Reservoir Capacitor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC), which periodically reverses direction, to direct current (DC), which flows in only one direction. The reverse operation (converting DC to AC) is performed by an inverter.
The process is known as ''rectification'', since it "straightens" the direction of current. Physically, rectifiers take a number of forms, including vacuum tube diodes, wet chemical cells, mercury-arc valves, stacks of copper and selenium oxide plates, semiconductor diodes, silicon-controlled rectifiers and other silicon-based semiconductor switches. Historically, even synchronous electromechanical switches and motor-generator sets have been used. Early radio receivers, called
A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC), which periodically reverses direction, to direct current (DC), which flows in only one direction. The reverse operation (converting DC to AC) is performed by an inverter.
The process is known as ''rectification'', since it "straightens" the direction of current. Physically, rectifiers take a number of forms, including vacuum tube diodes, wet chemical cells, mercury-arc valves, stacks of copper and selenium oxide plates, semiconductor diodes, silicon-controlled rectifiers and other silicon-based semiconductor switches. Historically, even synchronous electromechanical switches and motor-generator sets have been used. Early radio receivers, called
 The no-load output DC voltage of an ideal half-wave rectifier for a sinusoidal input voltage is:
where:
: ''V''dc, ''V''av – the DC or average output voltage,
: ''V''peak, the peak value of the phase input voltages,
: ''V''rms, the
The no-load output DC voltage of an ideal half-wave rectifier for a sinusoidal input voltage is:
where:
: ''V''dc, ''V''av – the DC or average output voltage,
: ''V''peak, the peak value of the phase input voltages,
: ''V''rms, the
 A full-wave rectifier converts the whole of the input waveform to one of constant polarity (positive or negative) at its output. Mathematically, this corresponds to the
A full-wave rectifier converts the whole of the input waveform to one of constant polarity (positive or negative) at its output. Mathematically, this corresponds to the  For single-phase AC, if the transformer is center-tapped, then two diodes back-to-back (cathode-to-cathode or anode-to-anode, depending on output polarity required) can form a full-wave rectifier. Twice as many turns are required on the transformer secondary to obtain the same output voltage than for a bridge rectifier, but the power rating is unchanged.
For single-phase AC, if the transformer is center-tapped, then two diodes back-to-back (cathode-to-cathode or anode-to-anode, depending on output polarity required) can form a full-wave rectifier. Twice as many turns are required on the transformer secondary to obtain the same output voltage than for a bridge rectifier, but the power rating is unchanged.
 The average and RMS no-load output voltages of an ideal single-phase full-wave rectifier are:
:
Very common double-diode rectifier vacuum tubes contained a single common cathode and two anodes inside a single envelope, achieving full-wave rectification with positive output. The 5U4 and the 80/5Y3 (4 pin)/(octal) were popular examples of this configuration.
The average and RMS no-load output voltages of an ideal single-phase full-wave rectifier are:
:
Very common double-diode rectifier vacuum tubes contained a single common cathode and two anodes inside a single envelope, achieving full-wave rectification with positive output. The 5U4 and the 80/5Y3 (4 pin)/(octal) were popular examples of this configuration.
