Ramath Gilead on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ramoth-Gilead (, meaning "Heights of Gilead"), was a
 According to (), Ramoth-Gilead was the base of Ben-Geber, one of
According to (), Ramoth-Gilead was the base of Ben-Geber, one of
Photos of Rumeith
at the
Levitical city
In the Hebrew Bible, the Levitical cities were 48 cities in ancient Israel set aside for the tribe of Levi, who were not allocated their own territorial land when the Israelites entered the Promised Land.
Numbers 35:1-8 relates God's command t ...
and city of refuge east of the Jordan River
The Jordan River or River Jordan (, ''Nahr al-ʾUrdunn''; , ''Nəhar hayYardēn''), also known as ''Nahr Al-Sharieat'' (), is a endorheic river in the Levant that flows roughly north to south through the Sea of Galilee and drains to the Dead ...
in the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
. '' Douay–Rheims Bible The Douay–Rheims Bible (, ), also known as the Douay–Rheims Version, Rheims–Douai Bible or Douai Bible, and abbreviated as D–R, DRB, and DRV, is a translation of the Bible from the Latin Vulgate into English made by member ...
. It was located in the tribal territorial allotment of the . '' Douay–Rheims Bible The Douay–Rheims Bible (, ), also known as the Douay–Rheims Version, Rheims–Douai Bible or Douai Bible, and abbreviated as D–R, DRB, and DRV, is a translation of the Bible from the Latin Vulgate into English made by member ...
tribe of Gad
According to the Bible, the Tribe of Gad () was one of the Twelve Tribes of Israel who, after the Exodus from Egypt, settled on the eastern side of the Jordan River. It is one of the ten lost tribes.
Biblical narrative
After the conquest of ...
.
Biblical events
 According to (), Ramoth-Gilead was the base of Ben-Geber, one of
According to (), Ramoth-Gilead was the base of Ben-Geber, one of King Solomon
King is a royal title given to a male monarch. A king is an absolute monarch if he holds unrestricted governmental power or exercises full sovereignty over a nation. Conversely, he is a constitutional monarch if his power is restrained by f ...
's regional governors. He was responsible for ("to him belonged") the towns
A town is a type of a human settlement, generally larger than a village but smaller than a city.
The criteria for distinguishing a town vary globally, often depending on factors such as population size, economic character, administrative stat ...
of Jair
In the Hebrew Bible, Biblical Book of Judges, Jair or Yair ( ''Yā’īr'', "he enlightens") was a man from Gilead. He was of the Tribe of Manasseh and also descended from the Tribe of Judah (Numbers 32:39-41, 1 Chronicles 2:21-23). Jair Hebrew ...
the son of Manasseh
Manasseh () is both a given name and a surname. Its variants include Manasses and Manasse.
Notable people with the name include:
Surname
* Ezekiel Saleh Manasseh (died 1944), Singaporean rice and opium merchant and hotelier
* Jacob Manasseh ( ...
, in Gilead and the region of Argob
The Lajat (/ALA-LC: ''al-Lajāʾ''), also spelled ''Lejat'', ''Lajah'', ''el-Leja'' or ''Laja'', is the largest lava field in southern Syria, spanning some 900 square kilometers. Located about southeast of Damascus, the Lajat borders the Haura ...
in Bashan
Bashan (; ; or ''Basanitis'') is the ancient, biblical name used for the northernmost region of Transjordan during the Iron Age. It is situated in modern-day Jordan and Syria. Its western part, nowadays known as the Golan Heights, was occupied b ...
: sixty large cities with walls and bronze gate-bars.
It appears to have been lost to Syria (Aram-Damascus
Aram-Damascus ( ) was an Arameans, Aramean polity that existed from the late-12th century BCE until 732 BCE, and was centred around the city of Damascus in the Southern Levant. Alongside various tribal lands, it was bounded in its later years b ...
) during the battles between the northern kingdom of Israel
The Kingdom of Israel ( ), also called the Northern Kingdom or the Kingdom of Samaria, was an Israelite kingdom that existed in the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. Its beginnings date back to the first half of the 10th century BCE. It c ...
and Syria, as Ahab
Ahab (; ; ; ; ) was a king of the Kingdom of Israel (Samaria), the son and successor of King Omri, and the husband of Jezebel of Sidon, according to the Hebrew Bible. He is depicted in the Bible as a Baal worshipper and is criticized for causi ...
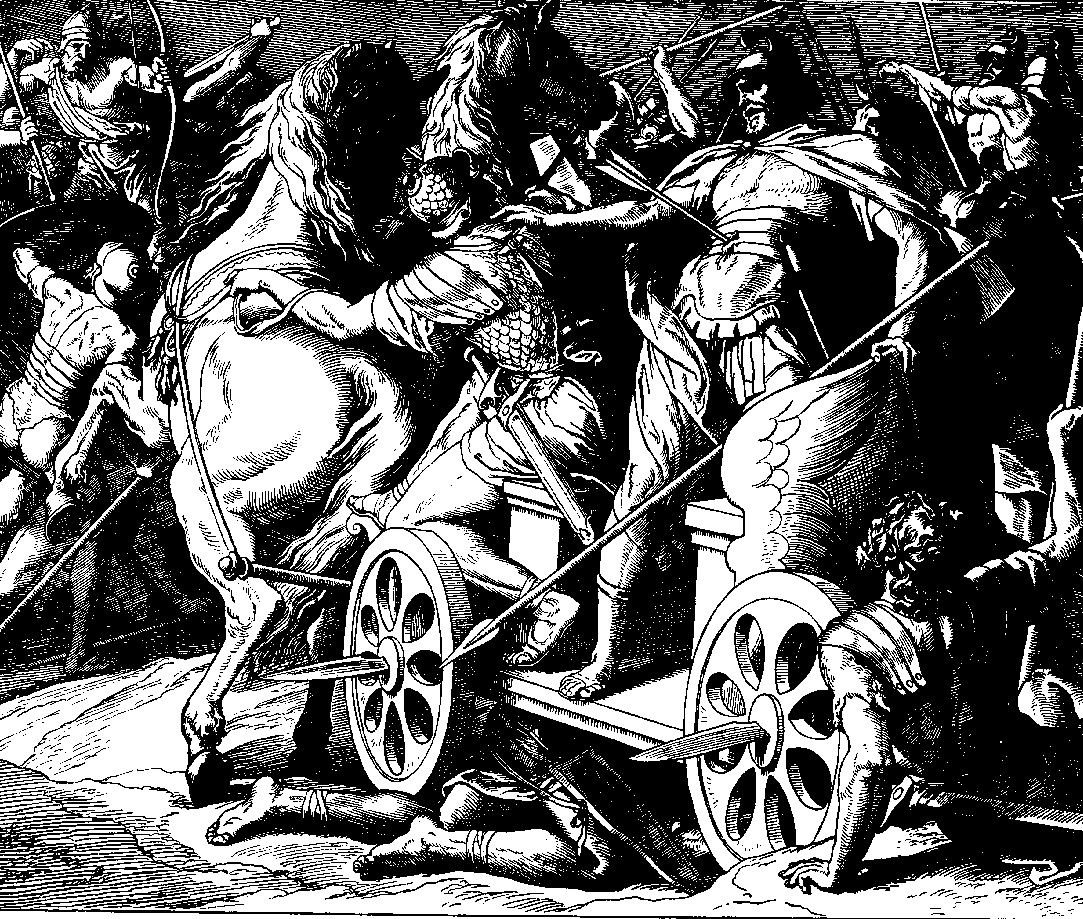
, King of Israel, proposed to go to battle to win it back. After consulting prophets about the prospects of success, Ahab went to fight for Ramoth in Gilead, aided by Jehoshaphat
Jehoshaphat (; alternatively spelled Jehosaphat, Josaphat, or Yehoshafat; ; ; ), according to the Hebrew Bible, was the son of Asa, and the fourth king of the Kingdom of Judah, in succession to his father. His children included Jehoram, who ...
, King of Judah. During the battle, Ahab was wounded by an arrow. He was propped up in his chariot facing the enemy, but by evening Ahab had bled to death and the Syrians won the battle.
Later, an incident occurred when Ahaziah Ahaziah (, "held by Yah(-weh)"; Douay–Rheims: Ochozias) was the name of two kings mentioned in the Hebrew Bible:
*Ahaziah of Israel
*Ahaziah of Judah
Ahaziah of Judah (; ''Okhozias''; ) or Jehoahaz I (; ), was the sixth king of Judah, an ...
and Joram fought against Hazael
Hazael (; ; Old Aramaic 𐤇𐤆𐤀𐤋 ''Ḥzʔl'') was a king of Aram-Damascus mentioned in the Bible. Under his reign, Aram-Damascus became an empire that ruled over large parts of contemporary Syria and Israel-Samaria. While he was likely ...
, king of Aram-Damascus
Aram-Damascus ( ) was an Arameans, Aramean polity that existed from the late-12th century BCE until 732 BCE, and was centred around the city of Damascus in the Southern Levant. Alongside various tribal lands, it was bounded in its later years b ...
, and Joram was wounded ( 2 Kings 8:28).
Also in this city, Elisha
Elisha was, according to the Hebrew Bible, a Jewish prophet and a wonder-worker. His name is commonly transliterated into English as Elisha via Hebrew, Eliseus via Greek and Latin, Ełishe (Yeghishe/Elisha) via Armenian or Alyasa via Arabic, a ...
, the prophet of God told one of the sons of the prophets to anoint Jehu
Jehu (; , meaning "Jah, Yah is He"; ''Ya'úa'' 'ia-ú-a'' ) was the tenth king of the Kingdom of Israel (Samaria), northern Kingdom of Israel since Jeroboam I, noted for exterminating the house of Ahab. He was the son of Jehoshaphat (father ...
, Joram's commander, king over Israel ().
The British Bible scholar, Hugh J. Schonfield theorized that the location of Armageddon
Armageddon ( ; ; ; from ) is the prophesied gathering of armies for a battle during the end times, according to the Book of Revelation in the New Testament of the Christian Bible. Armageddon is variously interpreted as either a literal or a ...
, mentioned only in the New Testament
The New Testament (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus, as well as events relating to Christianity in the 1st century, first-century Christianit ...
, at (), is a Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
garbling of a supposed late Aramaic
Aramaic (; ) is a Northwest Semitic language that originated in the ancient region of Syria and quickly spread to Mesopotamia, the southern Levant, Sinai, southeastern Anatolia, and Eastern Arabia, where it has been continually written a ...
name for Ramoth-Gilead; that this location, having anciently belonged to the Hebrew tribe of Gad, was, in New Testament times, part of the Greek region known as the Decapolis
The Decapolis (Greek: ) was a group of ten Greek Hellenistic cities on the eastern frontier of the Greek and late Roman Empire in the Southern Levant in the first centuries BC and AD. Most of the cities were located to the east of the Jordan ...
, it was (Schonfield theorized) known as ''Rama-Gad-Yavan'' (Yavan meaning Greek), which when translated into Greek became Armageddon (much as Ramathaim
Ramathaim-Zophim (), also called Ramah () and Ramatha in the Douay–Rheims Bible translation (Ramathaimsophim in the Vulgate), is a city from the Hebrew Bible, the home town and resting place of prophet Samuel. The name of the town means "the he ...
was translated to Aramathea).
Location
It has been tentatively identified with Reimun, on the northern slope of theZarqa River
The Zarqa River (, ''Nahr az-Zarqāʾ'', lit. "the River of the Blue ity) is the second largest tributary of the lower Jordan River, after the Yarmouk River. It is the third largest river in the region by annual discharge and its watershed enc ...
, about west of Jerash
Jerash (; , , ) is a city in northern Jordan. The city is the administrative center of the Jerash Governorate, and has a population of 50,745 as of 2015. It is located 30.0 miles north of the capital city Amman.
The earliest evidence of sett ...
or Gerasa, one of the cities of the Decapolis
The Decapolis (Greek: ) was a group of ten Greek Hellenistic cities on the eastern frontier of the Greek and late Roman Empire in the Southern Levant in the first centuries BC and AD. Most of the cities were located to the east of the Jordan ...
.
Other possible locations include:
# Tell er-Rumeith, about 3 miles south of ar-Ramtha
Ar-Ramtha (), colloquially transliterated as Ar-Romtha (), is a city situated in the far northwest of Jordan near the border with Syria. It covers 40 km2 on a plain 30 km northeast of the Jordan River and Irbid. In 2017, Ar-Ramtha had a ...
, JordanFinkelstein, I., Lipschits, O., and Sergi, O. 2013. Tell er-Rumeith in Northern Jordan: Some Archaeological and Historical Observations. Semitica 55: 7-23.
#as-Salt
Al-Salt ( ''Al-Salt''), also known as Salt, is an ancient trading city and administrative centre in west-central Jordan. It is on the old main highway leading from Amman to Jerusalem. Situated in the Balqa (region), Balqa highland, about 790– ...
.
References
External links
Photos of Rumeith
at the
American Center of Research
The American Center of Research (ACOR) is a private, not-for-profit scholarly and educational organization. Based in Alexandria, Virginia, with a facility in Amman, Jordan, ACOR promotes knowledge of Jordan and the interconnected region, past an ...
{{coord, 32, 30, N, 36, 01, E, region:JO_type:landmark_source:kolossus-dewiki, display=title
Torah cities
Hebrew Bible cities
Levitical cities
Jerash
Book of Deuteronomy
Book of Joshua