Radial Muscle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The iris dilator muscle (pupil dilator muscle, pupillary dilator, radial muscle of iris, radiating fibers), is a
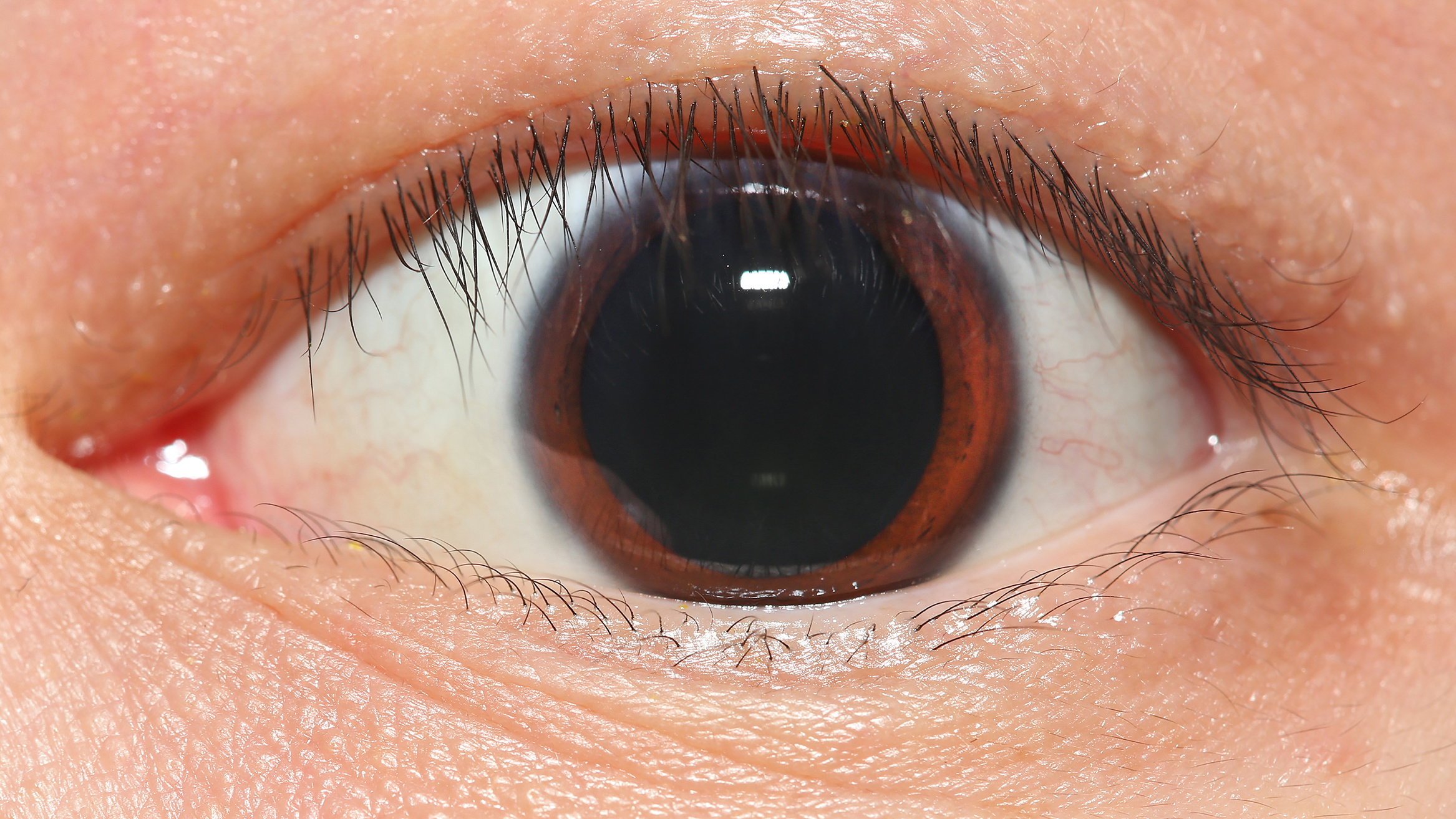 The pupillary dilator acts to increase the size of the pupil to allow more light to enter the eye. It works in opposition to the pupillary constrictor. Pupil dilation occurs when there is insufficient light for the normal function of the eye, and during heightened sympathetic activity, for example in the "fight-or-flight reflex".
The pupillary dilator acts to increase the size of the pupil to allow more light to enter the eye. It works in opposition to the pupillary constrictor. Pupil dilation occurs when there is insufficient light for the normal function of the eye, and during heightened sympathetic activity, for example in the "fight-or-flight reflex".
File:Horner's Syndrome and Autonomic innervation of the eye.svg, Scheme showing sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation of the pupil and sites of lesion in a Horner's syndrome.
File:Gray840.png, Sympathetic connections of the ciliary and superior cervical ganglia (red) (parasympathetic pathway in blue)
File:Iris_Dilator_Muscle_012909.jpg, The iris dilator muscle fibers course radially through the iris.
Description of function at tedmontgomery.com
at mscd.edu * {{DEFAULTSORT:Iris Dilator Muscle Muscular system Human iris
smooth muscle
Smooth muscle is one of the three major types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being skeletal and cardiac muscle. It can also be found in invertebrates and is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. It is non- striated, so-called bec ...
of the eye
An eye is a sensory organ that allows an organism to perceive visual information. It detects light and converts it into electro-chemical impulses in neurons (neurones). It is part of an organism's visual system.
In higher organisms, the ey ...
, running radially in the iris and therefore fit as a dilator. The pupillary dilator consists of a spokelike arrangement of modified contractile cells called myoepithelial cell
Myoepithelial cells (sometimes referred to as myoepithelium) are cells usually found in glandular epithelium as a thin layer above the basement membrane but generally beneath the lumen (anatomy), luminal cells. These may be positive for ACTA2, alph ...
s. These cells are stimulated by the sympathetic nervous system. When stimulated, the cells contract, widening the pupil and allowing more light to enter the eye.
The ciliary muscle
The ciliary muscle is an intrinsic muscle of the eye formed as a ring of smooth muscleSchachar, Ronald A. (2012). "Anatomy and Physiology." (Chapter 4) . in the eye's middle layer, the uvea ( vascular layer). It controls accommodation for vie ...
, pupillary sphincter muscle
The iris sphincter muscle (pupillary sphincter, pupillary constrictor, circular muscle of iris, circular fibers) is a muscle in the part of the eye called the iris. It encircles the pupil of the iris, appropriate to its function as a constrictor ...
and pupillary dilator muscle
The iris dilator muscle (pupil dilator muscle, pupillary dilator, radial muscle of iris, radiating fibers), is a smooth muscle of the eye, running radially in the iris and therefore fit as a dilator. The pupillary dilator consists of a spokelike ...
sometimes are called intrinsic ocular muscle
Intrinsic ocular muscles or intraocular muscles{{cite book , last1=Ludwig , first1=Parker E. , last2=Aslam , first2=Sanah , last3=Czyz , first3=Craig N. , title=StatPearls , date=2024 , publisher=StatPearls Publishing , chapter-url=https://www.nc ...
s or intraocular muscle
Intrinsic ocular muscles or intraocular muscles{{cite book , last1=Ludwig , first1=Parker E. , last2=Aslam , first2=Sanah , last3=Czyz , first3=Craig N. , title=StatPearls , date=2024 , publisher=StatPearls Publishing , chapter-url=https://www.nc ...
s.
Structure
Innervation
It is innervated by the sympathetic system, which acts by releasingnoradrenaline
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and body as a hormone, neurotransmitter and neuromodulator. The name "noradrenaline" (from ...
, which acts on α1-receptors
The adenosine A1 receptor (A1AR) is one member of the adenosine receptor group of G protein-coupled receptors with adenosine as endogenous ligand.
Biochemistry
A1 receptors are implicated in sleep promotion by inhibiting wake-promoting choline ...
. Thus, when presented with a threatening stimulus that activates the fight-or-flight response
The fight-or-flight or the fight-flight-freeze-or-fawn (also called hyperarousal or the acute stress response) is a physiological reaction that occurs in response to a perceived harmful event, attack, or threat to survival. It was first describ ...
, this innervation contracts the muscle and dilates the pupil
The pupil is a hole located in the center of the iris of the eye that allows light to strike the retina.Cassin, B. and Solomon, S. (1990) ''Dictionary of Eye Terminology''. Gainesville, Florida: Triad Publishing Company. It appears black becau ...
, thus temporarily letting more light reach the retina
The retina (; or retinas) is the innermost, photosensitivity, light-sensitive layer of tissue (biology), tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some Mollusca, molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focus (optics), focused two-dimensional ...
.
The dilator muscle is innervated more specifically by postganglionic
In the autonomic nervous system, nerve fibers from the ganglion to the wikt:effector, effector organ are called postganglionic nerve fibers.
Neurotransmitters
The neurotransmitters of postganglionic fibers differ:
* In the parasympathetic div ...
sympathetic nerves arising from the superior cervical ganglion
The superior cervical ganglion (SCG) is the upper-most and largest of the cervical sympathetic ganglia of the sympathetic trunk. It probably formed by the union of four sympathetic ganglia of the cervical spinal nerves C1–C4. It is the only ...
as the sympathetic root of ciliary ganglion. From there, they travel via the internal carotid artery
The internal carotid artery is an artery in the neck which supplies the anterior cerebral artery, anterior and middle cerebral artery, middle cerebral circulation.
In human anatomy, the internal and external carotid artery, external carotid ari ...
through the carotid canal
The carotid canal is a passage in the petrous part of the temporal bone of the skull through which the internal carotid artery and its internal carotid (nervous) plexus pass from the neck into (the middle cranial fossa of) the cranial cavity.
...
to foramen lacerum. They then enter the middle cranial fossa
The middle cranial fossa is formed by the sphenoid bones, and the temporal bones. It lodges the temporal lobes, and the pituitary gland. It is deeper than the anterior cranial fossa, is narrow medially and widens laterally to the sides of the skull ...
above foramen lacerum, travel through the cavernous sinus
The cavernous sinus within the human head is one of the dural venous sinuses creating a cavity called the lateral sellar compartment bordered by the temporal bone of the skull and the sphenoid bone, lateral to the sella turcica.
Structure
The ...
in the middle cranial fossa and then travel with the ophthalmic artery
The ophthalmic artery (OA) is an artery of the head. It is the first branch of the internal carotid artery distal to the cavernous sinus. Branches of the ophthalmic artery supply all the structures in the orbit around the eye, as well as some ...
in the optic canal
The ''optic foramen'' is the opening to the optic canal. The canal is located in the sphenoid bone; it is bounded medially by the body of the sphenoid and laterally by the lesser wing of the sphenoid.
The superior surface of the sphenoid bone is ...
or on the ophthalmic nerve
The ophthalmic nerve (CN V1) is a sensory nerve of the head. It is one of three divisions of the trigeminal nerve (CN V), a cranial nerve. It has three major branches which provide sensory innervation to the eye, and the skin of the upper face ...
through the superior orbital fissure. From there, they travel with the nasociliary nerve
The nasociliary nerve is a branch of the ophthalmic nerve (CN V1) (which is in turn a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V)). It is intermediate in size between the other two branches of the ophthalmic nerve, the frontal nerve and lacrimal ner ...
and then the long ciliary nerve. They then pierce the sclera
The sclera, also known as the white of the eye or, in older literature, as the tunica albuginea oculi, is the opaque, fibrous, protective outer layer of the eye containing mainly collagen and some crucial elastic fiber.
In the development of t ...
, travel between sclera and choroid
The choroid, also known as the choroidea or choroid coat, is a part of the uvea, the vascular layer of the eye. It contains connective tissues, and lies between the retina and the sclera. The human choroid is thickest at the far extreme rear o ...
to reach the iris dilator muscle. They will also pass through ciliary ganglion and travel in short ciliary nerves
The short ciliary nerves are nerves of the orbit around the eye. They are branches of the ciliary ganglion. They supply parasympathetic and sympathetic nerve fibers to the ciliary muscle, iris, and cornea. Damage to the short ciliary nerve may ...
to reach the iris dilator muscle.
Function
 The pupillary dilator acts to increase the size of the pupil to allow more light to enter the eye. It works in opposition to the pupillary constrictor. Pupil dilation occurs when there is insufficient light for the normal function of the eye, and during heightened sympathetic activity, for example in the "fight-or-flight reflex".
The pupillary dilator acts to increase the size of the pupil to allow more light to enter the eye. It works in opposition to the pupillary constrictor. Pupil dilation occurs when there is insufficient light for the normal function of the eye, and during heightened sympathetic activity, for example in the "fight-or-flight reflex".
History
Etymology
The English name ''dilator pupillae muscle''Federative Committee on Anatomical Terminology (FCAT) (1998). ''Terminologia Anatomica''. Stuttgart: Thieme as currently used in the list of English equivalents of the ''Terminologia Anatomica
''Terminologia Anatomica'' (commonly abbreviated TA) is the international standard for human anatomy, human anatomical terminology. It is developed by the Federative International Programme on Anatomical Terminology (FIPAT) a program of the Inter ...
'', the reference-work of the official anatomic nomenclature, can be considered as a corruption of the full Latin expression ''musculus dilatator pupillae''.His (1895). ''Die anatomische Nomenclatur. Nomina Anatomica. Der von der Anatomischen Gesellschaft auf ihrer IX. Versammlung in Basel angenommenen Namen''. Leipzig: Verlag von Veit & Comp. The full Latin expression exhibits three words that each can be traced back to Roman antiquity
In modern historiography, ancient Rome is the Roman civilisation from the founding of the Italian city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdo ...
. The Classical Latin
Classical Latin is the form of Literary Latin recognized as a Literary language, literary standard language, standard by writers of the late Roman Republic and early Roman Empire. It formed parallel to Vulgar Latin around 75 BC out of Old Latin ...
name ''musculus'' is actually a diminutive of the Classical Latin name ''mus'',Lewis, C.T. & Short, C. (1879). ''A Latin dictionary founded on Andrews' edition of Freund's Latin dictionary''. Oxford: Clarendon Press. and can be translated as ''little mouse''. In the medical writings of Aulus Cornelius Celsus
Aulus Cornelius Celsus ( 25 BC 50 AD) was a Roman encyclopedist, known for his extant medical work, '' De Medicina'', which is believed to be the only surviving section of a much larger encyclopedia. The ''De Medicina'' is a primary source on ...
we can also find this specific name to refer to a muscle instead of its literal meaning. Latin ''musculus'' can be explained by the fact that a muscle looks like a little mouse that moves under the skin.Kraus, L.A. (1844). ''Kritisch-etymologisches medicinisches Lexikon'' (Dritte Auflage). Göttingen: Verlag der Deuerlich- und Dieterichschen Buchhandlung. In the writings of Greek philosopher
Philosophy ('love of wisdom' in Ancient Greek) is a systematic study of general and fundamental questions concerning topics like existence, reason, knowledge, Value (ethics and social sciences), value, mind, and language. It is a rational an ...
Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
the Ancient Greek word for ''mouse'', i.e. μῦςLiddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon. revised and augmented throughout by Sir Henry Stuart Jones. with the assistance of. Roderick McKenzie.'' Oxford: Clarendon Press. is also used to refer to a muscle.
''Dilatator'' in the Latin expression ''musculus dilatator pupillae'' is derived from the classical Latin verb ''dilatare'',Foster, F.D. (1891–1893). ''An illustrated medical dictionary. Being a dictionary of the technical terms used by writers on medicine and the collateral sciences, in the Latin, English, French, and German languages.'' New York: D. Appleton and Company. to dilate, to spread out. Two possible explanations exist concerning the etymological derivation of this verb. The first explanation considers ''dilatare'' as frequentative of ''differere''. The Latin verb ''differe'' can mean, ''to carry different ways'', ''to spread abroad'', ''to scatter'', but also ''to delay''. The other explanation considers ''dilatare'' as a compound from ''di-'' and ''latus'', with the latter word meaning, ''broad'' or ''wide'', hence the German name ''Erweiterer'' for Latin ''dilatator''.
The expression ''dilator pupillae muscle'', as used in the list of English equivalents of the ''Terminologia Anatomica'', is actually partly Latin, i.e. ''dilator pupillae'', with ''pupillae'' (=of the pupil), a noun in the genitive case modifying ''dilator'', a noun in the nominative case, and partly English, i.e. ''muscle''. In previous editions (''Nomina Anatomica
''Nomina Anatomica'' (''NA'') was the international standard on human anatomic terminology from 1895 until it was replaced by '' Terminologia Anatomica'' in 1998.
In the late nineteenth century some 30,000 terms for various body parts were in us ...
'') this muscle was officially called the ''musculus dilator pupillae'',Donáth, T. & Crawford, G.C.N. (1969). ''Anatomical dictionary with nomenclature and explanatory notes.'' Oxford/London/Edinburgh/New York/Toronto/Sydney/Paris/Braunschweig: Pergamon Press.International Anatomical Nomenclature Committee (1966). ''Nomina Anatomica''. Amsterdam: Excerpta Medica Foundation.International Anatomical Nomenclature Committee (1977). ''Nomina Anatomica, together with Nomina Histologica and Nomina Embryologica''. Amsterdam-Oxford: Excerpta Medica.International Anatomical Nomenclature Committee (1983). ''Nomina Anatomica, together with Nomina Histologica and Nomina Embryologica''. Baltimore/London: Williams & WilkinsInternational Anatomical Nomenclature Committee (1989). ''Nomina Anatomica, together with Nomina Histologica and Nomina Embryologica''. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone. The ''Nomina Anatomica'' as authorized in 1895 in Basel
Basel ( ; ), also known as Basle ( ), ; ; ; . is a city in northwestern Switzerland on the river Rhine (at the transition from the High Rhine, High to the Upper Rhine). Basel is Switzerland's List of cities in Switzerland, third-most-populo ...
and in 1935 in Jena
Jena (; ) is a List of cities and towns in Germany, city in Germany and the second largest city in Thuringia. Together with the nearby cities of Erfurt and Weimar, it forms the central metropolitan area of Thuringia with approximately 500,000 in ...
Kopsch, F. (1941). ''Die Nomina anatomica des Jahres 1895 (B.N.A.) nach der Buchstabenreihe geordnet und gegenübergestellt den Nomina anatomica des Jahres 1935 (I.N.A.)'' (3. Auflage). Leipzig: Georg Thieme Verlag.Stieve, H. (1949). ''Nomina Anatomica. Zusammengestellt von der im Jahre 1923 gewählten Nomenklatur-Kommission, unter Berücksichtigung der Vorschläge der Mitglieder der Anatomischen Gesellschaft, der Anatomical Society of Great Britain and Ireland, sowie der American Association of Anatomists, überprüft und durch Beschluß der Anatomischen Gesellschaft auf der Tagung in Jena 1935 endgültig angenommen.'' (4th ed.). Jena: Verlag Gustav Fischer. used the full Latin expression.
Additional images
See also
*Iris sphincter muscle
The iris sphincter muscle (pupillary sphincter, pupillary constrictor, circular muscle of iris, circular fibers) is a muscle in the part of the eye called the iris. It encircles the pupil of the iris, appropriate to its function as a constricto ...
* Mydriasis
Mydriasis is the Pupillary dilation, dilation of the pupil, usually having a non-physiological cause, or sometimes a physiological pupillary response. Non-physiological causes of mydriasis include disease, Physical trauma, trauma, or the use of c ...
* Pupillary response
Pupillary response is a physiological response that varies the size of the pupil between 1.5 mm and 8 mm, via the optic and oculomotor cranial nerve.
A constriction response (miosis), is the narrowing of the pupil, which may be caused by scler ...
References
External links
Description of function at tedmontgomery.com
at mscd.edu * {{DEFAULTSORT:Iris Dilator Muscle Muscular system Human iris