|
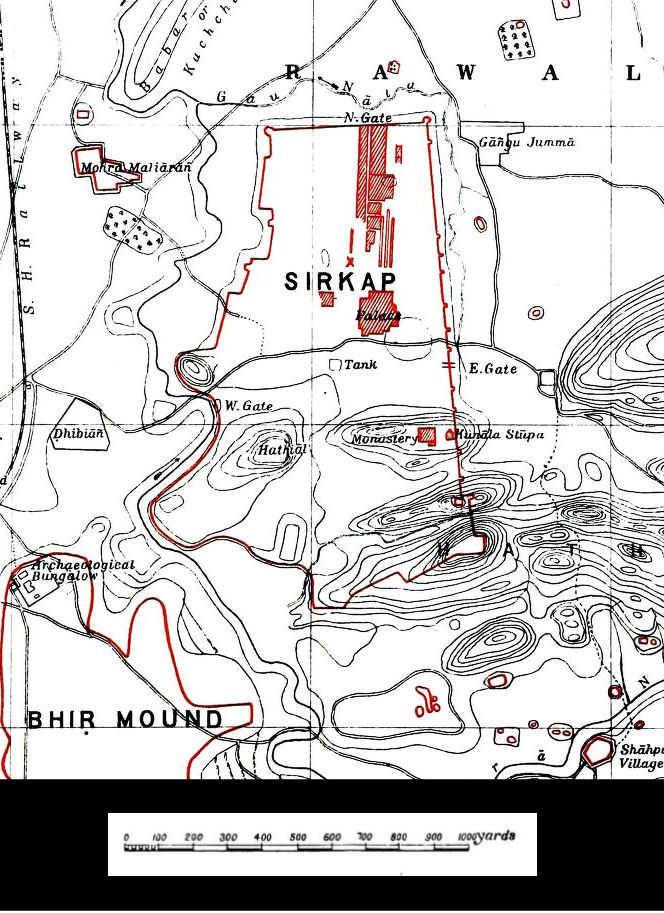
Sirkap
Sirkap (Urdu and ) is the name of an archaeological site on the bank opposite to the city of Taxila, Punjab, Pakistan. The city of Sirkap was built by the Greco-Bactrian king Demetrius after he invaded modern-day Pakistan around 180 BC. Demetrius founded an Indo-Greek kingdom that was to last until around 10 BC. Sirkap is also said to have been rebuilt by king Menander I. Archaeological excavations The excavation of the old city was carried out under the supervision of Sir John Marshall by Hergrew from 1912–1930. In 1944 and 1945 further parts were excavated by Mortimer Wheeler and his colleagues. Most of the discoveries at Sirkap related to the Indo-Scythian and Indo-Parthian periods (1st-2nd century CE). Overall excavations to the Greek levels have been very limited, and probably much remains hidden underground: in Sirkap, only about one eighth of the excavations were made down to the Indo-Greek and early Indo-Scythian levels, and this only in an area far removed from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxila
Taxila or Takshashila () is a city in the Pothohar region of Punjab, Pakistan. Located in the Taxila Tehsil of Rawalpindi District, it lies approximately northwest of the Islamabad–Rawalpindi metropolitan area and is just south of the Haripur District of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. Established during the Vedic period, Old Taxila was for a time the capital city of ancient Gandhāra. It was situated on the eastern shore of the Indus River—the pivotal junction of the Indian subcontinent and Central Asia;Raymond Allchin, Bridget Allchin''The Rise of Civilization in India and Pakistan''.Cambridge University Press, 1982 p.127 it was possibly founded around 1000 BCE. Takshashila and Pushkalavati remained prominent cities in Gandhāra during the Mahajanapadas. The city was later conquered by the Achaemenid Empire and incorporated into the Hindush satrap, between 550 – 326 BCE. In 326 BCE, the city was claimed by Alexander the Great, after overthrowing the Achaemenids. He gaine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sirsukh
Sirsukh () is an ancient city that forms part of the ruins at Taxila, near the modern day city of Taxila, Punjab, Pakistan. City The city of Sirsukh is said to have been founded during the Kushan era after 80 CE, and is the last of the great ancient cities of Taxila. The invaders decided to abandon the older city of Sirkap and build a newer city on the other side of the Lundi-nala. The wall of the city is about 5 kilometers long and about 5.4 meters thick. The city wall covers an area of around 2300 x 1000 meters seen along the east-west direction, and is laid out in a typical Central Asian style, complete with suburbs. Sirsukh was left uninhabited when the White Huns invaded the Punjab at the end of the fifth century CE. To the north-east of the city flows the Harro river whereas to the south the Lundi-ravine is present. The ancient city was excavated only on a very small scale in 1915-16 CE, and further excavation work has been impeded by a high water table which threatens t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Parthian Kingdom
The Indo-Parthian kingdom was a Parthian kingdom founded by Gondophares, and active from 19 CE to c. 226 CE. At their zenith, they ruled an area covering parts of eastern Iran, various parts of Afghanistan and the northwest regions of the Indian subcontinent (most of modern Pakistan and parts of northwestern India). The rulers may have been members of the House of Suren, and the kingdom has even been called the "Suren Kingdom" by some authors. The kingdom was founded in 19/20 when the governor of Drangiana ( Sakastan) Gondophares declared independence from the Parthian Empire. He would later make expeditions to the east, conquering territory from the Indo-Scythians and Indo-Greeks, thus transforming his kingdom into an empire. The domains of the Indo-Parthians were greatly reduced following the invasions of the Kushans in the second half of the 1st. century. They managed to retain control of Sakastan, until its conquest by the Sasanian Empire in c. 224/5. In Baluchistan, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Parthians
