Podlasie on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Podlachia, also known by its Polish name Podlasie (; ; ), is a historical region in north-eastern
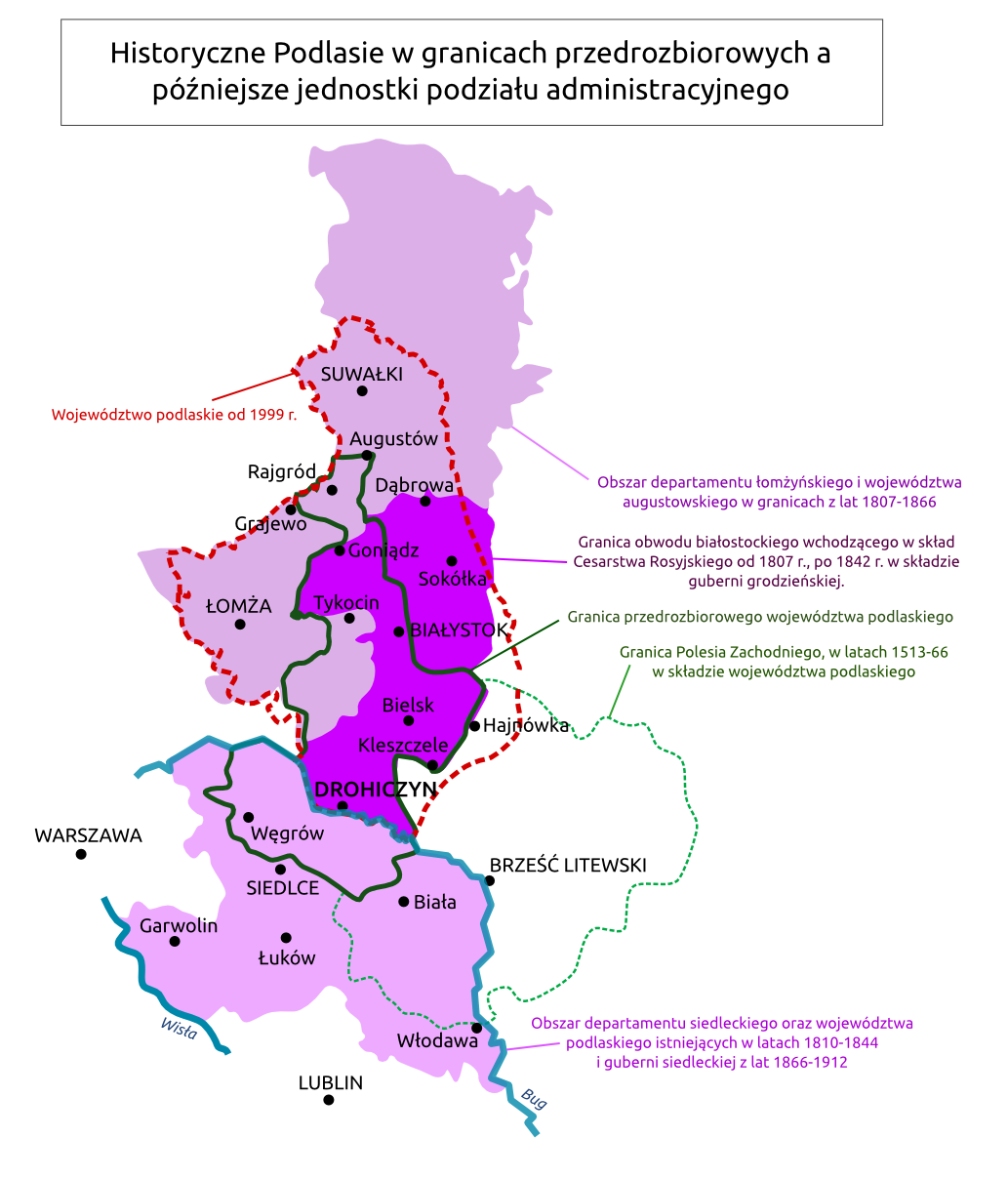 Podlachia is located along the middle stretch of the
Podlachia is located along the middle stretch of the
 In 1569, shortly before the
In 1569, shortly before the
 In the aftermath of World War I and the
In the aftermath of World War I and the
File:Pałac Branickich 3.JPG, Branicki Palace in
The Former Reformati Order’s Monasteries Route
Węgrów. *Górczyk, Wojciech Jerzy (2018),
Reformaci w Węgrowie. Architektura kościoła i miejsce fundacji węgrowskiej na tle działalności fundacyjnej Krasińskich
Drohiczyński Przeglad Naukowy. Drohiczyńskie Towarzystwo Naukowe: 307–326. * *
Journey in Wooden Podlachia
{{Authority control Historical regions in Belarus Historical regions in Poland
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
. Its largest city is Białystok
Białystok is the largest city in northeastern Poland and the capital of the Podlaskie Voivodeship. It is the List of cities and towns in Poland, tenth-largest city in Poland, second in terms of population density, and thirteenth in area.
Biał ...
, whereas the historical capital is Drohiczyn.
Similarly to several other historical regions of Poland, e.g. Greater Poland
Greater Poland, often known by its Polish name Wielkopolska (; ), is a Polish Polish historical regions, historical region of west-central Poland. Its chief and largest city is Poznań followed by Kalisz, the oldest city in Poland.
The bound ...
, Lesser Poland
Lesser Poland, often known by its Polish name ''Małopolska'' (; ), is a historical region situated in southern and south-eastern Poland. Its capital and largest city is Kraków. Throughout centuries, Lesser Poland developed a separate cult ...
, Mazovia
Mazovia or Masovia ( ) is a historical region in mid-north-eastern Poland. It spans the North European Plain, roughly between Łódź and Białystok, with Warsaw being the largest city and Płock being the capital of the region . Throughout the ...
, Pomerania
Pomerania ( ; ; ; ) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The central and eastern part belongs to the West Pomeranian Voivodeship, West Pomeranian, Pomeranian Voivod ...
, Silesia
Silesia (see names #Etymology, below) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at 8, ...
, Warmia, Podlachia possesses its own folk costumes, unique traditional architecture and cuisine. Between 1513 and 1795 it was a voivodeship
A voivodeship ( ) or voivodate is the area administered by a voivode (governor) in several countries of central and eastern Europe. Voivodeships have existed since medieval times and the area of extent of voivodeship resembles that of a duchy in ...
with the capital in Drohiczyn. Now the part north of the Bug River
The Bug or Western Bug is a major river in Central Europe that flows through Belarus (border), Poland, and Ukraine, with a total length of .Podlaskie Voivodeship
Podlaskie Voivodeship ( ) is a Voivodeships of Poland, voivodeship in northeastern Poland. The name of the voivodeship refers to the historical region of Podlachia (in Polish, ''Podlasie''), and significant part of its territory corresponds to th ...
with the capital in Białystok
Białystok is the largest city in northeastern Poland and the capital of the Podlaskie Voivodeship. It is the List of cities and towns in Poland, tenth-largest city in Poland, second in terms of population density, and thirteenth in area.
Biał ...
, whereas southern parts are located in the Masovian and Lublin Voivodeship
Lublin Voivodeship ( ) is a Voivodeships of Poland, voivodeship (province) of Poland, located in the southeastern part of the country, with its capital being the city of Lublin.
The region is named after its largest city and regional capital, Lu ...
s.
Names and etymology
The region is called , or in Polish, in Lithuanian, ''Padliašša'' (Падляшша) in Belarusian, ''Podljas’e'' (Подлясье) in Russian, פּאָדליאַשע ''Podlyashe'' inYiddish
Yiddish, historically Judeo-German, is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated in 9th-century Central Europe, and provided the nascent Ashkenazi community with a vernacular based on High German fused with ...
, and in Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
.
There are two hypotheses regarding the origin of the name of the region. According to the first one, the name is derived from the Polish word ''las'' , and means . However, this hypothesis conflicts with historical phonology; it fails to explain the vocalism and especially the ''-ch-''/''-š-'' in Slavic languages and the ''-nk-'' in Lithuanian.
According to the second hypothesis, the name is derived from the word ''liakh'' (or ''lach'', , ), and means . The second hypothesis holds that the term comes from the expression ''pod Lachem'', which may be translated literally as (see: Lechia). Some claim it to mean , though in the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
Podlachia was only partially under Polish rule, and since 1446 until 1569 the area belonged to the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a sovereign state in northeastern Europe that existed from the 13th century, succeeding the Kingdom of Lithuania, to the late 18th century, when the territory was suppressed during the 1795 Partitions of Poland, ...
. A better variant of this theory holds that the name originates from the period when the territory was within the Trakai Voivodeship of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, along the borderline with the Mazovia
Mazovia or Masovia ( ) is a historical region in mid-north-eastern Poland. It spans the North European Plain, roughly between Łódź and Białystok, with Warsaw being the largest city and Płock being the capital of the region . Throughout the ...
, primarily a fief of the Poland of the Piasts and later on part of the Kingdom of Poland of the Jagiellons. The origin of this name is apparently in East Slavic, probably Old Ruthenian ''ljax'', as the descendants of the Proto-Slavic word '' *lęxъ'' are most widespread there; there is no trace of nasalisation as would be expected in a native Polish word, but instead the typically East Slavic reflex ''-ja-'', betraying the non-Lechitic origin.
Geography
 Podlachia is located along the middle stretch of the
Podlachia is located along the middle stretch of the Bug River
The Bug or Western Bug is a major river in Central Europe that flows through Belarus (border), Poland, and Ukraine, with a total length of .Mazovia
Mazovia or Masovia ( ) is a historical region in mid-north-eastern Poland. It spans the North European Plain, roughly between Łódź and Białystok, with Warsaw being the largest city and Płock being the capital of the region . Throughout the ...
in the west, Polesia
Polesia, also called Polissia, Polesie, or Polesye, is a natural (geographic) and historical region in Eastern Europe within the East European Plain, including the Belarus–Ukraine border region and part of eastern Poland. This region shou ...
and Volhynia
Volhynia or Volynia ( ; see #Names and etymology, below) is a historic region in Central and Eastern Europe, between southeastern Poland, southwestern Belarus, and northwestern Ukraine. The borders of the region are not clearly defined, but in ...
in the east, the Narew
The Narew (; ; or ) is a 499-kilometre (310 mi) river primarily in north-eastern Poland. It is a tributary of the river Vistula. The Narew is one of Europe's few braided rivers, the term relating to the twisted channels resembling braided h ...
River in the north and the Chełm Land in the south. The borders of Podlachia changed with time and was not the same as historical Podlaskie Voivodeship
Podlaskie Voivodeship ( ) is a Voivodeships of Poland, voivodeship in northeastern Poland. The name of the voivodeship refers to the historical region of Podlachia (in Polish, ''Podlasie''), and significant part of its territory corresponds to th ...
. Podlachia is sometimes divided into two parts (southern and northern), which had different administrative subordination.
Traditional capital of Podlachia is Drohiczyn that lies into northern and southern parts. The former is included in the modern-day Podlaskie Voivodeship with its capital at Białystok (the historical boundary goes exactly through the city). Sometimes, Siedlce
Siedlce () ( ) is a city in the Masovian Voivodeship in eastern Poland with 77,354 inhabitants ().
The city is situated between two small rivers, the Muchawka and the Helenka, and lies along the European route E30, around east of Warsaw. It is ...
has been considered the capital of the region.
Coat of arms
The coat of arms of Podlachia was introduced in 1569. It was created by combining the coats of arms ofPoland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
(white eagle albeit without a crown) and Lithuania
Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, P ...
(mounted
Mount is often used as part of the name of specific mountains, e.g. Mount Everest.
Mount or Mounts may also refer to:
Places
* Mount, Cornwall, a village in Warleggan parish, England
* Mount, Perranzabuloe, a hamlet in Perranzabuloe parish, Co ...
armour
Armour (Commonwealth English) or armor (American English; see American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, spelling differences) is a covering used to protect an object, individual, or vehicle from physical injury or damage, e ...
ed knight
A knight is a person granted an honorary title of a knighthood by a head of state (including the pope) or representative for service to the monarch, the church, or the country, especially in a military capacity.
The concept of a knighthood ...
holding a sword
A sword is an edged and bladed weapons, edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter ...
and shield
A shield is a piece of personal armour held in the hand, which may or may not be strapped to the wrist or forearm. Shields are used to intercept specific attacks, whether from close-ranged weaponry like spears or long ranged projectiles suc ...
with the Jagiellonian Double Cross).
History
Podlachia is a multicultural and multi-religious region. It is the region where people's identity has been shaped throughout history by both the Orthodox and Roman Catholic churches, and since the Reformation, also by Evangelical churches. Until today, Podlachia has been considered Poland's most culturally diverse region. Throughout its early history, Podlachia was inhabited by various tribes of different ethnic roots. According to various sources, East Slavic tribes settled either in the 9th and 10th centuries (mostlyDrevlians
The Drevlians, Derevlians or Derevlianians ( or , ) were a tribe of East Slavs between the 6th and the 10th centuries, which inhabited the territories of Polesia and right-bank Ukraine, west of the Polans (eastern), eastern Polans and along the ...
, with Dregoviches in the north and likely Dulebes in the south), or in the 11th and 12th centuries in the eastern and southern part. The Polish Masovians
Masovians, also spelled as Mazovians, and historically known as Masurians, is an ethnographic group of Polish people that originates from the region of Masovia, located mostly within borders of the Masovian Voivodeship, Poland. They speak the ...
settled before the 11th century in the western part, as evidenced by Masovian-type strongholds from that period. In the 12th century, the northern part was settled by the Yotvingians, and afterwards the region was devastated by Yotvingian and Lithuanian raids. In the 13th century, the Yotvingians were driven out of Podlachia by Bolesław V the Chaste and Leszek II the Black, and the region was repopulated by Poles from Masovia, including minor nobility. Since the 13th century, Podlachia was contested by Poland and Lithuania, with varying ownership. In 1253 Pope Innocent IV
Pope Innocent IV (; – 7 December 1254), born Sinibaldo Fieschi, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 25 June 1243 to his death in 1254.
Fieschi was born in Genoa and studied at the universities of Parma and Bolo ...
recognized Polish sovereignty over Podlachia. In the 14th century, Polish King Casimir III the Great
Casimir III the Great (; 30 April 1310 – 5 November 1370) reigned as the King of Poland from 1333 to 1370. He also later became King of Ruthenia in 1340, retaining the title throughout the Galicia–Volhynia Wars. He was the last Polish king fr ...
granted the southern part to Lithuania. In 1379, the Teutonic Knights
The Teutonic Order is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem was formed to aid Christians on their pilgrimages to t ...
ravaged the region and unsuccessfully besieged Mielnik and Brześć.
In the late 14th century the area passed to Mazovian Piast rule. In 1446, Podlachia became part of the Grand Duchy again, but from 1496 southwestern parts of Podlachia ( Drohiczyn Land and Mielnik Land) and from 1501 the northern part ( Bielsk Land) used Polish law instead of Lithuanian. A renewal of the Polish–Lithuanian union Polish–Lithuanian can refer to:
* Polish–Lithuanian union (1385–1569)
* Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (1569–1795)
* Polish-Lithuanian identity as used to describe groups, families, or individuals with histories in the Polish–Lithuania ...
was concluded in Mielnik in 1501. In 1513 King Sigismund I the Old
Sigismund I the Old (, ; 1 January 1467 – 1 April 1548) was List of Polish monarchs, King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1506 until his death in 1548. Sigismund I was a member of the Jagiellonian dynasty, the son of Casimir IV of P ...
formed the Podlaskie Voivodeship
Podlaskie Voivodeship ( ) is a Voivodeships of Poland, voivodeship in northeastern Poland. The name of the voivodeship refers to the historical region of Podlachia (in Polish, ''Podlasie''), and significant part of its territory corresponds to th ...
(adjective of ''Podlasie''). In 1566, the southeastern part of the Voivodeship became part of the newly formed Brest Litovsk Voivodeship as Brest Litovsk County.
Union of Lublin
The Union of Lublin (; ) was signed on 1 July 1569 in Lublin, Poland, and created a single state, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, one of the largest countries in Europe at the time. It replaced the personal union of the Crown of the Kingd ...
which formally united Poland and Lithuania as the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, Podlasie was returned to the Kingdom of Poland
The Kingdom of Poland (; Latin: ''Regnum Poloniae'') was a monarchy in Central Europe during the Middle Ages, medieval period from 1025 until 1385.
Background
The West Slavs, West Slavic tribe of Polans (western), Polans who lived in what i ...
by the ''Privilege of restoration of Podlasie land to the Polish Crown''. It was the northernmost part of the Lesser Poland Province of Poland. The voivodeship was divided into three lands (): Drohiczyn, Mielnik and Bielsk. Knyszyn was the favorite residence of King Sigismund II Augustus, who died there in 1572, ending the reign of the Jagiellonian dynasty
The Jagiellonian ( ) or Jagellonian dynasty ( ; ; ), otherwise the Jagiellon dynasty (), the House of Jagiellon (), or simply the Jagiellons (; ; ), was the name assumed by a cadet branch of the Lithuanian ducal dynasty of Gediminids upon recep ...
in Poland. Polish Renaissance writer Łukasz Górnicki, after his appointment as starost of Tykocin in 1572, resided and wrote many of his works in Lipniki in Podlachia.
Podlachia was subtracted by extensive royal estates, numerous small estates of the nobility (with the exception of the eastern and southern outskirts) and a dense network of small towns. Petty nobility often cultivated their land on their own, and there were many places where the nobility had no serfs, making certain parts of Podlachia, according to Polish historian, geographer and ethnographer Zygmunt Gloger
Zygmunt Gloger (3November 184516August 1910) was a Polish historian, archaeologist, geographer and ethnographer, bearer of the Wilczekosy coat of arms. Gloger founded the precursor of modern and widely popular Polish Tourist and Sightseeing Socie ...
, the place with the highest percentage of free agricultural population in Europe in the feudal era. Polish nobles in Podlachia became so numerous that from the 16th century some migrated to other regions, including Lesser Poland
Lesser Poland, often known by its Polish name ''Małopolska'' (; ), is a historical region situated in southern and south-eastern Poland. Its capital and largest city is Kraków. Throughout centuries, Lesser Poland developed a separate cult ...
and Lithuania, where they often made significant fortunes.
In the 17th and early 18th century, the chief regional royal residence in Podlachia was Tykocin. In December 1630, King Sigismund III Vasa
Sigismund III Vasa (, ; 20 June 1566 – 30 April 1632
N.S.) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1587 to 1632 and, as Sigismund, King of Sweden from 1592 to 1599. He was the first Polish sovereign from the House of Vasa. Re ...
and his family took shelter there from an epidemic, and in 1633 Władysław IV Vasa
Władysław IV Vasa or Ladislaus IV (9 June 1595 – 20 May 1648) was King of Poland, Grand Duke of Lithuania and claimant of the thrones of Monarchy of Sweden, Sweden and List of Russian monarchs, Russia. Born into the House of Vasa as a prince ...
also stopped there. In 1653, Podlachia itself was hit by an epidemic. The region was invaded by Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
during the Deluge
A deluge is a large downpour of rain, often a flood.
The Deluge refers to the flood narrative in the biblical book of Genesis.
Deluge or Le Déluge may also refer to:
History
*Deluge (history), the Swedish and Russian invasion of the Polish-L ...
, but in 1657, Poles recaptured Tykocin. In 1661, renowned Polish military commander Stefan Czarniecki
Stefan Czarniecki (Polish: of the Łodzia coat of arms, 1599 – 16 February 1665) was a Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Polish szlachta, nobleman, general and military commander. In his career, he rose from a petty nobleman to a magnate hol ...
was granted the Tykocin starostwo with the towns of Tykocin and Białystok
Białystok is the largest city in northeastern Poland and the capital of the Podlaskie Voivodeship. It is the List of cities and towns in Poland, tenth-largest city in Poland, second in terms of population density, and thirteenth in area.
Biał ...
as a reward for his military service during the Swedish invasion of Poland of 1655–1660. Two Polish Protestant synod
A synod () is a council of a Christian denomination, usually convened to decide an issue of doctrine, administration or application. The word '' synod'' comes from the Ancient Greek () ; the term is analogous with the Latin word . Originally, ...
s were held in Podlachia, a Calvinist
Reformed Christianity, also called Calvinism, is a major branch of Protestantism that began during the 16th-century Protestant Reformation. In the modern day, it is largely represented by the Continental Reformed Protestantism, Continenta ...
one in Orla in 1644 and a Lutheran
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched ...
one in Węgrów
Węgrów (; ) is a town in eastern Poland with 12,796 inhabitants (2013), capital of Węgrów County in the Masovian Voivodeship.
History
First mentioned in historical records in 1414, Węgrów received its city charter in 1441. Between 16th ...
in 1780. Tykocin was the place where the Order of the White Eagle, Poland's oldest and highest order, was established.
During the Swedish invasion of Poland of 1701–1706, in 1702, Tykocin was the place of talks between delegates of Poland and Sweden. In 1704, Podlachia protested against the election
An election is a formal group decision-making process whereby a population chooses an individual or multiple individuals to hold Public administration, public office.
Elections have been the usual mechanism by which modern representative d ...
of Stanisław Leszczyński
Stanisław I Leszczyński (Stanisław Bogusław; 20 October 1677 – 23 February 1766), also Anglicized and Latinized as Stanislaus I, was twice King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania, and at various times Prince of Deux-Ponts, Duk ...
as King of Poland. Swedish and Russian troops often passed through the region during the war.
In the 18th and 19th century the private town of Białystok became the main center of the region, thanks to the patronage
Patronage is the support, encouragement, privilege, or financial aid that an organization or individual bestows on another. In the history of art, art patronage refers to the support that princes, popes, and other wealthy and influential people ...
of the Branicki family and the development of the textile industry
The textile industry is primarily concerned with the design, production and distribution of textiles: yarn, cloth and clothing.
Industry process
Cotton manufacturing
Cotton is the world's most important natural fibre. In the year 2007, th ...
. Due to the city's palace, parks and edifices, Białystok was dubbed the "Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; ) is a former royal residence commissioned by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, Yvelines, Versailles, about west of Paris, in the Yvelines, Yvelines Department of Île-de-France, Île-de-France region in Franc ...
of Podlachia". At that time, Polish kings traveling through Podlachia mainly resided in Białystok, i.e. Augustus II the Strong
Augustus II the Strong (12 May 1670 – 1 February 1733), was Elector of Saxony from 1694 as well as King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1697 to 1706 and from 1709 until his death in 1733. He belonged to the Albertine branch of the H ...
in 1726 and 1729 and Augustus III of Poland
Augustus III (; – "the Saxon"; ; 17 October 1696 5 October 1763) was List of Polish monarchs, King of Poland and Grand Duchy of Lithuania, Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1733 until 1763, as well as List of rulers of Saxony, Elector of Saxony i ...
in 1744, 1752 and 1755. The School of Civil and Military Engineering, Poland's first military technical college, and ''Komedialnia'', one of the oldest theaters in Poland, were founded in Białystok in 1745 and 1748, respectively. Białystok was a regional brewing
Brewing is the production of beer by steeping a starch source (commonly cereal grains, the most popular of which is barley) in water and #Fermenting, fermenting the resulting sweet liquid with Yeast#Beer, yeast. It may be done in a brewery ...
center with 33 breweries as of 1771, with the Podlachian Beer now listed as a protected traditional beverage by the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development of Poland.
In 1733, during the War of the Polish Succession
The War of the Polish Succession (; 1733–35) was a major European conflict sparked by a civil war in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth over the succession to Augustus II the Strong, which the other European powers widened in pursuit of ...
, supporters of Augustus III retreated from Warsaw
Warsaw, officially the Capital City of Warsaw, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the Vistula, River Vistula in east-central Poland. Its population is officially estimated at ...
to Węgrów. In 1767, Jan Klemens Branicki and Wacław Rzewuski protested against the Radom Confederation in Brańsk
Brańsk (Podlachian language: ''Бранськ, Branśk'', , ) is a town in eastern Poland. It is situated within Podlaskie Voivodeship (province).
Etymology
The name of the town comes from the river Bronka, a nearby tributary of the Nurzec River ...
.
Partition and Napoleonic Wars
Following the 1795 Third Partition of Poland, Podlachia was divided between theKingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (, ) was a German state that existed from 1701 to 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It played a signif ...
and the Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy, also known as Habsburg Empire, or Habsburg Realm (), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities (composite monarchy) that were ruled by the House of Habsburg. From the 18th century it is ...
(Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire, officially known as the Empire of Austria, was a Multinational state, multinational European Great Powers, great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the Habsburg monarchy, realms of the Habsburgs. Duri ...
from 1804), with the Bug forming the border between them. Part of Podlachia's eastern border became the boundary between Prussia and the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
. Within Prussia the Podlachian territory was organised as part of the Białystok Department of New East Prussia, which also included parts of the former Mazovian and Trakai Voivodeships; the Habsburg portion lay mostly within the Siedlce of West Galicia ( Galicia and Lodomeria from 1803).
In 1807, by the Treaties of Tilsit, Prussia ceded all of its gains in the second and third partitions, as well as part of the first. Most of this territory, including the western and northern parts of Prussian Podlachia, became part of the Duchy of Warsaw
The Duchy of Warsaw (; ; ), also known as the Grand Duchy of Warsaw and Napoleonic Poland, was a First French Empire, French client state established by Napoleon Bonaparte in 1807, during the Napoleonic Wars. It initially comprised the ethnical ...
, a Polish client state
A client state in the context of international relations is a State (polity), state that is economically, politically, and militarily subordinated to a more powerful controlling state. Alternative terms for a ''client state'' are satellite state, ...
of the First French Empire
The First French Empire or French Empire (; ), also known as Napoleonic France, was the empire ruled by Napoleon Bonaparte, who established French hegemony over much of continental Europe at the beginning of the 19th century. It lasted from ...
, while the east-central part including Białystok
Białystok is the largest city in northeastern Poland and the capital of the Podlaskie Voivodeship. It is the List of cities and towns in Poland, tenth-largest city in Poland, second in terms of population density, and thirteenth in area.
Biał ...
fell under Russian rule as the Belostok Oblast. The Podlachian territory within the Belostok Oblast corresponded with the Bielsk and Drohiczyn Uyezds (roughly "counties") and the western part of Belostoksky Uyezd. The small amounts of Podlachian territory in the Duchy of Warsaw lay within the Łomża Department, itself based on the territory of the Prussian Białystok Departement after the removal of the Belostock Oblast. The Habsburg part of Podlachia became part of the Duchy of Warsaw by the 1809 Treaty of Schönbrunn, forming much of the Siedlce Department. Although Prussian and Austrian rule was brief, it has remained administratively divided by the Bug ever since.
Russian rule
At the end of the Napoleonic wars in 1815, theCongress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon, Napol ...
transformed most of the Duchy of Warsaw, including the formerly Podlachian parts, into "Congress Poland
Congress Poland or Congress Kingdom of Poland, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland, was a polity created in 1815 by the Congress of Vienna as a semi-autonomous Polish state, a successor to Napoleon's Duchy of Warsaw. It was established w ...
" (formally the Kingdom of Poland) and placed it in a personal union with Russia; with that, all of Podlachia fell under Russian control. In theory this kingdom was created as an autonomous entity but in practice its separate laws and freedoms were simply ignored by the Emperors and control was steadily centralised, particularly following the November
November is the eleventh and penultimate month of the year in the Julian and Gregorian calendars. Its length is 30 days. November was the ninth month of the calendar of Romulus . November retained its name (from the Latin ''novem'' meaning " ...
and January Uprising
The January Uprising was an insurrection principally in Russia's Kingdom of Poland that was aimed at putting an end to Russian occupation of part of Poland and regaining independence. It began on 22 January 1863 and continued until the last i ...
s (1830–31, 1863–64). Within Congress Poland the former Siedlce Department became the Podlachia Voivodeship, while the former Łomża Department became the Augustów Voivodeship; these became the Podlachian and Augustów Governorates in 1837.
In 1842 the Belostok Oblast was dissolved and merged into Grodno Governorate
Grodno Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (''guberniya'') of the Northwestern Krai of the Russian Empire, with its capital in Grodno. It encompassed in area and consisted of a population of 1,603,409 inhabitants by 1897. Gro ...
, and the Drohiczyn Uyezd was merged into Bielsk Uyezd. In 1844 the Podlachian Governorate was merged into the Lublin Governorate.
In the second half of the 19th century, Białystok grew into a significant center of the textile industry
The textile industry is primarily concerned with the design, production and distribution of textiles: yarn, cloth and clothing.
Industry process
Cotton manufacturing
Cotton is the world's most important natural fibre. In the year 2007, th ...
, the largest after Łódź
Łódź is a city in central Poland and a former industrial centre. It is the capital of Łódź Voivodeship, and is located south-west of Warsaw. Łódź has a population of 655,279, making it the country's List of cities and towns in Polan ...
in then-partitioned Poland. Białystok was the largest industrial center between Warsaw
Warsaw, officially the Capital City of Warsaw, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the Vistula, River Vistula in east-central Poland. Its population is officially estimated at ...
and Łódź in the west, Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg, formerly known as Petrograd and later Leningrad, is the List of cities and towns in Russia by population, second-largest city in Russia after Moscow. It is situated on the Neva, River Neva, at the head of the Gulf of Finland ...
in the north and Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents with ...
in the east, and was nicknamed "Manchester
Manchester () is a city and the metropolitan borough of Greater Manchester, England. It had an estimated population of in . Greater Manchester is the third-most populous metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, with a population of 2.92&nbs ...
of the North".
In the 19th century the region was a stronghold of Polish resistance against Russian rule. The battles of Węgrów
Węgrów (; ) is a town in eastern Poland with 12,796 inhabitants (2013), capital of Węgrów County in the Masovian Voivodeship.
History
First mentioned in historical records in 1414, Węgrów received its city charter in 1441. Between 16th ...
and Siemiatycze
Siemiatycze ( ''Siamiatyčy'') is a town in eastern Poland, with 14,391 inhabitants (2019). It is the capital of Siemiatycze County in the Podlaskie Voivodeship.
History
The history of Siemiatycze dates back to the mid-16th century, when the vil ...
, both fought in Podlachia in 1863, were among the largest battles of the January Uprising. Stanisław Brzóska, the last partisan of the January Uprising, operated there until 1865. He was hanged publicly by the Russians in Sokołów Podlaski in May 1865. As a result of the uprising, in 1867 Congress Poland was formally absorbed into Russia as the Vistula Land
Vistula Land, also known as Vistula Country (; ), was the name applied to the lands of Congress Poland from 1867, following the defeats of the November Uprising (1830–1831) and January Uprising (1863–1864) as it was increasingly stripped of ...
(Privislinsky Krai), although the Kingdom still nominally existed. The Podlachian Governorate was also restored under the name Siedlce Governorate, and the Augustów Governorate was split between the Łomża
Łomża () is a city in north-eastern Poland, approximately to the north-east of Warsaw and west of Białystok. It is situated alongside the Narew river as part of the Podlaskie Voivodeship. It is the capital of Łomża County and has been the se ...
and Suwałki Governorates; Augustów itself went to Suwałki Governorate while the rest of the Podlachian territory went to the Łomża Governorate.
According to the Russian Imperial Census of 1897, the most spoken languages in the Siedlce Governorate were Polish (66.13%), Yiddish (15.56%) and Ukrainian (13.95%). At the same time the most spoken languages in Bielsk Uyezd were Ukrainian (39.1%), Polish (34.9%), Yiddish (14.9%), Russian (5.9%) and Belarusian (4.9%); those in the Białystok Uyezd were Polish (33.95%), Yiddish (28.34%), Belarusian (26.13%), Russian (6.68%) and German (3.59%).
In 1912 Siedlce Governorate was once again abolished and divided between the Lublin
Lublin is List of cities and towns in Poland, the ninth-largest city in Poland and the second-largest city of historical Lesser Poland. It is the capital and the centre of Lublin Voivodeship with a population of 336,339 (December 2021). Lublin i ...
, Łomża
Łomża () is a city in north-eastern Poland, approximately to the north-east of Warsaw and west of Białystok. It is situated alongside the Narew river as part of the Podlaskie Voivodeship. It is the capital of Łomża County and has been the se ...
and Kholm Governorates, with all three gaining some parts of the former Podlachia; Kholm Governorate was also removed administratively from the Vistula Land, instead being made part of the Kiev General Governorate.
World War I and interbellum
DuringWorld War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
the area was occupied by the German Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperia ...
, with most of the Vistula Land falling under the Government General of Warsaw (later the Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,; ; , ; were one of the two main coalitions that fought in World War I (1914–1918). It consisted of the German Empire, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Bulga ...
puppet Kingdom of Poland
The Kingdom of Poland (; Latin: ''Regnum Poloniae'') was a monarchy in Central Europe during the Middle Ages, medieval period from 1025 until 1385.
Background
The West Slavs, West Slavic tribe of Polans (western), Polans who lived in what i ...
) while the areas further east, including Białystok and the Suwałki Governorate, fell under .
 In the aftermath of World War I and the
In the aftermath of World War I and the Russian Revolution
The Russian Revolution was a period of Political revolution (Trotskyism), political and social revolution, social change in Russian Empire, Russia, starting in 1917. This period saw Russia Dissolution of the Russian Empire, abolish its mona ...
, parts of the region, particularly Białystok, were contested by several states but ultimately became part of the Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland, was a country in Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 7 October 1918 and 6 October 1939. The state was established in the final stage of World War I ...
following the Polish–Soviet War
The Polish–Soviet War (14 February 1919 – 18 March 1921) was fought primarily between the Second Polish Republic and the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, following World War I and the Russian Revolution.
After the collapse ...
. During the interwar period the northern part fell entirely within the Białystok Voivodeship while the southern part belonged to the Lublin Voivodeship
Lublin Voivodeship ( ) is a Voivodeships of Poland, voivodeship (province) of Poland, located in the southeastern part of the country, with its capital being the city of Lublin.
The region is named after its largest city and regional capital, Lu ...
; the April 1938 reforms transferred Węgrów
Węgrów (; ) is a town in eastern Poland with 12,796 inhabitants (2013), capital of Węgrów County in the Masovian Voivodeship.
History
First mentioned in historical records in 1414, Węgrów received its city charter in 1441. Between 16th ...
and Sokołów from Lublin to the Warsaw Voivodeship.
World War II to present
In 1939 Poland was invaded and partitioned betweenNazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
and the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
following the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact
The Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, officially the Treaty of Non-Aggression between Germany and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, and also known as the Hitler–Stalin Pact and the Nazi–Soviet Pact, was a non-aggression pact between Nazi Ge ...
. Although the border agreed upon in the Pact would have given all of Podlachia to the Soviet Union, the final border agreed upon in the German–Soviet Boundary and Friendship Treaty signed after the invasion gave the southern part to the Nazi General Government
The General Government (, ; ; ), formally the General Governorate for the Occupied Polish Region (), was a German zone of occupation established after the invasion of Poland by Nazi Germany, Slovak Republic (1939–1945), Slovakia and the Soviet ...
, while the northern part of Podlachia was annexed by the Soviet Union as the Belastok Region of the Byelorussian SSR. Nazi Germany would annex the Soviet part as the Bialystok District in 1941. The Polish resistance movement was active in the region, with Białystok becoming the seat of one of the six main commands of the Union of Armed Struggle in occupied Poland (alongside Warsaw
Warsaw, officially the Capital City of Warsaw, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the Vistula, River Vistula in east-central Poland. Its population is officially estimated at ...
, Kraków
, officially the Royal Capital City of Kraków, is the List of cities and towns in Poland, second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city has a population of 804,237 ...
, Poznań
Poznań ( ) is a city on the Warta, River Warta in west Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business center and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint John's ...
, Toruń
Toruń is a city on the Vistula River in north-central Poland and a World Heritage Sites of Poland, UNESCO World Heritage Site. Its population was 196,935 as of December 2021. Previously, it was the capital of the Toruń Voivodeship (1975–199 ...
and Lwów
Lviv ( or ; ; ; see #Names and symbols, below for other names) is the largest city in western Ukraine, as well as the List of cities in Ukraine, fifth-largest city in Ukraine, with a population of It serves as the administrative centre of ...
).
Under German occupation, the population was subjected to mass arrests, executions and deportations to forced labour, concentration camps
A concentration camp is a prison or other facility used for the internment of political prisoners or politically targeted demographics, such as members of national or ethnic minority groups, on the grounds of national security, or for exploit ...
and Nazi ghettos
Beginning with the invasion of Poland during World War II, the Nazi Germany, Nazi regime set up ghettos across German-occupied Europe, German-occupied Eastern Europe in order to segregate and confine Jews, and sometimes Romani people, into small ...
, whereas under Soviet occupation the population was subjected to mass arrests, executions, deportations to forced labour in Siberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states ...
, Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Pers ...
and the Far North. Sites of German massacres of either Polish or Jewish civilians include Mień, Olszewo (also Polish prisoners of war
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Polish people, people from Poland or of Polish descent
* Polish chicken
* Polish brothers (Mark Polish and Michael Polish, born 1970), American twin ...
), Moskwin, Grabarka, Białystok
Białystok is the largest city in northeastern Poland and the capital of the Podlaskie Voivodeship. It is the List of cities and towns in Poland, tenth-largest city in Poland, second in terms of population density, and thirteenth in area.
Biał ...
, Tykocin, Rajsk, Paulinów, Krasowo-Częstki, Wnory-Wandy, Jabłoń-Dobki (see ''Nazi crimes against the Polish nation
War crime, Crimes against the Polish nation committed by Nazi Germany and Axis powers, Axis collaborationist forces during the invasion of Poland, along with Schutzmannschaft#Police battalions, auxiliary battalions during the subsequent occu ...
''). Nowosiółki was the site of a massacre of hundreds of patients of a psychiatric hospital as part of ''Aktion T4
(German, ) was a campaign of Homicide#By state actors, mass murder by involuntary euthanasia which targeted Disability, people with disabilities and the mentally ill in Nazi Germany. The term was first used in post-WWII, war trials against d ...
''. German forces also committed crimes against Italian and French POWs at subcamps of the Stalag 366 POW camp with executions and massacres of Italians and French in Międzyrzec Podlaski
Międzyrzec Podlaski () is a town in Biała Podlaska County, Lublin Voivodeship, Poland, with a population of 17,102 inhabitants . The total area of the town is . Międzyrzec is located in the historic region of Podlachia, near the Krzna river, n ...
and Hola, respectively, with the Italians also subjected to mass starvation, epidemics, beatings and killings at Biała Podlaska
Biała Podlaska (; ) is a city in the Lublin Voivodeship in eastern Poland with 56,498 inhabitants It is the capital of Biała Podlaska County, although the city is not part of the county (it constitutes a separate city county). The city lies on ...
. Many Poles from Podlachia were among the victims of the Soviet-perpetrated Katyn massacre
The Katyn massacre was a series of mass killings under Communist regimes, mass executions of nearly 22,000 Polish people, Polish military officer, military and police officers, border guards, and intelligentsia prisoners of war carried out by t ...
.
The region once again returned to Polish control in 1945.
In 1999 the modern Podlaskie Voivodeship
Podlaskie Voivodeship ( ) is a Voivodeships of Poland, voivodeship in northeastern Poland. The name of the voivodeship refers to the historical region of Podlachia (in Polish, ''Podlasie''), and significant part of its territory corresponds to th ...
was established which encompasses the northern part of historic Podlachia, including Białystok and Drohiczyn, as well as surrounding areas, including Łomża and Suwałki. Its southern border lies along the Bug.
Demographics
Ethnic situation
While today Podlachia is mostly inhabited byPoles
Pole or poles may refer to:
People
*Poles (people), another term for Polish people, from the country of Poland
* Pole (surname), including a list of people with the name
* Pole (musician) (Stefan Betke, born 1967), German electronic music artist
...
, many Belarusians
Belarusians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Belarus. They natively speak Belarusian language, Belarusian, an East Slavic language. More than 9 million people proclaim Belarusian ethnicity worldwide. Nearly 7.99&n ...
live in the eastern parts. According to Polish census of 2002, in Podlaskie Voivodeship
Podlaskie Voivodeship ( ) is a Voivodeships of Poland, voivodeship in northeastern Poland. The name of the voivodeship refers to the historical region of Podlachia (in Polish, ''Podlasie''), and significant part of its territory corresponds to th ...
there were 46,041 Belarusians (3.9%) and 1,366 Ukrainians
Ukrainians (, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. Their native tongue is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and the majority adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, forming the List of contemporary eth ...
(0.1%). Autochthonous inhabitants have difficulties in national self-identification and identifying of their language. They often identify their nationality as " tutejszy" (literally "locals"). Based on comparison of a survey and the census, Marek Barwiński supposes that people with a low level of national identity
National identity is a person's identity or sense of belonging to one or more states or one or more nations. It is the sense of "a nation as a cohesive whole, as represented by distinctive traditions, culture, and language".
National identity ...
during the census usually choose the major nationality in their region.
Orthodox autochthonous inhabitants are known as '' khakhly'' (without any negative connotations, though today in Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
it is known as an ethnic slur
The following is a list of ethnic slurs, ethnophaulisms, or ethnic epithets that are, or have been, used as insinuations or allegations about members of a given ethnic, national, or racial group or to refer to them in a derogatory, pej ...
for Ukrainians). According to Mykhailo Lesiv, this name appeared after it was used to denote locals in the Russian Imperial Army
The Imperial Russian Army () was the army of the Russian Empire, active from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was organized into a standing army and a state militia. The standing army consisted of Regular army, regular troops and ...
. Many scientific researches prove that the orthodox population in Podlachia have Ukrainian origin (19th century censuses, historical and linguistic researches), though today the number of people with the Ukrainian identity is very small.
Until the 19th century, Podlachia was populated by the Polish-speaking yeomanry
Yeomanry is a designation used by a number of units and sub-units in the British Army Reserve which are descended from volunteer cavalry regiments that now serve in a variety of different roles.
History
Origins
In the 1790s, following the ...
(''drobna szlachta
The ''szlachta'' (; ; ) were the nobility, noble estate of the realm in the Kingdom of Poland, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Depending on the definition, they were either a warrior "caste" or a social ...
''), Jew
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, religion, and community are highly inte ...
s (primarily in towns), and Ruthenian Greek-Catholics speaking a dialect related to modern Ukrainian – the so-called '' Khakhlak'' (''Chachlak'') dialect, which derived its name from a derogatory term for Ukrainians (''khakhol'' or '' khokhol'' being the name of the traditional haircut
A hairstyle, hairdo, haircut, or coiffure refers to the styling of hair, usually on the human head but sometimes on the face or body. The fashioning of hair can be considered an aspect of personal grooming, fashion, and cosmetics, although ...
of Ukrainian Cossacks).
In the 19th century, the inhabitants of Podlachia were under the rule of the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
, with southern Podlachia constituting a part of Russian-controlled Congress Poland
Congress Poland or Congress Kingdom of Poland, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland, was a polity created in 1815 by the Congress of Vienna as a semi-autonomous Polish state, a successor to Napoleon's Duchy of Warsaw. It was established w ...
. After 1831, Russian authorities forbade the Greek-Catholic faith in northern Podlachia and it disappeared from the area. In 1875, Russians forbade this rite in the southern portion as well, and all Greek-Catholic inhabitants were forced to accept the Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, otherwise known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity or Byzantine Christianity, is one of the three main Branches of Christianity, branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholic Church, Catholicism and Protestantism ...
faith. However, the resistance of the local people was surprisingly strong and Ruthenian speakers from this area rejected the separation from the Pope
The pope is the bishop of Rome and the Head of the Church#Catholic Church, visible head of the worldwide Catholic Church. He is also known as the supreme pontiff, Roman pontiff, or sovereign pontiff. From the 8th century until 1870, the po ...
. In 1874, blessed Wincenty Lewoniuk and 12 companions were killed by Russian soldiers in Pratulin. In reaction to these measures, the Ruthenians of southern Podlachia began to identify themselves with the national movement of the Roman Catholic Poles. To preserve the full communion with the Pope, they changed their rite from Eastern to Latin before the compulsory conversion of Greek Catholics into Orthodox. In 1912, Russian authorities issued a tolerance edict that made it possible to change confession from Orthodox to Roman Catholic (but not to Greek-Catholic, which had been completely deleted). A majority of the inhabitants of southern Podlachia changed their faith from Orthodox to Roman Catholic. At present, very few people in this area speak Ruthenian and nearly all consider themselves Poles. Meanwhile, the eastern part of northern Podlachia is still populated by Belarusians.
Podlachia is also the cultural center of Poland's small Tatar minority as well. After the annexation of eastern Poland into the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
following World War II, Poland was left with only two Tatar villages, Bohoniki and Kruszyniany (both outside the historical borders of Podlachia). Some Tatars from the territories annexed to the USSR have been repatriated to Poland and clustered in cities, particularly Białystok. In 1925 the Muslim Religious Union ( Muzułmański Związek Religijny) was formed in Białystok. In 1992, the Union of Tatars of the Republic of Poland ( Związek Tatarów Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej) with autonomous branches in Białystok and Gdańsk
Gdańsk is a city on the Baltic Sea, Baltic coast of northern Poland, and the capital of the Pomeranian Voivodeship. With a population of 486,492, Data for territorial unit 2261000. it is Poland's sixth-largest city and principal seaport. Gdań ...
began operating.
Language
The dominant language in Podlaskie Voivodeship is Polish. Autochthonous inhabitants speak a Podlachian variety. Many linguists relate them to the Ukrainian language. Linguists have been exploring them since 19th century, when they were also known as Siedlce dialects (because of the name of Siedlce Governorate, where the dialects were mostly investigated). There is a problem if they should be considered as part of or as a separate subgroup of of the Ukrainian language. In the Northern Podlachia Podlachian subdialects are also often considered to be Belarusian dialects or sometimes Ruthenian dialects. Since the locals are known as '' khakhly'', the local language is also called ''Khakhlatska mova'' (, "khokhols' language"). S. Zhelekhov wrote in 1884 that the people call their language "Polesian, but those, who were in the army (in the soldiers) call it Khakhlatska".Cities and towns
Gallery
Białystok
Białystok is the largest city in northeastern Poland and the capital of the Podlaskie Voivodeship. It is the List of cities and towns in Poland, tenth-largest city in Poland, second in terms of population density, and thirteenth in area.
Biał ...
, the largest city of proper Podlachia
File:Bulwar w Augustowie.JPG, The former royal city of Augustów
Augustów is a town in north-eastern Poland. It lies on the Netta River and the Augustów Canal. It is the seat of Augustów County and of Gmina Augustów in the Podlaskie Voivodeship. Augustów has an area of , and as of June 2022 it has a popul ...
is the northernmost city of Podlachia and a popular summer tourist destination
File:Podlaskie - Bielsk Podlaski - Bielsk Podlaski - Mickiewicza 45 - Ratusz 02.JPG, Baroque town hall in Bielsk Podlaski
Bielsk Podlaski (, , ) is a town in eastern Poland, within Bielsk County in the Podlaskie Voivodeship. As of December 2021, the town has a population of 24,883.
Geography
Bielsk Podlaski is located in the geographical region of Europe known as ...
, a former royal city of Poland and capital of Bielsk Land
File:Parafia Św. Cyryla i Metodego2.JPG, Hajnówka is notable for its proximity to the Białowieża Forest
Białowieża Forest is a large forest complex on the border between Poland and Belarus. It is one of the last and the largest remaining part of the immense primeval forest that once stretched across the European Plain. The forest is home to more ...
, the biggest primaeval forest in Europe
File:Church in Siemiatycze 02.JPG, 17th-century Church of the Assumption in Siemiatycze
Siemiatycze ( ''Siamiatyčy'') is a town in eastern Poland, with 14,391 inhabitants (2019). It is the capital of Siemiatycze County in the Podlaskie Voivodeship.
History
The history of Siemiatycze dates back to the mid-16th century, when the vil ...
File:Pałac Branickich - Choroszcz 19.jpg, Branicki Palace in Choroszcz
File:Drohiczyn 1.JPG, Drohiczyn and Bug river
File:SM Tykocin Synagoga 2020 (3).jpg, Tykocin Synagogue. Tykocin is one of the best preserved shtetl
or ( ; , ; Grammatical number#Overview, pl. ''shtetelekh'') is a Yiddish term for small towns with predominantly Ashkenazi Jews, Ashkenazi Jewish populations which Eastern European Jewry, existed in Eastern Europe before the Holocaust. The t ...
s in Poland. The main synagogue dates back to the 17th century.
File:Grabarka as0046.JPG, Orthodox sanctuary in Grabarka
References
Sources
* * * *Górczyk, Wojciech Jerzy (2020),The Former Reformati Order’s Monasteries Route
Węgrów. *Górczyk, Wojciech Jerzy (2018),
Reformaci w Węgrowie. Architektura kościoła i miejsce fundacji węgrowskiej na tle działalności fundacyjnej Krasińskich
Drohiczyński Przeglad Naukowy. Drohiczyńskie Towarzystwo Naukowe: 307–326. * *
External links
Journey in Wooden Podlachia
{{Authority control Historical regions in Belarus Historical regions in Poland