The history of Rome includes the history of the
city of Rome as well as the
civilisation of ancient Rome. Roman history has been influential on the modern world, especially in the
history of the Catholic Church
The history of the Catholic Church is the formation, events, and historical development of the Catholic Church through time.
According to the Sacred tradition, tradition of the Catholic Church, it started from the day of Pentecost at the uppe ...
, and
Roman law
Roman law is the law, legal system of ancient Rome, including the legal developments spanning over a thousand years of jurisprudence, from the Twelve Tables (), to the (AD 529) ordered by Eastern Roman emperor Justinian I.
Roman law also den ...
has influenced many modern
legal systems
The contemporary national legal systems are generally based on one of four major legal traditions: civil law (legal system), civil law, common law, customary law, religious law or combinations of these. However, the legal system of each country i ...
. Roman history can be divided into the following periods:
*Pre-historical and early
Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
, covering Rome's earliest inhabitants and the legend of its founding by
Romulus
Romulus (, ) was the legendary founder and first king of Rome. Various traditions attribute the establishment of many of Rome's oldest legal, political, religious, and social institutions to Romulus and his contemporaries. Although many of th ...
*The
period of Etruscan dominance and the
regal period
The Roman Kingdom, also known as the Roman monarchy and the regal period of ancient Rome, was the earliest period of Roman history when the city and its territory were ruled by kings. According to tradition, the Roman Kingdom began with the c ...
, in which, according to tradition, Romulus was the first of seven kings
*The
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establis ...
, which commenced in 509 BC when kings were replaced with rule by elected magistrates. The period was marked by vast expansion of Roman territory. During the 5th century BC, Rome gained regional dominance in
Latium
Latium ( , ; ) is the region of central western Italy in which the city of Rome was founded and grew to be the capital city of the Roman Empire.
Definition
Latium was originally a small triangle of fertile, volcanic soil (Old Latium) on whic ...
. With the
Punic Wars
The Punic Wars were a series of wars fought between the Roman Republic and the Ancient Carthage, Carthaginian Empire during the period 264 to 146BC. Three such wars took place, involving a total of forty-three years of warfare on both land and ...
from 264 to 146 BC,
ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome is the Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of Rome, founding of the Italian city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, collapse of the Western Roman Em ...
gained dominance over the Western
Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
, displacing
Carthage
Carthage was an ancient city in Northern Africa, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classic ...
as the dominant regional power.
*The
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
followed the Republic, which waned with the rise of
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (12 or 13 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in Caesar's civil wa ...
, and by all measures concluded after a
period of civil war and the victory of Caesar's adopted son,
Octavian
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in ...
, in 27 BC over
Mark Antony
Marcus Antonius (14 January 1 August 30 BC), commonly known in English as Mark Antony, was a Roman people, Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the Crisis of the Roman Republic, transformation of the Roman Republic ...
.
* The
Western Roman Empire collapsed in 476 after the city was conquered by the Ostrogothic Kingdom. Consequently, Rome's power declined, and it eventually became part of the
Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
, as the
Duchy of Rome
A duchy, also called a dukedom, is a country, territory, fief, or domain ruled by a duke or duchess, a ruler hierarchically second to the king or queen in Western European tradition.
There once existed an important difference between "sovereign ...
, from the 6th to 8th centuries. At this time, the city was reduced to a fraction of its former size, being sacked several times in the 5th to 6th centuries, even temporarily depopulated entirely.
*
Medieval Rome
The history of Rome includes the history of the Rome, city of Rome as well as the Ancient Rome, civilisation of ancient Rome. Roman history has been influential on the modern world, especially in the history of the Catholic Church, and Roman la ...
is characterised by a break with Constantinople and the formation of the
Papal States
The Papal States ( ; ; ), officially the State of the Church, were a conglomeration of territories on the Italian peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope from 756 to 1870. They were among the major states of Italy from the 8th c ...
. The
Papacy
The pope is the bishop of Rome and the Head of the Church#Catholic Church, visible head of the worldwide Catholic Church. He is also known as the supreme pontiff, Roman pontiff, or sovereign pontiff. From the 8th century until 1870, the po ...
struggled to retain influence in the emerging
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
, and during the , the population of Rome fell to as low as 30,000 inhabitants. Following the
East–West Schism
The East–West Schism, also known as the Great Schism or the Schism of 1054, is the break of communion (Christian), communion between the Catholic Church and the Eastern Orthodox Church. A series of Eastern Orthodox – Roman Catholic eccle ...
and the limited success in the
Investiture Controversy
The Investiture Controversy or Investiture Contest (, , ) was a conflict between church and state in medieval Europe, the Church and the state in medieval Europe over the ability to choose and install bishops (investiture), abbots of monasteri ...
, the Papacy did gain considerable influence in the
High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the periodization, period of European history between and ; it was preceded by the Early Middle Ages and followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended according to historiographical convention ...
, but with the
Avignon Papacy
The Avignon Papacy (; ) was the period from 1309 to 1376 during which seven successive popes resided in Avignon (at the time within the Kingdom of Arles, part of the Holy Roman Empire, now part of France) rather than in Rome (now the capital of ...
and the
Western Schism
The Western Schism, also known as the Papal Schism, the Great Occidental Schism, the Schism of 1378, or the Great Schism (), was a split within the Catholic Church lasting from 20 September 1378 to 11 November 1417, in which bishops residing ...
, the city of Rome was reduced to irrelevance, its population falling below 20,000. Rome's decline into complete irrelevance during the medieval period, with the associated lack of construction activity, assured the survival of very significant
ancient Roman material remains in the centre of the city, some abandoned and others continuing in use.
*The
Roman Renaissance
The Renaissance in Rome occupied a period from the mid-15th to the mid-16th centuries, a period which spawned such masters as Michelangelo and Raphael, who left an indelible mark on Western figurative art. The city had been a magnet for artist ...
occurred in the 15th century, when Rome replaced
Florence
Florence ( ; ) is the capital city of the Italy, Italian region of Tuscany. It is also the most populated city in Tuscany, with 362,353 inhabitants, and 989,460 in Metropolitan City of Florence, its metropolitan province as of 2025.
Florence ...
as the centre of artistic and cultural influence. The Roman Renaissance was cut short abruptly with the
devastation of the city in 1527, but the Papacy reasserted itself in the
Counter-Reformation
The Counter-Reformation (), also sometimes called the Catholic Revival, was the period of Catholic resurgence that was initiated in response to, and as an alternative to or from similar insights as, the Protestant Reformations at the time. It w ...
, and the city continued to flourish during the
early modern period
The early modern period is a Periodization, historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There i ...
. Rome was annexed by
Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career ...
and was part of the
First French Empire
The First French Empire or French Empire (; ), also known as Napoleonic France, was the empire ruled by Napoleon Bonaparte, who established French hegemony over much of continental Europe at the beginning of the 19th century. It lasted from ...
from 1809 to 1814.
*Modern history, the period from the 19th century to the present. Rome came under siege again after the
Allied invasion of Italy
The Allied invasion of Italy was the Allies of World War II, Allied Amphibious warfare, amphibious landing on mainland Italy that took place from 3 September 1943, during the Italian campaign (World War II), Italian campaign of World War II. T ...
and was
bombed several times. It was declared an
open city on 14 August 1943. Rome became the capital of the
Italian Republic
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
(established in 1946). With a population of 4.4 million (; 2.9 million within city limits), it is the largest
city in Italy. It is among the
largest urban areas of the European Union and classified as a
global city
A global city (also known as a power city, world city, alpha city, or world center) is a city that serves as a primary node in the global economic network. The concept originates from geography and urban studies, based on the thesis that glo ...
.
Name
Attempts have been made to find a linguistic root for the name Rome. Possibilities include derivation from the
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
''Rhṓmē'' (), meaning "bravery" or "courage"; Compare also ''Rumon'', former name of the Tiber River. Its further etymology remains unknown, as with most Etruscan words.
Thomas G. Tucker's ''Concise Etymological Dictionary of Latin'' (1931) suggests that the name is most probably from ''*urobsma'' (cf. ''urbs'', ''robur'') and otherwise, "but less likely" from ''*urosma'' "hill" (cf. Skt. ''varsman-'' "height, point," Old Slavonic врьхъ "top, summit", Russ. верх "top; upward direction", Lith. ''virsus'' "upper").
Ancient Rome timeline
Earliest history
Prehistory
There is archaeological evidence of human occupation of the Rome area from at least 5,000 years, but the dense layer of much younger debris obscures Palaeolithic and Neolithic sites. The evidence suggesting the city's ancient foundation is also obscured by the legend of Rome's beginning involving
Romulus and Remus
In Roman mythology, Romulus and (, ) are twins in mythology, twin brothers whose story tells of the events that led to the Founding of Rome, founding of the History of Rome, city of Rome and the Roman Kingdom by Romulus, following his frat ...
.
The traditional date for the
founding of Rome
The founding of Rome was a prehistoric event or process later greatly embellished by Roman historians and poets. Archaeological evidence indicates that Rome developed from the gradual union of several hillfort, hilltop villages during the Prehi ...
is
21 April 753 BC,
following M. Terentius Varro,
and the city and surrounding region of
Latium
Latium ( , ; ) is the region of central western Italy in which the city of Rome was founded and grew to be the capital city of the Roman Empire.
Definition
Latium was originally a small triangle of fertile, volcanic soil (Old Latium) on whic ...
has continued to be inhabited with little interruption since around that time. Excavations made in 2014 have revealed a wall built long before the city's official founding year. Archaeologists discovered 9th-century BC walls and 8th-century BC pottery. The
Palatine Hill
The Palatine Hill (; Classical Latin: ''Palatium''; Neo-Latin: ''Collis/Mons Palatinus''; ), which relative to the seven hills of Rome is the centremost, is one of the most ancient parts of the city; it has been called "the first nucleus of the ...
may have been visited and settled around the 10th century BC.
The site of
Sant'Omobono Area
The Sant'Omobono Area (Italian: ''Area di Sant'Omobono'') is an archaeological site in Rome next to the church of Sant'Omobono, at the junction of via L. Petroselli and the Vico Jugario at the foot of the Campidoglio. It was discovered in 1937 a ...
is crucial for understanding the related processes of monumentalisation,
urbanisation
Urbanization (or urbanisation in British English) is the population shift from rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. It can also ...
, and state formation in Rome in the late Archaic period. The Sant'Omobono temple site dates to 7th–6th century BC, making these the oldest known temple remains in Rome.
Legendary origin
The city's name was long credited to the legendary
culture hero
A culture hero is a mythological hero specific to some group (Culture, cultural, Ethnic group, ethnic, Religion, religious, etc.) who changes the world through invention or Discovery (observation), discovery. Although many culture heroes help with ...
Romulus
Romulus (, ) was the legendary founder and first king of Rome. Various traditions attribute the establishment of many of Rome's oldest legal, political, religious, and social institutions to Romulus and his contemporaries. Although many of th ...
. It was said that Romulus and his twin brother
Remus were the offspring of the
rape
Rape is a type of sexual assault involving sexual intercourse, or other forms of sexual penetration, carried out against a person without consent. The act may be carried out by physical force, coercion, abuse of authority, or against a person ...
of an
Alban princess by the
war god Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmosph ...
and, via their mother, were further descended from the
Trojan
Trojan or Trojans may refer to:
* Of or from the ancient city of Troy
* Trojan language, the language of the historical Trojans
Arts and entertainment Music
* '' Les Troyens'' ('The Trojans'), an opera by Berlioz, premiered part 1863, part 18 ...
prince
Aeneas
In Greco-Roman mythology, Aeneas ( , ; from ) was a Troy, Trojan hero, the son of the Trojan prince Anchises and the Greek goddess Aphrodite (equivalent to the Roman Venus (mythology), Venus). His father was a first cousin of King Priam of Troy ...
, supposed son of the Greek
love goddess Aphrodite
Aphrodite (, ) is an Greek mythology, ancient Greek goddess associated with love, lust, beauty, pleasure, passion, procreation, and as her syncretism, syncretised Roman counterpart , desire, Sexual intercourse, sex, fertility, prosperity, and ...
.
Exposed
Expose, exposé, or exposed may refer to:
News sources
* Exposé (journalism), a form of investigative journalism
* '' The Exposé'', a British conspiracist website
* '' Exeposé'', a student-run newspaper of the University of Exeter
Film and TV ...
on the
Tiber
The Tiber ( ; ; ) is the List of rivers of Italy, third-longest river in Italy and the longest in Central Italy, rising in the Apennine Mountains in Emilia-Romagna and flowing through Tuscany, Umbria, and Lazio, where it is joined by the R ...
, they were
suckled by a
she-wolf and raised by a
shepherd
A shepherd is a person who tends, herds, feeds, or guards flocks of sheep. Shepherding is one of the world's oldest occupations; it exists in many parts of the globe, and it is an important part of Pastoralism, pastoralist animal husbandry. ...
and
his wife. Avenging themselves on
their usurping grand-uncle and restoring their grandfather
Numitor
In Roman mythology, King Numitor () of Alba Longa was the maternal grandfather of Rome's founder and first king, Romulus, and his twin brother Romulus and Remus, Remus. He was the son of Procas, descendant of Aeneas the Troy, Trojan, and father o ...
to
Alba Longa
Alba Longa (occasionally written Albalonga in Italian sources) was an ancient Latins (Italic tribe), Latin city in Central Italy in the vicinity of Lake Albano in the Alban Hills. The ancient Romans believed it to be the founder and head of the ...
's
throne
A throne is the seat of state of a potentate or dignitary, especially the seat occupied by a sovereign (or viceroy
A viceroy () is an official who reigns over a polity in the name of and as the representative of the monarch of the territory ...
, they were ordered or decided to settle the hills around Rome's later
Forum Boarium
The Forum Boarium (, ) was the cattle market or '' forum venalium'' of ancient Rome. It was located on a level piece of land near the Tiber between the Capitoline, the Palatine and Aventine hills. As the site of the original docks of Rome () ...
, an important river port connected in Roman myth with
Hercules
Hercules (, ) is the Roman equivalent of the Greek divine hero Heracles, son of Jupiter and the mortal Alcmena. In classical mythology, Hercules is famous for his strength and for his numerous far-ranging adventures.
The Romans adapted the Gr ...
's
tenth labour, capturing the cattle of
Geryon
In Greek mythology, Geryon ( ; , genitive ), also Geryone (, or ), son of Chrysaor and Callirrhoe, the grandson of Medusa and the nephew of Pegasus, was a fearsome giant who dwelt on the island Erytheia of the mythic Hesperides in the far ...
.
Disputing some point of the founding or its related
auguries
An augur was a priest and official in the ancient Rome, classical Roman world. His main role was the practice of augury, the interpretation of the will of the List of Roman deities, gods by studying events he observed within a predetermined s ...
, Remus was murdered by Romulus or one of his supporters. Romulus then established a
walled and
roughly square settlement, whose
sacred boundary and gates were established by a
ploughing ritual. Romulus then declared the town an asylum, permitted men of all classes to come to Rome as
citizens
Citizenship is a membership and allegiance to a sovereign state.
Though citizenship is often conflated with nationality in today's English-speaking world, international law does not usually use the term ''citizenship'' to refer to nationality; ...
, including criminals, runaway
slaves
Slavery is the ownership of a person as property, especially in regards to their labour. Slavery typically involves compulsory work, with the slave's location of work and residence dictated by the party that holds them in bondage. Enslavemen ...
, and freemen without distinction. To provide his citizens with wives, Romulus invited the neighbouring tribes to a festival in Rome where the Romans
abducted many of their young women. After the ensuing war with the
Sabines
The Sabines (, , , ; ) were an Italic people who lived in the central Apennine Mountains (see Sabina) of the ancient Italian Peninsula, also inhabiting Latium north of the Anio before the founding of Rome.
The Sabines divided int ...
, Romulus shared Rome's kingship with the Sabine king
Titus Tatius
According to the Roman foundation myth, Titus Tatius, also called Tatius Sabinus, was king of the Sabines from Cures and joint-ruler of the Kingdom of Rome for several years.
During the reign of Romulus, the first king of Rome, Tatius dec ...
. Romulus selected 100 of the most noble men to form the
Roman Senate
The Roman Senate () was the highest and constituting assembly of ancient Rome and its aristocracy. With different powers throughout its existence it lasted from the first days of the city of Rome (traditionally founded in 753 BC) as the Sena ...
, initially serving as his advisory council. These men he called fathers (), and their descendants became the
patricians
The patricians (from ) were originally a group of ruling class families in ancient Rome. The distinction was highly significant in the Roman Kingdom and the early Republic, but its relevance waned after the Conflict of the Orders (494 BC to 287 B ...
. He created three
centuries of
equites
The (; , though sometimes referred to as " knights" in English) constituted the second of the property/social-based classes of ancient Rome, ranking below the senatorial class. A member of the equestrian order was known as an ().
Descript ...
: Ramnes (meaning Romans), Tities (after the Sabine king), and Luceres (Etruscans). He also divided the general populace into thirty
curia
Curia (: curiae) in ancient Rome referred to one of the original groupings of the citizenry, eventually numbering 30, and later every Roman citizen was presumed to belong to one. While they originally probably had wider powers, they came to meet ...
e, named after thirty of the Sabine women who had intervened to end the war between Romulus and Tatius. The curiae formed the voting units in the
Comitia Curiata.
City's formation
Rome grew from pastoral settlements on the
Palatine Hill
The Palatine Hill (; Classical Latin: ''Palatium''; Neo-Latin: ''Collis/Mons Palatinus''; ), which relative to the seven hills of Rome is the centremost, is one of the most ancient parts of the city; it has been called "the first nucleus of the ...
and
surrounding hills approximately from the
Tyrrhenian Sea
The Tyrrhenian Sea (, ; or ) , , , , is part of the Mediterranean Sea off the western coast of Italy. It is named for the Tyrrhenians, Tyrrhenian people identified with the Etruscans of Italy.
Geography
The sea is bounded by the islands of C ...
on the south side of the
Tiber
The Tiber ( ; ; ) is the List of rivers of Italy, third-longest river in Italy and the longest in Central Italy, rising in the Apennine Mountains in Emilia-Romagna and flowing through Tuscany, Umbria, and Lazio, where it is joined by the R ...
. The
Quirinal Hill
The Quirinal Hill (; ; ) is one of the Seven Hills of Rome, at the north-east of the city center. It is the location of the official residence of the Italian head of state, who resides in the Quirinal Palace; by metonymy "the Quirinal" has c ...
was probably an outpost for the
Sabine
The Sabines (, , , ; ) were an Italic people who lived in the central Apennine Mountains (see Sabina) of the ancient Italian Peninsula, also inhabiting Latium north of the Anio before the founding of Rome.
The Sabines divided int ...
s, another
Italic-speaking people. At this location, the Tiber forms a Z-shaped curve that contains an
island
An island or isle is a piece of land, distinct from a continent, completely surrounded by water. There are continental islands, which were formed by being split from a continent by plate tectonics, and oceanic islands, which have never been ...
where the river can be forded. Because of the river and the ford, Rome was at a crossroads of traffic following the river valley and of traders travelling north and south on the west side of the
peninsula
A peninsula is a landform that extends from a mainland and is only connected to land on one side. Peninsulas exist on each continent. The largest peninsula in the world is the Arabian Peninsula.
Etymology
The word ''peninsula'' derives , . T ...
.
Archaeological
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, ...
finds have confirmed that there were two fortified settlements in the 8th century BC, in the area of the future Rome: Rumi on the Palatine Hill, and Titientes on the Quirinal Hill, backed by the Luceres living in the nearby woods.
These were simply three of numerous Italic-speaking communities that existed in
Latium
Latium ( , ; ) is the region of central western Italy in which the city of Rome was founded and grew to be the capital city of the Roman Empire.
Definition
Latium was originally a small triangle of fertile, volcanic soil (Old Latium) on whic ...
, a
plain
In geography, a plain, commonly known as flatland, is a flat expanse of land that generally does not change much in elevation, and is primarily treeless. Plains occur as lowlands along valleys or at the base of mountains, as coastal plains, and ...
on the
Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, a Romance ethnic group related to or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance languag ...
peninsula, by the 1st millennium BC. The origins of the
Italic peoples
The concept of Italic peoples is widely used in linguistics and historiography of ancient Italy. In a strict sense, commonly used in linguistics, it refers to the Osco-Umbrian languages, Osco-Umbrians and Latino-Faliscan languages, Latino-Falisca ...
lie in prehistory and are therefore not precisely known, but their
Indo-European languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the northern Indian subcontinent, most of Europe, and the Iranian plateau with additional native branches found in regions such as Sri Lanka, the Maldives, parts of Central Asia (e. ...
migrated from the east in the second half of the 2nd millennium BC.
According to
Dionysius of Halicarnassus
Dionysius of Halicarnassus (,
; – after 7 BC) was a Greek historian and teacher of rhetoric, who flourished during the reign of Emperor Augustus. His literary style was ''atticistic'' – imitating Classical Attic Greek in its prime.
...
, many Roman historiansincluding
Cato and
Semproniusconsidered the
Italian aborigines to have been prehistoric
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
colonists
A settler or a colonist is a person who establishes or joins a permanent presence that is separate to existing communities. The entity that a settler establishes is a settlement. A settler is called a pioneer if they are among the first settli ...
. The Romans then considered themselves a mix of these people, the
Albans, and the other
Latins
The term Latins has been used throughout history to refer to various peoples, ethnicities and religious groups using Latin or the Latin-derived Romance languages, as part of the legacy of the Roman Empire. In the Ancient World, it referred to th ...
, considered a blend of
Pelasgians
The name Pelasgians (, ) was used by Classical Greek writers to refer either to the predecessors of the Greeks, or to all the inhabitants of Greece before the emergence of the Greeks. In general, "Pelasgian" has come to mean more broadly all ...
,
Arcadians,
Epeans, and refugee
Trojans. Over time, the
Etruscans
The Etruscan civilization ( ) was an ancient civilization created by the Etruscans, a people who inhabited Etruria in List of ancient peoples of Italy, ancient Italy, with a common language and culture, and formed a federation of city-states. Af ...
and other
ancient Italic peoples were admitted as citizens as well. The Sabinesconsidered to be
Gaulish
Gaulish is an extinct Celtic languages, Celtic language spoken in parts of Continental Europe before and during the period of the Roman Empire. In the narrow sense, Gaulish was the language of the Celts of Gaul (now France, Luxembourg, Belgium, ...
along with the other
Umbri
The Umbri were an Italic peoples, Italic people of ancient Italy. A region called Umbria still exists and is now occupied by Italian speakers. It is somewhat smaller than the Regio VI Umbria, ancient Umbria.
Most ancient Umbrian cities were sett ...
peoples of central Italy were first mentioned in Dionysius's account for having captured the city of Lista by surprise, which was regarded as the mother-city of the Aborigines.
Italic context
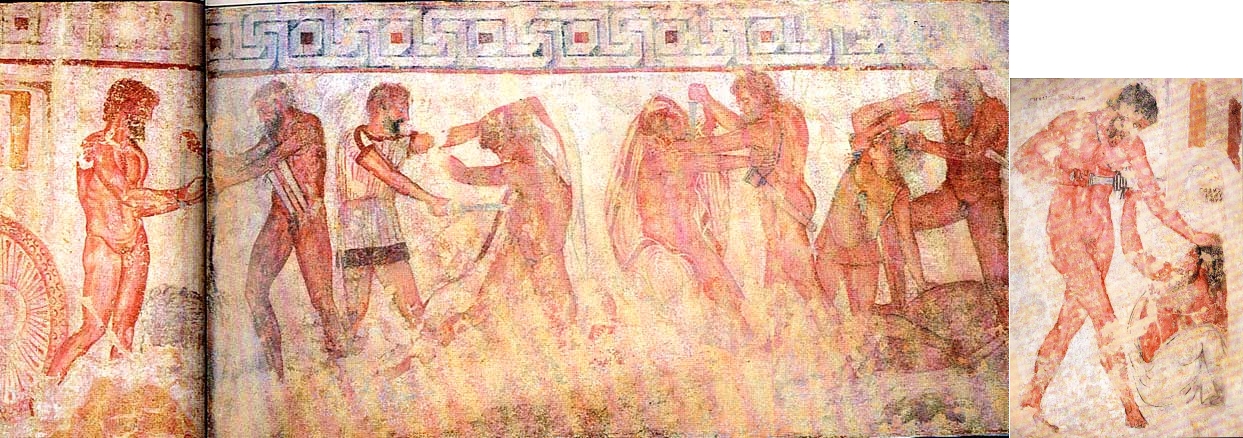

