Reuss (state) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Reuss ( ) was the name of several historical states located in present-day
 The position of ''vogt'' soon became hereditary. While the dominions of Heinrich von Gleissberg included the towns
The position of ''vogt'' soon became hereditary. While the dominions of Heinrich von Gleissberg included the towns
Album der Schlösser und Rittergüter im Königreiche Sachsen V 129.jpg,
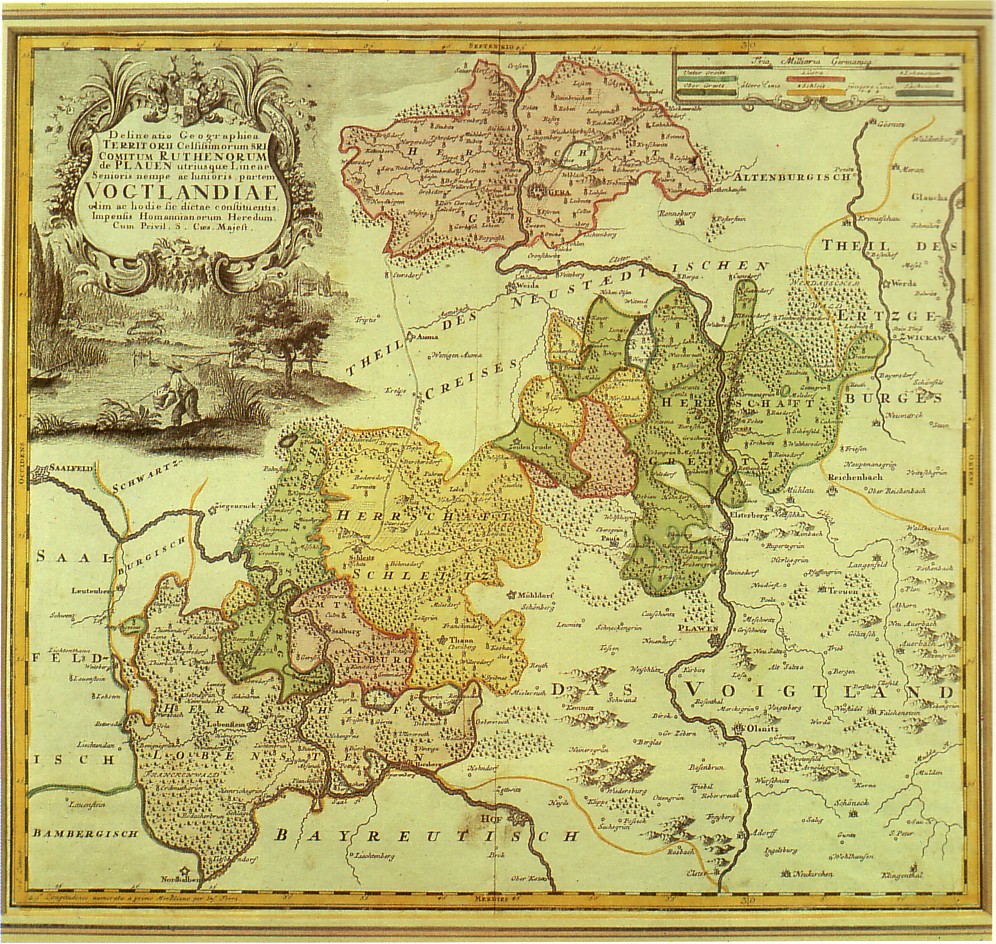 In 1564 the sons of Henry XIII of Reuss at Greiz divided the estates into
*Reuss at Lower Greiz, descendants of Henry XIV the Elder
*Reuss at Upper Greiz, descendants of Henry XV the Middle
*Reuss at Gera, descendants of Henry XVI the Younger.
While the Middle Reuss became extinct in 1616, the Older and Younger lines were divided again several times until in 1778 Count Henry XI united the possessions of Upper and Lower Greiz to the Principality of Reuss Elder Line. In return the remaining estates of Gera, considerably larger though, became the Principality of Reuss Younger Line in 1806. The two remaining Reuss principalities joined the German Confederation in 1815. Several subdivisions of the Younger Line merged into a unified state by 1848.
Henry XXII of Reuss Elder line is notable among the modern princes of this house for his enmity to
In 1564 the sons of Henry XIII of Reuss at Greiz divided the estates into
*Reuss at Lower Greiz, descendants of Henry XIV the Elder
*Reuss at Upper Greiz, descendants of Henry XV the Middle
*Reuss at Gera, descendants of Henry XVI the Younger.
While the Middle Reuss became extinct in 1616, the Older and Younger lines were divided again several times until in 1778 Count Henry XI united the possessions of Upper and Lower Greiz to the Principality of Reuss Elder Line. In return the remaining estates of Gera, considerably larger though, became the Principality of Reuss Younger Line in 1806. The two remaining Reuss principalities joined the German Confederation in 1815. Several subdivisions of the Younger Line merged into a unified state by 1848.
Henry XXII of Reuss Elder line is notable among the modern princes of this house for his enmity to
File:Blick zum "Oberen Schloß" vom "Weißen Kreuz".jpg, The Upper Castle at Greiz
File:Unteres Schloss Greiz.JPG, The Lower Castle at Greiz
File:Gera - Orangerie 01.jpg, Orangery at
online version
. * Sigismund Stucke: ''Die Reußen und ihr Land. Die Geschichte einer süddeutschen Dynastie.'' (The Reuss and their country. The history of a southern German dynasty), St. Michael 1984, ISBN 3-7053-1954-X. reissue: publisher Arnshaugk Verlag, Neustadt 2022, ISBN 978-3-95930-252-4. * Almanach de Gotha: ** Gothaischer Hofkalender 1781, Gotha 1780 (first publication). ** ''Gothaischer Hofkalender zum Nutzen und Vergnügen auf das Jahr 1792'', C. W. Ettinger, Gotha 1791
online version
** Gothaischer Hofkalender 1877, Gotha 1876
online version
** Gothaischer Hofkalender 1894, Gotha 1893
online version
* Gothaisches Genealogisches Handbuch, Fürstliche Häuser ''( Gotha Genealogical Handbook − german article−, Princely Houses)'', 2015, 1. Abteilung ''(first department)'', vol 1 of the complete series of the GGH books, publisher: Verlag des Deutschen Adelsarchivs ''(Publisher of the German Nobility Archive)'', Marburg 2015, pp. 227–247; 628–634. ISBN 978-3-9817243-0-1.
Thuringia
Thuringia (; officially the Free State of Thuringia, ) is one of Germany, Germany's 16 States of Germany, states. With 2.1 million people, it is 12th-largest by population, and with 16,171 square kilometers, it is 11th-largest in area.
Er ...
, Germany. Several lordships of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
which arose after 1300 and became Imperial Counties from 1673 and Imperial Principalities in the late 18th century were ruled by the House of Reuss.
A varying number of these counties came into being by partition; they were partially merged and divided again. After the end of the empire in 1806, the principality of the elder line, as well as several of the younger, became sovereign member states of the German Confederation, with the younger ones merging into a unified principality by 1848. The two remaining territories became federal principalities of the German Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperia ...
in 1871, the Principality of Reuss Elder Line with the state capital of Greiz and the Principality of Reuss Younger Line with the state capital of Gera
Gera () is a city in the German state of Thuringia. With around 93,000 inhabitants, it is the third-largest city in Thuringia after Erfurt and Jena as well as the easternmost city of the ''Thüringer Städtekette'', an almost straight string of ...
. Both states were ruled by the House of Reuss until the German Revolution of 1918–1919
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
. The head of each branch bore the German title ''Fürst
' (, female form ', plural '; from Old High German ', "the first", a translation of the Latin ') is a German language, German word for a ruler as well as a princely title. ' were, starting in the Middle Ages, members of the highest nobility who ...
'' (Prince, as head of a princely house) while their children and all other members of the house bore the title ''Prinz/Prinzessin'' (Prince/Princess, as agnate members of a princely house).
Since the end of the 12th century, all male members of the House of Reuss are named ''Heinrich'' (), in honour of Henry VI, Holy Roman Emperor (1190–1197), to whom they owed the dominions of Weida and Gera. For the purpose of differentiation, they are given order numbers according to certain systems (see below, section ''Numbering of the Heinrichs''), and in private life they are distinguished by nicknames.
History of the various states
Several different principalities of the House of Reuss which had previously existed had by the time of the formation of the German Confederation become part of the two remaining lines (the Elder and the Younger lines). Before then, they had been part first of theHoly Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
, and then the Confederation of the Rhine
The Confederated States of the Rhine, simply known as the Confederation of the Rhine or Rhine Confederation, was a confederation of German client states established at the behest of Napoleon some months after he defeated Austrian Empire, Austria ...
.
Origins
The region including what would become the Principality of Reuss was inhabited in early medieval times by Slavic people who were converted to Christianity by the German Emperor Otto I (936–973). In church matters the region was under the Diocese of Zeitz (founded in 968), which became a suffragan of Magdeburg. On account of the frequent inroads of the Slavs, the residence of the Bishop ofZeitz
Zeitz (; , ) is a town in the Burgenlandkreis district, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It is situated on the river White Elster, in the triangle of the federal states Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, and Saxony.
History
First a Slavic pagan settlem ...
was removed to Naumburg in 1028, after which the See was called Naumburg-Zeitz.
Upon its subjection to German authority, the whole province was allotted to the March of Zeitz. As early as the year 1000, however, Emperor Otto III permitted the entire part lying on the eastern boundary of Thuringia
Thuringia (; officially the Free State of Thuringia, ) is one of Germany, Germany's 16 States of Germany, states. With 2.1 million people, it is 12th-largest by population, and with 16,171 square kilometers, it is 11th-largest in area.
Er ...
, a wooded area, sparsely populated by the West Slavic people of the Sorbs
Sorbs (; ; ; ; ; also known as Lusatians, Lusatian Serbs and Wends) are a West Slavs, West Slavic ethnic group predominantly inhabiting the parts of Lusatia located in the German states of Germany, states of Saxony and Brandenburg. Sorbs tradi ...
, to be cleared for farmland and settled by German settlers. Emperor Henry IV appointed Henry the Pious of Gleissberg (c. 1040−1120) imperial vogt, or bailiff
A bailiff is a manager, overseer or custodian – a legal officer to whom some degree of authority or jurisdiction is given. There are different kinds, and their offices and scope of duties vary.
Another official sometimes referred to as a '' ...
(''advocatus imperii'') of this settlement area, under the rule of the imperial Quedlinburg Abbey
Quedlinburg Abbey ( or ) is a former abbey of secular canonesses ''( Frauenstift)'' in Quedlinburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It was founded in 936 on the initiative of Saint Matilda, the widow of the East Frankish King Henry the Fowler, as h ...
. He was a son of Erkenbert I of Weida, the oldest known ancestor of the family, who is mentioned in 1122 in the entourage of Count Adalbert of Everstein at the consecration of St John's church in Plauen. The name of the area Heinrich controlled derives from his office: Vogtland
Vogtland (; ) is a region spanning the German states of Bavaria, Saxony and Thuringia and north-western Bohemia in the Czech Republic. It overlaps with and is largely contained within Euroregio Egrensis. The name alludes to the former leadershi ...
(''Terra advocatorum'', Land of the Bailiff). This designation has remained to this day a geographical summary for a region of 3,467 km2 (comparable roughly to the county of Essex
Essex ( ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in the East of England, and one of the home counties. It is bordered by Cambridgeshire and Suffolk to the north, the North Sea to the east, Kent across the Thames Estuary to the ...
) which is located in Saxony
Saxony, officially the Free State of Saxony, is a landlocked state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, and Bavaria, as well as the countries of Poland and the Czech Republic. Its capital is Dresden, and ...
, Thuringia and, to a lesser extent, in northern Bavaria
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a States of Germany, state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the list of German states by area, largest German state by land area, comprising approximately 1/5 of the total l ...
.
The House of the ''Vogts'' (Bailiffs)
 The position of ''vogt'' soon became hereditary. While the dominions of Heinrich von Gleissberg included the towns
The position of ''vogt'' soon became hereditary. While the dominions of Heinrich von Gleissberg included the towns Gera
Gera () is a city in the German state of Thuringia. With around 93,000 inhabitants, it is the third-largest city in Thuringia after Erfurt and Jena as well as the easternmost city of the ''Thüringer Städtekette'', an almost straight string of ...
and Weida, his grandson Henry II the Rich (d. before 1209) also acquired Plauen
Plauen (; ; ) is a town in Saxony, Germany with a population of around 65,000. It is Saxony's 5th most populated city after Leipzig, Dresden, Chemnitz and Zwickau, the second-largest city of the Vogtland after Gera, as well as the largest cit ...
. When his three sons divided their inheritance, three independent areas emerged, ruled by the branches of the bailiffs of Weida-Ronneburg, Plauen-Gera and Greiz-Reichenbach. The bailiffs, initially unfree nobles ''(Ministerialis
The ''ministeriales'' (singular: ''ministerialis'') were a legally unfree but socially elite class of knights, administrators, and officials in the High Middle Ages in the Holy Roman Empire, drawn from a mix of servile origins, free commoners, and ...
)'', quickly rose to the rank of lords. After the division, the official title ''Vogt'' was carried on by all branches and passed on like a hereditary imperial fiefdom. When the bailiffs negotiated a treaty with Henry III, Margrave of Meissen
Henry III, called Henry the Illustrious (''Heinrich der Erlauchte'') (c. 1215 – 15 February 1288) from the House of Wettin was Margrave of Meissen and last Margrave of Lusatia (as Henry IV) from 1221 until his death; from 1242 also Landgrav ...
in 1254, they acted as equal partners. In 1329 Emperor Ludwig the Bavarian confirmed the bailiffs a rank equal to Princes of the Holy Roman Empire, albeit without the title itself, they continued to use the designation ''Vogt''.
In the 12th and 13th centuries, the bailiffs of Weida gradually became independent of the Quedlinburg Abbey on the lands they administered. Their area included what is generally understood today as Vogtland. Over time the dominions of the bailiffs extended beyond the Vogtland into the Western Ore Mountains, with areas extending into what is now the Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, also known as Czechia, and historically known as Bohemia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. The country is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the south ...
.
The Weida branch was extinct in 1535, the branch of Greiz-Reichenbach was soon inherited by the branch of Plauen-Gera which then divided into Plauen (elder and younger line) and Gera-Schleiz-Lobenstein (extinct in 1550). The elder Plauen line of the vogts was extinct in 1380, the founder of the younger Plauen line was Henry (d. about 1300), who on account of his stay in Eastern European regions and his marriage with a granddaughter of King Daniel of Galicia
Daniel Romanovich (1201–1264) was Prince of Galicia (1205–1207; 1211–1212; 1230–1232; 1233–1234; 1238–1264), Prince of Volhynia, Volhynia (1205–1208; 1215–1238), Grand Prince of Kiev (1240), and King of Ruthenia (1253–1264).
B ...
received the surname of "''der Reusse''" ( Ruthenus, a term for the Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rus', also known as Kyivan Rus,.
* was the first East Slavs, East Slavic state and later an amalgam of principalities in Eastern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical At ...
), whence the name later passed to his country. His descendants were styled ''Lords Reuss of Plauen, Greiz and Gera''. The House of Reuss is thus descended from the vogts of Plauen from whom they inherited the cities and lordships of Gera, Greiz, Schleiz and Lobenstein. However, in the fourteenth and fifteenth centuries the vogts had lost the greater part of their possessions, most of which fell to the Electorate of Saxony
The Electorate of Saxony, also known as Electoral Saxony ( or ), was a territory of the Holy Roman Empire from 1356 to 1806 initially centred on Wittenberg that came to include areas around the cities of Dresden, Leipzig and Chemnitz. It was a ...
, including Weida in 1427 and Plauen in 1482.
Plauen
Plauen (; ; ) is a town in Saxony, Germany with a population of around 65,000. It is Saxony's 5th most populated city after Leipzig, Dresden, Chemnitz and Zwickau, the second-largest city of the Vogtland after Gera, as well as the largest cit ...
city and castle (1859)
Osterburg Weida.jpg, Osterburg Castle at Weida
Gera, Thüringen - Schloss Osterstein (Zeno Ansichtskarten).jpg, Osterstein Castle at Gera (until 1918 state capital of the Principality of Reuss Younger Line)
Greiz Schlösser Unteres und Oberes Schloss oberhalb der Weißen Elster Foto 2009 Wolfgang Pehlemann Wiesbaden IMG 0796.jpg, Greiz with Upper and Lower Castle (until 1918 state capital of the Principality of Reuss Elder Line)
House of Reuss
In 1306 the Plauen branch of the vogts was subdivided into an elder line (at Plauen) that died out around 1380, and a younger line (at Greiz and Reichenbach), called ''Reuss''. In 1564 the latter was subdivided into three branches, the Elder (extinct in 1927), the Middle (extinct in 1616), and the Younger (of which the ruling line became extinct in 1945) and a side line, split off in 1692, Reuss- Köstritz, which had been raised to (however non-ruling) princes in 1806, still exists with about 30 male relatives, all named ''Heinrich'', as the last surviving branch of the family, with the senior of this branch, the Prince Reuss-Köstritz, as head of the entire house, hence now ''The Fürst Reuss'', while the others hold the agnatic title of prince. In 1673 the Lords Reuss were raised to Imperial Counts and (depending on the line) from 1778 (1790 or 1802) to Imperial Princes. The dynasty ruled divided areas in various lines and sub-lines; around 1700 there were ten Reussian counties of both main branches. The lords, counts and princes were never styled ''of'' Reuss, but rather count or ''prince Reuss'', as Reuss was originally not the name of a town or castle, but rather a personal designation for the founder of the branch that indicated his foreign connection through marriage (''Reussen'' is in fact an older German term for ''Russians''), and the family is still referred to today in the plural as ''die Reussen''. On account of the close relations of Reuss with the neighbouring Saxon states, Lutheranism speedily gained a foothold in Reuss. The rulers joined the Schmalkaldic League against the German emperor, and forfeited their possessions, but afterwards recovered them.Numbering of the Heinrichs
All the males of the House of Reuss are named Heinrich (Henry) plus a number. In the elder line the numbering covers all male children of the elder House, and the numbers increase until 100 is reached and then start again at 1. In the younger line the system is similar but the numbers increase until the end of the century before starting again at 1. This odd regulation was formulated as a Family Law in 1688, but the tradition of the uniformity of name was in practice as early as 1200. It was seen as a way of honoring theHohenstaufen
The Hohenstaufen dynasty (, , ), also known as the Staufer, was a noble family of unclear origin that rose to rule the Duchy of Swabia from 1079, and to royal rule in the Holy Roman Empire during the Middle Ages from 1138 until 1254. The dynast ...
Emperor
The word ''emperor'' (from , via ) can mean the male ruler of an empire. ''Empress'', the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), mother/grandmother (empress dowager/grand empress dowager), or a woman who rules ...
Heinrich/ Henry VI, who raised Heinrich der Reiche/Henry the Rich (+1209) to the office of provost of the Quedlinburg Abbey
Quedlinburg Abbey ( or ) is a former abbey of secular canonesses ''( Frauenstift)'' in Quedlinburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It was founded in 936 on the initiative of Saint Matilda, the widow of the East Frankish King Henry the Fowler, as h ...
, thus taking on the title of ''vogt''.
Main partition
 In 1564 the sons of Henry XIII of Reuss at Greiz divided the estates into
*Reuss at Lower Greiz, descendants of Henry XIV the Elder
*Reuss at Upper Greiz, descendants of Henry XV the Middle
*Reuss at Gera, descendants of Henry XVI the Younger.
While the Middle Reuss became extinct in 1616, the Older and Younger lines were divided again several times until in 1778 Count Henry XI united the possessions of Upper and Lower Greiz to the Principality of Reuss Elder Line. In return the remaining estates of Gera, considerably larger though, became the Principality of Reuss Younger Line in 1806. The two remaining Reuss principalities joined the German Confederation in 1815. Several subdivisions of the Younger Line merged into a unified state by 1848.
Henry XXII of Reuss Elder line is notable among the modern princes of this house for his enmity to
In 1564 the sons of Henry XIII of Reuss at Greiz divided the estates into
*Reuss at Lower Greiz, descendants of Henry XIV the Elder
*Reuss at Upper Greiz, descendants of Henry XV the Middle
*Reuss at Gera, descendants of Henry XVI the Younger.
While the Middle Reuss became extinct in 1616, the Older and Younger lines were divided again several times until in 1778 Count Henry XI united the possessions of Upper and Lower Greiz to the Principality of Reuss Elder Line. In return the remaining estates of Gera, considerably larger though, became the Principality of Reuss Younger Line in 1806. The two remaining Reuss principalities joined the German Confederation in 1815. Several subdivisions of the Younger Line merged into a unified state by 1848.
Henry XXII of Reuss Elder line is notable among the modern princes of this house for his enmity to Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, ...
, which he opposed in the Austro-Prussian War of 1866, when the Prussian troops occupied his domain. Henry joined the North German Confederation and the new German Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperia ...
in 1871. He alone of all the confederate princes remained until his death in 1902 an implacable enemy of Prince Bismarck and of the conditions created in Germany by the foundation of the empire. Despite his views, his daughter Hermine Reuss of Greiz later became the second wife of the exiled German Emperor Wilhelm II
Wilhelm II (Friedrich Wilhelm Viktor Albert; 27 January 18594 June 1941) was the last German Emperor and King of Prussia from 1888 until Abdication of Wilhelm II, his abdication in 1918, which marked the end of the German Empire as well as th ...
. Other daughters of the house also made important marriages: Countess Augusta Reuss of Ebersdorf, by marriage the Duchess of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld, was the maternal grandmother of Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in January 1901. Her reign of 63 year ...
and the paternal grandmother of Albert, Prince Consort. Princess Augusta Reuss of Köstritz married the Grand Duke of Mecklenburg-Schwerin in 1849 and Eleonore Reuss of Köstritz became queen consort ("Tsaritsa") of Bulgaria in 1908.
Heinrich XXIV, Prince Reuss of Greiz (1878–1927), was incapable of ruling and therefore the regency passed to the ruling prince of the younger line of Reuss. Since the childless Heinrich XXIV was the last of his line, it was to be expected that the principality of the elder line would fall to the younger line after his death, and that a united state of Reuss would emerge as a result. However, both lines lost their thrones in the German Revolution of 1918–19 and a united, albeit republican state, the People's State of Reuss, emerged in 1919, only to merge with the larger state of Thuringia
Thuringia (; officially the Free State of Thuringia, ) is one of Germany, Germany's 16 States of Germany, states. With 2.1 million people, it is 12th-largest by population, and with 16,171 square kilometers, it is 11th-largest in area.
Er ...
in 1920. The unified state of Reuss had a non-contiguous area of 1,143 square kilometers and 211,324 inhabitants (1919).
A (non-governing) side branch of the younger line had emerged in 1692 when Heinrich XXIV, Count Reuss of Köstritz, a younger son of the ruling count Heinrich I. Reuss of Schleiz, received a number of landed estates as a paréage within his eldest brother's county, with his main seat at Köstritz Castle. This branch connected through marriages with important ruling houses, did however not govern their own territory, but lived as landowners in the county of the Schleiz Line. Henry XLIII., count Reuss of Köstritz, was elevated to hereditary Fürst
' (, female form ', plural '; from Old High German ', "the first", a translation of the Latin ') is a German language, German word for a ruler as well as a princely title. ' were, starting in the Middle Ages, members of the highest nobility who ...
(prince) by Emperor Francis II in 1806 (however without governmental power); the paréage of Köstritz remained within the principality of the younger line.
When the elder line died out with Heinrich XXIV in 1927 and the younger one when Heinrich XLV, son of the last ruler, died childless in 1945 as a prisoner of the communists, thus both main branches having become extinct, the dynastic succession (and the theoretical claims to their thrones) passed to the princely House ''Reuss of Köstritz''. This side line of the Younger Line is therefore the only branch of the entire house that still exists today, but has over 30 male members, all named Heinrich. The family council decided on June 5, 1930, that all members of the remaining family should henceforth omit any line addition (Younger Line or Köstritz) from their names and call themselves ''Prince'' or ''Princess Reuss''. This name (as well as the Heinrichs' count) was retained by a court order even in the Weimar republic
The Weimar Republic, officially known as the German Reich, was the German Reich, German state from 1918 to 1933, during which it was a constitutional republic for the first time in history; hence it is also referred to, and unofficially proclai ...
. The current head of the family, Heinrich XIV, dynastic actually ''the Fürst (Prince) Reuss of Köstritz'' (b. 1952), is also styled ''The Fürst (Prince) Reuss'', as Köstritz is no longer a side line but the only branch of the house. His main seat is Ernstbrunn Castle in Austria which his family had inherited in 1822, while Köstritz Castle was expropriated by communist East Germany
East Germany, officially known as the German Democratic Republic (GDR), was a country in Central Europe from Foundation of East Germany, its formation on 7 October 1949 until German reunification, its reunification with West Germany (FRG) on ...
in 1945 and demolished in the 1970s. In 1945, the Princes Reuss lost all of their extended possessions and castles in their ancestral homeland through expropriation. Heinrich XIV and some of his relatives regained some properties in the former Reuss states following German Reunification
German reunification () was the process of re-establishing Germany as a single sovereign state, which began on 9 November 1989 and culminated on 3 October 1990 with the dissolution of the East Germany, German Democratic Republic and the int ...
in 1990.
Aftermath
AfterWorld War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, the Reuss territories were unified in 1919 as the People's State of Reuss, which was incorporated into the new state of Thuringia
Thuringia (; officially the Free State of Thuringia, ) is one of Germany, Germany's 16 States of Germany, states. With 2.1 million people, it is 12th-largest by population, and with 16,171 square kilometers, it is 11th-largest in area.
Er ...
in 1920.
Gera
Gera () is a city in the German state of Thuringia. With around 93,000 inhabitants, it is the third-largest city in Thuringia after Erfurt and Jena as well as the easternmost city of the ''Thüringer Städtekette'', an almost straight string of ...
File:Schloss Burgk vom Saaleturm.jpg, Burgk Castle
Rulers of Reuss
House of Reuss
Partitions of Reuss under Reuss rule
Table of rulers
Side branch member's links to Reichsbürger movement
On 7 December 2022, German police conducted an operation which resulted in the arrest of 25 alleged members of the far-right group Reichsbürger, including a member of the Köstritz branch of the House of Reuss, identified as Heinrich XIII Prince Reuss. The suspects arrested in the operation were allegedly planning to overturn the existing German government, and instate Heinrich XIII as the new German ''de facto'' leader. His distant cousin Heinrich XIV Prince Reuss, the head and speaker of the House of Reuss and its family association, had previously referred to Heinrich XIII as "a confused old man who had been radicalised through disappointments". On behalf of the family association, which Heinrich XIII had left years ago, Heinrich XIV sharply distanced himself from him again after he was arrested, saying that "30 years ago he was a modern businessman, but nowadays he is fooled by all sorts of conspiracy theories". In the line of succession to the House of Reuss, Heinrich XIII only ranked 17th, and the head of the house called him "a marginal figure". He said his behaviour was a "catastrophe" for the family, whose heritage as tolerant and cosmopolitan rulers was now associated with "terrorists and reactionaries". He believes Reuss' anti-government views derive from his resentment at the German judicial system for its failure to recognize his claims to family properties expropriated at the end of World War II.In fiction
A young Reuss count, sent to the 1815Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon, Napol ...
, is the protagonist of the 1899 operetta '' Wiener Blut'' and the 1942 film based on it. Much of the hilarity of the film centers around his impossible name of "Reuss-Schleiz-Greiz".
See also
* Burgraves of MeissenReferences
Sources
* Thomas Gehrlein: ''Das Haus Reuß'' (The House of Reuss), volumes I-IV. Publisher: Börde-Verlag, Werl 2015, ISBN 978-3-9815864-6-6 or ISBN 978-3-9815864-7-3. * Friedrich Majer: ''Chronik des Fürstlichen Hauses der Reussen von Plauen.'' (Chronicle of the Princely House Reuss of Plauen), Weimar and Leipzig 1811online version
. * Sigismund Stucke: ''Die Reußen und ihr Land. Die Geschichte einer süddeutschen Dynastie.'' (The Reuss and their country. The history of a southern German dynasty), St. Michael 1984, ISBN 3-7053-1954-X. reissue: publisher Arnshaugk Verlag, Neustadt 2022, ISBN 978-3-95930-252-4. * Almanach de Gotha: ** Gothaischer Hofkalender 1781, Gotha 1780 (first publication). ** ''Gothaischer Hofkalender zum Nutzen und Vergnügen auf das Jahr 1792'', C. W. Ettinger, Gotha 1791
online version
** Gothaischer Hofkalender 1877, Gotha 1876
online version
** Gothaischer Hofkalender 1894, Gotha 1893
online version
* Gothaisches Genealogisches Handbuch, Fürstliche Häuser ''( Gotha Genealogical Handbook − german article−, Princely Houses)'', 2015, 1. Abteilung ''(first department)'', vol 1 of the complete series of the GGH books, publisher: Verlag des Deutschen Adelsarchivs ''(Publisher of the German Nobility Archive)'', Marburg 2015, pp. 227–247; 628–634. ISBN 978-3-9817243-0-1.
External links
* * Family tree in German Wikipedia: '' Stammliste des Hauses Reuß'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Reuss (State) States of the Confederation of the Rhine Counties of the Holy Roman Empire Upper Saxon Circle States and territories established in the 1010s States and territories disestablished in 1778 States and territories disestablished in 1806 1010s establishments in the Holy Roman Empire 1778 disestablishments in the Holy Roman Empire 1806 disestablishments in the Holy Roman Empire Henry VI, Holy Roman Emperor States of the German Confederation