|
Ptolemies
The Ptolemaic dynasty (; , ''Ptolemaioi''), also known as the Lagid dynasty (, ''Lagidai''; after Ptolemy I's father, Lagus), was a Macedonian Greek royal house which ruled the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Ancient Egypt during the Hellenistic period. Reigning for 275 years, the Ptolemaic was the longest and last dynasty of ancient Egypt from 305 BC until its incorporation into the Roman Republic in 30 BC. Ptolemy, a general and one of the '' somatophylakes'' (bodyguard companions) of Alexander the Great, was appointed satrap of Egypt after Alexander's death in 323 BC. In 305 BC he declared himself Pharaoh Ptolemy I, later known as ''Sōter'' "Saviour". The Egyptians soon accepted the Ptolemies as the successors to the pharaohs of independent Egypt. The new dynasty showed respect to local traditions and adopted the Egyptian titles and iconography, while also preserving their own Greek language and culture. The Ptolemaic period was marked by the intense interactions and blending ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
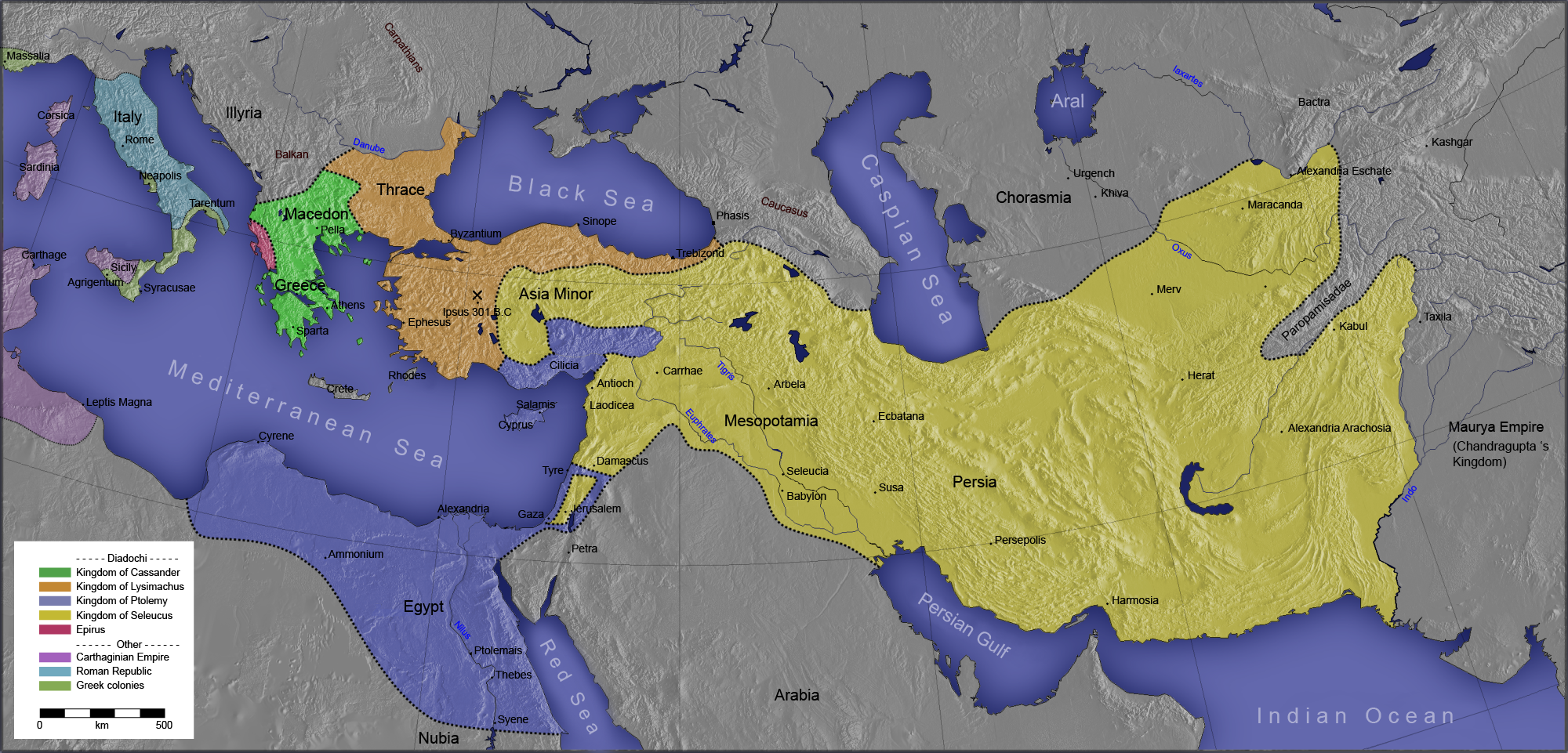
Ptolemaic Kingdom
The Ptolemaic Kingdom (; , ) or Ptolemaic Empire was an ancient Greek polity based in Ancient Egypt, Egypt during the Hellenistic period. It was founded in 305 BC by the Ancient Macedonians, Macedonian Greek general Ptolemy I Soter, a Diadochi, companion of Alexander the Great, and ruled by the Ptolemaic dynasty until the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC. Reigning for nearly three centuries, the Ptolemies were the longest and final Dynasties of ancient Egypt, dynasty of ancient Egypt, heralding a distinct era of Hellenistic religion, religious and cultural syncretism between Greek and Egyptian culture. Alexander the Great conquered Thirty-first Dynasty of Egypt, Persian-controlled Egypt in 332 BC during Wars of Alexander the Great, his campaigns against the Achaemenid Empire. Death of Alexander the Great, Alexander's death in 323 BC was followed by the Empire of Alexander the Great, rapid unraveling of the Macedonian Empire amid competing claims by the ''diadochi'', his closest fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleopatra VII
Cleopatra VII Thea Philopator (; The name Cleopatra is pronounced , or sometimes in both British and American English, see and respectively. Her name was pronounced in the Greek dialect of Egypt (see Koine Greek phonology). She was also styled as Thea Neotera () and Philopatris (); see 70/69 BC10 or 12 August 30 BC) was Queen of the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Ancient Egypt, Egypt from 51 to 30 BC, and the last active Hellenistic pharaoh.She was also a diplomat, Ancient navies and vessels, naval commander, linguist, and Ancient Greek medicine, medical author; see and . A member of the Ptolemaic dynasty, she was a descendant of its founder Ptolemy I Soter, a Ancient Macedonians, Macedonian Greek general and Government of Macedonia (ancient kingdom)#Companions, friends, councils, and assemblies, companion of Alexander the Great. writes about Ptolemy I Soter: "The Ptolemaic dynasty, of which Cleopatra was the last representative, was founded at the end of the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hellenistic Period
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in 31 BC and the Roman conquest of Ptolemaic Egypt the following year, which eliminated the last major Hellenistic kingdom. Its name stems from the Ancient Greek word ''Hellas'' (, ''Hellás''), which was gradually recognized as the name for Greece, from which the modern historiographical term ''Hellenistic'' was derived. The term "Hellenistic" is to be distinguished from "Hellenic" in that the latter refers to Greece itself, while the former encompasses all the ancient territories of the period that had come under significant Greek influence, particularly the Hellenized Middle East, after the conquests of Alexander the Great. After the Macedonian conquest of the Achaemenid Empire in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower Egypt were amalgamated by Menes, who is believed by the majority of List of Egyptologists, Egyptologists to have been the same person as Narmer. The history of ancient Egypt unfolded as a series of stable kingdoms interspersed by the "Periodization of ancient Egypt, Intermediate Periods" of relative instability. These stable kingdoms existed in one of three periods: the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom of the Early Bronze Age; the Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom of the Middle Bronze Age; or the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom of the Late Bronze Age. The pinnacle of ancient Egyptian power was achieved during the New Kingdom, which extended its rule to much of Nubia and a considerable portion of the Levant. After this period, Egypt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egyptian History
Ancient Egypt spans the period of Egyptian history from the early prehistoric settlements of the northern Nile valley to the Roman conquest of Egypt in 30 BC. The pharaonic period, the period in which Egypt was ruled by a pharaoh, is dated from the 32nd century BC, when Upper and Lower Egypt were unified, until the country fell under Macedonian rule in 332 BC. Chronology ;Note: For alternative 'revisions' to the chronology of Egypt, see Egyptian chronology. Egypt's history is split into several different periods according to the ruling dynasty of each pharaoh. The dating of events is still a subject of research. The conservative dates are not supported by any reliable absolute date for a span of about three millennia. The following is the list according to conventional Egyptian chronology. * Prehistoric Egypt (prior to 3100 BC) * Naqada III ("the protodynastic period", approximately 3100–3000 BC; sometimes referred to as "Dynasty 0") * Early Dynastic Period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egyptians
Egyptians (, ; , ; ) are an ethnic group native to the Nile, Nile Valley in Egypt. Egyptian identity is closely tied to Geography of Egypt, geography. The population is concentrated in the Nile Valley, a small strip of cultivable land stretching from the Cataracts of the Nile, First Cataract to the Mediterranean Basin, Mediterranean and enclosed by desert both to the Eastern Desert, east and to the Western Desert (North Africa), west. This unique geography has been the basis of the DNA history of Egypt, development of Egyptian society since Ancient Egypt, antiquity. The daily language of the Egyptians is a continuum of the local variety of Arabic, varieties of Arabic; the most famous dialect is known as Egyptian Arabic or ''Masri''. Additionally, a sizable minority of Egyptians living in Upper Egypt speak Sa'idi Arabic. Egyptians are predominantly adherents of Sunni Islam with a small Shia minority and a significant proportion who follow native Sufi tariqah, orders.Hoffman, Val ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy XV
Ptolemy XV Caesar (; , ; 47 BC – late August 30 BC), nicknamed Caesarion (, , "Little Caesar"), was the last pharaoh of the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt, reigning with his mother Cleopatra VII from 2 September 44 BC until her death by 10 or 12 August 30 BC, then as sole ruler until his death was ordered by Octavian (who would become the first Roman emperor as Augustus). Caesarion was the eldest son of Cleopatra, and was the only known biological son of Julius Caesar, after whom he was named. He was the last sovereign member of the Ptolemaic dynasty of Egypt. Early life Ptolemy Caesar was born in Egypt in mid to late 47 BC. His mother Cleopatra gave him the royal names Theos Philopator Philometor (lit. 'father-loving, mother-loving God') and insisted that he was the son of Roman politician and dictator Julius Caesar. While he was said to have inherited Caesar's looks and manner, Caesar did not officially acknowledge him. All accusations of bastardy against Caesarion were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hellenistic Religion
The concept of Hellenistic religion as the late form of Ancient Greek religion covers any of the various systems of beliefs and practices of the people who lived under the influence of ancient Greek culture during the Hellenistic period and the Roman Empire ( 300 BCE to 300 CE). There was much continuity in Hellenistic religion: people continued to worship the Greek gods and to practice the same rites as in Classical Greece. Change came from the addition of new religions from other countries, including the Egyptian deities Isis and Serapis, and the Syrian gods Atargatis and Hadad, which provided a new outlet for people seeking fulfillment in both the present life and the afterlife. The worship of deified Hellenistic rulers also became a feature of this period, most notably in Egypt, where the Ptolemies adapted earlier Egyptian practices and Greek hero-cults and established themselves as Pharaohs within the new syncretic Ptolemaic cult of Alexander III of Macedonia. Elsewhe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
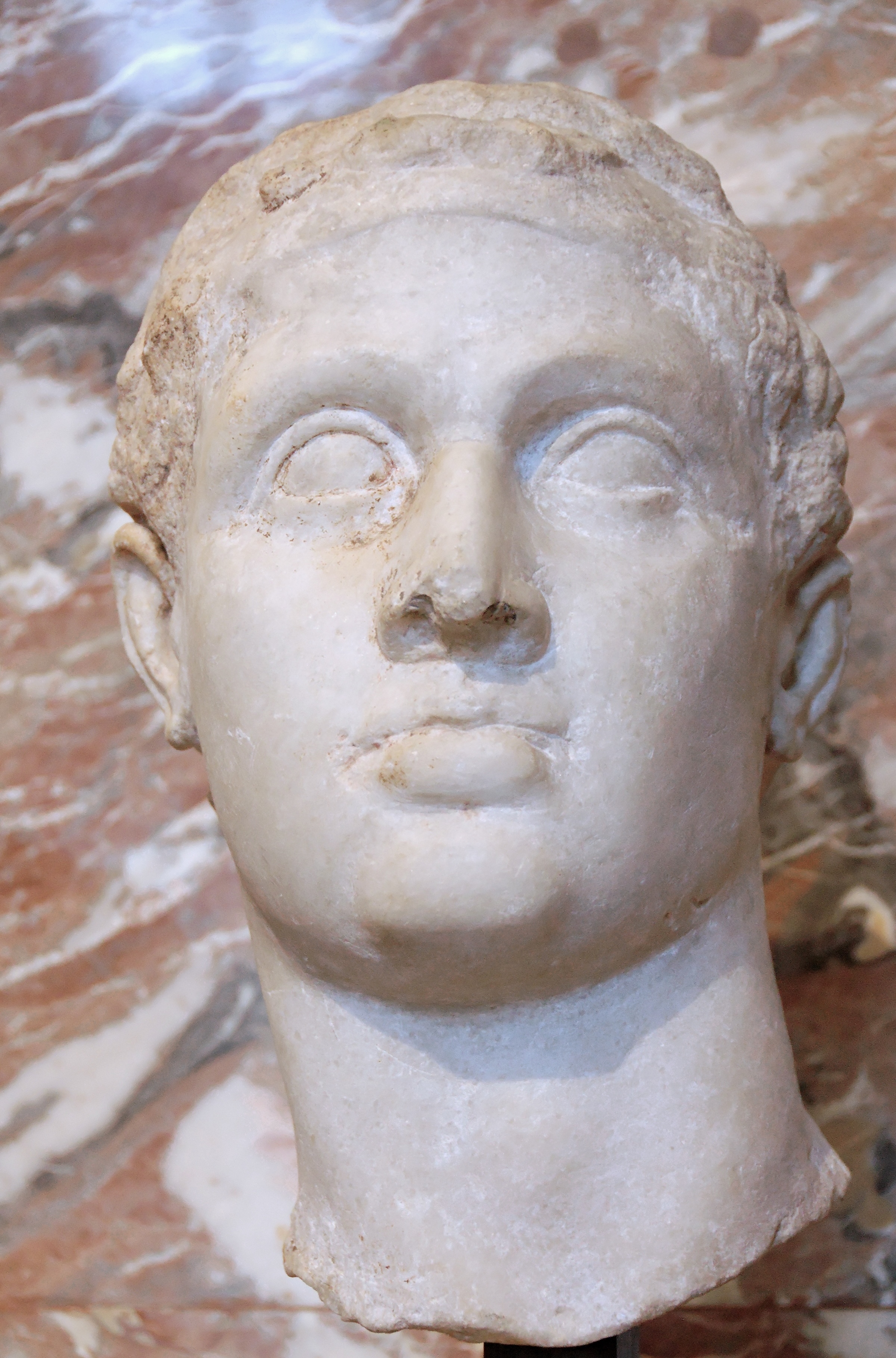
Ptolemy I Soter
Ptolemy I Soter (; , ''Ptolemaîos Sōtḗr'', "Ptolemy the Savior"; 367 BC – January 282 BC) was a Macedonian Greek general, historian, and successor of Alexander the Great who went on to found the Ptolemaic Kingdom centered on Egypt. Ptolemy was ''basileus'' and pharaoh of Ptolemaic Egypt from 305/304 BC to his death in 282 BC, and his descendants continued to rule Egypt until 30 BC. During their rule, Egypt became a thriving bastion of Hellenistic civilization and Alexandria a great seat of Greek culture. Ptolemy I was the son of Arsinoe of Macedon by either her husband Lagus or Philip II of Macedon, the father of Alexander. However, the latter is unlikely and may be a myth fabricated to glorify the Ptolemaic Dynasty. Ptolemy was one of Alexander's most trusted companions and military officers. After the death of Alexander in 323 BC, Ptolemy retrieved his body as it was en route to be buried in Macedon, placing it in Memphis instead, where it was later moved to Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
On Weights And Measures
''On Weights and Measures'' is a historical, lexical, metrological, and geographical treatise compiled in 392 AD in Constantia by Epiphanius of Salamis (c. 315–403). The greater part of the work is devoted to a discussion on Greek and Roman weights and measures. The composition was written at the request of a Persian priest, sent to Epiphanius by letter from the Roman emperor in Constantinople. Although five fragments of an early Greek version are known to exist, with one entitled Περὶ μέτρων καὶ στάθμων (''On Weights and Measures''), added by a later hand, this Syriac version is the only complete copy that has survived. Partial translations in Armenian and Georgian are also known to exist. Its modern title belies its content, as the work also contains important historical anecdotes about people and places not written about elsewhere. Two manuscripts of ''On Weights and Measures'', written in Syriac on parchment, are preserved at the British Museum i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy Of Mauretania
Ptolemy of Mauretania (, ''Ptolemaîos''; ; 13 9BC–AD40) was the last Roman client king and ruler of Mauretania for Rome. He was the son of Juba II, the king of Numidia and a member of the Berber Massyles tribe, as well as a descendant of the Ptolemaic dynasty via his mother Cleopatra Selene II. Life Ptolemy was the son of King Juba II and Queen Cleopatra Selene II of Mauretania. His birth date is not certainly known but must have occurred before his mother's death, which has been estimated to have taken place in 5BC. He had a sister (possibly younger) who is evidenced by an Athenian inscription, but her name has not been preserved. She may have been called Drusilla. His father Juba II was the son of King Juba I of Numidia, who was descended from the Berbers of North Africa and was an ally to the Roman Triumvir Pompey. His mother Cleopatra Selene II was the daughter of the Ptolemaic Greek Queen Cleopatra VII of Egypt and the Roman Triumvir Mark Antony. Ptolemy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy I
Ptolemy I Soter (; , ''Ptolemaîos Sōtḗr'', "Ptolemy the Savior"; 367 BC – January 282 BC) was a Macedonian Greek general, historian, and successor of Alexander the Great who went on to found the Ptolemaic Kingdom centered on Egypt. Ptolemy was ''basileus'' and pharaoh of Ptolemaic Egypt from 305/304 BC to his death in 282 BC, and his descendants continued to rule Egypt until 30 BC. During their rule, Egypt became a thriving bastion of Hellenistic civilization and Alexandria a great seat of Greek culture. Ptolemy I was the son of Arsinoe of Macedon by either her husband Lagus or Philip II of Macedon, the father of Alexander. However, the latter is unlikely and may be a myth fabricated to glorify the Ptolemaic Dynasty. Ptolemy was one of Alexander's most trusted companions and military officers. After the death of Alexander in 323 BC, Ptolemy retrieved his body as it was en route to be buried in Macedon, placing it in Memphis instead, where it was later moved to A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |