Protestantism and Islam on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Protestantism and Islam entered into contact during the early-16th century when the
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, expanding in the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
, first encountered Calvinist
Calvinism (also called the Reformed Tradition, Reformed Protestantism, Reformed Christianity, or simply Reformed) is a major branch of Protestantism that follows the theological tradition and forms of Christian practice set down by John Ca ...
Protestants
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
in present-day Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croa ...
and Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the ...
. As both parties opposed the Austrian Holy Roman Emperor and his Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
allies, numerous exchanges occurred, exploring religious similarities and the possibility of trade and military alliances.
The early Protestants and Turks established a sense of mutual tolerance and understanding, despite theological differences on Christology
In Christianity, Christology (from the Greek grc, Χριστός, Khristós, label=none and grc, -λογία, -logia, label=none), translated literally from Greek as "the study of Christ", is a branch of theology that concerns Jesus. Differ ...
, considering each other to be closer to one another than to Catholicism. The Ottoman Empire supported the early Protestant churches and contributed to their survival in dire times. Martin Luther
Martin Luther (; ; 10 November 1483 – 18 February 1546) was a German priest, theologian, author, hymnwriter, and professor, and Augustinian friar. He is the seminal figure of the Protestant Reformation and the namesake of Luther ...
regarded the Ottomans as allies against the papacy, considering them the "rod of God's wrath against Europe's sins." The allegiances of the Ottoman Empire and threat of Ottoman expansion in Eastern Europe pressured King Charles V to sign the Peace of Nuremberg
Peace is a concept of societal friendship and harmony in the absence of hostility and violence. In a social sense, peace is commonly used to mean a lack of conflict (such as war) and freedom from fear of violence between individuals or groups. ...
with the Protestant princes, accept the Peace of Passau
Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, Holy Roman Emperor Charles V had won a victory against Protestantism, Protestant forces in the Schmalkaldic War of 1547. Many Protestant princes were unhappy with the religious terms of the Augsburg Interim imposed af ...
, and the Peace of Augsburg, formally recognizing Protestantism in Germany and ending military threats to their existence.
Introduction
Protestantism
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
is a branch of the monotheistic Christian religion
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global populatio ...
which originated in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located enti ...
in the early 16th century. It adheres doctrinally to the doctrine of the Holy Trinity
The Christian doctrine of the Trinity (, from 'threefold') is the central dogma concerning the nature of God in most Christian churches, which defines one God existing in three coequal, coeternal, consubstantial divine persons: God the ...
and other theological doctrines of the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
and the Eastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, also called the Orthodox Church, is the second-largest Christian church, with approximately 220 million baptized members. It operates as a communion of autocephalous churches, each governed by its bishops vi ...
, but split from the Western (Roman) Catholic Church as a "Protest" against ecclesiastical corruption, pastoral abuses and certain doctrines of the Roman Catholic Church. Protestantism itself had multiple variations from the start, specifically among followers of Martin Luther
Martin Luther (; ; 10 November 1483 – 18 February 1546) was a German priest, theologian, author, hymnwriter, and professor, and Augustinian friar. He is the seminal figure of the Protestant Reformation and the namesake of Luther ...
, John Calvin
John Calvin (; frm, Jehan Cauvin; french: link=no, Jean Calvin ; 10 July 150927 May 1564) was a French theologian, pastor and reformer in Geneva during the Protestant Reformation. He was a principal figure in the development of the system ...
, Huldrych Zwingli
Huldrych or Ulrich Zwingli (1 January 1484 – 11 October 1531) was a leader of the Reformation in Switzerland, born during a time of emerging Swiss patriotism and increasing criticism of the Swiss mercenary system. He attended the Uni ...
and later, Thomas Cranmer
Thomas Cranmer (2 July 1489 – 21 March 1556) was a leader of the English Reformation and Archbishop of Canterbury during the reigns of Henry VIII, Edward VI and, for a short time, Mary I. He helped build the case for the annulment of Henry ...
.
Islam is a monotheistic
Monotheism is the belief that there is only one deity, an all-supreme being that is universally referred to as God. Cross, F.L.; Livingstone, E.A., eds. (1974). "Monotheism". The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church (2 ed.). Oxford: Oxfor ...
religion, arising around 600 AD, that considers itself the final authentic practice of the faith of the patriarch Abraham
Abraham, ; ar, , , name=, group= (originally Abram) is the common Hebrews, Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father of the Covenant (biblical), special ...
. While it is Abrahamic
The Abrahamic religions are a group of religions centered around worship of the God of Abraham. Abraham, a Hebrew patriarch, is extensively mentioned throughout Abrahamic religious scriptures such as the Bible and the Quran.
Jewish tradition ...
, it presents views of Jewish scripture (the Tanakh
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
''
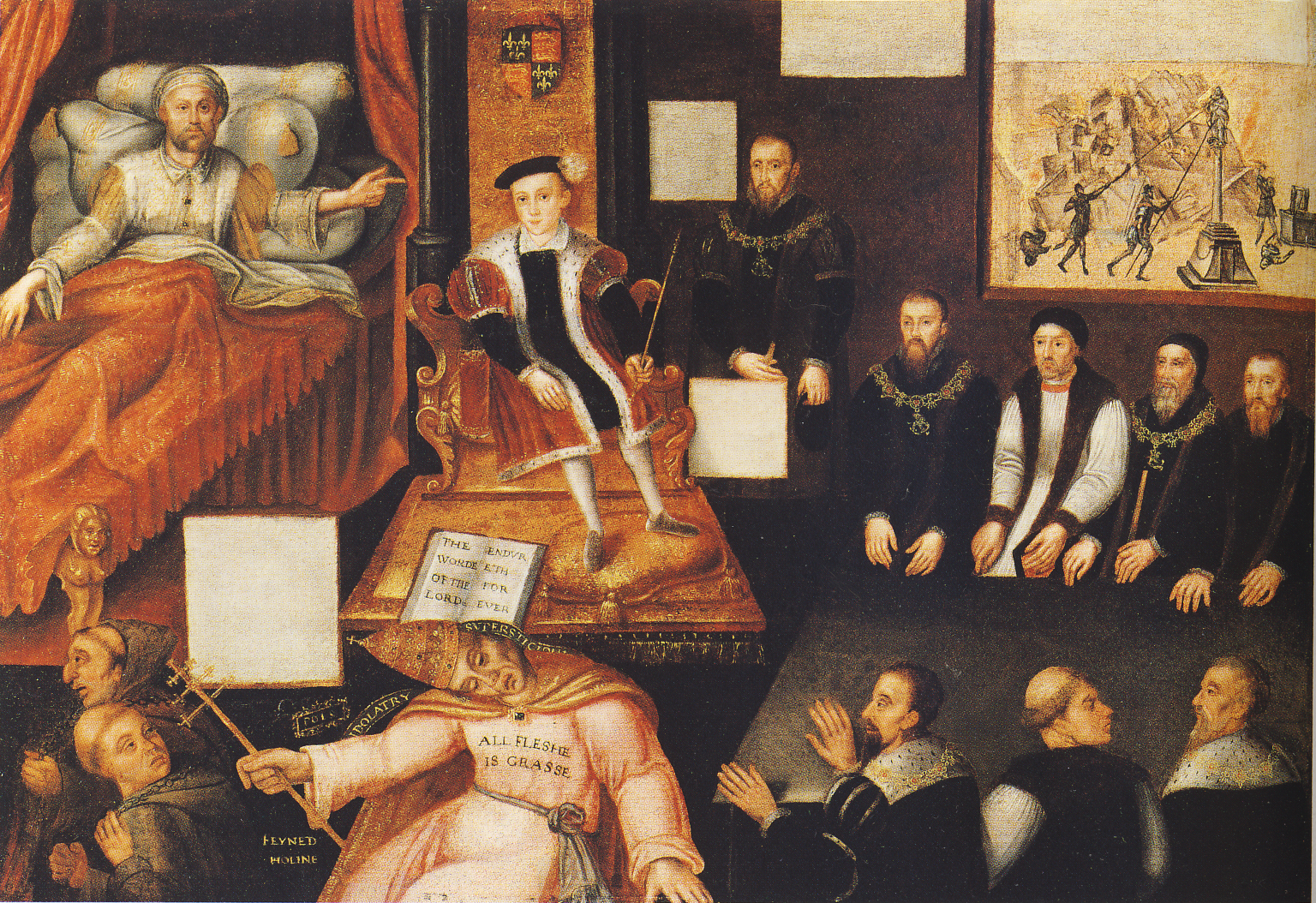 Following the Ottoman conquest of
Following the Ottoman conquest of 
 As a religious profession, however, Luther felt the same sense of tolerance for freedom of conscience to be given to Islam as to other faiths of its time:
However, this statement mentions "Turks", and it is not clear whether the meaning was of "Turks" as a representation of the specific rule of the Ottoman Empire, or as a representation of Islam in general.
Martin Luther's reasoning also appears in one of his other comments, in which he said that "A smart Turk makes a better ruler than a dumb Christian".
As a religious profession, however, Luther felt the same sense of tolerance for freedom of conscience to be given to Islam as to other faiths of its time:
However, this statement mentions "Turks", and it is not clear whether the meaning was of "Turks" as a representation of the specific rule of the Ottoman Empire, or as a representation of Islam in general.
Martin Luther's reasoning also appears in one of his other comments, in which he said that "A smart Turk makes a better ruler than a dumb Christian".
 Martin Luther also took note of the similarities between Islam and Protestantism in the rejection of idols, although he noted Islam was much more drastic in its complete rejection of images. In ''On War against the Turk'', Luther is actually less critical of the Turks than he is of the
Martin Luther also took note of the similarities between Islam and Protestantism in the rejection of idols, although he noted Islam was much more drastic in its complete rejection of images. In ''On War against the Turk'', Luther is actually less critical of the Turks than he is of the
 Military cooperation between the Ottoman Empire and European powers started in earnest with the
Military cooperation between the Ottoman Empire and European powers started in earnest with the
 Fundamentally, the Protestant Dutch had strong antagonisms to both the Catholics and the Muslims. In some cases however, alliances, or attempts at alliance between the Dutch and the Muslims were made possible, as when the Dutch allied with the Muslims of the
Fundamentally, the Protestant Dutch had strong antagonisms to both the Catholics and the Muslims. In some cases however, alliances, or attempts at alliance between the Dutch and the Muslims were made possible, as when the Dutch allied with the Muslims of the  Contacts soon became more direct. William of Orange sent ambassadors to the
Contacts soon became more direct. William of Orange sent ambassadors to the 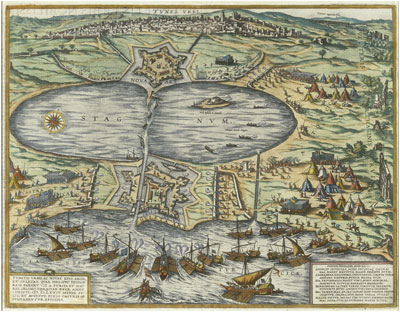 In 1574, William of Orange and
In 1574, William of Orange and  From 1608,
From 1608,
 Following the sailing of ''The Lion'' of Thomas Wyndham in 1551, and the 1585 establishment of the English
Following the sailing of ''The Lion'' of Thomas Wyndham in 1551, and the 1585 establishment of the English
 Diplomatic relations were established with the
Diplomatic relations were established with the
 In eastern
In eastern  In the 17th century Protestant communities again asked for Ottoman help against the Habsburg Catholics. When in 1606 Emperor
In the 17th century Protestant communities again asked for Ottoman help against the Habsburg Catholics. When in 1606 Emperor
 At about the same time England also maintained a significant relationship with Persia. In 1616, a trade agreement was reached between Shah Abbas and the
At about the same time England also maintained a significant relationship with Persia. In 1616, a trade agreement was reached between Shah Abbas and the
Wittenberg and Mecca
issue of ''Logia: A Journal of Lutheran Theology'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Protestantism And Islam Christianity and Islam Islam
''
Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religiou ...
that are incompatible with Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in the ...
and Christianity, respectively.
The subject of this page is to consider the historical political, military, and cultural/religious interactions of Protestant and Islamic rulers.
The bulk of this page examines a hypothesis that Protestant states and the Islamic Turkish state acted to align themselves based on various common interests. One aspect of this hypothesis posits that, in the 16th and 17th centuries, Turkish and Protestant rulers shared a common geopolitical opposition to the Roman Catholic Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
, and tensions with France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
and Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' ( Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
, the other large Roman Catholic states, and that this common interest gave rise to alignment in political and military alliances. It is also discussed whether Protestantism and Islam aligned theologically on iconoclasm
Iconoclasm (from Ancient Greek, Greek: grc, wikt:εἰκών, εἰκών, lit=figure, icon, translit=eikṓn, label=none + grc, wikt:κλάω, κλάω, lit=to break, translit=kláō, label=none)From grc, wikt:εἰκών, εἰκών + wi ...
, and, culturally—in terms of the religiously-motivated cultural mores of that era – in opposition to the person or office of the Roman Catholic Pope
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
.
Historical backgroundProtestantism and Islam
entered into contact during the 16th century when
Calvinist
Calvinism (also called the Reformed Tradition, Reformed Protestantism, Reformed Christianity, or simply Reformed) is a major branch of Protestantism that follows the theological tradition and forms of Christian practice set down by John Ca ...
Protestants
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
in present-day Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croa ...
and Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the ...
coincided with the expansion of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
in the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
. As Protestantism is divided into a few distinguishable branches and multiple denominations within the former, it is hard to determine the relations specifically. Many of these denominations can have a different approachment to this matter. Islam is divided as well into various denominations. This article focuses on Protestant-Muslim relations, but should be taken with caution.
Relations became more adversarial in the early modern and modern periods, although recent attempts have been made at rapprochement
In international relations, a rapprochement, which comes from the French word ''rapprocher'' ("to bring together"), is a re-establishment of cordial relations between two countries. This may be done due to a mutual enemy, as was the case with Germa ...
. In terms of comparative religion, there are interesting similarities especially with the Sunni, while Catholics are often noted for similarities with Shias
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, most n ...
, as well as differences, in both religious approaches.
 Following the Ottoman conquest of
Following the Ottoman conquest of Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth ( Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
in 1453 by Mehmed the Conqueror
Mehmed II ( ota, محمد ثانى, translit=Meḥmed-i s̱ānī; tr, II. Mehmed, ; 30 March 14323 May 1481), commonly known as Mehmed the Conqueror ( ota, ابو الفتح, Ebū'l-fetḥ, lit=the Father of Conquest, links=no; tr, Fâtih Su ...
and the unification of the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europ ...
under Selim I
Selim I ( ota, سليم الأول; tr, I. Selim; 10 October 1470 – 22 September 1520), known as Selim the Grim or Selim the Resolute ( tr, links=no, Yavuz Sultan Selim), was the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1512 to 1520. Despite las ...
and his son Suleiman the Magnificent
Suleiman I ( ota, سليمان اول, Süleyman-ı Evvel; tr, I. Süleyman; 6 November 14946 September 1566), commonly known as Suleiman the Magnificent in the West and Suleiman the Lawgiver ( ota, قانونى سلطان سليمان, Ḳ ...
managed to expand Ottoman rule into Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the ...
. The Habsburg Empire
The Habsburg monarchy (german: Habsburgermonarchie, ), also known as the Danubian monarchy (german: Donaumonarchie, ), or Habsburg Empire (german: Habsburgerreich, ), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities ...
thus entered into direct conflict with the Ottomans.
At the same time the Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
was taking place in numerous areas of northern and central Europe, in harsh opposition to Papal
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
authority and the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
led by Emperor Charles V Charles V may refer to:
* Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor (1500–1558)
* Charles V of Naples (1661–1700), better known as Charles II of Spain
* Charles V of France (1338–1380), called the Wise
* Charles V, Duke of Lorraine (1643–1690)
* Infant ...
. This situation led the Protestants to consider various forms of cooperation and rapprochement (religious, commercial, military) with the Muslim world, in opposition to their common Habsburg enemy.
Early religious accommodation (15th–17th centuries)
During the development of the Reformation, Protestantism and Islam were considered closer to each other than they were to Catholicism: "Islam was seen as closer to Protestantism in banning images from places of worship, in not treating marriage as a sacrament and in rejectingmonastic orders
Monasticism (from Ancient Greek , , from , , 'alone'), also referred to as monachism, or monkhood, is a religious way of life in which one renounces worldly pursuits to devote oneself fully to spiritual work. Monastic life plays an important rol ...
".. The dispute between Catholics and Protestants in a divided Europe opened the way for Islam to become a field of battle.
Mutual tolerance
The Sultan of theOttoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
was known for his tolerance of the Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words '' Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρ ...
and Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
faiths within his dominions, whereas the King of Spain did not tolerate the Protestant faith. The Ottoman Empire was indeed known at that time for its religious tolerance. Various religious refugees, such as the Huguenots
The Huguenots ( , also , ) were a religious group of French Protestants who held to the Reformed, or Calvinist, tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, the Genevan burgomaster Bez ...
, some Anglicans
Anglicanism is a Western Christianity, Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Euro ...
, Quakers
Quakers are people who belong to a historically Protestant Christian set of denominations known formally as the Religious Society of Friends. Members of these movements ("theFriends") are generally united by a belief in each human's abil ...
, Anabaptists
Anabaptism (from Neo-Latin , from the Greek : 're-' and 'baptism', german: Täufer, earlier also )Since the middle of the 20th century, the German-speaking world no longer uses the term (translation: "Re-baptizers"), considering it biased. ...
or even Jesuits
The Society of Jesus ( la, Societas Iesu; abbreviation: SJ), also known as the Jesuits (; la, Iesuitæ), is a religious order (Catholic), religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rom ...
or Capuchins
Capuchin can refer to:
*Order of Friars Minor Capuchin, an order of Roman Catholic friars
*Capuchin Poor Clares, an order of Roman Catholic contemplative religious sisters
*Capuchin monkey, primates of the genus ''Cebus'' and ''Sapajus'', named af ...
were able to find refuge at Istanbul
Istanbul ( , ; tr, İstanbul ), formerly known as Constantinople ( grc-gre, Κωνσταντινούπολις; la, Constantinopolis), is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, serving as the country's economic, ...
and in the Ottoman Empire, where they were given right of residence and worship. Further, the Ottomans supported the Calvinists in Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the ...
and Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croa ...
but also in France. The contemporary French thinker Jean Bodin
Jean Bodin (; c. 1530 – 1596) was a French jurist and political philosopher, member of the Parlement of Paris and professor of law in Toulouse. He is known for his theory of sovereignty. He was also an influential writer on demonology.
Bodin ...
wrote:
Martin Luther
Martin Luther (; ; 10 November 1483 – 18 February 1546) was a German priest, theologian, author, hymnwriter, and professor, and Augustinian friar. He is the seminal figure of the Protestant Reformation and the namesake of Luther ...
, in his 1528 pamphlet, '' On War against the Turk'', calls for the Germans to resist the Ottoman invasion of Europe, as the catastrophic Siege of Vienna Sieges of Vienna may refer to:
* Siege of Vienna (1239)
* Siege of Vienna (1276)
* Siege of Vienna (1287)
* Siege of Vienna (1477), unsuccessful Hungarian attempt during the Austro–Hungarian War.
*Siege of Vienna (1485), Hungarian victory during ...
was lurking, but expressed views of Islam which, compared to his aggressive speech against Catholicism (and later Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in the ...
), are relatively mild. Concerned with his personal preaching on divine atonement and Christian justification, he extensively criticized the principles of Islam as ''utterly despicable and blasphemous'', considering Qu'ran as void of any tract of divine truth. For Luther, it was mandatory to let the Qu'ran "speak for itself" as means to show what Christianity saw as a draft from prophetic and apostolic teaching, therefore allowing a proper Christian response. His knowledge on the subject was based on a medieval polemicist version of the Qu'ran made by Riccoldo da Monte di Croce
Riccoldo da Monte di Croce (Florence; 1320) or Ricold of Monte Croce ( la, Ricoldus de Monte Crucis) was an Italian Dominican friar, travel writer, missionary, and Christian apologist. He is most famous for his polemical works on Medieval Islam a ...
, which was the European scholarly reference of the subject. In 1542, while Luther was translating Riccoldo's ''Refutation of the Koran,'' which would become the first version of Koranic material in German, he wrote a letter to Basle's city council to relieve the ban on Theodore Bibliander
Theodore (or Theodorus) Bibliander (german: Theodor Buchmann; 1509 in Bischofszell – 26 September 1564 in Zurich) was a Swiss orientalist, publisher, Protestant reformer and linguist. Born Theodor Buchmann (''Bibliander'' is a Greek translati ...
's translation of the Qu'ran into Latin. Mostly due to his letter, Bibliander's translation was finally allowed and eventually published in 1543, with a preface made by Martin Luther himself. With access to a more accurate translation of the Qu'ran, Luther understood some of Riccoldo's critiques to be partial, but nevertheless concurred with virtually all of them.
 As a religious profession, however, Luther felt the same sense of tolerance for freedom of conscience to be given to Islam as to other faiths of its time:
However, this statement mentions "Turks", and it is not clear whether the meaning was of "Turks" as a representation of the specific rule of the Ottoman Empire, or as a representation of Islam in general.
Martin Luther's reasoning also appears in one of his other comments, in which he said that "A smart Turk makes a better ruler than a dumb Christian".
As a religious profession, however, Luther felt the same sense of tolerance for freedom of conscience to be given to Islam as to other faiths of its time:
However, this statement mentions "Turks", and it is not clear whether the meaning was of "Turks" as a representation of the specific rule of the Ottoman Empire, or as a representation of Islam in general.
Martin Luther's reasoning also appears in one of his other comments, in which he said that "A smart Turk makes a better ruler than a dumb Christian".
Efforts at doctrinal rapprochement
 Martin Luther also took note of the similarities between Islam and Protestantism in the rejection of idols, although he noted Islam was much more drastic in its complete rejection of images. In ''On War against the Turk'', Luther is actually less critical of the Turks than he is of the
Martin Luther also took note of the similarities between Islam and Protestantism in the rejection of idols, although he noted Islam was much more drastic in its complete rejection of images. In ''On War against the Turk'', Luther is actually less critical of the Turks than he is of the Pope
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
, whom he calls an anti-Christ
In Christian eschatology, the Antichrist refers to people prophesied by the Bible to oppose Jesus Christ and substitute themselves in Christ's place before the Second Coming. The term Antichrist (including one plural form)1 John ; . 2 John . i ...
, or the Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""T ...
, whom he describes as "the Devil incarnate". He urges his contemporaries to also see the good aspects in the Turks, and refers to some who were favourable to the Ottoman Empire, and "who actually want the Turk to come and rule, because they think that our German people are wild and uncivilized - indeed that they are half-devil and half-man".
The Ottomans also felt closer to the Protestants than to the Catholics. At one point, a letter was sent from Suleiman the Magnificent
Suleiman I ( ota, سليمان اول, Süleyman-ı Evvel; tr, I. Süleyman; 6 November 14946 September 1566), commonly known as Suleiman the Magnificent in the West and Suleiman the Lawgiver ( ota, قانونى سلطان سليمان, Ḳ ...
to the "Lutherans" in Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to cultu ...
, claiming that he felt close to them, "since they did not worship idols, believed in one God and fought against the Pope and Emperor".
This notion of religious similarities was again taken up in epistolary exchanges between Elizabeth I of England
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was Queen of England and Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. Elizabeth was the last of the five House of Tudor monarchs and is sometimes referred to as the "Virgin Queen".
Eli ...
and Sultan Murad III
Murad III ( ota, مراد ثالث, Murād-i sālis; tr, III. Murad; 4 July 1546 – 16 January 1595) was Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1574 until his death in 1595. His rule saw battles with the Habsburgs and exhausting wars with the Saf ...
. In one correspondence, Murad entertained the notion that Islam and Protestantism had "much more in common than either did with Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, as both rejected the worship of idols", and argued for an alliance between England and the Ottoman Empire.
In a 1574 letter to the "Members of the Lutheran sect in Flanders and Spain", Murad III
Murad III ( ota, مراد ثالث, Murād-i sālis; tr, III. Murad; 4 July 1546 – 16 January 1595) was Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1574 until his death in 1595. His rule saw battles with the Habsburgs and exhausting wars with the Saf ...
made considerable efforts to highlight the similarities between Islamic and Protestants principles. He wrote:
Such claims seem to have been politically inspired as well, with the Ottomans trying to establish religious common ground as a way to secure a political alliance. Elizabeth I herself however made efforts to adjust her own religious rhetoric in order to minimize differences with the Ottomans and facilitate relations. In her correspondence with Murad, she stresses the monotheism and the anti-idolatry of her religion, by uniquely describing herself as:
Military collaboration
 Military cooperation between the Ottoman Empire and European powers started in earnest with the
Military cooperation between the Ottoman Empire and European powers started in earnest with the Franco-Ottoman alliance
The Franco-Ottoman Alliance, also known as the Franco-Turkish Alliance, was an alliance established in 1536 between the King of France Francis I and the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire Suleiman I. The strategic and sometimes tactical alliance was o ...
of 1535. The alliance provided strategic support to, and effectively protected, the kingdom of France from the ambitions of Charles V Charles V may refer to:
* Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor (1500–1558)
* Charles V of Naples (1661–1700), better known as Charles II of Spain
* Charles V of France (1338–1380), called the Wise
* Charles V, Duke of Lorraine (1643–1690)
* Infant ...
. It also gave the opportunity for the Ottoman Empire to become involved in European diplomacy and gain prestige in its European dominions. Side effects included a lot of negative propaganda against the actions of France and its "unholy" alliance with a Muslim power. According to historian Arthur Hassall the consequences of the Franco-Ottoman alliance were far-reaching: "The Ottoman alliance had powerfully contributed to save France from the grasp of Charles V, it had certainly aided Protestantism
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
in Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
, and from a French point of view, it had rescued the North German allies of Francis I."
Even after the 1571 Battle of Lepanto
The Battle of Lepanto was a naval engagement that took place on 7 October 1571 when a fleet of the Holy League, a coalition of Catholic states (comprising Spain and its Italian territories, several independent Italian states, and the Sovere ...
Ottoman support for France would continue however, as well as support for the Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
and the English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national id ...
after 1580, and support for Protestants
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
and Calvinists
Calvinism (also called the Reformed Tradition, Reformed Protestantism, Reformed Christianity, or simply Reformed) is a major branch of Protestantism that follows the theological tradition and forms of Christian practice set down by John Ca ...
, as a way to counter Habsburg attempts at supremacy in Europe. Various overtures were made by Ottoman rulers to the Protestants, who were also fighting against a common enemy, the Catholic House of Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
. Suleiman the Magnificent
Suleiman I ( ota, سليمان اول, Süleyman-ı Evvel; tr, I. Süleyman; 6 November 14946 September 1566), commonly known as Suleiman the Magnificent in the West and Suleiman the Lawgiver ( ota, قانونى سلطان سليمان, Ḳ ...
is known to have sent at least one letter to the "Lutherans" in Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to cultu ...
, offering troops at the time they would request, Murad III
Murad III ( ota, مراد ثالث, Murād-i sālis; tr, III. Murad; 4 July 1546 – 16 January 1595) was Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1574 until his death in 1595. His rule saw battles with the Habsburgs and exhausting wars with the Saf ...
is also known to have advocated to Elizabeth I an alliance between England and the Ottoman Empire.
Overall, the military activism of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
on the southern European front probably was the reason why Lutheranism
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Cathol ...
was able to survive in spite of the opposition of Charles V Charles V may refer to:
* Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor (1500–1558)
* Charles V of Naples (1661–1700), better known as Charles II of Spain
* Charles V of France (1338–1380), called the Wise
* Charles V, Duke of Lorraine (1643–1690)
* Infant ...
and reach recognition at the Peace of Augsburg in September 1555: "the consolidation, expansion and legitimization of Lutheranism in Germany by 1555 should be attributed to Ottoman imperialism more than to any other single factor".
The Dutch Revolt and Islam
 Fundamentally, the Protestant Dutch had strong antagonisms to both the Catholics and the Muslims. In some cases however, alliances, or attempts at alliance between the Dutch and the Muslims were made possible, as when the Dutch allied with the Muslims of the
Fundamentally, the Protestant Dutch had strong antagonisms to both the Catholics and the Muslims. In some cases however, alliances, or attempts at alliance between the Dutch and the Muslims were made possible, as when the Dutch allied with the Muslims of the Moluccas
The Maluku Islands (; Indonesian: ''Kepulauan Maluku'') or the Moluccas () are an archipelago in the east of Indonesia. Tectonically they are located on the Halmahera Plate within the Molucca Sea Collision Zone. Geographically they are located ...
to oust the Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Port ...
, and the Dutch became rather tolerant of the Islamic religion in their colonial possessions after the final subjugation of Macassar in 1699.
During the Dutch Revolt, the Dutch were under such a desperate situation that they looked for help from every nationality, and "indeed even a Turk", as wrote the secretary of Jan van Nassau
Count John VI of Nassau-Dillenburg (22 November 1536 – 8 October 1606) was the second son of William the Rich and the younger brother of William the Silent. He has a special place in the history of the Netherlands because he is the male-lin ...
. The Dutch saw Ottoman successes against the Habsburgs with great interest, and saw Ottoman campaigns in the Mediterranean as an indicator of relief on the Dutch front. William wrote around 1565:
The Dutch looked expectantly at the development of the Siege of Malta (1565)
The Great Siege of Malta (Maltese: ''L-Assedju l-Kbir'') occurred in 1565 when the Ottoman Empire attempted to conquer the island of Malta, then held by the Knights Hospitaller. The siege lasted nearly four months, from 18 May to 13 September 1 ...
, hoping that the Ottomans "were in Valladolid
Valladolid () is a municipality in Spain and the primary seat of government and de facto capital of the autonomous community of Castile and León. It is also the capital of the province of the same name. It has a population around 300,000 peo ...
already", and used it as a way to obtain concessions from the Spanish crown.
 Contacts soon became more direct. William of Orange sent ambassadors to the
Contacts soon became more direct. William of Orange sent ambassadors to the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
for help in 1566. When no other European power would help, "the Dutch cause was offered active support, paradoxically enough, only by the Ottoman Turks". One of the Sultan principal advisers Joseph Miques
Joseph Nasi (1524, Portugal – 1579, Konstantiniyye), known in Portuguese as João Miques, was a Portuguese Sephardi diplomat and administrator, member of the House of Mendes/ Benveniste, nephew of Dona Gracia Mendes Nasi, and an influential f ...
, Duke of Naxos, delivered a letter to the Calvinists in Antwerp pledging that "the forces of the Ottomans would soon hit Philip II's affairs so hard that he would not even have the time to think of Flanders". The death of Suleiman the Magnificent later in 1566 however, meant that the Ottoman were unable to offer support for several years after. In 1568, William of Orange again sent a request to the Ottomans to attack Spain, without success. The 1566-1568 revolt of the Netherlands finally failed, largely due to the lack of foreign support.
 In 1574, William of Orange and
In 1574, William of Orange and Charles IX of France
Charles IX (Charles Maximilien; 27 June 1550 – 30 May 1574) was King of France from 1560 until his death in 1574. He ascended the French throne upon the death of his brother Francis II in 1560, and as such was the penultimate monarch of the ...
, through his pro-Huguenot ambassador François de Noailles
François de Noailles, (2 July 1519 – 19 September 1585) Papal Prothonotary, made Bishop of Dax in 1556, was French ambassador in Venice in the 1560s, and French ambassador of Charles IX to the Ottoman Empire from 1571 to 1575.
François was on ...
, Bishop of Dax, tried again to obtain the support of the Ottoman ruler Selim II
Selim II (Ottoman Turkish: سليم ثانى ''Selīm-i sānī'', tr, II. Selim; 28 May 1524 – 15 December 1574), also known as Selim the Blond ( tr, Sarı Selim) or Selim the Drunk ( tr, Sarhoş Selim), was the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire ...
. Selim II sent his support through a messenger, who endeavoured to put the Dutch in contact with the rebellious Moriscos
Moriscos (, ; pt, mouriscos ; Spanish for "Moorish") were former Muslims and their descendants whom the Roman Catholic church and the Spanish Crown commanded to convert to Christianity or face compulsory exile after Spain outlawed the open ...
of Spain and the pirates of Algiers. Selim also sent a great fleet which conquered Tunis in October 1574, thus succeeding in reducing Spanish pressure on the Dutch, and leading to negotiations at the Conference of Breda
A conference is a meeting of two or more experts to discuss and exchange opinions or new information about a particular topic.
Conferences can be used as a form of group decision-making, although discussion, not always decisions, are the main ...
. After the death of Charles IX in May 1574 however, contacts weakened, although the Ottomans are said to have supported the 1575-1576 revolt, and establish a Consulate in Antwerp (''De Griekse Natie''). The Ottomans made a truce with Spain, and shifted their attention to their conflict with Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkme ...
, starting the long Ottoman–Safavid War (1578–1590)
The Ottoman–Safavid War (1578–1590) was one of the many wars between the neighboring arch rivals of Safavid Empire and the Ottoman Empire.
Starting with several years prior to the war and up to including most of the war itself, the Safavid ...
.
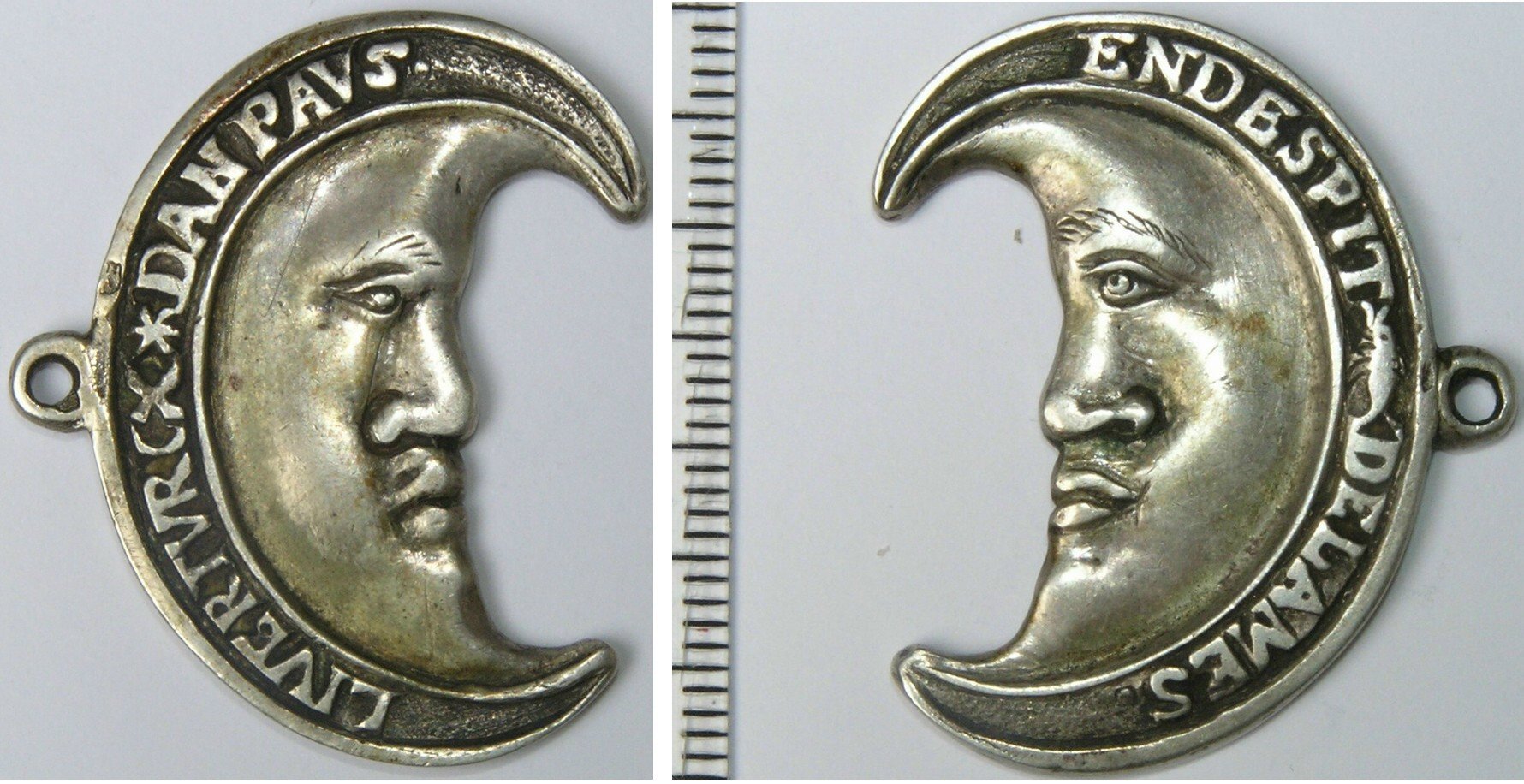
The British author William Rainolds (1544–1594) wrote a pamphlet entitled "Calvino-Turcismus" in criticism of these rapprochements.
The phrase ''Liever Turks dan Paaps
''Liever Turks dan Paaps'' ("Rather Turkish than Papist"), also ''Liever Turksch dan Paus'' ("Rather Turkish than Pope"), was a Dutch Christian slogan during the Dutch Revolt of the end of the 16th century. The slogan was used by the Dutch merce ...
'' ("Rather a Turk than a Papist") was a Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
slogan during the Dutch Revolt of the end of the 17th century. The slogan was used by the Dutch mercenary naval forces (the "Sea Beggars
Geuzen (; ; french: Les Gueux) was a name assumed by the confederacy of Calvinist Dutch nobles, who from 1566 opposed Spanish rule in the Netherlands. The most successful group of them operated at sea, and so were called Watergeuzen (; ; frenc ...
") in their fight against Catholic Spain. The banner of the Sea Beggars was also similar to that of the Turks, with a crescent on a red background. The phrase "Liever Turks dan Paaps" was coined as a way to express that life under the Ottoman Sultan would have been more desirable than life under the King of Spain. The Flemish noble D'Esquerdes wrote to this effect that he:
The slogan ''Liever Turks dan Paaps'' seems to have been largely rhetorical however, and the Dutch hardly contemplated life under the Sultan at all. Ultimately, the Turks were infidels, and the heresy of Islam alone disqualified them from assuming a more central (or consistent) role in the rebels' program of propaganda.
During the early 17th century the Dutch trading ports housed many Muslims, according to a Dutch traveler to Persia there would be no use in describing the Persians as "they are so numerous in Dutch cities". Dutch paintings from that time often show Turks, Persians and Jews strolling through the city. Officials that were sent to the Netherlands included Zeyn-Al-Din Beg of the Saffavid empire in 1607 and Ömer Aga of the Ottoman Empire in 1614. Like the Venetians en Genoese before them, the Dutch and English established a trade network in the eastern Mediterranean and had regular interactions with the ports of the Persian Gulf. Many Dutch painters even went to work in Isfahan, central Iran.
 From 1608,
From 1608, Samuel Pallache
Samuel Pallache (Arabic: صامويل آل بالاتش, ''Shmuel Baylash'', Hebrew: 'שמואל פאלאץ, ''Shmuel Palach'', c. 1550 – February 4, 1616) was a Jewish Moroccan-born merchant, diplomat, and pirate of the Pallache family, who, ...
served as an intermediary to discuss an alliance between Morocco and the Low Countries. In 1613, the Moroccan Ambassador Al-Hajari discussed in La Hague
La Hague () is a commune in the department of Manche, northwestern France. The municipality was established on 1 January 2017 by merger of the former communes of Beaumont-Hague (the seat), Acqueville, Auderville, Biville, Branville-Hague, ...
with the Dutch Prince Maurice of Orange
Maurice of Orange ( nl, Maurits van Oranje; 14 November 1567 – 23 April 1625) was ''stadtholder'' of all the provinces of the Dutch Republic except for Friesland from 1585 at the earliest until his death in 1625. Before he became Prince o ...
the possibility of an alliance between the Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands ( Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiography ...
, the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria ...
and the Moriscos, against the common enemy Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' ( Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
. His book mentions the discussion for a combined offensive on Spain, as well as the religious reasons for the good relations between Islam and Protestantism at the time:
During the Thirty Years War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of battle ...
(1618–1648), the Dutch would strengthen contacts with the Moriscos
Moriscos (, ; pt, mouriscos ; Spanish for "Moorish") were former Muslims and their descendants whom the Roman Catholic church and the Spanish Crown commanded to convert to Christianity or face compulsory exile after Spain outlawed the open ...
against Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' ( Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
.
French Huguenots and Islam
FrenchHuguenot
The Huguenots ( , also , ) were a religious group of French Protestants who held to the Reformed, or Calvinist, tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, the Genevan burgomaster Bez ...
s were in contact with the Moriscos
Moriscos (, ; pt, mouriscos ; Spanish for "Moorish") were former Muslims and their descendants whom the Roman Catholic church and the Spanish Crown commanded to convert to Christianity or face compulsory exile after Spain outlawed the open ...
in plans against Spain in the 1570s. Around 1575, plans were made for a combined attack of Aragonese Moriscos and Huguenots from Béarn
The Béarn (; ; oc, Bearn or ''Biarn''; eu, Bearno or ''Biarno''; or ''Bearnia'') is one of the traditional provinces of France, located in the Pyrenees mountains and in the plain at their feet, in southwest France. Along with the three B ...
under Henri de Navarre against Spanish Aragon
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and an, Aragón ; ca, Aragó ) is an autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces (from north to so ...
, in agreement with the king of Algiers and the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, but these projects foundered with the arrival of John of Austria
John of Austria ( es, Juan, link=no, german: Johann; 24 February 1547 – 1 October 1578) was the natural son born to Holy Roman Emperor Charles V late in life when he was a widower. Charles V met his son only once, recognizing him in a secret ...
in Aragon and the disarmament of the Moriscos. In 1576, a three-pronged fleet from Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth ( Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
was planned to disembark between Murcia
Murcia (, , ) is a city in south-eastern Spain, the Capital (political), capital and most populous city of the autonomous community of the Region of Murcia, and the List of municipalities of Spain, seventh largest city in the country. It has a ...
and Valencia
Valencia ( va, València) is the capital of the autonomous community of Valencia and the third-most populated municipality in Spain, with 791,413 inhabitants. It is also the capital of the province of the same name. The wider urban area al ...
while the French Huguenots would invade from the north and the Moriscos accomplish their uprising, but the Ottoman fleet failed to arrive.
Alliance between the Barbary states and England
 Following the sailing of ''The Lion'' of Thomas Wyndham in 1551, and the 1585 establishment of the English
Following the sailing of ''The Lion'' of Thomas Wyndham in 1551, and the 1585 establishment of the English Barbary Company
The Marocco Company or Barbary Company was a trading company established by Queen Elizabeth I of England in 1585 through a patent granted to the Earls of Warwick and Leicester, as well as forty others. When she wrote the patents, Elizabeth emphasi ...
, trade developed between England and the Barbary states, and especially Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria ...
. Diplomatic relations and an alliance were established between Elizabeth and the Barbary states. England entered in a trading relationship with Morocco detrimental to Spain, selling armour, ammunition, timber, metal in exchange for Moroccan sugar, in spite of a Papal
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
ban, prompting the Papal Nuncio in Spain to say of Elizabeth: "there is no evil that is not devised by that woman, who, it is perfectly plain, succoured Mulocco ( Abd-el-Malek) with arms, and especially with artillery".
In 1600, Abd el-Ouahed ben Messaoud
Abd al-Wahid bin Mas'ud bin Mohammed Anun ( ar, عبد الواحد بن مسعود بن محمد عنون) was principal secretary to the Moroccan ruler Mulay Ahmad al-Mansur, and ambassador to the court of Queen Elizabeth I of England in 1600, ...
, the principal secretary to the Moroccan ruler Mulai Ahmad al-Mansur, visited England as an ambassador to the court of Queen Elizabeth I. Abd el-Ouahed ben Messaoud spent 6 months at the court of Elizabeth, in order to negotiate an alliance against Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' ( Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
. The Moroccan ruler wanted the help of an English fleet to invade Spain, Elizabeth refused, but welcomed the embassy as a sign of insurance, and instead accepted to establish commercial agreements. Queen Elizabeth and king Ahmad continued to discuss various plans for combined military operations, with Elizabeth requesting a payment of 100,000 pounds in advance to king Ahmad for the supply of a fleet, and Ahmad asking for a tall ship to be sent to get the money. Elizabeth "agreed to sell munitions supplies to Morocco, and she and Mulai Ahmad al-Mansur talked on and off about mounting a joint operation against the Spanish". Discussions however remained inconclusive, and both rulers died within two years of the embassy.
Collaboration between the Ottoman Empire and England
 Diplomatic relations were established with the
Diplomatic relations were established with the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
during the reign of Elizabeth, with the chartering of the Levant Company
The Levant Company was an English chartered company formed in 1592. Elizabeth I of England approved its initial charter on 11 September 1592 when the Venice Company (1583) and the Turkey Company (1581) merged, because their charters had expired ...
and the dispatch of the first English ambassador to the Porte
Porte may refer to:
* Sublime Porte, the central government of the Ottoman empire
* Porte, Piedmont, a municipality in the Piedmont region of Italy
* John Cyril Porte, British/Irish aviator
* Richie Porte, Australian professional cyclist who compe ...
, William Harborne
William Harborne of Great Yarmouth, Norfolk (c.1542–1617) was a diplomat, businessman, and English Ambassador to the Ottoman Empire, appointed by Queen Elizabeth I of England.
Establishment of the English Embassy in Constantinople
Following a ...
, in 1578. Numerous envoys were dispatched in both directions and epistolary exchanges occurred between Elizabeth and Sultan Murad III
Murad III ( ota, مراد ثالث, Murād-i sālis; tr, III. Murad; 4 July 1546 – 16 January 1595) was Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1574 until his death in 1595. His rule saw battles with the Habsburgs and exhausting wars with the Saf ...
. In one correspondence, Murad entertained the notion that Islam and Protestantism had "much more in common than either did with Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, as both rejected the worship of idols", and argued for an alliance between England and the Ottoman Empire. To the dismay of Catholic Europe, England exported tin and lead (for cannon-casting) and ammunition to the Ottoman Empire, and Elizabeth seriously discussed joint military operations with Murad III during the outbreak of war with Spain in 1585, as Francis Walsingham
Sir Francis Walsingham ( – 6 April 1590) was principal secretary to Queen Elizabeth I of England from 20 December 1573 until his death and is popularly remembered as her " spymaster".
Born to a well-connected family of gentry, Wa ...
was lobbying for a direct Ottoman military involvement against the common Spanish enemy.
English writers of the period often expressed admiration towards the "Turks" and the "Ottoman Empire", describing it as endowed with "Majestical and August form and features" and being the "Powerfullest nation in Europe", saying that the Turks were "the only modern people, great in action- he who would behold these times in their greatest glory, could not find a better scene than Turky" and that they had "incredible civility".
Anglo-Turkish piracy
After peace was made with CatholicSpain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' ( Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
in 1604, English pirates nevertheless continued to raid Christian shipping in the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on th ...
, this time under the protection of the Muslim rulers of the Barbary States, and often converting to Islam in the process, in what has been described as Anglo-Turkish piracy.
Transylvania and Hungary
 In eastern
In eastern Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the ...
, particularly in Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the ...
, tolerant Ottoman rule meant that the Protestant communities there were protected from Catholic persecutions by the Habsburg. In the 16th century, the Ottomans supported the Calvinists in Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the ...
and Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croa ...
and practised religious toleration, giving almost complete freedom, although heavy taxation was imposed. Suleiman the Magnificent in particular supported John Sigismund of Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croa ...
, allowing him to establish the Unitarian Church in Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the ...
. By the end of the century, large parts of the population in Hungary thus became either Lutheran or Calvinist, to become the Reformed Church in Hungary
The Reformed Church in Hungary ( hu, Magyarországi Református Egyház, MRE) is the largest Protestant church in Hungary, with parishes among the Hungarian diaspora abroad. Today, it is made up of 1,249 congregations in 27 presbyteries and fou ...
.
 In the 17th century Protestant communities again asked for Ottoman help against the Habsburg Catholics. When in 1606 Emperor
In the 17th century Protestant communities again asked for Ottoman help against the Habsburg Catholics. When in 1606 Emperor Rudolph II
Rudolf II (18 July 1552 – 20 January 1612) was Holy Roman Emperor (1576–1612), King of Hungary and Croatia (as Rudolf I, 1572–1608), King of Bohemia (1575–1608/1611) and Archduke of Austria (1576–1608). He was a member of the Hou ...
suppressed religious liberty, Prince István Bocskay
Stephen Bocskai or Bocskay ( hu, Bocskai István; 1 January 155729 December 1606) was Prince of Transylvania and Hungary from 1605 to 1606. He was born to a Hungarian noble family. His father's estates were located in the eastern regions of th ...
(1558–1606) of Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the ...
, allied with the Ottoman Turks
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
, achieved autonomy for Transylvania, including guaranteeing religious freedom in the rest of Hungary for a short time. In 1620, the Transylvanian
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the A ...
Protestant prince Bethlen Gabor
Gabriel Bethlen ( hu, Bethlen Gábor; 15 November 1580 – 15 November 1629) was Prince of Transylvania from 1613 to 1629 and Duke of Opole from 1622 to 1625. He was also King-elect of Hungary from 1620 to 1621, but he never took control of th ...
, fearful of the Catholic policies of Ferdinand II, requested a protectorate by Sultan Osman II
Osman II ( ota, عثمان ثانى ''‘Osmān-i sānī''; tr, II. Osman; 3 November 1604 – 20 May 1622), also known as Osman the Young ( tr, Genç Osman), was Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 26 February 1618 until his regicide on 20 May 162 ...
, so that "the Ottoman Empire became the one and only ally of great-power status which the rebellious Bohemian states could muster after they had shaken off Habsburg rule and had elected Frederick V as a Protestant king", Ambassadors were exchanged, with Heinrich Bitter
Heinrich Bitter (fl. 1620) was an ambassador of the Bohemian estates
Bohemian or Bohemians may refer to:
*Anything of or relating to Bohemia
Beer
* National Bohemian, a brand brewed by Pabst
* Bohemian, a brand of beer brewed by Molson Coor ...
visiting Istanbul in January 1620, and Mehmed Aga
Sedefkar Mehmed Agha Biçakçiu or Sedefqar Mehmeti of Elbasan (Modern Turkish: ''Sedefkâr Mehmet Ağa'', about 1540–1617) is recorded as the Ottoman architect of the Sultan Ahmed Mosque (the "Blue Mosque") in Istanbul.
Biography
Mehmed Agh ...
visiting Prague in July 1620. The Ottomans offered a force of 60,000 cavalry to Frederick and plans were made for an invasion of Poland with 400,000 troops in exchange for the payment of an annual tribute to the Sultan. The Ottomans defeated the Poles, which were supporting the Habsburgs in the Thirty Years' War, at the Battle of Cecora in September–October 1620, but were not able to further intervene efficiently before the Bohemian defeat at the Battle of the White Mountain
), near Prague, Bohemian Confederation(present-day Czech Republic)
, coordinates =
, territory =
, result = Imperial-Spanish victory
, status =
, combatants_header =
, combatant1 = Catholic L ...
in November 1620.
At the end of the century, the Hungarian leader Imre Thököly, in resistance to the anti-Protestant policies of the Habsburg, asked and obtained, the military help of the Ottoman Grand Vizier Kara Mustafa
Merzifonlu Kara Mustafa Pasha ( ota, مرزيفونلى قره مصطفى پاشا, tr, Merzifonlu Kara Mustafa Paşa; "Mustafa Pasha the Courageous of Merzifon"; 1634/1635 – 25 December 1683) was an Ottoman nobleman, military figure and G ...
, leading to the 1683 Ottoman attack on the Habsburg Empire and the Battle of Vienna
The Battle of Vienna; pl, odsiecz wiedeńska, lit=Relief of Vienna or ''bitwa pod Wiedniem''; ota, Beç Ḳalʿası Muḥāṣarası, lit=siege of Beç; tr, İkinci Viyana Kuşatması, lit=second siege of Vienna took place at Kahlenberg Mo ...
.
In the 16th century Hungary had become almost entirely Protestant, with first Lutheranism
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Cathol ...
, then soon afterwards Calvinism
Calvinism (also called the Reformed Tradition, Reformed Protestantism, Reformed Christianity, or simply Reformed) is a major branch of Protestantism that follows the theological tradition and forms of Christian practice set down by John Ca ...
, but following the Habsburg policy of Counter-Reformation the western part of the country finally returned to Catholicism, while the eastern part has managed to this day to remain strongly Protestant: "although the Habsburg succeeded in re-Catholicising Royal Hungary, east of the Tisza
The Tisza, Tysa or Tisa, is one of the major rivers of Central and Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and ...
the Reformation remained almost intact in the spirit of peaceful coexistence between the three recognized nations and respect for their diverse creeds".
Rich Protestant Transylvanian Saxon
The Transylvanian Saxons (german: Siebenbürger Sachsen; Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjer Såksen''; ro, Sași ardeleni, sași transilvăneni/transilvani; hu, Erdélyi szászok) are a people of German ethnicity who settled in Transylvania ...
merchants traded with the Ottoman Empire and often donated
A donation is a gift for charity, humanitarian aid, or to benefit a cause. A donation may take various forms, including money, alms, services, or goods such as clothing, toys, food, or vehicles. A donation may satisfy medical needs such as ...
Anatolian rugs to their churches as a wall decoration more according to their iconoclastic
Iconoclasm (from Ancient Greek, Greek: grc, wikt:εἰκών, εἰκών, lit=figure, icon, translit=eikṓn, label=none + grc, wikt:κλάω, κλάω, lit=to break, translit=kláō, label=none)From grc, wikt:εἰκών, εἰκών + wi ...
beliefs than the images of the saints used by the Catholics and the Orthodox. Churches like the Black Church of Brașov
Black is a color which results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without hue, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness. Black and white ha ...
still hold collections of rugs.
Relations with Persia

East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Sout ...
and in 1622 "a joint Anglo-Persian force expelled the Portuguese and Spanish traders from the Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf ( fa, خلیج فارس, translit=xalij-e fârs, lit=Gulf of Fars, ), sometimes called the ( ar, اَلْخَلِيْجُ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Khalīj al-ˁArabī), is a mediterranean sea in Western Asia. The bo ...
" in the Capture of Ormuz.
A group of English adventurers, led by Robert Shirley
Sir Robert Shirley (or Sherley; c. 1581 – 13 July 1628) was an English traveller and adventurer, younger brother of Sir Anthony Shirley and Sir Thomas Shirley. He is notable for his help modernising and improving the Persian Safavid army ...
had a key role in modernizing the Persian army and developing its contacts with the West. In 1624, Robert Shirley led an embassy to England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
in order to obtain trade agreements.
Later relations
These unique relations between Protestantism and Islam mainly took place during the 16th and 17th century. The ability of Protestant nations to disregard Papal bans, and therefore to establish freer commercial and other types of relations with Muslim and pagan countries, may partly explain their success in developing influence and markets in areas previously discovered by Spain and Portugal. Progressively however, Protestantism became able to consolidate itself and became less dependent on external help. At the same time, the power of theOttoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
waned from its 16th century peak, making attempts at alliance and conciliation less relevant. However, in 1796 the Treaty of Tripoli
The Treaty of Tripoli (''Treaty of Peace and Friendship between the United States of America and the Bey and Subjects of Tripoli of Barbary'') was signed in 1796. It was the first treaty between the United States and Tripoli (now Libya) to secure ...
(between the United States of America and the Subjects of Tripoli of Barbary) noted "that no pretext arising from religious opinions shall ever produce an interruption of the harmony existing between the two countries."
Eventually, relations between Protestantism and Islam have often tended to become conflicted. Protestant slaves were acquired by Barbary pirates in slave raids on ships and by raids on coastal towns from Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
to the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Nether ...
and the southwest of Britain, as far north as Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its ...
. On some occasions, settlements such as Baltimore
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the List of municipalities in Maryland, most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, and List of United States cities by popula ...
in Ireland were abandoned following a raid, only being resettled many years later. Between 1609 and 1616, England alone lost 466 merchant ships to Barbary pirates. In the context of the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
, Protestant missionaries seem to have been active in portraying Islam in an unfavourable light, representing it as "the epitome of anti-Christian darkness and political tyranny", in a way that helped construct in opposition an American national identity as "modern, democratic and Christian". Some famous Protestants have criticized Islam like Pat Robertson
Marion Gordon "Pat" Robertson (born March 22, 1930) is an American media mogul, religious broadcaster, political commentator, former presidential candidate, and former Southern Baptist minister. Robertson advocates a conservative Christian ...
Jerry Falwell
Jerry Laymon Falwell Sr. (August 11, 1933 – May 15, 2007) was an American Baptist pastor, televangelist, and conservative activist. He was the founding pastor of the Thomas Road Baptist Church, a megachurch in Lynchburg, Virginia. He founded L ...
, Jerry Vines
Charles Jerry Vines (born September 1937) is an American preacher and former pastor of what was then the nation's third largest Southern Baptist church, the First Baptist Church of Jacksonville, Florida. Like his former co-pastor Homer G. Lin ...
, R. Albert Mohler, Jr. and Franklin Graham
William Franklin Graham III (born July 14, 1952) is an American evangelist and missionary. He frequently engages in Christian revival tours and political commentary. He is president and CEO of the Billy Graham Evangelistic Association (BGEA) and ...
.
Comparative elements
Besides the obvious differences between the two religious, there are also many similarities in their outlooks and attitudes to faith (especially with Sunni Islam), especially in respect to textual criticism, iconoclasm, tendencies to fundamentalism, rejection of marriage as a sacrament, rejection of necessary penance by priests, and the rejection of monastic orders.Textual criticism
Islam and Protestantism have in common a reliance on textual criticism of the Book. This historical precedence combines to fact that Islam incorporates to a certain extent the Jewish and Christian traditions, recognizing the same God and definingJesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religiou ...
as a prophet, as well as recognizing Hebrew prophets, thus having a claim to encompassing all the religions of the Book.
Iconoclasm
The rejection of images in worship, although more prominent in Islam, is a common point in Protestantism and Islam. This was already extensively recognized from the earliest times, as in the correspondence betweenElizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was Queen of England and Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. Elizabeth was the last of the five House of Tudor monarchs and is sometimes referred to as the "Virgin Queen".
Eli ...
of England and her Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
counterparts, in which she implied that Protestantism was closer to Islam than to Catholicism. This is also a point developed by Martin Luther
Martin Luther (; ; 10 November 1483 – 18 February 1546) was a German priest, theologian, author, hymnwriter, and professor, and Augustinian friar. He is the seminal figure of the Protestant Reformation and the namesake of Luther ...
in '' On War against the Turk'', in which he praised the Ottomans
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
for their rigorous iconoclasm:
Rich Protestant Transylvanian Saxon
The Transylvanian Saxons (german: Siebenbürger Sachsen; Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjer Såksen''; ro, Sași ardeleni, sași transilvăneni/transilvani; hu, Erdélyi szászok) are a people of German ethnicity who settled in Transylvania ...
merchants traded with the Ottoman Empire and often donated Anatolian rugs to their churches as a wall decoration more according to their iconoclastic
Iconoclasm (from Ancient Greek, Greek: grc, wikt:εἰκών, εἰκών, lit=figure, icon, translit=eikṓn, label=none + grc, wikt:κλάω, κλάω, lit=to break, translit=kláō, label=none)From grc, wikt:εἰκών, εἰκών + wi ...
beliefs than the images of the saints used by the Catholics and the Orthodox. Churches like the Black Church of Brasov
Black is a color which results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without hue, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness. Black and white ha ...
still hold collections of such rugs.
Fundamentalism
Islam and Protestantism have in common that they are both based on a direct analysis of the scriptures (theBible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts o ...
for Protestantism and the Quran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , sing.: ...
for Islam). This can be contrasted to Catholicism in which knowledge is analysed, formalized and distributed by the existing structure of the Church. Islam and Protestantism are thus both based on "a rhetorical commitment to a universal mission", when Catholicism is based on an international structure. This leads to possibilities of fundamentalism
Fundamentalism is a tendency among certain groups and individuals that is characterized by the application of a strict literal interpretation to scriptures, dogmas, or ideologies, along with a strong belief in the importance of distinguishing ...
, based on the popular reinterpretation of scriptures by radical elements. The term "fundamentalism" was first used in America in the 1920, to describe "the consciously anti-modernist wing of Protestantism".
Islamic and Protestant fundamentalism also tend to be very normative of individuals' behaviours: "Religious fundamentalism in Protestantism and Islam is very concerned with norms surrounding gender, sexuality, and family", although Protestant fundamentalism tends to focus on individual behaviour, whereas Islamic fundamentalism tends to develop laws for the community.
The most notable trend of Islamic fundamentalism, Salafism
The Salafi movement or Salafism () is a reform branch movement within Sunni Islam that originated during the nineteenth century. The name refers to advocacy of a return to the traditions of the "pious predecessors" (), the first three generat ...
, is based upon a literal reading of the Qur'an
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , si ...
and Sunnah
In Islam, , also spelled ( ar, سنة), are the traditions and practices of the Islamic prophet Muhammad that constitute a model for Muslims to follow. The sunnah is what all the Muslims of Muhammad's time evidently saw and followed and pass ...
without relying on the interpretations of Muslim philosophers, rejecting the need for Taqlid
''Taqlid'' (Arabic تَقْليد ''taqlīd'') is an Islamic term denoting the conformity of one person to the teaching of another. The person who performs ''taqlid'' is termed ''muqallid''. The definite meaning of the term varies depending on co ...
for recognized scholars. Fundamentalist Protestantism is similar, in that the 'traditions of men' and the Church Fathers are rejected in favor of a literalist interpretation of the Bible, which is seen as inerrant. Islamic Fundamentalists and Protestant Fundamentalists often reject contextual interpretation. Another similarity with Protestantism and Salafism is criticism of saint veneration and belief in the power of relics
In religion, a relic is an object or article of religious significance from the past. It usually consists of the physical remains of a saint or the personal effects of the saint or venerated person preserved for purposes of veneration as a tang ...
and tombs, and emphasis on praying to God alone.
Islamic Protestantism
Parallels have regularly been drawn in the similar attitudes of Islam and Protestantism towards the Scriptures. Some trends in Muslim revival have thus been defined as " Islamic Protestantism". In a sense "Islamization is a political movement to combat Westernization using the methods of Western culture, namely a form of Protestantism within Islam itself".Vitality
Islam and Protestantism share a common vitality in the modern world: "The two most dynamic religious movements in the contemporary world are what can loosely be called popular Protestantism and resurgent Islam", although their approach to civil society is different.See also
*Islam in England
Islam in England is the second largest religion after Christianity. Most Muslims are immigrants from South Asia (in particular Bangladesh, Pakistan and India) or descendants of immigrants from that region. Many others are from Muslim-dominated ...
* Protestantism in Turkey
* Protestantism in Pakistan
* Mormonism and Islam
Islam and Mormonism have been compared to one another ever since the earliest origins of the latter in the nineteenth century, often by detractors of one religion or the other—or both. For instance, Joseph Smith, founder of the Latter Day Saint ...
* Islam and other religions
Over the centuries of Islamic history, Muslim rulers, Islamic scholars, and ordinary Muslims have held many different attitudes towards other religions. Attitudes have varied according to time, place and circumstance.
Non-Muslims and Islam ...
* Divisions of the world in Islam
In classical Islamic law, the major divisions are ''dar al-Islam'' (lit. territory of Islam/voluntary submission to God), denoting regions where Islamic law prevails, ''dar al-sulh'' (lit. territory of treaty) denoting non-Islamic lands which have ...
* Pallache family
"Pallache" – also de Palacio(s), Palache, Palaçi, Palachi, Palacci, Palaggi, and many other variations (documented below) – is the surname of a prominent, Ladino-speaking, Sephardic Jewish family from the Iberian Peninsula, who spread mostl ...
* Protestantism and Judaism Relations between Protestantism and Judaism have existed since the time of the Reformation, although there has been more emphasis on dialogue since the 20th century, with Protestant and Jewish scholars in the United States being at the forefront of ...
* Schmalkaldic League
The Schmalkaldic League (; ; or ) was a military alliance of Lutheran princes within the Holy Roman Empire during the mid-16th century.
Although created for religious motives soon after the start of the Reformation, its members later came to ...
* On War Against the Turk
Notes
References
* * * * * * * *External links
Wittenberg and Mecca
issue of ''Logia: A Journal of Lutheran Theology'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Protestantism And Islam Christianity and Islam Islam