Shack–Hartmann Wavefront Sensor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
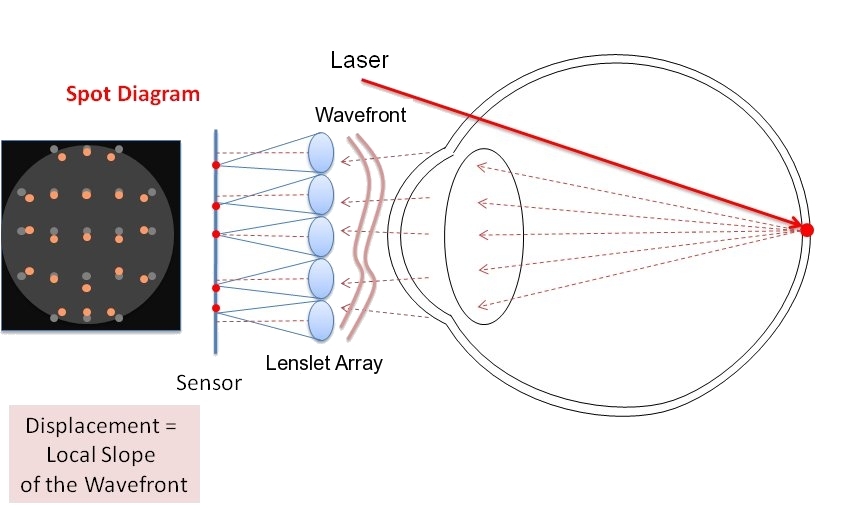

 A Shack–Hartmann (or Hartmann–Shack) wavefront sensor (SHWFS) is an optical instrument used for characterizing an imaging system. It is a
A Shack–Hartmann (or Hartmann–Shack) wavefront sensor (SHWFS) is an optical instrument used for characterizing an imaging system. It is a

wavefront sensor
In physics, the wavefront of a time-varying ''wave field'' is the set ( locus) of all points having the same ''phase''. The term is generally meaningful only for fields that, at each point, vary sinusoidally in time with a single temporal frequ ...
commonly used in adaptive optics
Adaptive optics (AO) is a technique of precisely deforming a mirror in order to compensate for light distortion. It is used in Astronomy, astronomical telescopes and laser communication systems to remove the effects of Astronomical seeing, atmo ...
systems. It consists of an array of lenses (called lenslets) of the same focal length. Each is focused onto a photon sensor (typically a CCD
CCD may refer to:
Science and technology
* Charge-coupled device, an electronic light sensor used in various devices including digital cameras
* .ccd, the filename extension for CloneCD's CD image file
* Carbonate compensation depth, a property ...
array or CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss
", , ) is a type of MOSFET, metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) semiconductor device fabrication, fabrication process that uses complementary an ...
array or quad-cell). If the sensor is placed at the geometric focal plane of the lenslet, and is uniformly illuminated, then, the integrated gradient of the wavefront
In physics, the wavefront of a time-varying ''wave field (physics), field'' is the set (locus (mathematics), locus) of all point (geometry), points having the same ''phase (waves), phase''. The term is generally meaningful only for fields that, a ...
across the lenslet is proportional to the displacement of the centroid. Consequently, any phase aberration can be approximated by a set of discrete tilts. By sampling the wavefront with an array of lenslets, all of these local tilts can be measured and the whole wavefront reconstructed. Since only tilts are measured the Shack–Hartmann cannot detect discontinuous steps in the wavefront.
The design of this sensor improves upon an array of holes in a mask that had been developed in 1904 by Johannes Franz Hartmann
Johannes Franz Hartmann (11 January 1865 – 13 September 1936) was a German physicist and astronomer. In 1904, while studying the spectroscopy of Delta Orionis he noticed that most of the spectrum had a shift, except the calcium lines, which ...
as a means of tracing individual rays of light through the optical system of a large telescope, thereby testing the quality of the image.
In the late 1960s, Roland Shack and Ben Platt modified the Hartmann screen by replacing the apertures in an opaque screen by an array of lenslets.
The terminology as proposed by Shack and Platt was ''Hartmann screen''. The fundamental principle seems to be documented even before Huygens by the Jesuit philosopher, Christopher Scheiner
Christoph Scheiner (25 July 1573 (or 1575) – 18 June 1650) was a Jesuit priest, physicist and astronomer in Ingolstadt.
Biography Augsburg/Dillingen: 1591–1605
Scheiner was born in Markt Wald near Mindelheim in Swabia, earlier margravate Burg ...
, in Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
.
Shack–Hartmann sensors are used in astronomy to measure telescopes and in medicine to characterize eyes for corneal treatment of complex refractive errors.
Recently, Pamplona et al.
developed and patented an inverse of the Shack–Hartmann system to measure one's eye lens aberrations. While Shack–Hartmann sensors measure the localized slope of the wavefront error using spot displacement in the sensor plane, Pamplona et al. replace the sensor plane with a high resolution visual display (e.g. a mobile phone screen) that displays spots that the user views through a lenslet array. The user then manually shifts the displayed spots (i.e. the generated wavefront) until the spots align. The magnitude of this shift provides data to estimate the first-order parameters such as radius of curvature and hence error due to defocus and spherical aberration.
References
See also
*Optical Telescope Element
Optical Telescope Element (OTE) is a sub-section of the James Webb Space Telescope, a large infrared space telescope launched on , consisting of its Primary mirror, main mirror, secondary mirrors, the framework and controls to support the mirro ...
(used this sensor in development of the James Webb Space Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a space telescope designed to conduct infrared astronomy. As the largest telescope in space, it is equipped with high-resolution and high-sensitivity instruments, allowing it to view objects too old, Lis ...
)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Shack-Hartmann wavefront sensor
Sensors
Optical metrology