|
Ahab
Ahab (; ; ; ; ) was a king of the Kingdom of Israel (Samaria), the son and successor of King Omri, and the husband of Jezebel of Sidon, according to the Hebrew Bible. He is depicted in the Bible as a Baal worshipper and is criticized for causing moral decline in Israel, though modern scholars argue that Ahab was a Yahwist himself. The existence of Ahab is historically supported outside the Bible. The contemporary Kurkh Monolith inscription of king Shalmaneser III from the Neo-Assyrian Empire documented in 853 BC that Shalmaneser III defeated an alliance of a dozen kings in the Battle of Qarqar; one of these was Ahab. Though not named, he is also mentioned on the inscriptions of the Mesha Stele. Ahab became king of Israel in the thirty-eighth year of King Asa of Judah, and reigned for twenty-two years, according to 1 Kings 16:29. William F. Albright dated his reign to 869–850 BC, while Edwin R. Thiele offered the dates 874–853 BC. Most recently, Michael Coogan has dated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurkh Monolith
The Kurkh Monoliths are two Assyrian stelae of and 879 BC that contain a description of the reigns of Ashurnasirpal II and his son Shalmaneser III. The Monoliths were discovered in 1861 by a British archaeologist John George Taylor, who was the British Consul-General stationed in the Ottoman Eyalet of Kurdistan, at a site called Kurkh, which is now known as Üçtepe Höyük, in the district of Bismil, in the province of Diyarbakir of Turkey. Both stelae were donated by Taylor to the British Museum in 1863. The Shalmaneser III monolith contains a description of the Battle of Qarqar at the end. This description contains the name "A-ha-ab-bu Sir-ila-a-a”, providing the first extrabiblical reference to Ahab, king of Israel; although this is the only reference to the term "Israel" in Assyrian and Babylonian records, which usually refer to the Northern Kingdom as the "House of Omri" in reference to its ruling dynasty—a fact brought up by some scholars who dispute the propo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jezebel
Jezebel ()"Jezebel" (US) and was the daughter of Ithobaal I of Tyre, Lebanon, Tyre and the wife of Ahab, Kingdom of Israel (Samaria), King of Israel, according to the Books of Kings, Book of Kings of the Hebrew Bible (1 Kings 16, ). In the biblical narrative, Jezebel replaced Yahwism with Baal and Asherah worship and was responsible for Naboth's death. This caused irreversible damage to the reputation of the Omrides, Omride dynasty, who were already unpopular among the Israelites. For these offences, Jezebel was Defenestration, defenestrated and devoured by dogs, under Jehu's orders, which Elijah prophesied (2 Kings 9, ). Later, in the Book of Revelation, the name Jezebel is contemptuously attributed to a prophetic woman of Thyatira, whom the author, through the v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Qarqar
The Battle of Qarqar (or Ḳarḳar) was fought in 853 BC when the army of the Neo-Assyrian Empire led by Emperor Shalmaneser III encountered an allied army of eleven kings at Qarqar led by Hadadezer, called in Assyrian ''Adad-idir'' and possibly to be identified with King Benhadad II of Aram-Damascus; and Ahab, king of Israel. This battle, fought during the 854–846 BC Assyrian conquest of Aram, is notable for having a larger number of combatants than any previous battle, and for being the first instance in which some peoples enter recorded history, such as the Arabs. The battle is recorded on the Kurkh Monoliths. Using a different rescension of the Assyrian Eponym List would put the battle's date at 854 BC. The ancient town of Qarqar at which the battle took place has generally been identified with the modern-day archaeological site of Tell Qarqur near the village of Qarqur in Hama Governorate, northwestern Syria. According to an inscription later erected by Shalmanese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1 Kings 16
1 Kings 16 is the sixteenth chapter of the Books of Kings in the Hebrew Bible or the First Book of Kings in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. The book is a compilation of various annals recording the acts of the kings of Israel and Judah by a Deuteronomic compiler in the seventh century BCE, with a supplement added in the sixth century BCE. 1 Kings 12:1-16:14 documents the consolidation of the kingdoms of northern Israel and Judah. This chapter focusses on the reigns of Baasha, Elah, Zimri, Omri and Ahab in the northern kingdom during the reign of Asa in the southern kingdom. Text This chapter was originally written in the Hebrew language and since the 16th century is divided into 34 verses. Textual witnesses Some early manuscripts containing the text of this chapter in Hebrew are of the Masoretic Text tradition, which includes the Codex Cairensis (895), Aleppo Codex (10th century), and Codex Leningradensis (1008). There is also a translation into Koine Greek know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omrides
The Omride dynasty, Omrides or House of Omri (; ) were the ruling dynasty of the Kingdom of Israel (Samaria), Kingdom of Samaria founded by King Omri (King of Israel), Omri. The dynasty's rule ended with the murder of Jehoram of Israel by Jehu in c. 841 BC. Five Assyrian records are known to refer to either "Land of Omri" or "House of Omri". An archaeological reference to Omri and his unnamed son is found in the Mesha Stele, the only Northwest Semitic languages, Northwest Semitic inscription known to reference this name. According to the Bible, the Omride rulers of Israel were Omri, Ahab, Ahaziah of Israel, Ahaziah and Jehoram of Israel, Jehoram. Ahab's daughter Athaliah also became queen regnant of the Kingdom of Judah. Biblical account Overall, the Bible portrays the Omrides as apostates, who abandoned Yahwism for Baal worship. In terms of foreign policy, they dealt with troublesome neighbors, such as Aram-Damascus and Moab, and allied with the Kingdom of Judah via Marriage of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athaliah
Athaliah ( ''Gotholía''; ) was the daughter of King Ahab and Queen Jezebel of Israel; she was queen consort of kingdom of Judah, Judah as the wife of Jehoram of Judah, King Jehoram, a descendant of King David, and was later queen regnant c. 841–835 BCE. Biblical narrative Accounts of Athaliah’s life are found in Books of Kings, 2 Kings 8:16–11:16 and Books of Chronicles, 2 Chronicles 2 Chronicles 22, 22:10–23:15 in the Hebrew Bible. According to the Deuteronomist, she was the daughter of king Omri of Israel Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...; however, she is usually considered to have been the daughter of King Ahab – the son of Omri – and his wife, Queen Jezebel. Some scholars believe Athaliah was the daughter of Omri, but that she grew up as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahaziah Of Israel
Ahaziah (, " Yah has grasped"; also , ''Ochozias'' in the Septuagint and the Douai-Rheims translation) was the eighth king of the northern Kingdom of Israel and the son of Ahab and Jezebel. Like his father, he reigned from Samaria. William F. Albright has dated his reign to 850–849 BC, while E. R. Thiele offers the dates 853–852 BC. The author of the ''Books of Kings'' criticized him for following the ways of his father Ahab and his mother Jezebel, and for making Israel sin "in the way of Jeroboam the son of Nebat". Biblical commentator Albert Barnes notes that the phrase "in the way of his mother" does not occur anywhere else in the Hebrew Bible, and demonstrates the strong feeling of the writer of the Books of Kings as to the influence of Jezebel. Reign During his reign the Moabites revolted against his authority (). This event is recorded on the Mesha stele, an extensive inscription written in the Moabite language. Ahaziah formed a business partnership with Je ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Israel (Samaria)
The Kingdom of Israel ( ), also called the Northern Kingdom or the Kingdom of Samaria, was an History of ancient Israel and Judah, Israelite kingdom that existed in the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. Its beginnings date back to the first half of the 10th century BCE. It controlled the areas of Samaria, Galilee and parts of Transjordan (region), Transjordan; the former two regions underwent a period in which a large number of new settlements were established shortly after the kingdom came into existence. It had four capital cities in succession: Shiloh (biblical city), Shiloh, Shechem, Tirzah (ancient city), Tirzah, and the Samaria (ancient city), city of Samaria. In the 9th century BCE, it was ruled by the Omrides, Omride dynasty, whose political centre was the city of Samaria. According to the Hebrew Bible, the territory of the Twelve Tribes of Israel was once amalgamated under a Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy), Kingdom of Israel and Judah, which was ruled by the Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samaria (ancient City)
Samaria ( ; ; ; ) was the capital city of the Kingdom of Israel (Samaria), Kingdom of Israel between and . It is the namesake of Samaria, a historical region bounded by Judea to the south and by Galilee to the north. After the Assyrian captivity, Assyrian conquest of Israel, Samaria was annexed by the Neo-Assyrian Empire and continued as an administrative centre. It retained this status in the Neo-Babylonian Empire and the Achaemenid Empire, Achaemenid Persian Empire before being destroyed during the Wars of Alexander the Great. Later, under the hegemony of the Roman Republic and the subsequent Roman Empire, the city was rebuilt and expanded by the Jewish king Herod the Great, who also fortified it and renamed it "Sebastia, Nablus, Sebastia" in honour of the Roman emperor Augustus. The ancient city's hill is where the Municipality (Palestinian Authority), modern Palestinian village, retaining the Roman-era name Sebastia, is situated. The local archeological site is jointly ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
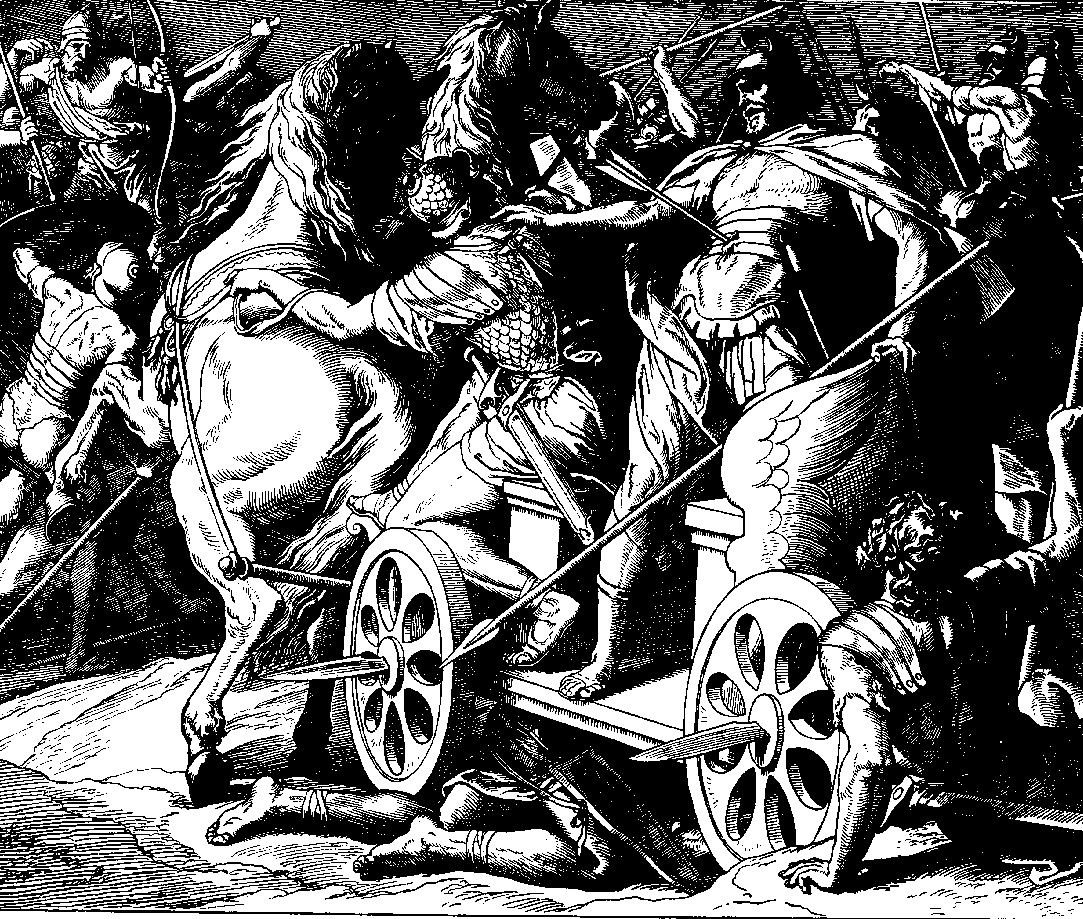
Ramoth-Gilead
Ramoth-Gilead (, meaning "Heights of Gilead"), was a Levitical city and city of refuge east of the Jordan River in the Hebrew Bible, also called "Ramoth in Gilead" (; ; ) or "Ramoth Galaad" in the Douay–Rheims Bible. It was located in the tribal territorial allotment of the tribe of Gad. Biblical events According to (), Ramoth-Gilead was the base of Ben-Geber, one of King Solomon's regional governors. He was responsible for ("to him belonged") the towns of Jair the son of Manasseh, in Gilead and the region of Argob in Bashan: sixty large cities with walls and bronze gate-bars. It appears to have been lost to Syria (Aram-Damascus) during the battles between the northern kingdom of Israel and Syria, as Ahab, King of Israel, proposed to go to battle to win it back. After consulting prophets about the prospects of success, Ahab went to fight for Ramoth in Gilead, aided by Jehoshaphat, King of Judah. During the battle, Ahab was wounded by an arrow. He was propped up in his c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jehoram Of Israel
Jehoram or Joram () was the ninth king of the northern Kingdom of Israel according to 2 Kings 8:16 and 2 Kings 8:25–28. He was the son of King Ahab and Jezebel and brother to Ahaziah and Athaliah. According to 2 Kings 8:16, in the fifth year of Jehoram of Israel, a different Jehoram became king of Judah. The author of the Books of Kings speaks of both Jehoram of Israel and Jehoram of Judah in the same passage. They were brothers-in-law since Jehoram of Judah married Athaliah, sister of Jehoram of Israel. Biblical narrative Jehoram began his reign in the 18th year of Jehoshaphat of Judah and ruled 12 years according to 2 Kings 3:1. William F. Albright dated his reign to 849–842 BCE, whereas E. R. Thiele proposed 852–841 BCE. Unlike his predecessors, Jehoram did not worship Ba'al. He removed the "pillar of Baal" according to 2 Kings 3:2, probably a special pillar that Ahab had erected near his palace at the then-capital of Jezreel. However, the writer of 2 Kings s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ithobaal I
Ithobaal I is the name of a 9th-century BCE king of Tyre mentioned in the story of Jezebel from the Hebrew Bible, and in a citation by Josephus of a list of the kings of Tyre put together by the Phoenician author Menander of Ephesus (2nd century BCE). Sources and chronology Primary information related to Ithobaal comes from Josephus's citation of the Phoenician author Menander of Ephesus, in ''Against Apion'' i.18. Here it is said that the previous king, Phelles, “was slain by Ithobalus, the priest of Astarte, who reigned thirty-two years, and lived sixty-eight years; he was succeeded by his son Badezorus ( Baal-Eser II).” Based on the work of F. M. Cross and other scholars who take 825 BC as the date of Dido's flight from her brother Pygmalion, after which she founded the city of Carthage in 814 BC, Ithobaal was born in 915 BC, killed King Phelles and assumed the throne in 883 BC, and died in 847 or 846 BC. Relation to Ahab of Israel Ithobaal held close diplomatic conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |