STEREO Experiment on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The STEREO experiment (Search for Sterile Reactor Neutrino Oscillations) investigated the possible
 The STEREO detector is placed at a distance of 10 m away from the research reactor at the ILL. The research reactor has a thermal power of 58 MW. STEREO is supposed to measure the neutrino flux and spectrum near the reactor. To be able to detect the neutrinos radiated from the reactor, the detector is filled up with 1800 litres of organic liquid
The STEREO detector is placed at a distance of 10 m away from the research reactor at the ILL. The research reactor has a thermal power of 58 MW. STEREO is supposed to measure the neutrino flux and spectrum near the reactor. To be able to detect the neutrinos radiated from the reactor, the detector is filled up with 1800 litres of organic liquid
B_4C .
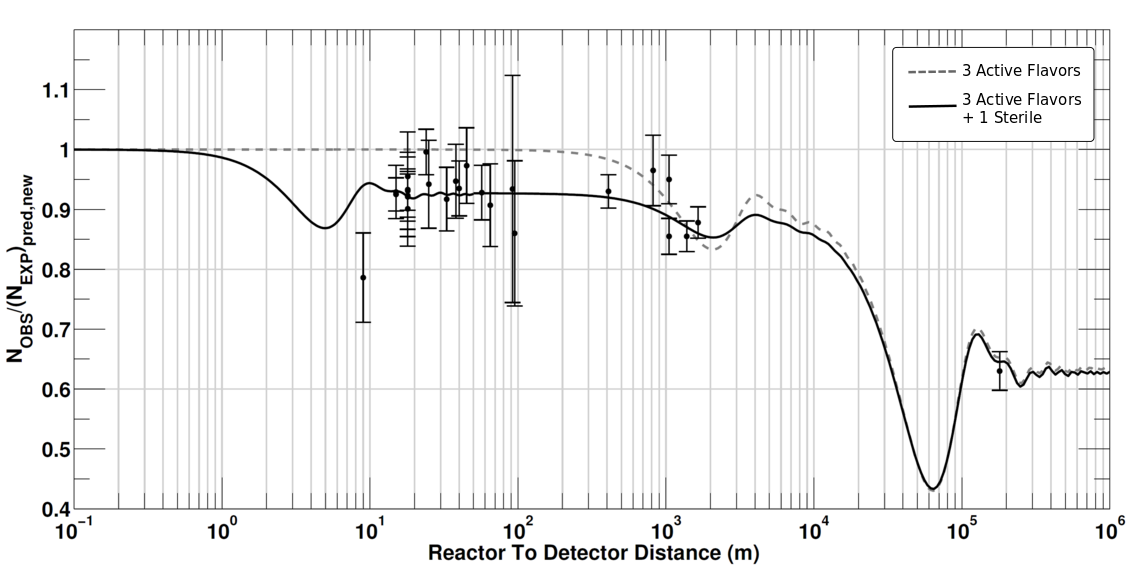 Although neutrino oscillation is a phenomenon that is quite well understood today, there are still some experimental observations that question the completeness of our understanding. The most prominent of these observations is the so-called ''reactor antineutrino anomaly'' (RAA) (see Figure 3). A number of short baseline reactor-neutrino experiments have measured a significantly lower anti-electron neutrino () flux compared to the theoretical predictions (a 2,7 deviation).
Further experimental anomalies are the unexpected appearance of in a short-baseline beam (LSND anomaly) as well as the disappearance of at short distances during the calibration phase of the
Although neutrino oscillation is a phenomenon that is quite well understood today, there are still some experimental observations that question the completeness of our understanding. The most prominent of these observations is the so-called ''reactor antineutrino anomaly'' (RAA) (see Figure 3). A number of short baseline reactor-neutrino experiments have measured a significantly lower anti-electron neutrino () flux compared to the theoretical predictions (a 2,7 deviation).
Further experimental anomalies are the unexpected appearance of in a short-baseline beam (LSND anomaly) as well as the disappearance of at short distances during the calibration phase of the 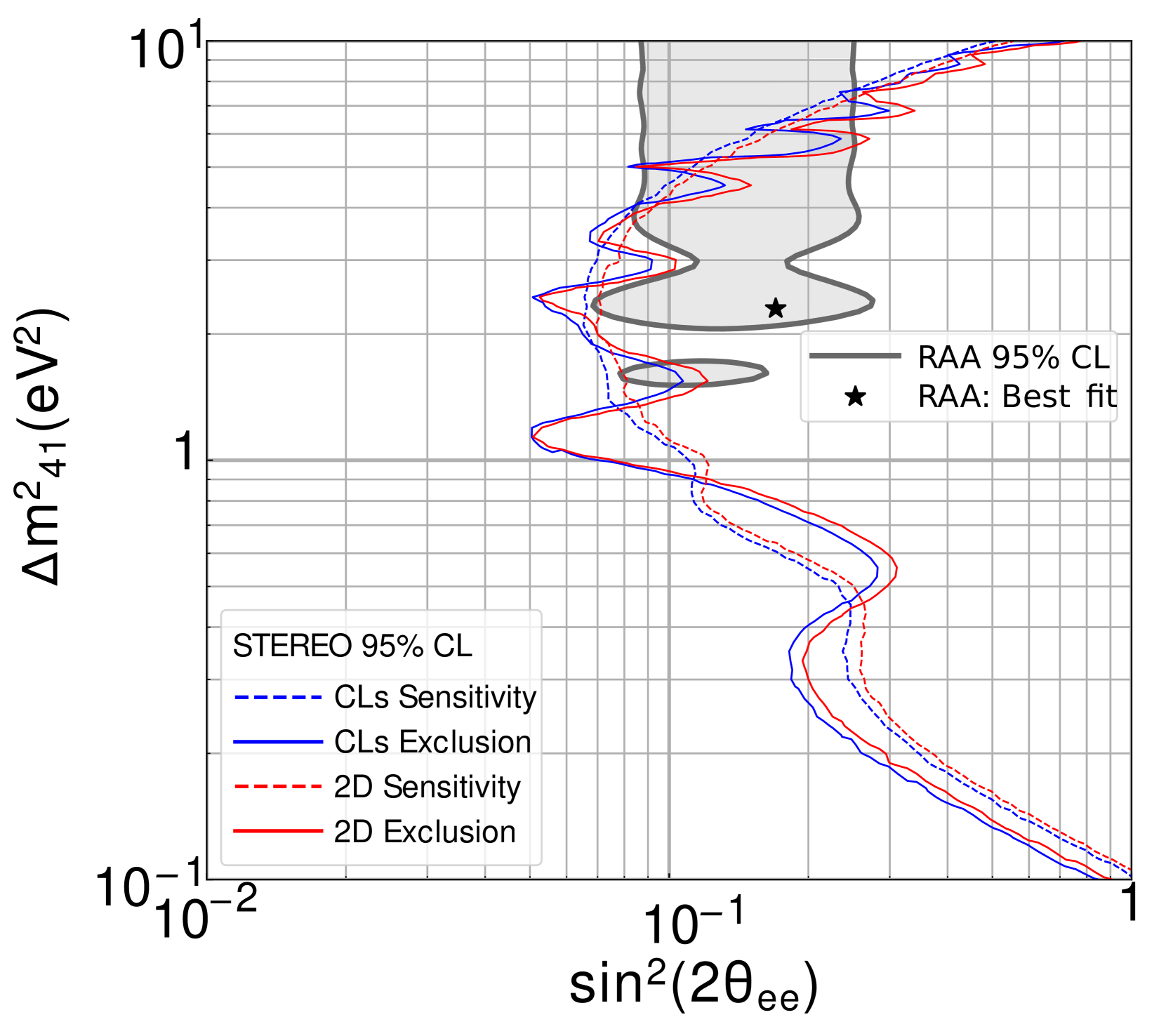 These anomalies could signify that our understanding of neutrino oscillations is not yet complete and that neutrinos oscillate into another 4th neutrino species. However measurements of the
These anomalies could signify that our understanding of neutrino oscillations is not yet complete and that neutrinos oscillate into another 4th neutrino species. However measurements of the
Website of the STEREO experiment
STEREO experiment
record on
oscillation
Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value (often a point of equilibrium) or between two or more different states. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum ...
of neutrino
A neutrino ( ; denoted by the Greek letter ) is an elementary particle that interacts via the weak interaction and gravity. The neutrino is so named because it is electrically neutral and because its rest mass is so small ('' -ino'') that i ...
s from a nuclear reactor into light so-called sterile neutrinos
Sterile or sterility may refer to:
*Asepsis, a state of being free from biological contaminants
* Sterile (archaeology), a sediment deposit which contains no evidence of human activity
*Sterilization (microbiology), any process that eliminates or ...
. It was located at the Institut Laue–Langevin
The Institut Laue–Langevin (ILL) is an internationally financed scientific facility, situated on the Polygone Scientifique in Grenoble, France. It is one of the world centres for research using neutrons. Founded in 1967 and honouring the phy ...
(ILL) in Grenoble, France. The experiment took data from November 2016 to November 2020. The final results of the experiment rejected the hypothesis of a light sterile neutrino.
Detector
Measuring principle
 The STEREO detector is placed at a distance of 10 m away from the research reactor at the ILL. The research reactor has a thermal power of 58 MW. STEREO is supposed to measure the neutrino flux and spectrum near the reactor. To be able to detect the neutrinos radiated from the reactor, the detector is filled up with 1800 litres of organic liquid
The STEREO detector is placed at a distance of 10 m away from the research reactor at the ILL. The research reactor has a thermal power of 58 MW. STEREO is supposed to measure the neutrino flux and spectrum near the reactor. To be able to detect the neutrinos radiated from the reactor, the detector is filled up with 1800 litres of organic liquid scintillator
A scintillator ( ) is a material that exhibits scintillation, the property of luminescence, when excited by ionizing radiation. Luminescent materials, when struck by an incoming particle, absorb its energy and scintillate (i.e. re-emit the ab ...
which is doped with gadolinium
Gadolinium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Gd and atomic number 64. It is a silvery-white metal when oxidation is removed. Gadolinium is a malleable and ductile rare-earth element. It reacts with atmospheric oxygen or moi ...
. Inside the scintillator neutrinos are captured via the process of inverse beta decay
In nuclear and particle physics, inverse beta decay, commonly abbreviated to IBD, is a nuclear reaction involving an electron antineutrino scattering off a proton, creating a positron and a neutron. This process is commonly used in the detect ...
:
In this process a positron
The positron or antielectron is the particle with an electric charge of +1''elementary charge, e'', a Spin (physics), spin of 1/2 (the same as the electron), and the same Electron rest mass, mass as an electron. It is the antiparticle (antimatt ...
is produced. When the positron moves through the scintillator a light signal is produced, which is detected by the 48 photomultiplier tubes
Photomultiplier tubes (photomultipliers or PMTs for short) are extremely sensitive detectors of light in the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum. They are members of the class of vacuum tubes, more spe ...
(PMTs) placed at the top of the detector cells. The capturing of the neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , that has no electric charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. The Discovery of the neutron, neutron was discovered by James Chadwick in 1932, leading to the discovery of nucle ...
which is also produced during the inverse beta decay produces a second coincidence signal.
The expected distance between the oscillation maximum and minimum of light sterile neutrinos is about 2 m. To see the oscillation the detector is divided into 6 separate detector cells, which each measure the energy spectrum of the detected neutrinos. By comparing the measured spectra a possible oscillation could be discovered (see Figure 2).
The STEREO experiment detects neutrinos per day.
Detector shielding
Neutrinos only interact weakly. Therefore, neutrino detectors such as STEREO need to be very sensitive and need a good shielding from additional background signals to be able to detect neutrinos precisely. To achieve this high sensitivity the 6 inner detector cells are surrounded by a liquid scintillator (without gadolinium) which acts as a "Gamma-Catcher" detecting in- and outgoinggamma radiation
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol ), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from high energy interactions like the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei or astronomical events like solar flares. It consists o ...
. This significantly increases the detection efficiency as well as the energy resolution of the detector. A cherenkov detector
A Cherenkov detector (pronunciation: /tʃɛrɛnˈkɔv/; Russian: Черенко́в) is a type particle detector designed to detect and identify particles by the Cherenkov Radiation produced when a charged particle travels through the medium of th ...
filled with water is placed on top of the detector to detect cosmic muon
A muon ( ; from the Greek letter mu (μ) used to represent it) is an elementary particle similar to the electron, with an electric charge of −1 '' e'' and a spin of ''ħ'', but with a much greater mass. It is classified as a ...
s which are produced in the atmosphere and would otherwise act as a large background source. To shield the detector from radioactive sources coming from surrounding experiments it is surrounded and shielded by many layers (65 t) of mostly lead and polyethylene but also iron, steel and Motivation
 Although neutrino oscillation is a phenomenon that is quite well understood today, there are still some experimental observations that question the completeness of our understanding. The most prominent of these observations is the so-called ''reactor antineutrino anomaly'' (RAA) (see Figure 3). A number of short baseline reactor-neutrino experiments have measured a significantly lower anti-electron neutrino () flux compared to the theoretical predictions (a 2,7 deviation).
Further experimental anomalies are the unexpected appearance of in a short-baseline beam (LSND anomaly) as well as the disappearance of at short distances during the calibration phase of the
Although neutrino oscillation is a phenomenon that is quite well understood today, there are still some experimental observations that question the completeness of our understanding. The most prominent of these observations is the so-called ''reactor antineutrino anomaly'' (RAA) (see Figure 3). A number of short baseline reactor-neutrino experiments have measured a significantly lower anti-electron neutrino () flux compared to the theoretical predictions (a 2,7 deviation).
Further experimental anomalies are the unexpected appearance of in a short-baseline beam (LSND anomaly) as well as the disappearance of at short distances during the calibration phase of the GALLEX
GALLEX or Gallium Experiment was a radiochemical neutrino detection experiment that ran between 1991 and 1997 at the Laboratori Nazionali del Gran Sasso (LNGS). This project was performed by an international collaboration of French, German, Ita ...
and SAGE experiments known as the gallium neutrino anomaly.
 These anomalies could signify that our understanding of neutrino oscillations is not yet complete and that neutrinos oscillate into another 4th neutrino species. However measurements of the
These anomalies could signify that our understanding of neutrino oscillations is not yet complete and that neutrinos oscillate into another 4th neutrino species. However measurements of the decay width
Decay may refer to:
Science and technology
* Bit decay, in computing
* Decay time (fall time), in electronics
* Distance decay, in geography
* Software decay, in computing
Biology
* Decomposition of organic matter
* Mitochondrial decay, in ...
of the Z boson at the Large Electron–Positron Collider
The Large Electron–Positron Collider (LEP) was one of the largest particle accelerators ever constructed. It was built at CERN, a multi-national centre for research in nuclear and particle physics near Geneva, Switzerland.
LEP collided electr ...
(LEP) exclude the existence of a light 4th "active" (i.e. interacting via the weak force) neutrino.
Hence the oscillation into additional light "sterile" neutrinos is considered as a possible explanation of the observed anomalies. In addition sterile neutrinos appear in many prominent extensions of the Standard Model of particle physics
The Standard Model of particle physics is the theory describing three of the four known fundamental forces (electromagnetic, weak and strong interactions – excluding gravity) in the universe and classifying all known elementary particles. It ...
, e.g. in the seesaw
A seesaw (also sometimes known as a teeter-totter in North America) is a long, narrow board supported by a single pivot point, most commonly located at the midpoint between both ends; as one end goes up, the other goes down. These are most comm ...
type 1 mechanism.
Results
Initial results were released in 2018 exploiting a dataset of 66 days of reactor turned on. Most of the parameter space that could account for the RAA was excluded at a 90% confidence level. The final results were published in 2023. 107,588 antineurinos were detected from October 2017 until November 2020. The sterile neutrino explanation for the RAA was rejected up to a few (eV)² for the square mass splitting between standard and sterile neutrino states (see figure 4).References
External links
Website of the STEREO experiment
STEREO experiment
record on
INSPIRE-HEP
INSPIRE-HEP is an open access digital library for the field of high energy physics (HEP). It is the successor of the Stanford Physics Information Retrieval System (SPIRES) database, the main literature database for high energy physics since the 1 ...
{{Neutrino detectors
Neutrino observatories
2016 establishments in France
Particle experiments