 An uncontrolled three-phase, half-wave midpoint circuit requires three diodes, one connected to each phase. This is the simplest type of three-phase rectifier but suffers from relatively high harmonic distortion on both the AC and DC connections. This type of rectifier is said to have a pulse-number of three, since the output voltage on the DC side contains three distinct pulses per cycle of the grid frequency:
An uncontrolled three-phase, half-wave midpoint circuit requires three diodes, one connected to each phase. This is the simplest type of three-phase rectifier but suffers from relatively high harmonic distortion on both the AC and DC connections. This type of rectifier is said to have a pulse-number of three, since the output voltage on the DC side contains three distinct pulses per cycle of the grid frequency:
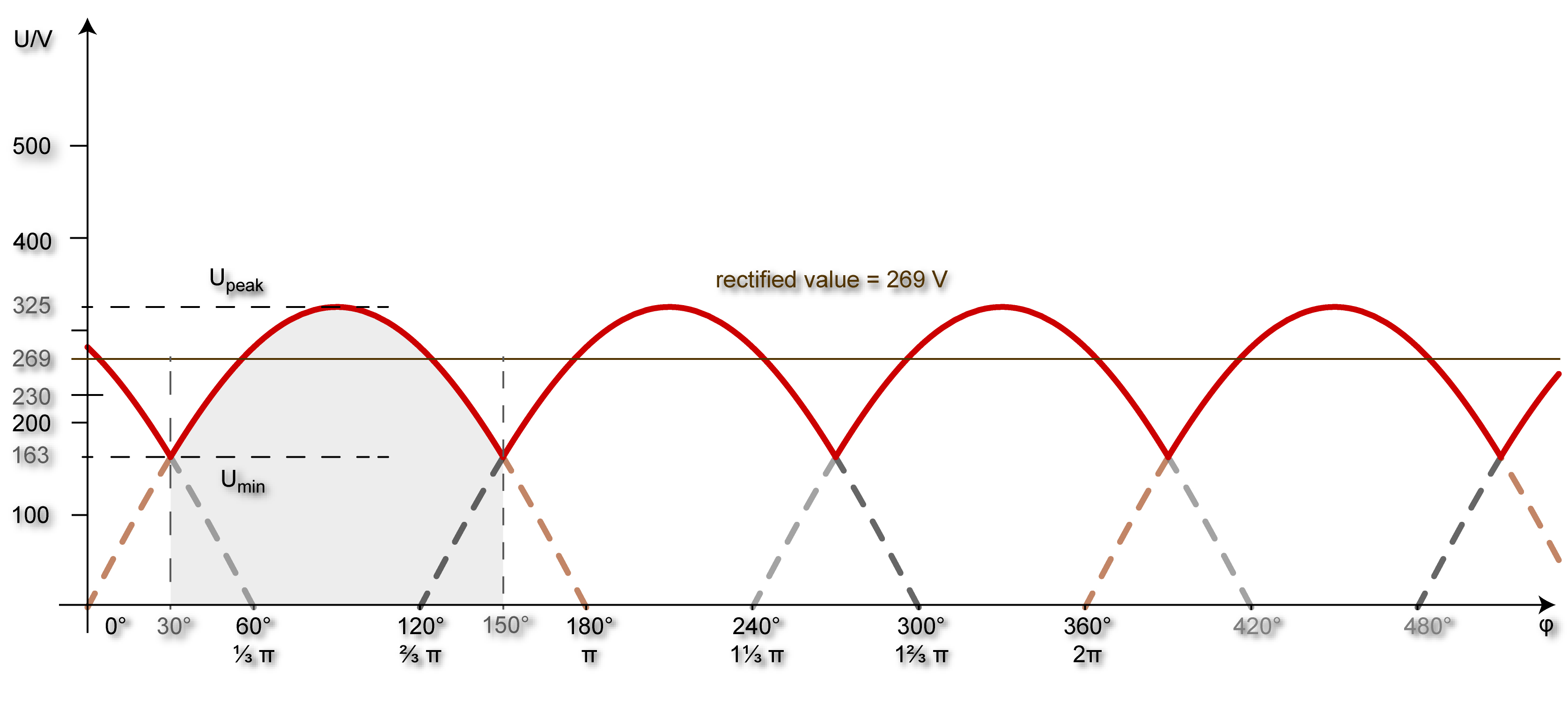 The peak values of this three-pulse DC voltage are calculated from the RMS value of the input phase voltage (line to neutral voltage, 120 V in North America, 230 V within Europe at mains operation): . The average no-load output voltage results from the integral under the graph of a positive half-wave with the period duration of (from 30° to 150°):
The peak values of this three-pulse DC voltage are calculated from the RMS value of the input phase voltage (line to neutral voltage, 120 V in North America, 230 V within Europe at mains operation): . The average no-load output voltage results from the integral under the graph of a positive half-wave with the period duration of (from 30° to 150°):
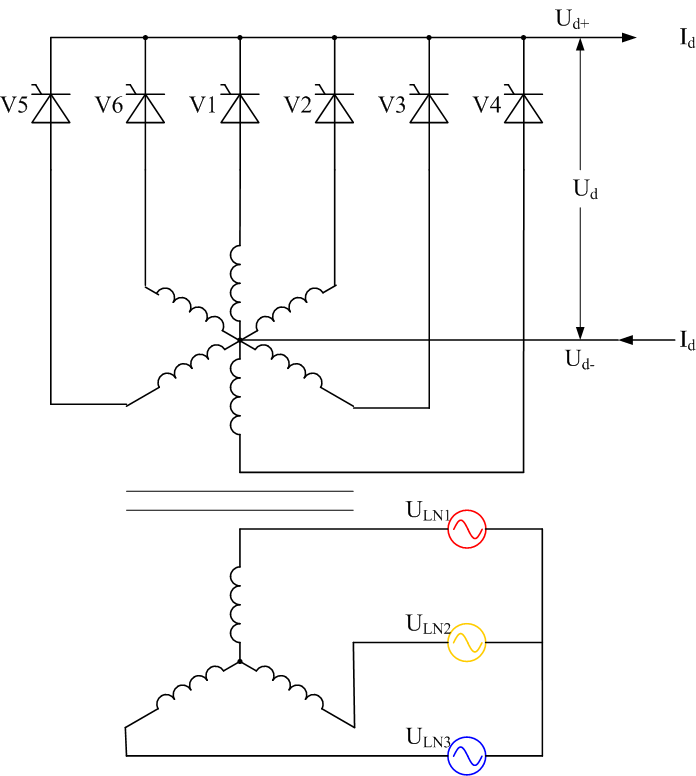 If the AC supply is fed via a transformer with a center tap, a rectifier circuit with improved harmonic performance can be obtained. This rectifier now requires six diodes, one connected to each end of each transformer secondary winding. This circuit has a pulse-number of six, and in effect, can be thought of as a six-phase, half-wave circuit.
Before
If the AC supply is fed via a transformer with a center tap, a rectifier circuit with improved harmonic performance can be obtained. This rectifier now requires six diodes, one connected to each end of each transformer secondary winding. This circuit has a pulse-number of six, and in effect, can be thought of as a six-phase, half-wave circuit.
Before
 A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC), which periodically reverses direction, to direct current (DC), which flows in only one direction. The reverse operation (converting DC to AC) is performed by an inverter.
The process is known as ''rectification'', since it "straightens" the direction of current. Physically, rectifiers take a number of forms, including vacuum tube diodes, wet chemical cells, mercury-arc valves, stacks of copper and selenium oxide plates, semiconductor diodes, silicon-controlled rectifiers and other silicon-based semiconductor switches. Historically, even synchronous electromechanical switches and motor-generator sets have been used. Early radio receivers, called
A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC), which periodically reverses direction, to direct current (DC), which flows in only one direction. The reverse operation (converting DC to AC) is performed by an inverter.
The process is known as ''rectification'', since it "straightens" the direction of current. Physically, rectifiers take a number of forms, including vacuum tube diodes, wet chemical cells, mercury-arc valves, stacks of copper and selenium oxide plates, semiconductor diodes, silicon-controlled rectifiers and other silicon-based semiconductor switches. Historically, even synchronous electromechanical switches and motor-generator sets have been used. Early radio receivers, called crystal radio
A crystal radio receiver, also called a crystal set, is a simple radio receiver, popular in the early days of radio. It uses only the power of the received radio signal to produce sound, needing no external power. It is named for its most impo ...
s, used a "cat's whisker
A crystal detector is an obsolete electronic component used in some early 20th century radio receivers that consists of a piece of crystalline mineral which rectifies the alternating current radio signal. It was employed as a detector (demod ...
" of fine wire pressing on a crystal of galena
Galena, also called lead glance, is the natural mineral form of lead(II) sulfide (PbS). It is the most important ore of lead and an important source of silver.
Galena is one of the most abundant and widely distributed sulfide minerals. It cryst ...
(lead sulfide) to serve as a point-contact rectifier or "crystal detector".
Rectifiers have many uses, but are often found serving as components of DC power supplies and high-voltage direct current power transmission systems. Rectification may serve in roles other than to generate direct current for use as a source of power. As noted, rectifiers can serve as detectors of radio signals. In gas heating systems flame rectification
Flame rectification is a phenomenon in which a flame can act as an electrical rectifier. The effect is commonly described as being caused by the greater mobility of electrons relative to that of positive ions within the flame, and the asymmetric ...
is used to detect presence of a flame.
Depending on the type of alternating current supply and the arrangement of the rectifier circuit, the output voltage may require additional smoothing to produce a uniform steady voltage. Many applications of rectifiers, such as power supplies for radio, television and computer equipment, require a ''steady'' constant DC voltage (as would be produced by a battery). In these applications the output of the rectifier is smoothed by an electronic filter
Electronic filters are a type of signal processing filter in the form of electrical circuits. This article covers those filters consisting of lumped electronic components, as opposed to distributed-element filters. That is, using components ...
, which may be a capacitor, choke, or set of capacitors, chokes and resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active el ...
s, possibly followed by a voltage regulator to produce a steady voltage.
More complex circuitry that performs the opposite function, that is converting DC to AC, is called an inverter.
Rectifier devices
Before the development of silicon semiconductor rectifiers, vacuum tube thermionic diodes and copper oxide- or selenium-based metal rectifier stacks were used. With the introduction of semiconductor electronics, vacuum tube rectifiers became obsolete, except for some enthusiasts of vacuum tubeaudio equipment
Audio equipment refers to devices that reproduce, record, or process sound. This includes microphones, radio receivers, AV receivers, CD players, tape recorders, amplifiers, mixing consoles, effects units, headphones, and Speaker (audio equipmen ...
. For power rectification from very low to very high current, semiconductor diodes of various types (junction diode
A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance); it has low (ideally zero) resistance in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other.
A diode ...
s, Schottky diodes, etc.) are widely used.
Other devices that have control electrodes as well as acting as unidirectional current valves are used where more than simple rectification is required—e.g., where variable output voltage is needed. High-power rectifiers, such as those used in high-voltage direct current power transmission, employ silicon semiconductor devices of various types. These are thyristors or other controlled switching solid-state switches, which effectively function as diodes to pass current in only one direction.
Rectifier circuits
Rectifier circuits may besingle-phase
In electrical engineering, single-phase electric power (abbreviated 1φ) is the distribution of alternating current electric power using a system in which all the voltages of the supply vary in unison. Single-phase distribution is used when loa ...
or multi-phase. Most low power rectifiers for domestic equipment are single-phase, but three-phase rectification is very important for industrial applications and for the transmission of energy as DC (HVDC).
Single-phase rectifiers
Half-wave rectification
In half-wave rectification of a single-phase supply, either the positive or negative half of the AC wave is passed, while the other half is blocked. Because only one half of the input waveform reaches the output, mean voltage is lower. Half-wave rectification requires a singlediode
A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance); it has low (ideally zero) resistance in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other.
A diode ...
in a single-phase supply, or three in a three-phase supply. Rectifiers yield a unidirectional but pulsating direct current; half-wave rectifiers produce far more ripple than full-wave rectifiers, and much more filtering is needed to eliminate harmonics of the AC frequency from the output.
root mean square
In mathematics and its applications, the root mean square of a set of numbers x_i (abbreviated as RMS, or rms and denoted in formulas as either x_\mathrm or \mathrm_x) is defined as the square root of the mean square (the arithmetic mean of the ...
(RMS) value of output voltage.
Full-wave rectification
 A full-wave rectifier converts the whole of the input waveform to one of constant polarity (positive or negative) at its output. Mathematically, this corresponds to the
A full-wave rectifier converts the whole of the input waveform to one of constant polarity (positive or negative) at its output. Mathematically, this corresponds to the absolute value
In mathematics, the absolute value or modulus of a real number x, is the non-negative value without regard to its sign. Namely, , x, =x if is a positive number, and , x, =-x if x is negative (in which case negating x makes -x positive), an ...
function. Full-wave rectification converts both polarities of the input waveform to pulsating DC (direct current), and yields a higher average output voltage. Two diodes and a center-tapped transformer, or four diodes in a bridge configuration and any AC source (including a transformer without center tap), are needed. Single semiconductor diodes, double diodes with a common cathode or common anode, and four- or six- diode bridges are manufactured as single components.
Three-phase rectifiers
Single-phase rectifiers are commonly used for power supplies for domestic equipment. However, for most industrial and high-power applications,three-phase
Three-phase electric power (abbreviated 3φ) is a common type of alternating current used in electricity generation, Electric power transmission, transmission, and Electric power distribution, distribution. It is a type of polyphase system empl ...
rectifier circuits are the norm. As with single-phase rectifiers, three-phase rectifiers can take the form of a half-wave circuit, a full-wave circuit using a center-tapped transformer, or a full-wave bridge circuit.
Thyristors are commonly used in place of diodes to create a circuit that can regulate the output voltage. Many devices that provide direct current actually ''generate'' three-phase AC. For example, an automobile alternator
An alternator is a type of electric generator used in modern automobiles to charge the automotive battery, battery and to power the electrical system when its internal combustion engine, engine is running.
Until the 1960s, automobiles used DC dyn ...
contains six diodes, which function as a full-wave rectifier for battery charging.
Three-phase, half-wave circuit
 An uncontrolled three-phase, half-wave midpoint circuit requires three diodes, one connected to each phase. This is the simplest type of three-phase rectifier but suffers from relatively high harmonic distortion on both the AC and DC connections. This type of rectifier is said to have a pulse-number of three, since the output voltage on the DC side contains three distinct pulses per cycle of the grid frequency:
An uncontrolled three-phase, half-wave midpoint circuit requires three diodes, one connected to each phase. This is the simplest type of three-phase rectifier but suffers from relatively high harmonic distortion on both the AC and DC connections. This type of rectifier is said to have a pulse-number of three, since the output voltage on the DC side contains three distinct pulses per cycle of the grid frequency:
 The peak values of this three-pulse DC voltage are calculated from the RMS value of the input phase voltage (line to neutral voltage, 120 V in North America, 230 V within Europe at mains operation): . The average no-load output voltage results from the integral under the graph of a positive half-wave with the period duration of (from 30° to 150°):
The peak values of this three-pulse DC voltage are calculated from the RMS value of the input phase voltage (line to neutral voltage, 120 V in North America, 230 V within Europe at mains operation): . The average no-load output voltage results from the integral under the graph of a positive half-wave with the period duration of (from 30° to 150°):
-\left(-\frac\right)+\frac \Biggl= \frac
: ⇒ ⇒ ≈ 1,17 ⋅
Three-phase, full-wave circuit using center-tapped transformer
 If the AC supply is fed via a transformer with a center tap, a rectifier circuit with improved harmonic performance can be obtained. This rectifier now requires six diodes, one connected to each end of each transformer secondary winding. This circuit has a pulse-number of six, and in effect, can be thought of as a six-phase, half-wave circuit.
Before
If the AC supply is fed via a transformer with a center tap, a rectifier circuit with improved harmonic performance can be obtained. This rectifier now requires six diodes, one connected to each end of each transformer secondary winding. This circuit has a pulse-number of six, and in effect, can be thought of as a six-phase, half-wave circuit.
Before solid state
Solid state, or solid matter, is one of the four fundamental states of matter.
Solid state may also refer to: