|
Naumburg
Naumburg () is a town in (and the administrative capital of) the district Burgenlandkreis, in the state of Saxony-Anhalt, Central Germany (cultural area), Central Germany. It has a population of around 33,000. The Naumburg Cathedral became a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2018. This UNESCO designation recognizes the processes that shaped the European continent during the High Middle Ages between 1000 and 1300: Christianization, the so-called "Landesausbau" and the dynamics of cultural exchange and transfer characteristic for this very period. History The first written record of Naumburg dates from 1012, when it was mentioned as the ''new castle'' of the Ekkehardinger, the Margrave of Meissen. It was founded at the crossing of two trade-routes, Via Regia and the Regensburg Road. The successful foundation not long beforehand of a ''Propstei'' Church on the site of the later Naumburg Cathedral was mentioned in the Merseburg Bishops' Chronicles in 1021. In 1028 Pope John XIX gave hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naumburg Cathedral
Naumburg Cathedral (, ), located in Naumburg, Germany, is the former cathedral of the Bishopric of Naumburg-Zeitz. The church building, most of which dates back to the 13th century, is a renowned landmark of the German late Romanesque architecture, Romanesque and was recognised as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2018. The west Choir (architecture), choir with the famous donor portrait statues of the twelve cathedral founders (''Stifterfiguren'') and the ''Rood screen, Lettner'', works of the Naumburg Master, is one of the most significant early Gothic art, Gothic monuments. The church was erected with the relocation of the episcopal see from Zeitz in 1028, next to an old parish church. Thus it is the proto-cathedral of the former Catholic Bishopric of Naumburg-Zeitz, Diocese of Naumburg-Zeitz. With the Reformation, Naumburg and its cathedral became Protestant. Naumburg Cathedral remains a Evangelical Church of the Church Province of Saxony, Protestant parish church to this day. Naum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nietzsche-Haus, Naumburg
The Nietzsche-Haus in Naumburg, Germany, is a building dedicated to the life and work of the German philosopher Friedrich Nietzsche. History In the summer of 1858, Nietzsche's mother, Franziska Nietzsche, moved with her two children, Elisabeth and Friedrich, to 18 Weingarten in Naumburg, the site of the Nietzsche-Haus. She rented a bright, spacious apartment on the upper floor. In 1878, she bought the house and continued to live there until her death in 1897. Modern use Since 1994, the Nietzsche-Haus has been open to the public as a museum. The philosopher's life and work are documented in a permanent exhibition, while the house library in the exhibition rooms offers visitors the opportunity to learn about Nietzsche's work. In October 2010, the "Nietzsche Documentation Center" (Nietzsche Dokumentationszentrum) was opened. The building was constructed immediately next to the Nietzsche-Haus following an international architectural design competition by the city of Naumburg won by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Province Of Saxony
The Province of Saxony (), also known as Prussian Saxony (), was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and later the Free State of Prussia from 1816 until 1944. Its capital was Magdeburg. It was formed by the merger of various territories ceded or returned to Prussia in 1815 by the Congress of Vienna: most of the former northern territories of the Kingdom of Saxony (the remainder of which became part of Brandenburg or Silesia), the former French Principality of Erfurt, the Duchy of Magdeburg, the Altmark, the Principality of Halberstadt, and some other districts. The province was bounded by the Electorate of Hesse (the province of Hesse-Nassau after 1866), the Kingdom of Hanover (the province of Hanover after 1866) and the Duchy of Brunswick to the west, Hanover (again) to the north, Brandenburg to the north and east, Silesia to the south-east, and the rump kingdom of Saxony and the small Ernestine duchies to the south. Its shape was very irregular and it entirely surrou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius Von Pflug
Julius von Pflug (1499 in Eythra – 3 September 1564 in Zeitz) was the last Catholic bishop of the Diocese of Naumburg from 1542 until his death. He was one of the most significant reformers involved with the Protestant Reformation. Life He was the son of Cæsar von Pflug, who acted as commissary for the Elector of Saxony in the Leipzig Disputation in 1519. He studied at the universities of Leipzig (1510–17) and Bologna (1517–19), and returned to Germany in 1519 to become canon in Meissen. Disturbed by the religious controversies at home, he returned to Bologna, whence he went to Padua, but in 1521, induced by offers of preferment from Duke George, he returned to his native state, first of all to Dresden, and then to Leipzig, where he still continued to devote himself chiefly to humanistic interests. In 1528–29 he was again in Italy, and in 1530 he accompanied Duke George to the Diet of Augsburg. At this time he became a correspondent of Erasmus, and in his lette ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burgenlandkreis
Burgenlandkreis () is a district in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Its area is . History The district was established as Landkreis Burgenland by the merger of the former Burgenlandkreis and Landkreis Weißenfels as part of the reform of 2007. On 16 July 2007, the district parliament decided to change the name to Burgenlandkreis, which came into effect on 1 August 2007. In 2015 the skeletal remains of an ancient inhabitant of Karsdorf dated from the Early Neolithic (7200 BP) were analyzed; he turned out to belong to the paternal T1a-M70 lineage and maternal lineage H1. Towns and municipalities The Burgenlandkreis consists of the following subdivisions: Free towns The district's free towns are Hohenmölsen, Lützen, Naumburg, Teuchern, Weißenfels, and Zeitz Zeitz (; , ) is a town in the Burgenlandkreis district, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It is situated on the river White Elster, in the triangle of the federal states Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, and Sax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxe-Zeitz
The Duchy of Saxe-Zeitz () was a territory of the Holy Roman Empire established in 1656–57 as a secundogeniture of the Electorate of Saxony, Electoral Saxon house of House of Wettin. Its capital was Zeitz. The territory fell back to the Wettin electoral line in 1718. History On 20 July 1652, the Saxon elector John George I, Elector of Saxony, John George I stipulated in his will that, while the electoral dignity passes to his eldest son John George II, Elector of Saxony, John George II, his three younger brothers should receive secundogeniture principalities upon his death. After the elector died on 8 October 1656, his sons concluded the "friend-brotherly main treaty" in the Saxon residence of Dresden on 22 April 1657 and a further treaty in 1663 delineating their territories and sovereign rights definitely. These treaties created three duchies: * Saxe-Zeitz, * Saxe-Weissenfels and * Saxe-Merseburg. Prince Maurice, the fourth-oldest son received the districts of Zeitz, Naumb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt ( ; ) is a States of Germany, state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony, Thuringia and Lower Saxony. It covers an area of and has a population of 2.17 million inhabitants, making it the List of German states by area, 8th-largest state in Germany by area and the List of German states by population, 11th-largest by population. Its capital and most populous city is Magdeburg. The state of Saxony-Anhalt was formed in July 1945 after World War II, when the Soviet Military Administration in Germany, Soviet army administration in Allied-occupied Germany formed it from the former Free State of Prussia, Prussian Province of Saxony and the Free State of Anhalt. Saxony-Anhalt became part of the East Germany, German Democratic Republic in 1949, but was dissolved in 1952 during Administrative divisions of East Germany, administrative reforms and its territory was divided into the districts of Halle (Bezirk), Halle and Magdeburg (Bezirk), Magdeburg. Follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeitz
Zeitz (; , ) is a town in the Burgenlandkreis district, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It is situated on the river White Elster, in the triangle of the federal states Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, and Saxony. History First a Slavic pagan settlement later Christianized, Zeitz was first recorded under the Medieval Latin name ''Cici'' in the Synod of Ravenna in 967. Between 965 and 982, it was the chief fortress of the March of Zeitz. Zeitz was a bishop's residence between 968 and 1028, when it was moved to Naumburg. Beginning at the end of the 13th century, the bishops again resided in their castle at Zeitz. The Herrmannsschacht (built in 1889) is one of the oldest brown coal brickette factories in the world. The city was captured by Swedish troops during the Thirty Years' War and was given to Electorate of Saxony in 1644. It was the centre of Saxe-Zeitz between 1657 and 1718, before returning to the Electorate (which became the Kingdom of Saxony in 1806). In 1815, it was gi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
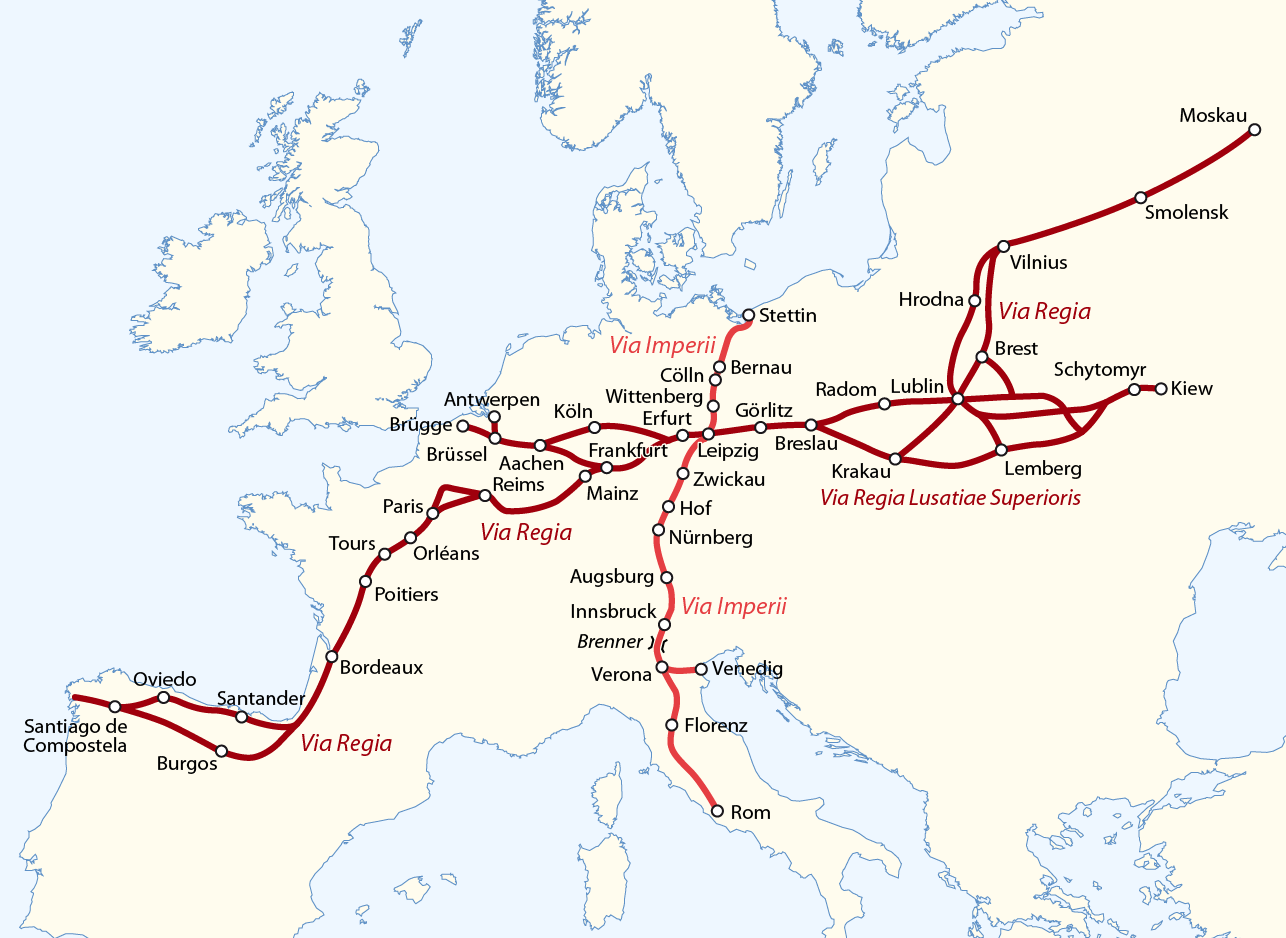
Via Regia
The Via Regia (Royal Highway) is a European Cultural Route following the route of the Historic roads, historic road of the Middle Ages. There were many such ''viae regiae'' associated with the king in the medieval Holy Roman Empire. History Origins The Via Regia ran west–east through the centre of the Holy Roman Empire, from the Rhine at Mainz-Kastel (''Elisabethenstraße'') to Frankfurt am Main, trade city and site of the Imperial election, election of the King of the Romans, continuing along Hanau, the ''Kaiserpfalz'' at Gelnhausen, the towns of Steinau an der Straße, Neuhof, Hesse, Neuhof, Fulda and Eisenach to Erfurt, a centre of Isatis tinctoria, woad production. It ran further eastwards to Eckartsberga, crossing the Saale river between Bad Kösen and Naumburg and reached Leipzig, another trade city. The eastern part continued through Upper Lusatia (''Via Regia Lusatiae Superioris'') along Großenhain, Königsbrück, Kamenz, Bautzen and Görlitz to Wrocław in Silesia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Germany (cultural Area)
Central Germany ( ) is an economic and cultural region in Germany. Its exact borders depend on context, but it is often defined as being a region within the federal states of Saxony, Thuringia and Saxony-Anhalt, or a smaller part of this region, such as the metropolitan area of Leipzig and Halle plus the surrounding counties. The name dates from the German Empire, when the region was approximately in the centre of the country. Since the German Empire's eastern territories became part of Poland and Russia in the aftermath of World War II, "Central Germany" has been located east of the centre of the country, but the name is still often used in business, media and by the Central German Metropolitan Region. Against this background, the term is not or no longer to be understood as a geographic term. History Historically also including most of Hesse, parts of Franconia and the south of Lower Saxony, the region is described as an area south of the linguistic Benrath line where C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianization
Christianization (or Christianisation) is a term for the specific type of change that occurs when someone or something has been or is being converted to Christianity. Christianization has, for the most part, spread through missions by individual conversions, but has also, in some instances, been the result of violence by individuals and groups such as governments and militaries. Christianization is also the term used to designate the conversion of previously non-Christian practices, spaces and places to Christian uses and names. In a third manner, the term has been used to describe the changes that naturally emerge in a nation when sufficient numbers of individuals convert, or when secular leaders require those changes. Christianization of a nation is an ongoing process. It began in the Roman Empire when the early individual followers of Jesus became itinerant preachers in response to the command recorded in Matthew 28:19 (sometimes called the Great Commission) to go to all the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John George I, Elector Of Saxony
John George I (5 March 1585 – 8 October 1656) was Elector of Saxony from 1611 to 1656. He led Saxony through the Thirty Years' War, which dominated his 45-year reign. Biography Born in Dresden, John George was the second son of the Elector Christian I and Sophie of Brandenburg. He belonged to the Albertine line of the House of Wettin. John George succeeded to the electorate on 23 June 1611 on the death of his elder brother, Christian II. The geographical position of the Electorate of Saxony rather than her high standing among the German Protestants gave her ruler much importance during the Thirty Years' War. At the beginning of his reign, however, the new elector took up a somewhat detached position. His personal allegiance to Lutheranism was sound, but he liked neither the growing strength of Brandenburg-Prussia nor the increasing prestige of the Palatinate; the adherence of the other branches of the Saxon ruling house to Protestantism seemed to him to suggest that the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |