in Gandhara, from donations such as the Ram Das Collection, or from material confiscated by the police and customs authorities.
Indo-Greek
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, also known as the Yavana Kingdom, was a Hellenistic period, Hellenistic-era Ancient Greece, Greek kingdom covering various parts of modern-day Afghanistan, Pakistan and northwestern India.
The term "Indo-Greek Kingdom" ...
king Antialcidas
Antialcidas Nikephoros (; epithet means "the Bearer of Victory" or "the Victorious", Brahmi: 𑀅𑀁𑀢𑀮𑀺𑀓𑀺𑀢𑀲 ''Aṃtalikitasa'', in the Heliodorus Pillar) was a king of the Indo-Greek Kingdom, who reigned from his capital at ...
ruled in Taxila around 100 BCE, according to the Heliodorus pillar
The Heliodorus pillar is a stone column that was erected around 113 BCE in central India in Besnagar (Vidisha), Madhya Pradesh. The pillar is commonly named after Heliodorus (identified by him as a Garuda-standard), who was an ambassador of the In ...
inscription.
Image:Taxila Pakistan juillet 2004.jpg, Jaulian, a World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
at Taxila.
Image:JaulianTaxilaSilverReliquaryAndContent.jpg, Jaulian silver Buddhist reliquary, with contents. British Museum
The British Museum is a Museum, public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is the largest in the world. It documents the story of human cu ...
.
Image:Double-Headed Eagle Stupa at Sirkap 08.jpg, Stupa base at Sirkap, decorated with Hindu, Buddhist and Greek temple fronts.
Image:Stupa in Taxila Pakistan.JPG, Stupa in Taxila.
Image:TaxilaCoin200-100BCE.JPG, A Taxila coin, 200–100 BCE. British Museum
The British Museum is a Museum, public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is the largest in the world. It documents the story of human cu ...
.
Gallery
Sirkap
Sirkap (Urdu and ) is the name of an archaeological site on the bank opposite to the city of Taxila, Punjab, Pakistan.
The city of Sirkap was built by the Greco-Bactrian king Demetrius after he invaded modern-day Pakistan around 180 BC. Demetr ...
See also
* Taxila (satrapy) *Harappa
Harappa () is an archaeological site in Punjab, Pakistan, about west of Sahiwal, that takes its name from a modern village near the former course of the Ravi River, which now runs to the north. Harappa is the type site of the Bronze Age Indus ...
* Hund
Notes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Explore Taxila with Google Earth
on
Global Heritage Network
Global Heritage Fund is a non-profit organization that operates internationally.
Founded in California in 2002, its mission is to "transform local communities by investing in global heritage."
To date, it has partnered with over 100 public and ...
''Guide to Historic Taxila'' by Ahmad Hasan Dani in 10 chapters
* ttps://www.srikanta-sastri.org/taxila-an-ancient-indian-university Taxila: An Ancient Indian Universityby S. Srikanta Sastri
John Marshall, ''A guide to Taxila'' (1918)
on
Archive.org
The Internet Archive is an American non-profit organization founded in 1996 by Brewster Kahle that runs a digital library website, archive.org. It provides free access to collections of digitized media including websites, software applic ...
''Telapatta Jataka''
also known as the ''Takkasila Jataka'' {{Authority control Taxila Tehsil Places in Hindu mythology Archaeological sites in Punjab, Pakistan World Heritage Sites in Pakistan Ancient Greek archaeological sites in Pakistan Hinduism in Pakistan Buddhism in Pakistan Gandhara Former populated places in Pakistan Buddhist sites in Pakistan Indo-Parthian kingdom Populated places in Taxila Tehsil Cities in Rawalpindi District Populated places established in the 1st millennium BC Ancient cities