Post-Secondary Learning Act on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Tertiary education (higher education, or post-secondary education) is the
Tertiary education (higher education, or post-secondary education) is the

 The oldest known institutions of higher education are credited to Dynastic Egypt, with Pr-Anx (houses of life) built as libraries and scriptoriums, containing works on law, architecture, mathematics, and medicine, and involved in the training of "swnw" and "swnwt" (male and female
The oldest known institutions of higher education are credited to Dynastic Egypt, with Pr-Anx (houses of life) built as libraries and scriptoriums, containing works on law, architecture, mathematics, and medicine, and involved in the training of "swnw" and "swnwt" (male and female
''A History of the University in Europe: Volume 1, Universities in the Middle Ages''
, Cambridge University Press, 1992, , pp. 47–55 and the first university in the sense of a higher-learning and degree-awarding institute, as the word ''universitas'' was coined at its foundation.
 The Higher education in the United States, higher education system in the United States is decentralized and regulated independently by each state with Higher education accreditation in the United States, accreditors playing a key role in ensuring institutions meet minimum standards. It is large and diverse with institutions that are privately governed and institutions that are owned and operated by state and local governments. Some private institutions are affiliated with religious organizations whereas others are secular with enrollment ranging from a few dozen to tens of thousands of students. The United States Department of Education presents a broad-spectrum view of tertiary education and detailed information on the nation's educational structure, accreditation procedures, and connections to state as well as federal agencies and entities.
The Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education provides one framework for classifying U.S. colleges and universities in several different ways. US tertiary education also includes various non-profit organizations promoting professional development of individuals in the field of higher education and helping expand awareness of related issues like international student services and complete campus internationalization.
The Higher education in the United States, higher education system in the United States is decentralized and regulated independently by each state with Higher education accreditation in the United States, accreditors playing a key role in ensuring institutions meet minimum standards. It is large and diverse with institutions that are privately governed and institutions that are owned and operated by state and local governments. Some private institutions are affiliated with religious organizations whereas others are secular with enrollment ranging from a few dozen to tens of thousands of students. The United States Department of Education presents a broad-spectrum view of tertiary education and detailed information on the nation's educational structure, accreditation procedures, and connections to state as well as federal agencies and entities.
The Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education provides one framework for classifying U.S. colleges and universities in several different ways. US tertiary education also includes various non-profit organizations promoting professional development of individuals in the field of higher education and helping expand awareness of related issues like international student services and complete campus internationalization.
 Italy has a large and international network of public or state-affiliated universities and schools offering degrees in higher education. State-run universities of Italy constitute the main percentage of tertiary education in Italy and are managed under the supervision of Italian's Ministry of Education.
Italian universities are among the oldest universities in the world; the University of Bologna (founded in 1088) notably, is List of oldest universities in continuous operation, the oldest one ever; also, University of Naples Federico II is the world's oldest state-funded university in continuous operation. Most universities in Italy are state-supported. 33 Italian universities were ranked among the world's top 500 in 2019, the third-largest number in Europe after the United Kingdom and Germany.
There are also a number of Superior Graduate Schools in Italy, Superior Graduate Schools (''Grandes écoles'') or ''Scuola Superiore Universitaria'', which offer officially recognized titles, including the ''Diploma di Perfezionamento'' equivalent to a Doctorate, Dottorato di ricerca, ''Dottorato di Ricerca'' i.e. Doctorate, Research Doctorate or ''Doctor Philosophiae'' i.e. PhD. Some of them also organize master's degree courses. There are three Superior Graduate Schools with "university status", three institutes with the status of Doctoral Colleges, which function at Graduate school, graduate and post-graduate level. Nine further schools are direct offshoots of the universities (i.e. do not have their own 'university status'). The first one is the Scuola Normale Superiore di Pisa (founded in 1810 by Napoleon as a branch of École Normale Supérieure), taking the model of organization from the famous École Normale Supérieure. These institutions are commonly referred to as "Schools of Excellence" (i.e. "Scuole di Eccellenza").
Italy hosts a broad variety of universities, colleges and academies. Founded in 1088, the University of Bologna is likely List of oldest universities in continuous operation, the oldest in the world. In 2009, the University of Bologna is, according to Times Higher Education-QS World University Rankings, The Times, the only Italian college in the top 200 World Universities. Milan's Bocconi University has been ranked among the top 20 best business schools in the world by The Wall Street Journal international rankings, especially thanks to its M.B.A. program, which in 2007 placed it no. 17 in the world in terms of graduate recruitment preference by major multinational companies. Bocconi was also ranked by Forbes as the best worldwide in the specific category Value for Money. In May 2008, Bocconi overtook several traditionally top global business schools in the Financial Times Executive education ranking, reaching no. 5 in Europe and no. 15 in the world.
Other top universities and polytechnics are the Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore in Milan, the LUISS in Rome, the Polytechnic University of Turin, the Politecnico di Milano (which in 2011 was ranked as the 48th best technical university in the world by QS World University Rankings), the Sapienza University of Rome, University of Rome La Sapienza (which in 2005 was Europe's 33rd best university, and ranks among Europe's 50 and the world's 150 best colleges and in 2013, the Center for World University Rankings ranked the Sapienza University of Rome 62nd in the world and the top in Italy in its ''World University Rankings''.) and the University of Milan (whose research and teaching activities have developed over the years and have received important international recognition). This university is the only Italian member of the League of European Research Universities (LERU), a prestigious group of twenty research-intensive European Universities. It has also been awarded ranking positions such as 1st in Italy and 7th in Europe (The CWTS Leiden Ranking, Leiden Ranking – Universiteit Leiden).
Italy has a large and international network of public or state-affiliated universities and schools offering degrees in higher education. State-run universities of Italy constitute the main percentage of tertiary education in Italy and are managed under the supervision of Italian's Ministry of Education.
Italian universities are among the oldest universities in the world; the University of Bologna (founded in 1088) notably, is List of oldest universities in continuous operation, the oldest one ever; also, University of Naples Federico II is the world's oldest state-funded university in continuous operation. Most universities in Italy are state-supported. 33 Italian universities were ranked among the world's top 500 in 2019, the third-largest number in Europe after the United Kingdom and Germany.
There are also a number of Superior Graduate Schools in Italy, Superior Graduate Schools (''Grandes écoles'') or ''Scuola Superiore Universitaria'', which offer officially recognized titles, including the ''Diploma di Perfezionamento'' equivalent to a Doctorate, Dottorato di ricerca, ''Dottorato di Ricerca'' i.e. Doctorate, Research Doctorate or ''Doctor Philosophiae'' i.e. PhD. Some of them also organize master's degree courses. There are three Superior Graduate Schools with "university status", three institutes with the status of Doctoral Colleges, which function at Graduate school, graduate and post-graduate level. Nine further schools are direct offshoots of the universities (i.e. do not have their own 'university status'). The first one is the Scuola Normale Superiore di Pisa (founded in 1810 by Napoleon as a branch of École Normale Supérieure), taking the model of organization from the famous École Normale Supérieure. These institutions are commonly referred to as "Schools of Excellence" (i.e. "Scuole di Eccellenza").
Italy hosts a broad variety of universities, colleges and academies. Founded in 1088, the University of Bologna is likely List of oldest universities in continuous operation, the oldest in the world. In 2009, the University of Bologna is, according to Times Higher Education-QS World University Rankings, The Times, the only Italian college in the top 200 World Universities. Milan's Bocconi University has been ranked among the top 20 best business schools in the world by The Wall Street Journal international rankings, especially thanks to its M.B.A. program, which in 2007 placed it no. 17 in the world in terms of graduate recruitment preference by major multinational companies. Bocconi was also ranked by Forbes as the best worldwide in the specific category Value for Money. In May 2008, Bocconi overtook several traditionally top global business schools in the Financial Times Executive education ranking, reaching no. 5 in Europe and no. 15 in the world.
Other top universities and polytechnics are the Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore in Milan, the LUISS in Rome, the Polytechnic University of Turin, the Politecnico di Milano (which in 2011 was ranked as the 48th best technical university in the world by QS World University Rankings), the Sapienza University of Rome, University of Rome La Sapienza (which in 2005 was Europe's 33rd best university, and ranks among Europe's 50 and the world's 150 best colleges and in 2013, the Center for World University Rankings ranked the Sapienza University of Rome 62nd in the world and the top in Italy in its ''World University Rankings''.) and the University of Milan (whose research and teaching activities have developed over the years and have received important international recognition). This university is the only Italian member of the League of European Research Universities (LERU), a prestigious group of twenty research-intensive European Universities. It has also been awarded ranking positions such as 1st in Italy and 7th in Europe (The CWTS Leiden Ranking, Leiden Ranking – Universiteit Leiden).
 In Nigeria, ''tertiary education'' refers to post-secondary education received at universities (government or privately funded), monotechnics, polytechnics and colleges of education. After completing a secondary education, students may enroll in a tertiary institution or acquire a Vocational school, vocational education. Students are required to sit for the Joint Admissions and Matriculation Board Entrance Examination (JAMB) as well as the West African Senior School Certificate Examination, Secondary School Certificate Examination (SSCE) or General Certificate Examination (GCE) and meet varying cut-off marks to gain admission into a tertiary institution.
In Nigeria, ''tertiary education'' refers to post-secondary education received at universities (government or privately funded), monotechnics, polytechnics and colleges of education. After completing a secondary education, students may enroll in a tertiary institution or acquire a Vocational school, vocational education. Students are required to sit for the Joint Admissions and Matriculation Board Entrance Examination (JAMB) as well as the West African Senior School Certificate Examination, Secondary School Certificate Examination (SSCE) or General Certificate Examination (GCE) and meet varying cut-off marks to gain admission into a tertiary institution.
Council of Europe Higher Education Series
Tertiary education statistics
, UNESCO
Association for the Study of Higher EducationAmerican Educational Research AssociationWorld Bank Tertiary Education
{{DEFAULTSORT:Tertiary Education Tertiary education, Educational stages id:Pendidikan tinggi
 Tertiary education (higher education, or post-secondary education) is the
Tertiary education (higher education, or post-secondary education) is the education
Education is the transmission of knowledge and skills and the development of character traits. Formal education occurs within a structured institutional framework, such as public schools, following a curriculum. Non-formal education als ...
al level following the completion of secondary education
Secondary education is the education level following primary education and preceding tertiary education.
Level 2 or ''lower secondary education'' (less commonly ''junior secondary education'') is considered the second and final phase of basic e ...
.
The World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and Grant (money), grants to the governments of Least developed countries, low- and Developing country, middle-income countries for the purposes of economic development ...
defines tertiary education as including universities
A university () is an educational institution, institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several Discipline (academia), academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly ...
, colleges
A college (Latin: ''collegium'') may be a tertiary education, tertiary educational institution (sometimes awarding academic degree, degrees), part of a collegiate university, an institution offering vocational education, a further educatio ...
, and vocational schools
A vocational school (alternatively known as a trade school, or technical school), is a type of educational institution, which, depending on the country, may refer to either secondary or post-secondary education designed to provide vocational ...
. ''Higher education'' is taken to include undergraduate
Undergraduate education is education conducted after secondary education and before postgraduate education, usually in a college or university. It typically includes all postsecondary programs up to the level of a bachelor's degree. For example, ...
and postgraduate education
Postgraduate education, graduate education, or graduate school consists of Academic degree, academic or professional degrees, certificates, diplomas, or other qualifications usually pursued by higher education, post-secondary students who have ...
, while vocational education
Vocational education is education that prepares people for a skilled craft. Vocational education can also be seen as that type of education given to an individual to prepare that individual to be gainfully employed or self employed with req ...
beyond secondary education is known as ''further education
Further education (often abbreviated FE) in the United Kingdom and Ireland is additional education to that received at secondary school that is distinct from the higher education (HE) offered in universities and other academic institutions. It ...
'' in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, or included under the category of ''continuing education
Continuing education is the education undertaken after initial education for either personal or professional reasons. The term is used mainly in the United States and Canada.
Recognized forms of post-secondary learning activities within the d ...
'' in the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
.
Tertiary education generally culminates in the receipt of certificate
Certificate may refer to:
* Birth certificate
* Marriage certificate
* Death certificate
* Gift certificate
* Certificate of authenticity, a document or seal certifying the authenticity of something
* Certificate of deposit, or CD, a financial p ...
s, diploma
A diploma is a document awarded by an educational institution (such as a college or university) testifying the recipient has graduated by successfully completing their courses of studies. Historically, it has also referred to a charter or offi ...
s, or academic degree
An academic degree is a qualification awarded to a student upon successful completion of a course of study in higher education, usually at a college or university. These institutions often offer degrees at various levels, usually divided into und ...
s. Higher education represents levels 5, 6, 7, and 8 of the 2011 version of the International Standard Classification of Education
The International Standard Classification of Education (ISCED) is a statistical framework for organizing information on education maintained by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). It is a member of the int ...
structure. Tertiary education at a nondegree level is sometimes referred to as further education
Further education (often abbreviated FE) in the United Kingdom and Ireland is additional education to that received at secondary school that is distinct from the higher education (HE) offered in universities and other academic institutions. It ...
or continuing education
Continuing education is the education undertaken after initial education for either personal or professional reasons. The term is used mainly in the United States and Canada.
Recognized forms of post-secondary learning activities within the d ...
as distinct from higher education.
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
stated that tertiary education focuses on learning endeavors in specialized fields. It includes academic and higher vocational education.
The World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and Grant (money), grants to the governments of Least developed countries, low- and Developing country, middle-income countries for the purposes of economic development ...
's 2019 World Development Report
The World Development Report (WDR) is an annual report published since 1978 by the World Bank. Each WDR provides in-depth analysis of a specific aspect of economic development. Past reports have considered such topics as agriculture, youth, equity ...
on the future of work argues that given the future of work and the increasing role of technology in value chains, tertiary education is becoming even more relevant for workers to compete in the labor market.
Definition
Higher education, also called post-secondary education, third-level or tertiary education, is an optional final stage offormal learning
Education is the transmission of knowledge and skills and the development of character traits. Formal education occurs within a structured institutional framework, such as public schools, following a curriculum. Non-formal education also fol ...
that occurs after completion of secondary education
Secondary education is the education level following primary education and preceding tertiary education.
Level 2 or ''lower secondary education'' (less commonly ''junior secondary education'') is considered the second and final phase of basic e ...
. This consists of universities
A university () is an educational institution, institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several Discipline (academia), academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly ...
, colleges
A college (Latin: ''collegium'') may be a tertiary education, tertiary educational institution (sometimes awarding academic degree, degrees), part of a collegiate university, an institution offering vocational education, a further educatio ...
and polytechnics that offer formal degrees beyond high school or secondary school education.
The International Standard Classification of Education
The International Standard Classification of Education (ISCED) is a statistical framework for organizing information on education maintained by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). It is a member of the int ...
in 1997 initially classified all tertiary education together in the 1997 version of its schema. They were referred to as level 5 and doctoral studies at level 6. In 2011, this was refined and expanded in the 2011 version of the structure. Higher education at undergraduate level, masters and doctoral level became levels 6, 7, and 8. Nondegree level tertiary education, sometimes referred to as further education
Further education (often abbreviated FE) in the United Kingdom and Ireland is additional education to that received at secondary school that is distinct from the higher education (HE) offered in universities and other academic institutions. It ...
or continuing education
Continuing education is the education undertaken after initial education for either personal or professional reasons. The term is used mainly in the United States and Canada.
Recognized forms of post-secondary learning activities within the d ...
was reordered as level 4, with level 5 for some higher courses.
In the days when few pupils progressed beyond primary education
Primary education is the first stage of Education, formal education, coming after preschool/kindergarten and before secondary education. Primary education takes place in ''primary schools'', ''elementary schools'', or first schools and middle s ...
or basic education
According to the International Standard Classification of Education (ISCED), basic education comprises the two stages primary education and secondary education, lower secondary education.
Universal basic education
Basic education featured heavi ...
, the term "higher education" was often used to refer to secondary education, which can create some confusion. This is the origin of the term ''high school
A secondary school, high school, or senior school, is an institution that provides secondary education. Some secondary schools provide both ''lower secondary education'' (ages 11 to 14) and ''upper secondary education'' (ages 14 to 18), i.e., ...
'' for various schools for children between the ages of 14 and 18 (United States) or 11 and 18 (United Kingdom and Australia).
Enrollment
Globally, the gross enrollment ratio in tertiaryeducation
Education is the transmission of knowledge and skills and the development of character traits. Formal education occurs within a structured institutional framework, such as public schools, following a curriculum. Non-formal education als ...
increased from 19% in 2000 to 38% in 2017, with the female
An organism's sex is female ( symbol: ♀) if it produces the ovum (egg cell), the type of gamete (sex cell) that fuses with the male gamete (sperm cell) during sexual reproduction.
A female has larger gametes than a male. Females and ...
enrollment ratio exceeding the male ratio by 4 percentage points.
The tertiary gross enrollment ratio ranges from 9% in low-income countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a less-developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to developed countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreemen ...
to 77% in high-income countries
A high-income economy is defined by the World Bank as a country with a gross national income per capita of US$14,005 or more in 2023, calculated using the Atlas method. While the term "high-income" is often used interchangeably with "First World" ...
, where, after rapid growth in the 2000s, reached a plateau in the 2010s.
Between now and 2030, the biggest increase in tertiary enrollment ratios is expected in middle-income countries, where it will reach 52%. Sustainable Development Goal 4
Sustainable Development Goal 4, or SDG 4, is a commitment to ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all. This goal aims to provide children and young people with quality and easy access t ...
(SDG 4) commits countries to providing lifelong learning
Lifelong learning is the "ongoing, voluntary, and self-motivated" pursuit of learning for either personal or professional reasons.
Lifelong learning is important for an individual's competitiveness and employability, but also enhances social in ...
opportunities for all, including tertiary education.
This commitment is monitored through the global indicator for target 4.3 in the sustainable development goal 4 (SDG 4), which measures the participation rate of youth
Youth is the time of life when one is young. The word, youth, can also mean the time between childhood and adulthood (Maturity (psychological), maturity), but it can also refer to one's peak, in terms of health or the period of life known as bei ...
and adult
An adult is an animal that has reached full growth. The biological definition of the word means an animal reaching sexual maturity and thus capable of reproduction. In the human context, the term ''adult'' has meanings associated with social an ...
s in formal and non-formal education and training in the previous 12 months, whether for work or non-work purposes.
The right of access to higher education is mentioned in a number of international human rights instruments
International human rights instruments are the treaties and other international texts that serve as legal sources for international human rights law and the protection of human rights in general. There are many varying types, but most can be cla ...
. The UN International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights
The International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (ICESCR) is a multilateral treaty adopted by the United Nations General Assembly (GA) on 16 December 1966 through GA. Resolution 2200A (XXI), and came into force on 3 January 197 ...
of 1966 declares, in Article 13, that "higher education shall be made equally accessible to all, on the basis of capacity, by every appropriate means, and in particular by the progressive introduction of free education". In Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
, Article 2 of the First Protocol to the European Convention on Human Rights, adopted in 1950, obliges all signatory parties to guarantee the right to education
The right to education has been recognized as a human rights, human right in a number of international conventions, including the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights which recognizes a right to free education, free, pr ...
.
University completion rates for students with disabilities are much lower compared to completion rates of students without disabilities.
Grade and educational inflation
Some tertiary schools have been criticized as having permitted or actively encouragedgrade inflation
Grade inflation (also known as grading leniency) is the general awarding of higher grades for the same quality of work over time, which devalues grades. However, higher average grades in themselves do not prove grade inflation. For this to be grad ...
. In addition, certain scholars contend that the supply of graduates in some fields of study is exceeding the demand for their skills, aggravating graduate unemployment
Graduate unemployment, or educated unemployment, is unemployment among people with an academic degree.
Aggravating factors for unemployment are the rapidly increasing quantity of international graduates competing for an inadequate number of suit ...
, underemployment
Underemployment is the underuse of a worker because their job does not use their skills, offers them too few hours, or leaves the worker idle. It is contrasted with unemployment, where a person lacks a job at all despite wanting one.
Examples ...
and educational inflation
Educational inflation, also known as credential inflation refers to the increasing overqualification required by employers beyond that which the occupations actually require.
A good example of credential inflation is the decline in the value of ...
.
Effects
Graduates of tertiary education are likely to have different worldviews and moral values than non-graduates. Graduates are also more likely to embrace cultural and ethnic diversity and express more positive views towards minority groups. For international relationships, graduates are more likely to favor openness, supporting policies likefree trade
Free trade is a trade policy that does not restrict imports or exports. In government, free trade is predominantly advocated by political parties that hold Economic liberalism, economically liberal positions, while economic nationalist politica ...
, open border
An open border is a border that enables Freedom of movement, free movement of people and often of goods between jurisdictions with no restrictions on movement and is lacking a border control. A border may be an open border due to intentional leg ...
s, and more liberal policies regarding international migration
International migration occurs when people cross state boundaries and stay in the host state for some minimum length of the time. Migration occurs for many reasons. Many people leave their home countries in order to look for economic opportunities ...
.
Tertiary education can increase human capital
Human capital or human assets is a concept used by economists to designate personal attributes considered useful in the production process. It encompasses employee knowledge, skills, know-how, good health, and education. Human capital has a subs ...
and economic growth
In economics, economic growth is an increase in the quantity and quality of the economic goods and Service (economics), services that a society Production (economics), produces. It can be measured as the increase in the inflation-adjusted Outp ...
.
Providers
In the U.S., higher education is provided byuniversities
A university () is an educational institution, institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several Discipline (academia), academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly ...
, academies
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of tertiary education. The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, founded approximately 386 BC at Akademia, a sanctuary of Athena, the go ...
, college
A college (Latin: ''collegium'') may be a tertiary educational institution (sometimes awarding degrees), part of a collegiate university, an institution offering vocational education, a further education institution, or a secondary sc ...
s, seminaries
A seminary, school of theology, theological college, or divinity school is an educational institution for educating students (sometimes called seminarians) in scripture and theology, generally to prepare them for ordination to serve as clerg ...
, conservatories, and institutes of technology
An institute of technology (also referred to as technological university, technical university, university of technology, polytechnic university) is an institution of tertiary education that specializes in engineering, technology, applied science ...
, and certain college-level institutions, including vocational school
A vocational school (alternatively known as a trade school, or technical school), is a type of educational institution, which, depending on the country, may refer to either secondary education#List of tech ed skills, secondary or post-secondar ...
s, universities of applied sciences, trade schools, and other career-based colleges that award degrees. Tertiary education at a nondegree level is sometimes referred to as further education
Further education (often abbreviated FE) in the United Kingdom and Ireland is additional education to that received at secondary school that is distinct from the higher education (HE) offered in universities and other academic institutions. It ...
or continuing education
Continuing education is the education undertaken after initial education for either personal or professional reasons. The term is used mainly in the United States and Canada.
Recognized forms of post-secondary learning activities within the d ...
as distinct from higher education.
Higher education includes teaching, research, exacting applied work, as exists in medical school
A medical school is a tertiary educational institution, professional school, or forms a part of such an institution, that teaches medicine, and awards a professional degree for physicians. Such medical degrees include the Bachelor of Medicine, ...
s and dental school
A dental school (school of dental medicine, school of dentistry, dental college) is a tertiary educational institution—or part of such an institution—that teaches dental medicine to prospective dentists and potentially other dental auxiliari ...
s, and social services activities of universities.
Within the realm of teaching, it includes both the ''undergraduate
Undergraduate education is education conducted after secondary education and before postgraduate education, usually in a college or university. It typically includes all postsecondary programs up to the level of a bachelor's degree. For example, ...
'' level, and beyond that, ''graduate-level
Postgraduate education, graduate education, or graduate school consists of academic or professional degrees, certificates, diplomas, or other qualifications usually pursued by post-secondary students who have earned an undergraduate (bachelo ...
'' (or ''postgraduate'' level). The latter level of education is often referred to as graduate school
Postgraduate education, graduate education, or graduate school consists of academic or professional degrees, certificates, diplomas, or other qualifications usually pursued by post-secondary students who have earned an undergraduate (bachel ...
, especially in North America. In addition to the skills that are specific to any particular degree, potential employers in any profession are looking for evidence of critical thinking
Critical thinking is the process of analyzing available facts, evidence, observations, and arguments to make sound conclusions or informed choices. It involves recognizing underlying assumptions, providing justifications for ideas and actions, ...
and analytical reasoning skills, teamwork
Teamwork is the collaborative effort of a group to achieve a common goal or to complete a task in an effective and efficient way. Teamwork is seen within the framework of a team, which is a group of interdependent individuals who work toge ...
ing skills, information literacy
The Association of College and Research Libraries defines information literacy as a "set of integrated abilities encompassing the reflective discovery of information, the understanding of how information is produced and valued and the use of infor ...
, ethical
Ethics is the philosophical study of moral phenomena. Also called moral philosophy, it investigates normative questions about what people ought to do or which behavior is morally right. Its main branches include normative ethics, applied e ...
judgment, decision-making
In psychology, decision-making (also spelled decision making and decisionmaking) is regarded as the Cognition, cognitive process resulting in the selection of a belief or a course of action among several possible alternative options. It could be ...
skills, fluency in speaking and writing, problem solving
Problem solving is the process of achieving a goal by overcoming obstacles, a frequent part of most activities. Problems in need of solutions range from simple personal tasks (e.g. how to turn on an appliance) to complex issues in business an ...
skills, and a wide knowledge of liberal arts and sciences.
Credential evaluation
Foreign tertiary degrees can be validated aftercredential evaluation Credential evaluation is the way in which academic and professional degrees earned in one country are compared to those earned in another. Universities, colleges and employers around the world use credential evaluations to understand foreign educati ...
, for example according to the Lisbon Recognition Convention
The Lisbon Recognition Convention, officially the Convention on the Recognition of Qualifications concerning Higher Education in the European Region, is an international convention of the Council of Europe elaborated together with the UNESCO. This ...
.
History

 The oldest known institutions of higher education are credited to Dynastic Egypt, with Pr-Anx (houses of life) built as libraries and scriptoriums, containing works on law, architecture, mathematics, and medicine, and involved in the training of "swnw" and "swnwt" (male and female
The oldest known institutions of higher education are credited to Dynastic Egypt, with Pr-Anx (houses of life) built as libraries and scriptoriums, containing works on law, architecture, mathematics, and medicine, and involved in the training of "swnw" and "swnwt" (male and female doctors
Doctor, Doctors, The Doctor or The Doctors may refer to:
Titles and occupations
* Physician, a medical practitioner
* Doctor (title), an academic title for the holder of a doctoral-level degree
** Doctorate
** List of doctoral degrees awarded b ...
); extant Egyptian papyri
This list of papyri from ancient Egypt includes some of the better known individual papyri written in hieroglyphs, hieratic, demotic or in ancient Greek. Excluded are papyri found abroad or containing Biblical texts which are listed in separate ...
from the 3rd millennia BC are in several collections.
In the Greek world, Plato's Academy
The Academy (), variously known as Plato's Academy, or the Platonic Academy, was founded in Athens by Plato ''circa'' 387 BC. The academy is regarded as the first institution of higher education in the west, where subjects as diverse as biolog ...
(), Aristotle's Lyceum () and other philosophical-mathematical schools became models for other establishments, particularly in Alexandria
Alexandria ( ; ) is the List of cities and towns in Egypt#Largest cities, second largest city in Egypt and the List of coastal settlements of the Mediterranean Sea, largest city on the Mediterranean coast. It lies at the western edge of the Nile ...
of Egypt, under the Ptolemies
The Ptolemaic dynasty (; , ''Ptolemaioi''), also known as the Lagid dynasty (, ''Lagidai''; after Ptolemy I's father, Lagus), was a Macedonian Greek royal house which ruled the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Ancient Egypt during the Hellenistic period. ...
.
In South Asia
South Asia is the southern Subregion#Asia, subregion of Asia that is defined in both geographical and Ethnicity, ethnic-Culture, cultural terms. South Asia, with a population of 2.04 billion, contains a quarter (25%) of the world's populatio ...
, the city of Taxila
Taxila or Takshashila () is a city in the Pothohar region of Punjab, Pakistan. Located in the Taxila Tehsil of Rawalpindi District, it lies approximately northwest of the Islamabad–Rawalpindi metropolitan area and is just south of the ...
, later the great Buddhist monastery of Nalanda
Nalanda (International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration, IAST: , ) was a renowned Buddhism, Buddhist ''mahavihara'' (great monastery) in medieval Magadha (Mahajanapada), Magadha (modern-day Bihar), eastern India. Widely considered to be am ...
(), attracted students and professors even from distant regions.
In China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
, the Han dynasty established chairs to teach the Four Books and Five Classics, Five Confucean Classics, in the Grand School, Taixue (), to train cadres for the imperial administration. All these higher-learning institutions became models for other schools within their sphere of cultural influence.
In 425 CE, the Byzantine emperor Theodosius II innovated as he established the Pandidakterion, with a faculty of 31 professors, to train public servants. In the 7th and 8th centuries, "cathedral schools" were created in Western Europe. Meanwhile, the first Madrasahs were founded in the Muslim empire – initially mere primary schools in the premises of major mosques, which gradually evolved toward secondary, later higher education. However high the intellectual level of these schools could be, it would be anachronistic to call them "universities". Their organization and purposes were markedly different from the corporations of students and teachers, independent from both the Church and the State, which established themselves from the 12th century in Western Europe as ''Universitas Studiorum''.
According to UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
and ''Guinness World Records'', the University of al-Qarawiyyin in Fez, Morocco is the List of oldest universities in continuous operation, oldest existing continually operating higher educational institution in the world. and is occasionally referred to as the oldest university by scholars. Undoubtedly, there are older institutions of higher education, for example, the University of Ez-Zitouna in Montfleury, Tunis, was first established in 737. The University of Bologna, Italy, founded in 1088, is the world's oldest university in continuous operation,de Ridder-Symoens, Hilde''A History of the University in Europe: Volume 1, Universities in the Middle Ages''
, Cambridge University Press, 1992, , pp. 47–55 and the first university in the sense of a higher-learning and degree-awarding institute, as the word ''universitas'' was coined at its foundation.
20th century
Since World War II, developed and many developing countries have increased the participation of the age group who mostly studies higher education from the elite rate, of up to 15 per cent, to the mass rate of 16 to 50 per cent. In many developed countries, participation in higher education has continued to increase towards universal or, what Trow later called, open access, where over half of the relevant age group participate in higher education. Higher education is important to national economy, economies, both as an industry, in its own right, and as a source of trained and educated personnel for the rest of the economy. College educated workers have commanded a measurable wage premium and are much less likely to become unemployed than less educated workers.21st century
In recent years, universities have been criticized for permitting or actively encouraginggrade inflation
Grade inflation (also known as grading leniency) is the general awarding of higher grades for the same quality of work over time, which devalues grades. However, higher average grades in themselves do not prove grade inflation. For this to be grad ...
. Widening participation can increase the supply of graduates in individual fields of study over the demand for their skills, aggravating graduate unemployment
Graduate unemployment, or educated unemployment, is unemployment among people with an academic degree.
Aggravating factors for unemployment are the rapidly increasing quantity of international graduates competing for an inadequate number of suit ...
, underemployment, overqualification and educational inflation
Educational inflation, also known as credential inflation refers to the increasing overqualification required by employers beyond that which the occupations actually require.
A good example of credential inflation is the decline in the value of ...
. Some commentators have suggested that the Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on education#Higher education, impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on education is rapidly making certain aspects of the traditional higher education system obsolete. The Israeli-funded Institute for the Study of Global Antisemitism and Policy and some Israeli media have claimed that Qatari involvement in higher education in the United States, involvement and funding by Qatar in higher education in the US has resulted in what they regard as growing anti-Semitism on campuses, in particular in connection with Gaza war protests.
Statistics
The total expenditure on tertiary education (International Standard Classification of Education, ISCED levels 5 to 8) as a percentage of GDP for individual countries is shown in the following table The percentage of adults who have attained individual tertiary education levels by country is shown in the following table. A 2014 report by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development states that by 2014, 84 percent of young people were completing upper secondary education over their lifetimes, in high-income countries. Tertiary-educated individuals were earning twice as much as median workers. In contrast to historical trends in education, young women were more likely to complete upper secondary education than young men. Additionally, access to education was expanding and growth in the number of people receiving university education was rising sharply. By 2014, close to 40 percent of people aged 25–34 (and around 25 percent of those aged 55–64), were being educated at university.United Kingdom
Under devolution in the United Kingdom, education is administered separately in England, Wales, Northern Ireland, and Scotland. In England, the term "tertiary education" aligns with the global term "higher education" (i.e. post-18 study). In 2018 the Welsh Government adopted the term "tertiary education" to refer to post-16 education and training in Wales. Since the 1970s, however, specialized further education, further education colleges in England and Wales have called themselves "tertiary colleges" although being part of thesecondary education
Secondary education is the education level following primary education and preceding tertiary education.
Level 2 or ''lower secondary education'' (less commonly ''junior secondary education'') is considered the second and final phase of basic e ...
process. These institutions cater for both school leavers and adults, thus combining the main functions of an FE college and a sixth form college. Generally, district councils with such colleges have adopted a tertiary system or structure where a single local institution provides all the 16–19 and adult education, and where schools do not universally offer sixth forms (i.e. schools only serve ages 11–16). However the Further and Higher Education Act 1992 has effectively prevented the creation of new tertiary colleges.
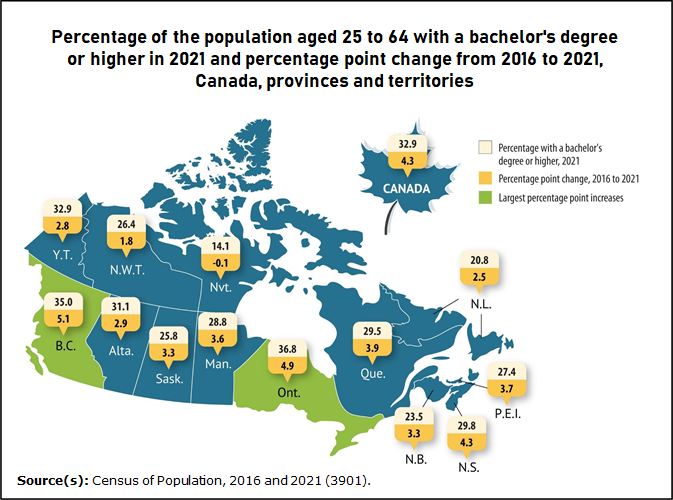
Canada

Australia
Within Australia "tertiary education" refers to continuing studies after a student completes secondary school. Tertiary education options include universities, technical and further education (TAFE) and private universities.United States
 The Higher education in the United States, higher education system in the United States is decentralized and regulated independently by each state with Higher education accreditation in the United States, accreditors playing a key role in ensuring institutions meet minimum standards. It is large and diverse with institutions that are privately governed and institutions that are owned and operated by state and local governments. Some private institutions are affiliated with religious organizations whereas others are secular with enrollment ranging from a few dozen to tens of thousands of students. The United States Department of Education presents a broad-spectrum view of tertiary education and detailed information on the nation's educational structure, accreditation procedures, and connections to state as well as federal agencies and entities.
The Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education provides one framework for classifying U.S. colleges and universities in several different ways. US tertiary education also includes various non-profit organizations promoting professional development of individuals in the field of higher education and helping expand awareness of related issues like international student services and complete campus internationalization.
The Higher education in the United States, higher education system in the United States is decentralized and regulated independently by each state with Higher education accreditation in the United States, accreditors playing a key role in ensuring institutions meet minimum standards. It is large and diverse with institutions that are privately governed and institutions that are owned and operated by state and local governments. Some private institutions are affiliated with religious organizations whereas others are secular with enrollment ranging from a few dozen to tens of thousands of students. The United States Department of Education presents a broad-spectrum view of tertiary education and detailed information on the nation's educational structure, accreditation procedures, and connections to state as well as federal agencies and entities.
The Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education provides one framework for classifying U.S. colleges and universities in several different ways. US tertiary education also includes various non-profit organizations promoting professional development of individuals in the field of higher education and helping expand awareness of related issues like international student services and complete campus internationalization.
European Union
Although tertiary education in the European Union, EU includes university, it can differ from country to country.France
After going to nursery school (French: école maternelle), elementary school (French: école primaire), secondary education in France, middle school (French: collège), and lycee, high school (French: lycée), a student may go to university, but may also stop at that point.Italy
Education in Italy is compulsory from 6 to 16 years of age, and is divided into five stages: kindergarten (''scuola dell'infanzia''), primary school (''scuola primaria'' or ''scuola elementare''), scuola media, lower secondary school (''scuola secondaria di primo grado'' or ''scuola media inferiore''), scuola superiore, upper secondary school (''scuola secondaria di secondo grado'' or ''scuola media superiore'') and university (''università''). Education is free in Italy and free education is available to children of all nationalities who are residents in Italy. Italy has both a private and public education system.
 Italy has a large and international network of public or state-affiliated universities and schools offering degrees in higher education. State-run universities of Italy constitute the main percentage of tertiary education in Italy and are managed under the supervision of Italian's Ministry of Education.
Italian universities are among the oldest universities in the world; the University of Bologna (founded in 1088) notably, is List of oldest universities in continuous operation, the oldest one ever; also, University of Naples Federico II is the world's oldest state-funded university in continuous operation. Most universities in Italy are state-supported. 33 Italian universities were ranked among the world's top 500 in 2019, the third-largest number in Europe after the United Kingdom and Germany.
There are also a number of Superior Graduate Schools in Italy, Superior Graduate Schools (''Grandes écoles'') or ''Scuola Superiore Universitaria'', which offer officially recognized titles, including the ''Diploma di Perfezionamento'' equivalent to a Doctorate, Dottorato di ricerca, ''Dottorato di Ricerca'' i.e. Doctorate, Research Doctorate or ''Doctor Philosophiae'' i.e. PhD. Some of them also organize master's degree courses. There are three Superior Graduate Schools with "university status", three institutes with the status of Doctoral Colleges, which function at Graduate school, graduate and post-graduate level. Nine further schools are direct offshoots of the universities (i.e. do not have their own 'university status'). The first one is the Scuola Normale Superiore di Pisa (founded in 1810 by Napoleon as a branch of École Normale Supérieure), taking the model of organization from the famous École Normale Supérieure. These institutions are commonly referred to as "Schools of Excellence" (i.e. "Scuole di Eccellenza").
Italy hosts a broad variety of universities, colleges and academies. Founded in 1088, the University of Bologna is likely List of oldest universities in continuous operation, the oldest in the world. In 2009, the University of Bologna is, according to Times Higher Education-QS World University Rankings, The Times, the only Italian college in the top 200 World Universities. Milan's Bocconi University has been ranked among the top 20 best business schools in the world by The Wall Street Journal international rankings, especially thanks to its M.B.A. program, which in 2007 placed it no. 17 in the world in terms of graduate recruitment preference by major multinational companies. Bocconi was also ranked by Forbes as the best worldwide in the specific category Value for Money. In May 2008, Bocconi overtook several traditionally top global business schools in the Financial Times Executive education ranking, reaching no. 5 in Europe and no. 15 in the world.
Other top universities and polytechnics are the Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore in Milan, the LUISS in Rome, the Polytechnic University of Turin, the Politecnico di Milano (which in 2011 was ranked as the 48th best technical university in the world by QS World University Rankings), the Sapienza University of Rome, University of Rome La Sapienza (which in 2005 was Europe's 33rd best university, and ranks among Europe's 50 and the world's 150 best colleges and in 2013, the Center for World University Rankings ranked the Sapienza University of Rome 62nd in the world and the top in Italy in its ''World University Rankings''.) and the University of Milan (whose research and teaching activities have developed over the years and have received important international recognition). This university is the only Italian member of the League of European Research Universities (LERU), a prestigious group of twenty research-intensive European Universities. It has also been awarded ranking positions such as 1st in Italy and 7th in Europe (The CWTS Leiden Ranking, Leiden Ranking – Universiteit Leiden).
Italy has a large and international network of public or state-affiliated universities and schools offering degrees in higher education. State-run universities of Italy constitute the main percentage of tertiary education in Italy and are managed under the supervision of Italian's Ministry of Education.
Italian universities are among the oldest universities in the world; the University of Bologna (founded in 1088) notably, is List of oldest universities in continuous operation, the oldest one ever; also, University of Naples Federico II is the world's oldest state-funded university in continuous operation. Most universities in Italy are state-supported. 33 Italian universities were ranked among the world's top 500 in 2019, the third-largest number in Europe after the United Kingdom and Germany.
There are also a number of Superior Graduate Schools in Italy, Superior Graduate Schools (''Grandes écoles'') or ''Scuola Superiore Universitaria'', which offer officially recognized titles, including the ''Diploma di Perfezionamento'' equivalent to a Doctorate, Dottorato di ricerca, ''Dottorato di Ricerca'' i.e. Doctorate, Research Doctorate or ''Doctor Philosophiae'' i.e. PhD. Some of them also organize master's degree courses. There are three Superior Graduate Schools with "university status", three institutes with the status of Doctoral Colleges, which function at Graduate school, graduate and post-graduate level. Nine further schools are direct offshoots of the universities (i.e. do not have their own 'university status'). The first one is the Scuola Normale Superiore di Pisa (founded in 1810 by Napoleon as a branch of École Normale Supérieure), taking the model of organization from the famous École Normale Supérieure. These institutions are commonly referred to as "Schools of Excellence" (i.e. "Scuole di Eccellenza").
Italy hosts a broad variety of universities, colleges and academies. Founded in 1088, the University of Bologna is likely List of oldest universities in continuous operation, the oldest in the world. In 2009, the University of Bologna is, according to Times Higher Education-QS World University Rankings, The Times, the only Italian college in the top 200 World Universities. Milan's Bocconi University has been ranked among the top 20 best business schools in the world by The Wall Street Journal international rankings, especially thanks to its M.B.A. program, which in 2007 placed it no. 17 in the world in terms of graduate recruitment preference by major multinational companies. Bocconi was also ranked by Forbes as the best worldwide in the specific category Value for Money. In May 2008, Bocconi overtook several traditionally top global business schools in the Financial Times Executive education ranking, reaching no. 5 in Europe and no. 15 in the world.
Other top universities and polytechnics are the Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore in Milan, the LUISS in Rome, the Polytechnic University of Turin, the Politecnico di Milano (which in 2011 was ranked as the 48th best technical university in the world by QS World University Rankings), the Sapienza University of Rome, University of Rome La Sapienza (which in 2005 was Europe's 33rd best university, and ranks among Europe's 50 and the world's 150 best colleges and in 2013, the Center for World University Rankings ranked the Sapienza University of Rome 62nd in the world and the top in Italy in its ''World University Rankings''.) and the University of Milan (whose research and teaching activities have developed over the years and have received important international recognition). This university is the only Italian member of the League of European Research Universities (LERU), a prestigious group of twenty research-intensive European Universities. It has also been awarded ranking positions such as 1st in Italy and 7th in Europe (The CWTS Leiden Ranking, Leiden Ranking – Universiteit Leiden).
Africa
Nigeria
 In Nigeria, ''tertiary education'' refers to post-secondary education received at universities (government or privately funded), monotechnics, polytechnics and colleges of education. After completing a secondary education, students may enroll in a tertiary institution or acquire a Vocational school, vocational education. Students are required to sit for the Joint Admissions and Matriculation Board Entrance Examination (JAMB) as well as the West African Senior School Certificate Examination, Secondary School Certificate Examination (SSCE) or General Certificate Examination (GCE) and meet varying cut-off marks to gain admission into a tertiary institution.
In Nigeria, ''tertiary education'' refers to post-secondary education received at universities (government or privately funded), monotechnics, polytechnics and colleges of education. After completing a secondary education, students may enroll in a tertiary institution or acquire a Vocational school, vocational education. Students are required to sit for the Joint Admissions and Matriculation Board Entrance Examination (JAMB) as well as the West African Senior School Certificate Examination, Secondary School Certificate Examination (SSCE) or General Certificate Examination (GCE) and meet varying cut-off marks to gain admission into a tertiary institution.
Asia
Japan
According to MEXT (Ministry of Education) and UNESCO, following types of education are classified as tertiary education: University education (undergraduate, postgraduate and professional degrees), two-year colleges (''Tanki Daigaku''), colleges of technology and specialised colleges.Hong Kong
In Hong Kong "tertiary education" or "higher education" refers to any education higher than secondary education. Tertiary education includes universities, post secondary colleges, statutory universities, and publicly funded institutions.Higher education by country
*Higher education in Canada *Higher education in Ukraine *Higher education in the Philippines *Higher education in PortugalSee also
* :Higher education by country * List of countries by tertiary education attainment * List of education articles by country, Education by country * List of higher education associations and alliances * List of universities and colleges by country * Student SPILL * College and university rankings ** Criticism of college and university rankings in North America * Governance in higher education * Graduation * Higher education accreditation * Higher education bubble * Higher education policy * Higher Education Price Index * Institute * UnCollege * ''Hochschule'' * League of European Research Universities * Technical and Further Education (TAFE)Notes
References
Sources
* *Further reading
*Council of Europe Higher Education Series
External links
Tertiary education statistics
, UNESCO
{{DEFAULTSORT:Tertiary Education Tertiary education, Educational stages id:Pendidikan tinggi