The Indo-Parthian kingdom was a Parthian kingdom founded by Gondophares, and active from 19 CE to c. 226 CE. At their zenith, they ruled an area covering parts of eastern Iran, various parts of Afghanistan and the northwest regions of the Indian subcontinent (most of modern Pakistan and parts of northwestern India). The rulers may have been members of the House of Suren, and the kingdom has even been called the "Suren Kingdom" by some authors. The kingdom was founded in 19/20 when the governor of Drangiana (Sistan, Sakastan) Gondophares declared independence from the Parthian Empire. He would later make expeditions to the east, conquering territory from the Indo-Scythians and Indo-Greeks, thus transforming his kingdom into an empire. The domains of the Indo-Parthians were greatly reduced following the invasions of the Kushan Empire, Kushans in the second half of the 1st. century. They managed to retain control of Sakastan, until its conquest by the Sasanian Empire in c. 224/5. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Parthian
The Indo-Parthian kingdom was a Parthian kingdom founded by Gondophares, and active from 19 CE to c. 226 CE. At their zenith, they ruled an area covering parts of eastern Iran, various parts of Afghanistan and the northwest regions of the Indian subcontinent (most of modern Pakistan and parts of northwestern India). The rulers may have been members of the House of Suren, and the kingdom has even been called the "Suren Kingdom" by some authors. The kingdom was founded in 19/20 when the governor of Drangiana ( Sakastan) Gondophares declared independence from the Parthian Empire. He would later make expeditions to the east, conquering territory from the Indo-Scythians and Indo-Greeks, thus transforming his kingdom into an empire. The domains of the Indo-Parthians were greatly reduced following the invasions of the Kushans in the second half of the 1st. century. They managed to retain control of Sakastan, until its conquest by the Sasanian Empire in c. 224/5. In Baluchistan, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhir Mound
The Bhir Mound () is an archaeological site in Taxila in the Punjab province of Pakistan. It contains some of the oldest ruins of Ancient Taxila, dated to sometime around the period 800–525 BC as its earliest layers bear "grooved" Red Burnished Ware, the Bhir Mound, along with several other nearby excavations, form part of the Ruins of Taxila – inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1980. Context The Bhir Mound archaeological remains represent one stage of the historic city of Taxila. The first town in Taxila was situated in the Hathial mound in the southwest corner of the Sirkap site. It lasted from the late second millennium BC until the Achaemenid period, with the Achaemenid period remains located in its Mound B. The Bhir Mound site represents the second city of Taxila, beginning in the pre-Achaemenid period and lasting till the early Hellenistic period. The earliest occupation on the Bhir mound began around 800-525 BC, and what now appears to be the second phas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hathial
Hathial is an ancient archaeological site next to Bhir Mound, just south of Sirkap, in the area of Taxila in Pakistan. It is quite a large site, in which red burnished ware and various materials were discovered similar to those of Charsadda. This suggest that the establishment of the Hathial site may go back as far as 1000 BCE. The adjoining settlement of Bhir Mound was only created later, probably around 500 BCE. The pottery found at the site has been dated to the period between 1000 BCE and 400 BCE, and thus constitute an interesting intermediary, pre-Achaemenid period, between the Late Harappan of the Indus Valley The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans- Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northwest through the disp ... and the Early Historic period. References Bibliography * * * {{Archaeological sites in Taxila , state ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Scythians
The Indo-Scythians, also known as Indo-Sakas, were a group of nomadic people of Iranic Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into the present-day regions of Afghanistan, Eastern Iran and the northwestern Indian subcontinent: present-day Pakistan and northern India. The migrations persisted from the middle of the second century BCE to the fourth century CE. The first Saka king in India was Maues/Moga (first century BCE) who established Saka power in Gandhara, the Indus Valley, and other regions. The Indo-Scythians extended their supremacy over the north-western subcontinent, conquering the Indo-Greeks and other local peoples. They were apparently subjugated by the Kushan Empire's Kujula Kadphises or Kanishka. The Saka continued to govern as satrapies, forming the Northern Satraps and Western Satraps. The power of the Saka rulers began to decline during the 2nd century CE after the Indo-Scythians were defeated by the Satavahana emperor Gautamiputra Satakarni. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Scythian
The Indo-Scythians, also known as Indo-Sakas, were a group of nomadic people of Iranian peoples, Iranic Scythians, Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into the present-day regions of Afghanistan, Eastern Iran and the northwestern Indian subcontinent: present-day Pakistan and northern India. The migrations persisted from the middle of the second century BCE to the fourth century CE. The first Saka king in Greater India, India was Maues, Maues/Moga (first century BCE) who established Saka power in Gandhara, the Indus Valley, and other regions. The Indo-Scythians extended their supremacy over the north-western subcontinent, conquering the Indo-Greeks and other local peoples. They were apparently subjugated by the Kushan Empire's Kujula Kadphises or Kanishka. The Saka continued to govern as satrapies, forming the Northern Satraps and Western Satraps. The power of the Saka rulers began to decline during the 2nd century CE after the Indo-Scythians were defeated by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Greek
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, also known as the Yavana Kingdom, was a Hellenistic period, Hellenistic-era Ancient Greece, Greek kingdom covering various parts of modern-day Afghanistan, Pakistan and northwestern India. The term "Indo-Greek Kingdom" loosely describes a number of various Hellenistic states, ruling from regional capitals like Taxila, Sagala, Pushkalavati, and Bagram. Other centers are only hinted at; e.g. Ptolemy's ''Geographia (Ptolemy), Geographia'' and the nomenclature of later kings suggest that a certain Theophilos (king), Theophilus in the south of the Indo-Greek sphere of influence may also have had a royal seat there at one time. The kingdom was founded when the Graeco-Bactrian king Demetrius I of Bactria invaded India from Bactria in about 200 BC. The Greeks to the east of the Seleucid Empire were eventually divided to the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom, Graeco-Bactrian Kingdom and the Indo-Greek Kingdoms in the North Western Indian Subcontinent. During the two cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urdu
Urdu (; , , ) is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in South Asia. It is the Languages of Pakistan, national language and ''lingua franca'' of Pakistan. In India, it is an Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of India, Eighth Schedule language, the status and cultural heritage of which are recognised by the Constitution of India. Quote: "The Eighth Schedule recognizes India's national languages as including the major regional languages as well as others, such as Sanskrit and Urdu, which contribute to India's cultural heritage. ... The original list of fourteen languages in the Eighth Schedule at the time of the adoption of the Constitution in 1949 has now grown to twenty-two." Quote: "As Mahapatra says: "It is generally believed that the significance for the Eighth Schedule lies in providing a list of languages from which Hindi is directed to draw the appropriate forms, style and expressions for its enrichment" ... Being recognized in the Constitution, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gandhara
Gandhara () was an ancient Indo-Aryan people, Indo-Aryan civilization in present-day northwest Pakistan and northeast Afghanistan. The core of the region of Gandhara was the Peshawar valley, Peshawar (Pushkalawati) and Swat valleys extending as far east as the Pothohar Plateau in Punjab, though the cultural influence of Greater Gandhara extended westwards into the Kabul, Kabul valley in Afghanistan, and northwards up to the Karakoram range. The region was a central location for the Silk Road transmission of Buddhism, spread of Buddhism to Central Asia and East Asia with many Chinese Buddhism, Buddhist pilgrims visiting the region. Between the third century BCE and third century CE, Gandhari language, Gāndhārī, a Middle Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language written in the Kharosthi script and linked with the modern Dardic languages, Dardic language family, acted as the lingua franca of the region and through Buddhism, the language spread as far as China based on Gandhār ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |