Reproductive on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The reproductive system of an organism, also known as the genital system, is the biological system made up of all the anatomical organs involved in
Body Guide powered by Adam

 Most
Most

sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex life cycle in which a gamete ( haploid reproductive cells, such as a sperm or egg cell) with a single set of chromosomes combines with another gamete to produce a zygote tha ...
. Many non-living substances such as fluids, hormone
A hormone (from the Ancient Greek, Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of cell signaling, signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physio ...
s, and pheromone
A pheromone () is a secreted or excreted chemical factor that triggers a social response in members of the same species. Pheromones are chemicals capable of acting like hormones outside the body of the secreting individual, to affect the behavio ...
s are also important accessories to the reproductive system. Unlike most organ system
An organ system is a biological system consisting of a group of organ (biology), organs that work together to perform one or more bodily functions. Each organ has a specialized role in an organism body, and is made up of distinct Tissue (biolog ...
s, the sexes of differentiated species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
often have significant differences. These differences allow for a combination of genetic material between two individuals, which allows for the possibility of greater genetic fitness of the offspring
In biology, offspring are the young creation of living organisms, produced either by sexual reproduction, sexual or asexual reproduction. Collective offspring may be known as a brood or progeny. This can refer to a set of simultaneous offspring ...
.Reproductive System 2001Body Guide powered by Adam
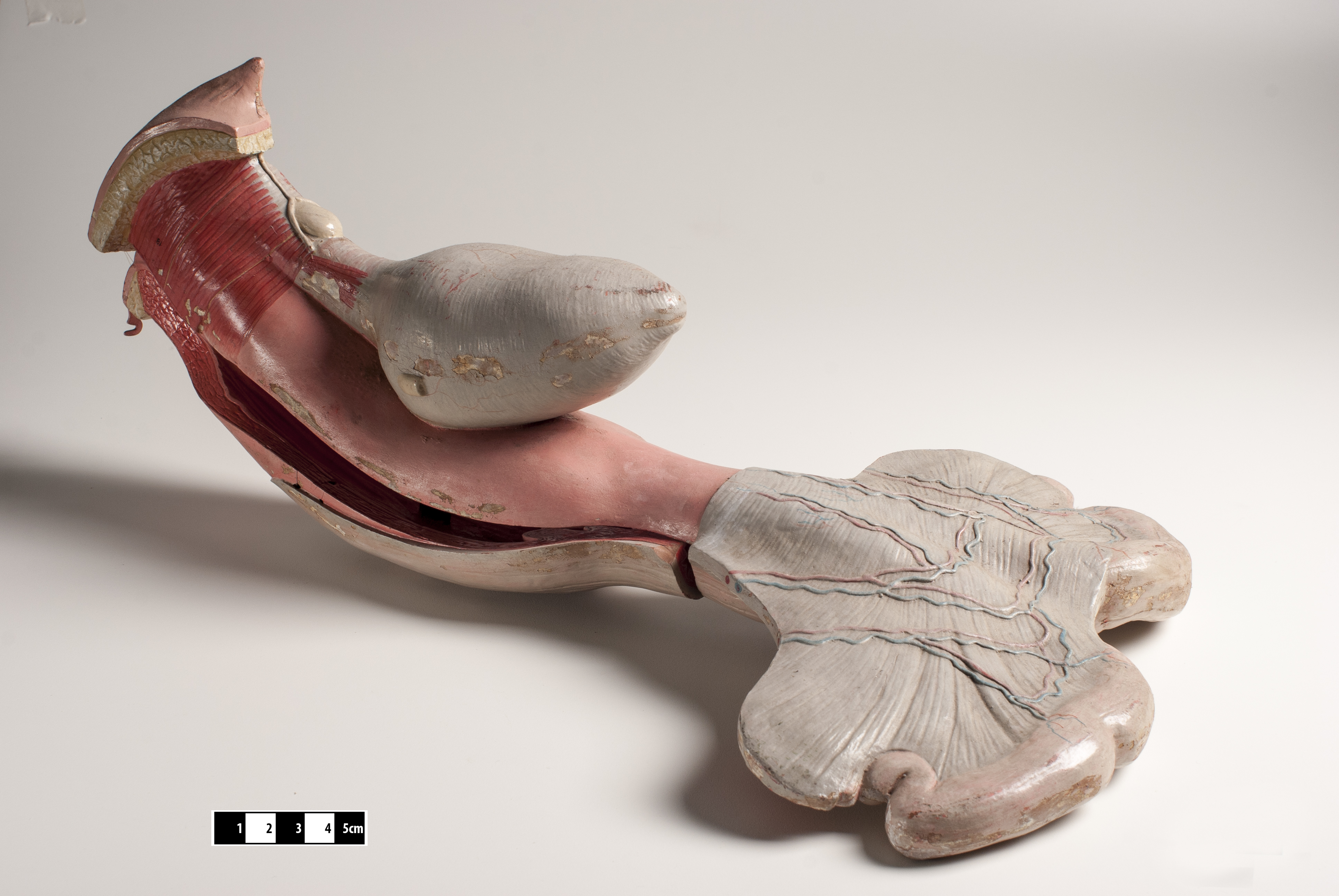
Animals
In mammals, the major organs of the reproductive system include the external genitalia (penis
A penis (; : penises or penes) is a sex organ through which male and hermaphrodite animals expel semen during copulation (zoology), copulation, and through which male placental mammals and marsupials also Urination, urinate.
