postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) is a condition characterized by an abnormally large increase in heart rate upon sitting up or standing. POTS is a disorder of the
 POTS is a complex and multifaceted clinical disorder, the etiology and management of which remain incompletely understood. This syndrome is typified by a diverse array of nonspecific symptoms, making it a challenging condition to describe.
Individuals living with POTS experience a diminished quality of life compared to healthy individuals, due to disruptions in various domains such as standing, playing sports, symptom anxiety, and impacts on school, work, or spiritual (religious) domains—these disruptions affect their daily life and overall well-being.
In adults, the primary manifestation is an increase in heart rate of more than 30 beats per minute within ten minutes of standing up. The resulting heart rate is typically more than 120 beats per minute. For people between ages 12 and 19, the minimum increase for a POTS diagnosis is 40 beats per minute. POTS is often accompanied by common features of orthostatic intolerance—in which symptoms that develop while upright are relieved by reclining. These orthostatic symptoms include
POTS is a complex and multifaceted clinical disorder, the etiology and management of which remain incompletely understood. This syndrome is typified by a diverse array of nonspecific symptoms, making it a challenging condition to describe.
Individuals living with POTS experience a diminished quality of life compared to healthy individuals, due to disruptions in various domains such as standing, playing sports, symptom anxiety, and impacts on school, work, or spiritual (religious) domains—these disruptions affect their daily life and overall well-being.
In adults, the primary manifestation is an increase in heart rate of more than 30 beats per minute within ten minutes of standing up. The resulting heart rate is typically more than 120 beats per minute. For people between ages 12 and 19, the minimum increase for a POTS diagnosis is 40 beats per minute. POTS is often accompanied by common features of orthostatic intolerance—in which symptoms that develop while upright are relieved by reclining. These orthostatic symptoms include
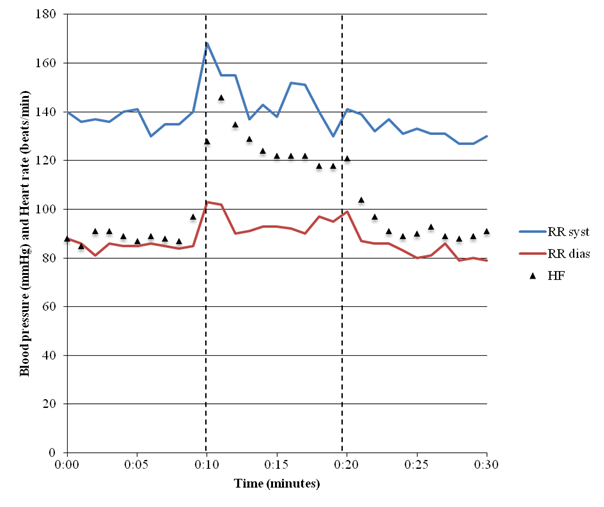 POTS is a complex disorder with a multifactorial etiology, and the diagnostics of POTS is challenging.
POTS is most commonly diagnosed by a cardiologist (41%), cardiac electrophysiologist (15%), or neurologist (19%). The average number of physicians seen before receiving diagnosis is seven, and the average delay before diagnosis is 4.7 years.
POTS is a complex disorder with a multifactorial etiology, and the diagnostics of POTS is challenging.
POTS is most commonly diagnosed by a cardiologist (41%), cardiac electrophysiologist (15%), or neurologist (19%). The average number of physicians seen before receiving diagnosis is seven, and the average delay before diagnosis is 4.7 years.
autonomic nervous system
The autonomic nervous system (ANS), sometimes called the visceral nervous system and formerly the vegetative nervous system, is a division of the nervous system that operates viscera, internal organs, smooth muscle and glands. The autonomic nervo ...
that can lead to a variety of symptoms, including lightheadedness, brain fog
Clouding of consciousness, also called brain fog or mental fog, occurs when a person is conscious but slightly less wakeful or aware than normal. They are less aware of time and their surroundings, and find it difficult to pay attention. Peopl ...
, blurred vision, weakness, fatigue
Fatigue is a state of tiredness (which is not sleepiness), exhaustion or loss of energy. It is a signs and symptoms, symptom of any of various diseases; it is not a disease in itself.
Fatigue (in the medical sense) is sometimes associated wit ...
, headache
A headache, also known as cephalalgia, is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of Depression (mood), depression in those with severe ...
s, heart palpitations, exercise intolerance, nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. It can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the throat.
Over 30 d ...
, difficulty concentrating, tremulousness (shaking), syncope (fainting), coldness, pain, or numbness in the extremities, chest pain, and shortness of breath. Many symptoms are exacerbated with postural changes, especially standing up. Other conditions associated with POTS include myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome, migraine headaches, Ehlers–Danlos syndrome, asthma
Asthma is a common long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wh ...
, autoimmune disease, vasovagal syncope, chiari malformation, and mast cell activation syndrome. POTS symptoms may be treated with lifestyle changes such as increasing fluid, electrolyte, and salt intake, wearing compression stockings, gentle postural changes, exercise, medication
Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal product, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to medical diagnosis, diagnose, cure, treat, or preventive medicine, prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmaco ...
, and physical therapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is a healthcare profession, as well as the care provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through patient education, physical intervention, disease preventio ...
.
The causes of POTS are varied. In some cases, it develops after a viral infection
A viral disease (or viral infection) occurs when an organism's body is invaded by pathogenic viruses, and infectious virus particles (virions) attach to and enter susceptible cells.
Examples include the common cold, gastroenteritis, COVID-19, t ...
, surgery, trauma, autoimmune disease, or pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestation, gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Conception (biology), Conception usually occurs ...
. It has also been shown to emerge in previously healthy patients after contracting COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. In January 2020, the disease spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic.
The symptoms of COVID‑19 can vary but often include fever ...
, in people with Long COVID
Long may refer to:
Measurement
* Long, characteristic of something of great duration
* Long, characteristic of something of great length
* Longitude (abbreviation: long.), a geographic coordinate
* Longa (music), note value in early music mens ...
(post-COVID-19 condition), about 30 % present with POTS-like orthostatic tachycardia, or possibly in rare cases after COVID-19 vaccination, though causative evidence is limited and further study is needed. POTS is more common among people who got infected with SARS-CoV-2
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is a strain of coronavirus that causes COVID-19, the respiratory illness responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. The virus previously had the Novel coronavirus, provisional nam ...
than among those who got vaccinated against COVID-19. Risk factors include a family history of the condition. POTS in adults is characterized by a heart rate increase of 30 beats per minute within ten minutes of standing up, accompanied by other symptoms. This increased heart rate should occur in the absence of orthostatic hypotension (>20 mm Hg drop in systolic blood pressure) to be considered POTS. A spinal fluid leak (called spontaneous intracranial hypotension) may have the same signs and symptoms as POTS and should be excluded. Prolonged bedrest may lead to multiple symptoms, including blood volume loss and postural tachycardia
Tachycardia, also called tachyarrhythmia, is a heart rate that exceeds the normal resting rate. In general, a resting heart rate over 100 beats per minute is accepted as tachycardia in adults. Heart rates above the resting rate may be normal ...
. Other conditions that can cause similar symptoms, such as dehydration
In physiology, dehydration is a lack of total body water that disrupts metabolic processes. It occurs when free water loss exceeds intake, often resulting from excessive sweating, health conditions, or inadequate consumption of water. Mild deh ...
, orthostatic hypotension, heart problems, adrenal insufficiency, epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of Non-communicable disease, non-communicable Neurological disorder, neurological disorders characterized by a tendency for recurrent, unprovoked Seizure, seizures. A seizure is a sudden burst of abnormal electrical activit ...
, and Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a neurodegenerative disease primarily of the central nervous system, affecting both motor system, motor and non-motor systems. Symptoms typically develop gradually and non-motor issues become ...
, must not be present.
Treatment may include:
* avoiding factors that bring on symptoms,
* increasing dietary salt and water,
* small and frequent meals,
* avoidance of immobilization,
* wearing compression stockings, and
* medication. Medications used may include:
** beta blockers,
** pyridostigmine,
** midodrine, or
** fludrocortisone.
More than 50% of patients whose condition was triggered by a viral infection get better within five years. About 80% of patients have symptomatic improvement with treatment, while 25% are so disabled they are unable to work. A retrospective study on patients with adolescent-onset has shown that five years after diagnosis, 19% of patients had full resolution of symptoms.
It is estimated that 1–3 million people in the United States have POTS. The average age for POTS onset is 20, and it occurs about five times more frequently in females than in males.
Signs and symptoms
 POTS is a complex and multifaceted clinical disorder, the etiology and management of which remain incompletely understood. This syndrome is typified by a diverse array of nonspecific symptoms, making it a challenging condition to describe.
Individuals living with POTS experience a diminished quality of life compared to healthy individuals, due to disruptions in various domains such as standing, playing sports, symptom anxiety, and impacts on school, work, or spiritual (religious) domains—these disruptions affect their daily life and overall well-being.
In adults, the primary manifestation is an increase in heart rate of more than 30 beats per minute within ten minutes of standing up. The resulting heart rate is typically more than 120 beats per minute. For people between ages 12 and 19, the minimum increase for a POTS diagnosis is 40 beats per minute. POTS is often accompanied by common features of orthostatic intolerance—in which symptoms that develop while upright are relieved by reclining. These orthostatic symptoms include
POTS is a complex and multifaceted clinical disorder, the etiology and management of which remain incompletely understood. This syndrome is typified by a diverse array of nonspecific symptoms, making it a challenging condition to describe.
Individuals living with POTS experience a diminished quality of life compared to healthy individuals, due to disruptions in various domains such as standing, playing sports, symptom anxiety, and impacts on school, work, or spiritual (religious) domains—these disruptions affect their daily life and overall well-being.
In adults, the primary manifestation is an increase in heart rate of more than 30 beats per minute within ten minutes of standing up. The resulting heart rate is typically more than 120 beats per minute. For people between ages 12 and 19, the minimum increase for a POTS diagnosis is 40 beats per minute. POTS is often accompanied by common features of orthostatic intolerance—in which symptoms that develop while upright are relieved by reclining. These orthostatic symptoms include palpitations
Palpitations occur when a person becomes aware of their heartbeat. The heartbeat may feel hard, fast, or uneven in their chest.
Symptoms include a very fast or irregular heartbeat. Palpitations are a sensory symptom. They are often described as ...
, light-headedness, chest discomfort, shortness of breath
Shortness of breath (SOB), known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that con ...
, nausea, weakness or "heaviness" in the lower legs, blurred vision, and cognitive difficulties. Symptoms may be exacerbated with prolonged sitting, prolonged standing, alcohol, heat, exercise, or eating a large meal.
POTS and dysautonomia often presents with narrowed pulse pressures. In some cases, patients experience a drop in pulse pressure to 0 mm Hg upon standing, rendering them practically pulseless while upright. This condition leads to significant morbidity, as many affected individuals struggle to remain standing.
Up to one-third of POTS patients experience fainting for many reasons, including but not limited to standing, physical exertion, or heat exposure. POTS patients may also experience orthostatic headaches. Some POTS patients may develop blood pooling in the extremities, characterized by a reddish-purple color of the legs and/or hands upon standing. 48% of people with POTS report chronic fatigue
Fatigue is a state of tiredness (which is not sleepiness), exhaustion or loss of energy. It is a signs and symptoms, symptom of any of various diseases; it is not a disease in itself.
Fatigue (in the medical sense) is sometimes associated wit ...
and 32% report sleep disturbances. Other POTS patients only exhibit the cardinal symptom of orthostatic tachycardia. Additional signs and symptoms are varied, and may include excessive sweating, lack of sweating, heat intolerance, digestive issues such as nausea, indigestion, bloating, constipation or diarrhea, post-exertional malaise
Post-exertional malaise (PEM), sometimes referred to as post-exertional symptom exacerbation (PESE) or post-exertional neuroimmune exhaustion (PENE), is a worsening of symptoms that occurs after minimal exertion. It is the hallmark symptom of m ...
, coat-hanger pain, brain fog, and syncope or presyncope.
Whereas POTS is primarily characterized by its profound impact on the autonomic and cardiovascular systems, it can lead to substantial functional impairment. This impairment, often manifesting as symptoms such as fatigue, cognitive dysfunction, and sleep disturbances, can significantly diminish the patient's quality of life.
Brain fog
One of the most disabling and prevalent symptoms in POTS is "brain fog
Clouding of consciousness, also called brain fog or mental fog, occurs when a person is conscious but slightly less wakeful or aware than normal. They are less aware of time and their surroundings, and find it difficult to pay attention. Peopl ...
", a term used by patients to describe the cognitive difficulties they experience. In one survey of 138 POTS patients, brain fog was defined as "forgetful" (91%), "difficulty thinking" (89%), and "difficulty focusing" (88%). Other common descriptions were "difficulty processing what others say" (80%), "confusion
In psychology, confusion is the quality or emotional state of being bewildered or unclear. The term "acute mental confusion"
" (71%), "getting lost" (64%), and "thoughts moving too quickly" (40%). The same survey described the most common triggers of brain fog to be fatigue (91%), lack of sleep (90%), prolonged standing (87%), and dehydration
In physiology, dehydration is a lack of total body water that disrupts metabolic processes. It occurs when free water loss exceeds intake, often resulting from excessive sweating, health conditions, or inadequate consumption of water. Mild deh ...
(86%).
Neuropsychological testing has shown that a POTS patient has reduced attention
Attention or focus, is the concentration of awareness on some phenomenon to the exclusion of other stimuli. It is the selective concentration on discrete information, either subjectively or objectively. William James (1890) wrote that "Atte ...
(Ruff 2&7 speed and WAIS-III digits forward), short-term memory
Short-term memory (or "primary" or "active memory") is the capacity for holding a small amount of information in an active, readily available state for a short interval. For example, short-term memory holds a phone number that has just been recit ...
( WAIS-III digits back), cognitive processing speed ( symbol digits modalities test), and executive function
In cognitive science and neuropsychology, executive functions (collectively referred to as executive function and cognitive control) are a set of cognitive processes that support goal-directed behavior, by regulating thoughts and actions thro ...
( Stroop word color and trails B).
A potential cause for brain fog is a decrease in cerebral blood flow
Cerebral circulation is the movement of blood through a network of cerebral arteries and veins supplying the brain. The rate of cerebral blood flow in an adult human is typically 750 milliliters per minute, or about 15% of cardiac output. ...
(CBF), especially in upright position.
There may be a loss of neurovascular coupling and reduced functional hyperemia in response to cognitive challenge under orthostatic stress – perhaps related to a loss of autoregulatory buffering of beat-by-beat fluctuations in arterial blood flow.
Comorbidities
Conditions that are commonly reported with POTS include: * Migraine headaches (40%) * Ehlers–Danlos syndrome (18–25%) *Asthma
Asthma is a common long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wh ...
(20%)
* Autoimmune disease (16%)
* Vasovagal syncope (13%)
* Mast cell activation disorder (9%)
Causes
The pathophysiology of POTS is not attributable to a single cause or unified hypothesis—it is the result of multiple interacting mechanisms, each contributing to the overall clinical presentation; the mechanisms may include autonomic dysfunction, hypovolemia, deconditioning, hyperadrenergic states, etc. The symptoms of POTS can be caused by several distinct pathophysiological mechanisms. These mechanisms are poorly understood, and can overlap, with many patients showing features of multiple POTS types. Many people with POTS exhibit low blood volume (hypovolemia
Hypovolemia, also known as volume depletion or volume contraction, is a state of abnormally low extracellular fluid in the body. This may be due to either a loss of both salt and water or a decrease in blood volume. Hypovolemia refers to the loss ...
), which can decrease the rate of blood flow to the heart. To compensate for low blood volume, the heart increases its cardiac output by beating faster ( reflex tachycardia), leading to the symptoms of presyncope.
In the 30% to 60% of cases classified as ''hyperadrenergic POTS'', norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic compound, organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and human body, body as a hormone, neurotransmitter and neuromodulator. The ...
levels are elevated on standing, often due to hypovolemia or partial autonomic neuropathy. A smaller minority of people with POTS have (typically very high) standing norepinephrine levels that are elevated even in the absence of hypovolemia and autonomic neuropathy; this is classified as ''central hyperadrenergic POTS''. The high norepinephrine levels contribute to symptoms of tachycardia. Another subtype, ''neuropathic POTS'', is associated with denervation of sympathetic nerves in the lower limbs. In this subtype, it is thought that impaired constriction of the blood vessels causes blood to pool in the veins of the lower limbs. Heart rate increases to compensate for this blood pooling.
A subset of POTS patients have markedly reduced myocardial MIBG reuptake via MIBG myocardial scintigraphy, interpreted to be a potential manifestation of autonomic cardiac neuropathy, although reduced expression of the norepinephrine transporter may also result in impaired MIBG reuptake and has been implicated in POTS.
In up to 50% of cases, there was an onset of symptoms following a viral illness. It may also be linked to physical trauma, concussion, pregnancy, surgery or psychosocial stress. It is believed that these events could act as a trigger for an autoimmune response that result in POTS. It has been shown to emerge in previously healthy patients after COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. In January 2020, the disease spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic.
The symptoms of COVID‑19 can vary but often include fever ...
, or after COVID-19 vaccination. A 2023 review found that the chances of being diagnosed with POTS within 90 days after mRNA vaccination were 1.33 times higher compared to 90 days before vaccination, still, the results are inconclusive due to a small sample size; only 12 cases of newly diagnosed POTS after mRNA vaccination were reported, all these 12 patients having autoimmune antibodies. However, the risk of POTS-related diagnoses was 5.35 times higher after getting infected with SARS-CoV-2
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is a strain of coronavirus that causes COVID-19, the respiratory illness responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. The virus previously had the Novel coronavirus, provisional nam ...
compared to after mRNA vaccination. Possible mechanisms for COVID-induced POTS are hypovolemia, autoimmunity/inflammation from antibody production against autonomic nerve fibers, and direct toxic effects of COVID-19, or secondary sympathetic nervous system stimulation.
POTS is more common in female
An organism's sex is female ( symbol: ♀) if it produces the ovum (egg cell), the type of gamete (sex cell) that fuses with the male gamete (sperm cell) during sexual reproduction.
A female has larger gametes than a male. Females and ...
s than male
Male (Planet symbols, symbol: ♂) is the sex of an organism that produces the gamete (sex cell) known as sperm, which fuses with the larger female gamete, or Egg cell, ovum, in the process of fertilisation. A male organism cannot sexual repro ...
s. POTS also has been linked to patients with a history of autoimmune diseases, long Covid
Long may refer to:
Measurement
* Long, characteristic of something of great duration
* Long, characteristic of something of great length
* Longitude (abbreviation: long.), a geographic coordinate
* Longa (music), note value in early music mens ...
, irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a functional gastrointestinal disorder characterized by a group of symptoms that commonly include abdominal pain, abdominal bloating, and changes in the consistency of bowel movements. These symptoms may ...
, anemia
Anemia (also spelt anaemia in British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen. This can be due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin availabl ...
, hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is a endocrine disease in which the thyroid gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones. Thyrotoxicosis is a condition that occurs due to elevated levels of thyroid hormones of any cause and therefore includes hyperth ...
, fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia (FM) is a functional somatic syndrome with symptoms of widespread chronic pain, accompanied by fatigue, sleep disturbance including awakening unrefreshed, and Cognitive deficit, cognitive symptoms. Other symptoms can include he ...
, diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of th ...
, amyloidosis, sarcoidosis, systemic lupus erythematosus
Lupus, formally called systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body. Symptoms vary among people and may be mild to severe. Common ...
, and cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
. Genetics likely plays a role, with one study finding that one in eight POTS patients reported a history of orthostatic intolerance in their family.
Physical deconditioning may be a factor involved in POTS. Strong parallels have been found between POTS and strong physical deconditioning or people who have undergone prolonged periods of bed rest. Both POTS and deconditioning are marked by cardiac atrophy, reduced blood volume, and other physical changes. There are also similarities between POTS and deconditioning in response to exercise
Exercise or workout is physical activity that enhances or maintains fitness and overall health. It is performed for various reasons, including weight loss or maintenance, to aid growth and improve strength, develop muscles and the cardio ...
.
There are however distinct differences between classic cardiovascular deconditioning and POTS in most cases
There appears to be some overlap between POTS and certain other conditions like chronic fatigue syndrome
Myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) is a disabling Chronic condition, chronic illness. People with ME/CFS experience profound fatigue that does not go away with rest, as well as sleep issues and problems with memory ...
and fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia (FM) is a functional somatic syndrome with symptoms of widespread chronic pain, accompanied by fatigue, sleep disturbance including awakening unrefreshed, and Cognitive deficit, cognitive symptoms. Other symptoms can include he ...
.
Autoimmunity
There is an increasing number of studies indicating that POTS is an autoimmune disease. A high number of patients has elevated levels of autoantibodies against the α1-adrenergic receptor and against the muscarinic acetylcholine M4 receptor. Elevations of autoantibodies targeting the α1-adrenergic receptor has been associated with symptoms severity in patients with POTS. More recently, autoantibodies against other targets have been identified in small cohorts of POTS patients. Signs of innate immune system activation with elaboration of pro-inflammatory cytokines has also been reported in a cohort of POTS patients. Studies suggest the involvement of adrenergic, cholinergic, and angiotensin II type I autoantibodies in the pathogenesis of orthostatic intolerance, so that these autoantibodies are thought to interfere with the normal functioning of the autonomic nervous system, leading to the symptoms observed in POTS; as such, there is growing interest in the use of immunomodulation therapy as a potential treatment strategy for POTS: immunomodulation therapy aims to regulate or normalize the immune response, thereby reducing the production of harmful autoantibodies.Secondary POTS
If POTS is caused by another condition, it may be classified as ''secondary POTS''. Chronicdiabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained hyperglycemia, high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or th ...
is one common cause. POTS can also be secondary to gastrointestinal disorders that are associated with low fluid intake due to nausea or fluid loss through diarrhea, leading to hypovolemia. Systemic lupus erythematosus and other autoimmune diseases have also been linked to POTS.
There is a subset of patients who present with both POTS and mast cell activation syndrome (MCAS), and it is not yet clear whether MCAS is a secondary cause of POTS or simply comorbid, however, treating MCAS for these patients can significantly improve POTS symptoms.
POTS can also co-occur in all types of Ehlers–Danlos syndrome (EDS), a hereditary connective tissue disorder marked by loose hypermobile joints prone to subluxations and dislocations, skin that exhibits moderate or greater laxity, easy bruising, and many other symptoms. A trifecta of POTS, EDS, and mast cell activation syndrome (MCAS) is becoming increasingly more common, with a genetic marker common among all three conditions. POTS is also often accompanied by vasovagal syncope, with a 25% overlap being reported. There are some overlaps between POTS and myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS), with evidence of POTS in 10–20% of ME/CFS cases. Fatigue and reduced exercise tolerance are prominent symptoms of both conditions, and dysautonomia may underlie both conditions.
POTS can sometimes be a paraneoplastic syndrome associated with cancer.
There have also been reports of patients experiencing co-occurring POTS, May-Thurner Syndrome, and EDS.
There are case reports of people developing POTS and other forms of dysautonomia post-COVID. There is no good large-scale empirical evidence yet to prove a connection, so for now the evidence is preliminary.
Diagnosis
 POTS is a complex disorder with a multifactorial etiology, and the diagnostics of POTS is challenging.
POTS is most commonly diagnosed by a cardiologist (41%), cardiac electrophysiologist (15%), or neurologist (19%). The average number of physicians seen before receiving diagnosis is seven, and the average delay before diagnosis is 4.7 years.
POTS is a complex disorder with a multifactorial etiology, and the diagnostics of POTS is challenging.
POTS is most commonly diagnosed by a cardiologist (41%), cardiac electrophysiologist (15%), or neurologist (19%). The average number of physicians seen before receiving diagnosis is seven, and the average delay before diagnosis is 4.7 years.
Diagnostic criteria
A POTS diagnosis requires the following characteristics: * For patients age 20 or older, a sustained increase in heart rate ≥30 bpm within ten minutes of upright posture ( tilt table test or standing) from a supine position. ** For patients age 12–19, heart rate increase must be >40 bpm. * Associated with frequent symptoms of lightheadedness, palpitations, tremulousness, generalized weakness, blurred vision, or fatigue that are worse with upright posture and that improve with recumbence. * An absence of orthostatic hypotension (i.e., no sustained systolic blood pressure drop of 20 mmHg or more). * Chronic symptoms that have lasted for longer than three months. * In the absence of other disorders, medications, or functional states that are known to predispose to orthostatic tachycardia. Alternative tests to the tilt table test are also used, such as the NASA Lean Test and the adapted Autonomic Profile (aAP) which require less equipment to complete. Nonpostural testing, such as the Valsalva maneuver, which may minimize the triggering of POTS symptoms, can be used prior to or in conjunction with the aforementioned techniques as a potential indicator of orthostatic intolerance, including POTS.Orthostatic intolerance
An increase in heart rate upon moving to an upright posture is known as orthostatic (upright)tachycardia
Tachycardia, also called tachyarrhythmia, is a heart rate that exceeds the normal resting rate. In general, a resting heart rate over 100 beats per minute is accepted as tachycardia in adults. Heart rates above the resting rate may be normal ...
(fast heart rate). It occurs without any coinciding drop in blood pressure, as that would indicate orthostatic hypotension. Certain medications to treat POTS may cause orthostatic hypotension. It is accompanied by other features of orthostatic intolerance—symptoms that develop in an upright position and are relieved by reclining. These orthostatic symptoms include palpitations
Palpitations occur when a person becomes aware of their heartbeat. The heartbeat may feel hard, fast, or uneven in their chest.
Symptoms include a very fast or irregular heartbeat. Palpitations are a sensory symptom. They are often described as ...
, light-headedness, chest discomfort, shortness of breath
Shortness of breath (SOB), known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that con ...
, nausea, weakness or "heaviness" in the lower legs, blurred vision, and cognitive difficulties.
Differential diagnoses
A variety of autonomic tests are employed to exclude autonomic disorders that could underlie symptoms, whileendocrine
The endocrine system is a messenger system in an organism comprising feedback loops of hormones that are released by internal glands directly into the circulatory system and that target and regulate distant organs. In vertebrates, the hypotha ...
testing is used to exclude hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is a endocrine disease in which the thyroid gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones. Thyrotoxicosis is a condition that occurs due to elevated levels of thyroid hormones of any cause and therefore includes hyperth ...
and rarer endocrine conditions. Electrocardiography
Electrocardiography is the process of producing an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), a recording of the heart's electrical activity through repeated cardiac cycles.
It is an electrogram of the heart which is a graph of voltage versus time of t ...
is normally performed on all patients to exclude other possible causes of tachycardia. In cases where a particular associated condition or complicating factor are suspected, other non-autonomic tests may be used: echocardiography
Echocardiography, also known as cardiac ultrasound, is the use of ultrasound to examine the heart. It is a type of medical imaging, using standard ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound. The visual image formed using this technique is called an ec ...
to exclude mitral valve prolapse
Mitral valve prolapse (MVP) is a valvular heart disease characterized by the displacement of an abnormally thickened mitral valve leaflet into the atria of the heart, left atrium during Systole (medicine), systole. It is the primary form of myxom ...
, and thermal threshold tests for small-fiber neuropathy.
Testing the cardiovascular response to prolonged head-up tilting, exercise, eating, and heat stress may help determine the best strategy for managing symptoms. POTS has also been divided into several types (see § Causes), which may benefit from distinct treatments. People with neuropathic POTS show a loss of sweating in the feet during sweat tests, as well as impaired norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic compound, organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and human body, body as a hormone, neurotransmitter and neuromodulator. The ...
release in the leg, but not arm. This is believed to reflect peripheral sympathetic denervation in the lower limbs. People with hyperadrenergic POTS show a marked increase of blood pressure and norepinephrine levels when standing, and are more likely to have from prominent palpitations, anxiety, and tachycardia.
People with POTS can be misdiagnosed with inappropriate sinus tachycardia (IST) as they present similarly. One distinguishing feature is those with POTS rarely exhibit >100 bpm while in a supine position, while patients with IST often have a resting heart rate >100 bpm. Additionally patients with POTS display a more pronounced change in heart rate in response to postural change.
Treatment
Despite numerous therapeutic interventions proposed for the management of POTS, none have received approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) specifically for this indication, and no effective treatment strategies have been identified that would have been confirmed by large clinical trials. POTS treatment involves using multiple methods in combination to counteract cardiovascular dysfunction, address symptoms, and simultaneously address any associated disorders. For most patients, water intake should be increased, especially after waking, in order to expand blood volume (reducinghypovolemia
Hypovolemia, also known as volume depletion or volume contraction, is a state of abnormally low extracellular fluid in the body. This may be due to either a loss of both salt and water or a decrease in blood volume. Hypovolemia refers to the loss ...
). Eight to ten cups of water daily are recommended. Increasing salt
In common usage, salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl). When used in food, especially in granulated form, it is more formally called table salt. In the form of a natural crystalline mineral, salt is also known as r ...
intake, by adding salt to food, taking salt tablets, or drinking sports drinks and other electrolyte
An electrolyte is a substance that conducts electricity through the movement of ions, but not through the movement of electrons. This includes most soluble Salt (chemistry), salts, acids, and Base (chemistry), bases, dissolved in a polar solven ...
solutions is an effective way to raise blood pressure by helping the body retain water. Different physicians recommend different amounts of sodium to their patients. Combining these techniques with gradual physical training enhances their effect. In some cases, when increasing oral fluids and salt intake is not enough, intravenous saline or the drug desmopressin is used to help increase fluid retention.
Large meals worsen symptoms for some people. These people may benefit from eating small meals frequently throughout the day instead. Alcohol
Alcohol may refer to:
Common uses
* Alcohol (chemistry), a class of compounds
* Ethanol, one of several alcohols, commonly known as alcohol in everyday life
** Alcohol (drug), intoxicant found in alcoholic beverages
** Alcoholic beverage, an alco ...
and food high in carbohydrate
A carbohydrate () is a biomolecule composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms. The typical hydrogen-to-oxygen atomic ratio is 2:1, analogous to that of water, and is represented by the empirical formula (where ''m'' and ''n'' ...
s can also exacerbate symptoms of orthostatic hypotension. Excessive consumption of caffeine
Caffeine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant of the methylxanthine chemical classification, class and is the most commonly consumed Psychoactive drug, psychoactive substance globally. It is mainly used for its eugeroic (wakefulness pr ...
beverages should be avoided, because they can promote urine production (leading to fluid loss) and consequently hypovolemia. Exposure to extreme heat may also aggravate symptoms.
Prolonged physical inactivity can worsen the symptoms of POTS. POTS may be caused or exacerbated by deconditioning. Techniques that increase a person's capacity for exercise, such as endurance training or graded exercise therapy, can relieve symptoms for some patients. Exercise
Exercise or workout is physical activity that enhances or maintains fitness and overall health. It is performed for various reasons, including weight loss or maintenance, to aid growth and improve strength, develop muscles and the cardio ...
programs can be very effective and can lead to remission in many people with POTS. Aerobic exercise
Aerobic exercise, also known as cardio, is physical exercise of low to high intensity that depends primarily on the aerobic energy-generating process. "Aerobic" is defined as "relating to, involving, or requiring oxygen", and refers to the use of ...
performed for 20 minutes a day, three times a week, is sometimes recommended for patients who can tolerate it. Exercise may have the immediate effect of worsening tachycardia, especially after a meal or on a hot day. In these cases, it may be easier to exercise in a semi-reclined position, such as riding a recumbent bicycle
A recumbent bicycle is a bicycle that places the rider in a laid-back reclining position, and often called a Human-powered_land_vehicle, human-powered vehicle or HPV, especially if it has an aerodynamic fairing. Recumbents are available in a w ...
, rowing, or swimming
Swimming is the self-propulsion of a person through water, such as saltwater or freshwater environments, usually for recreation, sport, exercise, or survival. Swimmers achieve locomotion by coordinating limb and body movements to achieve hydrody ...
. Although exercise may be difficult initially, it becomes progressively easier as physical conditioning improves.
When changing to an upright posture, finishing a meal, or concluding exercise, a sustained hand grip can briefly raise the blood pressure, possibly reducing symptoms. Compression garments can also be of benefit by constricting blood pressures with external body pressure.
Aggravating factors include exertion (81%), continued standing (80%), heat (79%), and after meals (42%).
Medication
If non-pharmacological methods are ineffective,medication
Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal product, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to medical diagnosis, diagnose, cure, treat, or preventive medicine, prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmaco ...
may be necessary. Medications used may include beta blocker
Beta blockers, also spelled β-blockers, are a class of medications that are predominantly used to manage abnormal heart rhythms ( arrhythmia), and to protect the heart from a second heart attack after a first heart attack ( secondary prevention ...
s, pyridostigmine, midodrine, or fludrocortisone, among others. As of 2013, no medication has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respo ...
to treat POTS, but a variety are used off-label Off-label use is the use of pharmaceutical drugs for an unapproved indication (medicine), indication or in an unapproved age group, dose (biochemistry), dosage, or route of administration. Both prescription drugs and over-the-counter drugs (OTCs) ca ...
. Their efficacy has not yet been examined in long-term randomized controlled trial
A randomized controlled trial (or randomized control trial; RCT) is a form of scientific experiment used to control factors not under direct experimental control. Examples of RCTs are clinical trials that compare the effects of drugs, surgical ...
s.
Fludrocortisone, a mineralocorticoid
Mineralocorticoids are a class of corticosteroids, which in turn are a class of steroid hormones. Mineralocorticoids are produced in the adrenal cortex and influence salt and water balances (electrolyte balance and fluid balance). The primary ...
, may be used to enhance sodium retention and blood volume, which may be beneficial not only by augmenting sympathetically mediated vasoconstriction, but also because a large subset of POTS patients appear to have low absolute blood volume. However, fludrocortisone may cause hypokalemia (low potassium levels).
While people with POTS typically have normal or even elevated arterial blood pressure, the neuropathic form of POTS is presumed to constitute a selective sympathetic venous denervation. In these patients the selective α1-adrenergic receptor agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a Receptor (biochemistry), receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are Cell (biology), cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an R ...
midodrine may increase venous return, enhance stroke volume, and improve symptoms. Midodrine should only be taken during the daylight hours as it may promote supine hypertension.
Sinus node blocker ivabradine can successfully restrain heart rate in POTS without affecting blood pressure, demonstrated in approximately 60% of people with POTS treated in an open-label trial of ivabradine experienced symptom improvement.
Pyridostigmine, an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs) also often called cholinesterase inhibitors, inhibit the enzyme acetylcholinesterase from breaking down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine into choline and acetate, thereby increasing both the level an ...
and parasympathomimetic, has been reported to restrain heart rate and improve chronic symptoms in approximately half of people. However, it may cause GI side effects that limit its use in around 20% of its patient population.
The selective α1-adrenergic receptor agonist phenylephrine has been used successfully to enhance venous return and stroke volume in some people with POTS. However, this medication may be hampered by poor oral bioavailability. Indirectly acting sympathomimetics, like the norepinephrine releasing agents ephedrine
Ephedrine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant and sympathomimetic agent that is often used to prevent hypotension, low blood pressure during anesthesia. It has also been used for asthma, narcolepsy, and obesity but is not the preferred ...
and pseudoephedrine and the norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor
A norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI) is a type of drug that inhibits the reuptake of the monoamine neurotransmitters norepinephrine and dopamine and thereby increases extracellular levels of these neurotransmitters and nor ...
s methylphenidate
Methylphenidate, sold under the brand names Ritalin ( ) and Concerta ( ) among others, is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. It may be taken Oral adm ...
and bupropion, have also been used in the treatment of POTS. The norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic compound, organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and human body, body as a hormone, neurotransmitter and neuromodulator. The ...
prodrug droxidopa has been used as well.
Prognosis
POTS has a favorableprognosis
Prognosis ( Greek: πρόγνωσις "fore-knowing, foreseeing"; : prognoses) is a medical term for predicting the likelihood or expected development of a disease, including whether the signs and symptoms will improve or worsen (and how quickly) ...
when managed appropriately. Symptoms improve within five years of diagnosis for many patients, and 60% return to their original level of functioning. Approximately 90% of people with POTS respond to a combination of pharmacological and physical treatments. Those who develop POTS in their early to mid teens will likely respond well to a combination of physical methods as well as pharmacotherapy. Outcomes are more guarded for adults newly diagnosed with POTS. Some people do not recover, and a few even worsen with time. The hyperadrenergic type of POTS typically requires continuous therapy. If POTS is caused by another condition, outcomes depend on the prognosis of the underlying disorder.
Epidemiology
Theprevalence
In epidemiology, prevalence is the proportion of a particular population found to be affected by a medical condition (typically a disease or a risk factor such as smoking or seatbelt use) at a specific time. It is derived by comparing the number o ...
of POTS is unknown. One study estimated a minimal rate of 170 POTS cases per 100,000 individuals, but the true prevalence is likely higher due to underdiagnosis. Another study estimated that there are at least 500,000 cases in the United States. POTS is more common in women than men, with a female-to-male ratio of 4:1. Most people with POTS are aged between 20 and 40, with an average onset of 21. Diagnoses of POTS beyond age 40 are rare, perhaps because symptoms improve with age.
Research directions
A key area for further exploration of POTS management is the autonomic nervous system and its response to the orthostatic challenge. The autonomic nervous system plays a crucial role in maintaining cardiovascular homeostasis during changes in posture. A deeper understanding of its function and the alterations that occur in POTS could provide valuable insights into potential therapeutic targets and the mechanisms of POTS treatment.History
In 1871, physician Jacob Mendes Da Costa described a condition that resembled the modern concept of POTS. He named it ''irritable heart syndrome''. Cardiologist Thomas Lewis expanded on the description, coining the term ''soldier's heart'' because it was often found among military personnel. The condition came to be known as Da Costa's syndrome, which is now recognized as several distinct disorders, including POTS. ''Postural tachycardia syndrome'' was coined in 1982 in a description of a patient who had postural tachycardia, but not orthostatic hypotension. Ronald Schondorf and Phillip A. Low of theMayo Clinic
Mayo Clinic () is a Nonprofit organization, private American Academic health science centre, academic Medical centers in the United States, medical center focused on integrated health care, healthcare, Mayo Clinic College of Medicine and Science ...
first used the name ''postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome'', POTS, in 1993.
Notable cases
British politician Nicola Blackwood revealed in March 2015 that she had been diagnosed with Ehlers–Danlos syndrome in 2013 and that she had later been diagnosed with POTS. She was appointed Parliamentary Under-Secretary of State for Life Science by Prime MinisterTheresa May
Theresa Mary May, Baroness May of Maidenhead (; ; born 1 October 1956), is a British politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom and Leader of the Conservative Party from 2016 to 2019. She previously served as Home Secretar ...
in 2019 and given a life peerage
In the United Kingdom, life peers are appointed members of the peerage whose titles cannot be inherited, in contrast to hereditary peers. Life peers are appointed by the monarch on the advice of the prime minister. With the exception of the D ...
that enabled her to take a seat in Parliament. As a junior minister, it is her responsibility to answer questions in parliament on the subjects of Health and departmental business. When answering these questions, it is customary for ministers to sit when listening to the question and then to rise to give an answer from the despatch box
A despatch box (alternatively dispatch box) is one of several types of boxes used in government business. Despatch boxes primarily include both those sometimes known as Red box (government), red boxes or ministerial boxes, which are used by the ...
, thus standing up and sitting down numerous times in quick succession throughout a series of questions. On 17 June 2019, she fainted during one of these questioning sessions after standing up from a sitting position four times in the space of twelve minutes, Baroness Blackwood of North Oxford makes four speeches (thus standing up four times) between 5:52 PM and 6:04 PM. and it was suggested that her POTS was a factor in her fainting. Asked about the incident, she stated: "I was frustrated and embarrassed my body gave up on me at work ... But I am grateful it gives me a chance to shine a light on a condition many others are also living with."
In 2024, Taiwanese tennis player Latisha Chan revealed that she was diagnosed with POTS back in 2014 and has been receiving treatments before Summer Olympics as well. Her condition was considered career-threatening, but has had her career extended by over a decade due to external counterpulsation.
In her 2024 memoir ''Just Add Water'', Olympic gold medalist swimmer Katie Ledecky shared that she has a mild form of POTS.
References
Further reading
* * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome Vascular diseases Peripheral nervous system disorders Endocrine diseases Syndromes Ailments of unknown cause Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia neurology articles ready to translate de:Orthostatische Dysregulation#Posturales Tachykardiesyndrom (POTS)