Room Temperature Ionic Liquid on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 An ionic liquid (IL) is a
An ionic liquid (IL) is a
 Some ionic liquids can be
Some ionic liquids can be
 Classically, ILs consist of salts of unsymmetrical, flexible organic cations with symmetrical
Classically, ILs consist of salts of unsymmetrical, flexible organic cations with symmetrical
Ionic Liquids Biological Effects Database
, free database on toxicology and ecotoxicology of ionic liquids
Corresponding states for ionic fluids
{{Authority control Ions
 An ionic liquid (IL) is a
An ionic liquid (IL) is a salt
In common usage, salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl). When used in food, especially in granulated form, it is more formally called table salt. In the form of a natural crystalline mineral, salt is also known as r ...
in the liquid
Liquid is a state of matter with a definite volume but no fixed shape. Liquids adapt to the shape of their container and are nearly incompressible, maintaining their volume even under pressure. The density of a liquid is usually close to th ...
state at ambient conditions. In some contexts, the term has been restricted to salts whose melting point
The melting point (or, rarely, liquefaction point) of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state of matter, state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase (matter), phase exist in Thermodynamic equilib ...
is below a specific temperature, such as . While ordinary liquids such as water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...
and gasoline
Gasoline ( North American English) or petrol ( Commonwealth English) is a petrochemical product characterized as a transparent, yellowish, and flammable liquid normally used as a fuel for spark-ignited internal combustion engines. When for ...
are predominantly made of electrically neutral
Electric charge (symbol ''q'', sometimes ''Q'') is a physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. Electric charge can be ''positive'' or ''negative''. Like charges repel each other an ...
molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemi ...
s, ionic liquids are largely made of ion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
s. These substances are variously called liquid electrolytes, ionic melts, ionic fluids, fused salts, liquid salts, or ionic glasses.
Ionic liquids have many potential applications. They are powerful solvent
A solvent (from the Latin language, Latin ''wikt:solvo#Latin, solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a Solution (chemistry), solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas ...
s and can be used as electrolyte
An electrolyte is a substance that conducts electricity through the movement of ions, but not through the movement of electrons. This includes most soluble Salt (chemistry), salts, acids, and Base (chemistry), bases, dissolved in a polar solven ...
s. Salts that are liquid at near-ambient temperature are important for electric battery
An electric battery is a source of electric power consisting of one or more electrochemical cells with external connections for powering electrical devices. When a battery is supplying power, its positive Terminal (electronics), terminal is the ...
applications, and have been considered as sealant
Sealant is a substance used to block the passage of fluids through openings in materials, a type of Seal (mechanical), mechanical seal. In building construction ''sealant'' is sometimes synonymous with ''caulk'' (especially if acrylic latex or ...
s due to their very low vapor pressure
Vapor pressure or equilibrium vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases (solid or liquid) at a given temperature in a closed system. The equilibrium vapor pressure is an indicat ...
.
Any salt that melts without decomposing or vaporizing usually yields an ionic liquid. Sodium chloride
Sodium chloride , commonly known as Salt#Edible salt, edible salt, is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. It is transparent or translucent, brittle, hygroscopic, and occurs a ...
(NaCl), for example, melts at into a liquid that consists largely of sodium
Sodium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 element, group 1 of the peri ...
cations () and chloride anions (). Conversely, when an ionic liquid is cooled, it often forms an ionic solid—which may be either crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macros ...
line or glass
Glass is an amorphous (non-crystalline solid, non-crystalline) solid. Because it is often transparency and translucency, transparent and chemically inert, glass has found widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in window pane ...
y.
The ionic bond
Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bond
A chemical bond is the association of atoms or ions to form molecules, crystals, and other structures. The bond may result from the electrostatic force between oppositely charged ions as in ionic ...
is usually stronger than the Van der Waals force
In molecular physics and chemistry, the van der Waals force (sometimes van der Waals' force) is a distance-dependent interaction between atoms or molecules. Unlike ionic or covalent bonds, these attractions do not result from a chemical elec ...
s between the molecules of ordinary liquids. Because of these strong interactions, salts tend to have high lattice energies, manifested in high melting points. Some salts, especially those with organic cations, have low lattice energies and thus are liquid at or below room temperature
Room temperature, colloquially, denotes the range of air temperatures most people find comfortable indoors while dressed in typical clothing. Comfortable temperatures can be extended beyond this range depending on humidity, air circulation, and ...
. Examples include compounds based on the 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium (EMIM) cation and include: EMIM:Cl, EMIMAc (acetate anion), EMIM dicyanamide
Dicyanamide, also known as dicyanamine, is an anion having the formula . It contains two cyanide groups bound to a central nitrogen anion. The chemical is formed by decomposition of 2-cyanoguanidine. It is used extensively as a counterion of o ...
, ()()·, that melts at ; and 1-butyl-3,5-dimethylpyridinium bromide which becomes a glass below .
Low-temperature ionic liquids can be compared to ionic solution
An electrolyte is a substance that conducts electricity through the movement of ions, but not through the movement of electrons. This includes most soluble salts, acids, and bases, dissolved in a polar solvent like water. Upon dissolving, the ...
s, liquids that contain both ions and neutral molecules, and in particular to the so-called deep eutectic solvent
Deep eutectic solvents or DESs are solutions of Lewis or Brønsted acids and bases which form a eutectic mixture. Deep eutectic solvents are highly tunable through varying the structure or relative ratio of parent components and thus have a wide ...
s, mixtures of ionic and non-ionic solid substances which have much lower melting points than the pure compounds. Certain mixtures of nitrate salts can have melting points below 100 °C.
History
The term "ionic liquid" in the general sense was used as early as 1943. The discovery date of the "first" ionic liquid is disputed, along with the identity of its discoverer. Ethanolammonium nitrate (m.p. 52–55 °C) was reported in 1888 by S. Gabriel and J. Weiner. In 1911 Ray and Rakshit, during preparation of the nitrite salts of ethylamine, dimethylamine, and trimethylamine observed that the reaction between ethylamine hydrochloride and silver nitrate yielded an unstable ethylammonium nitrite ()· , a heavy yellow liquid which on immersion in a mixture of salt and ice could not be solidified and was probably the first report of room-temperature ionic liquid. Later in 1914, Paul Walden reported one of the first stable room-temperature ionic liquidsethylammonium nitrate
Ethylammonium nitrate or ethylamine nitrate (EAN) is a salt with formula . It is an odorless and colorless to slightly yellowish liquid with a melting point of 12 °C. This compound was described by Paul Walden in 1914,
and is believed to ...
()· (m.p. 12 °C). In the 1970s and 1980s, ionic liquids based on alkyl-substituted imidazolium and pyridinium
Pyridinium refers to the cation . It is the conjugate acid of pyridine. Many related cations are known involving substituted pyridines, e.g. picolines, lutidines, collidines. They are prepared by treating pyridine with acids.
As pyridine is often ...
cations, with halide
In chemistry, a halide (rarely halogenide) is a binary chemical compound, of which one part is a halogen atom and the other part is an element or radical that is less electronegative (or more electropositive) than the halogen, to make a fl ...
or tetrahalogenoaluminate anions, were developed as potential electrolytes in batteries.
For the imidazolium halogenoaluminate salts, their physical properties—such as viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's rate-dependent drag (physics), resistance to a change in shape or to movement of its neighboring portions relative to one another. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of ''thickness''; for e ...
, melting point
The melting point (or, rarely, liquefaction point) of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state of matter, state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase (matter), phase exist in Thermodynamic equilib ...
, and acidity
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis acid.
The first category of acids are the ...
—could be adjusted by changing the alkyl
In organic chemistry, an alkyl group is an alkane missing one hydrogen.
The term ''alkyl'' is intentionally unspecific to include many possible substitutions.
An acyclic alkyl has the general formula of . A cycloalkyl group is derived from a cy ...
substituent
In organic chemistry, a substituent is one or a group of atoms that replaces (one or more) atoms, thereby becoming a moiety in the resultant (new) molecule.
The suffix ''-yl'' is used when naming organic compounds that contain a single bond r ...
s and the imidazolium/pyridinium and halide/halogenoaluminate ratios. Two major drawbacks for some applications were moisture sensitivity and acidity or basicity. In 1992, Wilkes and Zawarotko obtained ionic liquids with 'neutral' weakly coordinating anion
Anions that interact weakly with cations are termed non-coordinating anions, although a more accurate term is weakly coordinating anion. Non-coordinating anions are useful in studying the reactivity of electrophilic cations. They are commonly found ...
s such as hexafluorophosphate
Hexafluorophosphate is an fluoroanion, anion with chemical formula of . It is an Octahedral molecular geometry, octahedral species that imparts no color to its salts. is isoelectronic with sulfur hexafluoride, , and the Hexafluorosilicic acid, h ...
() and tetrafluoroborate (), allowing a much wider range of applications.
Characteristics
ILs are typically colorless viscous liquids. They are often moderate to poor conductors of electricity, and rarely self-ionize. They do, however, have a very largeelectrochemical window The electrochemical window (EW) of a substance is the electrode electric potential range between which the substance is neither oxidized nor reduced. The EW is one of the most important characteristics to be identified for solvents and electrolyte ...
, enabling electrochemical refinement of otherwise intractable ores.
They exhibit low vapor pressure
Vapor pressure or equilibrium vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases (solid or liquid) at a given temperature in a closed system. The equilibrium vapor pressure is an indicat ...
, which can be as low as 10−10 Pa. Many have low combustibility and are thermally stable.
The solubility properties of ILs are diverse. Saturated aliphatic
In organic chemistry, hydrocarbons ( compounds composed solely of carbon and hydrogen) are divided into two classes: aromatic compounds and aliphatic compounds (; G. ''aleiphar'', fat, oil). Aliphatic compounds can be saturated (in which all ...
compounds are generally only sparingly soluble
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a substance, the solute, to form a solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution.
The extent of the solubi ...
in ionic liquids, whereas alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene, or olefin, is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond. The double bond may be internal or at the terminal position. Terminal alkenes are also known as Alpha-olefin, α-olefins.
The Internationa ...
s show somewhat greater solubility, and aldehyde
In organic chemistry, an aldehyde () (lat. ''al''cohol ''dehyd''rogenatum, dehydrogenated alcohol) is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure . The functional group itself (without the "R" side chain) can be referred ...
s often completely miscible. Solubility differences can be exploited in biphasic catalysis, such as hydrogenation
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to redox, reduce or Saturated ...
and hydrocarbonylation
In chemistry, carbonylation refers to reactions that introduce carbon monoxide (CO) into organic and inorganic substrates. Carbon monoxide is abundantly available and conveniently reactive, so it is widely used as a reactant in industrial chemis ...
processes, allowing for relatively easy separation of products and/or unreacted substrate(s). Gas solubility follows the same trend, with carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
gas showing good solubility in many ionic liquids. Carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a poisonous, flammable gas that is colorless, odorless, tasteless, and slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the si ...
is less soluble in ionic liquids than in many popular organic solvents, and hydrogen is only slightly soluble (similar to the solubility in water) and may vary relatively little between the more common ionic liquids.
Many classes of chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemistry, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. When chemical reactions occur, the atoms are rearranged and the reaction is accompanied by an Gibbs free energy, ...
s, The miscibility of ionic liquids with water or organic solvent
A solvent (from the Latin language, Latin ''wikt:solvo#Latin, solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a Solution (chemistry), solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas ...
s varies with side chain lengths on the cation and with choice of anion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conven ...
. They can be functionalized to act as acid
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. Hydron, hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis ...
s, bases, or ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule with a functional group that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's el ...
s, and are precursors salts in the preparation of stable carbene
In organic chemistry, a carbene is a molecule containing a neutral carbon atom with a Valence (chemistry), valence of two and two unshared valence electrons. The general formula is or where the R represents substituents or hydrogen atoms.
Th ...
s. Because of their distinctive properties, ionic liquids have been investigated for many applications.
 Some ionic liquids can be
Some ionic liquids can be distill
Distillation, also classical distillation, is the process of separation process, separating the component substances of a liquid mixture of two or more chemically discrete substances; the separation process is realized by way of the selective ...
ed under vacuum conditions at temperatures near 300 °C. The vapor is not made up of separated ions, but consists of ion pairs.
ILs have a wide liquid range. Some ILs do not freeze down to very low temperatures (even −150 °C), The glass transition temperature
The glass–liquid transition, or glass transition, is the gradual and reversible transition in amorphous materials (or in amorphous regions within semicrystalline materials) from a hard and relatively brittle "glassy" state into a viscous or rub ...
was detected below −100 °C in the case of N-methyl-N-alkylpyrrolidinium cations fluorosulfonyl-trifluoromethanesulfonylimide (FTFSI). Low-temperature ionic liquids (below 130 K) have been proposed as the fluid base for an extremely large diameter spinning liquid-mirror telescope to be based on the Moon.
Water is a common impurity in ionic liquids, as it can be absorbed from the atmosphere and influences the transport properties of RTILs, even at relatively low concentrations.
Varieties
weakly coordinating anion
Anions that interact weakly with cations are termed non-coordinating anions, although a more accurate term is weakly coordinating anion. Non-coordinating anions are useful in studying the reactivity of electrophilic cations. They are commonly found ...
s. Both cationic and anionic components have been widely varied.
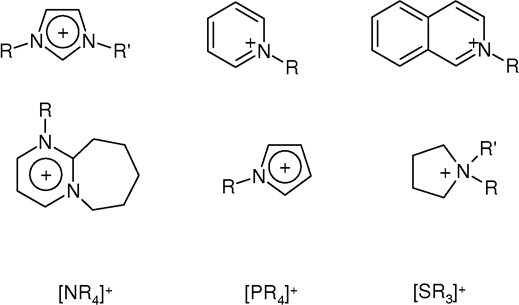
Cations
Room-temperature ionic liquids (RTILs) are dominated by salts derived from 1-methylimidazole, i.e., 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium. Examples include 1-ethyl-3-methyl- (EMIM), 1-butyl-3-methyl- (BMIM), 1-octyl-3 methyl (OMIM), 1-decyl-3-methyl-(DMIM), 1-dodecyl-3-methyl- (dodecylMIM). Other imidazolium cations are 1-butyl-2,3-dimethylimidazolium (BMMIM or DBMIM) and 1,3-di(N,N-dimethylaminoethyl)-2-methylimidazolium (DAMI). Other N-heterocyclic cations are derived frompyridine
Pyridine is a basic (chemistry), basic heterocyclic compound, heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula . It is structurally related to benzene, with one methine group replaced by a nitrogen atom . It is a highly flammable, weak ...
: 4-methyl-N-butyl-pyridinium (MBPy) and N-octylpyridinium (C8Py). Conventional quaternary ammonium cations also form ILs, e.g. tetraethylammonium
Tetraethylammonium (TEA) is a quaternary ammonium cation with the chemical formula , consisting of four ethyl groups (, denoted Et) attached to a central nitrogen atom. It is a counterion used in the research laboratory to prepare lipophilic salt ...
(TEA) and tetrabutylammonium
Tetrabutylammonium is a quaternary ammonium cation with the formula , also denoted (where Bu = butyl group). It is used in the research laboratory to prepare lipophilic salts of inorganic anions. Relative to tetraethylammonium derivatives, tetr ...
(TBA).
Anions
Typical anions in ionic liquids include the following: tetrafluoroborate (BF4),hexafluorophosphate
Hexafluorophosphate is an fluoroanion, anion with chemical formula of . It is an Octahedral molecular geometry, octahedral species that imparts no color to its salts. is isoelectronic with sulfur hexafluoride, , and the Hexafluorosilicic acid, h ...
(PF6), bis-trifluoromethanesulfonimide (NTf2), trifluoromethanesulfonate
In organic chemistry, triflate (systematic name: trifluoromethanesulfonate), is a functional group with the formula and structure . The triflate group is often represented by , as opposed to −Tf, which is the triflyl group, . For example, ...
(OTf), dicyanamide
Dicyanamide, also known as dicyanamine, is an anion having the formula . It contains two cyanide groups bound to a central nitrogen anion. The chemical is formed by decomposition of 2-cyanoguanidine. It is used extensively as a counterion of o ...
(N(CN)2), hydrogensulfate
The sulfate or sulphate ion is a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula . Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salts of sulfuric acid and many ...
(), and ethyl sulfate
Ethyl sulfate (IUPAC name: ethyl hydrogen sulfate), also known as sulfovinic acid, is an organic chemical compound used as an intermediate in the production of ethanol from ethylene. It is the ethyl ester of sulfuric acid.
History
This substanc ...
(EtOSO3). Magnetic ionic liquids can be synthesized by incorporating paramagnetic
Paramagnetism is a form of magnetism whereby some materials are weakly attracted by an externally applied magnetic field, and form internal, induced magnetic fields in the direction of the applied magnetic field. In contrast with this behavior, ...
anions, illustrated by 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrachloroferrate.
Specialized ILs
Protic ionic liquids are formed via aproton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , Hydron (chemistry), H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' (elementary charge). Its mass is slightly less than the mass of a neutron and approximately times the mass of an e ...
transfer from an acid
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. Hydron, hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis ...
to a base. In contrast to other ionic liquids, which generally are formed through a sequence of synthesis
Synthesis or synthesize may refer to:
Science Chemistry and biochemistry
*Chemical synthesis, the execution of chemical reactions to form a more complex molecule from chemical precursors
**Organic synthesis, the chemical synthesis of organi ...
steps, protic ionic liquids can be created more easily by simply mixing the acid and base.
Phosphonium
In chemistry, the term phosphonium (more obscurely: phosphinium) describes polyatomic cations with the chemical formula (where R is a hydrogen or an alkyl, aryl, organyl or halogen group). These cations have tetrahedral structures. The ...
cations (R4P+) are less common but offer some advantageous properties. Some examples of phosphonium cations are trihexyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium (P6,6,6,14) and tributyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium (P4,4,4,14).
Poly(ionic liquid)s
Polymerized ionic liquids, poly(ionic liquid)s or polymeric ionic liquids, all abbreviated as PIL is the polymeric form of ionic liquids. They have half of the ionicity of ionic liquids since one ion is fixed as the polymer moiety to form a polymeric chain. PILs have a similar range of applications, comparable with those of ionic liquids but the polymer architecture provides a better chance for controlling the ionic conductivity. They have extended the applications of ionic liquids for designing smart materials or solid electrolytes.Commercial applications
Many applications have been considered, but few have been commercialized. ILs are used in the production of gasoline by catalyzingalkylation Alkylation is a chemical reaction that entails transfer of an alkyl group. The alkyl group may be transferred as an alkyl carbocation, a free radical, a carbanion, or a carbene (or their equivalents). Alkylating agents are reagents for effecting al ...
.
An IL based on tetraalkylphosphonium
In chemistry, the term phosphonium (more obscurely: phosphinium) describes polyatomic cations with the chemical formula (where R is a hydrogen or an alkyl, aryl, organyl or halogen group). These cations have tetrahedral structures. The ...
iodide is a solvent for tributyltin
Tributyltin (TBT) is an umbrella term for a class of organotin compounds which contain the group, with a prominent example being tributyltin oxide. For 40 years TBT was used as a biocide in anti-fouling paint, commonly known as bottom paint, ...
iodide, which functions as a catalyst to rearrange the monoepoxide of butadiene
1,3-Butadiene () is the organic compound with the formula CH2=CH-CH=CH2. It is a colorless gas that is easily condensed to a liquid. It is important industrially as a precursor to synthetic rubber. The molecule can be viewed as the union of two ...
. This process was commercialized as a route to 2,5-dihydrofuran
2,5-Dihydrofuran is an organic compound classified as a monounsaturated derivative of furan
Furan is a Heterocyclic compound, heterocyclic organic compound, consisting of a five-membered aromatic Ring (chemistry), ring with four carbon Atom, ...
, but later discontinued.
Potential applications
Catalysis
ILs improve the catalytic performance of palladium nanoparticles. Furthermore, ionic liquids can be used as pre-catalysts for chemical transformations. In this regard dialkylimidazoliums such as MIMc have been used in the combination with a base to generate N-heterocyclic carbenes (NHCs). These imidazolium based NHCs are known to catalyse a number transformations such as thebenzoin condensation
In organic chemistry, the benzoin addition is an addition reaction involving two aldehydes (). The reaction generally occurs between aromatic compound, aromatic aldehydes or glyoxals (), and results in formation of an acyloin (). In the classic ex ...
and the OTHO reaction.
Pharmaceuticals
Recognizing that approximately 50% of commercial pharmaceuticals are salts, ionic liquid forms of a number of pharmaceuticals have been investigated. Combining a pharmaceutically active cation with a pharmaceutically active anion leads to a Dual Active ionic liquid in which the actions of two drugs are combined. ILs can extract specific compounds from plants for pharmaceutical, nutritional and cosmetic applications, such as theantimalarial
Antimalarial medications or simply antimalarials are a type of antiparasitic chemical agent, often naturally derived, that can be used to treat or to prevent malaria, in the latter case, most often aiming at two susceptible target groups, young ...
drug artemisinin
Artemisinin () and its semisynthetic derivatives are a group of drugs used in the treatment of malaria due to ''Plasmodium falciparum''. It was discovered in 1972 by Tu Youyou, who shared the 2015 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for he ...
from the plant '' Artemisia annua''.
Biopolymer processing
The dissolution ofcellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the chemical formula, formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of glycosidic bond, β(1→4) linked glucose, D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important s ...
by ILs has attracted interest. A patent application from 1930 showed that 1-alkylpyridinium chlorides dissolve cellulose. Following in the footsteps of the lyocell
Lyocell is a semi-synthetic fibre used to make textiles for clothing and other purposes. It is a form of regenerated cellulose made by dissolving pulp and dry jet-wet spinning. Unlike rayon, which is made by the more common viscose processe ...
process, which uses hydrated N-methylmorpholine N-oxide
''N''-Methylmorpholine ''N''-oxide (more correctly 4-methylmorpholine 4-oxide), NMO or NMMO is an organic compound. This heterocyclic amine oxide and morpholine derivative is used in organic chemistry as a co-oxidant and sacrificial catalyst in ...
as a solvent for pulp and paper. The "valorization" of cellulose, i.e. its conversion to more valuable chemicals, has been achieved by the use of ionic liquids. Representative products are glucose esters, sorbitol
Sorbitol (), less commonly known as glucitol (), is a sugar alcohol with a sweet taste which the human body metabolizes slowly. It can be obtained by reduction of glucose, which changes the converted aldehyde group (−CHO) to a primary alco ...
, and alkylgycosides. IL 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride dissolves freeze-dried
Freeze drying, also known as lyophilization or cryodesiccation, is a low temperature dehydration process that involves freezing the product and lowering pressure, thereby removing the ice by sublimation. This is in contrast to dehydration by m ...
banana
A banana is an elongated, edible fruit – botanically a berry – produced by several kinds of large treelike herbaceous flowering plants in the genus '' Musa''. In some countries, cooking bananas are called plantains, distinguishing the ...
pulp and with an additional 15% dimethyl sulfoxide
Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is an organosulfur compound with the formula . This colorless liquid is the sulfoxide most widely used commercially. It is an important polar aprotic solvent that dissolves both polar and nonpolar compounds and is ...
, lends itself to carbon-13 NMR
Carbon-13 (C13) nuclear magnetic resonance (most commonly known as carbon-13 NMR spectroscopy or 13C NMR spectroscopy or sometimes simply referred to as carbon NMR) is the application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy to carbon. It ...
analysis. In this way the entire complex of starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diet ...
, sucrose
Sucrose, a disaccharide, is a sugar composed of glucose and fructose subunits. It is produced naturally in plants and is the main constituent of white sugar. It has the molecular formula .
For human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined ...
, glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae d ...
, and fructose
Fructose (), or fruit sugar, is a Ketose, ketonic monosaccharide, simple sugar found in many plants, where it is often bonded to glucose to form the disaccharide sucrose. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and gal ...
can be monitored as a function of banana ripening.
Beyond cellulose, ILs have also shown potential in the dissolution, extraction, purification, processing and modification of other biopolymer
Biopolymers are natural polymers produced by the cells of living organisms. Like other polymers, biopolymers consist of monomeric units that are covalently bonded in chains to form larger molecules. There are three main classes of biopolymers, ...
s such as chitin
Chitin (carbon, C8hydrogen, H13oxygen, O5nitrogen, N)n ( ) is a long-chain polymer of N-Acetylglucosamine, ''N''-acetylglucosamine, an amide derivative of glucose. Chitin is the second most abundant polysaccharide in nature (behind only cell ...
/chitosan
Chitosan is a linear polysaccharide composed of randomly distributed β-(1→4)-linked D-glucosamine (deacetylated unit) and ''N''-acetyl-D-glucosamine (acetylated unit). It is made by treating the chitin shells of shrimp and other crusta ...
, starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diet ...
, alginate
Alginic acid, also called algin, is a naturally occurring, edible polysaccharide found in brown algae. It is hydrophilic and forms a viscous gum when hydrated. When the alginic acid binds with sodium and calcium ions, the resulting salts are k ...
, collagen, gelatin
Gelatin or gelatine () is a translucent, colorless, flavorless food ingredient, commonly derived from collagen taken from animal body parts. It is brittle when dry and rubbery when moist. It may also be referred to as hydrolyzed collagen, coll ...
, keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. It is the key structural material making up Scale (anatomy), scales, hair, Nail (anatomy), nails, feathers, horn (anatomy), horns, claws, Hoof, hoove ...
, and fibroin
Fibroin is an insoluble protein present in silk produced by numerous insects, such as the larvae of ''Bombyx mori'', and other moth genera such as ''Antheraea'', ''Cricula trifenestrata, Cricula'', ''Samia (moth), Samia'' and ''Gonometa''. Sil ...
. For example, ILs allow for the preparation of biopolymer materials in different forms (e.g. sponges, films, microparticles, nanoparticles, and aerogels) and better biopolymer chemical reactions, leading to biopolymer-based drug/gene-delivery carriers. Moreover, ILs enable the synthesis of chemically modified starches with high efficiency and degrees of substitution (DS) and the development of various starch-based materials such as thermoplastic starch, composite films, solid polymer electrolytes, nanoparticles and drug carriers.
Nuclear fuel reprocessing
The IL 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride has been investigated for the recovery ofuranium
Uranium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Ura ...
and other metals from spent nuclear fuel
Nuclear fuel refers to any substance, typically fissile material, which is used by nuclear power stations or other atomic nucleus, nuclear devices to generate energy.
Oxide fuel
For fission reactors, the fuel (typically based on uranium) is ...
and other sources.
Solar thermal energy
ILs are potential heat transfer and storage media insolar thermal energy
Solar thermal energy (STE) is a form of energy and a technology for harnessing solar energy to generate thermal energy for use in Industrial sector, industry, and in the residential and commercial sectors. Solar thermal collectors are classified ...
systems. Concentrating solar thermal facilities such as parabolic trough
A parabolic trough collector (PTC) is a type of solar thermal collector that is straight in one dimension and curved as a parabola in the other two, lined with a polished metal mirror. The sunlight which enters the mirror parallel to its plane of ...
s and solar power tower
A solar power tower, also known as 'central tower' power plant or 'heliostat' power plant, is a type of solar furnace using a tower to receive focused sunlight. It uses an array of flat, movable mirrors (called heliostats) to focus the sun's ra ...
s focus the sun's energy onto a receiver, which can generate temperatures of around . This heat can then generate electricity in a steam or other cycle. For buffering during cloudy periods or to enable generation overnight, energy can be stored by heating an intermediate fluid. Although nitrate salts have been the medium of choice since the early 1980s, they freeze at and thus require heating to prevent solidification. Ionic liquids such as 4mim] have more favorable liquid-phase temperature ranges (−75 to 459 °C) and could therefore be excellent liquid thermal storage media and heat transfer fluids.
Waste recycling
ILs can aid the recycling of synthetic goods, plastics, and metals. They offer the specificity required to separate similar compounds from each other, such as separatingpolymer
A polymer () is a chemical substance, substance or material that consists of very large molecules, or macromolecules, that are constituted by many repeat unit, repeating subunits derived from one or more species of monomers. Due to their br ...
s in plastic waste
Plastic pollution is the accumulation of plastic objects and particles (e.g. plastic bottles, bags and microbeads) in the Earth's environment that adversely affects humans, wildlife and their habitat. Plastics that act as pollutants are cate ...
streams. This has been achieved using lower temperature extraction processes than current approaches and could help avoid incinerating plastics or dumping them in landfill.
Batteries
ILs can replace water as the electrolyte in metal-air batteries. ILs are attractive because of their low vapor pressure. Furthermore, ILs have anelectrochemical window The electrochemical window (EW) of a substance is the electrode electric potential range between which the substance is neither oxidized nor reduced. The EW is one of the most important characteristics to be identified for solvents and electrolyte ...
of up to six volts (versus 1.23 for water) supporting more energy-dense metals. Energy densities from 900 to 1600 watt-hours per kilogram appear possible.
Dispersing agent
ILs can act as dispersing agents inpaint
Paint is a material or mixture that, when applied to a solid material and allowed to dry, adds a film-like layer. As art, this is used to create an image or images known as a painting. Paint can be made in many colors and types. Most paints are ...
s to enhance finish, appearance, and drying properties. ILs are used for dispersing nanomaterial
Nanomaterials describe, in principle, chemical substances or materials of which a single unit is sized (in at least one dimension) between 1 and 100 nm (the usual definition of nanoscale).
Nanomaterials research takes a materials science ...
s at IOLITEC.
Carbon capture
ILs andamine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are organic compounds that contain carbon-nitrogen bonds. Amines are formed when one or more hydrogen atoms in ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups. The nitrogen atom in an amine possesses a lone pair of elec ...
s have been investigated for capturing carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
and purifying natural gas.
Tribology
Some ionic liquids have been shown to reduce friction and wear in basictribological
Tribology is the science and engineering of understanding friction, lubrication and wear phenomena for interacting surfaces in relative motion. It is highly interdisciplinary, drawing on many academic fields, including physics, chemistry, material ...
testing, and their polar nature makes them candidate lubricant
A lubricant (sometimes shortened to lube) is a substance that helps to reduce friction between surfaces in mutual contact, which ultimately reduces the heat generated when the surfaces move. It may also have the function of transmitting forces, ...
s for tribotronic applications. While the comparatively high cost of ionic liquids currently prevents their use as neat lubricants, adding ionic liquids in concentrations as low as 0.5 wt% may significantly alter the lubricating performance of conventional base oils. Thus, the current focus of research is on using ionic liquids as additives to lubricating oils, often with the motivation to replace widely used, ecologically harmful lubricant additives. However, the claimed ecological advantage of ionic liquids has been questioned repeatedly and is yet to be demonstrated from a life-cycle perspective.
Safety
Ionic liquids' low volatility effectively eliminates a major pathway for environmental release and contamination. Ionic liquids' aquatic toxicity is as severe as or more so than many current solvents.Ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound with frequency, frequencies greater than 20 Hertz, kilohertz. This frequency is the approximate upper audible hearing range, limit of human hearing in healthy young adults. The physical principles of acoustic waves apply ...
can degrade solutions of imidazolium-based ionic liquids with hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscosity, viscous than Properties of water, water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usua ...
and acetic acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main compone ...
to relatively innocuous compounds.
Despite low vapor pressure
Vapor pressure or equilibrium vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases (solid or liquid) at a given temperature in a closed system. The equilibrium vapor pressure is an indicat ...
many ionic liquids are combustible
A combustible material is a material that can burn (i.e., sustain a flame) in air under certain conditions. A material is flammable if it ignites easily at ambient temperatures. In other words, a combustible material ignites with some effort a ...
.
See also
*1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate
1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate, also known as BMIM-PF6, is a viscous, colourless, hydrophobic and non-water-soluble ionic liquid
An ionic liquid (IL) is a salt (chemistry), salt in the liquid state at ambient conditions. In som ...
(BMIM-PF6) for an often encountered ionic liquid
* Ionic liquids in carbon capture The use of ionic liquids in carbon capture is a potential application of ionic liquids as absorbents for use in carbon capture and sequestration. Ionic liquids, which are salts that exist as liquids near room temperature, are polar, nonvolatile ma ...
* Ion gel
* Ioliomics
Ioliomics (from a portmanteau of ions and liquids) is the study of ions in liquids (or liquid phases) and stipulated with fundamental differences of ionic interactions. Ioliomics covers a broad research area concerning structure, properties and ...
, or studies of ions in liquids
* MDynaMix
Molecular Dynamics of Mixtures (MDynaMix) is a computer software package for general purpose molecular dynamics to simulate mixtures of molecules, interacting by AMBER- and CHARMM-like force fields in periodic boundary conditions.
Algorithms are ...
software for ionic liquids simulations
* Molten salt
Molten salt is salt which is solid at standard temperature and pressure but liquified due to elevated temperature. A salt that is liquid even at standard temperature and pressure is usually called a room-temperature ionic liquid, and molten salts ...
* nanoFlowcell which uses ionic liquid in its car batteries
* Trioctylmethylammonium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide
Further reading
*References
External links
Ionic Liquids Biological Effects Database
, free database on toxicology and ecotoxicology of ionic liquids
Corresponding states for ionic fluids
{{Authority control Ions