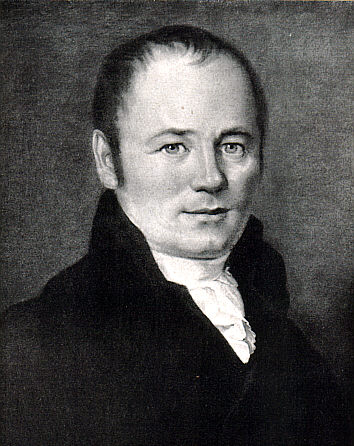|
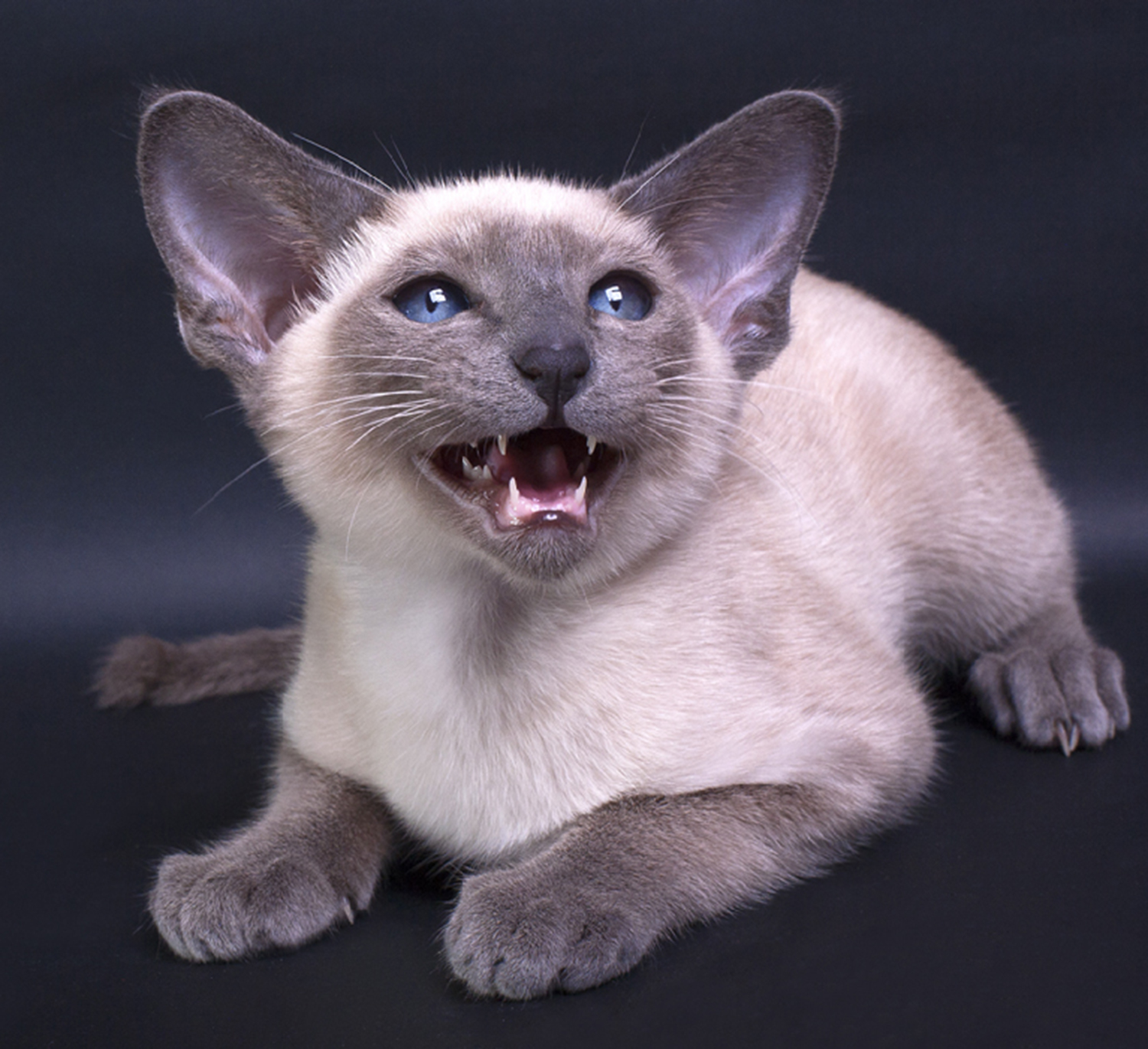
Cat
The cat (''Felis catus''), also referred to as the domestic cat or house cat, is a small domesticated carnivorous mammal. It is the only domesticated species of the family Felidae. Advances in archaeology and genetics have shown that the domestication of the cat occurred in the Near East around 7500 BC. It is commonly kept as a pet and working cat, but also ranges freely as a feral cat avoiding human contact. It is valued by humans for companionship and its ability to kill vermin. Its retractable claws are adapted to killing small prey species such as mice and rats. It has a strong, flexible body, quick reflexes, and sharp teeth, and its night vision and sense of smell are well developed. It is a social species, but a solitary hunter and a crepuscular predator. Cat intelligence is evident in their ability to adapt, learn through observation, and solve problems. Research has shown they possess strong memories, exhibit neuroplasticity, and display cognitive skills comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feral Cat
A feral cat or a stray cat is an unowned domestic cat (''Felis catus'') that lives outdoors and avoids human contact; it does not allow itself to be handled or touched, and usually remains hidden from humans. Feral cats may breed over dozens of generations and become a local apex predator in urban, savannah and bushland environments, and especially on islands where native animals did not evolve alongside predators. Some feral cats may become more comfortable with people who regularly feed them, but even with long-term attempts at socialization of animals, socialization, they usually remain aloof and reject human touch. Of the 700 million cats in the world, an estimated 480 million are feral. Feral cats are devastating to wildlife, and conservation biologists consider them to be one of the worst invasive species on Earth. They are included in the list of 100 of the World's Worst Invasive Alien Species, the world's 100 worst invasive alien species. Attempts to control feral cat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
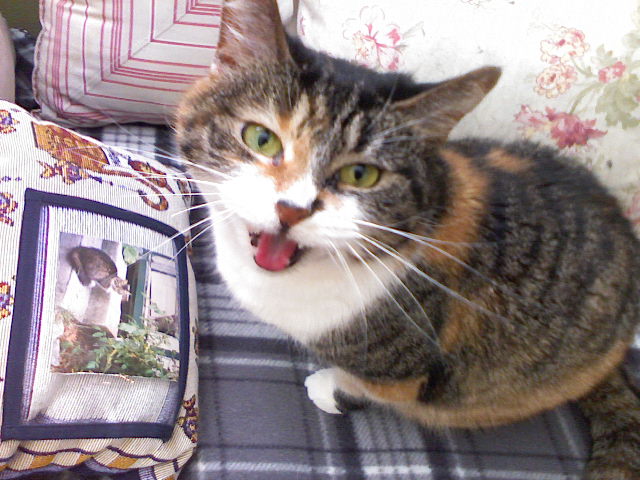
Cat Body Language
Cats communicate for a variety of reasons, including to show happiness, express anger, solicit attention, and observe potential prey. Additionally, they collaborate, play, and share resources. When cats communicate with humans, they do so to get what they need or want, such as food, water, attention, or play. As such, cat communication methods have been significantly altered by domestication. Studies have shown that domestic cats tend to meow much more than feral cats. They rarely meow to communicate with fellow cats or other animals. Cats can socialize with each other and are known to form " social ladders," where a dominant cat is leading a few lesser cats. This is common in multi-cat households. Cats can use a range of communication methods, including vocal, visual, tactile and olfactory communication. Up to 21 different cat vocalizations have been observed. They use visual signals, or body language, to express emotions like relaxation, fear, and aggression. Cats use several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cat Communication
Cats communicate for a variety of reasons, including to show happiness, express anger, solicit attention, and observe potential prey. Additionally, they collaborate, play, and share resources. When cats communicate with humans, they do so to get what they need or want, such as food, water, attention, or play. As such, cat communication methods have been significantly altered by domestication. Studies have shown that domestic cats tend to meow much more than Feral cat, feral cats. They rarely meow to communicate with fellow cats or other animals. Cats can socialize with each other and are known to form "Social status, social ladders," where a dominant cat is leading a few lesser cats. This is common in multi-cat households. Cats can use a range of communication methods, including vocal, visual, tactile communication, tactile and Olfactic communication, olfactory communication. Up to 21 different cat vocalizations have been observed. They use visual signals, or body language, to exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was the son of a curate and was born in Råshult, in the countryside of Småland, southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cat Intelligence
Cat intelligence refers to a cat’s ability to solve problems, adapt to its environment, learn new behaviors, and communicate its needs. Structurally, a cat’s brain shares similarities with the human brain, containing around 250 million neurons in the cerebral cortex, which is responsible for complex processing. Cats display neuroplasticity, allowing their brains to reorganize based on experiences. They have well-developed memory retaining information for a decade or longer. These memories are often intertwined with emotions, allowing cats to recall both positive and negative experiences associated with specific places. While they excel in observational learning and problem-solving, studies conclude that they struggle with understanding cause-and-effect relationships in the same way that humans do. The study of cat intelligence is mostly focused on domesticated cats. Living in urban environments has exposed them to challenges that require adaptive behaviors, contributing to c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Felidae
Felidae ( ) is the Family (biology), family of mammals in the Order (biology), order Carnivora colloquially referred to as cats. A member of this family is also called a felid ( ). The 41 extant taxon, extant Felidae species exhibit the greatest diversity in fur patterns of all terrestrial carnivores. Cats have retractile claws, slender muscular bodies and strong flexible forelimbs. Their teeth and facial muscles allow for a powerful bite. They are all obligate carnivores, and most are solitary predators ambushing or stalking their prey. Wild cats occur in Africa, Europe, Asia and the Americas. Some wild cat species are adapted to forest and savanna habitats, some to arid environments, and a few also to wetlands and mountainous terrain. Their activity patterns range from nocturnal and crepuscular to Diurnality, diurnal, depending on their preferred prey species. Reginald Innes Pocock divided the extant Felidae into three subfamilies: the Pantherinae, the Felinae and the Acin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domestication Of The Cat
The domestic cat originated from Near-Eastern and Egyptian populations of the African wildcat, ''Felis silvestris lybica''. The family Felidae, to which all living feline species belong, is theorized to have arisen about 12 to 13 million years ago and is divided into eight major phylogenetic lineages. The ''Felis'' lineage in particular is the lineage to which the domestic cat belongs. Several investigations have shown that all domestic varieties of cats come from a single species of the ''Felis'' lineage, ''Felis catus''. Variations of this lineage are found across the world, and until recently scientists have found it difficult to identify exactly which region gave rise to modern domestic cat breeds. Scientists believed that it was not just one incident that led to the domesticated cat but multiple independent incidents at different places that led to these breeds. More complications arose from the fact that wildcat populations as a whole are very widespread and very similar to o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purr
A purr or whirr is a tonal fluttering sound made by some species of felids, including both larger, wild cats and the domestic cat (''Felis catus''), as well as two species of genets. It varies in loudness and tone among species and in the same animal. In smaller and domestic cats it is known as a purr, while in larger felids, such as the cheetah, it is called a whirr. Although true purring is exclusive to felids and viverrids, other animals such as raccoons produce vocalizations that sound similar to true purring. Animals that produce purr-like sounds include mongooses, kangaroos, wallabies, wallaroos, badgers, rabbits and guinea pigs. Animals purr for a variety of reasons, including to express happiness or fear, and as a defense mechanism. It has also been shown that cats purr to manage pain and soothe themselves. Purring is a soft buzzing sound, similar to a rolled 'r' in human speech, with a fundamental frequency of around 25 Hz. This sound occurs with notic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meow
A meow or miaow is a cat vocalization. ''Meows'' may have diverse tones in terms of their sound, and what is heard can vary from being chattered to calls, murmurs, and whispers. Adult cats rarely meow to each other. Thus, an adult cat meowing to human beings is generally considered a post-domestication extension of meowing by kittens: a call for attention. Felines usually communicate with each other via their shared sense of smell, yet with people they often make verbal cues around behavior, such as having a specific sound indicate a desire to go outside. A mew is a high-pitched meow often produced by kittens. It is apparently used to solicit attention from the kitten's mother, and adult cats may use it as well. The mew is similar to what is described in ''Brown et al. 1978'' as an isolation call. By around three to four weeks of age kittens do not mew when at least one littermate is present, and at four to five months of age kittens stop mewing altogether. Background an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology (biology), morphology, behaviour, or ecological niche. In addition, palaeontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. About 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a binomial nomenclature, two-part name, a "binomen". The first part of a binomen is the name of a genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name (zoology), specific name or the specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Christian Gmelin
Karl (Carl) Christian Gmelin (18 March 1762, in Badenweiler – 26 June 1837, in Karlsruhe) was a German botanist. He was the brother of engraver Wilhelm Friedrich Gmelin (1760–1820). He studied medicine and natural sciences at the universities of Strasbourg and Erlangen, receiving his doctorate at the latter school in 1784. Following graduation, he worked as teacher of natural history at the high school in Karlsruhe, a post he maintained for the next 50 years. Among his better known students was future botanist Alexander Braun. In Karlsruhe he also served as director of the botanical garden and was in charge of the margravial natural history collection. He was the author of the three-volume ''Flora Badensis Alsatica'' (1805–08). Some plants with the specific epithet of ''gmelinii'' commemorate his name. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Working Cat
A working cat, also known as a mouser, is type of domestic cat that "works" for its keep by hunting vermin, such as rodents. They are commonly employed where pest control is needed, such as barns, farms, factories, warehouses, stores, churchyards, and private property. Types of working cats include the bodega cat, farm cat, ship's cat, and library cat. A benefit of using a working cat is that they alleviate the need for harmful pesticides. Working cats are often placed in their environment as a part of a working cats program. The resident cat at the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, British Prime Minister's home at 10 Downing Street has been given the title Chief Mouser to the Cabinet Office. Working cats programs A working cats program is designed to place cats in safe environments where they are valued for their hunting skills as working cats. These programs are typically offered by animal shelters who will use otherwise unadoptable cats in the program as an alternative to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |