reading frames on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In 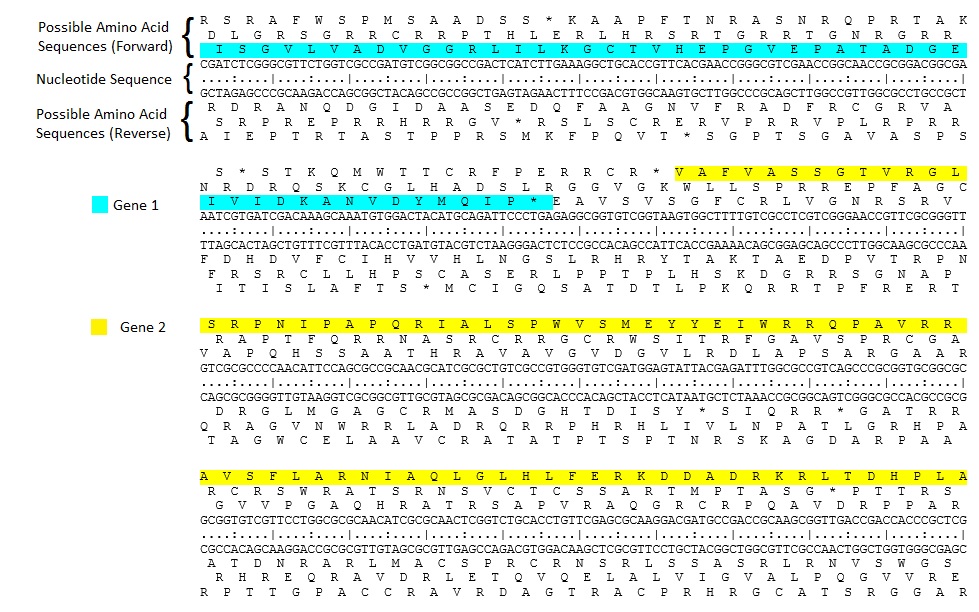
 In
In molecular biology
Molecular biology is a branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecule, molecular basis of biological activity in and between Cell (biology), cells, including biomolecule, biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactio ...
, a reading frame is a specific choice out of the possible ways to read the sequence of nucleotides in a nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are large biomolecules that are crucial in all cells and viruses. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomer components: a pentose, 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main classes of nuclei ...
(DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
or RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself (non-coding RNA) or by forming a template for the production of proteins (messenger RNA). RNA and deoxyrib ...
) molecule as a sequence of triplets. Where these triplets equate to amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
s or stop signals during translation
Translation is the communication of the semantics, meaning of a #Source and target languages, source-language text by means of an Dynamic and formal equivalence, equivalent #Source and target languages, target-language text. The English la ...
, they are called codons.
A single strand of a nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are large biomolecules that are crucial in all cells and viruses. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomer components: a pentose, 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main classes of nuclei ...
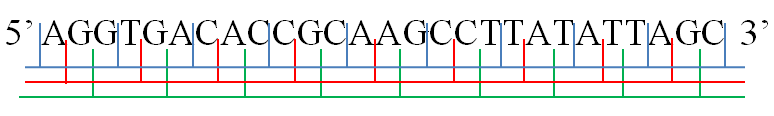
molecule has a phosphoryl end, called the 5′-end, and a hydroxyl or 3′-end. These define the 5′→3′ direction. There are three reading frames that can be read in this 5′→3′ direction, each beginning from a different nucleotide in a triplet. In a double stranded nucleic acid, an additional three reading frames may be read from the other, complementary strand in the 5′→3′ direction along this strand. As the two strands of a double-stranded nucleic acid molecule are antiparallel, the 5′→3′ direction on the second strand corresponds to the 3′→5′ direction along the first strand.
In general, at the most, one reading frame in a given section of a nucleic acid, is biologically relevant (open reading frame
In molecular biology, reading frames are defined as spans of DNA sequence between the start and stop codons. Usually, this is considered within a studied region of a prokaryotic DNA sequence, where only one of the six possible reading frames ...
). Some viral transcripts can be translated using multiple, overlapping reading frames. There is one known example of overlapping reading frames in mammalian mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA and mDNA) is the DNA located in the mitochondrion, mitochondria organelles in a eukaryotic cell that converts chemical energy from food into adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is a small portion of the D ...
: coding portions of genes for 2 subunits of ATPase overlap.

Genetic code
DNA encodes protein sequence by a series of three-nucleotide codons. Any given sequence of DNA can therefore be read in six different ways: Three reading frames in one direction (starting at different nucleotides) and three in the opposite direction. During transcription, the RNA polymerase read the template DNA strand in the 3′→5′ direction, but the mRNA is formed in the 5′ to 3′ direction. The mRNA is single-stranded and therefore only contains three possible reading frames, of which only one is translated. The codons of the mRNA reading frame are translated in the 5′→3′ direction intoamino acids
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the Proteinogenic amino acid, 22 α-amino acids incorporated into p ...
by a ribosome
Ribosomes () are molecular machine, macromolecular machines, found within all cell (biology), cells, that perform Translation (biology), biological protein synthesis (messenger RNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order s ...
to produce a polypeptide chain.
Open reading frame
Anopen reading frame
In molecular biology, reading frames are defined as spans of DNA sequence between the start and stop codons. Usually, this is considered within a studied region of a prokaryotic DNA sequence, where only one of the six possible reading frames ...
(ORF) is a reading frame that has the potential to be transcribed into RNA and translated into protein. It requires a continuous sequence of DNA which may include a start codon
The start codon is the first codon of a messenger RNA (mRNA) transcript translated by a ribosome. The start codon always codes for methionine in eukaryotes and archaea and a ''N''-formylmethionine (fMet) in bacteria, mitochondria and plastids.
...
, through a subsequent region which has a length that is a multiple of 3 nucleotides, to a stop codon
In molecular biology, a stop codon (or termination codon) is a codon (nucleotide triplet within messenger RNA) that signals the termination of the translation process of the current protein. Most codons in messenger RNA correspond to the additio ...
in the same reading frame.
When a putative amino acid sequence resulting from the translation of an ORF remained unknown in mitochondrial and chloroplast genomes, the corresponding open reading frame was called an unidentified reading frame (URF). For example, the MT-ATP8 gene was first described as URF A6L when the complete human mitochondrial genome was sequenced.
Multiple reading frames
The usage of multiple reading frames leads to the possibility of overlapping genes; there may be many of these in viral, prokaryote, and mitochondrialgenome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as ...
s. Some viruses, e.g. hepatitis B virus and BYDV, use several overlapping genes in different reading frames.
In rare cases, a ribosome may shift from one frame to another during translation of an mRNA ( translational frameshift). This causes the first part of the mRNA to be translated in one reading frame, and the latter part to be translated in a different reading frame. This is distinct from a frameshift mutation, as the nucleotide sequence (DNA or RNA) is not altered—only the frame in which it is read.
See also
*Genetic code
Genetic code is a set of rules used by living cell (biology), cells to Translation (biology), translate information encoded within genetic material (DNA or RNA sequences of nucleotide triplets or codons) into proteins. Translation is accomplished ...
* Directionality (molecular biology)
Directionality, in molecular biology and biochemistry, is the end-to-end chemical orientation of a single strand of nucleic acid. In a single strand of DNA or RNA, the chemical convention of naming carbon atoms in the nucleotide Pentose, pentose- ...
* Sense (molecular biology)
References