The Italic speakers in the area included
Latins
The term Latins has been used throughout history to refer to various peoples, ethnicities and religious groups using Latin or the Latin-derived Romance languages, as part of the legacy of the Roman Empire. In the Ancient World, it referred to th ...
(in the west),
Sabine
The Sabines (, , , ; ) were an Italic people who lived in the central Apennine Mountains (see Sabina) of the ancient Italian Peninsula, also inhabiting Latium north of the Anio before the founding of Rome.
The Sabines divided int ...
s (in the upper valley of the
Tiber
The Tiber ( ; ; ) is the List of rivers of Italy, third-longest river in Italy and the longest in Central Italy, rising in the Apennine Mountains in Emilia-Romagna and flowing through Tuscany, Umbria, and Lazio, where it is joined by the R ...
),
Umbrian
Umbrian is an extinct Italic language formerly spoken by the Umbri in the ancient Italian region of Umbria. Within the Italic languages it is closely related to the Oscan group and is therefore associated with it in the group of Osco-Umbr ...
s (in the north-east),
Samnites
The Samnites () were an ancient Italic peoples, Italic people who lived in Samnium, which is located in modern inland Abruzzo, Molise, and Campania in south-central Italy.
An Oscan language, Oscan-speaking Osci, people, who originated as an offsh ...
(in the South),
Oscans
The Osci (also called Oscans, Opici, Opsci, Obsci, Opicans) were an Italic people of Campania and Latium adiectum before and during Roman times. They spoke the Oscan language, also spoken by the Samnites of Southern Italy. Although the language ...
, and others. In the 8th century BC, they shared the peninsula with two other major ethnic groups: the
Etruscans
The Etruscan civilization ( ) was an ancient civilization created by the Etruscans, a people who inhabited Etruria in List of ancient peoples of Italy, ancient Italy, with a common language and culture, and formed a federation of city-states. Af ...
in the North and the
Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
in the south.
The
Etruscans
The Etruscan civilization ( ) was an ancient civilization created by the Etruscans, a people who inhabited Etruria in List of ancient peoples of Italy, ancient Italy, with a common language and culture, and formed a federation of city-states. Af ...
(''Etrusci'' or ''Tusci'' in
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
) are attested north of Rome in
Etruria
Etruria ( ) was a region of Central Italy delimited by the rivers Arno and Tiber, an area that covered what is now most of Tuscany, northern Lazio, and north-western Umbria. It was inhabited by the Etruscans, an ancient civilization that f ...
(modern northern Lazio,
Tuscany
Tuscany ( ; ) is a Regions of Italy, region in central Italy with an area of about and a population of 3,660,834 inhabitants as of 2025. The capital city is Florence.
Tuscany is known for its landscapes, history, artistic legacy, and its in ...
and part of
Umbria
Umbria ( ; ) is a Regions of Italy, region of central Italy. It includes Lake Trasimeno and Cascata delle Marmore, Marmore Falls, and is crossed by the Tiber. It is the only landlocked region on the Italian Peninsula, Apennine Peninsula. The re ...
). They founded cities such as
Tarquinia
Tarquinia (), formerly Corneto, is an old city in the province of Viterbo, Lazio, Central Italy, known chiefly for its ancient Etruscans, Etruscan tombs in the widespread necropolis, necropoleis, or cemeteries. Tarquinia was designated as a ...
,
Veii
Veii (also Veius; ) was an important ancient Etruscan city situated on the southern limits of Etruria and north-northwest of Rome, Italy. It now lies in Isola Farnese, in the comune of Rome. Many other sites associated with and in the city-st ...
, and
Volterra
Volterra (; Latin: ''Volaterrae'') is a walled mountaintop town in the Tuscany region of Italy. Its history dates from before the 8th century BC and it has substantial structures from the Etruscan, Roman, and Medieval periods.
History
...
and deeply influenced Roman culture, as clearly shown by the Etruscan origin of some of the mythical Roman kings. Historians have no literature, nor texts of religion or philosophy; therefore, much of what is known about this civilisation is derived from grave goods and tomb findings.
[ Larissa Bonfante, 'Etruscan Inscriptions and Etruscan Religion' in ''The Religion of the Etruscans'' – University of Texas Press 2006, page 9]
The Greeks had founded many colonies in Southern
Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
between 750 and 550 BC (which the Romans later called
Magna Graecia
Magna Graecia refers to the Greek-speaking areas of southern Italy, encompassing the modern Regions of Italy, Italian regions of Calabria, Apulia, Basilicata, Campania, and Sicily. These regions were Greek colonisation, extensively settled by G ...
), such as
Cumae
Cumae ( or or ; ) was the first ancient Greek colony of Magna Graecia on the mainland of Italy and was founded by settlers from Euboea in the 8th century BCE. It became a rich Roman city, the remains of which lie near the modern village of ...
,
Naples
Naples ( ; ; ) is the Regions of Italy, regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 908,082 within the city's administrative limits as of 2025, while its Metropolitan City of N ...
,
Reggio Calabria
Reggio di Calabria (; ), commonly and officially referred to as Reggio Calabria, or simply Reggio by its inhabitants, is the List of cities in Italy, largest city in Calabria as well as the seat of the Metropolitan City of Reggio Calabria. As ...
,
Crotone
Crotone (; ; or ) is a city and ''comune'' in Calabria, Italy.
Founded as the Achaean colony of Kroton ( or ; ), it became a great Greek city, home of the renowned mathematician-philosopher Pythagoras amongst other famous citizens, and one ...
,
Sybaris
Sybaris (; ) was an important ancient Greek city situated on the coast of the Gulf of Taranto in modern Calabria, Italy.
The city was founded around 720 BC by Achaeans (tribe), Achaean and Troezenian settlers and the Achaeans also went on ...
, and
Taranto
Taranto (; ; previously called Tarent in English) is a coastal city in Apulia, Southern Italy. It is the capital of the province of Taranto, serving as an important commercial port as well as the main Italian naval base.
Founded by Spartans ...
, as well as in the eastern two-thirds of
Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
.
Etruscan dominance


After 650 BC, the
Etruscans
The Etruscan civilization ( ) was an ancient civilization created by the Etruscans, a people who inhabited Etruria in List of ancient peoples of Italy, ancient Italy, with a common language and culture, and formed a federation of city-states. Af ...
became dominant in Italy and expanded into north-central Italy. Roman tradition claimed that Rome had been under the control of
seven kings
Seven Kings is an area of Ilford in Greater London, England, part of the London Borough of Redbridge. Situated approximately two miles from Ilford town centre, Seven Kings forms part of the Ilford post town. Historically part of Essex, it was p ...
from 753 to
509 BC beginning with the mythical
Romulus
Romulus (, ) was the legendary founder and first king of Rome. Various traditions attribute the establishment of many of Rome's oldest legal, political, religious, and social institutions to Romulus and his contemporaries. Although many of th ...
who was said to have
founded the city of Rome along with his brother
Remus. The last three kings were said to be Etruscan (at least partially)—namely
Tarquinius Priscus
Lucius Tarquinius Priscus (), or Tarquin the Elder, was the legendary fifth king of Rome and first of its Etruscan dynasty. He reigned for thirty-eight years.Livy, '' ab urbe condita libri'', I Tarquinius expanded Roman power through military ...
,
Servius Tullius
Servius Tullius was the legendary sixth king of Rome, and the second of its Etruscan dynasty. He reigned from 578 to 535 BC. Roman and Greek sources describe his servile origins and later marriage to a daughter of Lucius Tarquinius Pri ...
and
Tarquinius Superbus
Lucius Tarquinius Superbus (died 495 BC) was the legendary seventh and final king of Rome, reigning 25 years until the popular uprising that led to the establishment of the Roman Republic.Livy, '' ab urbe condita libri'', I He is commonly ...
. (Priscus is said by the ancient literary sources to be the son of a Greek refugee and an Etruscan mother.) Their names refer to the Etruscan town of
Tarquinia
Tarquinia (), formerly Corneto, is an old city in the province of Viterbo, Lazio, Central Italy, known chiefly for its ancient Etruscans, Etruscan tombs in the widespread necropolis, necropoleis, or cemeteries. Tarquinia was designated as a ...
.
Livy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding i ...
,
Plutarch
Plutarch (; , ''Ploútarchos'', ; – 120s) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo (Delphi), Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his ''Parallel Lives'', ...
,
Dionysius of Halicarnassus
Dionysius of Halicarnassus (,
; – after 7 BC) was a Greek historian and teacher of rhetoric, who flourished during the reign of Emperor Augustus. His literary style was ''atticistic'' – imitating Classical Attic Greek in its prime.
...
, and others claim that Rome was ruled during its first centuries by a succession of seven kings. The traditional chronology, as codified by
Varro
Marcus Terentius Varro (116–27 BCE) was a Roman polymath and a prolific author. He is regarded as ancient Rome's greatest scholar, and was described by Petrarch as "the third great light of Rome" (after Virgil and Cicero). He is sometimes call ...
, allots 243 years for their reigns, an average of almost 35 years, which has been generally discounted by modern scholarship since the work of
Barthold Georg Niebuhr
Barthold Georg Niebuhr (27 August 1776 – 2 January 1831) was a Danish–German statesman, banker, and historian who became Germany's leading historian of Ancient Rome and a founding father of modern scholarly historiography. By 1810 Niebuhr wa ...
. The
Gauls
The Gauls (; , ''Galátai'') were a group of Celts, Celtic peoples of mainland Europe in the Iron Age Europe, Iron Age and the Roman Gaul, Roman period (roughly 5th century BC to 5th century AD). Their homeland was known as Gaul (''Gallia''). Th ...
destroyed much of Rome's historical records when they sacked the city after the
Battle of the Allia
The Battle of the Allia was fought between the Senones – a Gauls, Gallic tribe led by Brennus (leader of the Senones), Brennus, who had invaded Northern Italy – and the Roman Republic.
The battle was fought at the confluence of the Tibe ...
in 390 BC (according to Polybius, the battle occurred in 387/386) and what was left was eventually lost to time or theft. With no contemporary records of the kingdom existing, all accounts of the kings must be carefully questioned. The list of kings is also of dubious historical value, though the last-named kings may be historical figures.
It is believed by some historians (again, this is disputed) that Rome was under the influence of the Etruscans for about a century. During this period, a bridge was built called the
Pons Sublicius to replace the
Tiber
The Tiber ( ; ; ) is the List of rivers of Italy, third-longest river in Italy and the longest in Central Italy, rising in the Apennine Mountains in Emilia-Romagna and flowing through Tuscany, Umbria, and Lazio, where it is joined by the R ...
ford, and the
Cloaca Maxima was also built; the Etruscans are said to have been great engineers of this type of structure. From a cultural and technical point of view, Etruscans had arguably the second-greatest impact on Roman development, only surpassed by the Greeks.
Expanding further south, the Etruscans came into direct contact with the Greeks and initially had success in conflicts with the Greek colonists; after which, Etruria went into a decline. Taking advantage of this, Rome rebelled and gained independence from the Etruscans around 500 BC. It also abandoned monarchy in favour of a republican system based on a
Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
, composed of the nobles of the city, along with popular assemblies which ensured political participation for most of the freeborn men and elected magistrates annually.
The Etruscans left a lasting influence on Rome. The Romans learned to build temples from them, and the Etruscans may have introduced the worship of a triad of gods—
Juno,
Minerva
Minerva (; ; ) is the Roman goddess of wisdom, justice, law, victory, and the sponsor of arts, trade, and strategy. She is also a goddess of warfare, though with a focus on strategic warfare, rather than the violence of gods such as Mars. Be ...
, and
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a Jupiter mass, mass more than 2.5 times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined a ...
—from the
Etruscan gods
Etruscan religion comprises a set of stories, beliefs, and religious practices of the Etruscan civilization, heavily influenced by the mythology of ancient Greece, and sharing similarities with concurrent Roman mythology and religion. As the ...
:
Uni,
Menrva
Menrva (also spelled Menerva or Menfra) was an Etruscan goddess of war, art, wisdom, and medicine. She contributed much of her character to the Roman Minerva. She was the child of Uni and Tinia.
Although Menrva was seen by Hellenized Etruscans ...
, and
Tinia
Tinia (also Tin, Tinh, Tins or Tina) was the sky god and the highest deity in Etruscan religion, equivalent to the Roman Jupiter and the Greek Zeus.
However, a primary source from the Roman Varro states that Veltha, not Tins, was the sup ...
. However, the influence of Etruscan people in the development of Rome is often overstated. Rome was primarily a Latin city. It never became fully Etruscan. Also, evidence shows that Romans were heavily influenced by the Greek cities in the South, mainly through trade.
Roman Republic

The commonly held stories of the early part of the Republic (before roughly 300 BC, when Old Latin inscriptions and Greek histories about Rome provide more concrete evidence of events) are generally considered to be legendary, their historicity being a topic of debate among classicists. The Roman Republic traditionally dates from 509 BC to 27 BC. After 500 BC, Rome is said to have joined with the Latin cities in defence against incursions by the
Sabine
The Sabines (, , , ; ) were an Italic people who lived in the central Apennine Mountains (see Sabina) of the ancient Italian Peninsula, also inhabiting Latium north of the Anio before the founding of Rome.
The Sabines divided int ...
s. Winning the
Battle of Lake Regillus
The Battle of Lake Regillus was a legendary Roman victory over the Latin League shortly after the establishment of the Roman Republic and as part of a wider Latin War (498–493 BC), Latin War. The Latins were led by an elderly Lucius Tar ...
in 493 BC, Rome established again the supremacy over the Latin countries it had lost after the fall of the monarchy. After a lengthy series of struggles, this supremacy became fixed in 393, when the Romans finally subdued the
Volsci
The Volsci (, , ) were an Italic tribe, well known in the history of the first century of the Roman Republic. At the time they inhabited the partly hilly, partly marshy district of the south of Latium, bounded by the Aurunci and Samnites on the ...
and
Aequi
300px, Location of the Aequi (Equi) in central Italy, 5th century BC.
The Aequi were an Italic tribe on a stretch of the Apennine Mountains to the east of Latium in central Italy who appear in the early history of ancient Rome. After a long stru ...
. In 394 BC, they also conquered the menacing Etruscan neighbour of
Veii
Veii (also Veius; ) was an important ancient Etruscan city situated on the southern limits of Etruria and north-northwest of Rome, Italy. It now lies in Isola Farnese, in the comune of Rome. Many other sites associated with and in the city-st ...
. The Etruscan power was now limited to Etruria itself, and Rome was the dominant city in Latium.
A formal treaty was agreed with the city-state of
Carthage
Carthage was an ancient city in Northern Africa, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classic ...
in 509 BC which defined the spheres of influence of each city and regulated trade between them.

At the same time,
Heraclides stated that 4th-century Rome was a
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
city (Plut. Cam. 22).
Rome's early enemies were the neighbouring hill tribes of the Volscians, the Aequi, and of course the Etruscans. As years passed and military successes increased Roman territory, new adversaries appeared. The fiercest were the
Gauls
The Gauls (; , ''Galátai'') were a group of Celts, Celtic peoples of mainland Europe in the Iron Age Europe, Iron Age and the Roman Gaul, Roman period (roughly 5th century BC to 5th century AD). Their homeland was known as Gaul (''Gallia''). Th ...
, a loose collective of peoples who controlled much of Northern Europe including what is modern North and Central-East Italy.
In 387 BC, Rome was sacked and burned by the
Senones
The Senones or Senonii (Gaulish: "the ancient ones") were an ancient Gallic tribe dwelling in the Seine basin, around present-day Sens, during the Iron Age and the Roman period.
Part of the Senones settled in the Italian peninsula, where the ...
coming from eastern Italy and led by
Brennus, who had successfully defeated the Roman army at the
Battle of the Allia
The Battle of the Allia was fought between the Senones – a Gauls, Gallic tribe led by Brennus (leader of the Senones), Brennus, who had invaded Northern Italy – and the Roman Republic.
The battle was fought at the confluence of the Tibe ...
in
Etruria
Etruria ( ) was a region of Central Italy delimited by the rivers Arno and Tiber, an area that covered what is now most of Tuscany, northern Lazio, and north-western Umbria. It was inhabited by the Etruscans, an ancient civilization that f ...
. Multiple contemporary records suggest that the Senones hoped to punish Rome for violating its diplomatic neutrality in Etruria. The Senones marched to Rome without harming the surrounding countryside; once they had sacked the city, the Senones withdrew from Rome. Brennus was defeated by the dictator
Furius Camillus at
Tusculum
Tusculum is a ruined Classical Rome, Roman city in the Alban Hills, in the Latium region of Italy. Tusculum was most famous in Roman times for the many great and luxurious patrician country villas sited close to the city, yet a comfortable dist ...
soon afterwards.
Plutarch
Plutarch (; , ''Ploútarchos'', ; – 120s) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo (Delphi), Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his ''Parallel Lives'', ...
, ''Lives''.
After that, Rome hastily rebuilt its buildings and went on the offensive, conquering the Etruscans and seizing territory from the Gauls in the north. After 345 BC, Rome pushed south against other Latins. Their main enemy in this quadrant were the fierce
Samnites
The Samnites () were an ancient Italic peoples, Italic people who lived in Samnium, which is located in modern inland Abruzzo, Molise, and Campania in south-central Italy.
An Oscan language, Oscan-speaking Osci, people, who originated as an offsh ...
, who outsmarted and trapped the legions in 321 BC at the
Battle of Caudine Forks. In spite of these and other temporary setbacks, the Romans advanced steadily. By 290 BC, Rome controlled over half of the Italian peninsula. In the 3rd century BC, Rome brought the Greek
poleis
Polis (: poleis) means 'city' in Ancient Greek. The ancient word ''polis'' had socio-political connotations not possessed by modern usage. For example, Modern Greek πόλη (polē) is located within a (''khôra''), "country", which is a πατ ...
in the south under its control as well.
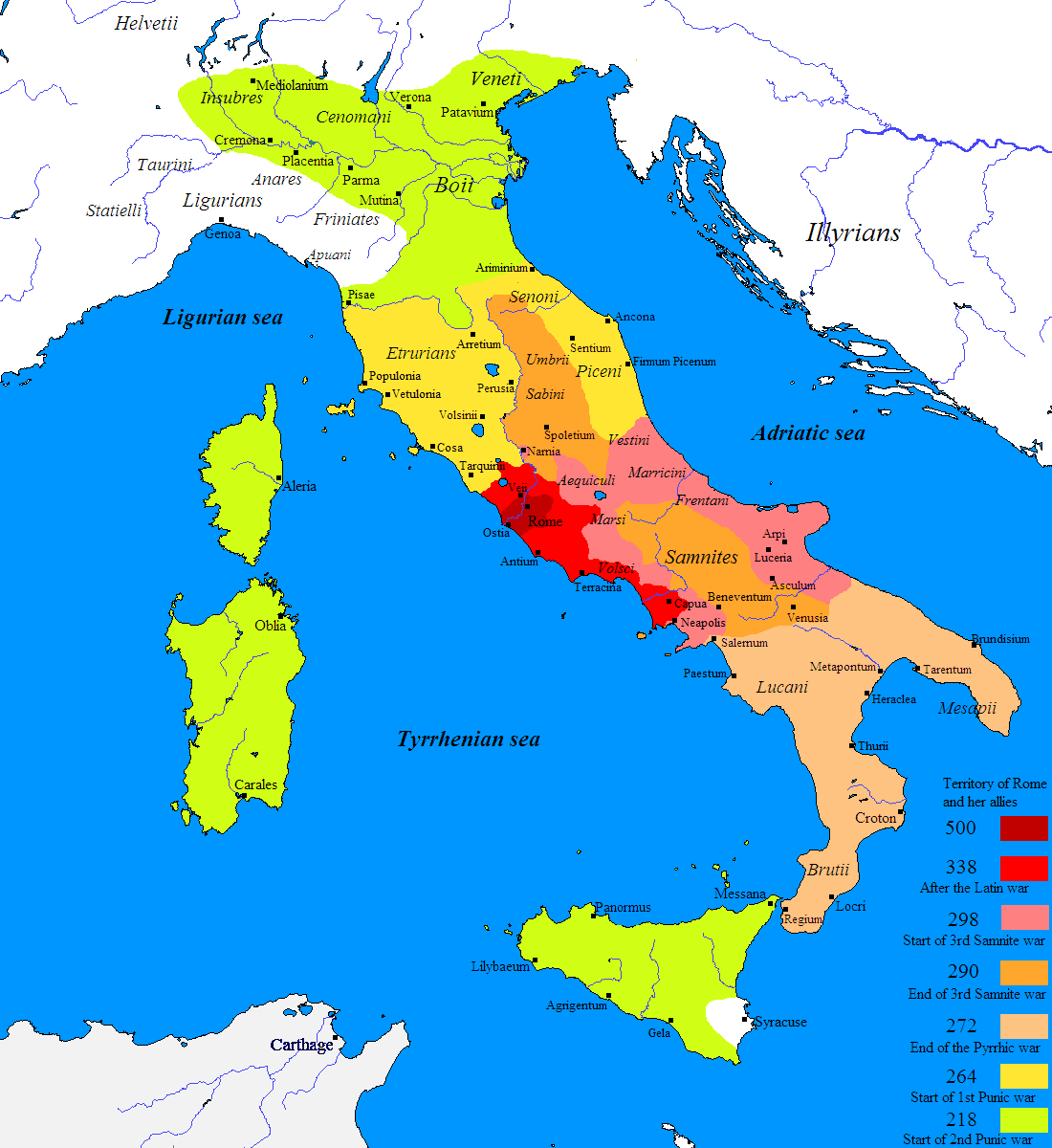
Amidst the never-ending wars (from the beginning of the Republic up to the Principate, the doors of the temple of
Janus
In ancient Roman religion and myth, Janus ( ; ) is the god of beginnings, gates, transitions, time, duality, doorways, passages, frames, and endings. He is usually depicted as having two faces. The month of January is named for Janus (''Ianu ...
were closed only twice—when they were open it meant that Rome was at war), Rome had to face a severe major social crisis, the
Conflict of the Orders
The Conflict of the Orders or the Struggle of the Orders was a political struggle between the plebeians (commoners) and patricians (aristocrats) of the ancient Roman Republic lasting from 500 BC to 287 BC in which the plebeians sought political ...
, a political struggle between the
Plebeian
In ancient Rome, the plebeians or plebs were the general body of free Roman citizens who were not patricians, as determined by the census, or in other words "commoners". Both classes were hereditary.
Etymology
The precise origins of the gro ...
s (commoners) and
Patricians (aristocrats) of the ancient
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establis ...
, in which the Plebeians sought political equality with the Patricians. It played a major role in the development of the
Constitution of the Roman Republic
The constitution of the Roman Republic was a set of Uncodified constitution, uncodified norms and customs which, together with various Roman law, written laws, guided the procedural governance of the Roman Republic. The constitution emerged from ...
. It began in 494 BC, when, while Rome was at war with two neighbouring tribes, the Plebeians all left the city (the first
Plebeian Secession). The result of this first secession was the creation of the office of
Plebeian Tribune
Tribune of the plebs, tribune of the people or plebeian tribune () was the first office of the Roman state that was open to the plebeians, and was, throughout the history of the Republic, the most important check on the power of the Roman Senate ...
, and with it the first acquisition of real power by the Plebeians.
[Abbott, 28.]
According to tradition, Rome became a
republic
A republic, based on the Latin phrase ''res publica'' ('public affair' or 'people's affair'), is a State (polity), state in which Power (social and political), political power rests with the public (people), typically through their Representat ...
in 509 BC. However, it took a few centuries for Rome to become the great city of popular imagination. By the 3rd century BC, Rome had become the pre-eminent city of the Italian peninsula. During the
Punic Wars
The Punic Wars were a series of wars fought between the Roman Republic and the Ancient Carthage, Carthaginian Empire during the period 264 to 146BC. Three such wars took place, involving a total of forty-three years of warfare on both land and ...
between Rome and the great Mediterranean empire of Carthage (264–146 BC), Rome's stature increased further as it became the capital of an overseas empire for the first time. Beginning in the 2nd century BC, Rome went through a significant population expansion as Italian farmers, driven from their ancestral farmlands by the advent of massive, slave-operated farms called
latifundia
A ''latifundium'' (Latin: ''latus'', "spacious", and ''fundus'', "farm", "estate") was originally the term used by ancient Romans for great landed estates specialising in agriculture destined for sale: grain, olive oil, or wine. They were charac ...
, flocked to the city in great numbers. The victory over Carthage in the
First Punic War
The First Punic War (264–241 BC) was the first of three wars fought between Rome and Carthage, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the early 3rd century BC. For 23 years, in the longest continuous conflict and grea ...
brought the first two provinces outside the Italian peninsula,
Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
and
Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; ; ) is the Mediterranean islands#By area, second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, and one of the Regions of Italy, twenty regions of Italy. It is located west of the Italian Peninsula, north of Tunisia an ...
.
[.] Parts of
Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
(
Hispania
Hispania was the Ancient Rome, Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two Roman province, provinces: Hispania Citerior and Hispania Ulterior. During the Principate, Hispania Ulterior was divide ...
) followed, and in the beginning of the 2nd century the Romans got involved in the affairs of the Greek world. By then all Hellenistic kingdoms and the Greek city-states were in decline, exhausted from endless civil wars and relying on mercenary troops.
The Romans looked upon the Greek civilisation with great admiration. The Greeks saw Rome as a useful ally in their civil strifes, and it was not long before the Roman legions were invited to intervene in Greece. In less than 50 years the whole of mainland Greece was subdued. The Roman legions crushed the Macedonian phalanx twice, in 197 and 168 BC; in 146 BC the Roman consul
Lucius Mummius
Lucius Mummius (2nd century BC) was a Roman statesman and general. He was consul in the year 146 BC along with Gnaeus Cornelius Lentulus.
Mummius was the first of his family to rise to the rank of consul thereby making him a novus homo. He r ...
razed
Corinth
Corinth ( ; , ) is a municipality in Corinthia in Greece. The successor to the ancient Corinth, ancient city of Corinth, it is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Sin ...
, marking the end of free Greece. The same year
Cornelius Scipio Aemilianus, the son of
Scipio Africanus
Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus (, , ; 236/235–) was a Roman general and statesman who was one of the main architects of Rome's victory against Ancient Carthage, Carthage in the Second Punic War. Often regarded as one of the greatest milit ...
, destroyed the city of
Carthage
Carthage was an ancient city in Northern Africa, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classic ...
, making it a Roman province.

In the following years, Rome continued its conquests in Spain with
Tiberius Gracchus
Tiberius Sempronius Gracchus (; 163 – 133 BC) was a Roman politician best known for his agrarian reform law entailing the transfer of land from the Roman state and wealthy landowners to poorer citizens. He had also served in the ...
, and it set foot in Asia, when the last king of
Pergamum
Pergamon or Pergamum ( or ; ), also referred to by its modern Greek form Pergamos (), was a rich and powerful ancient Greek city in Aeolis. It is located from the modern coastline of the Aegean Sea on a promontory on the north side of the river ...
gave his kingdom to the Roman people. The end of the 2nd century brought another threat, when a great host of
Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples were tribal groups who lived in Northern Europe in Classical antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. In modern scholarship, they typically include not only the Roman-era ''Germani'' who lived in both ''Germania'' and parts of ...
, namely
Cimbri
The Cimbri (, ; ) were an ancient tribe in Europe. Ancient authors described them variously as a Celtic, Gaulish, Germanic, or even Cimmerian people. Several ancient sources indicate that they lived in Jutland, which in some classical texts was ...
and
Teutones
The Teutons (, ; ) were an ancient northern European tribe mentioned by Roman authors. The Teutons are best known for their participation, together with the Cimbri and other groups, in the Cimbrian War with the Roman Republic in the late secon ...
, crossed the river Rhone and moved to Italy.
Gaius Marius
Gaius Marius (; – 13 January 86 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. Victor of the Cimbrian War, Cimbric and Jugurthine War, Jugurthine wars, he held the office of Roman consul, consul an unprecedented seven times. Rising from a fami ...
was consul five consecutive times (seven total), and won two decisive battles in 102 and 101 BC. He also reformed the Roman army, giving it such a good reorganisation that it remained unchanged for centuries.
The first thirty years of the last century BC were characterised by serious internal problems that threatened the existence of the Republic. The
Social War, between Rome and its allies, and the
Servile Wars
The Servile Wars were a series of three slave revolts ("servile" is derived from ''servus'', Latin for "slave") in the late Roman Republic:
* First Servile War (135−132 BC) — in Sicily, led by Eunus, a former slave claiming to be a prophet, ...
(slave uprisings) were hard conflicts, all within Italy, and forced the Romans to change their policy with regards to their allies and subjects. By then Rome had become an extensive power, with great wealth which derived from the conquered people (as tribute, food or manpower, i.e. slaves). The allies of Rome felt bitter since they had fought by the side of the Romans, and yet they were not citizens and shared little in the rewards. Although they lost the war, they finally got what they asked, and by the beginning of the 1st century AD practically all free inhabitants of Italy were Roman citizens.
However, the growth of the Imperium Romanum (Roman power) created new problems, and new demands, that the old political system of the Republic, with its annually elected magistrates and its sharing of power, could not solve.
Sulla's civil war
Sulla's civil war was fought between the Roman general Sulla and his opponents, the Cinna-Marius faction (usually called the Marians or the Cinnans after their former leaders Gaius Marius and Lucius Cornelius Cinna), in the years 83–82 BC. ...
and his later dictatorship, the extraordinary commands of
Pompey Magnus
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey ( ) or Pompey the Great, was a Roman general and statesman who was prominent in the last decades of the Roman Republic. ...
, and the first
triumvirate
A triumvirate () or a triarchy is a political institution ruled or dominated by three individuals, known as triumvirs (). The arrangement can be formal or informal. Though the three leaders in a triumvirate are notionally equal, the actual distr ...
made that clear. In January 49 BC,
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (12 or 13 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in Caesar's civil wa ...
the conqueror of Gaul,
crossed the Rubicon with his legions, occupying Rome and beginning a
civil war
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
with Pompey. In the following years, he vanquished his opponents, and ruled Rome for four years. After his assassination in 44 BC, the Senate tried to reestablish the Republic, but its champions,
Marcus Junius Brutus
Marcus Junius Brutus (; ; 85 BC – 23 October 42 BC) was a Roman politician, orator, and the most famous of the assassins of Julius Caesar. After being adopted by a relative, he used the name Quintus Servilius Caepio Brutus, which was reta ...
(descendant of the founder of the republic) and
Gaius Cassius Longinus
Gaius Cassius Longinus (; – 3 October 42 BC) was a Roman senator and general best known as a leading instigator of the plot to assassinate Julius Caesar on 15 March 44 BC. He was the brother-in-law of Brutus, another leader of the conspir ...
were defeated by Caesar's lieutenant
Marcus Antonius
Marcus Antonius (14 January 1 August 30 BC), commonly known in English as Mark Antony, was a Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the transformation of the Roman Republic from a constitutional republic into the ...
and Caesar's nephew,
Octavian
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in ...
.
The years 44–31 BC mark the struggle for power between Marcus Antonius and Octavian (later known as Augustus). Finally, on 2 September 31 BC, in the Greek promontory of
Actium, the final battle took place in the sea. Octavian was victorious, and became the sole ruler of Rome (and its empire). That date marks the end of the Republic and the beginning of the
Principate
The Principate was the form of imperial government of the Roman Empire from the beginning of the reign of Augustus in 27 BC to the end of the Crisis of the Third Century in AD 284, after which it evolved into the Dominate. The principate was ch ...
.
Roman Empire
Early Empire
By the end of the Republic, the city of Rome had achieved a grandeur befitting the capital of an empire dominating the whole of the
Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
. It was, at the time, the largest city in the world. Estimates of its peak population range from 450,000 to over 3.5 million people with estimates of 1 to 2 million being most popular with historians. This grandeur increased under
Augustus
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in A ...
, who completed Caesar's projects and added many of his own, such as the
Forum of Augustus and the
Ara Pacis
The (Latin, "Altar of Augustan Peace"; commonly shortened to ) is an altar in Rome dedicated to the Pax Romana. The monument was commissioned by the Roman Senate on July 4, 13 BC to honour the return of Augustus to Rome after three years in Hisp ...
. He is said to have remarked that he found Rome a city of brick and left it a city of marble (). Augustus's successors sought to emulate his success in part by adding their own contributions to the city. In AD 64, during the reign of
Nero
Nero Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; born Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus; 15 December AD 37 – 9 June AD 68) was a Roman emperor and the final emperor of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, reigning from AD 54 until his ...
, the
Great Fire of Rome
The Great Fire of Rome () began on 19 July 64 AD. The fire started in the merchant shops around Rome's chariot stadium, Circus Maximus. After six days, the fire was brought under control, but before the damage could be assessed, the fire reignit ...
left much of the city destroyed, but in many ways it was used as an excuse for new development.
[Tacitus, ''Annals''XV.40.]
Rome was a subsidised city at the time, with roughly 15 to 25 percent of its grain supply being paid by the central government. Commerce and industry played a smaller role compared to that of other cities like
Alexandria
Alexandria ( ; ) is the List of cities and towns in Egypt#Largest cities, second largest city in Egypt and the List of coastal settlements of the Mediterranean Sea, largest city on the Mediterranean coast. It lies at the western edge of the Nile ...
. This meant that Rome had to depend upon goods and production from other parts of the Empire to sustain such a large population. This was mostly paid by taxes that were levied by the Roman government. If it had not been subsidised, Rome would have been significantly smaller.

Rome's population declined after its apex in the 2nd century. At the end of that century, during the reign of
Marcus Aurelius
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus ( ; ; 26 April 121 – 17 March 180) was Roman emperor from 161 to 180 and a Stoicism, Stoic philosopher. He was a member of the Nerva–Antonine dynasty, the last of the rulers later known as the Five Good Emperors ...
, the
Antonine Plague
The Antonine Plague of AD 165 to 180, also known as the Plague of Galen (after Galen, the Greek physician who described it), was a prolonged and destructive epidemic, which affected the Roman Empire. It was possibly contracted and spread by so ...
killed 2,000 people a day. Marcus Aurelius died in 180, his reign being the last of the "Five Good Emperors" and Pax Romana. His son Commodus, who had been co-emperor since AD 177, assumed full imperial power, which is generally associated with the beginning of the decline of the Western Roman Empire. Rome's population was only a fraction of its peak when the Aurelian Walls, Aurelian Wall was completed in AD 273 (in that year its population was only around 500,000).
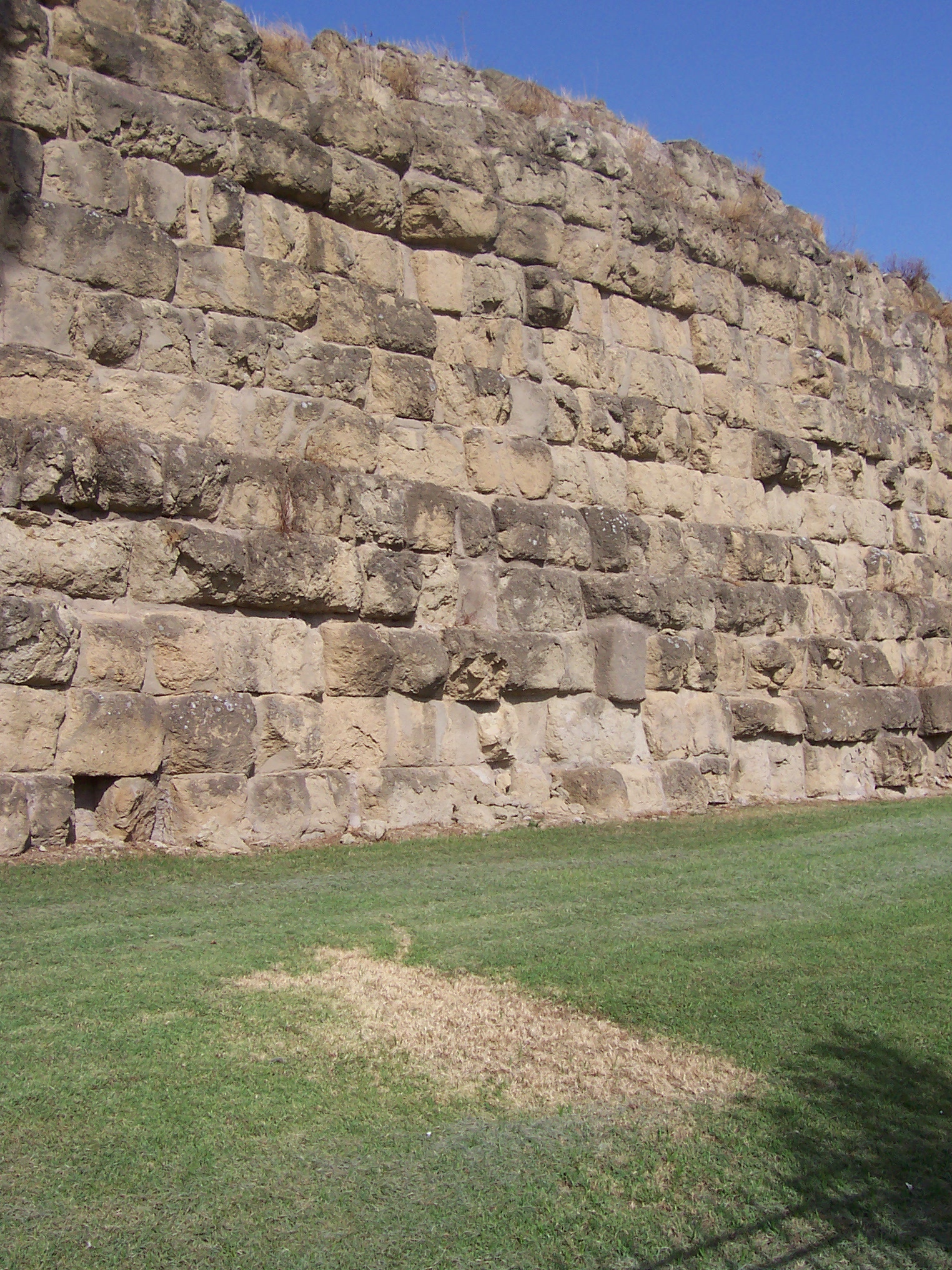
Crisis of the third century
Starting in the early 3rd century, matters changed. The "Crisis of the Third Century" defines the disasters and political troubles for the Empire, which nearly collapsed. The new feeling of danger and the menace of barbarian invasions was clearly shown by the decision of Emperor Aurelian, who at year 273 finished encircling the capital itself with a massive Aurelian Walls, wall which had a perimeter that measured close to . Rome formally remained capital of the Roman Empire, empire, but emperors spent less and less time there. At the end of 3rd century Diocletian's political reforms, Rome was deprived of its traditional role of administrative capital of the Empire. Later, Western Roman Empire, western emperors ruled from Milan or Ravenna, or cities in Gaul. In 330, Constantine I established a second capital at Constantinople.
Christianisation
Christianity reached Rome during the 1st century AD. For the first two centuries of the Christian era, Imperial authorities largely viewed Christianity simply as a Jewish sect rather than a distinct religion. No emperor issued general laws against the faith or its Church, and persecutions, such as they were, were carried out under the authority of local government officials. A surviving letter from Pliny the Younger, governor of Bythinia, to the emperor Trajan describes his persecution and executions of Christians; Trajan notably responded that Pliny should not seek out Christians nor heed anonymous denunciations, but only punish open Christians who refused to recant.
Suetonius mentions in passing that during the reign of
Nero
Nero Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; born Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus; 15 December AD 37 – 9 June AD 68) was a Roman emperor and the final emperor of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, reigning from AD 54 until his ...
"punishment was inflicted on the Christians, a class of men given to a new and mischievous Religion in ancient Rome#Superstitio and magic, superstition" (). He gives no reason for the punishment. Tacitus reports that after the
Great Fire of Rome
The Great Fire of Rome () began on 19 July 64 AD. The fire started in the merchant shops around Rome's chariot stadium, Circus Maximus. After six days, the fire was brought under control, but before the damage could be assessed, the fire reignit ...
in AD 64, some among the population held Nero responsible and that the emperor attempted to deflect blame onto the Christians.
[Tacitus, ''Annals'' s:The Annals (Tacitus)/Book 15#44, XV.44] The war against the Jews during Nero's reign, which so destabilised the empire that it led to civil war and Nero's suicide, provided an additional rationale for suppression of this 'Jewish' sect.
Diocletian undertook what was to be the Diocletianic Persecution, most severe and last major persecution of Christians, lasting from 303 to 311. Christianity had become too widespread to suppress, and in 313, the Edict of Milan made tolerance the official policy. Constantine I (sole ruler 324–337) became the first Christian emperor, and in 380 Theodosius I established Christianity as the official religion.
Christian persecution of paganism under Theodosius I, Under Theodosius, visits to the pagan temples were forbidden,
[Routery, Michael (1997]
''The First Missionary War. The Church take over of the Roman Empire'', Ch. 4, ''The Serapeum of Alexandria''
the Sacred fire of Vesta, eternal fire in the Temple of Vesta (mythology), Vesta in the Roman Forum extinguished, the Vestal Virgins disbanded, auspices and witchcraft punished. Theodosius refused to restore the Altar of Victory in the Senate House, as asked by remaining pagan Senators.
The Empire's conversion to Christianity made the Pope, Bishop of Rome (later called the Pope) the senior religious figure in the Western Empire, as officially stated in 380 by the Edict of Thessalonica. In spite of its increasingly marginal role in the Empire, Rome retained its historic prestige, and this period saw the last wave of construction activity: Constantine's predecessor Maxentius built buildings such as its basilica in the Roman Forum, Forum, Constantine himself erected the Arch of Constantine to celebrate his victory over Maxentius, and Diocletian built the greatest Baths of Diocletian, baths of all. Constantine was also the first patron of official Christian buildings in the city. He donated the Lateran Palace to the Pope, and built the first great basilica, the old St. Peter's Basilica.
Germanic invasions and collapse of the Western Empire

Still Rome remained one of the strongholds of paganism, led by the aristocrats and senators. However, the new walls did not stop the city being sacked first by Alaric I, Alaric on 24 August 410, by Genseric, Geiseric on 2 June 455, and even by general Ricimer's unpaid Roman troops (largely composed of barbarians) on 11 July 472.
This was the first time in almost 800 years that Rome had fallen to an enemy. The previous Battle of the Allia, sack of Rome had been accomplished by the Gauls under their leader Brennus (4th century), Brennus in 387 BC. The sacking of 410 is seen as a major landmark in the Decline of the Roman Empire, decline and fall of the Western Roman Empire. St. Jerome, living in Bethlehem at the time, wrote that "The City which had taken the whole world was itself taken."
[St Jerome, Letter CXXVII. :s:Nicene and Post-Nicene Fathers: Series II/Volume VI/The Letters of St. Jerome/Letter 127, ''To Principia'', paragraph 12.] These sackings of the city astonished all the Roman world. In any case, the damage caused by the sackings may have been overestimated. The population already started to decline from the late 4th century onward, although around the middle of the fifth century it seems that Rome continued to be the most populous city of the two parts of the Empire, with a population of no fewer than 650,000 inhabitants. The decline greatly accelerated following the capture of Africa Proconsularis by the Vandals. Many inhabitants now fled as the city no longer could be supplied with grain from Africa from the mid-5th century onward.
At the end of the 6th century Rome's population had reduced to around 30,000.
Many monuments were being destroyed by the citizens themselves, who stripped stones from closed temples and other precious buildings, and even burned statues to make lime for their personal use. In addition, most of the increasing number of churches were built in this way. For example, the Old Saint Peter's Basilica, first Saint Peter's Basilica was erected using spoils from the abandoned Circus of Nero.
This architectural cannibalism was a constant feature of Roman life until the Renaissance. From the 4th century, imperial edicts against stripping of stones and especially marble were common, but the need for their repetition shows that they were ineffective. Sometimes new churches were created by simply taking advantage of early Pagan temples, while sometimes changing the Pagan god or hero to a corresponding Christian saint or martyr. In this way, the Temple of Romulus and Remus became the basilica of the twin saints Santi Cosma e Damiano, Rome, Cosmas and Damian. Later, the Pantheon, Rome, Pantheon, Temple of All Gods, became the church of All Martyrs.
Eastern Roman (Byzantine) restoration

In 480, the last Western Roman emperor, Julius Nepos, was murdered and a Roman general of barbarian origin, Odoacer, declared allegiance to Eastern Roman emperor Zeno (emperor), Zeno.
Despite owing nominal allegiance to Constantinople, Odoacer and later the Ostrogoths continued, like the last emperors, to rule Italy as a virtually independent realm from Ravenna. Meanwhile, the Senate, even though long since stripped of wider powers, continued to administer Rome itself, with the Pope usually coming from a senatorial family. This situation continued until Theodahad murdered Amalasuntha, a pro-imperial Gothic queen, and usurped the power in 535. The List of Byzantine emperors, Eastern Roman emperor, Justinian I (reigned 527–565), used this as a pretext to send forces to Italy under his famed general Belisarius, recapturing the city next year, on 9 December AD 536. In 537–538, the Eastern Romans successfully defended the city in a Siege of Rome (537–538), year-long siege against the Ostrogothic army, and eventually took Ravenna, too.
Gothic resistance revived however, and on 17 December 546, the Ostrogoths under Totila recaptured and Sack of Rome (546), sacked Rome. Belisarius soon recovered the city, but the Ostrogoths retook it in 549. Belisarius was replaced by Narses, who captured Rome from the Ostrogoths for good in 552, ending the so-called Gothic War (535–554), Gothic Wars which had devastated much of Italy. The continual war around Rome in the 530s and 540s left it in a state of total disrepair – near-abandoned and desolate with much of its lower-lying parts turned into unhealthy marshes as the drainage systems were neglected and the Tiber's embankments fell into disrepair in the course of the latter half of the 6th century. Here, malaria developed. The Roman aqueduct, aqueducts, except for one, were not repaired. The population, without imports of grain and oil from Sicily, shrank to less than 50,000 concentrated near the
Tiber
The Tiber ( ; ; ) is the List of rivers of Italy, third-longest river in Italy and the longest in Central Italy, rising in the Apennine Mountains in Emilia-Romagna and flowing through Tuscany, Umbria, and Lazio, where it is joined by the R ...
and around the Campus Martius, abandoning those districts without water supply. There is a legend, significant though untrue, that there was a moment where no one remained living in Rome.
Justinian I provided grants for the maintenance of public buildings, aqueducts and bridges—though, being mostly drawn from an
Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
dramatically impoverished by the recent wars, these were not always sufficient. He also styled himself the patron of its remaining scholarly method, scholars, orators, physicians and lawyers in the stated hope that eventually more youths would seek a better education. After the wars, the Senate was theoretically restored, but under the supervision of the Praefectus urbi, urban prefect and other officials appointed by, and responsible to, the Eastern Roman authorities in Ravenna.
However, the Pope was now one of the leading religious figures in the entire Byzantine Roman Empire and effectively more powerful locally than either the remaining senators or local Eastern Roman (Byzantine) officials. In practice, local power in Rome devolved to the Pope and, over the next few decades, both much of the remaining possessions of the senatorial aristocracy and the local Byzantine Roman administration in Rome were absorbed by the Catholic Church, Church.
The reign of Justinian's nephew and successor Justin II (reigned 565–578) was marked from the
Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, a Romance ethnic group related to or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance languag ...
point of view by the invasion of the Lombards under Alboin (568). In capturing the regions of Benevento, Lombardy, Piedmont, Spoleto and
Tuscany
Tuscany ( ; ) is a Regions of Italy, region in central Italy with an area of about and a population of 3,660,834 inhabitants as of 2025. The capital city is Florence.
Tuscany is known for its landscapes, history, artistic legacy, and its in ...
, the invaders effectively restricted Imperial authority to small islands of land surrounding a number of coastal cities, including Ravenna,
Naples
Naples ( ; ; ) is the Regions of Italy, regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 908,082 within the city's administrative limits as of 2025, while its Metropolitan City of N ...
,
Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
and the area of the future Venice. The one inland city continuing under Eastern Roman control was Perugia, which provided a repeatedly threatened overland link between Rome and Ravenna. In 578 and again in 580, the Senate, in some of its last recorded acts, had to ask for the support of Tiberius II Constantine (reigned 578–582) against the approaching Dukes, Faroald I of Spoleto and Zotto of Duchy of Benevento, Benevento.
Maurice (emperor), Maurice (reigned 582–602) added a new factor in the continuing conflict by creating an alliance with Childebert II, Childebert II of Austrasia (reigned 575–595). The armies of the List of Frankish kings, Frankish King invaded the Lombard territories in 584, 585, 588 and 590. Rome had suffered badly from a disastrous flood of the Tiber in 589, described by Paul the Deacon as a "swarm of snakes." This was followed by a plague in 590, which was notable for the legend of the angel seen, while the newly elected Pope Gregory I (term 590–604) was passing in procession by Castel Sant'Angelo, Hadrian's Tomb, to hover over the building and to sheathe his flaming sword as a sign that the pestilence was about to cease.
The city was safe from capture at least.
Agilulf, however, the new Lombard King (reigned 591 to c. 616), managed to secure peace with Childebert II, Childebert, reorganised his territories and resumed activities against both Naples and Rome by 592. With the Emperor preoccupied with wars in the eastern borders and the various succeeding Exarchs unable to secure Rome from invasion, Gregory took personal initiative in starting negotiations for a peace treaty. This was completed in the autumn of 598—later recognised by Maurice—lasting until the end of his reign.
The position of the Pope, Bishop of Rome was further strengthened under the usurper Phocas (reigned 602–610). Phocas recognised his primacy over that of the Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople, Patriarch of Constantinople and even decreed Pope Boniface III (607) to be "the head of all the Christian Church, Churches". Phocas's reign saw the erection of the last imperial monument in the Roman Forum, the column of Phocas, column bearing his name. He also gave the Pope the Pantheon, Rome, Pantheon, at the time closed for centuries, and thus probably saved it from destruction.
During the 7th century, an influx of both Byzantine Roman officials and churchmen from elsewhere in the empire made both the local lay aristocracy and Church leadership largely Greek speaking. The population of Rome, a magnet for pilgrims, may have increased to 90,000. Eleven of thirteen popes between 678 and 752 were of Greek or Syrian descent. However, the strong Byzantine Roman cultural influence did not always lead to political harmony between Rome and Constantinople. In the controversy over Monothelitism, popes found themselves under severe pressure (sometimes amounting to physical force) when they failed to keep in step with Constantinople's shifting theological positions. In 653, Pope Martin I was deported to Constantinople and, after a show trial, exiled to the Crimea, where he died.
Then, in 663, Rome had its first imperial visit for two centuries, by Constans II—its worst disaster since the Gothic Wars when the Emperor proceeded to strip Rome of metal, including that from buildings and statues, to provide armament materials for use against the Saracens. However, for the next half century, despite further tensions, Rome and the Papacy continued to prefer continued Byzantine Roman rule: in part because the alternative was Lombard rule, and in part because Rome's food was largely coming from Papal estates elsewhere in the Empire, particularly
Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
.
Medieval Rome
Break with Constantinople and formation of the Papal States
In 727, Pope Gregory II refused to accept the decrees of Emperor Leo III the Isaurian, Leo III, which promoted the Emperor's Byzantine Iconoclasm, iconoclasm. Leo reacted first by trying in vain to abduct the Pontiff, and then by sending a force of Exarchate of Ravenna, Ravennate troops under the command of the Exarch Paulus, but they were pushed back by the Lombards of Tuscia and Benevento. Byzantine general Eutychius (exarch), Eutychius sent west by the Emperor successfully captured Rome and restored it as a part of the empire in 728.
On 1 November 731, a council was called in St. Peter's Basilica, St. Peter's by Pope Gregory III, Gregory III to excommunicate the iconoclasts. The Emperor responded by confiscating large Papal estates in
Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
and Calabria and transferring areas previously ecclesiastically under the Pope to the Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople, Patriarch of Constantinople. Despite the tensions Gregory III never discontinued his support to the imperial efforts against external threats.
In this period the Lombard kingdom revived under the leadership of King Liutprand, King of the Lombards, Liutprand. In 730, he razed the countryside of Rome to punish the Pope, who had supported Duke Transamund II of Spoleto.
Though still protected by his massive walls, the Pope could do little against the Lombard king, who managed to ally himself with the Byzantines.
Other protectors were now needed. Gregory III was the first Pope to ask for concrete help from the Frankish Kingdom, then under the command of Charles Martel (739).
Liutprand's successor Aistulf was even more aggressive. He conquered Ferrara and Ravenna, ending the Exarchate of Ravenna. Rome seemed his next victim. In 754, Pope Stephen II went to France to name Pepin the Short, Pippin the Younger, king of the Franks, as ''patricius Romanorum'', i.e. protector of Rome. In the August of that year the King and Pope together crossed back the Alps and defeated Aistulf at Pavia. When Pippin went back to St. Denis however, Aistulf did not keep his promises, and in 756 besieged Rome for 56 days. The Lombards returned north when they heard news of Pippin again moving to Italy. This time he agreed to give the Pope the promised territories, and the
Papal States
The Papal States ( ; ; ), officially the State of the Church, were a conglomeration of territories on the Italian peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope from 756 to 1870. They were among the major states of Italy from the 8th c ...
were born.
In 771 the new King of the Lombards, Desiderius, devised a plot to conquer Rome and seize Pope Stephen III during a feigned pilgrimage within its walls. His main ally was one Paulus Afiarta, chief of the Lombard party within the city. He conquered Rome in 772 but angered Charlemagne. However the plan failed, and Stephen's successor, Pope Adrian I, Pope Hadrian I called Charlemagne against Desiderius, who was finally defeated in 773. The Lombard Kingdom was no more, and now Rome entered into the orbit of a new, greater political institution.
Numerous remains from this period, along with a museum devoted to Medieval Rome, can be seen at Museo Nazionale Romano Crypta Balbi, Crypta Balbi in Rome.
Formation of the Holy Roman Empire
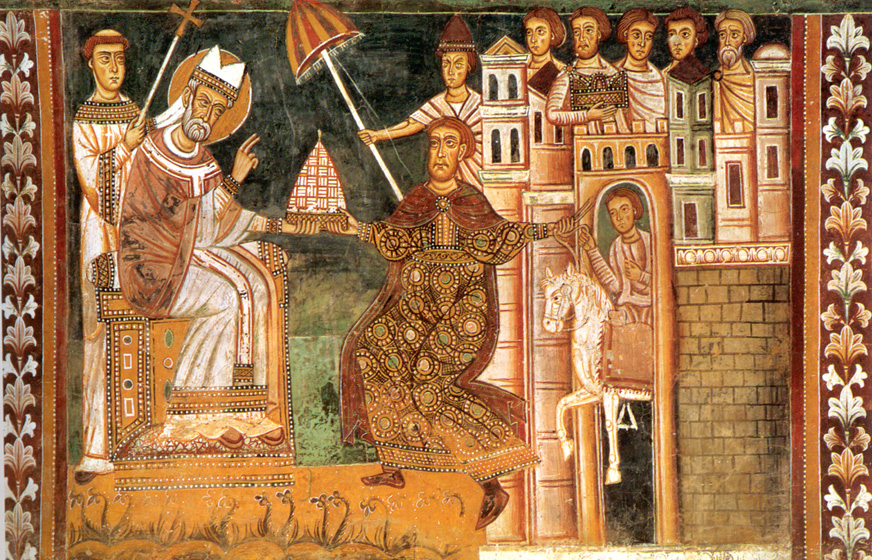

On 25 April 799 the new Pope, Pope Leo III, Leo III, led the traditional procession from the Lateran to the Church of San Lorenzo in Lucina along the Via Flaminia (now Via del Corso). Two nobles (followers of his predecessor Hadrian) who disliked the weakness of the Pope with regards to Charlemagne, attacked the processional train and delivered a life-threatening wound to the Pope. Leo fled to the King of the Franks, and in November, 800, the King entered Rome with a strong army and a number of French bishops. He declared a judicial trial to decide if Leo III were to remain Pope, or if the deposers' claims had reasons to be upheld. This trial, however, was only a part of a well thought out chain of events which ultimately surprised the world. The Pope was declared legitimate and the attempters subsequently exiled. On 25 December 800, Pope Leo III crowned Charlemagne Holy Roman Emperor in St. Peter's Basilica.
This act forever severed the loyalty of
Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
from its imperial progenitor, Constantinople. It created instead a rival empire which, after a long series of conquests by Charlemagne, now encompassed most of the Christian Western territories.
Following the death of Charlemagne, the lack of a figure with equal prestige led the new institution into disagreement. At the same time the universal Catholic Church, church of Rome had to face emergence of the lay interests of the City itself, spurred on by the conviction that the Roman people, though impoverished and abased, had again the right to elect the Western Emperor. The famous counterfeit document called the ''Donation of Constantine'', prepared by the Papal notaries, guaranteed to the Pope a dominion stretching from Ravenna to Gaeta. This nominally included the suzerainty over Rome, but this was often highly disputed, and as the centuries passed, only the strongest Popes were to be able to assert it. The main element of weakness of the Papacy within the walls of the city was the continued necessity of the election of new popes, in which the emerging noble families soon managed to insert a leading role for themselves. The neighbouring powers, namely the Duchy of Spoleto and Tuscany, Toscana, and later the Emperors, learned how to take their own advantage of this internal weakness, playing the role of arbiters among the contestants.
Rome was indeed prey of anarchy in this age. The lowest point was touched in 897, when a raging crowd exhumed the corpse of a dead pope, Pope Formosus, Formosus, and Cadaver Synod, put it on trial.
Roman Commune
From 1048 to 1257, the papacy experienced increasing conflict with the leaders and churches of the Holy Roman Empire and the Byzantine (Eastern Roman) Empire. The latter culminated in the East-West Schism, dividing the Catholic Church and Eastern Orthodox Church. From 1257 to 1377, the pope, though the bishop of Rome, resided in Viterbo, Orvieto, and Perugia, and then Avignon. The return of the popes to Rome after the Avignon Papacy was followed by the Western Schism: the division of the western church between two, and for a time three, competing papal claimants.
In this period the renovated Catholic Church, Church was again attracting pilgrims and prelates from all the Christian world, and money with them: even with a population of only 30,000, Rome was again becoming a city of consumers dependent upon the presence of a governmental bureaucracy. In the meantime, Italian cities were acquiring increasing autonomy, mainly led by new families which were replacing the old aristocracy with a new class formed by entrepreneurs, traders and merchants. After the sack of Rome by the Italo-Norman, Normans in 1084, the rebuilding of the city was supported by powerful families such as the Frangipani family, Frangipane family and the Pierleoni family, whose wealth came from commerce and banking rather than landholdings. Inspired by neighbouring cities like Tivoli, Italy, Tivoli and Viterbo, Rome's people began to consider adopting a communal status and gaining a substantial amount of freedom from papal authority.
Led by Giordano Pierleoni, the Romans rebelled against the aristocracy and Church rule in 1143. The Senate and the Roman Republic, the Commune of Rome, were born again. Through the inflammatory words of preacher Arnold of Brescia, Arnaldo da Brescia, an idealistic, fierce opponent of ecclesiastical property and church interference in temporal affairs, the revolt that led to the creation of the Commune of Rome continued until it was put down in 1155, though it left its mark on the civil government of the Eternal City for centuries. 12th-century Rome, however, had little in common with the empire which had ruled over the Mediterranean some 700 years before, and soon the new Senate had to work hard to survive, choosing an ambiguous policy of shifting its support from the Pope to the
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
and vice versa as the political situation required. At Battle of Monte Porzio, Monteporzio, in 1167, during one of these shifts, in the war with Tusculum, Roman troops were defeated by the imperial forces of Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor, Frederick Barbarossa. Luckily, the winning enemies were soon dispersed by a plague and Rome was saved.

In 1188 the new communal government was finally recognised by Pope Clement III. The Pope had to make large cash payments to the communal officials, while the 56 senators became papal vassals. The Senate always had problems in the accomplishment of its function, and various changes were tried. Often a single Senator was in charge. This sometimes led to tyrannies, which did not help the stability of the newborn organism.
Guelphs and Ghibellines
In 1204 the streets of Rome were again in flames when the struggle between Pope Innocent III, Pope Innocent III's family and its rivals, the powerful Orsini family, led to riots in the city. Many ancient buildings were then destroyed by machines used by the rival bands to besiege their enemies in the innumerable towers and strongholds which were a hallmark of the Middle Age Italian towns.
The struggle between the Popes and the emperor Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor, Frederick II, also king of
Naples
Naples ( ; ; ) is the Regions of Italy, regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 908,082 within the city's administrative limits as of 2025, while its Metropolitan City of N ...
and
Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
, saw Rome support the Guelphs and Ghibellines, Ghibellines. To repay his loyalty, Frederick sent to the commune the Carroccio he had won from the Lombardy, Lombards at the battle of Cortenuova in 1234, and which was exposed in the Capitoline Hill, Campidoglio.
In that year, during another revolt against the Pope, the Romans headed by senator Luca Savelli sacked the Lateran. Savelli was the father of Pope Honorius IV, Honorius IV, but in that age family ties often did not determine one's allegiance.
Rome was never to evolve into an autonomous, stable reign, as happened to other communes like
Florence
Florence ( ; ) is the capital city of the Italy, Italian region of Tuscany. It is also the most populated city in Tuscany, with 362,353 inhabitants, and 989,460 in Metropolitan City of Florence, its metropolitan province as of 2025.
Florence ...
, Siena or Milan. The endless struggles between noble families (Savelli family, Savelli, Orsini family, Orsini, Colonna family, Colonna, Annibaldi family, Annibaldi), the ambiguous position of the Popes, the haughtiness of a population which never abandoned the dreams of their splendid past but, at the same time, thought only of immediate advantage, and the weakness of the republican institutions always deprived the city of this possibility.
In an attempt to imitate more successful communes, in 1252 the people elected a foreign Senator, the Bologna, Bolognese Brancaleone degli Andalò. In order to bring peace in the city he suppressed the most powerful nobles (destroying some 140 towers), reorganised the working classes and issued a code of laws inspired by those of northern Italy. Brancaleone was a tough figure, but died in 1258 with almost nothing of his reforms turned into reality. Five years later Charles I of Naples, Charles I of Anjou, then king of Kingdom of Naples, Naples, was elected Senator. He entered the city only in 1265, but soon his presence was needed to face Conradin, the House of Hohenstaufen, Hohenstaufen's heir who was coming to claim his family's rights over southern Italy, and left the city. After June 1265 Rome was again a democratic republic, electing Henry of Castile the Senator, Henry of Castile as senator. But Conradin and the Ghibelline party were crushed in the Battle of Tagliacozzo (1268), and therefore Rome fell again in the hands of Charles.
Pope Nicholas III, Nicholas III, a member of Orsini family, was elected in 1277 and moved the seat of the List of popes, Popes from the Lateran Palace, Lateran to the more defensible Vatican City, Vatican. He also ordered that no foreigner could become senator of Rome. Being a Roman himself, he had himself elected senator by the people. With this move, the city began again to side for the papal party. In 1285 Charles was again Senator, but the Sicilian Vespers reduced his charisma, and the city was thenceforth free from his authority. The next senator was again a Roman, and again a pope, Pope Honorius IV, Honorius IV of the Savelli.
Boniface VIII and the Avignon captivity
The successor to Pope Celestine V, Celestine V was a Roman of the Caetani family, Pope Boniface VIII, Boniface VIII. Entangled in a local feud against the traditional rivals of his family, the Colonna family, Colonna, at the same time he struggled to assure the universal supremacy of the Holy See. In 1300 he launched the first Jubilee (Christian), Jubilee and in 1303 founded the Sapienza University of Rome, first University of Rome.
The Jubilee was an important move for Rome, as it further increased its international prestige and, most of all, the city's economy was boosted by the flow of pilgrims.
Boniface died in 1303 after the humiliation of the ''Anagni, Schiaffo di Anagni'' ("Slap of Anagni"), which signalled instead the rule of the France, King of France over the Pope, Papacy and marked another period of decline for Rome.
Boniface's successor, Pope Clement V, Clement V, never entered the city, starting the so-called "Avignon Papacy, Avignon captivity", the absence of the Popes from their Roman seat in favour of Avignon, which would last for more than 70 years.
[Morris, Colin, ''The papal monarchy: the Western church from 1050 to 1250 '', (Oxford University Press, 2001), 271.] This situation brought the independence of the local powers, but these were revealed to be largely unstable; and the lack of the holy revenues caused a deep decay of Rome.
For more than a century Rome had no new major buildings. Furthermore, many of the monuments of the city, including the main churches, began to fall into ruin.
Cola di Rienzo and the Pope's return to Rome

In spite of its decline and the absence of the Pope, Rome had not lost its spiritual prestige: in 1341 the famous poet Petrarch, Petrarca came to the city to be crowned as Poet laureate in Capitoline Hill. Noblemen and poor people at one time demanded with one voice the return of the Pope. Among the many ambassadors that in this period took their way to Avignon, emerged the bizarre but eloquent figure of Cola di Rienzo. As his personal power among the people increased by time, on 20 May 1347 he conquered the Capitoline at the head of an enthusiastic crowd. The period of his power, though very short-lived, aspired to the prestige of Ancient Rome. Now in possession of dictatorial powers, he took the title of "tribune", referring to the plebs, pleb's tribune, magistracy of the
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establis ...
. Cola also considered himself at an equal status of that of the Holy Roman Emperor. On 1 August, he conferred Roman citizenship on all the Italian cities, and even prepared for the election of a Roman emperor of Italy. It was too much: the Pope denounced him as heretic, criminal and pagan, the populace had begun to be disenchanted with him, while the nobles had always hated him. On 15 December, he was forced to flee.

In August 1354, Cola was again a protagonist, when Cardinal Gil Álvarez Carrillo de Albornoz, Gil Alvarez De Albornoz entrusted him with the role of "senator of Rome" in his programme of reassuring the Pope's rule in the
Papal States
The Papal States ( ; ; ), officially the State of the Church, were a conglomeration of territories on the Italian peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope from 756 to 1870. They were among the major states of Italy from the 8th c ...
. In October the tyrannical Cola, who had become again very unpopular for his delirious behaviour and heavy bills, was killed in a riot provoked by the powerful family of the Colonna family, Colonna. In April 1355, Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles IV of Bohemia entered the city for the ritual coronation as Emperor. His visit was very disappointing for the citizens. He had little money, received the crown not from the Pope but from a Cardinal, and moved away after a few days.
With the emperor back in his lands, Albornoz could regain a certain control over the city, while remaining in his safe citadel in Montefiascone, in the Northern Lazio. The senators were chosen directly by the Pope from several cities of Italy, but the city was in fact independent. The Senate council included six judges, five notaries, six marshals, several familiars, twenty knights and twenty armed men. Albornoz had heavily suppressed the traditional aristocratic families, and the "democratic" party felt confident enough to start an aggressive policy. In 1362 Rome declared war on Velletri. This move, however, provoked a civil war. The countryside party hired a condottieri band called "Del Cappello" ("Hat"), while the Romans bought the services of Germany, German and Hungary, Hungarian troops, plus a citizen levy of 600 knights and even 22,000 infantry. This was the period in which condottieri bands were active in Italy. Many of the Savelli, Orsini and Annibaldi expelled from Rome became leaders of such military units. The war with Velletri languished, and Rome again gave itself to the new Pope, Pope Urban V, Urban V, provided Albornoz did not enter the walls.
On 16 October 1367, in reply to the prayers of Brigid of Kildare, St Brigid and Petrarch, Petrarca, Urban finally visited for the city. During his presence, Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles IV was again crowned in the city (October 1368). In addition, the Byzantine Empire, Byzantine emperor John V Palaiologos, John V Palaeologus came in Rome to beg for a crusade against the Ottoman Empire, but in vain. However, Urban did not like the unhealthy air of the city, and on 5 September 1370 he sailed again to Avignon. His successor, Pope Gregory XI, Gregory XI, officially set the date of his return to Rome at May 1372, but again the France, French cardinals and the King stopped him.
Only on 17 January 1377, Gregory XI could finally reinstate the Holy See in Rome.
Western schism and conflict with Milan
The incoherent behaviour of his successor, the Italian Pope Urban VI, Urban VI, provoked in 1378 the
Western Schism
The Western Schism, also known as the Papal Schism, the Great Occidental Schism, the Schism of 1378, or the Great Schism (), was a split within the Catholic Church lasting from 20 September 1378 to 11 November 1417, in which bishops residing ...
, which impeded any true attempt of improving the conditions of the decaying Rome.
The 14th century, with the absence of the popes during the
Avignon Papacy
The Avignon Papacy (; ) was the period from 1309 to 1376 during which seven successive popes resided in Avignon (at the time within the Kingdom of Arles, part of the Holy Roman Empire, now part of France) rather than in Rome (now the capital of ...
, had been a century of neglect and misery for the city of Rome, which dropped to its lowest level of population.
With the return of the papacy to Rome repeatedly postponed because of the bad conditions of the city and the lack of control and security, it was first necessary to strengthen the political and doctrinal aspects of the pontiff.
When in 1377 Gregory XI was in fact returned to Rome, he found a city in anarchy because of the struggles between the nobility and the popular faction, and in which his power was now more formal than real. There followed four decades of instability, characterised by the local power struggle between the commune and the papacy, and internationally by the great
Western Schism
The Western Schism, also known as the Papal Schism, the Great Occidental Schism, the Schism of 1378, or the Great Schism (), was a split within the Catholic Church lasting from 20 September 1378 to 11 November 1417, in which bishops residing ...
, at the end of which was elected Pope, Martin V. He restored order, laying the foundations of its rebirth.

In 1433 the List of rulers of Milan, Duke of Milan, Filippo Maria Visconti signed a peace treaty with
Florence
Florence ( ; ) is the capital city of the Italy, Italian region of Tuscany. It is also the most populated city in Tuscany, with 362,353 inhabitants, and 989,460 in Metropolitan City of Florence, its metropolitan province as of 2025.
Florence ...
and Republic of Venice, Venice. He then sent the condottieri Niccolò Fortebraccio and Francesco I Sforza, Francesco Sforza to harass the
Papal States
The Papal States ( ; ; ), officially the State of the Church, were a conglomeration of territories on the Italian peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope from 756 to 1870. They were among the major states of Italy from the 8th c ...
, in vengeance for Pope Eugene IV, Eugene IV's support to the two former republics.
Fortebraccio, supported by the Colonna family, Colonna, occupied Tivoli in October 1433 and ravaged Rome's countryside. Despite the concessions made by Eugene to the Visconti, the Milanese soldiers did not stop their destruction. This led the Romans, on 29 May 1434 to institute a Republican government under the ''Banderesi''. Eugene left the city a few days later, during the night of 4 June.
However, the ''Banderesi'' proved incapable of governing the city, and their inadequacies and violence soon deprived them of popular support. The city was therefore returned to Eugene by the army of Giovanni Vitelleschi on 26 October 1434. After the death in mysterious circumstances of Vitelleschi, the city came under the control of Ludovico Scarampo, List of bishops and patriarchs of Aquileia, Patriarch of Aquileia. Eugene returned to Rome on 28 September 1443.
Renaissance Rome
The latter half of the 15th century saw the seat of the Italian Renaissance move to Rome from
Florence
Florence ( ; ) is the capital city of the Italy, Italian region of Tuscany. It is also the most populated city in Tuscany, with 362,353 inhabitants, and 989,460 in Metropolitan City of Florence, its metropolitan province as of 2025.
Florence ...
. The Papacy wanted to surpass the grandeur of other Italian cities. To this end the popes created increasingly extravagant churches, bridges, town squares and public spaces, including a new St. Peter's Basilica, Saint Peter's Basilica, the Sistine Chapel, ''Ponte Sisto'' (the first bridge to be built across the
Tiber
The Tiber ( ; ; ) is the List of rivers of Italy, third-longest river in Italy and the longest in Central Italy, rising in the Apennine Mountains in Emilia-Romagna and flowing through Tuscany, Umbria, and Lazio, where it is joined by the R ...
since antiquity), and Piazza Navona. The Popes were also patrons of the arts engaging such artists as Michelangelo, Pietro Perugino, Perugino, Raphael, Domenico Ghirlandaio, Ghirlandaio, Luca Signorelli, Sandro Botticelli, Botticelli, and Cosimo Rosselli.
Under Pope Nicholas V, who became Pontiff on 19 March 1447, the Renaissance can be said to have begun in Rome, heralding a period in which the city became the centre of Humanism. He was the first Pope to embellish the Roman court with scholars and artists, including Lorenzo Valla and Vespasiano da Bisticci.
On 4 September 1449 Nicholas proclaimed a Jubilee (Christianity), Jubilee for the following year, which saw a great influx of pilgrims from all Europe. The crowd was so large that in December, on Ponte Sant'Angelo, some 200 people died, crushed underfoot or drowned in the River Tiber. Later that year the Plague (disease), Plague reappeared in the city, and Nicholas fled.

However Nicholas brought stability to the temporal power of the Papacy, a power in which the Emperor was to have no part at all. In this way, the coronation and the marriage of Frederick III, Holy Roman Emperor on 16 March 1452, was more a civil ceremony. The Papacy now controlled Rome with a strong hand. A plot by Stefano Porcari, whose aim was the restoration of the Republic, was ruthlessly suppressed in January 1453. Porcari was hanged together with the other plotters, Francesco Gabadeo, Pietro de Monterotondo, Battista Sciarra and Angiolo Ronconi, but the Pope gained a treacherous reputation, as when the execution was beginning he was too drunk to confirm the grace he had previously given to Sciarra and Ronconi.
Nicholas was also actively involved in Rome's urban renewal, in collaboration with Leon Battista Alberti, including the construction of a new St. Peter's Basilica, St Peter's Basilica.

Nicholas' successor Pope Callixtus III, Calixtus III neglected Nicholas's cultural policies, instead devoting himself to his greatest passion, his nephews. The Tuscany, Tuscan Pope Pius II, Pius II, who took the reins after his death in 1458, was a great Humanist, but did little for Rome. During his reign Lorenzo Valla demonstrated that the Donation of Constantine was a forgery. Pius was the first Pope to use guns, in campaign against the rebel barons Savelli in the neighbourhood of Rome, in 1461. One year later the bringing to Rome of the head of the Apostles in the New Testament, Apostle Saint Andrew, St. Andrew produced a great number of pilgrims. The reign of Pope Paul II (1464–1471) was notable only for the reintroduction of the Carnival, which was to become a very popular feast in Rome in the following centuries. In the same year (1468) a plot against the Pope was uncovered, organised by the intellectuals of the Roman Academies, Roman Academy founded by Julius Pomponius Laetus, Pomponio Leto. The conspirators were sent to Castel Sant'Angelo.

More important by far was the Pontificate of Pope Sixtus IV, Sixtus IV, considered the first Pope-King of Rome. In order to favour his relative Girolamo Riario, he promoted the unsuccessful Pazzi, Congiura dei Pazzi against the House of Medici, Medici of Florence (26 April 1478) and in Rome fought the Colonna family, Colonna and the Orsini family, Orsini. The personal politics of intrigue and war required much money, but in spite of this Sixtus was a true patron of art in the manner of Pope Nicholas V, Nicholas V. He reopened the academy and reorganised the Collegio degli Abbreviatori, and in 1471 began the construction of the Vatican Library, whose first curator was Platina. The Library was officially founded on 15 June 1475. He restored several churches, including Santa Maria del Popolo, the Aqua Virgo and the Hospital of the Holy Spirit; paved several streets and also built a famous bridge over the Tiber river, which still bears his name. His main building project was the Sistine Chapel in the Apostolic Palace, Vatican Palace. Its decoration called on some of the most renowned artists of the age, including Mino da Fiesole, Sandro Botticelli, Domenico Ghirlandaio, Pietro Perugino, Luca Signorelli and Pinturicchio, and in the 16th century Michelangelo decorated the ceiling with his famous masterpiece, contributing to what became one of the most famous monuments of the world. Sixtus died on 12 August 1484.
Chaos, corruption and nepotism appeared in Rome under the reign of his successors, Pope Innocent VIII, Innocent VIII and Pope Alexander VI (1492–1503). During the vacation period between the death of the former and the election of the latter there were 220 murders in the city. Alexander had to face Charles VIII of France, who invaded Italy in 1494 and entered Rome on 31 December of that year. The Pope could only barricade himself into Castel Sant'Angelo, which had been turned into a true fortress by Antonio da Sangallo the Younger. In the end, the skilful Alexander was able to gain the support of the king, assigning his son Cesare Borgia as military counsellor for the subsequent invasion of the Kingdom of Naples. Rome was safe and, as the King directed himself southwards, the Pope again changed his position, joining the anti-French League of the Italian States which finally compelled Charles to flee to France.
The most nepotist Pope of all, Alexander, favoured his ruthless son Cesare, creating for him a personal Duchy out of territories of the
Papal States
The Papal States ( ; ; ), officially the State of the Church, were a conglomeration of territories on the Italian peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope from 756 to 1870. They were among the major states of Italy from the 8th c ...
, and banning from Rome Cesare's most relentless enemy, the Orsini family. In 1500 the city hosted a new Jubilee, but grew ever more unsafe as, especially at night, the streets were controlled by bands of lawless "bravi". Cesare himself assassinated Alfonso of Bisceglie; as well as, presumably, the Pope's son, Giovanni of Gandia.
The Renaissance had a great impact on Rome's appearance, with works like the ''Pietà'' by Michelangelo and the frescoes of the Borgia Apartment, all made during Innocent's reign. Rome reached the highest point of splendour under Pope Julius II (1503–1513) and his successors Pope Leo X, Leo X and Pope Clement VII, Clement VII, both members of the Medici family. During this twenty-year period Rome became the greatest centre of art in the world. The old St. Peter's Basilica was demolished and a new one begun. The city hosted artists like Donato Bramante, Bramante, who built the Temple of San Pietro in Montorio and planned a great project to renovate the Vatican; Raphael, who in Rome became the most famous painter in Italy, creating frescos in the Niccoline Chapel, Cappella Niccolina, the Villa Farnesina, the Raphael Rooms, Raphael's Rooms, and many other famous paintings. Michelangelo began the decoration of the ceiling of the Sistine Chapel and executed the famous statue of Moses (Michelangelo), Moses for the tomb of Julius. Rome lost in part its religious character, becoming increasingly a true Renaissance city, with a great number of popular feasts, horse races, parties, intrigues and licentious episodes. Its economy was prosperous, with the presence of several Tuscan bankers, including Agostino Chigi, a friend of Raphael and a patron of the arts. Despite his premature death, and to his eternal credit, Raphael also promoted for the first time the preservation of the ancient ruins.
Sack of Rome (1527)

In 1527 the ambiguous policy followed by the second House of Medici, Medici Pope, Pope Clement VII, resulted in the dramatic Sack of Rome (1527), sack of the city by the unruly Holy Roman Empire, Imperial troops of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor. After the execution of some 1,000 defenders, the pillage began.
The city was devastated for several days, many of the citizens were killed or took shelter outside the walls. Of 189 Swiss Guards on duty only 42 survived.
The Pope himself was imprisoned for months in Castel Sant'Angelo. The sack marked the end of one of the most splendid eras of modern Rome.
The 1525's Jubilee resulted in a farce, as Martin Luther's claims had spread criticism and even hatred against the Pope's greed throughout Europe. The prestige of Rome was then challenged by the defections of the churches of Germany and England. Pope Paul III (1534–1549) tried to recover the situation by summoning the Council of Trent, although being, at the same time, the most nepotist Pope of all. He even separated Parma and Piacenza from the
Papal States
The Papal States ( ; ; ), officially the State of the Church, were a conglomeration of territories on the Italian peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope from 756 to 1870. They were among the major states of Italy from the 8th c ...
to create an independent Duchy of Parma, duchy for his son Pier Luigi Farnese, Duke of Parma, Pier Luigi.
He continued the patronage of art supporting the Michelangelo's ''Last Judgment'', asking him to renovate the Capitoline Hill, Campidoglio and the ongoing construction of St. Peter's Basilica, St. Peter's. After the shock of the sack, he also called the brilliant architect Giuliano da Sangallo, Giuliano da Sangallo the Younger to strengthen the walls of the Leonine City.
The need for renovation in the religious customs became evident in the vacancy period after Paulus' death, when the streets of Rome became seat of masked carousels which satirised the Cardinals attending the Papal conclave, conclave. His two immediate successors were feeble figures who did nothing to escape the actual Spanish suzerainty over Rome.
Counter-Reformation
Pope Paul IV, elected in 1555, was a member of the anti-Spanish party in the Italian War of 1551–59, but his policy resulted in the Kingdom of Naples, Neapolitan troops of the viceroy again besieging Rome in 1556. Paul sued for peace, but had to accept the supremacy of Philip II of Spain.
He was one of the most hated Popes of all, and, after his death the raging populace burned the Inquisition, Holy Inquisition's palace and destroyed his marble statue on the Campidoglio.
Pope Paul's
Counter-Reformation
The Counter-Reformation (), also sometimes called the Catholic Revival, was the period of Catholic resurgence that was initiated in response to, and as an alternative to or from similar insights as, the Protestant Reformations at the time. It w ...
views are well shown by his order that a central area of Rome, around the ''Porticus Octaviae'', be delimited, creating the famous Roman Ghetto, the very constricted area in which the city's Jews were forced to live in seclusion. They had to remain in the rioni of Rome, rione Sant'Angelo (rione of Rome), Sant'Angelo and locked in at night. The Pope decreed that Jews should wear a distinctive sign, yellow hats for men and veils or shawls for women. Jewish ghettos existed in Europe for the next 315 years.
The
Counter-Reformation
The Counter-Reformation (), also sometimes called the Catholic Revival, was the period of Catholic resurgence that was initiated in response to, and as an alternative to or from similar insights as, the Protestant Reformations at the time. It w ...
gained pace under his successors, the milder Pope Pius IV and the severe Pope Pius V. The former was a nepotist lover of court splendours, but more severe customs arrived anyway through the ideas of his advisor, the prelate Charles Borromeo, who was to become one of the most popular figures among Rome's people. Pius V and Borromeo gave Rome a true Counter-Reformation character. All pomp was removed from the court, the jokers were expelled, and cardinals and bishops were obliged to live in the city. Blasphemy and concubinage were severely punished. Prostitutes were expelled or confined in a reserved district. The Inquisition's power in the city was reasserted, and its palace rebuilt with an increased space for prisons. During this period Michelangelo opened the Porta Pia and turned the Baths of Diocletian into the spectacular basilica of Santa Maria degli Angeli e dei Martiri, where Pius IV was buried. The expression of mannerism was meticulously widespread with Giacomo Barozzi da Vignola, Vignola, for civil and religious buildings in Rome and throughout the
Papal States
The Papal States ( ; ; ), officially the State of the Church, were a conglomeration of territories on the Italian peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope from 756 to 1870. They were among the major states of Italy from the 8th c ...
, his masterpieces, even before the Church of the Gesù (1568), became villas such as Villa Giulia and Villa Farnese.
The pontificate of his successor, Pope Gregory XIII, Gregory XIII, was considered a failure. As he tried to use milder measures than those of St. Pius, the worst element of the Roman population felt free to scourge again the streets. The French writer and philosopher Michel de Montaigne, Montaigne maintained that "life and goods were never as unsure as at the time of Gregorius XIII, perhaps", and that a confraternity even held same-sex marriage in the church of San Giovanni a Porta Latina. The courtesans repressed by Pius had now returned.
Pope Sixtus V, Sixtus V was of very different temper. Although short (1585–1590), his reign however is remembered as one of the most effective in the modern Rome's history. He was even tougher than Pius V, and was variously nicknamed ''castigamatti'' ("punisher of the mad"), ''papa di ferro'' ("Iron Pope"), ''dictator'' and even, ironically, ''demon'', since no other Pope before him pursued with such a determination the reform of the church and the customs. Sixtus profoundly reorganised the Papal States' administration, and cleaned the streets of Rome of thugs, procurers, duelling and so on. Even the nobles and Cardinals could not consider themselves free from the arms of Sixtus' police. The money from taxes, which were not now wasted in corruption, permitted an ambitious building programme. Some ancient aqueducts were restored, and a new one, the Acquedotto Felice (from Sixtus' name, Felice Peretti) was constructed. New houses were built in the desolate district of Esquiline Hill, Esquilino, Viminal Hill, Viminale and Quirinal Palace, Quirinale, while old houses in the centre of the city were destroyed to open new, larger streets. Sixtus's principal aim was to make Rome a better destination for Christian pilgrimage, pilgrimages, and the new streets were intended to permit a better access to the major Basilicas. Old obelisks were moved or erected to embellish St. John in Lateran, Santa Maria Maggiore and St. Peter, as well as Piazza del Popolo, in front of Santa Maria del Popolo.
Baroque period

In the 18th century, the Papacy reached the peak of its temporal power, the Papal States including most of Central Italy, including Latium, Umbria, Marche and the Legations of Ravenna, Ferrara and Bologna extending north into the Romagna, as well as the small enclaves of Benevento and Pontecorvo in southern Italy and the larger Comtat Venaissin around Avignon in southern France.
Baroque architecture, Baroque and Rococo architecture flourished in Rome, with several famous works being completed. Work on the Trevi Fountain began in 1732 and was completed in 1762. The Spanish Steps were designed in 1735. Pope Clement XIII's tomb by Canova was completed in 1792.
The arts also flourished throughout this period. Palazzo Nuovo became the world's first public museum in 1734 and some of the most famous views of Rome in the 18th century were etched by Giovanni Battista Piranesi. His grand vision of classic Rome inspired many to visit the city and examine the ruins themselves.
Modern history
Italian unification
In 1870, the Pope's holdings were left in an uncertain situation when Rome itself was annexed by the Piedmont-led forces which had united the rest of Italy, after a nominal resistance by the papal forces. Between 1861 and 1929 the status of the Pope was referred to as the "Roman Question". The successive Popes were undisturbed in their palace, and certain prerogatives recognised by the Law of Guarantees, including the right to send and receive ambassadors. But the Popes did not recognise the Italian king's right to rule in Rome, and they prisoner in the Vatican, refused to leave the Vatican compound until the dispute was resolved in 1929. Other states continued to maintain international recognition of the Holy See as a sovereign entity.
The rule of the Popes was interrupted by the short-lived Roman Republic (18th century), Roman Republic (1798–1799), which was under the influence of the French Revolution. During Napoleon I of France, Napoleon's reign, Rome was annexed into the First French Empire, French Empire as the capital of the French department, department of Rome (department), Rome. After the fall of Napoleon's Empire, the Papal States were restored by the Congress of Vienna, with the exception of Avignon and the Comtat Venaissin, which remained part of France.
Another Roman Republic (19th century), Roman Republic arose in 1849, within the framework of Revolutions of 1848 in the Italian states, revolutions of 1848. Two of the most influential figures of the Italian unification, Giuseppe Mazzini and Giuseppe Garibaldi, fought for the short-lived republic. However, the actions of these two great men would not have resulted in unification without the sly leadership of Camillo Benso, conte di Cavour, Camillo Benso di Cavour, Prime Minister of Kingdom of Sardinia, Piedmont-Sardinia.
Even among those who wanted to see the peninsula unified into one country, different groups could not agree on what form a unified state would take. Vincenzo Gioberti, a Piedmontese priest, had suggested a confederation of Italian states under rulership of the Pope. His book, ''Of the Moral and Civil Primacy of the Italians'', was published in 1843 and created a link between the Papacy and the Risorgimento. Many leading Carbonari, revolutionaries wanted a republic, but eventually it was a Victor Emmanuel II of Italy, king and his Count Cavour, chief minister who had the power to unite the Italian states as a monarchy.
In his attempt to unify Northern Italy under the Kingdom of Sardinia, Kingdom of Piedmont-Sardinia, Cavour enacted major industrialisation of the country in order to become the economic leader of Italy. In doing so, he believed that the other states would naturally come under his rule. Next, he sent the army of Piedmont to the Crimean War to join the French and British. Making minor successes in the war against Russia, cordial relations were established between Piedmont-Sardinia and France; a relationship to be exploited in the future.
The return of Pope Pius IX in Rome, with help of French troops, marked the exclusion of Rome from the unification process that was embodied in the Second Italian War of Independence, Second Italian Independence War and the Expedition of the Thousand, ''Mille'' expedition, after which all the Italian peninsula, except Rome and Venetia (region), Venetia, would be unified under the House of Savoy. Garibaldi first attacked Sicily, luckily under the guise of passing British ships and landing with little resistance.
Taking the island, Garibaldi's actions were publicly denounced by Cavour but secretly encouraged via weapons supplements. This policy or real-politik, where the ends justified the means of unification, was continued as Garibaldi faced crossing the Strait of Messina. Cavour privately asked the British navy to allow Garibaldi's troops across the sea, while publicly he again, denounced Garibaldi's actions. The manoeuvre was a success and Garibaldi's military genius carried him on to take the entire kingdom.
Cavour then moved to take Venetia and Lombardy via an alliance with France. The Italians and French together would attack the two states with France getting the city of Nice and the region of Savoy in return. However, the French pulled out of their agreement soon after, enraging Cavour who subsequently resigned. Only Lombardy had been captured at the time.
With French units still stationed at Rome however, Cavour, being called back to office, foresaw a possibility of Garibaldi attacking the Papal States and accidentally disrupting French-Italian relations. The army of Sardinia was therefore mobilised to attack the Papal States but remain outside Rome.
In the Austro-Prussian war however, a deal was made between the new Italy and Prussia, where Italy would attack Austria in return for the region of Venetia. The war was a major success for the Prussians (though the Italians did not win a single battle), and the northern front of Italy was complete.
In July 1870, the Franco-Prussian War started, and French Emperor Napoleon III of France, Napoleon III could no longer protect the Papal States. Soon after, the Italian army under general Raffaele Cadorna entered Rome on 20 September, after a cannonade of three hours, through Porta Pia (see capture of Rome). The Leonine City was occupied the following day, a provisional Government Joint created by Cadorna out of local noblemen to avoid the rise of the radical factions. Rome and
Latium
Latium ( , ; ) is the region of central western Italy in which the city of Rome was founded and grew to be the capital city of the Roman Empire.
Definition
Latium was originally a small triangle of fertile, volcanic soil (Old Latium) on whic ...
were annexed to the Kingdom of Italy after a Referendum, plebiscite held on 2 October. 133,681 voted for annexation, 1,507 opposed (in Rome itself, there were 40,785 "Yes" and 57 "No").
When Rome was eventually taken, the Italian government reportedly intended to let Pope Pius IX keep the part of Rome, west of the Tiber, known as the Leonine City as a small remaining Papal State, but Pius IX rejected the offer because acceptance would have been an implied endorsement of the legitimacy of the Italian kingdom's rule over his former domain. One week after entering Rome, the Italian troops had taken the entire city save for the Apostolic Palace; the inhabitants of the city then voted to join Italy. On 1 July 1871, Rome became the official capital of united Italy and from then until June 1929 the popes had no temporal power.
The pope referred to himself during this time as the "prisoner of the Vatican", although he was not actually restrained from coming and going. Pius IX took steps to ensure self-sufficiency, such as the construction of the Vatican Pharmacy. Italian nobility who owed their titles to the pope rather than the royal family became known as the Black Nobility during this period because of their purported mourning.
Kingdom of Italy

Rome became the focus of hopes of Italian reunification when the rest of Italy was reunited under the Kingdom of Italy (1861–1946), Kingdom of Italy with a temporary capital at
Florence
Florence ( ; ) is the capital city of the Italy, Italian region of Tuscany. It is also the most populated city in Tuscany, with 362,353 inhabitants, and 989,460 in Metropolitan City of Florence, its metropolitan province as of 2025.
Florence ...
. In 1861, Rome was declared the capital of Italy even though it was still under the control of the Pope. During the 1860s, the last vestiges of the
Papal States
The Papal States ( ; ; ), officially the State of the Church, were a conglomeration of territories on the Italian peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope from 756 to 1870. They were among the major states of Italy from the 8th c ...
were under the French protection of Napoleon III. And it was only when this was lifted in 1870, owing to the outbreak of the Franco-Prussian War, that Italian troops were able to Capture of Rome, capture Rome entering the city through a breach near Porta Pia. Afterwards, Pope Pius IX declared himself as prisoner in the Vatican, and in 1871 the capital of Italy was moved from Florence to Rome.
Soon after World War I, Rome witnessed the rise to power of Italian Fascism guided by Benito Mussolini, who, at the request of Victor Emmanuel III of Italy, King Victor Emmanuel III, March on Rome, marched on the city in 1922, eventually declaring a new Italian Colonial Empire, Empire and allying Italy with Nazi Germany.
The interwar period saw a rapid growth in the city's population, that surpassed 1,000,000 inhabitants.

This Roman Question was finally resolved on 11 February 1929 between the Holy See and the Kingdom of Italy. The Lateran Treaty was signed by Benito Mussolini on behalf of King Victor Emmanuel III and by Cardinal Secretary of State Pietro Gasparri for Pope Pius XI. The treaty, which became effective on 7 June 1929, and the Concordat established the independent State of the Vatican City and granted Roman Catholicism special status in Italy.
During World War II, Rome suffered few bombings (notably at San Lorenzo fuori le Mura, San Lorenzo) and relatively little damage because none of the nations involved wanted to endanger the life of Pope Pius XII in Vatican City. There were some bitter fights between Italian and German troops in the south of the city and even in sight of the Colosseum, shortly after the armistice between Italy and Allied armed forces. On 4 June 1944 Rome became the first capital city of an Axis powers, Axis nation to fall to the Allies of World War II, Allies, but was relatively undamaged because on 14 August 1943, a day after bombing of Rome in World War II, the last allied bombing, the Germans declared it an "
open city" and withdrew, meaning that the Allies did not have to fight their way in.
In practice Italy made no attempt to interfere with the Holy See within the Vatican walls. However, they confiscated church property in many other places, including the Quirinal Palace, formerly the pope's official residence. Pope Pius IX (1846–78), the last ruler of the Papal States, claimed that after Rome was annexed he was a "Prisoner in the Vatican".
Vatican City officially pursued a policy of neutrality during World War II, under the leadership of Pope Pius XII. Although the city of Rome was occupied by Germany from 1943 and the Allies from 1944, Vatican City itself was not occupied. One of Pius XII's main diplomatic priorities was to prevent the bombing of Rome; so sensitive was the pontiff that he protested even the British air dropping of pamphlets over Rome, claiming that the few landing within the city-state violated the Vatican's neutrality. Before the American entry into the war, there was little impetus for such a bombing, as the British saw little strategic value in it.
After the American entry, the US opposed such a bombing, fearful of offending Catholic members of its military forces, while the British then supported it. Pius XII similarly advocated for the declaration of Rome as an "
open city", but this occurred only on 14 August 1943, after Rome had already been bombed twice. Although the Italians consulted the Vatican on the wording of the open city declaration, the impetus for the change had little to do with the Vatican.
Capital of the Italian Republic
Rome grew substantially after the war, as one of the driving forces behind the "Italian economic miracle" of post-war reconstruction and modernisation. It became a fashionable city in the 1950s and early 1960s, the years of "la dolce vita" ("the sweet life"), with popular classic films such as ''Ben-Hur (1959 film), Ben Hur'', ''Quo Vadis (1951 film), Quo Vadis'', ''Roman Holiday'' and ''La Dolce Vita''
being filmed in the city's iconic Cinecittà Studios.
A new rising trend in population continued until the mid-1980s, when the commune had more than 2.8 million residents; after that, population started to slowly decline as more residents moved to nearby suburbs. The Rome metropolitan area has about 4.4 million inhabitants .
Being the capital city of Italy, all the principal institutions of the nation are located there, including the President; the seat of government with its single Ministeri; the Parliament; the main judicial Courts, and the diplomatic representatives for both Italy and the Vatican City. A number of notable international cultural, scientific and humanitarian institutions are located in Rome, including the German Archaeological Institute, and the Food and Agriculture Organization, FAO.
Rome hosted the 1960 Summer Olympics, using many ancient sites such as the Villa Borghese gardens, Villa Borghese and the Baths of Caracalla, Thermae of Caracalla as venues.
For the Olympic Games new structures were created: the Olympic Stadium (which was itself enlarged and renovated to host qualifying rounds and the final match of the 1990 FIFA football World Cup); the Villaggio Olimpico (Olympic Village), created to house the athletes, was later redeveloped as a residential district.
Rome's Leonardo da Vinci–Fiumicino Airport opened in 1961. Tourism in Rome, Tourism brings an average of 7–10 million visitors a year. Rome is the 2nd most visited city in the European Union, after Paris.
The Colosseum (4 million tourists) and the Vatican Museums (4.2 million tourists) are the 39th and 37th (respectively) most visited places in the world, according to a 2009 study.
Many of the ancient monuments of Rome were restored by the Italian state and by the Vatican City, Vatican for the Great Jubilee, 2000 Jubilee.
Historical city centre
Today's Rome is a modern metropolis, yet it reflects the stratification of the epochs of its long history. The historical centre, identified as those parts within the limits of the ancient Imperial walls, contains archaeological remains from Ancient Rome. These are continuously being excavated and opened to the public, such as the Colosseum; the Roman Forum, and the Catacombs of Rome, Catacombs. There are areas with remains from Medieval times. There are palaces and artistic treasures from the Renaissance; fountains, churches and palaces from Baroque times. There is art and architecture from the Art Nouveau, Neoclassical architecture, Neoclassic, Modernist and Rationalist periods. There are museums, such as the Capitoline Museums, Musei Capitolini, the Vatican Museums, Galleria Borghese.
Parts of the historical centre were reorganised after the 19th-century Italian Unification (1880–1910 – ''Roma Umbertina''). The increase of population caused by the centralisation of the Italian state necessitated new infrastructure and accommodation. There were also substantial alterations and adaptations made during the Fascist period, for example, the creation of the Via dei Fori Imperiali; and the Via della Conciliazione in front of the Vatican. These projects involved the destruction of a large part of the old Borgo (rione of Rome), Borgo neighbourhood. New quartieri were founded, such as EUR (Esposizione Universale Roma), San Basilio, Garbatella, Cinecittà, Trullo and Quarticciolo. So great was the influx of people that on the coast, there was restructuring of Ostia (quarter of Rome), Ostia and the inclusion of bordering villages such as Labaro, Osteria del Curato, Quarto Miglio, Capannelle, Pisana, Torrevecchia, Ottavia, Casalotti.
See also
*Roman technology
*Timeline of the city of Rome
*Timeline of Roman history
References
Notes
Bibliography
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*Döge, F.U. (2004) "Die militärische und innenpolitische Entwicklung in Italien 1943–1944", Chapter 11, ''in'':
Pro- und antifaschistischer Neorealismus'. PhD Thesis, Free University, Berlin. 960 p. [in German]
*Ekonomou, Andrew J. 2007. ''Byzantine Rome and the Greek Popes: Eastern influences on Rome and the papacy from Gregory the Great to Zacharias, A.D. 590–752''. Lexington Books.
*Ferdinand Gregorovius, Gregorovius, Ferdinand. ''History of the City of Rome in the Middle Ages''.
*
*
*
*
*Theodor Mommsen ''The History of Rome, Books I, II, III, IV, V.''
Attribution
*
''Römische Geschichte'', in German
Further reading
online edition*
*
*
online editiononline editionexcerpt and text search
*Grant, Michael. ''History of Rome'' (1997), good survey
*
* (1985). 386 pp. good introduction
*Jenkyns, Richard
''The Legacy of Rome: A New Appraisal''
(1992
online edition
*Levine, Rabbi Menachem
The Jewish History of Rome
* (1961), standard scholarly histor
online edition
*Scullard, H. H
''From the Gracchi to Nero: A History of Rome from 133 B.C. to A.D. 68''
(1968), standard scholarly histor
online edition
Imperial Rome
* (2002) 636pp, a
Google Books
* (2002
online edition
* (1951
online edition
* Volume 6, Issue 3, Pages 855–883 Online at Wiley-Interscience; historiography
* (2009), 560pp; by leading schola
excerpt and text search
*Michael Grant (author), Grant, Michael. ''The Roman Emperors: A Biographical Guide to the Rulers of Imperial Rome 31 B.C.–A.D. 476'' (1997)
*Heather, Peter. ''The Fall of the Roman Empire: A New History of Rome and the Barbarians'' (2006) 572pp
*Potter, David. ''The Roman Empire at Bay: AD 180–395'' (2004)
online edition
*Rodgers, Nigel. ''The Illustrated Encyclopedia of the Roman Empire: A complete history of the rise and fall of the Roman Empire'' (2008)
*Michael Rostovtzeff, Rostovtzeff, M. ''The Social and Economic History of the Roman Empire'' (2 vol 1957); famous classi
vol 2 online
*Chester Starr, Starr; Chester G. ''The Emergence of Rome as Ruler of the Western World'' (1953
online edition
*Bryan Ward-Perkins, Ward-Perkins, Bryan. ''The Fall of Rome and the End of Civilization'' (2005) 239 pp.
Medieval, Renaissance, early modern
*Blunt, Anthony. ''Guide to Baroque Rome'' (1982) architecture 1621–1750
*Brentano, Robert; ''Rome before Avignon: A Social History of Thirteenth-Century Rome'' (1974
online edition
*Dorothy Habel, Habel, Dorothy Metzger. ''The Urban Development of Rome in the Age of Alexander VII'' (2002) 424 pp. + 223 plates; on 1660s
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:History of Rome
History of Rome,
Histories of cities in Italy, Rome
 The Italic speakers in the area included
The Italic speakers in the area included 
 After 650 BC, the
After 650 BC, the  The commonly held stories of the early part of the Republic (before roughly 300 BC, when Old Latin inscriptions and Greek histories about Rome provide more concrete evidence of events) are generally considered to be legendary, their historicity being a topic of debate among classicists. The Roman Republic traditionally dates from 509 BC to 27 BC. After 500 BC, Rome is said to have joined with the Latin cities in defence against incursions by the
The commonly held stories of the early part of the Republic (before roughly 300 BC, when Old Latin inscriptions and Greek histories about Rome provide more concrete evidence of events) are generally considered to be legendary, their historicity being a topic of debate among classicists. The Roman Republic traditionally dates from 509 BC to 27 BC. After 500 BC, Rome is said to have joined with the Latin cities in defence against incursions by the  At the same time, Heraclides stated that 4th-century Rome was a
At the same time, Heraclides stated that 4th-century Rome was a  In the following years, Rome continued its conquests in Spain with
In the following years, Rome continued its conquests in Spain with  Rome's population declined after its apex in the 2nd century. At the end of that century, during the reign of
Rome's population declined after its apex in the 2nd century. At the end of that century, during the reign of  Still Rome remained one of the strongholds of paganism, led by the aristocrats and senators. However, the new walls did not stop the city being sacked first by Alaric I, Alaric on 24 August 410, by Genseric, Geiseric on 2 June 455, and even by general Ricimer's unpaid Roman troops (largely composed of barbarians) on 11 July 472. This was the first time in almost 800 years that Rome had fallen to an enemy. The previous Battle of the Allia, sack of Rome had been accomplished by the Gauls under their leader Brennus (4th century), Brennus in 387 BC. The sacking of 410 is seen as a major landmark in the Decline of the Roman Empire, decline and fall of the Western Roman Empire. St. Jerome, living in Bethlehem at the time, wrote that "The City which had taken the whole world was itself taken."St Jerome, Letter CXXVII. :s:Nicene and Post-Nicene Fathers: Series II/Volume VI/The Letters of St. Jerome/Letter 127, ''To Principia'', paragraph 12. These sackings of the city astonished all the Roman world. In any case, the damage caused by the sackings may have been overestimated. The population already started to decline from the late 4th century onward, although around the middle of the fifth century it seems that Rome continued to be the most populous city of the two parts of the Empire, with a population of no fewer than 650,000 inhabitants. The decline greatly accelerated following the capture of Africa Proconsularis by the Vandals. Many inhabitants now fled as the city no longer could be supplied with grain from Africa from the mid-5th century onward.
At the end of the 6th century Rome's population had reduced to around 30,000. Many monuments were being destroyed by the citizens themselves, who stripped stones from closed temples and other precious buildings, and even burned statues to make lime for their personal use. In addition, most of the increasing number of churches were built in this way. For example, the Old Saint Peter's Basilica, first Saint Peter's Basilica was erected using spoils from the abandoned Circus of Nero. This architectural cannibalism was a constant feature of Roman life until the Renaissance. From the 4th century, imperial edicts against stripping of stones and especially marble were common, but the need for their repetition shows that they were ineffective. Sometimes new churches were created by simply taking advantage of early Pagan temples, while sometimes changing the Pagan god or hero to a corresponding Christian saint or martyr. In this way, the Temple of Romulus and Remus became the basilica of the twin saints Santi Cosma e Damiano, Rome, Cosmas and Damian. Later, the Pantheon, Rome, Pantheon, Temple of All Gods, became the church of All Martyrs.
Still Rome remained one of the strongholds of paganism, led by the aristocrats and senators. However, the new walls did not stop the city being sacked first by Alaric I, Alaric on 24 August 410, by Genseric, Geiseric on 2 June 455, and even by general Ricimer's unpaid Roman troops (largely composed of barbarians) on 11 July 472. This was the first time in almost 800 years that Rome had fallen to an enemy. The previous Battle of the Allia, sack of Rome had been accomplished by the Gauls under their leader Brennus (4th century), Brennus in 387 BC. The sacking of 410 is seen as a major landmark in the Decline of the Roman Empire, decline and fall of the Western Roman Empire. St. Jerome, living in Bethlehem at the time, wrote that "The City which had taken the whole world was itself taken."St Jerome, Letter CXXVII. :s:Nicene and Post-Nicene Fathers: Series II/Volume VI/The Letters of St. Jerome/Letter 127, ''To Principia'', paragraph 12. These sackings of the city astonished all the Roman world. In any case, the damage caused by the sackings may have been overestimated. The population already started to decline from the late 4th century onward, although around the middle of the fifth century it seems that Rome continued to be the most populous city of the two parts of the Empire, with a population of no fewer than 650,000 inhabitants. The decline greatly accelerated following the capture of Africa Proconsularis by the Vandals. Many inhabitants now fled as the city no longer could be supplied with grain from Africa from the mid-5th century onward.
At the end of the 6th century Rome's population had reduced to around 30,000. Many monuments were being destroyed by the citizens themselves, who stripped stones from closed temples and other precious buildings, and even burned statues to make lime for their personal use. In addition, most of the increasing number of churches were built in this way. For example, the Old Saint Peter's Basilica, first Saint Peter's Basilica was erected using spoils from the abandoned Circus of Nero. This architectural cannibalism was a constant feature of Roman life until the Renaissance. From the 4th century, imperial edicts against stripping of stones and especially marble were common, but the need for their repetition shows that they were ineffective. Sometimes new churches were created by simply taking advantage of early Pagan temples, while sometimes changing the Pagan god or hero to a corresponding Christian saint or martyr. In this way, the Temple of Romulus and Remus became the basilica of the twin saints Santi Cosma e Damiano, Rome, Cosmas and Damian. Later, the Pantheon, Rome, Pantheon, Temple of All Gods, became the church of All Martyrs.
 On 25 April 799 the new Pope, Pope Leo III, Leo III, led the traditional procession from the Lateran to the Church of San Lorenzo in Lucina along the Via Flaminia (now Via del Corso). Two nobles (followers of his predecessor Hadrian) who disliked the weakness of the Pope with regards to Charlemagne, attacked the processional train and delivered a life-threatening wound to the Pope. Leo fled to the King of the Franks, and in November, 800, the King entered Rome with a strong army and a number of French bishops. He declared a judicial trial to decide if Leo III were to remain Pope, or if the deposers' claims had reasons to be upheld. This trial, however, was only a part of a well thought out chain of events which ultimately surprised the world. The Pope was declared legitimate and the attempters subsequently exiled. On 25 December 800, Pope Leo III crowned Charlemagne Holy Roman Emperor in St. Peter's Basilica.
This act forever severed the loyalty of
On 25 April 799 the new Pope, Pope Leo III, Leo III, led the traditional procession from the Lateran to the Church of San Lorenzo in Lucina along the Via Flaminia (now Via del Corso). Two nobles (followers of his predecessor Hadrian) who disliked the weakness of the Pope with regards to Charlemagne, attacked the processional train and delivered a life-threatening wound to the Pope. Leo fled to the King of the Franks, and in November, 800, the King entered Rome with a strong army and a number of French bishops. He declared a judicial trial to decide if Leo III were to remain Pope, or if the deposers' claims had reasons to be upheld. This trial, however, was only a part of a well thought out chain of events which ultimately surprised the world. The Pope was declared legitimate and the attempters subsequently exiled. On 25 December 800, Pope Leo III crowned Charlemagne Holy Roman Emperor in St. Peter's Basilica.
This act forever severed the loyalty of  In 1188 the new communal government was finally recognised by Pope Clement III. The Pope had to make large cash payments to the communal officials, while the 56 senators became papal vassals. The Senate always had problems in the accomplishment of its function, and various changes were tried. Often a single Senator was in charge. This sometimes led to tyrannies, which did not help the stability of the newborn organism.
In 1188 the new communal government was finally recognised by Pope Clement III. The Pope had to make large cash payments to the communal officials, while the 56 senators became papal vassals. The Senate always had problems in the accomplishment of its function, and various changes were tried. Often a single Senator was in charge. This sometimes led to tyrannies, which did not help the stability of the newborn organism.
 In spite of its decline and the absence of the Pope, Rome had not lost its spiritual prestige: in 1341 the famous poet Petrarch, Petrarca came to the city to be crowned as Poet laureate in Capitoline Hill. Noblemen and poor people at one time demanded with one voice the return of the Pope. Among the many ambassadors that in this period took their way to Avignon, emerged the bizarre but eloquent figure of Cola di Rienzo. As his personal power among the people increased by time, on 20 May 1347 he conquered the Capitoline at the head of an enthusiastic crowd. The period of his power, though very short-lived, aspired to the prestige of Ancient Rome. Now in possession of dictatorial powers, he took the title of "tribune", referring to the plebs, pleb's tribune, magistracy of the
In spite of its decline and the absence of the Pope, Rome had not lost its spiritual prestige: in 1341 the famous poet Petrarch, Petrarca came to the city to be crowned as Poet laureate in Capitoline Hill. Noblemen and poor people at one time demanded with one voice the return of the Pope. Among the many ambassadors that in this period took their way to Avignon, emerged the bizarre but eloquent figure of Cola di Rienzo. As his personal power among the people increased by time, on 20 May 1347 he conquered the Capitoline at the head of an enthusiastic crowd. The period of his power, though very short-lived, aspired to the prestige of Ancient Rome. Now in possession of dictatorial powers, he took the title of "tribune", referring to the plebs, pleb's tribune, magistracy of the  In August 1354, Cola was again a protagonist, when Cardinal Gil Álvarez Carrillo de Albornoz, Gil Alvarez De Albornoz entrusted him with the role of "senator of Rome" in his programme of reassuring the Pope's rule in the
In August 1354, Cola was again a protagonist, when Cardinal Gil Álvarez Carrillo de Albornoz, Gil Alvarez De Albornoz entrusted him with the role of "senator of Rome" in his programme of reassuring the Pope's rule in the  In 1433 the List of rulers of Milan, Duke of Milan, Filippo Maria Visconti signed a peace treaty with
In 1433 the List of rulers of Milan, Duke of Milan, Filippo Maria Visconti signed a peace treaty with  However Nicholas brought stability to the temporal power of the Papacy, a power in which the Emperor was to have no part at all. In this way, the coronation and the marriage of Frederick III, Holy Roman Emperor on 16 March 1452, was more a civil ceremony. The Papacy now controlled Rome with a strong hand. A plot by Stefano Porcari, whose aim was the restoration of the Republic, was ruthlessly suppressed in January 1453. Porcari was hanged together with the other plotters, Francesco Gabadeo, Pietro de Monterotondo, Battista Sciarra and Angiolo Ronconi, but the Pope gained a treacherous reputation, as when the execution was beginning he was too drunk to confirm the grace he had previously given to Sciarra and Ronconi.
Nicholas was also actively involved in Rome's urban renewal, in collaboration with Leon Battista Alberti, including the construction of a new St. Peter's Basilica, St Peter's Basilica.
However Nicholas brought stability to the temporal power of the Papacy, a power in which the Emperor was to have no part at all. In this way, the coronation and the marriage of Frederick III, Holy Roman Emperor on 16 March 1452, was more a civil ceremony. The Papacy now controlled Rome with a strong hand. A plot by Stefano Porcari, whose aim was the restoration of the Republic, was ruthlessly suppressed in January 1453. Porcari was hanged together with the other plotters, Francesco Gabadeo, Pietro de Monterotondo, Battista Sciarra and Angiolo Ronconi, but the Pope gained a treacherous reputation, as when the execution was beginning he was too drunk to confirm the grace he had previously given to Sciarra and Ronconi.
Nicholas was also actively involved in Rome's urban renewal, in collaboration with Leon Battista Alberti, including the construction of a new St. Peter's Basilica, St Peter's Basilica.
 Nicholas' successor Pope Callixtus III, Calixtus III neglected Nicholas's cultural policies, instead devoting himself to his greatest passion, his nephews. The Tuscany, Tuscan Pope Pius II, Pius II, who took the reins after his death in 1458, was a great Humanist, but did little for Rome. During his reign Lorenzo Valla demonstrated that the Donation of Constantine was a forgery. Pius was the first Pope to use guns, in campaign against the rebel barons Savelli in the neighbourhood of Rome, in 1461. One year later the bringing to Rome of the head of the Apostles in the New Testament, Apostle Saint Andrew, St. Andrew produced a great number of pilgrims. The reign of Pope Paul II (1464–1471) was notable only for the reintroduction of the Carnival, which was to become a very popular feast in Rome in the following centuries. In the same year (1468) a plot against the Pope was uncovered, organised by the intellectuals of the Roman Academies, Roman Academy founded by Julius Pomponius Laetus, Pomponio Leto. The conspirators were sent to Castel Sant'Angelo.
Nicholas' successor Pope Callixtus III, Calixtus III neglected Nicholas's cultural policies, instead devoting himself to his greatest passion, his nephews. The Tuscany, Tuscan Pope Pius II, Pius II, who took the reins after his death in 1458, was a great Humanist, but did little for Rome. During his reign Lorenzo Valla demonstrated that the Donation of Constantine was a forgery. Pius was the first Pope to use guns, in campaign against the rebel barons Savelli in the neighbourhood of Rome, in 1461. One year later the bringing to Rome of the head of the Apostles in the New Testament, Apostle Saint Andrew, St. Andrew produced a great number of pilgrims. The reign of Pope Paul II (1464–1471) was notable only for the reintroduction of the Carnival, which was to become a very popular feast in Rome in the following centuries. In the same year (1468) a plot against the Pope was uncovered, organised by the intellectuals of the Roman Academies, Roman Academy founded by Julius Pomponius Laetus, Pomponio Leto. The conspirators were sent to Castel Sant'Angelo.
 More important by far was the Pontificate of Pope Sixtus IV, Sixtus IV, considered the first Pope-King of Rome. In order to favour his relative Girolamo Riario, he promoted the unsuccessful Pazzi, Congiura dei Pazzi against the House of Medici, Medici of Florence (26 April 1478) and in Rome fought the Colonna family, Colonna and the Orsini family, Orsini. The personal politics of intrigue and war required much money, but in spite of this Sixtus was a true patron of art in the manner of Pope Nicholas V, Nicholas V. He reopened the academy and reorganised the Collegio degli Abbreviatori, and in 1471 began the construction of the Vatican Library, whose first curator was Platina. The Library was officially founded on 15 June 1475. He restored several churches, including Santa Maria del Popolo, the Aqua Virgo and the Hospital of the Holy Spirit; paved several streets and also built a famous bridge over the Tiber river, which still bears his name. His main building project was the Sistine Chapel in the Apostolic Palace, Vatican Palace. Its decoration called on some of the most renowned artists of the age, including Mino da Fiesole, Sandro Botticelli, Domenico Ghirlandaio, Pietro Perugino, Luca Signorelli and Pinturicchio, and in the 16th century Michelangelo decorated the ceiling with his famous masterpiece, contributing to what became one of the most famous monuments of the world. Sixtus died on 12 August 1484.
Chaos, corruption and nepotism appeared in Rome under the reign of his successors, Pope Innocent VIII, Innocent VIII and Pope Alexander VI (1492–1503). During the vacation period between the death of the former and the election of the latter there were 220 murders in the city. Alexander had to face Charles VIII of France, who invaded Italy in 1494 and entered Rome on 31 December of that year. The Pope could only barricade himself into Castel Sant'Angelo, which had been turned into a true fortress by Antonio da Sangallo the Younger. In the end, the skilful Alexander was able to gain the support of the king, assigning his son Cesare Borgia as military counsellor for the subsequent invasion of the Kingdom of Naples. Rome was safe and, as the King directed himself southwards, the Pope again changed his position, joining the anti-French League of the Italian States which finally compelled Charles to flee to France.
The most nepotist Pope of all, Alexander, favoured his ruthless son Cesare, creating for him a personal Duchy out of territories of the
More important by far was the Pontificate of Pope Sixtus IV, Sixtus IV, considered the first Pope-King of Rome. In order to favour his relative Girolamo Riario, he promoted the unsuccessful Pazzi, Congiura dei Pazzi against the House of Medici, Medici of Florence (26 April 1478) and in Rome fought the Colonna family, Colonna and the Orsini family, Orsini. The personal politics of intrigue and war required much money, but in spite of this Sixtus was a true patron of art in the manner of Pope Nicholas V, Nicholas V. He reopened the academy and reorganised the Collegio degli Abbreviatori, and in 1471 began the construction of the Vatican Library, whose first curator was Platina. The Library was officially founded on 15 June 1475. He restored several churches, including Santa Maria del Popolo, the Aqua Virgo and the Hospital of the Holy Spirit; paved several streets and also built a famous bridge over the Tiber river, which still bears his name. His main building project was the Sistine Chapel in the Apostolic Palace, Vatican Palace. Its decoration called on some of the most renowned artists of the age, including Mino da Fiesole, Sandro Botticelli, Domenico Ghirlandaio, Pietro Perugino, Luca Signorelli and Pinturicchio, and in the 16th century Michelangelo decorated the ceiling with his famous masterpiece, contributing to what became one of the most famous monuments of the world. Sixtus died on 12 August 1484.
Chaos, corruption and nepotism appeared in Rome under the reign of his successors, Pope Innocent VIII, Innocent VIII and Pope Alexander VI (1492–1503). During the vacation period between the death of the former and the election of the latter there were 220 murders in the city. Alexander had to face Charles VIII of France, who invaded Italy in 1494 and entered Rome on 31 December of that year. The Pope could only barricade himself into Castel Sant'Angelo, which had been turned into a true fortress by Antonio da Sangallo the Younger. In the end, the skilful Alexander was able to gain the support of the king, assigning his son Cesare Borgia as military counsellor for the subsequent invasion of the Kingdom of Naples. Rome was safe and, as the King directed himself southwards, the Pope again changed his position, joining the anti-French League of the Italian States which finally compelled Charles to flee to France.
The most nepotist Pope of all, Alexander, favoured his ruthless son Cesare, creating for him a personal Duchy out of territories of the  In 1527 the ambiguous policy followed by the second House of Medici, Medici Pope, Pope Clement VII, resulted in the dramatic Sack of Rome (1527), sack of the city by the unruly Holy Roman Empire, Imperial troops of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor. After the execution of some 1,000 defenders, the pillage began. The city was devastated for several days, many of the citizens were killed or took shelter outside the walls. Of 189 Swiss Guards on duty only 42 survived. The Pope himself was imprisoned for months in Castel Sant'Angelo. The sack marked the end of one of the most splendid eras of modern Rome.
The 1525's Jubilee resulted in a farce, as Martin Luther's claims had spread criticism and even hatred against the Pope's greed throughout Europe. The prestige of Rome was then challenged by the defections of the churches of Germany and England. Pope Paul III (1534–1549) tried to recover the situation by summoning the Council of Trent, although being, at the same time, the most nepotist Pope of all. He even separated Parma and Piacenza from the
In 1527 the ambiguous policy followed by the second House of Medici, Medici Pope, Pope Clement VII, resulted in the dramatic Sack of Rome (1527), sack of the city by the unruly Holy Roman Empire, Imperial troops of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor. After the execution of some 1,000 defenders, the pillage began. The city was devastated for several days, many of the citizens were killed or took shelter outside the walls. Of 189 Swiss Guards on duty only 42 survived. The Pope himself was imprisoned for months in Castel Sant'Angelo. The sack marked the end of one of the most splendid eras of modern Rome.
The 1525's Jubilee resulted in a farce, as Martin Luther's claims had spread criticism and even hatred against the Pope's greed throughout Europe. The prestige of Rome was then challenged by the defections of the churches of Germany and England. Pope Paul III (1534–1549) tried to recover the situation by summoning the Council of Trent, although being, at the same time, the most nepotist Pope of all. He even separated Parma and Piacenza from the 
 In the 18th century, the Papacy reached the peak of its temporal power, the Papal States including most of Central Italy, including Latium, Umbria, Marche and the Legations of Ravenna, Ferrara and Bologna extending north into the Romagna, as well as the small enclaves of Benevento and Pontecorvo in southern Italy and the larger Comtat Venaissin around Avignon in southern France.
Baroque architecture, Baroque and Rococo architecture flourished in Rome, with several famous works being completed. Work on the Trevi Fountain began in 1732 and was completed in 1762. The Spanish Steps were designed in 1735. Pope Clement XIII's tomb by Canova was completed in 1792.
The arts also flourished throughout this period. Palazzo Nuovo became the world's first public museum in 1734 and some of the most famous views of Rome in the 18th century were etched by Giovanni Battista Piranesi. His grand vision of classic Rome inspired many to visit the city and examine the ruins themselves.
In the 18th century, the Papacy reached the peak of its temporal power, the Papal States including most of Central Italy, including Latium, Umbria, Marche and the Legations of Ravenna, Ferrara and Bologna extending north into the Romagna, as well as the small enclaves of Benevento and Pontecorvo in southern Italy and the larger Comtat Venaissin around Avignon in southern France.
Baroque architecture, Baroque and Rococo architecture flourished in Rome, with several famous works being completed. Work on the Trevi Fountain began in 1732 and was completed in 1762. The Spanish Steps were designed in 1735. Pope Clement XIII's tomb by Canova was completed in 1792.
The arts also flourished throughout this period. Palazzo Nuovo became the world's first public museum in 1734 and some of the most famous views of Rome in the 18th century were etched by Giovanni Battista Piranesi. His grand vision of classic Rome inspired many to visit the city and examine the ruins themselves.