The term ''pen ...
and vulva
In mammals, the vulva (: vulvas or vulvae) comprises mostly external, visible structures of the female sex organ, genitalia leading into the interior of the female reproductive tract. For humans, it includes the mons pubis, labia majora, lab ...
) as well as a number of internal organs, including the gamete
A gamete ( ) is a Ploidy#Haploid and monoploid, haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as s ...
-producing gonad
A gonad, sex gland, or reproductive gland is a Heterocrine gland, mixed gland and sex organ that produces the gametes and sex hormones of an organism. Female reproductive cells are egg cells, and male reproductive cells are sperm. The male gon ...
s (testicles and ovaries). Diseases of the human reproductive system are very common and widespread, particularly communicable sexually transmitted infection
A sexually transmitted infection (STI), also referred to as a sexually transmitted disease (STD) and the older term venereal disease (VD), is an infection that is Transmission (medicine), spread by Human sexual activity, sexual activity, e ...
s.
Most other vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
s have similar reproductive systems consisting of gonads, ducts, and openings. However, there is a great diversity of physical adaptation
In biology, adaptation has three related meanings. Firstly, it is the dynamic evolutionary process of natural selection that fits organisms to their environment, enhancing their evolutionary fitness. Secondly, it is a state reached by the p ...
s as well as reproductive strategies in every group of vertebrates.
Vertebrates
Vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
s share key elements of their reproductive systems. They all have gamete-producing organs known as gonad
A gonad, sex gland, or reproductive gland is a Heterocrine gland, mixed gland and sex organ that produces the gametes and sex hormones of an organism. Female reproductive cells are egg cells, and male reproductive cells are sperm. The male gon ...
s. In females, these gonads are then connected by oviduct
The oviduct in vertebrates is the passageway from an ovary. In human females, this is more usually known as the fallopian tube. The eggs travel along the oviduct. These eggs will either be fertilized by spermatozoa to become a zygote, or will dege ...
s to an opening to the outside of the body, typically the cloaca, but sometimes to a unique pore such as a vagina
In mammals and other animals, the vagina (: vaginas or vaginae) is the elastic, muscular sex organ, reproductive organ of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vulval vestibule to the cervix (neck of the uterus). The #Vag ...
.
Humans
The human reproductive system usually involves internal fertilization bysexual intercourse
Sexual intercourse (also coitus or copulation) is a sexual activity typically involving the insertion of the Erection, erect male Human penis, penis inside the female vagina and followed by Pelvic thrust, thrusting motions for sexual pleasure ...
. During this process, the male inserts their erect penis
An erection (clinically: penile erection or penile tumescence) is a Physiology, physiological phenomenon in which the penis becomes firm, engorged, and enlarged. Penile erection is the result of a complex interaction of psychological, neural, ...
into the female
An organism's sex is female ( symbol: ♀) if it produces the ovum (egg cell), the type of gamete (sex cell) that fuses with the male gamete (sperm cell) during sexual reproduction.
A female has larger gametes than a male. Females and ...
's vagina
In mammals and other animals, the vagina (: vaginas or vaginae) is the elastic, muscular sex organ, reproductive organ of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vulval vestibule to the cervix (neck of the uterus). The #Vag ...
and ejaculates semen
Semen, also known as seminal fluid, is a bodily fluid that contains spermatozoon, spermatozoa which is secreted by the male gonads (sexual glands) and other sexual organs of male or hermaphrodite, hermaphroditic animals. In humans and placen ...
