molecular biology
Molecular biology is a branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecule, molecular basis of biological activity in and between Cell (biology), cells, including biomolecule, biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactio ...
, a protein-fragment complementation assay, or PCA, is a method for the identification and quantification of protein–protein interactions. In the PCA, the proteins of interest ("bait" and "prey") are each covalently linked to fragments of a third protein (e.g. DHFR, which acts as a "reporter"). Interaction between the bait and the prey proteins brings the fragments of the reporter protein in close proximity to allow them to form a functional reporter protein whose activity can be measured. This principle can be applied to many different reporter proteins and is also the basis for the yeast two-hybrid system, an archetypical PCA assay.
Split protein assays
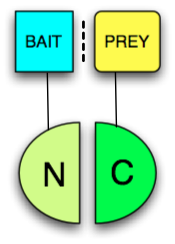 Any protein that can be split into two parts and reconstituted non-covalently to form a functional protein may be used in a PCA. The two fragments however have low affinity for each other and must be brought together by other interacting proteins fused to them (often called "bait" and "prey" since the bait protein can be used to identify a prey protein, see figure). The protein that produces a detectable readout is called "reporter". Usually enzymes which confer resistance to nutrient deprivation or antibiotics, such as
Any protein that can be split into two parts and reconstituted non-covalently to form a functional protein may be used in a PCA. The two fragments however have low affinity for each other and must be brought together by other interacting proteins fused to them (often called "bait" and "prey" since the bait protein can be used to identify a prey protein, see figure). The protein that produces a detectable readout is called "reporter". Usually enzymes which confer resistance to nutrient deprivation or antibiotics, such as dihydrofolate reductase
Dihydrofolate reductase, or DHFR, is an enzyme that reduces dihydrofolic acid to tetrahydrofolic acid, using NADPH as an electron donor, which can be converted to the kinds of tetrahydrofolate cofactors used in one-carbon transfer chemistry. ...
or beta-lactamase
Beta-lactamases (β-lactamases) are enzymes () produced by bacteria that provide multi-resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics such as penicillins, cephalosporins, cephamycins, monobactams and carbapenems ( ertapenem), although carbapene ...
respectively, or proteins that give colorimetric or fluorescent signals are used as reporters. When fluorescent proteins are reconstituted the PCA is called Bimolecular fluorescence complementation assay. The following proteins have been used in split protein PCAs:
*Beta-lactamase
Beta-lactamases (β-lactamases) are enzymes () produced by bacteria that provide multi-resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics such as penicillins, cephalosporins, cephamycins, monobactams and carbapenems ( ertapenem), although carbapene ...
*Dihydrofolate reductase
Dihydrofolate reductase, or DHFR, is an enzyme that reduces dihydrofolic acid to tetrahydrofolic acid, using NADPH as an electron donor, which can be converted to the kinds of tetrahydrofolate cofactors used in one-carbon transfer chemistry. ...
(DHFR)
* Focal adhesion kinase (FAK)
*Gal4, a yeast transcription factor (as in the classical yeast two-hybrid system)
*GFP (split-GFP), e.g. EGFP (enhanced green fluorescent protein
The green fluorescent protein (GFP) is a protein that exhibits green fluorescence when exposed to light in the blue to ultraviolet range. The label ''GFP'' traditionally refers to the protein first isolated from the jellyfish ''Aequorea victo ...
)
*Horseradish peroxidase
The enzyme horseradish peroxidase (HRP), found in the roots of horseradish, is used extensively in biochemistry applications. It is a metalloenzyme with many isoforms, of which the most studied type is C. It catalyzes the oxidation of various or ...
*Infrared fluorescent protein IFP1.4, an engineered chromophore
A chromophore is the part of a molecule responsible for its color. The word is derived .
The color that is seen by our eyes is that of the light not Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorbed by the reflecting object within a certain wavele ...
-binding domain (CBD) of a bacteriophytochrome from ''Deinococcus radiodurans
''Deinococcus radiodurans'' is a bacterium, an extremophile and one of the most radiation-resistant organisms known. It can survive cold, dehydration, vacuum, and acid, and therefore is known as a polyextremophile. ''The Guinness Book Of World ...
''
*LacZ ( beta-galactosidase)
*Luciferase
Luciferase is a generic term for the class of oxidative enzymes that produce bioluminescence, and is usually distinguished from a photoprotein. The name was first used by Raphaël Dubois who invented the words ''luciferin'' and ''luciferase'' ...
, including ReBiL (recombinase enhanced bimolecular luciferase) and '' Gaussia princeps'' luciferase. Commercial products using luciferase include NanoLuc and NanoBIT. A modification has also been developed for lipid droplet-associated interactions.
*FAST
Fast or FAST may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* "Fast" (Juice Wrld song), 2019
* "Fast" (Luke Bryan song), 2016
* "Fast" (Sueco song), 2019
* "Fast" (GloToven song), 2019
* ''Fast'', an album by Custom, 2002
* ''Fast'', a 2010 short fil ...
(splitFAST)
*TEV ( Tobacco etch virus protease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalysis, catalyzes proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the formation of new protein products ...
)
*Ubiquitin
Ubiquitin is a small (8.6 kDa) regulatory protein found in most tissues of eukaryotic organisms, i.e., it is found ''ubiquitously''. It was discovered in 1975 by Gideon Goldstein and further characterized throughout the late 1970s and 19 ...
Genome-wide applications
The methods mentioned above have been applied to wholegenome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as ...
s, e.g. yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom (biology), kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are est ...
or syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms depend on the stage it presents: primary, secondary, latent syphilis, latent or tertiary. The prim ...
bacteria.
References
Further reading
* {{refend Molecular biology Laboratory techniques