seventh (chord) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
Dictionary of Music
'. Trans. J.A. Shedlock. Augener, 1900. 730. When the seventh is the bass note, or lowest note, of the expressed chord, the chord is in third inversion . Conventionally, the seventh is fourth in importance to the root, fifth, and third, with third inversion being the third strongest inversion and the seventh variably minor or major.
\new PianoStaff <<
\new Staff <<
\relative c'
>>
\new Staff <<
\new Voice \relative c'
>>
>>

 In
In music
Music is the arrangement of sound to create some combination of Musical form, form, harmony, melody, rhythm, or otherwise Musical expression, expressive content. Music is generally agreed to be a cultural universal that is present in all hum ...
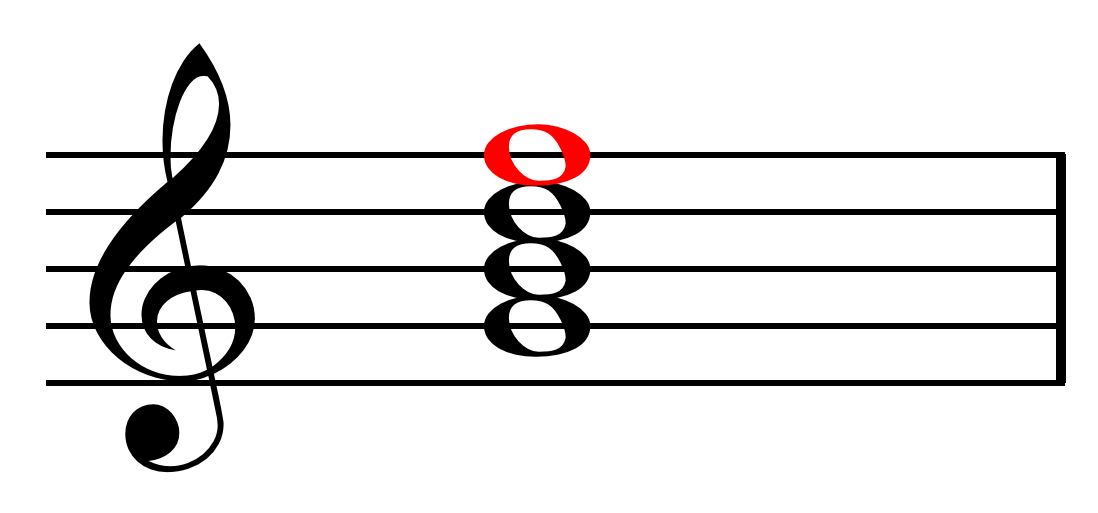
, the seventh factor of a chord is the note or pitch seven scale degrees
In music theory, the scale degree is the position of a particular note on a scale relative to the tonic—the first and main note of the scale from which each octave is assumed to begin. Degrees are useful for indicating the size of intervals ...
above the root
In vascular plants, the roots are the plant organ, organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often bel ...
or tonal center.Riemann, Hugo. Dictionary of Music
'. Trans. J.A. Shedlock. Augener, 1900. 730. When the seventh is the bass note, or lowest note, of the expressed chord, the chord is in third inversion . Conventionally, the seventh is fourth in importance to the root, fifth, and third, with third inversion being the third strongest inversion and the seventh variably minor or major.
In jazz
In jazz chords and theory, and classical music theory, the seventh is what defines a chord as a "seventh chord
A seventh chord is a chord (music), chord consisting of a triad (music), triad plus a note forming an interval (music), interval of a Interval (music), seventh above the chord's root (chord), root. When not otherwise specified, a "seventh chord" ...
". Moreover, most triads that appear in lead sheets or fake books can have sevenths added to them, using the performer's discretion and "ear". For example, if a tune is in the key of C, if there is a G chord, the chord-playing performer will usually "voice" this chord as G7. While in a strict classical music
Classical music generally refers to the art music of the Western world, considered to be #Relationship to other music traditions, distinct from Western folk music or popular music traditions. It is sometimes distinguished as Western classical mu ...
context, the notes of a G7 chord would be "G–B–D–F", in jazz, the fifth of the chord is often omitted. The root is also often omitted if playing in a jazz group, as it will usually be played by the bassist. Omitting the root and fifth gives the improvising chord-playing musician the option to play other notes.
In voicing jazz chords, performers focus first on the seventh and the major or minor third of the chord, with the latter indicating the chord quality, along with added chord extensions (e.g., elevenths, even if not indicated in the lead sheet or fake book) to add tone "colour" to the chord. As such, a jazz guitar
Jazz guitar may refer to either a type of electric guitar or a guitar playing style in jazz, using Guitar amplifier, electric amplification to increase the volume of acoustic guitars.
In the early 1930s, jazz musicians sought to amplify their ...
ist or jazz piano
Jazz piano is a collective term for the techniques pianists use when playing jazz. The piano has been an integral part of the jazz idiom since its inception, in both solo and ensemble settings. Its role is multifaceted due largely to the instru ...
player might "voice" a printed G chord with the notes "B–E–F–A", which would be the third, sixth (a.k.a. 13th), seventh, and ninth of the chord. Jazz chord-playing musicians may also add altered chord tones (e.g., #11) and added tones. An example of an altered dominant chord in the key of C, built on a G would be to voice the chord as "B–C–E–F–A"; this would be G7 (b9,#11).
Types
The seventh note of a chord is most commonly a minor seventh (in C, B) or major seventh interval (in C, B). Less often, the seventh note of a chord is diminished or augmented (B=A ( enharmonic notes) or B=C (also enharmonic notes).Resolution
In thecommon practice period
In Western classical music, the common practice period (CPP) was the period of about 250 years during which the tonal system was regarded as the only basis for composition. It began when composers' use of the tonal system had clearly supersede ...
the "strict resolution" the chord's seventh degree is stepwise downward. For example, the seventh of the dominant seventh
Domination or dominant may refer to:
Society
* World domination, structure where one dominant power governs the planet
* Colonialism in which one group (usually a nation) invades another region for material gain or to eliminate competition
* Ch ...
chord, resolving to tonic, moves downward to the third of the following chord. In the key of C major, the dominant seventh chord would be G7; the seventh note of this G7 chord is F, which should resolve downwards to an E in the next bar (typically supported by a C-major chord).
:References
{{Chord factors Chord factors