, which contains sperm
Sperm (: sperm or sperms) is the male reproductive Cell (biology), cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm ...
. The sperm then travels through the vagina and cervix into the uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', : uteri or uteruses) or womb () is the hollow organ, organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans, that accommodates the embryonic development, embryonic and prenatal development, f ...
or fallopian tube
The fallopian tubes, also known as uterine tubes, oviducts or salpinges (: salpinx), are paired tubular sex organs in the human female body that stretch from the Ovary, ovaries to the uterus. The fallopian tubes are part of the female reproduct ...
s for fertilization of the ovum. Upon successful fertilization
Fertilisation or fertilization (see American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), spelling differences), also known as generative fertilisation, syngamy and impregnation, is the fusion of gametes to give ...
and implantation, gestation
Gestation is the period of development during the carrying of an embryo, and later fetus, inside viviparous animals (the embryo develops within the parent). It is typical for mammals, but also occurs for some non-mammals. Mammals during pregn ...
of the fetus
A fetus or foetus (; : fetuses, foetuses, rarely feti or foeti) is the unborn offspring of a viviparous animal that develops from an embryo. Following the embryonic development, embryonic stage, the fetal stage of development takes place. Pren ...
then occurs within the female's uterus for approximately nine months, this process is known as pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestation, gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Conception (biology), Conception usually occurs ...
in humans. Gestation ends with childbirth
Childbirth, also known as labour, parturition and delivery, is the completion of pregnancy, where one or more Fetus, fetuses exits the Womb, internal environment of the mother via vaginal delivery or caesarean section and becomes a newborn to ...
, delivery following labor. Labor consists of the muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contra ...
s of the uterus contracting, the cervix dilating, and the baby passing out the vagina (the female genital organ). Human's babies and children are nearly helpless and require high levels of parental care for many years. One important type of parental care is the use of the mammary gland
A mammary gland is an exocrine gland that produces milk in humans and other mammals. Mammals get their name from the Latin word ''mamma'', "breast". The mammary glands are arranged in organs such as the breasts in primates (for example, human ...
s in the female breast
The breasts are two prominences located on the upper ventral region of the torso among humans and other primates. Both sexes develop breasts from the same embryology, embryological tissues. The relative size and development of the breasts is ...
s to nurse the baby.
The female reproductive system has two functions: The first is to produce egg cells, and the second is to protect and nourish the offspring until birth. The male reproductive system has one function, and it is to produce and deposit sperm. Humans have a high level of sexual differentiation. In addition to differences in nearly every reproductive organ, numerous differences typically occur in secondary sexual characteristic
A secondary sex characteristic is a physical characteristic of an organism that is related to or derived from its sex, but not directly part of its reproductive system. In humans, these characteristics typically start to appear during puberty ...
s.
=Male
= The male reproductive system is a series of organs located outside of the body and around the pelvic region of amale
Male (Planet symbols, symbol: ♂) is the sex of an organism that produces the gamete (sex cell) known as sperm, which fuses with the larger female gamete, or Egg cell, ovum, in the process of fertilisation. A male organism cannot sexual repro ...
that contribute towards the reproduction process. The primary direct function of the male reproductive system is to provide the male sperm for fertilization of the ovum.
The major reproductive organs of the male can be grouped into three categories. The first category is sperm production and storage. Production takes place in the testicle
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is Homology (biology), homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of Androgen, androgens, p ...
s, which are housed in the temperature regulating scrotum, immature sperm then travel to the epididymides
The epididymis (; : epididymides or ) is an elongated tubular genital organ attached to the posterior side of each one of the two male reproductive glands, the testicles. It is a single, narrow, tightly coiled tube in adult humans, in length; ...
for development and storage. The second category is the ejaculatory fluid-producing glands which include the seminal vesicles, prostate
The prostate is an male accessory gland, accessory gland of the male reproductive system and a muscle-driven mechanical switch between urination and ejaculation. It is found in all male mammals. It differs between species anatomically, chemica ...
, and the vasa deferentia. The final category are those used for copulation, and deposition of the spermatozoa (sperm
Sperm (: sperm or sperms) is the male reproductive Cell (biology), cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm ...
) within the male, these include the penis
A penis (; : penises or penes) is a sex organ through which male and hermaphrodite animals expel semen during copulation (zoology), copulation, and through which male placental mammals and marsupials also Urination, urinate.
The term ''pen ...
, urethra, vas deferens
The vas deferens (: vasa deferentia), ductus deferens (: ductūs deferentes), or sperm duct is part of the male reproductive system of many vertebrates. In mammals, spermatozoa are produced in the seminiferous tubules and flow into the epididyma ...
, and Cowper's gland.
Major secondary sex characteristics include larger, more muscular stature, deepened voice, facial and body hair, broad shoulders, and development of an Adam's apple
The Adam's apple is the protrusion in the neck formed by the angle of the thyroid cartilage surrounding the larynx, typically visible in men, less frequently in women. The prominence of the Adam's apple increases in some men as a secondary mal ...
. An important sexual hormone of males is androgen
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning ) is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This includes ...
, and particularly testosterone
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and androgen in Male, males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testicles and prostate, as well as promoting se ...
.
The testes release a hormone that controls the development of sperm. This hormone is also responsible for the development of physical characteristics in men such as facial hair and a deep voice.
=Female
= The human female reproductive system is a series of organs primarily located inside of the body and around the pelvic region of afemale
An organism's sex is female ( symbol: ♀) if it produces the ovum (egg cell), the type of gamete (sex cell) that fuses with the male gamete (sperm cell) during sexual reproduction.
A female has larger gametes than a male. Females and ...
that contribute towards the reproductive process. The human female reproductive system contains three main parts: the vulva
In mammals, the vulva (: vulvas or vulvae) comprises mostly external, visible structures of the female sex organ, genitalia leading into the interior of the female reproductive tract. For humans, it includes the mons pubis, labia majora, lab ...
, which leads to the vagina, the vaginal opening, to the uterus; the uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', : uteri or uteruses) or womb () is the hollow organ, organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans, that accommodates the embryonic development, embryonic and prenatal development, f ...
, which holds the developing fetus; and the ovaries
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are endocr ...
, which produce the female's ova. The breast
The breasts are two prominences located on the upper ventral region of the torso among humans and other primates. Both sexes develop breasts from the same embryology, embryological tissues. The relative size and development of the breasts is ...
s are involved during the parenting stage of reproduction, but in most classifications they are not considered to be part of the female reproductive system.
The vagina meets the outside at the vulva
In mammals, the vulva (: vulvas or vulvae) comprises mostly external, visible structures of the female sex organ, genitalia leading into the interior of the female reproductive tract. For humans, it includes the mons pubis, labia majora, lab ...
, which also includes the labia
The labia are the major externally visible structures of the vulva. In humans and other primates, there are two pairs of labia: the ''labia majora'' (outer lips) are large and thick folds of skin that cover the vulva's other parts, while the ''la ...
, clitoris
In amniotes, the clitoris ( or ; : clitorises or clitorides) is a female sex organ. In humans, it is the vulva's most erogenous zone, erogenous area and generally the primary anatomical source of female Human sexuality, sexual pleasure. Th ...
and urethra; during intercourse, this area is lubricated by mucus secreted by the Bartholin's glands. The vagina is attached to the uterus through the cervix
The cervix (: cervices) or cervix uteri is a dynamic fibromuscular sexual organ of the female reproductive system that connects the vagina with the uterine cavity. The human female cervix has been documented anatomically since at least the time ...
, while the uterus is attached to the ovaries via the fallopian tubes. Each ovary contains hundreds of ova (singular '' ovum'').
Approximately every 28 days, the pituitary gland
The pituitary gland or hypophysis is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, the pituitary gland is located at the base of the human brain, brain, protruding off the bottom of the hypothalamus. The pituitary gland and the hypothalamus contr ...
releases a hormone
A hormone (from the Ancient Greek, Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of cell signaling, signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physio ...
that stimulates some of the ova to develop and grow. One ovum is released and it passes through the fallopian tube into the uterus. Hormones produced by the ovaries prepare the uterus to receive the ovum. The ovum will move through her fallopian tubes and awaits the sperm for fertilization to occur. When this does not occur, i.e. no sperm for fertilization, the lining of the uterus, called the endometrium
The endometrium is the inner epithelium, epithelial layer, along with its mucous membrane, of the mammalian uterus. It has a basal layer and a functional layer: the basal layer contains stem cells which regenerate the functional layer. The funct ...
, and unfertilized ova are shed each cycle through the process of menstruation
Menstruation (also known as a period, among other colloquial terms) is the regular discharge of blood and Mucous membrane, mucosal tissue from the endometrium, inner lining of the uterus through the vagina. The menstrual cycle is characterized ...
. If the ovum is fertilized by sperm, it will attach to the endometrium and embryonic development will begin.
Other mammals

 Most
Most mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
reproductive systems are similar, however, there are some notable differences between the non-human mammals and humans. For instance, most male mammals have a penis which is stored internally until erect, and most have a penis bone or baculum
The baculum (: bacula), also known as the penis bone, penile bone, ''os penis'', ''os genitale'', or ''os priapi'', is a bone in the penis of many placental mammals. It is not present in humans, but is present in the penises of some primates, ...
. Additionally, both males and females of most species do not remain continually sexually fertile as humans do and the females of most mammalian species don't grow permanent mammaries like human females do either. Like humans, most groups of mammals have descended testicles found within a scrotum, however, others have descended testicles that rest on the ventral body wall, and a few groups of mammals, such as elephants, have undescended testicles found deep within their body cavities near their kidney
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organ (anatomy), organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and rig ...
s.
The reproductive system of marsupials is unique in that the female has two vaginae, both of which open externally through one orifice but lead to different compartments within the uterus; males usually have a two-pronged penis, which corresponds to the females' two vaginae. Marsupials typically develop their offspring in an external pouch containing teats to which their newborn young ( joeys) attach themselves for post uterine development. Also, marsupials have a unique prepenial scrotum. The long newborn joey instinctively crawls and wriggles the , while clinging to fur, on the way to its mother's pouch.
In regards to males, the mammalian penis has a similar structure in reptiles and a small percentage of birds while the scrotum is only present in mammals. Regarding females, the vulva is unique to mammals with no homologue in birds, reptiles, amphibians, or fish. The clitoris, however, can be found in some reptiles and birds.
In place of the uterus and vagina, non-mammal vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
groups have an unmodified oviduct leading directly to a cloaca
A cloaca ( ), : cloacae ( or ), or vent, is the rear orifice that serves as the only opening for the digestive (rectum), reproductive, and urinary tracts (if present) of many vertebrate animals. All amphibians, reptiles, birds, cartilagin ...
, which is a shared exit-hole for gametes, urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and many other animals. In placental mammals, urine flows from the Kidney (vertebrates), kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder and exits the urethra through the penile meatus (mal ...
, and feces
Feces (also known as faeces American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, or fæces; : faex) are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the ...
. Monotremes (i.e. platypus and echidnas), a group of egg-laying mammals, also lack a uterus, vagina, and vulva, and in that respect have a reproductive system resembling that of a reptile.
=Dogs
= In domestic canines, sexual maturity (puberty) occurs between the ages of 6 and 12 months for both males and females, although this can be delayed until up to two years of age for some large breeds.=Horses
= The mare's reproductive system is responsible for controlling gestation, birth, and lactation, as well as her estrous cycle and mating behavior. The stallion's reproductive system is responsible for his sexual behavior and secondary sex characteristics (such as a large crest).=Even-toed ungulates
=Birds
Male and female birds have acloaca
A cloaca ( ), : cloacae ( or ), or vent, is the rear orifice that serves as the only opening for the digestive (rectum), reproductive, and urinary tracts (if present) of many vertebrate animals. All amphibians, reptiles, birds, cartilagin ...
, an opening through which eggs, sperm, and wastes pass. Intercourse is performed by pressing the lips of the cloacae together, which is sometimes known as an intromittent organ which is known as a phallus that is analogous to the mammals' penis. The female lays amniotic eggs in which the young fetus continues to develop after it leaves the female's body. Unlike most vertebrates, female birds typically have only one functional ovary and oviduct
The oviduct in vertebrates is the passageway from an ovary. In human females, this is more usually known as the fallopian tube. The eggs travel along the oviduct. These eggs will either be fertilized by spermatozoa to become a zygote, or will dege ...
. As a group, birds, like mammals, are noted for their high level of parental care.
Reptiles
Reptiles are almost allsexually dimorphic
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where sexes of the same species exhibit different Morphology (biology), morphological characteristics, including characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most dioecy, di ...
, and exhibit internal fertilization through the cloaca. Some reptiles lay eggs while others are ovoviviparous (animals that deliver live young). Reproductive organs are found within the cloaca of reptiles. Most male reptiles have copulatory organs, which are usually retracted or inverted and stored inside the body. In turtles and crocodilians, the male has a single median penis-like organ, while male snakes and lizards each possess a pair of penis-like organs.

Amphibians
Mostamphibian
Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniote, anamniotic, tetrapod, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class (biology), class Amphibia. In its broadest sense, it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all Tetrapod, tetrapods, but excl ...
s exhibit external fertilization of eggs, typically within the water, though some amphibians such as caecilian
Caecilians (; ) are a group of limbless, vermiform (worm-shaped) or serpentine (snake-shaped) amphibians with small or sometimes nonexistent eyes. They mostly live hidden in soil or in streambeds, and this cryptic lifestyle renders caecilians ...
s have internal fertilization. All have paired, internal gonads, connected by ducts to the cloaca.
Fish
Fish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ...
exhibit a wide range of different reproductive strategies. Most fish, however, are oviparous
Oviparous animals are animals that reproduce by depositing fertilized zygotes outside the body (i.e., by laying or spawning) in metabolically independent incubation organs known as eggs, which nurture the embryo into moving offsprings kno ...
and exhibit external fertilization. In this process, females use their cloaca to release large quantities of their gametes, called spawn into the water and one or more males release "milt", a white fluid containing many sperm over the unfertilized eggs. Other species of fish are oviparous and have internal fertilization aided by pelvic or anal fins that are modified into an intromittent organ analogous to the human penis. A small portion of fish species are either viviparous or ovoviviparous, and are collectively known as livebearers.
Fish gonads are typically pairs of either ovaries or testicles. Most fish are sexually dimorphic but some species are hermaphroditic or unisexual.
Invertebrates
Invertebrate
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordata, chordate s ...
s have an extremely diverse array of reproductive systems, the only commonality may be that they all lay eggs. Also, aside from cephalopod
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan Taxonomic rank, class Cephalopoda (Greek language, Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral symm ...
s and arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metam ...
s, nearly all other invertebrates are hermaphroditic and exhibit external fertilization.
Cephalopods
Allcephalopod
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan Taxonomic rank, class Cephalopoda (Greek language, Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral symm ...
s are sexually dimorphic
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where sexes of the same species exhibit different Morphology (biology), morphological characteristics, including characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most dioecy, di ...
and reproduce by laying eggs. Most cephalopods have semi-internal fertilization, in which the male places his gametes inside the female's mantle cavity or pallial cavity to fertilize the ova found in the female's single ovary
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/ oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are end ...
. Likewise, male cephalopods have only a single testicle
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is Homology (biology), homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of Androgen, androgens, p ...
. In the female of most cephalopods the nidamental glands aid in development of the egg.
The "penis" in most unshelled male cephalopods (Coleoidea
Coleoidea
or Dibranchiata is one of the two subclasses of cephalopod molluscs containing all the various taxa popularly thought of as "soft-bodied" or "shell-less" (i.e. octopus, squid and cuttlefish). Unlike its extant sister group Nauti ...
) is a long and muscular end of the gonoduct used to transfer spermatophores to a modified arm called a hectocotylus. That in turn is used to transfer the spermatophores to the female. In species where the hectocotylus is missing, the "penis" is long and able to extend beyond the mantle cavity and transfer the spermatophores directly to the female.
Insects
Mostinsect
Insects (from Latin ') are Hexapoda, hexapod invertebrates of the class (biology), class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (Insect morphology#Head, head, ...
s reproduce oviparous
Oviparous animals are animals that reproduce by depositing fertilized zygotes outside the body (i.e., by laying or spawning) in metabolically independent incubation organs known as eggs, which nurture the embryo into moving offsprings kno ...
ly, i.e. by laying eggs. The eggs are produced by the female in a pair of ovaries
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are endocr ...
. Sperm
Sperm (: sperm or sperms) is the male reproductive Cell (biology), cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm ...
, produced by the male in one testis
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is Homology (biology), homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of Androgen, androgens, p ...
or more commonly two, is transmitted to the female during mating by means of external genitalia. The sperm is stored within the female in one or more spermatheca
The spermatheca (pronounced : spermathecae ), also called ''receptaculum seminis'' (: ''receptacula seminis''), is an organ of the female reproductive tract in insects, e.g. ants, bees, some molluscs, Oligochaeta worms and certain other in ...
e. At the time of fertilization
Fertilisation or fertilization (see American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), spelling differences), also known as generative fertilisation, syngamy and impregnation, is the fusion of gametes to give ...
, the eggs travel along oviduct
The oviduct in vertebrates is the passageway from an ovary. In human females, this is more usually known as the fallopian tube. The eggs travel along the oviduct. These eggs will either be fertilized by spermatozoa to become a zygote, or will dege ...
s to be fertilized by the sperm and are then expelled from the body ("laid"), in most cases via an ovipositor.
Arachnids
Arachnids may have one or twogonad
A gonad, sex gland, or reproductive gland is a Heterocrine gland, mixed gland and sex organ that produces the gametes and sex hormones of an organism. Female reproductive cells are egg cells, and male reproductive cells are sperm. The male gon ...
s, which are located in the abdomen. The genital opening is usually located on the underside of the second abdominal segment. In most species, the male transfers sperm to the female in a package, or spermatophore. Complex courtship rituals have evolved in many arachnids to ensure the safe delivery of the sperm to the female.
Arachnids usually lay yolky eggs, which hatch into immatures that resemble adults. Scorpions, however, are either ovoviviparous or viviparous, depending on species, and bear live young.
Plants
Among all living organisms,flower
Flowers, also known as blooms and blossoms, are the reproductive structures of flowering plants ( angiosperms). Typically, they are structured in four circular levels, called whorls, around the end of a stalk. These whorls include: calyx, m ...
s, which are the reproductive structures of angiosperms, are the most varied physically and show a correspondingly great diversity in methods of reproduction. Plants that are not flowering plants (green alga
The green algae (: green alga) are a group of chlorophyll-containing autotrophic eukaryotes consisting of the phylum Prasinodermophyta and its unnamed sister group that contains the Chlorophyta and Charophyta/ Streptophyta. The land plants ( ...
e, moss
Mosses are small, non-vascular plant, non-vascular flowerless plants in the taxonomic phylum, division Bryophyta (, ) ''sensu stricto''. Bryophyta (''sensu lato'', Wilhelm Philippe Schimper, Schimp. 1879) may also refer to the parent group bryo ...
es, liverwort
Liverworts are a group of non-vascular land plants forming the division Marchantiophyta (). They may also be referred to as hepatics. Like mosses and hornworts, they have a gametophyte-dominant life cycle, in which cells of the plant carry ...
s, hornworts, fern
The ferns (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta) are a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. They differ from mosses by being vascular, i.e., having specialized tissue ...
s and gymnosperm
The gymnosperms ( ; ) are a group of woody, perennial Seed plant, seed-producing plants, typically lacking the protective outer covering which surrounds the seeds in flowering plants, that include Pinophyta, conifers, cycads, Ginkgo, and gnetoph ...
s such as conifer
Conifers () are a group of conifer cone, cone-bearing Spermatophyte, seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the phylum, division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a sin ...
s) also have complex interplays between morphological adaptation and environmental factors in their sexual reproduction. The breeding system, or how the sperm from one plant fertilizes the ovum of another, depends on the reproductive morphology, and is the single most important determinant of the genetic structure of nonclonal plant populations. Christian Konrad Sprengel (1793) studied the reproduction of flowering plants and for the first time it was understood that the pollination
Pollination is the transfer of pollen from an anther of a plant to the stigma (botany), stigma of a plant, later enabling fertilisation and the production of seeds. Pollinating agents can be animals such as insects, for example bees, beetles or bu ...
process involved both biotic and abiotic interactions.
Fungi
Fungal reproduction is complex, reflecting the differences in lifestyles and genetic makeup within this diverse kingdom of organisms. It is estimated that a third of all fungi reproduce using more than one method of propagation; for example, reproduction may occur in two well-differentiated stages within the life cycle of a species, the teleomorph and the anamorph.Kirk ''et al''., p. 633. Environmental conditions trigger genetically determined developmental states that lead to the creation of specialized structures for sexual or asexual reproduction. These structures aid reproduction by efficiently dispersing spores or spore-containing propagules.See also
* Major systems of the human body * Reproductive system disease * Human sexuality * Human sexual behavior *Plant sexuality
Plant reproductive morphology is the study of the physical form and structure (the morphology) of those parts of plants directly or indirectly concerned with sexual reproduction.
Among all living organisms, flowers, which are the reproductive ...
*Meiosis
Meiosis () is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one c ...
References
Cited literature
* * *External links
{{Authority control Fertility Endocrine system