reticulocytes on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
 The normal fraction of reticulocytes in the blood depends on the clinical situation but is usually 0.5% to 2.5% in adults and 2% to 6% in infants. A reticulocyte percentage that is higher than "normal" can be a sign of anemia, but this depends on the health of a person's bone marrow. Calculating the reticulocyte production index is an important step in understanding whether or not the reticulocyte count is appropriate to the situation. This is often a more important question than whether the percentage is in the normal range; for instance, if someone is anemic but has a reticulocyte percentage of only 1%, the bone marrow is likely not producing new blood cells at a rate that will correct the anemia.
The normal fraction of reticulocytes in the blood depends on the clinical situation but is usually 0.5% to 2.5% in adults and 2% to 6% in infants. A reticulocyte percentage that is higher than "normal" can be a sign of anemia, but this depends on the health of a person's bone marrow. Calculating the reticulocyte production index is an important step in understanding whether or not the reticulocyte count is appropriate to the situation. This is often a more important question than whether the percentage is in the normal range; for instance, if someone is anemic but has a reticulocyte percentage of only 1%, the bone marrow is likely not producing new blood cells at a rate that will correct the anemia.
hematology
Hematology (American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, spelled haematology in British English) is the branch of medicine concerned with the study of the cause, prognosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases related to bloo ...
, reticulocytes are immature red blood cells (RBCs). In the process of erythropoiesis (red blood cell formation), reticulocytes develop and mature in the bone marrow and then circulate for about a day in the blood stream before developing into mature red blood cells. Like mature red blood cells, in mammals, reticulocytes do not have a cell nucleus
The cell nucleus (; : nuclei) is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have #Anucleated_cells, ...
. They are called reticulocytes because of a reticular (mesh-like) network of ribosomal RNA
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes, essential to all cells. rRNA is a ribozyme which carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA is transcribed from ribosomal ...
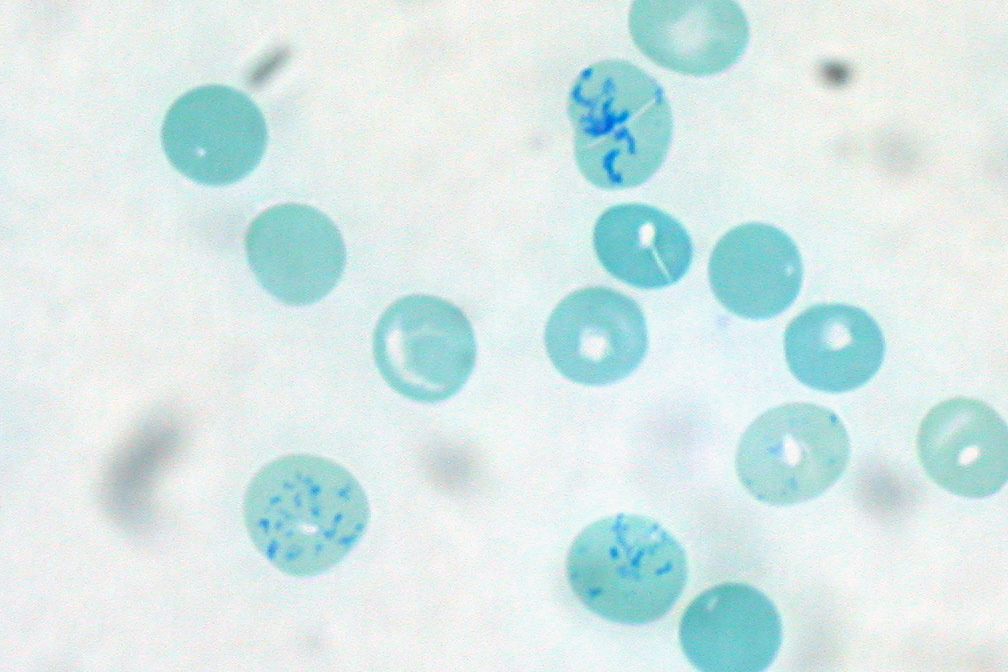
that becomes visible under a microscope with certain stains such as new methylene blue and Romanowsky stain.
Clinical significance
To accurately measure reticulocyte counts, automated counters use a combination of laser excitation, detectors and a fluorescent dye that marksRNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself (non-coding RNA) or by forming a template for the production of proteins (messenger RNA). RNA and deoxyrib ...
and DNA (such as titan yellow or polymethine).
Reticulocytes appear slightly bluer than other red cells when looked at with the normal Romanowsky stain. Reticulocytes are also relatively large, a characteristic that is described by the mean corpuscular volume.
 The normal fraction of reticulocytes in the blood depends on the clinical situation but is usually 0.5% to 2.5% in adults and 2% to 6% in infants. A reticulocyte percentage that is higher than "normal" can be a sign of anemia, but this depends on the health of a person's bone marrow. Calculating the reticulocyte production index is an important step in understanding whether or not the reticulocyte count is appropriate to the situation. This is often a more important question than whether the percentage is in the normal range; for instance, if someone is anemic but has a reticulocyte percentage of only 1%, the bone marrow is likely not producing new blood cells at a rate that will correct the anemia.
The normal fraction of reticulocytes in the blood depends on the clinical situation but is usually 0.5% to 2.5% in adults and 2% to 6% in infants. A reticulocyte percentage that is higher than "normal" can be a sign of anemia, but this depends on the health of a person's bone marrow. Calculating the reticulocyte production index is an important step in understanding whether or not the reticulocyte count is appropriate to the situation. This is often a more important question than whether the percentage is in the normal range; for instance, if someone is anemic but has a reticulocyte percentage of only 1%, the bone marrow is likely not producing new blood cells at a rate that will correct the anemia.
Immature reticulocyte fraction (IRF)
Reticulocytes at less mature levels can be detected by having higher intensity fluorescence regions. An increased immature reticulocyte fraction (IRF), specifically an IRF more than or equal to 0.23, together with an increased absolute reticulocyte count, generally indicates an adequate erythroid response to anemia. An IRF of more than 0.23 but a subnormal or normal absolute reticulocyte count (with a corresponding reticulocyte production index of less than or equal to 2) is seen in for example acute infection, iron deficiency anemia, human immunodeficiency virus infection, sickle disease with crisis, pregnancy, and myelodysplastic syndrome. An IRF of less than 0.23 is seen in diseases that lead to decreased erythropoietic activity, predominantly chronic renal insufficiency.Development
The development begins with the expulsion of the normoblast nucleus, and is followed by loss of organelles and remodeling of the plasma membrane, giving rise to an erythrocyte.Research
Reticulocytes are a valuable tool for biologists who study protein translation. Reticulocytes are unusual among cells in that they contain all of the machinery necessary to translate proteins but lack a nucleus. Since a cell's nucleus contains many components that make studying translation difficult, these cells are quite useful. Scientists can collect reticulocytes from animals such as rabbits and extract themRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of Protein biosynthesis, synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is ...
and translation enzymes to study protein translation in a cell-free, in vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning ''in glass'', or ''in the glass'') Research, studies are performed with Cell (biology), cells or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in ...
system, allowing greater control over the environment in which proteins are being synthesized.
References
{{Authority control Blood cells Human cells