SOBER1 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
SOBER1 is an
enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecule ...
that catalyzes
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycl ...
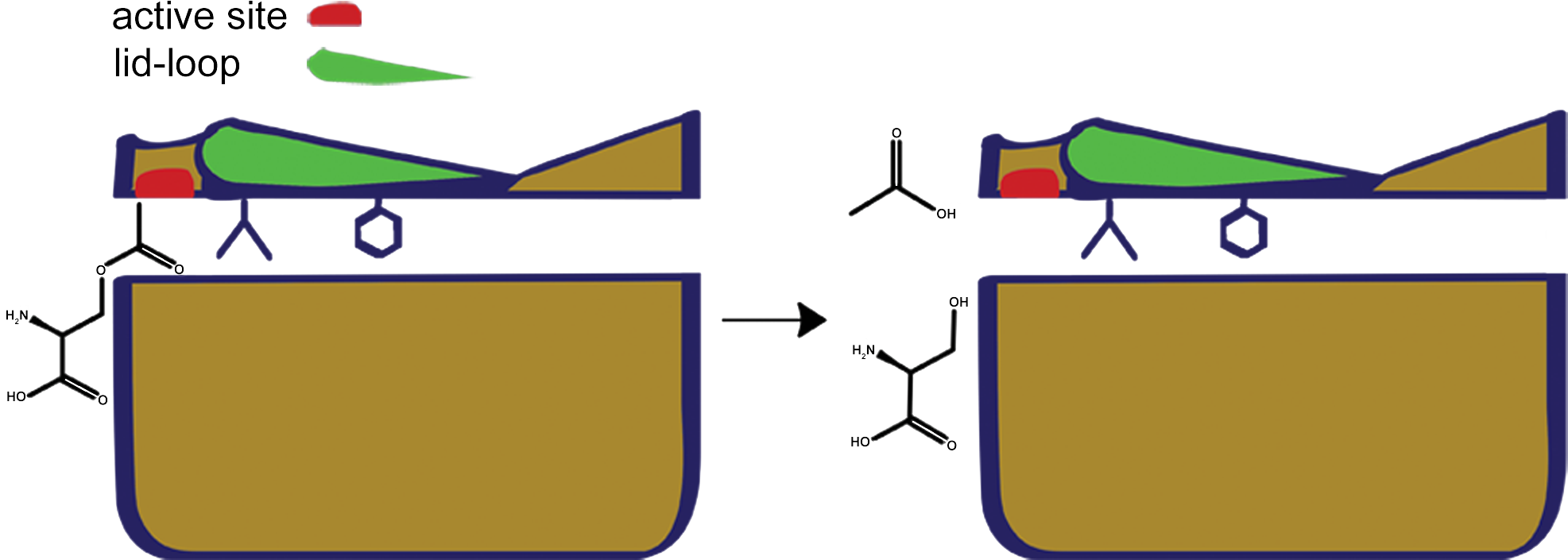
the biochemical reaction of deacetylation
:
In organic chemistry, acetylation is an organic esterification reaction with acetic acid. It introduces an acetyl group into a chemical compound. Such compounds are termed ''acetate esters'' or simply ''acetates''. Deacetylation is the opposit ...
. The SOBER (Suppressor of AvrBsT-elicited resistance) 1 protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respon ...
is conserved in plants and it suppresses the plant's ability to carry out the hypersensitive response
Hypersensitive response (HR) is a mechanism used by plants to prevent the spread of infection by microbial pathogens. HR is characterized by the rapid death of cells in the local region surrounding an infection and it serves to restrict the grow ...
against infection by certain pathogenic effector proteins from the YopJ family. SOBER1 belongs to the protein superfamily
A protein superfamily is the largest grouping (clade) of proteins for which common ancestry can be inferred (see homology). Usually this common ancestry is inferred from structural alignment and mechanistic similarity, even if no sequence similarit ...
of α/β hydrolases and possesses a canonical serine
Serine (symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α- amino group (which is in the protonated − form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated − for ...
/histidine
Histidine (symbol His or H) is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated –NH3+ form under biological conditions), a carboxylic acid group (which is in the ...
/aspartate
Aspartic acid (symbol Asp or D; the ionic form is known as aspartate), is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Like all other amino acids, it contains an amino group and a carboxylic acid. Its α-amino group is in the pro ...
catalytic triad
A catalytic triad is a set of three coordinated amino acids that can be found in the active site of some enzymes. Catalytic triads are most commonly found in hydrolase and transferase enzymes (e.g. proteases, amidases, esterases, acylases, l ...
to carry out the deacetylation reaction. There have been contradicting reports about SOBER1's potential phospholipase
A phospholipase is an enzyme that hydrolyzes phospholipids into fatty acids and other lipophilic substances. Acids trigger the release of bound calcium from cellular stores and the consequent increase in free cytosolic Ca2+, an essential step i ...
activity, with one study claiming phospholipase A2 activity of the protein and another study being unable to reproduce this result.
Relationship to acyl-protein thioesterases
Members of the SOBER1 family are considered closely related toacyl-protein thioesterase
Acyl-protein thioesterases are enzymes that cleave off lipid modifications on proteins, located on the sulfur atom of cysteine residues linked via a thioester bond. Acyl-protein thioesterases are part of the α/β hydrolase superfamily of protein ...
s, judged by their protein structure
Protein structure is the molecular geometry, three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in an amino acid-chain molecule. Proteins are polymers specifically polypeptides formed from sequences of amino acids, the monomers of the polymer. A single ami ...
. However, a change in their amino acid sequence
Protein primary structure is the linear sequence of amino acids in a peptide or protein. By convention, the primary structure of a protein is reported starting from the amino-terminal (N) end to the carboxyl-terminal (C) end. Protein biosynthesi ...
renders SOBER1's biochemical properties into a deacetylase; in particular the hydrophobic
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the physical property of a molecule that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water (known as a hydrophobe). In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water.
Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, ...
tunnel, which is found in acyl-protein thioesterases, is impaired by additional amino acids in the lid structure of SOBER1, creating a new surface for binding of the acetyl group
In organic chemistry, acetyl is a functional group with the chemical formula and the structure . It is sometimes represented by the symbol Ac (not to be confused with the element actinium). In IUPAC nomenclature, acetyl is called ethanoyl ...
.

Targets
So far, the following proteins have been identified as SOBER1targets
''Targets'' is a 1968 American crime thriller film directed by Peter Bogdanovich, produced by Roger Corman, and written by Polly Platt and Bogdanovich, with cinematography by László Kovács.Stephen Jacobs, ''Boris Karloff: More Than a Monste ...
: AvrBsT; ACIP1.
See also
*Acylation
In chemistry, acylation (or alkanoylation) is the chemical reaction in which an acyl group () is added to a compound. The compound providing the acyl group is called the acylating agent.
Because they form a strong electrophile when treated wit ...
*Catalytic triad
A catalytic triad is a set of three coordinated amino acids that can be found in the active site of some enzymes. Catalytic triads are most commonly found in hydrolase and transferase enzymes (e.g. proteases, amidases, esterases, acylases, l ...
*Compendium of protein lysine acetylation The compendium of protein lysine acetylation (CPLA) database contains the sites of experimentally identified lysine acetylation
:
In organic chemistry, acetylation is an organic esterification reaction with acetic acid. It introduces an acetyl ...
*Enzyme assay
Enzyme assays are laboratory methods for measuring enzymatic activity. They are vital for the study of enzyme kinetics and enzyme inhibition.
Enzyme units
The quantity or concentration of an enzyme can be expressed in molar amounts, as with ...
*Organic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the intentional construction of organic compounds. Organic molecules are often more complex than inorganic compounds, and their synthesis has developed into one o ...
*Protein dynamics Proteins are generally thought to adopt unique structures determined by their amino acid sequences. However, proteins are not strictly static objects, but rather populate ensembles of (sometimes similar) conformations. Transitions between these stat ...
*Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called protease ...
*The Proteolysis Map
The Proteolysis MAP (PMAP) is an integrated web resource focused on proteases.
Rationale
PMAP is to aid the protease researchers in reasoning about proteolytic networks and metabolic pathways.
History and funding
PMAP was originally create ...
References
{{reflist Catalysis Enzymes Organic reactions Post-translational modification